Presentation1
Download as PPSX, PDF1 like641 views
This document defines key concepts in statistics including: - Descriptive statistics which organizes and summarizes data, and inferential statistics which makes predictions about populations based on samples. - Qualitative vs. quantitative variables, and discrete vs. continuous quantitative variables. - Different levels of measurement for variables including nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio scales. - The concepts of mutually exclusive and exhaustive categories.
1 of 18
Download to read offline
















Recommended
Chapter six



Chapter sixhisled
Ėý
This document discusses inductive arguments. It defines inductive arguments as those whose premises provide evidence for but do not guarantee the conclusion. It then examines 4 types of inductive arguments: enumerative induction, statistical syllogism, causal argument, and analogy. It provides examples of each type and criteria for evaluating the reliability and strength of inductive arguments.Business plan



Business planRajesh Patel
Ėý
1. The document provides details about starting a tray manufacturing business, including production, marketing, and finance departments.
2. Key aspects covered include the selection of Junagadh as the business location, implementation schedule, machinery and production process details, marketing strategy focusing on quality and price, and fixed capital requirements including land, building, machinery, and preliminary expenses totaling Rs. 2440000.
3. Working capital needs are also summarized, including raw material, salary, utilities, and other expenses amounting to Rs. 245000, Rs. 43440, Rs. 7000, and Rs. 11500 respectively.What is the business market, and how does it differ from the consumer market



What is the business market, and how does it differ from the consumer marketSameer Mathur
Ėý
Business markets involve fewer but larger buyers who purchase raw materials and components for resale or manufacturing. Close supplier-customer relationships are important as purchases are made by trained agents following organizational policies. Buying committees consisting of technical and senior management experts commonly influence major purchases through a long sales cycle sometimes lasting years. Demand for business goods is ultimately derived from consumer demand and tends to be inelastic but fluctuating based on consumer demand levels.Analyzing marketing opportunities



Analyzing marketing opportunitiesDIFFY LUMACTOD
Ėý
The document discusses the importance of marketing information systems for companies in today's changing marketing environment. It outlines three key changes driving the need for real-time market data: from local to global marketing, from buyer needs to wants, and from price to non-price competition. It then describes the components of a modern marketing information system, including internal records, marketing intelligence, marketing research, and how they are used to assess needs, develop information, distribute it to decision makers. Effective MIS allows companies to quickly understand customer preferences and respond to market changes.The language of research



The language of researchelymar soriano
Ėý
The document discusses the language of research, which involves searching for truth in a systematic, scientific way. It examines characteristics like using multi-syllable words and specific types of questions, as well as concepts like variables, hypotheses, data, units of analysis, and operational definitions. Operational definitions specify how a research study will measure concepts by defining them in terms of the activities and operations used to assess them.Chapter 3-THE RESEARCH PROBLEM



Chapter 3-THE RESEARCH PROBLEMLudy Mae Nalzaro,BSM,BSN,MN
Ėý
This document outlines the basic components and structure of a research paper. It discusses the typical chapters which include an introduction describing the problem, a literature review, the research methodology, presentation of findings, and conclusions. It also provides examples of developing a research topic, writing a research question, and stating the purpose and significance of a study. The document provides guidance on formulating a research problem and selecting a topic that meets criteria such as novelty, practical value, and feasibility.Entrep report



Entrep reportWacks Venzon
Ėý
The document discusses entrepreneurship and entrepreneurs. It defines entrepreneurship as self-employment and engaging in small and medium sized businesses. An entrepreneur is described as someone who takes risks to start a business and organize, manage and assume the risks of the business. Successful entrepreneurs have characteristics like creativity, confidence, determination and vision. The document also discusses common myths and excuses for not becoming an entrepreneur, such as perceived financial, career and social risks. Key advantages of becoming an entrepreneur include creating your own destiny, financial rewards, self-knowledge, and contributing to society.Retailing



RetailingSAROJ BEHERA
Ėý
Retailing includes all activities involved in selling goods or services directly to final consumers for personal use. Any organization that sells to final consumers is engaging in retailing, whether they are a manufacturer, wholesaler, or retailer. Retailers can be classified into types such as department stores, specialty stores, convenience stores, discount stores, off-price retailers, and super stores. Retail strategies include broad or narrow product assortment, high or low value added services, and targeting high or low margins with high or low volumes. Non-store retailing includes direct selling, direct marketing, automated vending, and buying services.Topic father's day



Topic father's dayNatthaya Khaothong
Ėý
This document provides biographical information about King Bhumibol Adulyadej of Thailand. It states that he was born in Cambridge, Massachusetts on December 5, 1927 as his father was studying at Harvard University. In 1928, he returned to Thailand with his family. He received his early education in Thailand and Switzerland. He became the King of Thailand in 1946 and was the longest-reigning monarch in Thai history.Does africa need the bw is challenges v4



Does africa need the bw is challenges v4Mark Ellyne
Ėý
This document discusses Africa's economic challenges and its relationship with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and Bretton Woods institutions. It provides an overview of the IMF and World Bank's intervention models in African countries. It also examines the Washington Consensus policies promoted by these institutions in the 1980s, including fiscal discipline, trade liberalization, and privatization. While these policies aimed to address Africa's deficient economic policies, their results were mixed, with average growth rates remaining low. Critics argue the policies failed to consider local contexts and market failures. Overall, the document analyzes debates around the IMF's role and the effectiveness of its policy advice in Africa.Internet Guide



Internet GuideMariaClaraL
Ėý
Dreamweaver is an application that allows easy website design through a drag-and-drop interface, automatically generating the underlying HTML and CSS code. HTML stands for Hypertext Markup Language, the primary language used for web content. An HTML tag defines text elements and formatting, such as the <a> tag for hyperlinks. A URL is a Uniform Resource Locator, the address of a file or resource on the web. A search engine searches documents for keywords and returns relevant results. WWW stands for World Wide Web. A browser is a software application used to access websites.

Daniel acero taller 4Daniel Acero
Ėý
El documento habla sobre bucles en programaciÃģn. Explica que los bucles permiten repetir un conjunto de instrucciones varias veces de forma automÃĄtica. AdemÃĄs menciona que los bucles son una herramienta Útil para programar secuencias que se repiten constantemente.2016_BioITWorld_whitepaper



2016_BioITWorld_whitepaperMark Evans
Ėý
This document describes two integrated software tools, SeqAgentTM and XAbTrackerTM, designed for antibody phage display workflows. SeqAgentTM is a sequence analysis pipeline that processes DNA sequences from phage display experiments, identifies antibody structural features, and clusters similar sequences. XAbTrackerTM is a laboratory information management system (LIMS) that tracks clones through assays, links sequencing data from SeqAgentTM, and allows integrated data analysis to facilitate clone selection. The tools were developed in-house to address bottlenecks in data analysis and management during antibody discovery using phage display.āđķÄāļāļĢāļ·āđāļāļāđāļāđāđāļāļāđāļēāđāļĨāļ°āļāļĢāļ°āđāļ āļāđķÄāļāļĢāļ·āđāļāļāđāļāđāđāļāļāđāļē



āđķÄāļāļĢāļ·āđāļāļāđāļāđāđāļāļāđāļēāđāļĨāļ°āļāļĢāļ°āđāļ āļāđķÄāļāļĢāļ·āđāļāļāđāļāđāđāļāļāđāļēPleum Ps
Ėý
Topic mother's day



Topic mother's daynutchaya-hall
Ėý
Queen Sirikit of Thailand was born in 1932 in Thailand. As a child, she attended school in Bangkok during World War II when the city was often bombed. She later studied in Britain and met her future husband, King Bhumibol Adulyadej of Thailand, while he was studying in Switzerland. They married in 1950 after a one-year engagement. Queen Sirikit has been by King Bhumibol's side during his reign and supported him during his recovery from a car accident in 1948 that injured his back and cost him an eye.Hime insurance rutherford nj



Hime insurance rutherford njmanzoins56
Ėý
Manzo Insurance provides affordable and comprehensive auto insurance policies to protect drivers for any trip, whether it's a short drive around town or a long road trip across the country. Their auto insurance solutions are designed to offer drivers and their families protection for a necessity of modern life - driving.

Father's day



Father's dayNatthaya Khaothong
Ėý
This document provides biographical information about King Bhumibol Adulyadej of Thailand. It states that he was born in Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA on December 5, 1927 to Prince Mahidol Adulyadej and Mom Sangwan. His name means "Strength of the Land, Incomparable Power." In 1928, he returned to Thailand with his family. He received his education in Switzerland and received a high school diploma with a major in history.A.introduction tech.



A.introduction tech.girlie22
Ėý
This document provides information on the skills and responsibilities of an Instrument Technician. It discusses that an Instrument Technician is responsible for calibrating process instruments in the field and bench. They also have skills in troubleshooting, testing loops, and commissioning process equipment. The document then lists various skills and knowledge required, including calibrating different types of instruments, installing tubing and instruments, understanding diagrams, and ensuring safety practices.Japan Quiz!



Japan Quiz!MariaClaraL
Ėý
This document appears to be a quiz about basic Japanese language and culture. It contains multiple choice questions about phrases for common expressions in Japanese like "see you later", cultural practices like the tea ceremony, popular foods like Kit Kat being given before exams, and Japanese music with song titles to identify. The quiz covers vocabulary, customs, and music to test knowledge of basic aspects of Japanese language and culture.Pressure measurements new 2007



Pressure measurements new 2007girlie22
Ėý
Pascal's law states that pressure in a confined fluid is transmitted equally in all directions, and increases at any point in the fluid are directly proportional to the increase in external pressure. Boyle's law describes the inverse relationship between the volume and pressure of a gas at constant temperature, while Charles's law specifies the direct relationship between the volume and temperature of a gas at constant pressure. Common pressure sensing elements include the bourdon tube, bellows, and diaphragm, which undergo mechanical deformation in response to changes in applied pressure that can be measured to indicate pressure levels.ÐŋŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļŅ Ðū ŅÐĩКŅÐŋÐļŅÐĩ 1



ÐŋŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļŅ Ðū ŅÐĩКŅÐŋÐļŅÐĩ 1yulia_nik
Ėý
ÐŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļŅ "ÐÐļÐŧŅŅО ÐĻÐĩКŅÐŋÐļŅ (ŅаÐđÐ―Ņ Ðļ заÐģаÐīКÐļ ÐķÐļÐ·Ð―Ðļ Ðļ
ŅÐēÐūŅŅÐĩŅŅÐēа)"Chapter 01 mis



Chapter 01 misRong Mohol
Ėý
This document introduces key concepts in statistics. It discusses descriptive statistics, which organizes and summarizes data, and inferential statistics, which makes estimates about populations based on samples. Variables can be qualitative, involving categories, or quantitative, involving numbers. Quantitative variables can be discrete, with separate values, or continuous, able to assume any value. Variables are also classified by their level of measurement - nominal involves categories, ordinal involves ranking, interval allows comparing differences, and ratio has a true zero point. Statistics is used across many fields to help make effective decisions based on numerical data.Statistics: Chapter One



Statistics: Chapter OneSaed Jama
Ėý
In this chapter you learn:
Definition of Statistics & Identify variables in a statistics.
Types of Statistics
Distinguish b/w quantitative & qualitative variables.
Determine the 4 levels of measurement.
Identify populations & samples.
Distinguish different types of Sampling7jjjjjjjjjjjjjvcxzffghjknbvfhjknbvcduukkk



7jjjjjjjjjjjjjvcxzffghjknbvfhjknbvcduukkkyeasmin75648
Ėý
Statistics is the science of collecting, organizing, and analyzing numerical data to assist in decision making. Descriptive statistics summarize and present data, while inferential statistics make generalizations about populations based on samples. Variables can be qualitative like gender or quantitative like income. Quantitative variables can be discrete with gaps between values or continuous taking any value. Variables are also measured at nominal, ordinal, interval, or ratio levels depending on their properties.Chapter 01



Chapter 01bmcfad01
Ėý
This document provides an introduction to statistics, covering key concepts such as descriptive versus inferential statistics, qualitative versus quantitative variables, discrete versus continuous variables, and the four levels of measurement (nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio). Descriptive statistics are used to organize and summarize data, while inferential statistics allow generalizing from a sample to a population. Variables can be qualitative (non-numeric attributes) or quantitative (numeric values), and quantitative variables can be discrete (taking on countable values) or continuous (taking on any value within a range). The levels of measurement refer to the type of data and whether differences and relationships can be determined.More Related Content
Viewers also liked (18)
Topic father's day



Topic father's dayNatthaya Khaothong
Ėý
This document provides biographical information about King Bhumibol Adulyadej of Thailand. It states that he was born in Cambridge, Massachusetts on December 5, 1927 as his father was studying at Harvard University. In 1928, he returned to Thailand with his family. He received his early education in Thailand and Switzerland. He became the King of Thailand in 1946 and was the longest-reigning monarch in Thai history.Does africa need the bw is challenges v4



Does africa need the bw is challenges v4Mark Ellyne
Ėý
This document discusses Africa's economic challenges and its relationship with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and Bretton Woods institutions. It provides an overview of the IMF and World Bank's intervention models in African countries. It also examines the Washington Consensus policies promoted by these institutions in the 1980s, including fiscal discipline, trade liberalization, and privatization. While these policies aimed to address Africa's deficient economic policies, their results were mixed, with average growth rates remaining low. Critics argue the policies failed to consider local contexts and market failures. Overall, the document analyzes debates around the IMF's role and the effectiveness of its policy advice in Africa.Internet Guide



Internet GuideMariaClaraL
Ėý
Dreamweaver is an application that allows easy website design through a drag-and-drop interface, automatically generating the underlying HTML and CSS code. HTML stands for Hypertext Markup Language, the primary language used for web content. An HTML tag defines text elements and formatting, such as the <a> tag for hyperlinks. A URL is a Uniform Resource Locator, the address of a file or resource on the web. A search engine searches documents for keywords and returns relevant results. WWW stands for World Wide Web. A browser is a software application used to access websites.

Daniel acero taller 4Daniel Acero
Ėý
El documento habla sobre bucles en programaciÃģn. Explica que los bucles permiten repetir un conjunto de instrucciones varias veces de forma automÃĄtica. AdemÃĄs menciona que los bucles son una herramienta Útil para programar secuencias que se repiten constantemente.2016_BioITWorld_whitepaper



2016_BioITWorld_whitepaperMark Evans
Ėý
This document describes two integrated software tools, SeqAgentTM and XAbTrackerTM, designed for antibody phage display workflows. SeqAgentTM is a sequence analysis pipeline that processes DNA sequences from phage display experiments, identifies antibody structural features, and clusters similar sequences. XAbTrackerTM is a laboratory information management system (LIMS) that tracks clones through assays, links sequencing data from SeqAgentTM, and allows integrated data analysis to facilitate clone selection. The tools were developed in-house to address bottlenecks in data analysis and management during antibody discovery using phage display.āđķÄāļāļĢāļ·āđāļāļāđāļāđāđāļāļāđāļēāđāļĨāļ°āļāļĢāļ°āđāļ āļāđķÄāļāļĢāļ·āđāļāļāđāļāđāđāļāļāđāļē



āđķÄāļāļĢāļ·āđāļāļāđāļāđāđāļāļāđāļēāđāļĨāļ°āļāļĢāļ°āđāļ āļāđķÄāļāļĢāļ·āđāļāļāđāļāđāđāļāļāđāļēPleum Ps
Ėý
Topic mother's day



Topic mother's daynutchaya-hall
Ėý
Queen Sirikit of Thailand was born in 1932 in Thailand. As a child, she attended school in Bangkok during World War II when the city was often bombed. She later studied in Britain and met her future husband, King Bhumibol Adulyadej of Thailand, while he was studying in Switzerland. They married in 1950 after a one-year engagement. Queen Sirikit has been by King Bhumibol's side during his reign and supported him during his recovery from a car accident in 1948 that injured his back and cost him an eye.Hime insurance rutherford nj



Hime insurance rutherford njmanzoins56
Ėý
Manzo Insurance provides affordable and comprehensive auto insurance policies to protect drivers for any trip, whether it's a short drive around town or a long road trip across the country. Their auto insurance solutions are designed to offer drivers and their families protection for a necessity of modern life - driving.

Father's day



Father's dayNatthaya Khaothong
Ėý
This document provides biographical information about King Bhumibol Adulyadej of Thailand. It states that he was born in Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA on December 5, 1927 to Prince Mahidol Adulyadej and Mom Sangwan. His name means "Strength of the Land, Incomparable Power." In 1928, he returned to Thailand with his family. He received his education in Switzerland and received a high school diploma with a major in history.A.introduction tech.



A.introduction tech.girlie22
Ėý
This document provides information on the skills and responsibilities of an Instrument Technician. It discusses that an Instrument Technician is responsible for calibrating process instruments in the field and bench. They also have skills in troubleshooting, testing loops, and commissioning process equipment. The document then lists various skills and knowledge required, including calibrating different types of instruments, installing tubing and instruments, understanding diagrams, and ensuring safety practices.Japan Quiz!



Japan Quiz!MariaClaraL
Ėý
This document appears to be a quiz about basic Japanese language and culture. It contains multiple choice questions about phrases for common expressions in Japanese like "see you later", cultural practices like the tea ceremony, popular foods like Kit Kat being given before exams, and Japanese music with song titles to identify. The quiz covers vocabulary, customs, and music to test knowledge of basic aspects of Japanese language and culture.Pressure measurements new 2007



Pressure measurements new 2007girlie22
Ėý
Pascal's law states that pressure in a confined fluid is transmitted equally in all directions, and increases at any point in the fluid are directly proportional to the increase in external pressure. Boyle's law describes the inverse relationship between the volume and pressure of a gas at constant temperature, while Charles's law specifies the direct relationship between the volume and temperature of a gas at constant pressure. Common pressure sensing elements include the bourdon tube, bellows, and diaphragm, which undergo mechanical deformation in response to changes in applied pressure that can be measured to indicate pressure levels.ÐŋŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļŅ Ðū ŅÐĩКŅÐŋÐļŅÐĩ 1



ÐŋŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļŅ Ðū ŅÐĩКŅÐŋÐļŅÐĩ 1yulia_nik
Ėý
ÐŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļŅ "ÐÐļÐŧŅŅО ÐĻÐĩКŅÐŋÐļŅ (ŅаÐđÐ―Ņ Ðļ заÐģаÐīКÐļ ÐķÐļÐ·Ð―Ðļ Ðļ
ŅÐēÐūŅŅÐĩŅŅÐēа)"

āđķÄāļāļĢāļ·āđāļāļāđāļāđāđāļāļāđāļēāđāļĨāļ°āļāļĢāļ°āđāļ āļāđķÄāļāļĢāļ·āđāļāļāđāļāđāđāļāļāđāļē



āđķÄāļāļĢāļ·āđāļāļāđāļāđāđāļāļāđāļēāđāļĨāļ°āļāļĢāļ°āđāļ āļāđķÄāļāļĢāļ·āđāļāļāđāļāđāđāļāļāđāļēPleum Ps
Ėý


Similar to Presentation1 (20)
Chapter 01 mis



Chapter 01 misRong Mohol
Ėý
This document introduces key concepts in statistics. It discusses descriptive statistics, which organizes and summarizes data, and inferential statistics, which makes estimates about populations based on samples. Variables can be qualitative, involving categories, or quantitative, involving numbers. Quantitative variables can be discrete, with separate values, or continuous, able to assume any value. Variables are also classified by their level of measurement - nominal involves categories, ordinal involves ranking, interval allows comparing differences, and ratio has a true zero point. Statistics is used across many fields to help make effective decisions based on numerical data.Statistics: Chapter One



Statistics: Chapter OneSaed Jama
Ėý
In this chapter you learn:
Definition of Statistics & Identify variables in a statistics.
Types of Statistics
Distinguish b/w quantitative & qualitative variables.
Determine the 4 levels of measurement.
Identify populations & samples.
Distinguish different types of Sampling7jjjjjjjjjjjjjvcxzffghjknbvfhjknbvcduukkk



7jjjjjjjjjjjjjvcxzffghjknbvfhjknbvcduukkkyeasmin75648
Ėý
Statistics is the science of collecting, organizing, and analyzing numerical data to assist in decision making. Descriptive statistics summarize and present data, while inferential statistics make generalizations about populations based on samples. Variables can be qualitative like gender or quantitative like income. Quantitative variables can be discrete with gaps between values or continuous taking any value. Variables are also measured at nominal, ordinal, interval, or ratio levels depending on their properties.Chapter 01



Chapter 01bmcfad01
Ėý
This document provides an introduction to statistics, covering key concepts such as descriptive versus inferential statistics, qualitative versus quantitative variables, discrete versus continuous variables, and the four levels of measurement (nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio). Descriptive statistics are used to organize and summarize data, while inferential statistics allow generalizing from a sample to a population. Variables can be qualitative (non-numeric attributes) or quantitative (numeric values), and quantitative variables can be discrete (taking on countable values) or continuous (taking on any value within a range). The levels of measurement refer to the type of data and whether differences and relationships can be determined.business statistics 1430 important questions 2025.pdf



business statistics 1430 important questions 2025.pdfNaveedHussainKhokhar
Ėý
Business Statistics 1430 Important Questions 2025Statistics (2).doc



Statistics (2).docAtoshe Elmi
Ėý
This document provides an introduction to statistics, including definitions of key terms like population, sample, parameter, statistic, descriptive statistics, and inferential statistics. It discusses types of variables like qualitative, quantitative discrete, and quantitative continuous variables. It also outlines the four levels of measurement: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. Overall, the document serves as a high-level overview of basic statistical concepts.Stat11t Chapter1



Stat11t Chapter1gueste87a4f
Ėý
This document provides an overview of key concepts from Chapter 1 of the textbook "Elementary Statistics". It defines important statistical terms like population, sample, parameter, and statistic. It also distinguishes between different types of data and levels of measurement. Additionally, it discusses the importance of collecting sample data through appropriate random sampling methods. Critical thinking in statistics is emphasized, highlighting factors like the context, source, and sampling method of data when evaluating statistical claims. Different ways of collecting data through studies and experiments are also introduced.Stat11t chapter1



Stat11t chapter1raylenepotter
Ėý
The document summarizes key concepts from Chapter 1 of the textbook "Elementary Statistics" including:
- The difference between a population and a sample, and how statistics uses samples to make inferences about populations.
- The different types of data: quantitative, categorical, discrete vs. continuous data.
- The different levels of measurement for data: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio.
- The importance of critical thinking when analyzing data and statistics, including considering context, sources, sampling methods, and avoiding misleading graphs, samples, conclusions, or survey questions.Meaning and Importance of Statistics



Meaning and Importance of StatisticsFlipped Channel
Ėý
If you happen to like this powerpoint, you may contact me at flippedchannel@gmail.com
I offer some educational services like:
-powerpoint presentation maker
-grammarian
-content creator
-layout designer
Subscribe to our online platforms:
FlippED Channel (Youtube)
http://bit.ly/FlippEDChannel
LET in the NET (facebook)
http://bit.ly/LETndNETwhat is statistics? Mc Graw Hills/Irwin



what is statistics? Mc Graw Hills/IrwinMaryam Xahra
Ėý
This document provides an introduction to statistics, including definitions, goals, and key concepts. It defines statistics as the science of collecting, organizing, presenting, analyzing, and interpreting numerical data to assist in making effective decisions. Descriptive statistics are used to summarize and present data, while inferential statistics allow generalizing from samples to populations. Variables can be qualitative or quantitative, with quantitative variables further divided into discrete and continuous types. Data can be measured at the nominal, ordinal, interval, or ratio levels, with different analyses appropriate for each level of measurement. Understanding these statistical fundamentals helps inform decision-making across many fields.Chap001



Chap001Sandra Nicks
Ėý
This document discusses key concepts in statistics. It defines statistics as the science of collecting, organizing, analyzing, and interpreting data to assist decision making. Descriptive statistics are used to summarize and present data, while inferential statistics allow generalization from a sample to a population. A population is the total group being studied, while a sample is a subset. Variables can be qualitative, involving categories, or quantitative, involving numbers. Quantitative variables can be discrete, taking certain values, or continuous. The level of measurement for data, such as nominal, ordinal, interval, or ratio, determines what analyses can be done.chapter_01_12.ppt



chapter_01_12.pptSaleemBhatti5
Ėý
This chapter introduces key concepts in statistics including:
- Descriptive statistics which organizes and summarizes data, and inferential statistics which makes predictions from samples.
- The difference between populations and samples, with populations representing all possible values and samples being subsets.
- Types of variables including qualitative, quantitative, discrete and continuous. Quantitative variables can further be classified based on their level of measurement as nominal, ordinal, interval or ratio.
- Common uses of statistics across various fields such as marketing, healthcare, education and more.Bab 1.ppt



Bab 1.pptakhmadakbarsusamto1
Ėý
This document provides an overview of key statistical concepts. It discusses descriptive statistics which organize and summarize data, and inferential statistics which make generalizations from samples to populations. It defines a population as all possible values and a sample as a subset of the population. Variables are described as either qualitative involving categories or quantitative involving numbers, with quantitative variables further divided into discrete using separate values or continuous using any value in a range. Finally, it outlines the four levels of measurement for data - nominal involving simple categories, ordinal as categories with a rank order, interval where differences are meaningful, and ratio where a true zero value exists.Lesson 3 basic terms in statistics



Lesson 3 basic terms in statisticsMaris Ganace
Ėý
This document defines key statistical terms and concepts. It begins by defining the terms "universe," "population," "variable," and "sample." It then classifies variables as either qualitative or quantitative. Qualitative variables express categorical attributes like gender or religion, while quantitative variables have numeric values and can measure things like height, weight, or income. Quantitative variables are further divided into discrete variables, which can be counted, and continuous variables, which can be measured. The document provides examples of different variable types and has learners practice classifying variables. Its overall purpose is to define fundamental statistical terms.Research Method chapter 6.pptx



Research Method chapter 6.pptxAsegidHmeskel
Ėý
This document provides an overview of qualitative data analysis. It discusses that qualitative data analysis involves coding, categorizing, comparing and interpreting collected data to find meanings and implications. The researcher's perspective influences the analysis. It also describes techniques for qualitative data analysis like becoming familiar with the data, providing in-depth descriptions, and categorizing data into themes. Ensuring credibility involves considering factors like the researcher's observations and biases. The document also contrasts qualitative data analysis with quantitative analysis.English



Englishsehrish shahid
Ėý
This document contains an assignment submission for a course on introduction to statistical theory. It includes answers to several questions about key statistical concepts. The questions cover topics such as defining statistics, explaining the importance and uses of statistics, distinguishing between different statistical terms like population and sample, descriptive and inferential statistics, and classifying different types of variables. The student provides detailed explanations and examples for each question.Recently uploaded (20)
EaseUS Partition Master Crack 2025 + Serial Key



EaseUS Partition Master Crack 2025 + Serial Keykherorpacca127
Ėý
https://ncracked.com/7961-2/
Note: >> Please copy the link and paste it into Google New Tab now Download link
EASEUS Partition Master Crack is a professional hard disk partition management tool and system partition optimization software. It is an all-in-one PC and server disk management toolkit for IT professionals, system administrators, technicians, and consultants to provide technical services to customers with unlimited use.
EASEUS Partition Master 18.0 Technician Edition Crack interface is clean and tidy, so all options are at your fingertips. Whether you want to resize, move, copy, merge, browse, check, convert partitions, or change their labels, you can do everything with a few clicks. The defragmentation tool is also designed to merge fragmented files and folders and store them in contiguous locations on the hard drive.
[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web Apps![[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web Apps](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/webinarscalingmadesimplegettingstartedwithno-codewebapps-mar52025-250305183437-f03c78a3-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web Apps](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/webinarscalingmadesimplegettingstartedwithno-codewebapps-mar52025-250305183437-f03c78a3-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web Apps](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/webinarscalingmadesimplegettingstartedwithno-codewebapps-mar52025-250305183437-f03c78a3-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web Apps](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/webinarscalingmadesimplegettingstartedwithno-codewebapps-mar52025-250305183437-f03c78a3-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web AppsSafe Software
Ėý
Ready to simplify workflow sharing across your organization without diving into complex coding? With FME Flow Apps, you can build no-code web apps that make your data work harder for you â fast.
In this webinar, weâll show you how to:
Build and deploy Workspace Apps to create an intuitive user interface for self-serve data processing and validation.
Automate processes using Automation Apps. Learn to create a no-code web app to kick off workflows tailored to your needs, trigger multiple workspaces and external actions, and use conditional filtering within automations to control your workflows.
Create a centralized portal with Gallery Apps to share a collection of no-code web apps across your organization.
Through real-world examples and practical demos, youâll learn how to transform your workflows into intuitive, self-serve solutions that empower your team and save you time. We canât wait to show you whatâs possible!Endpoint Backup: 3 Reasons MSPs Ignore It



Endpoint Backup: 3 Reasons MSPs Ignore ItMSP360
Ėý
Many MSPs overlook endpoint backup, missing out on additional profit and leaving a gap that puts client data at risk.
Join our webinar as we break down the top challenges of endpoint backupâand how to overcome them.Wondershare Dr.Fone Crack Free Download 2025



Wondershare Dr.Fone Crack Free Download 2025maharajput103
Ėý
copy & paste ð ð âĪâĪðĄ https://filedownloadx.com/download-link/
Wondershare Dr.Fone Crack is a comprehensive mobile phone management and recovery software designed to help users recover lost data, repair system issues, and manage mobile devices. It supports both Android and iOS platforms, offering a wide range of features aimed at restoring files, repairing software problems, and backing up or transferring data.L01 Introduction to Nanoindentation - What is hardness



L01 Introduction to Nanoindentation - What is hardnessRostislavDaniel
Ėý
Introduction to NanoindentationComputational Photography: How Technology is Changing Way We Capture the World



Computational Photography: How Technology is Changing Way We Capture the WorldHusseinMalikMammadli
Ėý
ðļ Computational Photography (Computer Vision/Image): How Technology is Changing the Way We Capture the World
Heç dÞÅÞnmÞsÞnÞzmÞ, mÞasir smartfonlar vÉ kameralar necÉ bu qÉdÉr gÃķzÉl gÃķrÞntÞlÉr yaradÄąr? Bunun sirri Computational FotoqrafiyasÄąnda(Computer Vision/Imaging) gizlidirâÅÉkillÉri çÉkmÉ vÉ emal etmÉ Ãžsulumuzu tÉkmillÉÅdirÉn, kompÞter elmi ilÉ fotoqrafiyanÄąn inqilabi birlÉÅmÉsi.UiPath Document Understanding - Generative AI and Active learning capabilities



UiPath Document Understanding - Generative AI and Active learning capabilitiesDianaGray10
Ėý
This session focus on Generative AI features and Active learning modern experience with Document understanding.
Topics Covered:
Overview of Document Understanding
How Generative Annotation works?
What is Generative Classification?
How to use Generative Extraction activities?
What is Generative Validation?
How Active learning modern experience accelerate model training?
Q/A
â If you have any questions or feedback, please refer to the "Women in Automation 2025" dedicated Forum thread. You can find there extra details and updates. BoxLang JVM Language : The Future is Dynamic



BoxLang JVM Language : The Future is DynamicOrtus Solutions, Corp
Ėý
Just like life, our code must evolve to meet the demands of an ever-changing world. Adaptability is key in developing for the web, tablets, APIs, or serverless applications. Multi-runtime development is the future, and that future is dynamic. Enter BoxLang: Dynamic. Modular. Productive. (www.boxlang.io)
BoxLang transforms development with its dynamic design, enabling developers to write expressive, functional code effortlessly. Its modular architecture ensures flexibility, allowing easy integration into your existing ecosystems.
Interoperability at Its Core
BoxLang boasts 100% interoperability with Java, seamlessly blending traditional and modern development practices. This opens up new possibilities for innovation and collaboration.
Multi-Runtime Versatility
From a compact 6MB OS binary to running on our pure Java web server, CommandBox, Jakarta EE, AWS Lambda, Microsoft Functions, WebAssembly, Android, and more, BoxLang is designed to adapt to any runtime environment. BoxLang combines modern features from CFML, Node, Ruby, Kotlin, Java, and Clojure with the familiarity of Java bytecode compilation. This makes it the go-to language for developers looking to the future while building a solid foundation.
Empowering Creativity with IDE Tools
Unlock your creative potential with powerful IDE tools designed for BoxLang, offering an intuitive development experience that streamlines your workflow. Join us as we redefine JVM development and step into the era of BoxLang. Welcome to the future.
DealBook of Ukraine: 2025 edition | AVentures Capital



DealBook of Ukraine: 2025 edition | AVentures CapitalYevgen Sysoyev
Ėý
The DealBook is our annual overview of the Ukrainian tech investment industry. This edition comprehensively covers the full year 2024 and the first deals of 2025. Technology use over time and its impact on consumers and businesses.pptx



Technology use over time and its impact on consumers and businesses.pptxkaylagaze
Ėý
In this presentation, I explore how technology has changed consumer behaviour and its impact on consumers and businesses. I will focus on internet access, digital devices, how customers search for information and what they buy online, video consumption, and lastly consumer trends.30B Images and Counting: Scaling Canva's Content-Understanding Pipelines by K...



30B Images and Counting: Scaling Canva's Content-Understanding Pipelines by K...ScyllaDB
Ėý
Scaling content understanding for billions of images is no easy feat. This talk dives into building extreme label classification models, balancing accuracy & speed, and optimizing ML pipelines for scale. You'll learn new ways to tackle real-time performance challenges in massive data environments.FinTech - US Annual Funding Report - 2024.pptx



FinTech - US Annual Funding Report - 2024.pptxTracxn
Ėý
US FinTech 2024, offering a comprehensive analysis of key trends, funding activities, and top-performing sectors that shaped the FinTech ecosystem in the US 2024. The report delivers detailed data and insights into the region's funding landscape and other developments. We believe this report will provide you with valuable insights to understand the evolving market dynamics.Technology use over time and its impact on consumers and businesses.pptx



Technology use over time and its impact on consumers and businesses.pptxkaylagaze
Ėý
In this presentation, I will discuss how technology has changed consumer behaviour and its impact on consumers and businesses. I will focus on internet access, digital devices, how customers search for information and what they buy online, video consumption, and lastly consumer trends.
Early Adopter's Guide to AI Moderation (Preview)



Early Adopter's Guide to AI Moderation (Preview)nick896721
Ėý
Early Adopter's Guide to AI Moderation preview by User Interviews.Understanding Traditional AI with Custom Vision & MuleSoft.pptx



Understanding Traditional AI with Custom Vision & MuleSoft.pptxshyamraj55
Ėý
Understanding Traditional AI with Custom Vision & MuleSoft.pptx | ### šÝšÝßĢ Deck Description:
This presentation features Atul, a Senior Solution Architect at NTT DATA, sharing his journey into traditional AI using Azure's Custom Vision tool. He discusses how AI mimics human thinking and reasoning, differentiates between predictive and generative AI, and demonstrates a real-world use case. The session covers the step-by-step process of creating and training an AI model for image classification and object detectionâspecifically, an ad display that adapts based on the viewer's gender. Atulavan highlights the ease of implementation without deep software or programming expertise. The presentation concludes with a Q&A session addressing technical and privacy concerns.A Framework for Model-Driven Digital Twin Engineering



A Framework for Model-Driven Digital Twin EngineeringDaniel Lehner
Ėý
šÝšÝßĢs from my PhD Defense at Johannes Kepler University, held on Janurary 10, 2025.
The full thesis is available here: https://epub.jku.at/urn/urn:nbn:at:at-ubl:1-83896Computational Photography: How Technology is Changing Way We Capture the World



Computational Photography: How Technology is Changing Way We Capture the WorldHusseinMalikMammadli
Ėý
Presentation1
- 1. 1. Define what is meant by statistics. 2. Explain what is meant by descriptive statistics and inferential statistics. 3. Distinguish between a qualitative variable and a quantitative variable. 4. Distinguish between a discrete variable and a continuous variable. 5. Distinguish among the nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio levels of measurement. 6. Define the terms mutually exclusive and exhaustive. GOALS When you have completed this chapter, you will be able to: Chapter One: Introduction Important: This file is a modified electronic version of Statistical Techniques in Business and Economics ÂĐ The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 1999
- 2. What is Meant by Statistics? ï Statistics is the science of collecting, organizing, presenting, ana lyzing, and interpreting numerical data for the purpose of assisting in making a more effective decision. 1-2
- 3. Who Uses Statistics? ï In todayâs information society, decisions are made on the basis of data. A family checks the neighborhood before purchasing a house, a company checks the labor and transportation conditions before opening a new branch, an engineer tests the tensile strength of a wire before winding it into a cable, and so on. 1-3
- 4. Types of Statistics ï Descriptive Statistics: Methods of organizing, summarizing, and presenting data in an informative way. ï EXAMPLE 1: A survey found that 49% of the people knew the name of the first book of the Bible. The statistic 49 describes the number out of every 100 persons who knew the answer. ï EXAMPLE 2: According to Consumer Reports, Whirlpool washing machine owners reported 9 problems per 100 machines during 2005. The statistic 9 describes the number of problems out of every 100 machines. 1-4
- 5. Types of Statistics ï Inferential Statistics: A decision, estimate, prediction, or generalization about a population, based on a sample. ï A population is a collection of all possible individuals, objects, or measurements of interest. ï A sample is a portion, or part, of the population of interest. 1-5
- 6. Types of Statistics (examples of inferential statistics) ï EXAMPLE 1: Measuring lifetimes of transistors ï EXAMPLE 2: Classifying air as healthy or unhealthy based on the Air Quality Index (AQI) ï EXAMPLE 3: Collecting data on the volume of traffic flow in a busy street of Manila. 1-6
- 7. Types of Variables ï Qualitative or Attribute variable: data in the form of classifications into different groups or categories. The characteristic or variable being studied is nonnumeric. ï EXAMPLES: Gender, religious affiliation, type of automobile owned, place of birth, eye color. 1-7
- 8. Types of Variables ï Quantitative variable: data in the form of numerical measurements or counts. The variable can be reported numerically. ï EXAMPLE: ozone level of the air, minutes remaining in class, number of children in a family. 1-8
- 9. Types of Variables ï Quantitative variables can be classified as either discrete or continuous. ï Discrete variables:Variables which assume a finite or countable number of possible values. Usually obtained by counting. ï EXAMPLE: the number of bedrooms in a house. (1,2,3,..., etc...). ï Continuous variables: Variables which assume an infinite number of possible values. Usually obtained by measurement. ï EXAMPLE: The time it takes to fly from Manila to Cebu. 1-9
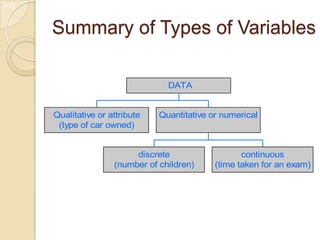
- 10. Summary of Types of Variables Qualitative or attribute (type of car owned) discrete (number of children) continuous (time taken for an exam) Quantitative or numerical DATA 1-11
- 11. Sources of Statistical Data ï Researching problems usually requires published data. Statistics on these problems can be found in published articles, journals, and magazines. ï Published data is not always available on a given subject. In such cases, information will have to be collected and analyzed. ï One way of collecting data is via questionnaires. 1-12
- 12. Levels of Measurement ï Nominal level (scaled): Data that can only be classified into categories and cannot be arranged in an ordering scheme. ï EXAMPLES: eye color, gender, religious affiliation. 1-13
- 13. Levels of Measurement ï Mutually exclusive: An individual or item that, by virtue of being included in one category, must be excluded from any other category. ï EXAMPLE: eye color. ï Exhaustive: each person, object, or item must be classified in at least one category. ï EXAMPLE: religious affiliation. 1-14
- 14. Levels of Measurement ï Ordinal level: involves data that may be arranged in some order, but differences between data values cannot be determined or are meaningless. ï EXAMPLE: During a taste test of 4 colas, cola C was ranked number 1, cola B was ranked number 2, cola A was ranked number 3, and cola D was ranked number 4. 1-15
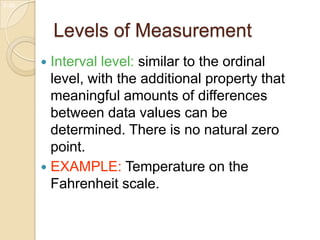
- 15. Levels of Measurement ï Interval level: similar to the ordinal level, with the additional property that meaningful amounts of differences between data values can be determined. There is no natural zero point. ï EXAMPLE: Temperature on the Fahrenheit scale. 1-16
- 16. Levels of Measurement ï Ratio level: the interval level with an inherent zero starting point. Differences and ratios are meaningful for this level of measurement. ï EXAMPLES: money, heights of NBA players. 1-17
- 17. Assessment: 1.A statistic is a. collection of values b. single value. c. The sum of several values. d. The largest value in a set of observations 17 2. In descriptive statistics our main objective is to a. Describe the population. b. Describe the data we collected. c. Infer something about the population. d.Compute an average. 3. Which of the following statements is true regarding a population? a. It must be a large number of values. b. It must refer to people. c. It is a collection individuals, objects, or measurements. d. None of the above. 4. Which of the following statements is true regarding a sample? a. It is a part of population. b. It must contain at least five observations. c. It refers to descriptive statistics. d. All of the above are correct. 5. A qualitative variable a. Always refers to a sample. b. Is nonumeric. c. Always has only two possible outcomes. d. All of the above are correct.
- 18. Assessment:6. A discrete variable a. Is an example of a qualitative variable. b.Can assume only whole number values. c. Can assume only certain clearly separated values. d. Cannot be negative. 18 7. A nominal scale variable is a. Usually the result of counting something. b. Has a meaningful zero point. c. May assume negative values. d. Cannot have more than two categories. 8. The ratio scale of measurement a. Usually involves ranking. b. Cannot assume negative values. c. Has a meaningful zero point. d. Is usually based on counting. 9. The ordinal scale of measurement a. Has a meaningful zero point. b. Is based on ranks. c. Cannot assume negative values. d. All of the above. 10. Categories are exhaustive when a. There is a meaningful zero point. b. The objects can be ranked. c. Each object must appear in at least one category. d. Each object can be included in only one category.











