physiology of labour.pptx
Download as pptx, pdf0 likes14 views
Labor is a complex process involving four phases: 1) Quiescent phase characterized by uterine tranquility and cervical integrity. 2) Activation phase beginning 6-8 weeks before term, resulting in uterine contractions and cervical ripening. 3) Stimulation phase where cervical effacement and dilatation occurs in the first stage, and expulsion of the fetus in the second stage. 4) Involution phase where the uterus and cervix return to their pre-pregnant states over time.
1 of 16
Download to read offline



![FEATURES AND MEDIATORS
Changes in the myometrium
’é┤ Increase in contractility
’é┤ Increase in uterine responsiveness
’é┤ Increase in gap junctions
Changes in the cervix
- Cervical ripening
’é┤ Changes in collagen structure
’é┤ Increase in collagen solubility
’é┤ Infiltration by inflammatory cells
’é┤ Estrogen
’é┤ Progesterone
’é┤ CAPs ŌĆō OXY Rreceptors,pg F rep,
connexin 43 [ gap jn pro]
’é┤ Glycosaminogly-cans
’é┤ Proteoglycans
’é┤ pCRH
’é┤ Prostaglandins
’é┤ Cortisol
’é┤ Interleukin-8
’é┤ MMP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physiologyoflabour-230924042442-92060946/85/physiology-of-labour-pptx-5-320.jpg)








Ad
Recommended
Physiology of labor
Physiology of labor Nupur Prakash
╠²
The physiology of labor involves three main phases:
1) Uterine quiescence and cervical softening in which the cervix prepares for labor through changes in vascularity and collagen.
2) Preparation for labor in which cervical ripening and increases in hormones like oxytocin and prostaglandins make the uterus more contractile.
3) Active labor consisting of 3 stages - dilation of the cervix, delivery of the fetus, and delivery of the placenta through uterine contractions and retraction. A combination of hormonal, mechanical, and fetal factors all contribute to initiating the complex process of parturition.Causesandonsetoflabour 130108101535-phpapp02
Causesandonsetoflabour 130108101535-phpapp02Krupa Meet Patel
╠²
Labour is characterized by spontaneous uterine contractions that result in the delivery of the fetus and placenta. The onset of labour involves several key changes, including cervical effacement and dilation as well as the formation of the amniotic sac. Various hormonal and mechanical factors contribute to labour onset, such as an increase in oxytocin receptors and prostaglandins in the uterus and membranes stretching the cervix. Near term, the fetus and placenta release hormones like cortisol and CRH that help trigger labour by stimulating prostaglandin production.Physiology of normal labour
Physiology of normal labourrajeev sood
╠²
This document describes the four phases of parturition: quiescence, activation, stimulation, and involution. It discusses the factors that influence each phase such as hormones and uterine activity. There are three stages of labor: first stage involves cervical dilation, second stage is delivery of the baby, and third stage involves placental separation and expulsion. The document provides details on the characteristics of uterine contractions during labor, cervical dilation, formation of the lower uterine segment, and mechanisms of placental separation and hemostasis after delivery.Labour and its stages
Labour and its stagesShrooti Shah
╠²
The document discusses the processes and stages of labour, defining and differentiating between normal (eutocia) and abnormal (dystocia) labour. It details the physiological factors and stages involved from the onset of true labour pain to the delivery of the baby and placenta, including the hormonal influences and uterine actions. Key points include characteristics of false versus true labour pains, stages of labour, and the mechanics of delivery, along with critical definitions and terminologies related to childbirth.Causes and onset of labour
Causes and onset of labourDrpawan Jhalta
╠²
Labour is initiated by various biochemical and physiological changes that occur in late pregnancy. These include increased production of uterotonins like oxytocin, prostaglandins, and CRH by the fetus and placenta. There is also a withdrawal of progesterone's inhibitory effects and an increase in oxytocin receptors in the uterus. Together, these changes make the uterus more sensitive and responsive to contractions. The cervix simultaneously undergoes ripening, becoming softer, shorter, and more dilated in preparation for labour and delivery.Fiirts stage new
Fiirts stage newSikandar Kumar
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive overview of labor, defining it as a series of events that expel the products of conception from the womb. It distinguishes between normal and abnormal labor, details the features of true and false labor pains, and outlines the stages of labor, including their physiological processes and average durations. Key concepts like cervical effacement, dilation, and the mechanics of uterine contractions are also discussed, emphasizing their importance for understanding labor dynamics.physiology labour.pptx
physiology labour.pptx04IZATULSHAFIKABINTI
╠²
The document summarizes the physiology of labour, including the three stages. The first stage begins with contractions and ends when the cervix is fully dilated. It can be divided into early/latent labour and active labour. Hormonal changes like dropping progesterone and rising oxytocin help initiate labour. The second stage begins at full dilation and ends with baby's birth. Strong contractions help baby descend through soft tissue displacement. The third stage involves separation and delivery of the placenta within 1 hour after birth.Clinic of the labor obstetric
Clinic of the labor obstetricMuhammad Khadhari
╠²
The document summarizes key aspects of labor and delivery:
1. The myometrium consists of 4 layers of smooth muscle cells that contract during labor, driven by hormones like oxytocin and prostaglandins, to expel the fetus.
2. Labor progresses through three stages - early labor involving cervical changes, active labor of rapid cervical dilation, and third stage of delivering the placenta.
3. Multiple signs and assessments are used to monitor labor including cervical exams, fetal monitoring, and assessing contractions.Normal labour and its physiology
Normal labour and its physiologyAtul Yadav
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive overview of normal labor, defining it as a physiological process involving spontaneous uterine contractions that lead to the expulsion of viable products of conception. It outlines the phases of labor, characteristics of normal labor, and the physiological mechanisms involved, including uterine contractions and retraction, as well as the roles of hormones in facilitating labor. Additionally, it addresses management during different stages of labor, including monitoring and interventions to ensure maternal and fetal well-being.Normal Labor based on William's Obstetrics
Normal Labor based on William's ObstetricsFRANZDOMINIQUEROBINB
╠²
The document discusses the complex physiological processes of labor and childbirth, detailing the stages of parturition, uterine contractions, and cervical changes necessary for delivery. It emphasizes the roles of various hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone, as well as the interactions between maternal and fetal factors that signal the onset of labor. Additionally, it outlines the stages of labor, including the active and latent phases, and highlights the importance of monitoring labor progression and maternal-fetal health.Labor-5 (2).pptx
Labor-5 (2).pptxIndrajithIrissappan
╠²
The document defines labor as the series of events involving the expulsion of the fetus, placenta, and membranes from the uterus through the vagina. It describes the three stages of labor and the normal physiological changes that occur in each stage, including cervical dilation, fetal descent, and uterine contractions. Key points are provided on the engagement and descent of the fetal head through the birth canal, as well as the rotation, flexion, and extension movements involved in the normal birthing mechanism when the fetus is in the vertex position.Labor, PUERPERIUM, Infant, ą¤čĆąŠčćą░ąĮ_b5e062ae4f105da975e276044c4cea06.pdf
Labor, PUERPERIUM, Infant, ą¤čĆąŠčćą░ąĮ_b5e062ae4f105da975e276044c4cea06.pdfKeshav177622
╠²
1. The document discusses the physiological processes involved in labor and delivery.
2. It describes how contractions increase in the weeks before birth, initially as irregular Braxton Hicks contractions but becoming more frequent and rhythmic.
3. Labor involves three stages - cervical dilation, fetal expulsion, and placental delivery. Key events in each stage are outlined.Introduction and physiology of labor
Introduction and physiology of laborJyothi Swaroop
╠²
The document details the physiological and biochemical processes of labor, defining normal and abnormal labor and outlining the stages of labor. It discusses the mechanisms that trigger labor onset, including hormonal contributions and the role of the placenta and fetus. Additionally, the document explains the characteristics of true and false labor pains, cervical changes, and uterine contractions during the different stages of labor.Normal labour.pptx
Normal labour.pptxPreeti Kulshreshtha
╠²
The first stage of normal labour involves gradually increasing uterine contractions that cause dilation of the cervix from 0-10cm over time. It is divided into latent, active, and transition phases. Nursing management in this stage includes emotional support, encouraging rest and ambulation, monitoring diet and bladder, assessing cervical dilation and fetal heart rate, administering pain relief as needed, and using a partograph to track labour progress. The goal is to support the natural physiological process through this first stage until full cervical dilation is achieved.stages of labor.pptx....................
stages of labor.pptx....................MadhuSM4
╠²
The document outlines the four stages of labor: the first stage involves cervical dilation and effacement, the second stage focuses on the expulsion of the fetus, the third stage pertains to the expulsion of the placenta, and the fourth stage is the observation period post-delivery. It details the clinical features, duration, events, and physiological processes occurring in each stage, as well as potential complications during the puerperium. The document also addresses maternal and fetal effects throughout labor and the mechanisms for controlling bleeding post-delivery.Stages of labour presentation in obstetrics.pptx
Stages of labour presentation in obstetrics.pptxTHANMAYAJ
╠²
The document outlines the four stages of labor: the first stage involves cervical effacement and dilation, the second stage is the expulsion of the fetus, the third stage focuses on the delivery of the placenta, and the fourth stage includes post-delivery observation. It details the physiological processes, contractions, pain mechanisms, and significant changes in the uterus during labor. Key concepts include the phases of cervical dilation and the impact of various factors on labor progression.labour 2.pdf
labour 2.pdfSurakshyaGyawali2
╠²
The document summarizes the normal physiology of labour and delivery. It describes the three stages of labour as: 1) cervical dilation and effacement, 2) descent and expulsion of the fetus, and 3) delivery of the placenta. Key events in each stage include progressive cervical changes, descent and rotation of the fetus, and uterine contraction and retraction to deliver the placenta. Optimal management focuses on monitoring labour progress, relieving pain, and preventing complications to support the natural birth process.labour.pdf
labour.pdfSurakshyaGyawali2
╠²
The document summarizes the normal physiology of labour and delivery. It describes the three stages of labour as: 1) cervical dilation, 2) descent and expulsion of the fetus, and 3) delivery of the placenta. Key points include the hormonal and mechanical factors involved in labour onset, the progression of uterine contractions and cervical changes in stage one, and management approaches to minimize tearing during stage two expulsion of the fetus.Normal labour and management
Normal labour and managementSyaza Syazana Nordin
╠²
The document discusses the structure and function of the myometrium, the muscular layer of the uterine wall, during labor and delivery. It contains three layers of smooth muscle (longitudinal, circular, and oblique) that contract during labor due to hormones like oxytocin and prostaglandins. Calcium entry into uterine muscle cells allows the interaction of actin and myosin fibers to cause contractions. Synchronized contractions of the myometrium expel the fetus through the birth canal in three stages: cervical dilation and effacement in stage one; fetal expulsion in stage two; and placental separation and delivery in stage three.normal labour.pptx labour and its stages
normal labour.pptx labour and its stagesbhavanimsc23
╠²
The document serves as a comprehensive overview of labor, its stages, and the physiological role of midwifery practice, outlining definitions, causes of labor onset, and detailed stages of labor. Key aspects include the management roles of nurses, the physiological mechanisms involved in each stage, and distinctions between true and false labor pains. Additionally, it discusses the importance of hormonal and neurological factors in labor processes and outlines standard procedures in midwifery care.NORMAL LABOUR by dr surya pratap.pptx
NORMAL LABOUR by dr surya pratap.pptxsuryapratapsinghrajp2
╠²
1. The document discusses the mechanism of labour, beginning with definitions of labour and delivery. It then describes the cardinal movements that occur as the fetus' head engages, descends, flexes, internally rotates, and is eventually delivered through extension.
2. The causes of labour onset are proposed to include uterine distension, fetal and placental hormones like estrogen and prostaglandins, and neurological factors. Oxytocin, calcium, and the contractile proteins actin and myosin are also involved in uterine contractions.
3. The stages of labour and associated terminology are defined. Normal labour relies on longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation, and occiput anterior position for efficient progression through theStages of labor
Stages of laborDr. Vijayalakshmi Rajasekaran
╠²
This document summarizes the stages of labor. It describes 4 stages: 1) preparatory stage with lightening and cervical changes, 2) active labor involving cervical dilation until fully dilated, 3) expulsion stage when the fetus is pushed through the birth canal, and 4) delivery of the placenta. Each stage is defined with details on duration, phenomena, cervical dilation curve, and management techniques to ensure delivery and control of hemorrhage.First stage of labor and it's management.pptx
First stage of labor and it's management.pptxBlessyAsirvatham
╠²
The document provides an in-depth overview of the normal physiology of the first stage of labor, including definitions, stages, and the management of labor pain. Key components discussed include the physiological changes in the uterus, the role of hormones, and the characteristics of true versus false labor. It emphasizes the importance of understanding these aspects for effective nursing care during labor.1536.pptx
1536.pptxmayank singh
╠²
The document discusses the process of labor and delivery. It defines labor as the series of events that lead to the expulsion of the fetus, placenta, and membranes from the uterus through the vagina. Normal labor is spontaneous in onset, involves a vertex presentation, and does not prolong unduly without complications. Abnormal labor is referred to as dystocia. The document then examines the various hormonal and physical changes involved in initiating and progressing labor, including uterine distension, fetal contributions, estrogen, progesterone, prostaglandins, and oxytocin. It describes the stages of labor and how contractions become more frequent, intense, and prolonged over time.stagesmanagementoflabour-190204140838.pptx
stagesmanagementoflabour-190204140838.pptxArun072
╠²
Labor is a process involving painful uterine contractions that lead to the expulsion of the fetus, placenta, and membranes through the vagina. It comprises four stages: the preparatory stage, cervical dilatation, expulsion of the fetus, and placental delivery. The duration and characteristics of labor vary between primigravida and multigravida women, with specific physiological changes occurring at each stage.NORMAL LABOUR
NORMAL LABOURJAYDIP NINAMA
╠²
Normal labour is defined as delivery of a single baby by vertex presentation through the vagina at term, with spontaneous onset and completion within 24 hours, leaving a healthy mother and baby. Labour is caused by hormonal and mechanical factors that lead to cervical dilation and descent and rotation of the fetal head through the birth canal in four stages. The first stage involves cervical dilation. The second stage is the birth of the baby. The third stage is delivery of the placenta, and the fourth involves recovery of the mother. A series of movements including engagement, descent, flexion, internal rotation, and extension help the fetal head navigate the birth canal. Normal labour
Normal labour golden4host
╠²
Normal labour involves a series of events that expel the fetus from the uterus through the vagina. It is considered normal when it is spontaneous, occurs at term with a single fetus in vertex presentation, has no undue prolongation, and no maternal or fetal complications. Labour is divided into stages - the first stage involves cervical dilation until full dilation, the second stage is expulsion of the fetus, and the third stage involves delivery of the placenta. Uterine contractions and retraction are the primary forces that cause cervical dilation and expulsion of the fetus, while voluntary abdominal muscle contractions aid in the second stage.Inhalational agents for Anesthesia students
Inhalational agents for Anesthesia studentsBalamurugan Muthuram
╠²
The document discusses inhalational agents used in general anesthesia, detailing their mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics. It emphasizes the induction, maintenance, and emergence phases of anesthesia, explaining how inhalational agents influence neuronal activity, consciousness, and muscle immobility through various receptor interactions. The pharmacokinetic properties of different inhaled anesthetics, including their absorption, distribution, and elimination, are also analyzed to highlight factors affecting anesthesia induction and recovery times.Advanced cardiac life support for anesthesiologist
Advanced cardiac life support for anesthesiologistBalamurugan Muthuram
╠²
The document outlines recent updates to ACLS and BLS guidelines, emphasizing the importance of high-quality CPR techniques such as compression-only CPR for untrained lay rescuers and updated compression rates and depths. It includes details on advanced airway management, recommendations for drug administration during cardiac arrest, and considerations for pediatrics and pregnant women. Additionally, it discusses prognostication based on CO2 levels, the use of advanced monitoring and interventions during CPR, and guidelines for post-cardiac arrest care.More Related Content
Similar to physiology of labour.pptx (20)
Clinic of the labor obstetric
Clinic of the labor obstetricMuhammad Khadhari
╠²
The document summarizes key aspects of labor and delivery:
1. The myometrium consists of 4 layers of smooth muscle cells that contract during labor, driven by hormones like oxytocin and prostaglandins, to expel the fetus.
2. Labor progresses through three stages - early labor involving cervical changes, active labor of rapid cervical dilation, and third stage of delivering the placenta.
3. Multiple signs and assessments are used to monitor labor including cervical exams, fetal monitoring, and assessing contractions.Normal labour and its physiology
Normal labour and its physiologyAtul Yadav
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive overview of normal labor, defining it as a physiological process involving spontaneous uterine contractions that lead to the expulsion of viable products of conception. It outlines the phases of labor, characteristics of normal labor, and the physiological mechanisms involved, including uterine contractions and retraction, as well as the roles of hormones in facilitating labor. Additionally, it addresses management during different stages of labor, including monitoring and interventions to ensure maternal and fetal well-being.Normal Labor based on William's Obstetrics
Normal Labor based on William's ObstetricsFRANZDOMINIQUEROBINB
╠²
The document discusses the complex physiological processes of labor and childbirth, detailing the stages of parturition, uterine contractions, and cervical changes necessary for delivery. It emphasizes the roles of various hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone, as well as the interactions between maternal and fetal factors that signal the onset of labor. Additionally, it outlines the stages of labor, including the active and latent phases, and highlights the importance of monitoring labor progression and maternal-fetal health.Labor-5 (2).pptx
Labor-5 (2).pptxIndrajithIrissappan
╠²
The document defines labor as the series of events involving the expulsion of the fetus, placenta, and membranes from the uterus through the vagina. It describes the three stages of labor and the normal physiological changes that occur in each stage, including cervical dilation, fetal descent, and uterine contractions. Key points are provided on the engagement and descent of the fetal head through the birth canal, as well as the rotation, flexion, and extension movements involved in the normal birthing mechanism when the fetus is in the vertex position.Labor, PUERPERIUM, Infant, ą¤čĆąŠčćą░ąĮ_b5e062ae4f105da975e276044c4cea06.pdf
Labor, PUERPERIUM, Infant, ą¤čĆąŠčćą░ąĮ_b5e062ae4f105da975e276044c4cea06.pdfKeshav177622
╠²
1. The document discusses the physiological processes involved in labor and delivery.
2. It describes how contractions increase in the weeks before birth, initially as irregular Braxton Hicks contractions but becoming more frequent and rhythmic.
3. Labor involves three stages - cervical dilation, fetal expulsion, and placental delivery. Key events in each stage are outlined.Introduction and physiology of labor
Introduction and physiology of laborJyothi Swaroop
╠²
The document details the physiological and biochemical processes of labor, defining normal and abnormal labor and outlining the stages of labor. It discusses the mechanisms that trigger labor onset, including hormonal contributions and the role of the placenta and fetus. Additionally, the document explains the characteristics of true and false labor pains, cervical changes, and uterine contractions during the different stages of labor.Normal labour.pptx
Normal labour.pptxPreeti Kulshreshtha
╠²
The first stage of normal labour involves gradually increasing uterine contractions that cause dilation of the cervix from 0-10cm over time. It is divided into latent, active, and transition phases. Nursing management in this stage includes emotional support, encouraging rest and ambulation, monitoring diet and bladder, assessing cervical dilation and fetal heart rate, administering pain relief as needed, and using a partograph to track labour progress. The goal is to support the natural physiological process through this first stage until full cervical dilation is achieved.stages of labor.pptx....................
stages of labor.pptx....................MadhuSM4
╠²
The document outlines the four stages of labor: the first stage involves cervical dilation and effacement, the second stage focuses on the expulsion of the fetus, the third stage pertains to the expulsion of the placenta, and the fourth stage is the observation period post-delivery. It details the clinical features, duration, events, and physiological processes occurring in each stage, as well as potential complications during the puerperium. The document also addresses maternal and fetal effects throughout labor and the mechanisms for controlling bleeding post-delivery.Stages of labour presentation in obstetrics.pptx
Stages of labour presentation in obstetrics.pptxTHANMAYAJ
╠²
The document outlines the four stages of labor: the first stage involves cervical effacement and dilation, the second stage is the expulsion of the fetus, the third stage focuses on the delivery of the placenta, and the fourth stage includes post-delivery observation. It details the physiological processes, contractions, pain mechanisms, and significant changes in the uterus during labor. Key concepts include the phases of cervical dilation and the impact of various factors on labor progression.labour 2.pdf
labour 2.pdfSurakshyaGyawali2
╠²
The document summarizes the normal physiology of labour and delivery. It describes the three stages of labour as: 1) cervical dilation and effacement, 2) descent and expulsion of the fetus, and 3) delivery of the placenta. Key events in each stage include progressive cervical changes, descent and rotation of the fetus, and uterine contraction and retraction to deliver the placenta. Optimal management focuses on monitoring labour progress, relieving pain, and preventing complications to support the natural birth process.labour.pdf
labour.pdfSurakshyaGyawali2
╠²
The document summarizes the normal physiology of labour and delivery. It describes the three stages of labour as: 1) cervical dilation, 2) descent and expulsion of the fetus, and 3) delivery of the placenta. Key points include the hormonal and mechanical factors involved in labour onset, the progression of uterine contractions and cervical changes in stage one, and management approaches to minimize tearing during stage two expulsion of the fetus.Normal labour and management
Normal labour and managementSyaza Syazana Nordin
╠²
The document discusses the structure and function of the myometrium, the muscular layer of the uterine wall, during labor and delivery. It contains three layers of smooth muscle (longitudinal, circular, and oblique) that contract during labor due to hormones like oxytocin and prostaglandins. Calcium entry into uterine muscle cells allows the interaction of actin and myosin fibers to cause contractions. Synchronized contractions of the myometrium expel the fetus through the birth canal in three stages: cervical dilation and effacement in stage one; fetal expulsion in stage two; and placental separation and delivery in stage three.normal labour.pptx labour and its stages
normal labour.pptx labour and its stagesbhavanimsc23
╠²
The document serves as a comprehensive overview of labor, its stages, and the physiological role of midwifery practice, outlining definitions, causes of labor onset, and detailed stages of labor. Key aspects include the management roles of nurses, the physiological mechanisms involved in each stage, and distinctions between true and false labor pains. Additionally, it discusses the importance of hormonal and neurological factors in labor processes and outlines standard procedures in midwifery care.NORMAL LABOUR by dr surya pratap.pptx
NORMAL LABOUR by dr surya pratap.pptxsuryapratapsinghrajp2
╠²
1. The document discusses the mechanism of labour, beginning with definitions of labour and delivery. It then describes the cardinal movements that occur as the fetus' head engages, descends, flexes, internally rotates, and is eventually delivered through extension.
2. The causes of labour onset are proposed to include uterine distension, fetal and placental hormones like estrogen and prostaglandins, and neurological factors. Oxytocin, calcium, and the contractile proteins actin and myosin are also involved in uterine contractions.
3. The stages of labour and associated terminology are defined. Normal labour relies on longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation, and occiput anterior position for efficient progression through theStages of labor
Stages of laborDr. Vijayalakshmi Rajasekaran
╠²
This document summarizes the stages of labor. It describes 4 stages: 1) preparatory stage with lightening and cervical changes, 2) active labor involving cervical dilation until fully dilated, 3) expulsion stage when the fetus is pushed through the birth canal, and 4) delivery of the placenta. Each stage is defined with details on duration, phenomena, cervical dilation curve, and management techniques to ensure delivery and control of hemorrhage.First stage of labor and it's management.pptx
First stage of labor and it's management.pptxBlessyAsirvatham
╠²
The document provides an in-depth overview of the normal physiology of the first stage of labor, including definitions, stages, and the management of labor pain. Key components discussed include the physiological changes in the uterus, the role of hormones, and the characteristics of true versus false labor. It emphasizes the importance of understanding these aspects for effective nursing care during labor.1536.pptx
1536.pptxmayank singh
╠²
The document discusses the process of labor and delivery. It defines labor as the series of events that lead to the expulsion of the fetus, placenta, and membranes from the uterus through the vagina. Normal labor is spontaneous in onset, involves a vertex presentation, and does not prolong unduly without complications. Abnormal labor is referred to as dystocia. The document then examines the various hormonal and physical changes involved in initiating and progressing labor, including uterine distension, fetal contributions, estrogen, progesterone, prostaglandins, and oxytocin. It describes the stages of labor and how contractions become more frequent, intense, and prolonged over time.stagesmanagementoflabour-190204140838.pptx
stagesmanagementoflabour-190204140838.pptxArun072
╠²
Labor is a process involving painful uterine contractions that lead to the expulsion of the fetus, placenta, and membranes through the vagina. It comprises four stages: the preparatory stage, cervical dilatation, expulsion of the fetus, and placental delivery. The duration and characteristics of labor vary between primigravida and multigravida women, with specific physiological changes occurring at each stage.NORMAL LABOUR
NORMAL LABOURJAYDIP NINAMA
╠²
Normal labour is defined as delivery of a single baby by vertex presentation through the vagina at term, with spontaneous onset and completion within 24 hours, leaving a healthy mother and baby. Labour is caused by hormonal and mechanical factors that lead to cervical dilation and descent and rotation of the fetal head through the birth canal in four stages. The first stage involves cervical dilation. The second stage is the birth of the baby. The third stage is delivery of the placenta, and the fourth involves recovery of the mother. A series of movements including engagement, descent, flexion, internal rotation, and extension help the fetal head navigate the birth canal. Normal labour
Normal labour golden4host
╠²
Normal labour involves a series of events that expel the fetus from the uterus through the vagina. It is considered normal when it is spontaneous, occurs at term with a single fetus in vertex presentation, has no undue prolongation, and no maternal or fetal complications. Labour is divided into stages - the first stage involves cervical dilation until full dilation, the second stage is expulsion of the fetus, and the third stage involves delivery of the placenta. Uterine contractions and retraction are the primary forces that cause cervical dilation and expulsion of the fetus, while voluntary abdominal muscle contractions aid in the second stage.More from Balamurugan Muthuram (11)
Inhalational agents for Anesthesia students
Inhalational agents for Anesthesia studentsBalamurugan Muthuram
╠²
The document discusses inhalational agents used in general anesthesia, detailing their mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics. It emphasizes the induction, maintenance, and emergence phases of anesthesia, explaining how inhalational agents influence neuronal activity, consciousness, and muscle immobility through various receptor interactions. The pharmacokinetic properties of different inhaled anesthetics, including their absorption, distribution, and elimination, are also analyzed to highlight factors affecting anesthesia induction and recovery times.Advanced cardiac life support for anesthesiologist
Advanced cardiac life support for anesthesiologistBalamurugan Muthuram
╠²
The document outlines recent updates to ACLS and BLS guidelines, emphasizing the importance of high-quality CPR techniques such as compression-only CPR for untrained lay rescuers and updated compression rates and depths. It includes details on advanced airway management, recommendations for drug administration during cardiac arrest, and considerations for pediatrics and pregnant women. Additionally, it discusses prognostication based on CO2 levels, the use of advanced monitoring and interventions during CPR, and guidelines for post-cardiac arrest care.Labour Analgesia and pain free Labour anasthesia
Labour Analgesia and pain free Labour anasthesiaBalamurugan Muthuram
╠²
The document outlines various methods and types of labor analgesia, highlighting pharmacological and non-pharmacological approaches used to manage labor pain. Key topics include the history of analgesics, mechanisms of pain during labor, effects of narcotic analgesics on mothers and neonates, as well as the use and complications of different anesthesia techniques. Additionally, comparisons between various analgesic methods and their efficacy in managing labor pain are discussed.CENTRAL VENOUS PRESSURE MONITORINGG.pptx
CENTRAL VENOUS PRESSURE MONITORINGG.pptxBalamurugan Muthuram
╠²
Central venous pressure (CVP) is a measurement of right atrial pressure and is used to evaluate cardiac preload and filling pressures, with normal values ranging from 8-12 mmHg. Accurate CVP interpretation requires understanding the factors affecting right atrial pressure and specific measurement techniques, and its reliability as a predictor of volume status is limited. The CVP waveform, consisting of various components influenced by cardiac events, can indicate numerous physiological conditions and requires precise monitoring to avoid significant errors.Anaphylaxis pathophysiology and managaemnet
Anaphylaxis pathophysiology and managaemnetBalamurugan Muthuram
╠²
This document provides information about anaphylaxis, including:
1. It was discovered in 1902 by Portier and Richet while attempting to immunize dogs to sea anemone venom. The dogs unexpectedly reacted to a previously nonlethal dose, coining the term "anaphylaxis".
2. Anaphylaxis is a systemic, immediate hypersensitivity reaction caused by IgE-mediated release of histamine and other mediators from mast cells and basophils, presenting with multi-organ symptoms.
3. Epidemiology studies found hospitalization rates of anaphylaxis to be around 3.2 cases per 100,000 people per year, with a 5% mortality rate.Advanced cardiac life support presentation
Advanced cardiac life support presentationBalamurugan Muthuram
╠²
This document discusses cardiac arrest in special situations. It covers cardiac arrest associated with conditions like asthma, anaphylaxis, hypothermia, avalanches, drowning, and more. For each situation, it provides an introduction, discusses modifications that may be needed for basic and advanced life support, and outlines initial care and treatment considerations. The overall aim is to guide resuscitation efforts for cardiac arrests occurring in these unique contexts.Pheochromocytoma..ppt
Pheochromocytoma..pptBalamurugan Muthuram
╠²
The document discusses pheochromocytoma, a catecholamine-producing tumor that originates from chromaffin tissue. It covers the epidemiology, signs and symptoms, diagnosis through biochemical testing and imaging, and management approaches including preoperative preparation with alpha and beta blockade to prevent hypertensive crises during tumor removal. Effective preoperative management is key to reducing the mortality rate from excising pheochromocytomas.RISK FACTORS , IDENTIFY.pptx
RISK FACTORS , IDENTIFY.pptxBalamurugan Muthuram
╠²
This document outlines various general and specific risk factors to consider when assessing a pregnancy. It discusses factors related to maternal age, weight, height, parity and socioeconomic status. It also discusses risk factors based on previous reproductive and medical history, complications in the present pregnancy, and previous surgeries. Various methods for monitoring the pregnancy through clinical, biochemical and biophysical means are also outlined.REFERRED CASES FOR THE YEAR 2022.pptx
REFERRED CASES FOR THE YEAR 2022.pptxBalamurugan Muthuram
╠²
The document provides referral case statistics from various medical facilities for the year 2022, showing 254 cases from medical colleges, 2467 from government headquarters, 8943 from primary health centers, 152 from urban primary health centers, 507 from private hospitals, and 63 from ESI hospitals. A chart also shows that referral cases have remained almost the same over the last three years, with the highest numbers coming from primary health centers.steril_tech_and_or_sitting.pptx
steril_tech_and_or_sitting.pptxBalamurugan Muthuram
╠²
This document discusses surgical asepsis and sterile technique. It begins by defining key terms like asepsis, sterile technique, and principles of sterile technique. It then covers topics like surgical hand antisepsis, skin preparation, surgical instruments, the operating room environment, and preoperative preparation. Specific guidelines are provided for each topic, such as using sterile instruments and drapes, maintaining sterility, proper hand washing and skin preparation techniques. Maintaining strict sterile protocols is emphasized to prevent surgical site infections.usg in normal menstrual cycle
usg in normal menstrual cycleBalamurugan Muthuram
╠²
This document discusses the normal ultrasound appearance of the endometrium and ovaries throughout the menstrual cycle. It provides details on the expected endometrial thickness at different phases of the cycle. It also describes the sonographic signs of ovulation and the appearance and development of the corpus luteum. Post-menopausal endometrial thickness is also addressed. Failure of ovulation and the development of luteinized unruptured follicles are summarized at the end.Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
ELECTROMYOGRAPHY.pptX by GOKULAKRISHNAN.
ELECTROMYOGRAPHY.pptX by GOKULAKRISHNAN.GOKULAKRISHNAN JANARTHANAN
╠²
Electromyography is basically the study of motor unit activity.
In electromyography, the study of the electrical activity of contracting muscle provides information concerning the structure and function of the motor units.
OUR SRS SBRT EXPERIENCE BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATRO
OUR SRS SBRT EXPERIENCE BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATROKanhu Charan
╠²
OUR SRS SBRT EXPERIENCE BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATRO5-Lift Analysis in ergonomics focuses on evaluating the safety and efficienc...
5-Lift Analysis in ergonomics focuses on evaluating the safety and efficienc...Bolan University of Medical and Health Sciences ,Quetta
╠²
Lift Analysis in ergonomics focuses on evaluating the safety and efficiency of manual lifting tasks in the workplace. It involves assessing the physical demands placed on the human body during lifting activities to prevent musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs), particularly lower back injuriesCell Injuri. pathophpysiology sem- II B Pharmacypptx
Cell Injuri. pathophpysiology sem- II B PharmacypptxUmeshMali25
╠²
This presentation provides a comprehensive overview of cell injury, a fundamental concept in pathology. It covers the causes, types (reversible and irreversible), mechanisms of injury (including hypoxia, free radicals, and chemical agents), and the morphological and biochemical changes that occur during cell injury. The slides are ideal for medical, pharmacy, and life sciences students preparing for pathology coursework or exams.
Clinical Signs Overview: PICCKLE Mnemonic
Clinical Signs Overview: PICCKLE MnemonicDr Aman Suresh Tharayil
╠²
This presentation provides a concise yet comprehensive review of common clinical signs and their diagnostic significance, summarized under the acronym PICCKLE ŌĆō Pallor, Icterus, Clubbing, Cyanosis, Koilonychia, Lymphadenopathy, and Edema. Each condition is defined, followed by key causes, pathophysiology, diagnostic techniques, and clinical relevance. The content is tailored for undergraduate and postgraduate students in medicine and pharmacy, as well as early-career clinicians seeking to reinforce their clinical examination skillsDrugs Acting on the Autonomic Nervous System ŌĆō Classification, Properties & Uses
Drugs Acting on the Autonomic Nervous System ŌĆō Classification, Properties & UsesSajini
╠²
This presentation offers a comprehensive overview of drugs acting on the autonomic nervous system (ANS), including sympathomimetic, sympatholytic, parasympathomimetic, and anticholinergic agents. It explains the classification, mechanism of action, properties, formulation, brand names, and clinical uses of key drugs like adrenaline, dopamine, propranolol, atropine, and pilocarpine. Ideal for students and professionals in pharmacy, medicine, and healthcare.Growth hormone by Dr Kondam AmbareeshaGoud
Growth hormone by Dr Kondam AmbareeshaGoudDr K Ambareesha Goud PhD
╠²
Growth hormone (GH) secretion from anterior pituitary is regulated by the hypothalamus and the mediators of GH actions. Major regulatory factors include GH releasing hormone (GHRH), somatostatin (SRIF), GH releasing peptide (ghrerin) and insulin-like growth factor (IGF-I).AD-SAFE: An Initiative to Build Understanding of ARIA and Skills Needed to Gu...
AD-SAFE: An Initiative to Build Understanding of ARIA and Skills Needed to Gu...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Chair and Presenter, Ana M. Franceschi, MD, PhD, and Petrice M. Cogswell, MD, PhD, discuss AlzheimerŌĆÖs disease in this CME/MOC/NCPD/CPE/AAPA/IPCE activity titled ŌĆ£AD-SAFE: An Initiative to Build Understanding of ARIA and Skills Needed to Guide Treatment Decisions and Support Rapid Recognition and Response in Radiology.ŌĆØ For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME/MOC/NCPD/CPE/AAPA/IPCE information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/42nd09H. CME/MOC/NCPD/CPE/AAPA/IPCE credit will be available until May 26, 2026.nanoparticle and liposomes ppt .(NTDS)pdf
nanoparticle and liposomes ppt .(NTDS)pdfsiddhikalbande
╠²
Nanoparticles and liposomes are advanced carriers used for targeted drug delivery.
Nanoparticles enhance drug effectiveness by directing treatment to specific sites.
Liposomes are biocompatible vesicles that enable controlled and sustained drug release.GAIT in Biomechanics along with abnormal gait
GAIT in Biomechanics along with abnormal gaitNerusu sai priyanka
╠²
Gait , ab normal gait,normal biomechanics,pathomechanics of gait,unilateral stance,factors affectoing gait Biography and Professional Career of Dr. Seth Eidemiller
Biography and Professional Career of Dr. Seth EidemillerDr. Seth Eidemiller
╠²
Dr. Seth A. Eidemiller is a board-certified emergency physician whose professional journey began on a fourth-generation dairy farm in Idaho. Early on, he gained experience through farming, wildfire suppression, and construction work, which gave him a strong foundation in practical skills and resilience. After completing degrees in International Studies and Spanish, he returned to Boise to fulfill the prerequisites for medical school and study laboratory sciences. He then attended the University of Nevada, Reno School of Medicine, and continued his training with a residency in emergency medicine in Fresno. Today, he serves as Vice Chair of the Chico Emergency Medicine Physician Group.Aspirin powder or Acetyl salicylic acid powder.docx
Aspirin powder or Acetyl salicylic acid powder.docxkopalsharma85
╠²
pharmacy exercise on aspirin powderUnlocking the Potential of Long-Acting PrEP to Halt HIV Transmissions
Unlocking the Potential of Long-Acting PrEP to Halt HIV TransmissionsPVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Chair, Allison Agwu, MD, ScM, FAAP, FIDSA, discusses HIV in this CME/MOC/NCPD/CPE/AAPA/IPCE activity titled ŌĆ£Unlocking the Potential of Long-Acting PrEP to Halt HIV Transmissions.ŌĆØ For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME/MOC/NCPD/CPE/AAPA/IPCE information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/40Mr2AC. CME/MOC/NCPD/CPE/AAPA/IPCE credit will be available until June 12, 2026.Tuberculosis Nepal 2025 National Plan.pptx
Tuberculosis Nepal 2025 National Plan.pptxDr. Anu Marhatta
╠²
The presentation contains preventive therapy, the DOTS program, and the national program of Nepal. This material is intended for educational purposes only.INTERPRETATION OF LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS.pptx
INTERPRETATION OF LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS.pptxEliLawluvi
╠²
THE DOCUMENT SUMMARIZES THE KEY COMPONENTS OF INTERPRETING FULL BLOOD CUNT5-Lift Analysis in ergonomics focuses on evaluating the safety and efficienc...
5-Lift Analysis in ergonomics focuses on evaluating the safety and efficienc...Bolan University of Medical and Health Sciences ,Quetta
╠²
AD-SAFE: An Initiative to Build Understanding of ARIA and Skills Needed to Gu...
AD-SAFE: An Initiative to Build Understanding of ARIA and Skills Needed to Gu...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Unlocking the Potential of Long-Acting PrEP to Halt HIV Transmissions
Unlocking the Potential of Long-Acting PrEP to Halt HIV TransmissionsPVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Ad
physiology of labour.pptx
- 1. Labor is a complex process that ultimately results in the expulsion of the fetus and placenta through the birth canal.
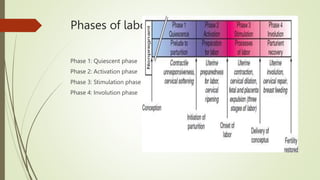
- 2. Phases of labor Phase 1: Quiescent phase Phase 2: Activation phase Phase 3: Stimulation phase Phase 4: Involution phase
- 3. Phase 1 Features ŌĆó Unresponsive myometrium ŌĆó Cervical softening-due to inc vascularity, stromal and glandular hypertrophy- hegar ŌĆó Changes in the matrix ŌĆó Changes in collagen Mediators : ŌĆó Progesterone ŌĆó Relaxin ŌĆó Prostaglandin I2 ŌĆó Nitric oxide ŌĆó PTH-RP ’é┤ This phase normally comprises 95 percent of pregnancy and is characterized by uterine smooth muscle tranquility with maintenance of cervical structural integrity. ’é┤ Some low-intensity myometrial contractions are felt during the quiescent phase, but they do not normally cause cervical dilatation. Contractions of this type become more common toward the end of pregnancy, especially in multiparous women, and are referred to as Braxton
- 4. PHASE 2 ŌĆō parturition cascade The activation phase begins about 6ŌĆō8 weeks before term and ends with the onset of regular uterine contractions. Changes in the myometrium and cervix that are essential to this phase are regulated by the fetal hypothalamo pituitaryŌĆōadrenal axis, maternal hypothalamoŌĆōpituitaryaxis, and placental endocrine/paracrine factors. ’é┤ lead to increased uterine irritability and responsiveness to uterotoninsŌĆö agents that stimulate contractions. ’é┤ formation of the lower uterine segment from the isthmus - the fetal head often descends to or even through the pelvic inletŌĆöso-called lightening.
- 5. FEATURES AND MEDIATORS Changes in the myometrium ’é┤ Increase in contractility ’é┤ Increase in uterine responsiveness ’é┤ Increase in gap junctions Changes in the cervix - Cervical ripening ’é┤ Changes in collagen structure ’é┤ Increase in collagen solubility ’é┤ Infiltration by inflammatory cells ’é┤ Estrogen ’é┤ Progesterone ’é┤ CAPs ŌĆō OXY Rreceptors,pg F rep, connexin 43 [ gap jn pro] ’é┤ Glycosaminogly-cans ’é┤ Proteoglycans ’é┤ pCRH ’é┤ Prostaglandins ’é┤ Cortisol ’é┤ Interleukin-8 ’é┤ MMP
- 6. Cervical ripening ’é┤ The cervix must undergo more extensive remodeling - eventually leading to cervical yielding and dilatation upon initiation of forceful uterine contractions ’é┤ principally involve connective tissue changes proteoglycans, glycosaminoglycans -cervical ripening. ’é┤ Many of the processes that aid cervical remodeling are controlled by the same hormones regulating uterine function ’é┤ The uterine corpus is predominantly smooth muscle, whereas the cervix is primarily connective tissue. Cellular components of the cervix include fibroblasts, epithelia, and few smooth muscle cells.
- 7. Fetus in cascade ’é┤ activation of the fetal hypothalamicŌĆō pituitaryŌĆōadrenal axis ’é┤ Fetal CRHŌĆō ACTH ŌĆō DHEAS ŌĆō17 OH DHEAS BY FETAL LIVER-- ESTRIOL BY PLACENTA- PGF2 ŌĆ”.= OXY REC, PG REC, GAP JN, ’é┤ FETAL ADRENAL-FETAL CORTISOL ŌĆō PG , OXY BY PLA . ’é┤ ANENCEPALY ’é┤ FETAL ADRENAL HYPOPLASIA
- 8. PLACENTAL ROLE ’é┤ The placenta actively participates in the process of labor through the production of estrogens, progesterone, placental corticotropin releasing hormone and other substances ’é┤ PLACENTAL SULFATASE DEFICIENCY ŌĆō X LINKED DIS prevents conversion of sulphated estrogen precursors. ŌĆó Estrogens ’é¦ Alter estrogen: Progesterone receptor ratio ’é¦ Stimulate production of CAPs by placenta ’é¦ Cause uterine contraction ŌĆó Progesterone Causes uterine quiescence ANTIINFLAMMATORY EFF ON MYOMETRIUM Undergoes functional withdrawal at term ’é┤ Placental corticotropin-releasing hormone (pCRH) FETAL CORTISOL- Pcrh- ACTH and DHEAS- PG, OXYTOCIN
- 9. MOTHER ROLE ’é┤ OXYTOCIN FETAL PIT, PLACENTA NO RISE AS SUCH Oxy receptors inc (100 -200) , inc in myometrial sensitivity to oxy Pg in decidua and membranes ’é┤ PG ’é┤ Fetal membranes and decidua contain phos-pholipase and cyclooxygenase enzymes. They are activated by local inflammatory reaction, trauma,stretch, estrogens, and progesterone. The increase in oxytocin and PG receptors in the myometrium plays a key role in uterine contractions. calcium influx to hormonal stimuli is the most important event in the initiation of contractions. Myometrial contraction during the parturition cascade is through actin and myosin interaction and interaction between myometrial cells via gap junctions.
- 10. Phase 3 ŌĆō stimulation phase- labor ’é┤ I STAGE - stage of cervical effacement and dilatation. ’é┤ extrusion of the mucus plug that had previously filled the cervical canal during pregnancy is referred to as ŌĆ£showŌĆØ or ŌĆ£bloody show.ŌĆØ ’é┤ Mechanical stretching of cx ŌĆō uterine activity ŌĆō ferguson reflex ’é┤ the upper segment contracts, retracts, and expels the fetus PAINFUL SMOOTH MSL CONTRACTION: 1) hypoxia of the contracted myometriumŌĆösuch as that with angina pectoris; (2) compression of nerve ganglia in the cervix and lower uterus by contracted interlocking muscle bundles; (3) cervical stretching during dilatation; and (4) stretching of the peritoneum overlying the fundus.
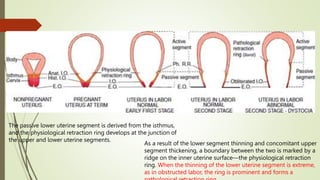
- 11. The passive lower uterine segment is derived from the isthmus, and the physiological retraction ring develops at the junction of the upper and lower uterine segments. As a result of the lower segment thinning and concomitant upper segment thickening, a boundary between the two is marked by a ridge on the inner uterine surfaceŌĆöthe physiological retraction ring. When the thinning of the lower uterine segment is extreme, as in obstructed labor, the ring is prominent and forms a
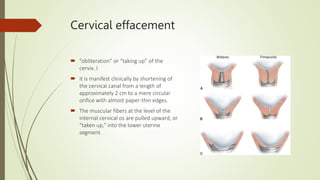
- 12. Cervical effacement ’é┤ ŌĆ£obliterationŌĆØ or ŌĆ£taking upŌĆØ of the cervix. I ’é┤ it is manifest clinically by shortening of the cervical canal from a length of approximately 2 cm to a mere circular orifice with almost paper-thin edges. ’é┤ The muscular fibers at the level of the internal cervical os are pulled upward, or ŌĆ£taken up,ŌĆØ into the lower uterine segment.
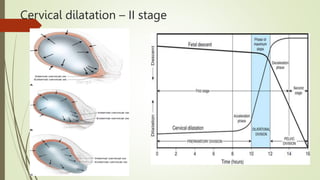
- 13. Cervical dilatation ŌĆō II stage
- 14. III STAGE ’é┤ This sudden diminution in uterine size is inevitably accompanied by a decrease in the area of the placental implantation site ’é┤ For the placenta to accommodate itself to this reduced area, it increases in thickness, but because of limited placental elasticity, it is forced to buckle. The resulting tension pulls the weakest layerŌĆödecidua spongiosaŌĆöfrom that site.
- 15. Phase 4 ŌĆō involution phase Features ŌĆó Involution of uterus and cervix ŌĆó Responsiveness of endometrium to ovarian hormones Mediators : Oxytocin Local factors ’é┤ Phase 4 or involution phase is known as the puerperium. The uterus and cervix return to the prepregnant state during this phase.
