Rec ref gct
- 1. Management of recurrent and refractory germ cell tumors
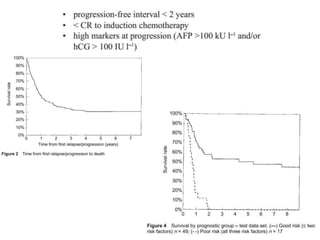
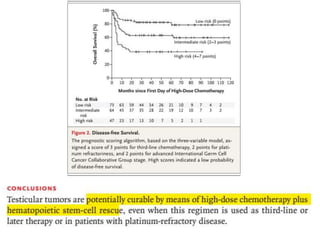
- 2. ŌĆó Good risk GCTs achieve a very good long term cure approaching 95% ŌĆó Poor-risk GCTs require four cycles of BEP that attains an approximately 45% long-term disease-free survival ŌĆó A significant proportion are either refractory to the platinum first line chemo regimens,,or the relapse early
- 3. Standard guidelines for advanced disease
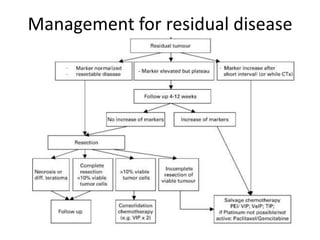
- 4. Management for residual disease
- 5. What does the NCCN say?
- 6. Therapy for early relapse and refractory disease Salvage regimensŌĆ”
- 7. VeIP/VIP
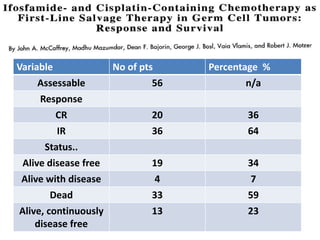
- 8. Results.. ŌĆó N : 135 ŌĆó 49.6 % pts achieved dis. free status after chemotherapy ( with or without surgery for residual) ŌĆó 32% are alive ŌĆó 23.7% are continually free of disease ŌĆó All pts had a minimal f/u of 6 yrs from entry into study
- 9. Variable No of pts Percentage % Assessable 56 n/a Response CR 20 36 IR 36 64 Status.. Alive disease free 19 34 Alive with disease 4 7 Dead 33 59 Alive, continuously disease free 13 23
- 10. ŌĆó N : 189 ( 1985 to 2012) ŌĆó CR: 18.5% ŌĆó Marker normalization: 35.4% ŌĆó 2yr PFS: 34.3% ŌĆó 5yr OS: 42.1%
- 16. Prognostic factors with salvage chemo
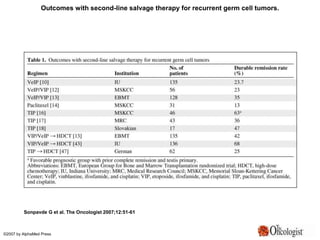
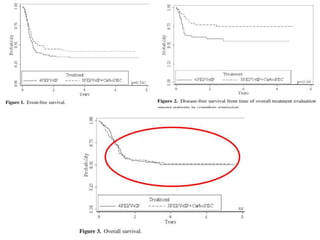
- 19. Outcomes with second-line salvage therapy for recurrent germ cell tumors. Sonpavde G et al. The Oncologist 2007;12:51-61 ┬®2007 by AlphaMed Press
- 20. Role of HDCT and auto BMT?
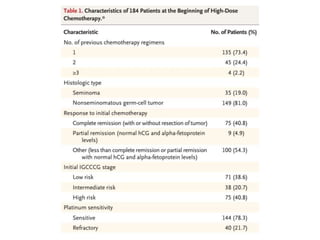
- 22. ŌĆó Pts included: ŌĆō Those , who received high dose chemotherpay as salvage and has not progressed within 4 weeks after the last dose ŌĆó Stem cells were harvested with GCSF stimulation ŌĆó High dose chemo was given with ŌĆō Carboplatin 700mg/m2 ŌĆō Etoposide 750mg/m2 ŌĆō On days -5, -4 and -3 of stem cell infusion
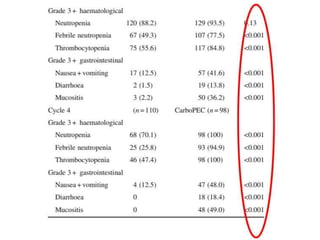
- 26. German data.. ŌĆó N : 74pts ŌĆó ORR : 63% with CR in 31% ŌĆó EFS of sensitive disease at 2 yrs: 50% ŌĆó Only one pt of 23 who had refractory disease had 7mo event free survival ŌĆó OS at 2 yrs: 44%
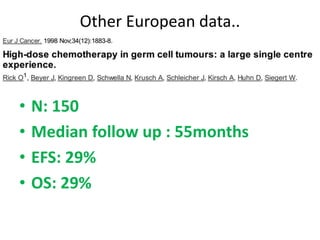
- 27. Other European data.. ŌĆó N: 150 ŌĆó Median follow up : 55months ŌĆó EFS: 29% ŌĆó OS: 29%
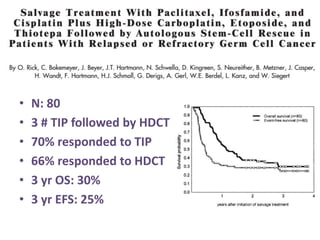
- 28. ŌĆó N: 80 ŌĆó 3 # TIP followed by HDCT ŌĆó 70% responded to TIP ŌĆó 66% responded to HDCT ŌĆó 3 yr OS: 30% ŌĆó 3 yr EFS: 25%
- 29. Italian experience. ŌĆó N : 84 ŌĆó Median follow up 46months ŌĆó DFS rates: ŌĆō Good risk: 69% ŌĆō Int. risk: 13% ŌĆō Poor risk: 0%
- 30. High dose chemo: blessing or a curse??
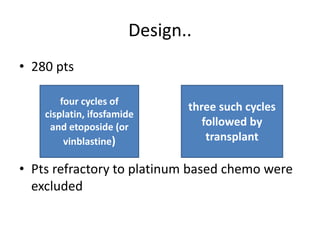
- 31. Design.. ŌĆó 280 pts ŌĆó Pts refractory to platinum based chemo were excluded four cycles of cisplatin, ifosfamide and etoposide (or vinblastine) three such cycles followed by transplant
- 34. Roles of surgery?? ŌĆó N: 125 pts who underwent postchemotherapeutic resention ŌĆó Mean f/u: 120monthns ŌĆó 57% long term survivors who had raised TM ŌĆó Conslusion: salvage surgery results in long term survival of more than 50%
- 35. ŌĆó N : 16pts ŌĆó Six patients (37%) are alive and free of disease at a mean of seventy-four months following surgery (range 20 to 145 months). ŌĆó Five had RP disease only. ŌĆó Ten patients died of disease at a mean of eight months postoperatively (range 5 to 21 months).
- 38. ŌĆó N: 114 ŌĆó 5 yr OS: 53.9% ŌĆó Sixty-one patients (53.5%) are alive with a medium follow-up of 72 months ŌĆó Retroperitoneal pathology revealed ŌĆō germ cell cancer in 53.5% of patients, ŌĆō teratoma in 34.2% of patients, and ŌĆō fibrosis in 12.2% of patients, with ŌĆō 5-year survival rates of 31.4%, 77.5%, and 85.7%, respectively (P < .0001).
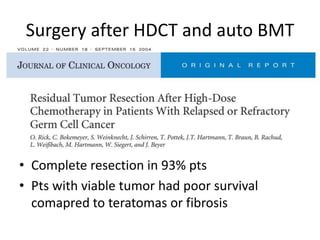
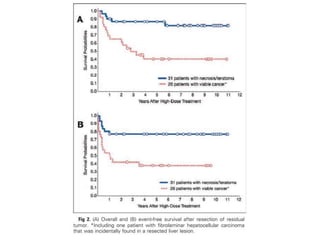
- 39. Surgery after HDCT and auto BMT ŌĆó Complete resection in 93% pts ŌĆó Pts with viable tumor had poor survival comapred to teratomas or fibrosis
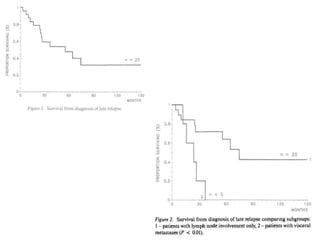
- 41. Therapy of late relapses ŌĆó Defn: relapses occurring after 2 yrs and in the absence of a second primary tumor ŌĆó Typically chemo refractory ŌĆó Different disease biology
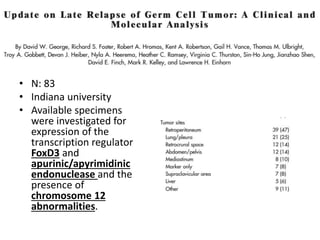
- 42. ŌĆó N: 83 ŌĆó Indiana university ŌĆó Available specimens were investigated for expression of the transcription regulator FoxD3 and apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease and the presence of chromosome 12 abnormalities.
- 43. ResultsŌĆ” ŌĆó Forty-three of 49 patients who underwent surgery were rendered disease free (NED), and 20 (46.5%) remain continuously NED ŌĆó Thirty-two patients received chemotherapy, but only six (18.8%) obtained a complete remission. ŌĆó Eighteen of these 32 patients were successfully rendered NED by postchemotherapy surgery, and 12 remain continuously NED.
- 44. Overall.. ŌĆó 69 of the 81 treated patients (85.2%) ultimately achieved an NED state, and ŌĆō 38 (46.9%) remain continuously NED with median follow-up from LR therapy of 24.5 months (range, 1 to 83 months), ŌĆō whereas nine other patients are currently NED after therapy for subsequent relapses ŌĆō Conclusion on moleular markers could not be made i/v/o low no. of samples tested
- 45. ŌĆó Follow up of 530pts ŌĆó 25 cases of late relapse identified ŌĆó Risk was lower with good risk pts
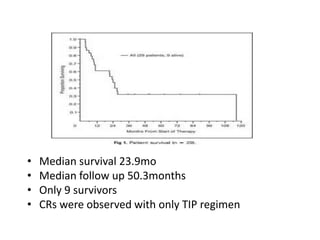
- 49. ŌĆó Median survival 23.9mo ŌĆó Median follow up 50.3months ŌĆó Only 9 survivors ŌĆó CRs were observed with only TIP regimen
- 50. To summarize.. ŌĆó Refractory disease and early relapse to be managed in same lines with salvage chemo +/- surgery ŌĆó HDCT with auto BMT also has shown promising results ŌĆó Later relapse: ŌĆō Poor prognosis ŌĆō Surgical resection whenever feasible ŌĆō Chemo has poor outcomes
Editor's Notes
- #20: Outcomes with second-line salvage therapy for recurrent germ cell tumors