Physiology Retreat 2016 - Blitz- Shayan
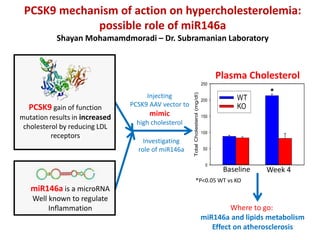
- 1. miR146a is a microRNA Well known to regulate Inflammation Injecting PCSK9 AAV vector to mimic high cholesterol Where to go: miR146a and lipids metabolism Effect on atherosclerosis PCSK9 gain of function mutation results in increased cholesterol by reducing LDL receptors TotalCholesterol(mg/dl) 0 50 100 150 200 250 WT KO Plasma Cholesterol PCSK9 mechanism of action on hypercholesterolemia: possible role of miR146a Shayan Mohamamdmoradi ŌĆō Dr. Subramanian Laboratory Investigating role of miR146a * Baseline Week 4 *P<0.05 WT vs KO
Editor's Notes
- PCSK9 is an enzyme that its GOF mutation will result in increased cholesterol. Also, miR146a is a microRNA that seems to play a role in cholesterol efflux. In this project, we investigated the role of miR146a in PCSK9 induced hypercholesterolemia. Using miR146a WT and KO mice, miR146a KO mice showed a significant reduction of plasma total cholesterol, inducing HDL-C levels irrespective to comparable PCSK9 levels. Our current focus is to understand the mechanism i.e. identifying its targets by which miR146a regulates HDL-C and its effect on atherosclerosis development.