Probe machintosh
- 1. PROBE MACHINTOSH PREPARED FOR: PUAN SURIANI NASUTION BINTI PADZLAN PREPARED BY: KARTINA BINTI SAZALI MUHAMMAD SHABERY BIN SAINUDIN SYED AHMAD HAKIM BIN SYED MUZAMIL
- 2. INTRODUCTION OF SITE INVESTIGATION Site Investigation is the geotechnical investigations performed by geotechnical engineers or engineering geologists to obtain information on the physical properties of soil and rock around a site to design earthworks and foundations for proposed structures and for repair of distress to earthworks and structures
- 3. PURPOSE OF SITE INVESTIGATION 1. Support planning and define the project feasibility. 2. Determine most economical and appropriate: ï Route and depth definition. ï Excavation and support methods definition. 3. Define physical characteristics of the soil, rock, and groundwater. 4. To minimize uncertainties of physical conditions for the bidder & to improve safety. 5. Provide specific data needed to evaluate: ï Constructability, Cost, Productivity, Schedule. âĒ To document as: ï Built conditions of the completed project
- 4. INTRODUCTION OF PROBE MACKINTOSH The site investigation is the one thing that must be done before starting the construction of the building. This is because the soil condition at the site need to be identifies to determine the suitable foundation use for the building and soil play a main role to support the load that come from the building and the building need a suitable foundation to transfer the load to the ground. Therefore, the investigation of soil need to be done to identify the type of soil to ensure the soil can carry the load.
- 5. OBJECTIVE OF PROBE MACKINTOSH âĒ Collecting a disturbed soil sample for grain-size analysis and soil classification âĒ Determine sub-surface straits graphed and identity materials present âĒ Evaluate soil density and in-situ stress conditions âĒ Estimate geotechnical parameters
- 6. THE DIFFERENCES OF MACKINTOSH PROBE, JKR PROBE AND STANDARD PENETRATION TEST (SPT). CONE ENERGY PER TYPE OF WEIGHT OF HEIGHT OF FALL UNIT AREA PENETROMETER DIAMETER (mm) AREA (mm2) HAMMER (kg) (mm) (N.m/m2) JKR PROBE 25 491 5 280 27972 MACKINTOSH PROBE 27.9 611 4.5 300 21675 SPT 50 1963 65 760 246874
- 7. EQUIPMENT PROBE MACKINTOSH TOOLS MARKING TOOLS HAMMER LIFTING TOOLS WRENCH PENETRATION CONE
- 8. PROCEDURES 1. Equipment for the test is assembled. The cone diameter is measured in SI unit. 2. Distance of 0.3 m is measured and marked on the rod start from the tip of the cone 3. The equipment is set up on the ground 4. The hammer is pulled until it reached the maximum. The hammer is dropped freely to driven the cone into the soils. 5. The sum of the number of blow for penetration of 0.3 m is recorded in the data sheet. 6. The hammer is taken off on the last 0.3 of each rod and joined and existing rod with another rod and lastly the hammer. The blow is continued and stopped when : ï The blow is more than 400 for 0.3 m penetration ï The depth reached 15 m
- 10. SITE INVESTIGATION REPORT CADANGAN MEMBINA DAN MENYIAPKAN SEKOLAH MENENGAH KEBANGSAAN RAJA MUDA DIATAS LOT PT 1107, MUKIM PARIT JAWA, DAERAH MUAR, JOHOR CLIENT: JABATAN KERJA RAYA (JKR) MUAR JOHOR DARUL TAKZIM MALAYSIA
- 11. DATA RELATED
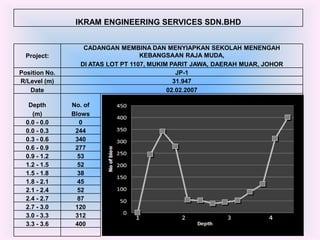
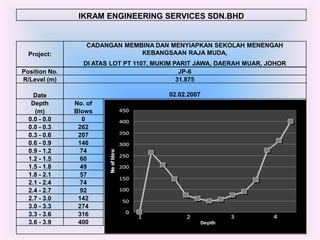
- 12. IKRAM ENGINEERING SERVICES SDN.BHD CADANGAN MEMBINA DAN MENYIAPKAN SEKOLAH MENENGAH Project: KEBANGSAAN RAJA MUDA, DI ATAS LOT PT 1107, MUKIM PARIT JAWA, DAERAH MUAR, JOHOR Position No. JP-1 R/Level (m) 31.947 Date 02.02.2007 Depth No. of (m) Blows 0.0 - 0.0 0 0.0 - 0.3 244 0.3 - 0.6 340 0.6 - 0.9 277 0.9 - 1.2 53 1.2 - 1.5 52 1.5 - 1.8 38 1.8 - 2.1 45 2.1 - 2.4 52 2.4 - 2.7 87 2.7 - 3.0 120 3.0 - 3.3 312 3.3 - 3.6 400
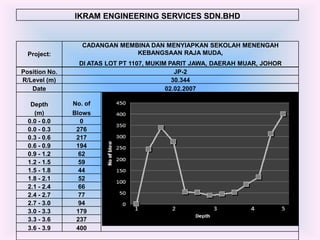
- 13. IKRAM ENGINEERING SERVICES SDN.BHD CADANGAN MEMBINA DAN MENYIAPKAN SEKOLAH MENENGAH Project: KEBANGSAAN RAJA MUDA, DI ATAS LOT PT 1107, MUKIM PARIT JAWA, DAERAH MUAR, JOHOR Position No. JP-2 R/Level (m) 30.344 Date 02.02.2007 Depth No. of (m) Blows 0.0 - 0.0 0 0.0 - 0.3 276 0.3 - 0.6 217 0.6 - 0.9 194 0.9 - 1.2 62 1.2 - 1.5 59 1.5 - 1.8 44 1.8 - 2.1 52 2.1 - 2.4 66 2.4 - 2.7 77 2.7 - 3.0 94 3.0 - 3.3 179 3.3 - 3.6 237 3.6 - 3.9 400
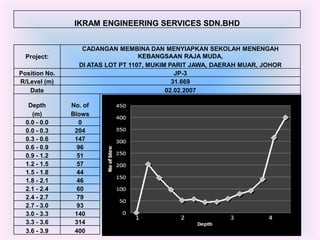
- 14. IKRAM ENGINEERING SERVICES SDN.BHD CADANGAN MEMBINA DAN MENYIAPKAN SEKOLAH MENENGAH Project: KEBANGSAAN RAJA MUDA, DI ATAS LOT PT 1107, MUKIM PARIT JAWA, DAERAH MUAR, JOHOR Position No. JP-3 R/Level (m) 31.669 Date 02.02.2007 Depth No. of (m) Blows 0.0 - 0.0 0 0.0 - 0.3 204 0.3 - 0.6 147 0.6 - 0.9 96 0.9 - 1.2 51 1.2 - 1.5 57 1.5 - 1.8 44 1.8 - 2.1 46 2.1 - 2.4 60 2.4 - 2.7 79 2.7 - 3.0 93 3.0 - 3.3 140 3.3 - 3.6 314 3.6 - 3.9 400
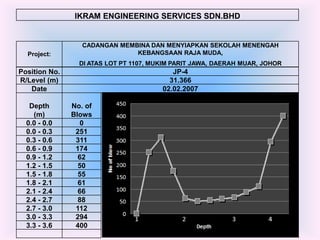
- 15. IKRAM ENGINEERING SERVICES SDN.BHD CADANGAN MEMBINA DAN MENYIAPKAN SEKOLAH MENENGAH Project: KEBANGSAAN RAJA MUDA, DI ATAS LOT PT 1107, MUKIM PARIT JAWA, DAERAH MUAR, JOHOR Position No. JP-4 R/Level (m) 31.366 Date 02.02.2007 Depth No. of (m) Blows 0.0 - 0.0 0 0.0 - 0.3 251 0.3 - 0.6 311 0.6 - 0.9 174 0.9 - 1.2 62 1.2 - 1.5 50 1.5 - 1.8 55 1.8 - 2.1 61 2.1 - 2.4 66 2.4 - 2.7 88 2.7 - 3.0 112 3.0 - 3.3 294 3.3 - 3.6 400
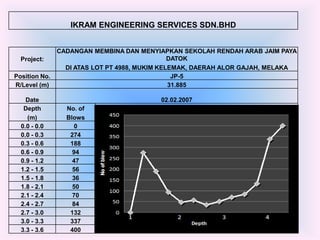
- 16. IKRAM ENGINEERING SERVICES SDN.BHD CADANGAN MEMBINA DAN MENYIAPKAN SEKOLAH RENDAH ARAB JAIM PAYA Project: DATOK DI ATAS LOT PT 4988, MUKIM KELEMAK, DAERAH ALOR GAJAH, MELAKA Position No. JP-5 R/Level (m) 31.885 Date 02.02.2007 Depth No. of (m) Blows 0.0 - 0.0 0 0.0 - 0.3 274 0.3 - 0.6 188 0.6 - 0.9 94 0.9 - 1.2 47 1.2 - 1.5 56 1.5 - 1.8 36 1.8 - 2.1 50 2.1 - 2.4 70 2.4 - 2.7 84 2.7 - 3.0 132 3.0 - 3.3 337 3.3 - 3.6 400
- 17. IKRAM ENGINEERING SERVICES SDN.BHD CADANGAN MEMBINA DAN MENYIAPKAN SEKOLAH MENENGAH Project: KEBANGSAAN RAJA MUDA, DI ATAS LOT PT 1107, MUKIM PARIT JAWA, DAERAH MUAR, JOHOR Position No. JP-6 R/Level (m) 31.875 Date 02.02.2007 Depth No. of (m) Blows 0.0 - 0.0 0 0.0 - 0.3 262 0.3 - 0.6 207 0.6 - 0.9 146 0.9 - 1.2 74 1.2 - 1.5 60 1.5 - 1.8 49 1.8 - 2.1 57 2.1 - 2.4 74 2.4 - 2.7 92 2.7 - 3.0 142 3.0 - 3.3 274 3.3 - 3.6 316 3.6 - 3.9 400
- 18. CONCLUSION JKR Probe Mackintosh is can be used to determine the thickness of unsuitable material to be removed and also for preliminary design of embankments, limited to about 15 m and must be record no. of blows/ft. then correlates to established chart to determine bearing capacity of soil. Mackintosh Probe which has 30° cone penetrometer while JKR Probes has 60° cone penetrometer. This is a light dynamic test and the cone is driven directly into the soil by driving a hammer 5 kg. Weight dropping through a free height of 280mm. The probe is unable to penetrate into medium strength soil and gravelly ground.
- 19. ATTACHMENT
- 20. REFERENCES http://www.scribd.com/doc/41535291/7/JKR-Mackintosh-Probe http://www.foundtest.com.my/services/mpt.html http://www.scribd.com/doc/43714071/Probe-Mackintosh-Test http://www.geolab-sdn-bhd.com/soil.htm http://www.geotechlanka.com/?q=services_mackintosh_probe_testing http://theconstructor.org/geotechnical/mackintosh-probe-test/3801/ http://www.zaxco.com.my/index2.php?option=com_content&do_pdf=1&id= 149 http://www.scribd.com/doc/4633102/Correlation-between-JKR-Probe-and- SPT-Test