ppt final.pptx
- 1. BIG DATA
- 2. Content 1. Introduction 2. What is Big Data 3. Characteristic of Big Data 4. Storing,selecting and processing of Big Data 5. Why Big Data 6. How it is Different 7. Big Data sources 8. Tools used in Big Data 9. Application of Big Data 10. Risks of Big Data 11. Benefits of Big Data 12. How Big Data Impact on IT 13. Future of Big Data
- 3. Introduction ? Big Data may well be the Next Big Thing in the IT world. ? Big data burst upon the scene in the first decade of the 21st century. ? The first organizations to embrace it were online and startup firms. Firms like Google, eBay, LinkedIn, and Facebook were built around big data from the beginning. ? Like many new information technologies, big data can bring about dramatic cost reductions, substantial improvements in the time required to perform a computing task, or new product and service offerings.
- 4. ? ˇ®Big DataˇŻ is similar to ˇ®small dataˇŻ, but bigger in size ? but having data bigger it requires different approaches: ¨C Techniques, tools and architecture ? an aim to solve new problems or old problems in a better way ? Big Data generates value from the storage and processing of very large quantities of digital information that cannot be analyzed with traditional computing techniques. What is BIG DATA?
- 5. What is BIG DATA ? Walmart handles more than 1 million customer transactions every hour. ? Facebook handles 40 billion photos from its user base. ? Decoding the human genome originally took 10years to process; now it can be achieved in one week.
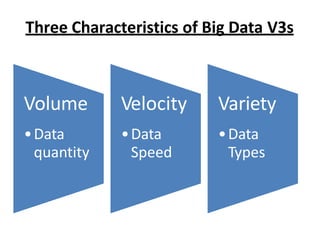
- 6. Three Characteristics of Big Data V3s Volume ?Data quantity Velocity ?Data Speed Variety ?Data Types
- 7. 1st Character of BigData Volume ?A typical PC might have had 10 gigabytes of storage in 2000. ?Today, Facebook ingests 500 terabytes of new data every day. ?Boeing 737 will generate 240 terabytes of flight data during a single flight across the US. ?The smart phones, the data they create and consume; sensors embedded into everyday objects will soon result in billions of new, constantly-updated data feeds containing environmental, location, and other information, including video.
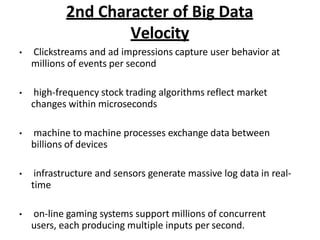
- 8. 2nd Character of Big Data Velocity ? Clickstreams and ad impressions capture user behavior at millions of events per second ? high-frequency stock trading algorithms reflect market changes within microseconds ? machine to machine processes exchange data between billions of devices ? infrastructure and sensors generate massive log data in real- time ? on-line gaming systems support millions of concurrent users, each producing multiple inputs per second.
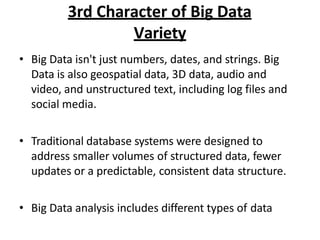
- 9. 3rd Character of Big Data Variety ? Big Data isn't just numbers, dates, and strings. Big Data is also geospatial data, 3D data, audio and video, and unstructured text, including log files and social media. ? Traditional database systems were designed to address smaller volumes of structured data, fewer updates or a predictable, consistent data structure. ? Big Data analysis includes different types of data
- 10. Storing Big Data ?Analyzing your data characteristics ? Selecting data sources for analysis ? Eliminating redundant data ? Establishing the role of NoSQL ?Overview of Big Data stores ? Data models: key value, graph, document, column-family ? Hadoop Distributed File System ? HBase ? Hive
- 11. Selecting Big Data stores ? Choosing the correct data stores based on your data characteristics ? Moving code to data ? Implementing polyglot data store solutions ? Aligning business goals to the appropriate data store
- 12. Processing Big Data ?Integrating disparate data stores ? Mapping data to the programming framework ? Connecting and extracting data from storage ? Transforming data for processing ? Subdividing data in preparation for Hadoop MapReduce ?Employing Hadoop MapReduce ? Creating the components of Hadoop MapReduce jobs ? Distributing data processing across server farms ? Executing Hadoop MapReduce jobs ? Monitoring the progress of job flows
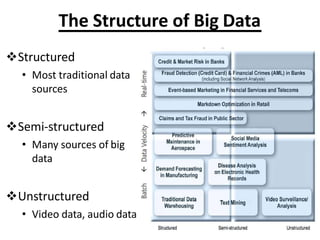
- 13. The Structure of Big Data ?Structured ? Most traditional data sources ?Semi-structured ? Many sources of big data ?Unstructured ? Video data, audio data 13
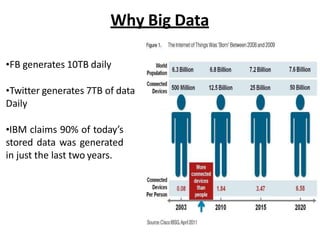
- 14. Why Big Data ? Growth of Big Data is needed ¨C Increase of storage capacities ¨C Increase of processing power ¨C Availability of data(different data types) ¨C Every day we create 2.5 quintillion bytes of data; 90% of the data in the world today has been created in the last two years alone
- 15. Why Big Data ?FB generates 10TB daily ?Twitter generates 7TB of data Daily ?IBM claims 90% of todayˇŻs stored data was generated in just the last two years.
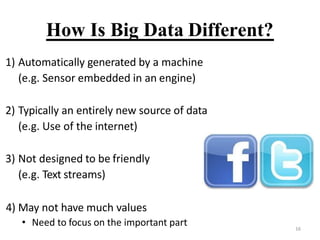
- 16. How Is Big Data Different? 1) Automatically generated by a machine (e.g. Sensor embedded in an engine) 2) Typically an entirely new source of data (e.g. Use of the internet) 3) Not designed to be friendly (e.g. Text streams) 4) May not have much values ? Need to focus on the important part 16
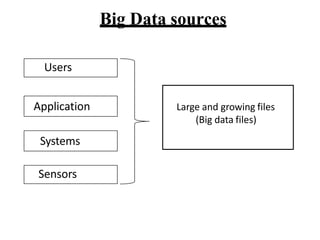
- 17. Big Data sources Users Application Systems Sensors Large and growing files (Big data files)
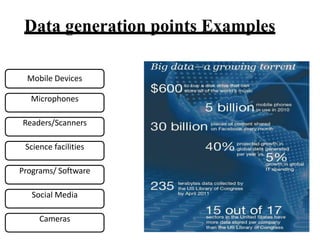
- 18. Data generation points Examples Mobile Devices Microphones Readers/Scanners Science facilities Programs/ Software Social Media Cameras
- 19. Big Data Analytics ? Examining large amount of data ? Appropriate information ? Identification of hidden patterns, unknown correlations ? Competitive advantage ? Better business decisions: strategic and operational ? Effective marketing, customer satisfaction, increased revenue
- 20. ? Where processing is hosted? ¨C Distributed Servers / Cloud (e.g. Amazon EC2) ? Where data is stored? ¨C Distributed Storage (e.g. Amazon S3) ? What is the programming model? ¨C Distributed Processing (e.g. MapReduce) ? How data is stored & indexed? ¨C High-performance schema-free databases (e.g. MongoDB) ? What operations are performed on data? ¨C Analytic / Semantic Processing Types of tools used in Big-Data
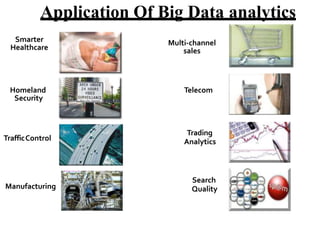
- 21. Application Of Big Data analytics Homeland Security Smarter Healthcare Multi-channel sales Telecom Manufacturing TrafficControl Trading Analytics Search Quality
- 22. Risks of Big Data ? Will be so overwhelmed ? Need the right people and solve the right problems ? Costs escalate too fast ? IsnˇŻt necessary to capture 100% ? Many sources of big data is privacy ? self-regulation ? Legal regulation 22
- 23. Leading Technology Vendors Example Vendors ? IBM ¨C Netezza ? EMC ¨C Greenplum ? Oracle ¨C Exadata Commonality ? MPP architectures ? Commodity Hardware ? RDBMS based ? Full SQL compliance
- 24. How Big data impacts on IT ? Big data is a troublesome force presenting opportunities with challenges to IT organizations. ? By 2015 4.4 million IT jobs in Big Data ; 1.9 million is in US itself ? India will require a minimum of 1 lakh data scientists in the next couple of years in addition to data analysts and data managers to support the Big Data space.
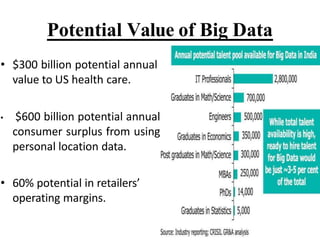
- 25. Potential Value of Big Data ? $300 billion potential annual value to US health care. ? $600 billion potential annual consumer surplus from using personal location data. ? 60% potential in retailersˇŻ operating margins.
- 26. India ¨C Big Data ? Gaining attraction ? Huge market opportunities for IT services (82.9% of revenues) and analytics firms (17.1 % ) ? Current market size is $200 million. By 2015 $1 billion ? The opportunity for Indian service providers lies in offering services around Big Data implementation and analytics for global multinationals
- 27. Benefits of Big Data ?Real-time big data isnˇŻt just a process for storing petabytes or exabytes of data in a data warehouse, ItˇŻs about the ability to make better decisions and take meaningful actions at the right time. ?Fast forward to the present and technologies like Hadoop give you the scale and flexibility to store data before you know how you are going to process it. ?Technologies such as MapReduce,Hive and Impala enable you to run queries without changing the data structures underneath.
- 28. Benefits of Big Data ? Our newest research finds that organizations are using big data to target customer-centric outcomes, tap into internal data and build a better information ecosystem. ? Big Data is already an important part of the $64 billion database and data analytics market ? It offers commercial opportunities of a comparable scale to enterprise software in the late 1980s ? And the Internet boom of the 1990s, and the social media explosion of today.
- 29. Future of Big Data ? $15 billion on software firms only specializing in data management and analytics. ? This industry on its own is worth more than $100 billion and growing at almost 10% a year which is roughly twice as fast as the software business as a whole. ? In February 2012, the open source analyst firm Wikibon released the first market forecast for Big Data , listing $5.1B revenue in 2012 with growth to $53.4B in 2017 ? The McKinsey Global Institute estimates that data volume is growing 40% per year, and will grow 44x between 2009 and 2020.
- 30. References ? www.şÝşÝߣshare.com ? www.wikipedia.com ? www.computereducation.org ? Books- ?Big Data by Viktor Mayer-Schonberger
- 31. Thank You.