Presentation[1]---------------------.pdf
0 likes9 views
Presentation[1]---------------------.pdf
1 of 13
Download to read offline











Recommended
Ethics and Responsible AI Deployment.pptx



Ethics and Responsible AI Deployment.pptxPetar Radanliev
Ěý
Ethics and Responsible AI Deployment
Abstract: As Artificial Intelligence (AI) becomes more prevalent, protecting personal privacy is a critical ethical issue that must be addressed. This article explores the need for ethical AI systems that safeguard individual privacy while complying with ethical standards. By taking a multidisciplinary approach, the research examines innovative algorithmic techniques such as differential privacy, homomorphic encryption, federated learning, international regulatory frameworks, and ethical guidelines. The study concludes that these algorithms effectively enhance privacy protection while balancing the utility of AI with the need to protect personal data. The article emphasises the importance of a comprehensive approach that combines technological innovation with ethical and regulatory strategies to harness the power of AI in a way that respects and protects individual privacy.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to significantly impact employment, social equity, and economic systems in ways that require careful ethical analysis and aggressive legislative measures to mitigate negative consequences. This means that the implications of AI in different industries, such as healthcare, finance, and transportation, must be carefully considered.
Due to the global nature of AI technology, global collaboration must be fostered to establish standards and regulatory frameworks that transcend national boundaries. This includes the establishment of ethical guidelines that AI researchers and developers worldwide should follow.
To address emergent ethical concerns with AI, future research must focus on several recommendations. Firstly, ethical considerations must be integrated into the design phase of AI systems and not treated as an afterthought. This is known as "Ethics by Design" and involves incorporating ethical standards during the development phase of AI systems to ensure that the technology aligns with ethical principles.
Secondly, interdisciplinary research that combines AI, ethics, law, social science, and other relevant domains should be promoted to produce well-rounded solutions to ethical dilemmas. This requires the participation of experts from different fields to identify and address ethical issues.
Thirdly, regulatory frameworks must be dynamic and adaptive to keep pace with the rapid evolution of AI technologies. This means that regulatory frameworks must be flexible enough to accommodate changes in AI technology while ensuring ethical standards are maintained.
Fourthly, empirical research should be conducted to understand the real-world implications of AI systems on individuals and society, which can then inform ethical principles and policies. This means that empirical data must be collected to understand how AI affects people in different contexts.
Finally, risk assessment procedures should be improved to better analyse the ethical hazards associated with AI applications.A koene un_bias_ieee_ebdvf_nov2017



A koene un_bias_ieee_ebdvf_nov2017Ansgar Koene
Ěý
Presentation at European Big Data Values forum on Fairness, Bias and the role of Ethics Standards in Algorithmic Decision Making. Part of the Data & Society session.Trust, Context and, Regulation: Achieving More Explainable AI in Financial Se...



Trust, Context and, Regulation: Achieving More Explainable AI in Financial Se...Databricks
Ěý
This presentation seeks to advance the thinking on how financial services firms can implement a framework that supports explainable artificial intelligence (AI), thus building trust among consumers, shareholders and other stakeholders, and helping ensure compliance with emerging regulatory and ethical norms.Ethical Considerations in AI Development- Ensuring Fairness and Transparency



Ethical Considerations in AI Development- Ensuring Fairness and TransparencyArpan Buwa
Ěý
Ethical considerations in AI development, particularly ensuring fairness and transparency, are crucial to mitigate potential harms and ensure equitable outcomes. Fairness involves ensuring that AI systems do not discriminate against individuals or groups based on characteristics like race, gender, or socioeconomic status. This can be achieved through unbiased data selection, diverse training datasets, and regular audits to detect and mitigate biases.
Transparency refers to making AI systems understandable and explainable to users and stakeholders. It involves disclosing how AI decisions are made, what data is used, and providing mechanisms for recourse or appeal in case of errors or unintended consequences. Transparency fosters trust and accountability in AI systems, crucial for user acceptance and regulatory compliance.
Overall, addressing ethical considerations in AI development requires interdisciplinary collaboration, adherence to established ethical frameworks, and ongoing evaluation and adaptation of practices to uphold fairness and transparency standards.Information System Design and Implementation



Information System Design and ImplementationYasmeenKhalsa
Ěý
1. What is man-made information system?
2. How would an analysis determine the user’s needs for a system?
3. A system leads to a lot of planning and less of implementation. Do you agree?
4. What are the advantages and uses of structured English?
5. What is the importance of end-user training?
6. What is the difference between logical and physical design?
7. Define a Project.
8. What are the various elements of system environment?
9. Differentiate between reliability and security.
10. What are the primary steps in interviewing?
11. What is rapport?
12. Differentiate between HIPO and IPO.
13. What is the FM concept?
14. What is feasibility study of a system?
15. Differentiate between physical and abstract system.
16. What is stress testing?
17. Differentiate between decision table and structure chart with example.
18. What is MTBF?
19. What training aids are used for training users on new system?
20. Open and Closed Systems.
21. What do you mean by audit trail?
22. What is DFD?
23. Explain fact finding techniques.
24. On-site Observation.
25. Discuss Evaluation and Validation.
26. List the characteristics of a system.
27. Define information system. Give an example.
28. How on-site observation is useful in information gathering?
29. What are the required skills for a system analyst?
30. What is the difference between logical and physical design?
31. What are the types of maintenance?
32. What is post installation review?
Information System Design and Implementation



Information System Design and ImplementationYASMEENSIDDIQUI13
Ěý
Information System Design and implementation
1. What is man-made information system?
2. How would an analysis determine the user’s needs for a system?
3. A system leads to a lot of planning and less of implementation. Do you agree?
4. What are the advantages and uses of structured English?
5. What is the importance of end-user training?
6. What is the difference between logical and physical design?
7. Define a Project.
8. What are the various elements of system environment?
9. Differentiate between reliability and security.
10. What are the primary steps in interviewing?
11. What is rapport?
12. Differentiate between HIPO and IPO.
13. What is the FM concept?
14. What is feasibility study of a system?
15. Differentiate between physical and abstract system.
16. What is stress testing?
17. Differentiate between decision table and structure chart with example.
18. What is MTBF?
19. What training aids are used for training users on new system?
20. Open and Closed Systems.
21. What do you mean by audit trail?
22. What is DFD?
23. Explain fact finding techniques.
24. On-site Observation.
25. Discuss Evaluation and Validation.
26. List the characteristics of a system.
27. Define information system. Give an example.
28. How on-site observation is useful in information gathering?
29. What are the required skills for a system analyst?
30. What is the difference between logical and physical design?
31. What are the types of maintenance?
32. What is post installation review?
Responsible AI: AI that benefits society ethically



Responsible AI: AI that benefits society ethicallyVincentNatalie
Ěý
The conversation around what is responsible AI has gained significant momentum across industries, yet a universally accepted definition remains puzzling. Often, responsible AI is seen merely as a way to avoid risks, but its scope is much broader. Moreover, it not only involves mitigating risks and managing complexities, but also using AI to transform lives and experiences. AI Governance Playbook



AI Governance PlaybookAntony Turner
Ěý
The document discusses the need for AI governance frameworks to build trust in AI systems. It outlines key pillars of governance including governing bodies, roles and responsibilities, and standard operating procedures. It also discusses the importance of model documentation, validation and certification. Effective governance requires a risk-based approach and measures to minimize bias and ensure fairness, transparency and human-centric AI. Governance spans the full model lifecycle from data collection and preprocessing to model deployment and use.Franklin Burgess - Understanding Ethical Considerations in AI Development



Franklin Burgess - Understanding Ethical Considerations in AI DevelopmentFranklin Burgess
Ěý
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence has opened up new possibilities across various industries. However, it also raises significant ethical considerations that developers must address. Franklin Burgess emphasizes that understanding these concerns is crucial to ensure AI technologies are developed responsibly and beneficially.Chapter_1_INTRODUCTION.pdf



Chapter_1_INTRODUCTION.pdfKamal Acharya
Ěý
The document provides an overview of a student information management system. It discusses how the system will maintain student records online and make it easier for schools and colleges to manage student data and activities. The system will store all student details and allow for easy searching of student records. It will also enable online registration and updating of student profiles. The document outlines the objectives, scope, requirements analysis, and design of the student information management system.Project Access Control ProposalPurposeThis course project i.docx



Project Access Control ProposalPurposeThis course project i.docxstilliegeorgiana
Ěý
Project: Access Control Proposal
Purpose
This course project is intended to assess your ability to comprehend and apply the basic concepts related to information security management, such as the following:
The ability to discern when a risk assessment should be performed and carrying out the task
Understanding user or customer access requirements, whether remote or local
Using a layered security approach to establish and maintain access controls
Working with other departments, such as the human resources department, to identify and implement methods to prevent unwarranted exposure to information by inappropriate personnel
Your ability to execute the tasks within these information security domains and others will be evaluated against the learning objectives as identified and described in previous lessons of instruction for this course. Required Source Information and Tools
Web References: Links to Web references in this Instructor Guide and related materials are subject to change without prior notice. These links were last verified on August 2, 2014.
The following tools and resources will be needed to complete this project:
· Course textbook
· Access to the Internet
· Access to the library
· Text sheet: Integrated Distributors Incorporated (access_project_ts_integrateddistributors)Learning Objectives and Outcomes
Successful completion of this project will ensure that you are capable of supporting the implementation and management of an information systems security framework. To be able to do so, you need to be able to do the following:
Relate how an access control policy framework is used to define authorization and access to an information technology (IT) infrastructure for compliance.
Mitigate risks to an IT infrastructure’s confidentiality, integrity, and availability with sound access controls.
Relate how a data classification standard influences an IT infrastructure’s access control requirements and implementation.
Develop an access control policy framework consisting of best practices for policies, standards, procedures, and guidelines to mitigate unauthorized access.
Define proper security controls within the User Domain to mitigate risks and threats caused by human nature and behavior.
Implement appropriate access controls for information systems within IT infrastructures.
Mitigate risks from unauthorized access to IT systems through proper testing and reporting.Project Checkpoints
The course project has a checkpoint strategy. Checkpoint deliverables allow you to receive valuable feedback on your interim work. In this project, you have four ungraded checkpoint deliverables. (See the syllabus for the schedule.) You may discuss project questions with the instructor, and you should receive feedback from the instructor on previously submitted work. The checkpoint deliverable ensures refinement of the final deliverables, if incorporated effectively. The final deliverable for this project is a professional report and a PowerPoint presenta ...Ethical AI at VDAB, presented by Vincent Buekenhout (Ethical AI Lead, VDAB) a...



Ethical AI at VDAB, presented by Vincent Buekenhout (Ethical AI Lead, VDAB) a...Patrick Van Renterghem
Ěý
Digital ethics and ensuring fair and unbiased AI systems are important priorities for VDAB. They have developed principles of trust, transparency and benefit and are working to operationalize them. This includes qualitative and quantitative assessments of AI systems to identify any biases and ensure fair treatment of all users. VDAB aims to be a leader in the ethical development and use of AI to best serve citizens and employers.Responsible Machine Learning



Responsible Machine LearningEng Teong Cheah
Ěý
Data scientists have a duty to ensure they analyze data and train machine learning models responsibly; respecting individual privacy, mitigating bias, and ensuring transparency. This module explores some considerations and techniques for applying responsible machine learning principles.Key Concepts And Principles Of Internal Quality Assurance...



Key Concepts And Principles Of Internal Quality Assurance...Lanate Drummond
Ěý
The document discusses strategies for quality improvement and innovation at Dover Saddlery, Inc., an equestrian tack and apparel retailer. It outlines concepts like total quality management, balanced scorecards, six sigma, and benchmarking that Dover Saddlery could implement. The company aims to enhance customer satisfaction and retention by applying these quality assurance methods and developing new products based on customer data and feedback.Unit Iii



Unit IiiRam Dutt Shukla
Ěý
The document contains questions related to concepts of planning and control for information systems. It includes questions about total quality management, levels of management, importance of planning for information systems, organizational planning, business models, information technology architecture, system analysis and design, MIS development procedures, quality in information systems, acquisition of hardware/software, computer peripherals, software types, structured/unstructured decisions, information system audits, the planning process, computational support for planning, importance of control, feedback, factors for IS organization, Nolan's stage models of IS growth, and content of an IS master plan.AI Governance Training Program Building Ethical and Transparent AI Systems



AI Governance Training Program Building Ethical and Transparent AI Systemsaicertsnews
Ěý
"Unlock the power of ethical AI with our AI governance training programs. Build transparent systems and lead the way in responsible AI development. Enroll today!"Improved Interpretability and Explainability of Deep Learning Models.pdf



Improved Interpretability and Explainability of Deep Learning Models.pdfNarinder Singh Punn
Ěý
This file aims to give a thorough overview of the current state and future prospects of interpretability and explainability in deep learning, making it a valuable resource for students, researchers, and professionals in the field. The post will comprehensively cover the following aspects:
Introduction to Interpretability and Explainability: Explaining what these concepts mean in the context of deep learning and why they are critical.
The Need for Transparency: Discussing the importance of interpretability and explainability in AI, focusing on ethical considerations, trust in AI systems, and regulatory compliance.
Key Concepts and Definitions: Clarifying terms like “black-box” models, interpretability, explainability, and their relevance in deep learning.
Methods and Techniques:
Visualization Techniques: Detailing methods like feature visualization, attention mechanisms, and tools like Grad-CAM.
Feature Importance Analysis: Exploring techniques like SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) and LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations) for understanding feature contributions.
Decision Boundary Analysis: Discussing methods to analyze and visualize the decision boundaries of models.
Practical Implementations and Code Examples: Providing examples of how these techniques can be implemented using popular deep learning frameworks like TensorFlow or PyTorch.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications: Presenting real-world scenarios where interpretability and explainability have played a vital role, especially in fields like healthcare, finance, and autonomous systems.
Challenges and Limitations: Addressing the challenges in achieving interpretability and the trade-offs with model complexity and performance.
Future Directions and Research Trends: Discussing ongoing research, emerging trends, and potential future advancements in making deep learning models more interpretable and explainable.
Conclusion: Summarizing the key takeaways and the importance of continued efforts in this area.
References and Further Reading: Providing a list of academic papers, articles, and resources for readers who wish to delve deeper into the topic.
Section 1: Introduction to Interpretability and Explainability
The field of deep learning has witnessed exponential growth in recent years, leading to significant advancements in various applications such as image recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous systems. However, as these neural network models become increasingly complex, they often resemble “black boxes”, where the decision-making process is not transparent or understandable to users. This obscurity raises concerns, especially in critical applications, and underscores the need for interpretability and explainability in deep learning models.
What are Interpretability and Explainability?
Interpretability: This refers to the degree to which a human can understand the cause of a decision made by a machine learning model. It’s about answering the questioWhat regulation for Artificial Intelligence?



What regulation for Artificial Intelligence?Nozha Boujemaa
Ěý
Should we regulate Artificial Intelligence? What are the challenges to face bias in data and algorithms? What is trustworthy AI? AI HLEG (European Commission) and AIGO (OECD) feedback experiences and recommendations. Example in precision medicine: AI/ML for medical devices Unlocking AI Potential: Leveraging PIA Processes for Comprehensive Impact Ass...



Unlocking AI Potential: Leveraging PIA Processes for Comprehensive Impact Ass...TrustArc
Ěý
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force in various industries, from healthcare to finance and beyond. While AI offers incredible opportunities, it also raises ethical, legal, and social challenges that must be addressed. To navigate this complex landscape in the world of privacy, it is crucial to conduct comprehensive Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs).
Conducting PIAs in this dynamic and evolving world of AI has brought new challenges to the privacy world. With AI increasingly being integrated into different areas of our lives, understanding the intersection between AI and PIAs is essential for any organization to ensure they are privacy forward.
Take advantage of this opportunity to gain a comprehensive understanding of AI impact assessments and their role in shaping the future of AI. In this insightful webinar, our experts will explore the power of Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs) in ensuring responsible AI development and deployment.
In this webinar, some key topics that will be covered include:
- Introduction to AI PIAs
- PIAs demystified (why they are essential in the context of AI)
- Explore the evolving legal and regulatory landscape governing AI and privacy, including GDPR, CCPA, and other international standards
- Best practices for conducting effective PIAs in AI projects
- Future outlooks for AI and PIAs
Ethical Issues in Artificial Intelligence: Examining Bias and Discrimination



Ethical Issues in Artificial Intelligence: Examining Bias and DiscriminationTechCyber Vision
Ěý
The document discusses several key issues regarding ensuring ethical and unbiased artificial intelligence (AI), including:
1. AI systems can unintentionally learn and perpetuate biases from historical data, resulting in discriminatory outcomes. Addressing bias requires attention to diverse and representative datasets, identification and removal of biases in data, and fairness metrics in algorithm design.
2. Governance frameworks and regulations are needed to establish ethical principles, promote transparency, accountability and privacy, require impact assessments and audits, and mandate algorithmic explainability. International collaboration is important for consistent standards.
3. Mitigating discrimination involves defining fairness metrics, addressing biases in training data, regular evaluation, stakeholder involvement, transparency, and continuous improvement ofDancyrityshy 1foundatioieh



Dancyrityshy 1foundatioiehAnne Starr
Ěý
The document provides information about Leo Lourdes and his foundation in cyber security. Leo Lourdes has extensive training and certifications in IT management, project management, information security and service management. The objective of his cyber security foundation is to prevent harm to computer networks, applications, devices and data. The training covers topics such as the CIA triad, security governance, risk management and cyber threats.Responsible AI in Industry: Practical Challenges and Lessons Learned



Responsible AI in Industry: Practical Challenges and Lessons LearnedKrishnaram Kenthapadi
Ěý
How do we develop machine learning models and systems taking fairness, accuracy, explainability, and transparency into account? How do we protect the privacy of users when building large-scale AI based systems? Model fairness and explainability and protection of user privacy are considered prerequisites for building trust and adoption of AI systems in high stakes domains such as hiring, lending, and healthcare. We will first motivate the need for adopting a “fairness, explainability, and privacy by design” approach when developing AI/ML models and systems for different consumer and enterprise applications from the societal, regulatory, customer, end-user, and model developer perspectives. We will then focus on the application of responsible AI techniques in practice through industry case studies. We will discuss the sociotechnical dimensions and practical challenges, and conclude with the key takeaways and open challenges.Capgemini ses - security po v (gr)



Capgemini ses - security po v (gr)Gord Reynolds
Ěý
Capgemini's Identity and Access Management solution places identity management at the core of an integrated security infrastructure. It comprises processes and technologies that help strengthen compliance, secure operations, and improve agility. Capgemini takes a three-stage approach to implementation: planning to understand needs, preparation to design technical and process solutions, and implementation to realize the solution. Capgemini's advantage is experience in diverse sectors, alliances with leading vendors, and expertise in both commercial and public security solutions.ANIn Kolkata April 2024 |Ethics of AI by Abhishek Nandy



ANIn Kolkata April 2024 |Ethics of AI by Abhishek NandyAgileNetwork
Ěý
Agile Network India - Kolkata
Title: Ethics of AI by Abhishek Nandy
Date: 20th April 2024
Hosted by: PrediQt Business Solutions Pvt. Ltd
To meet the requirements for lab 10 you were to perform Part 1, S



To meet the requirements for lab 10 you were to perform Part 1, STakishaPeck109
Ěý
To meet the requirements for lab 10 you were to perform: Part 1, Step 2: evaluate the policy document against the summarized NIST best practices, identify by number which, if any, of the eight best practices the policy satisfies, and for each practice that you identify, provide a reference to the statement in the policy that aligns with that best practice; Part 1 Step 3: suggest how you would revise the policy to directly align with the standards and provide specific statements that you would add/modify in the policy; Part 1, Step 4: describe whether the policy document is best titled as a policy or whether it would be better described using another element of the policy framework. Part 2, Step 3: describe the process that the Center uses to ensure that its standards represent the consensus of the cybersecurity community; Part 2, Step 5: identify the section of the recommendations that achieves this goal; Part 2, Step 7: for each of the five best practices in the previous step, classify the practice as: satisfied (indicate recommendation number that achieves the best practice), violated (indicate recommendation number that violates the best practice) or not addressed.
Unfortunately it looks like you were off target for this assignment; you needed to:
Part 1, Step 2: identify by number the best practices (given in the lab) that are satisfied by the policy - partial credit given;Ěý
Part 1 Step 3: provide specific statements on how you would revise the policy; you needed to align your statements with the best practices (e.g. Best Practice 2: add to Section 4.2) - partial credit given;
Part 1, Step 4: describe whether the policy document is best titled as a policy or whether it would be better described using another element of the policy framework; this "policy" is better described as a standard (see technical implementation details);
Part 2, Step 3: describe the process that the Center uses to ensure its standards represent the consensus of the cybersecurity community; see the Consensus Guidance portion of the document - partial credit given;
Part 2, Step 5: identify the section of the recommendations that achieves the goal of Step 3 - partial credit given;
Part 2, Step 7: classify the five best practices; indicate the recommendation number for each - partial credit given.
Applying the Security Policy Framework to an Access Control Environment (3e)
Access Control and Identity Management, Third Edition - Lab 10
Student: Email:
HARSHAVARDHAN POCHARAM [emailĚýprotected]
Time on Task: Progress:
100%
Report Generated: Sunday, June 20, 2021 at 9:45 AM
Guided Exercises
Part 1: Evaluate a Security Policy
2. Evaluate the policy document against the NIST best practices summarized above. Identify by
number which, if any, of the eight best practices the policy satisfies. For each practice that you
identify, provide a reference to the statement in the policy that aligns with that best practice.
In line with relevant policy, the information s ...Ethical Considerations in Data Analysis_ Balancing Power, Privacy, and Respon...



Ethical Considerations in Data Analysis_ Balancing Power, Privacy, and Respon...Soumodeep Nanee Kundu
Ěý
The explosion of data and the increasing capabilities of data analysis have transformed various aspects of our lives. From healthcare and finance to marketing and law enforcement, data analysis has become an essential tool for decision-making and problem-solving. However, with great power comes great responsibility. Ethical considerations in data analysis are more critical than ever as data professionals grapple with questions related to privacy, fairness, transparency, and accountability. In this article, we will delve into the ethical challenges that data analysts and organizations face and explore strategies to address them.SOC 2 Certification Unveiled: Understanding the Core Principles



SOC 2 Certification Unveiled: Understanding the Core PrinciplesShyamMishra72
Ěý
In today's interconnected digital world, safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring the security of information systems is paramount. This is where SOC 2 certification steps in. It has become a benchmark for service organizations to prove their commitment to data security and privacy. In this blog, we will unveil the core principles of SOC 2 certification to help you understand its significance and how it can benefit your organization.More Related Content
Similar to Presentation[1]---------------------.pdf (20)
AI Governance Playbook



AI Governance PlaybookAntony Turner
Ěý
The document discusses the need for AI governance frameworks to build trust in AI systems. It outlines key pillars of governance including governing bodies, roles and responsibilities, and standard operating procedures. It also discusses the importance of model documentation, validation and certification. Effective governance requires a risk-based approach and measures to minimize bias and ensure fairness, transparency and human-centric AI. Governance spans the full model lifecycle from data collection and preprocessing to model deployment and use.Franklin Burgess - Understanding Ethical Considerations in AI Development



Franklin Burgess - Understanding Ethical Considerations in AI DevelopmentFranklin Burgess
Ěý
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence has opened up new possibilities across various industries. However, it also raises significant ethical considerations that developers must address. Franklin Burgess emphasizes that understanding these concerns is crucial to ensure AI technologies are developed responsibly and beneficially.Chapter_1_INTRODUCTION.pdf



Chapter_1_INTRODUCTION.pdfKamal Acharya
Ěý
The document provides an overview of a student information management system. It discusses how the system will maintain student records online and make it easier for schools and colleges to manage student data and activities. The system will store all student details and allow for easy searching of student records. It will also enable online registration and updating of student profiles. The document outlines the objectives, scope, requirements analysis, and design of the student information management system.Project Access Control ProposalPurposeThis course project i.docx



Project Access Control ProposalPurposeThis course project i.docxstilliegeorgiana
Ěý
Project: Access Control Proposal
Purpose
This course project is intended to assess your ability to comprehend and apply the basic concepts related to information security management, such as the following:
The ability to discern when a risk assessment should be performed and carrying out the task
Understanding user or customer access requirements, whether remote or local
Using a layered security approach to establish and maintain access controls
Working with other departments, such as the human resources department, to identify and implement methods to prevent unwarranted exposure to information by inappropriate personnel
Your ability to execute the tasks within these information security domains and others will be evaluated against the learning objectives as identified and described in previous lessons of instruction for this course. Required Source Information and Tools
Web References: Links to Web references in this Instructor Guide and related materials are subject to change without prior notice. These links were last verified on August 2, 2014.
The following tools and resources will be needed to complete this project:
· Course textbook
· Access to the Internet
· Access to the library
· Text sheet: Integrated Distributors Incorporated (access_project_ts_integrateddistributors)Learning Objectives and Outcomes
Successful completion of this project will ensure that you are capable of supporting the implementation and management of an information systems security framework. To be able to do so, you need to be able to do the following:
Relate how an access control policy framework is used to define authorization and access to an information technology (IT) infrastructure for compliance.
Mitigate risks to an IT infrastructure’s confidentiality, integrity, and availability with sound access controls.
Relate how a data classification standard influences an IT infrastructure’s access control requirements and implementation.
Develop an access control policy framework consisting of best practices for policies, standards, procedures, and guidelines to mitigate unauthorized access.
Define proper security controls within the User Domain to mitigate risks and threats caused by human nature and behavior.
Implement appropriate access controls for information systems within IT infrastructures.
Mitigate risks from unauthorized access to IT systems through proper testing and reporting.Project Checkpoints
The course project has a checkpoint strategy. Checkpoint deliverables allow you to receive valuable feedback on your interim work. In this project, you have four ungraded checkpoint deliverables. (See the syllabus for the schedule.) You may discuss project questions with the instructor, and you should receive feedback from the instructor on previously submitted work. The checkpoint deliverable ensures refinement of the final deliverables, if incorporated effectively. The final deliverable for this project is a professional report and a PowerPoint presenta ...Ethical AI at VDAB, presented by Vincent Buekenhout (Ethical AI Lead, VDAB) a...



Ethical AI at VDAB, presented by Vincent Buekenhout (Ethical AI Lead, VDAB) a...Patrick Van Renterghem
Ěý
Digital ethics and ensuring fair and unbiased AI systems are important priorities for VDAB. They have developed principles of trust, transparency and benefit and are working to operationalize them. This includes qualitative and quantitative assessments of AI systems to identify any biases and ensure fair treatment of all users. VDAB aims to be a leader in the ethical development and use of AI to best serve citizens and employers.Responsible Machine Learning



Responsible Machine LearningEng Teong Cheah
Ěý
Data scientists have a duty to ensure they analyze data and train machine learning models responsibly; respecting individual privacy, mitigating bias, and ensuring transparency. This module explores some considerations and techniques for applying responsible machine learning principles.Key Concepts And Principles Of Internal Quality Assurance...



Key Concepts And Principles Of Internal Quality Assurance...Lanate Drummond
Ěý
The document discusses strategies for quality improvement and innovation at Dover Saddlery, Inc., an equestrian tack and apparel retailer. It outlines concepts like total quality management, balanced scorecards, six sigma, and benchmarking that Dover Saddlery could implement. The company aims to enhance customer satisfaction and retention by applying these quality assurance methods and developing new products based on customer data and feedback.Unit Iii



Unit IiiRam Dutt Shukla
Ěý
The document contains questions related to concepts of planning and control for information systems. It includes questions about total quality management, levels of management, importance of planning for information systems, organizational planning, business models, information technology architecture, system analysis and design, MIS development procedures, quality in information systems, acquisition of hardware/software, computer peripherals, software types, structured/unstructured decisions, information system audits, the planning process, computational support for planning, importance of control, feedback, factors for IS organization, Nolan's stage models of IS growth, and content of an IS master plan.AI Governance Training Program Building Ethical and Transparent AI Systems



AI Governance Training Program Building Ethical and Transparent AI Systemsaicertsnews
Ěý
"Unlock the power of ethical AI with our AI governance training programs. Build transparent systems and lead the way in responsible AI development. Enroll today!"Improved Interpretability and Explainability of Deep Learning Models.pdf



Improved Interpretability and Explainability of Deep Learning Models.pdfNarinder Singh Punn
Ěý
This file aims to give a thorough overview of the current state and future prospects of interpretability and explainability in deep learning, making it a valuable resource for students, researchers, and professionals in the field. The post will comprehensively cover the following aspects:
Introduction to Interpretability and Explainability: Explaining what these concepts mean in the context of deep learning and why they are critical.
The Need for Transparency: Discussing the importance of interpretability and explainability in AI, focusing on ethical considerations, trust in AI systems, and regulatory compliance.
Key Concepts and Definitions: Clarifying terms like “black-box” models, interpretability, explainability, and their relevance in deep learning.
Methods and Techniques:
Visualization Techniques: Detailing methods like feature visualization, attention mechanisms, and tools like Grad-CAM.
Feature Importance Analysis: Exploring techniques like SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) and LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations) for understanding feature contributions.
Decision Boundary Analysis: Discussing methods to analyze and visualize the decision boundaries of models.
Practical Implementations and Code Examples: Providing examples of how these techniques can be implemented using popular deep learning frameworks like TensorFlow or PyTorch.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications: Presenting real-world scenarios where interpretability and explainability have played a vital role, especially in fields like healthcare, finance, and autonomous systems.
Challenges and Limitations: Addressing the challenges in achieving interpretability and the trade-offs with model complexity and performance.
Future Directions and Research Trends: Discussing ongoing research, emerging trends, and potential future advancements in making deep learning models more interpretable and explainable.
Conclusion: Summarizing the key takeaways and the importance of continued efforts in this area.
References and Further Reading: Providing a list of academic papers, articles, and resources for readers who wish to delve deeper into the topic.
Section 1: Introduction to Interpretability and Explainability
The field of deep learning has witnessed exponential growth in recent years, leading to significant advancements in various applications such as image recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous systems. However, as these neural network models become increasingly complex, they often resemble “black boxes”, where the decision-making process is not transparent or understandable to users. This obscurity raises concerns, especially in critical applications, and underscores the need for interpretability and explainability in deep learning models.
What are Interpretability and Explainability?
Interpretability: This refers to the degree to which a human can understand the cause of a decision made by a machine learning model. It’s about answering the questioWhat regulation for Artificial Intelligence?



What regulation for Artificial Intelligence?Nozha Boujemaa
Ěý
Should we regulate Artificial Intelligence? What are the challenges to face bias in data and algorithms? What is trustworthy AI? AI HLEG (European Commission) and AIGO (OECD) feedback experiences and recommendations. Example in precision medicine: AI/ML for medical devices Unlocking AI Potential: Leveraging PIA Processes for Comprehensive Impact Ass...



Unlocking AI Potential: Leveraging PIA Processes for Comprehensive Impact Ass...TrustArc
Ěý
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force in various industries, from healthcare to finance and beyond. While AI offers incredible opportunities, it also raises ethical, legal, and social challenges that must be addressed. To navigate this complex landscape in the world of privacy, it is crucial to conduct comprehensive Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs).
Conducting PIAs in this dynamic and evolving world of AI has brought new challenges to the privacy world. With AI increasingly being integrated into different areas of our lives, understanding the intersection between AI and PIAs is essential for any organization to ensure they are privacy forward.
Take advantage of this opportunity to gain a comprehensive understanding of AI impact assessments and their role in shaping the future of AI. In this insightful webinar, our experts will explore the power of Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs) in ensuring responsible AI development and deployment.
In this webinar, some key topics that will be covered include:
- Introduction to AI PIAs
- PIAs demystified (why they are essential in the context of AI)
- Explore the evolving legal and regulatory landscape governing AI and privacy, including GDPR, CCPA, and other international standards
- Best practices for conducting effective PIAs in AI projects
- Future outlooks for AI and PIAs
Ethical Issues in Artificial Intelligence: Examining Bias and Discrimination



Ethical Issues in Artificial Intelligence: Examining Bias and DiscriminationTechCyber Vision
Ěý
The document discusses several key issues regarding ensuring ethical and unbiased artificial intelligence (AI), including:
1. AI systems can unintentionally learn and perpetuate biases from historical data, resulting in discriminatory outcomes. Addressing bias requires attention to diverse and representative datasets, identification and removal of biases in data, and fairness metrics in algorithm design.
2. Governance frameworks and regulations are needed to establish ethical principles, promote transparency, accountability and privacy, require impact assessments and audits, and mandate algorithmic explainability. International collaboration is important for consistent standards.
3. Mitigating discrimination involves defining fairness metrics, addressing biases in training data, regular evaluation, stakeholder involvement, transparency, and continuous improvement ofDancyrityshy 1foundatioieh



Dancyrityshy 1foundatioiehAnne Starr
Ěý
The document provides information about Leo Lourdes and his foundation in cyber security. Leo Lourdes has extensive training and certifications in IT management, project management, information security and service management. The objective of his cyber security foundation is to prevent harm to computer networks, applications, devices and data. The training covers topics such as the CIA triad, security governance, risk management and cyber threats.Responsible AI in Industry: Practical Challenges and Lessons Learned



Responsible AI in Industry: Practical Challenges and Lessons LearnedKrishnaram Kenthapadi
Ěý
How do we develop machine learning models and systems taking fairness, accuracy, explainability, and transparency into account? How do we protect the privacy of users when building large-scale AI based systems? Model fairness and explainability and protection of user privacy are considered prerequisites for building trust and adoption of AI systems in high stakes domains such as hiring, lending, and healthcare. We will first motivate the need for adopting a “fairness, explainability, and privacy by design” approach when developing AI/ML models and systems for different consumer and enterprise applications from the societal, regulatory, customer, end-user, and model developer perspectives. We will then focus on the application of responsible AI techniques in practice through industry case studies. We will discuss the sociotechnical dimensions and practical challenges, and conclude with the key takeaways and open challenges.Capgemini ses - security po v (gr)



Capgemini ses - security po v (gr)Gord Reynolds
Ěý
Capgemini's Identity and Access Management solution places identity management at the core of an integrated security infrastructure. It comprises processes and technologies that help strengthen compliance, secure operations, and improve agility. Capgemini takes a three-stage approach to implementation: planning to understand needs, preparation to design technical and process solutions, and implementation to realize the solution. Capgemini's advantage is experience in diverse sectors, alliances with leading vendors, and expertise in both commercial and public security solutions.ANIn Kolkata April 2024 |Ethics of AI by Abhishek Nandy



ANIn Kolkata April 2024 |Ethics of AI by Abhishek NandyAgileNetwork
Ěý
Agile Network India - Kolkata
Title: Ethics of AI by Abhishek Nandy
Date: 20th April 2024
Hosted by: PrediQt Business Solutions Pvt. Ltd
To meet the requirements for lab 10 you were to perform Part 1, S



To meet the requirements for lab 10 you were to perform Part 1, STakishaPeck109
Ěý
To meet the requirements for lab 10 you were to perform: Part 1, Step 2: evaluate the policy document against the summarized NIST best practices, identify by number which, if any, of the eight best practices the policy satisfies, and for each practice that you identify, provide a reference to the statement in the policy that aligns with that best practice; Part 1 Step 3: suggest how you would revise the policy to directly align with the standards and provide specific statements that you would add/modify in the policy; Part 1, Step 4: describe whether the policy document is best titled as a policy or whether it would be better described using another element of the policy framework. Part 2, Step 3: describe the process that the Center uses to ensure that its standards represent the consensus of the cybersecurity community; Part 2, Step 5: identify the section of the recommendations that achieves this goal; Part 2, Step 7: for each of the five best practices in the previous step, classify the practice as: satisfied (indicate recommendation number that achieves the best practice), violated (indicate recommendation number that violates the best practice) or not addressed.
Unfortunately it looks like you were off target for this assignment; you needed to:
Part 1, Step 2: identify by number the best practices (given in the lab) that are satisfied by the policy - partial credit given;Ěý
Part 1 Step 3: provide specific statements on how you would revise the policy; you needed to align your statements with the best practices (e.g. Best Practice 2: add to Section 4.2) - partial credit given;
Part 1, Step 4: describe whether the policy document is best titled as a policy or whether it would be better described using another element of the policy framework; this "policy" is better described as a standard (see technical implementation details);
Part 2, Step 3: describe the process that the Center uses to ensure its standards represent the consensus of the cybersecurity community; see the Consensus Guidance portion of the document - partial credit given;
Part 2, Step 5: identify the section of the recommendations that achieves the goal of Step 3 - partial credit given;
Part 2, Step 7: classify the five best practices; indicate the recommendation number for each - partial credit given.
Applying the Security Policy Framework to an Access Control Environment (3e)
Access Control and Identity Management, Third Edition - Lab 10
Student: Email:
HARSHAVARDHAN POCHARAM [emailĚýprotected]
Time on Task: Progress:
100%
Report Generated: Sunday, June 20, 2021 at 9:45 AM
Guided Exercises
Part 1: Evaluate a Security Policy
2. Evaluate the policy document against the NIST best practices summarized above. Identify by
number which, if any, of the eight best practices the policy satisfies. For each practice that you
identify, provide a reference to the statement in the policy that aligns with that best practice.
In line with relevant policy, the information s ...Ethical Considerations in Data Analysis_ Balancing Power, Privacy, and Respon...



Ethical Considerations in Data Analysis_ Balancing Power, Privacy, and Respon...Soumodeep Nanee Kundu
Ěý
The explosion of data and the increasing capabilities of data analysis have transformed various aspects of our lives. From healthcare and finance to marketing and law enforcement, data analysis has become an essential tool for decision-making and problem-solving. However, with great power comes great responsibility. Ethical considerations in data analysis are more critical than ever as data professionals grapple with questions related to privacy, fairness, transparency, and accountability. In this article, we will delve into the ethical challenges that data analysts and organizations face and explore strategies to address them.SOC 2 Certification Unveiled: Understanding the Core Principles



SOC 2 Certification Unveiled: Understanding the Core PrinciplesShyamMishra72
Ěý
In today's interconnected digital world, safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring the security of information systems is paramount. This is where SOC 2 certification steps in. It has become a benchmark for service organizations to prove their commitment to data security and privacy. In this blog, we will unveil the core principles of SOC 2 certification to help you understand its significance and how it can benefit your organization.Ethical AI at VDAB, presented by Vincent Buekenhout (Ethical AI Lead, VDAB) a...



Ethical AI at VDAB, presented by Vincent Buekenhout (Ethical AI Lead, VDAB) a...Patrick Van Renterghem
Ěý
Ethical Considerations in Data Analysis_ Balancing Power, Privacy, and Respon...



Ethical Considerations in Data Analysis_ Balancing Power, Privacy, and Respon...Soumodeep Nanee Kundu
Ěý
Recently uploaded (20)
A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...



A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...Beena E S
Ěý
A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by Aaron ShepardLesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1...



Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1...pinkdvil200
Ěý
Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 How to Configure Restaurants in Odoo 17 Point of Sale



How to Configure Restaurants in Odoo 17 Point of SaleCeline George
Ěý
Odoo, a versatile and integrated business management software, excels with its robust Point of Sale (POS) module. This guide delves into the intricacies of configuring restaurants in Odoo 17 POS, unlocking numerous possibilities for streamlined operations and enhanced customer experiences.Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
Prelims of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. FESTIVAL: SINULOG & THINGYAN-LESSON 4.pptx



FESTIVAL: SINULOG & THINGYAN-LESSON 4.pptxDanmarieMuli1
Ěý
Sinulog Festival of Cebu City, and Thingyan Festival of Myanmar.Blind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...



Blind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...Ajaz Hussain
Ěý
This presentation delves into the systemic blind spots within pharmaceutical science and regulatory systems, emphasizing the significance of "inactive ingredients" and their influence on therapeutic equivalence. These blind spots, indicative of normalized systemic failures, go beyond mere chance occurrences and are ingrained deeply enough to compromise decision-making processes and erode trust.
Historical instances like the 1938 FD&C Act and the Generic Drug Scandals underscore how crisis-triggered reforms often fail to address the fundamental issues, perpetuating inefficiencies and hazards.
The narrative advocates a shift from reactive crisis management to proactive, adaptable systems prioritizing continuous enhancement. Key hurdles involve challenging outdated assumptions regarding bioavailability, inadequately funded research ventures, and the impact of vague language in regulatory frameworks.
The rise of large language models (LLMs) presents promising solutions, albeit with accompanying risks necessitating thorough validation and seamless integration.
Tackling these blind spots demands a holistic approach, embracing adaptive learning and a steadfast commitment to self-improvement. By nurturing curiosity, refining regulatory terminology, and judiciously harnessing new technologies, the pharmaceutical sector can progress towards better public health service delivery and ensure the safety, efficacy, and real-world impact of drug products.Eng7-Q4-Lesson 1 Part 1 Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and T...



Eng7-Q4-Lesson 1 Part 1 Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and T...sandynavergas1
Ěý
Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and Technical TermsN.C. DPI's 2023 Language Diversity Briefing



N.C. DPI's 2023 Language Diversity BriefingMebane Rash
Ěý
The number of languages spoken in NC public schools.Computer Application in Business (commerce)



Computer Application in Business (commerce)Sudar Sudar
Ěý
The main objectives
1. To introduce the concept of computer and its various parts. 2. To explain the concept of data base management system and Management information system.
3. To provide insight about networking and basics of internet
Recall various terms of computer and its part
Understand the meaning of software, operating system, programming language and its features
Comparing Data Vs Information and its management system Understanding about various concepts of management information system
Explain about networking and elements based on internet
1. Recall the various concepts relating to computer and its various parts
2 Understand the meaning of software’s, operating system etc
3 Understanding the meaning and utility of database management system
4 Evaluate the various aspects of management information system
5 Generating more ideas regarding the use of internet for business purpose Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
Finals of Rass MELAI : a Music, Entertainment, Literature, Arts and Internet Culture Quiz organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. Research & Research Methods: Basic Concepts and Types.pptx



Research & Research Methods: Basic Concepts and Types.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
Ěý
This ppt has been made for the students pursuing PG in social science and humanities like M.Ed., M.A. (Education), Ph.D. Scholars. It will be also beneficial for the teachers and other faculty members interested in research and teaching research concepts.Essentials of a Good PMO, presented by Aalok Sonawala



Essentials of a Good PMO, presented by Aalok SonawalaAssociation for Project Management
Ěý
APM event hosted by the South Wales and West of England Network (SWWE Network)
Speaker: Aalok Sonawala
The SWWE Regional Network were very pleased to welcome Aalok Sonawala, Head of PMO, National Programmes, Rider Levett Bucknall on 26 February, to BAWA for our first face to face event of 2025. Aalok is a member of APM’s Thames Valley Regional Network and also speaks to members of APM’s PMO Interest Network, which aims to facilitate collaboration and learning, offer unbiased advice and guidance.
Tonight, Aalok planned to discuss the importance of a PMO within project-based organisations, the different types of PMO and their key elements, PMO governance and centres of excellence.
PMO’s within an organisation can be centralised, hub and spoke with a central PMO with satellite PMOs globally, or embedded within projects. The appropriate structure will be determined by the specific business needs of the organisation. The PMO sits above PM delivery and the supply chain delivery teams.
For further information about the event please click here.APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
Ěý
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
-Autonomy, Teams and Tension: Projects under stress
-Tim Lyons
-The neurological levels of
team-working: Harmony and tensions
With a background in projects spanning more than 40 years, Tim Lyons specialised in the delivery of large, complex, multi-disciplinary programmes for clients including Crossrail, Network Rail, ExxonMobil, Siemens and in patent development. His first career was in broadcasting, where he designed and built commercial radio station studios in Manchester, Cardiff and Bristol, also working as a presenter and programme producer. Tim now writes and presents extensively on matters relating to the human and neurological aspects of projects, including communication, ethics and coaching. He holds a Master’s degree in NLP, is an NLP Master Practitioner and International Coach. He is the Deputy Lead for APM’s People Interest Network.
Session | The Neurological Levels of Team-working: Harmony and Tensions
Understanding how teams really work at conscious and unconscious levels is critical to a harmonious workplace. This session uncovers what those levels are, how to use them to detect and avoid tensions and how to smooth the management of change by checking you have considered all of them.Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptx



Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxmansk2
Ěý
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxKaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
Ěý
Presentation[1]---------------------.pdf
- 1. PROFESSIONAL ETHICS PRESENTATION Dr. / Dina Saif Ragab
- 2. INTERPRETABILITY TRANSPARENCY IN AI 1.Definition of Transparency ⚬ Common Meaning: The ability to see through something clearly or explain a process openly. ⚬ In AI: Combines two aspects — understanding how decisions are made and justifying those decisions ethically. KEY ASPECTS OF AI TRANSPARENCY EXPLAINS HOW THE AI SYSTEM WORKS AND WHY IT BEHAVES A CERTAIN WAY. Known as "opening the black box" of AI. Ensures the system is clear and understandable. JUSTIFIES THE PROCESSES BEHIND THE AI'S DESIGN AND ITS OUTCOMES. Ensures decisions are ethical, fair, and trustworthy. JUSTIFIABILITY
- 3. WHY TRANSPARENCY IS IMPORTANT : ⚬ Builds trust between AI systems and users. ⚬ Ensures fairness and non-discrimination in AI decisions ⚬ Provides accountability for errors or unethical outcomes 3 CRITICAL TASKS FOR DESIGNING AND IMPLEMENTING TRANSPARENT AI 1.Process Transparency, Task 1: Justify Process 2.Outcome Transparency, Task 2: Clarify Content and Explain Outcome 3.Outcome Transparency, Task 3: Justify Outcome
- 4. Process Transparency, Task 1: Justify Process. To ensure process transparency, stakeholders must see that ethical considerations, fairness, and public trust were prioritized throughout the AI system's design and implementation. This involves adhering to best practices across the AI lifecycle and establishing strong auditability measures using an accountability-by-design framework. These steps build confidence in the system's integrity and decision- making process.
- 5. Outcome Transparency, Task 2: Clarify Content and Explain Outcome. Outcome explanations should be simple and accessible to non-specialists, focusing on the reasoning behind a model’s decisions in a socially meaningful way. Instead of relying on technical or mathematical details, the explanation should connect to real-world practices and societal factors, ensuring stakeholders understand the decision’s impact. Example: If an AI denies a loan application, rather than saying "credit score below 100," explain: "The loan was declined because the financial history shows repeated late payments, suggesting challenges in future repayments."
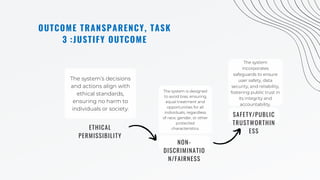
- 6. OUTCOME TRANSPARENCY, TASK 3 :JUSTIFY OUTCOME ETHICAL PERMISSIBILITY The system’s decisions and actions align with ethical standards, ensuring no harm to individuals or society. NON- DISCRIMINATIO N/FAIRNESS The system is designed to avoid bias, ensuring equal treatment and opportunities for all individuals, regardless of race, gender, or other protected characteristics. SAFETY/PUBLIC TRUSTWORTHIN ESS The system incorporates safeguards to ensure user safety, data security, and reliability, fostering public trust in its integrity and accountability.
- 7. Purpose: This framework outlines key principles and actionable steps to ensure transparency, trust, and ethical justifiability in AI systems. Core Justifiability Criteria: • Ethical Permissibility Promotes human dignity, autonomy, and flourishing. Aligns with values like justice, public good, and human connection. • Non-Discrimination / Fairness Ensures fairness in data, design, outcomes, and implementation. Aims to prevent discriminatory harm. • Safety / Public Trust Focuses on accuracy, reliability, security, and robustness. Supports sustainability in AI operations. • Explicability Provides clear, understandable explanations. Yields socially meaningful and interpretable outcomes. Key Transparency Processes: • Process Transparency: Stakeholder Impact Assessments and re-assessments. Fairness Statements and Dataset Factsheets. Testing, verification, and monitoring of AI safety. • Outcome Transparency: Development of interpretable AI for clear communication. Justified outcomes through normative explanations.
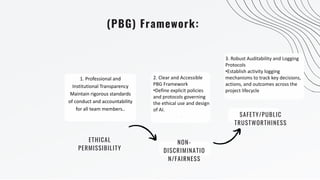
- 8. (PBG) Framework: ETHICAL PERMISSIBILITY 1. Professional and Institutional Transparency Maintain rigorous standards of conduct and accountability for all team members.. NON- DISCRIMINATIO N/FAIRNESS 2. Clear and Accessible PBG Framework •Define explicit policies and protocols governing the ethical use and design of AI. . SAFETY/PUBLIC TRUSTWORTHINESS 3. Robust Auditability and Logging Protocols •Establish activity logging mechanisms to track key decisions, actions, and outcomes across the project lifecycle
- 9. Integrity ETHICAL GOVERNANCE 1. Professional Conduct Standards: Team members should adhere to rigorous conduct standards to ensure professionalism and institutional transparency throughout the AI project lifecycle. 2.Core Values: These standards should include values such as integrity, honesty, neutrality, objectivity, and impartiality, guiding all professionals involved. 1. Serving the Public Interest: Professionals in AI development must prioritize the public interest over any other concerns, in line with core civil service values. 2. Transparency and Public Scrutiny: The design and implementation process should be transparent and open to public scrutiny, with reasonable protection of sensitive information. Accountability
- 10. Governance and Auditability in AI Development. Purpose of a PBG Framework:. 1)Provides structured integration of values into AI workflows 2)Supports CRISP-DM, KDD, models. why use a BGB framework? 1)Overview of governance structures 2)Timeframes and follow-up actions 3)Highlights team roles and workflow stages 4)End-to-end auditability protocols Key Stages in the AI Workflow: Problem Formation Data Extraction & Acquisition Data Processing Modeling Testing & Validation Deployment Monitoring Reassessment
- 11. Enabling Auditability with a Process Log. 1)Ensure end-to-end auditability 2)Maintain records and track activities. 3)Collect data across all phases (modelling, training, testing, etc.). 4)Enhances transparency, supports compliance, improves workflows. Summary : _PBG Framework ensures responsible AI innovation. _Auditability provides transparency and accountability.
- 12. OUR TEAM Everest Cantu Ceo Of Ingoude Company Drew Holloway Ahmed Mohamed Hassan 4221320 Yousef Ahmed Abdelrahman 4221244 Remas Saad Mahmoud 4221275 Nour Ali 4221601 Salma Hazem Mostafa 4221280 Foad Reda Foad 4221041 Elsayed Mohamed Ali 4211268 Marwan Ahmed Foad 4241810 Waleed Mohamed 4241803 Seif Zaki 4231291
- 13. THANK'S






