Outbreak Simulator First Presentation
- 1. Epidemic and Endemic Outbreak Simulator: A Global Stochastic Cellular Automata Approach Presented by: Hector Cuesta-Arvizu Advisor: Armin R. Mikler Center for Computational Epidemiology and Response Analysis University of North Texas October 24, 2011 Hector Cuesta-Arvizu (CeCERA) Epidemic and Endemic Outbreak Simulator October 24, 2011 1 / 16
- 2. Outline Introduction (why this is important?). Infectious Disease Model SEIR. Infectious Disease Model SEIRS. Cellular Automata (...the computational part). Global Stochastic Contact Model. Outbreak Simulator. Vaccination Strategies. Conclusions. Hector Cuesta-Arvizu (CeCERA) Epidemic and Endemic Outbreak Simulator October 24, 2011 2 / 16
- 3. Introduction Why is this important? The epidemiologist use Models to study the spread of an Infectious disease outbreak. These Models include, Mathematical, Statistical and Computational approaches. Simulating these models is the way that epidemiologist can observe di?erent outbreak outcomes. With the simulation we can try di?erent interventions strategies that a?ects the prevalence of an Epidemic or Endemic outbreak. Hector Cuesta-Arvizu (CeCERA) Epidemic and Endemic Outbreak Simulator October 24, 2011 3 / 16
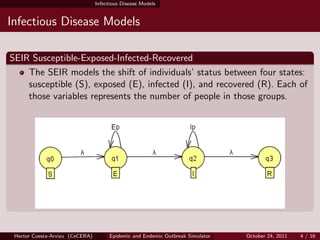
- 4. Infectious Disease Models Infectious Disease Models SEIR Susceptible-Exposed-Infected-Recovered The SEIR models the shift of individuals¡¯ status between four states: susceptible (S), exposed (E), infected (I), and recovered (R). Each of those variables represents the number of people in those groups. Hector Cuesta-Arvizu (CeCERA) Epidemic and Endemic Outbreak Simulator October 24, 2011 4 / 16
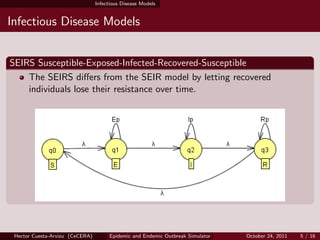
- 5. Infectious Disease Models Infectious Disease Models SEIRS Susceptible-Exposed-Infected-Recovered-Susceptible The SEIRS di?ers from the SEIR model by letting recovered individuals lose their resistance over time. Hector Cuesta-Arvizu (CeCERA) Epidemic and Endemic Outbreak Simulator October 24, 2011 5 / 16
- 6. Cellular Automata Cellular Automata What is a Cellular Automata? Discrete model studied in computability theory and mathematics for a non-linear problems. Facts: It consist of an in?nite, regular grid of cells, each in one of a ?nite number of states. The grid can be any ?nite number of dimensions. Each cell is a particular individual o group. Hector Cuesta-Arvizu (CeCERA) Epidemic and Endemic Outbreak Simulator October 24, 2011 6 / 16
- 7. Cellular Automata Cellular Automata Neighbourhood The Neighbourhood is a selection of cells relative to some speci?ed cell and does not change. Each cell has the same rules for updating based on the values in this neighbourhood. Each time the rules are applied to the whole grid a new generation is produced. Local an Global Neighborhoods, Von Newmnan and Moore Neighborhood Hector Cuesta-Arvizu (CeCERA) Epidemic and Endemic Outbreak Simulator October 24, 2011 7 / 16
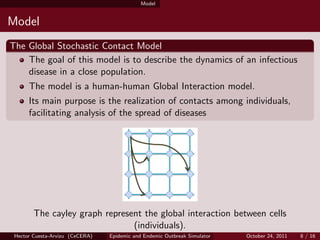
- 8. Model Model The Global Stochastic Contact Model The goal of this model is to describe the dynamics of an infectious disease in a close population. The model is a human-human Global Interaction model. Its main purpose is the realization of contacts among individuals, facilitating analysis of the spread of diseases The cayley graph represent the global interaction between cells (individuals). Hector Cuesta-Arvizu (CeCERA) Epidemic and Endemic Outbreak Simulator October 24, 2011 8 / 16
- 9. Model Model The global contact interaction Contacts per Time Step: CR?N C= 2 Total of Contacts in the Event: Ctot = ¦²t¦Ğ CR?N where te = (1, 2, 3, ..., n) t=1 2 C = Number of interactions per each Time Step. CR = Contact Rate. N = Number of individual in the population. t¦Ğ = Number of Time Steps. Ctot = Total Number of interactions in the event Hector Cuesta-Arvizu (CeCERA) Epidemic and Endemic Outbreak Simulator October 24, 2011 9 / 16
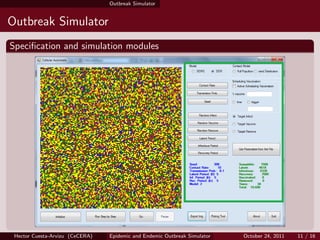
- 10. Outbreak Simulator Outbreak Simulator Technological choices for the Simulator The main contribution of this work is to present a software system that incorporates a global stochastic cellular automata model. Technological Choice: C# .NET (as a programming language) WindowsForms and MonoDesktop (to create graphic interface and grid animations during simulations) Modules: The speci?cation module. The simulation module. The visualization module. Hector Cuesta-Arvizu (CeCERA) Epidemic and Endemic Outbreak Simulator October 24, 2011 10 / 16
- 11. Outbreak Simulator Outbreak Simulator Speci?cation and simulation modules Hector Cuesta-Arvizu (CeCERA) Epidemic and Endemic Outbreak Simulator October 24, 2011 11 / 16
- 12. Outbreak Simulator Outbreak Simulator Visualization module In ?gure A we can observe the SEIR Epidemic Curve and in ?gure B we can observe the SEIRS Endemic Curve. (A) (B) Hector Cuesta-Arvizu (CeCERA) Epidemic and Endemic Outbreak Simulator October 24, 2011 12 / 16
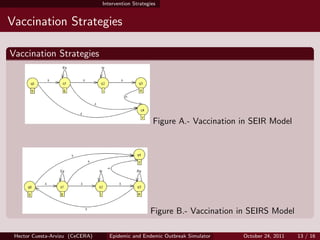
- 13. Intervention Strategies Vaccination Strategies Vaccination Strategies Figure A.- Vaccination in SEIR Model Figure B.- Vaccination in SEIRS Model Hector Cuesta-Arvizu (CeCERA) Epidemic and Endemic Outbreak Simulator October 24, 2011 13 / 16
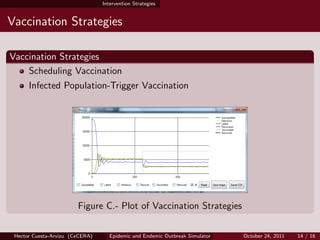
- 14. Intervention Strategies Vaccination Strategies Vaccination Strategies Scheduling Vaccination Infected Population-Trigger Vaccination Figure C.- Plot of Vaccination Strategies Hector Cuesta-Arvizu (CeCERA) Epidemic and Endemic Outbreak Simulator October 24, 2011 14 / 16
- 15. Conclusions Conclusions and Future Work Conclusions and Future Work Simulation help to understand spread of diseases. Also we can observe di?erent outcomes from intervention strategies. Future Work: Try di?erent kinds of contact models. Integrate Seasonality. Hector Cuesta-Arvizu (CeCERA) Epidemic and Endemic Outbreak Simulator October 24, 2011 15 / 16
- 16. Conclusions Questions?? Questions ??? Hector Cuesta-Arvizu (CeCERA) Epidemic and Endemic Outbreak Simulator October 24, 2011 16 / 16