research methods.ppt
- 2. ? Research is the step by step process of gathering information ? Reasons for doing research: 1) To generate new knowledge 2) To solve a problem 3) To test a theory 4) To be able to predict an event or outcome
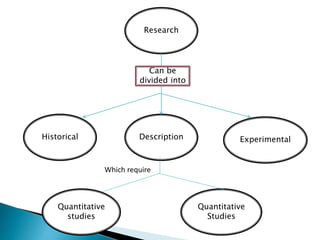
- 3. Research Historical Description Experimental Quantitative studies Quantitative Studies Can be divided into Which require
- 4. Historical research-describes the past Descriptive research- describes records, analyses and interprets conditions that permanently exist. Experimental research-focus on variable--- and describes what happens when the variables are carefully controlled or manipulated.
- 5. ? usually takes the form of statistical or numerical information. ? It can also be expressed in the form of a rate. ? It is believed that the analysis of statistical data can indicate both cause and correlation. ? it is used in the Mainstream or conventional ideas of research which are based on the scientific method
- 6. ? Study easily replicable ? Method saves time ? It is cost effective ? It collects standard data ? Validity is enhanced by the use of large samples ? Data is more objective
- 7. ? No indication about the respondents personal state ? Unrepresentative samples can lead to inaccurate and invalid data ? Generalization may not apply to all people in all circumstances
- 8. ? There are 4 types of quantitative research methods: 1. Surveys 2. Questionnaire 3. Structured interviews 4. Official statistics
- 9. ? usually large-scale research projects that collect standardized data from a large cross- section of the population. ? E.g. Government census. ? There are three (3) types of surveys: ? Descriptive - questions are close-ended and allow the researcher to make correlations about social phenomena. ?
- 10. ? Attitude - asks mainly close-ended questions that attempt to find out people’s feelings or opinions: e.g. a party, political figure or brand of food. ? Explanatory - seeks answers that require more than a simple yes or no response. They are given the opportunity to clarify their feelings in greater depth
- 11. ? Valid due to data collected from a large cross- section of the population ? Data can be used to make generalizations ? Statistical technique can be used to analyze data, thus time-saving ? An unbiased representative sample saves the researcher the time of having to find all individuals with relevant information.
- 12. ? Invalid data if sample not representative
- 13. ? A number of pre-set questions that can contain open-ended and close-ended or a combination of both type of questions. ? Steps to constructing a questionnaire: 1. Operationalize key terms and concepts therefore breaking up terms into sub- concepts. 2. Formulate questions based on each sub- topic. ? ?
- 14. 1) Easy to administer 2) They can reach a large number of people even if they are geographically disperse 3) It saves time 4) It is not costly 5) Data can be easily tabulated, measured and analyzed
- 15. 1) What is gained in reliability may be lost in terms of validity. e.g. The wording may intentionally or not, mislead the respondent Researcher bias Respondents may lie or treat the issues lightly Respondents may forget 2) Postal questionnaires have a low rate of return and may be filled out by someone other than the intended respondent.
- 16. ? Secondary source of data. ? The researcher relies upon other people to collect data.
- 17. ? Saves time as it is a readily available source of data. ? Conclusions drawn are objective because of lack of interaction. ? Generalizations can be made. ? Researcher can understand the nature of social change by comparing statistics from different times. ? Statistics could be used to gain a deeper understanding of human relationships.
- 18. ? Producers may be biased in collecting the data. ? The validity of some official reports (e.g. crime) could be inaccurate because trivial crimes may not be reported. ? Technological developments make it appear that more crimes are taking place, therefore comparisons from past to present would be inaccurate. ? Due to the fact that it is secondary data, there is a low level of reliability
- 19. ? collects subjective data such as information about people’s emotions, feelings and values. ? The researcher usually interacts directly with the respondents (i.e. face-to-face) or by actually joining in their everyday activities ? ? There are 4 forms of qualitative research: ? Unstructured interviews ? Participant observation ? Case studies ? Documents
- 20. ? Face-to-face interaction process in which the researcher tries to get as much useful information as possible from a respondent or a number of respondents ? It can take the form of a one-session interview or a number of session ? The respondents’ trust must be gained and factors such as social class, sex or ethnicity can influence the level of trust gained
- 21. 1. The validity of the data is enhanced by the following: ? Researcher can detect lies or inconsistencies by observing facial reactions and body language ? Misunderstanding can be clarified ? The researcher can understand the world from the point of view of the interviewee ? Researcher can gain information that he never thought about asking
- 22. 2. It is a more practical research technique for explaining specific issues, e.g. rape 2. Due to the small sample, it can be useful for challenging or refuting already existing ideas
- 23. 1. Validity is reduced by the following: ? Observer effect ? Deliberate lies on the part of the interviewee 2. Time consuming 3. Large quantities of information can pose problems for analysis 4. Some interviewees can have limited knowledge of a particular topic 5. Not cost effective
- 24. ? Is regarded as a scientific tool because the researcher studies people in their natural environment by joining their daily activities ? The researcher must remain as objective – non- judgemental and not overly involved – as possible ? Researcher can be overt – letting the group members know that they are being studied - or covert – choose to keep his identity secret ? Unlike interviews, trust must be gained from the start
- 25. 1. Validity is enhanced by the following: ?The researcher witnesses the group first hand ?Observer effect is minimized ?Questions can be asked to clarify events and actions of the group ?Group’s subjective point of view can be understood ?Information can be used to formulate theories about human behaviour 2. It is a practical method for studying deviant or secret groups and activities, e.g. gangs, homosexuality
- 26. 1. Validity may be compromised by the following: ?Covert observer may forget information ?Covert observer may provide his own interpretation because asking questions may reveal his identity ?Overt observation may produce the ob server effect ?There is no standardized way to study human behaviour 2. It is costly 3. It is time-consuming
- 27. ? Contains information usually qualitative form ? There are 2 main types of documents – historical and personal ? Personal documents include letters, diaries, biographies and autobiographies ? Historical documents are usually information written by people who lived during a particular era ? Documents are a secondary source of data
- 28. ? Saves time and money ? Practical method of studying past events ? Provides insight in areas that otherwise one may not have access to ? Information could be used to measure the extent of social change
- 29. ? Invalid because of producer bias ? Information may be difficult to read and may contain missing pages ? Some documents may be difficult to access ? Information may be limited in scope or outdated
- 31. ? This is a sentence in which you clearly state what you wish to find out. E.g.. What is the level of hurricane preparedness of a sample of households in Windy village, Barbados? Theme The Environment Sub Theme Natural Disasters Problem Statement?
- 32. ? A statement which suggests the possible answer to your problem statement. It mentions a variable or the relationship between 2 or more variables. ? A variable is a thing/concept that changes. ? E.g. ? 1. Windy Village, St Silas, Barbados is not prepared for hurricanes. ? 2. The level of preparedness amongst households in Windy Village, St Silas is affected by their experiences of hurricanes.
- 33. Identifies Problem One must be able to study the problem. E.g. drug use makes problem manageable Narrow down problems or issues Impacts on human development Stage 1
- 34. Formulating Research Questions Devise once main question or point Devise a set of sub- questions or concerns Focus on what the researcher wants to be informed about Create a hypothesis that can either be accepted or rejected Stage 2
- 35. Literature Reviews Research must be related to problem being researched e.g. books, journals, articles, newspapers Read as much as possible on topic Find info to definition point Look at strategies and methods of other researchers and compare Stage 3
- 36. Data Collection Choose sample Questions must be focused on what he/she wants to know Choose a strategy relative to study Design instruments that will be reliable and valid Method used must bias free Stage 4
- 37. Data Analysis Organizes the data collected for presentation Use thin marginal questions, concerns or concepts as a guide This presentation is guided by research question or hypothesis There must be at least 5 different ways of presentations The most popular formats were pie charts, bar and live graphs, flow diagrams, maps, photographs etc. Stage 5
- 38. Interpretation of Findings Consider the implications Stage 6 Describes patterns and trends averages, ranges. States what the data implies Explains the results and include contradictions Accounts for all the findings presented
- 39. Discussion of findings Compares your findings with those presented in the Literature Review in relation to the original questions Stage 7 Identifies similarities and differences in the pattern and trend of the studies Ensures all research questions are answered
- 40. Conclusion States the limitation of research/ Methodology. Suggest at least three (3) recommendations that should be practical solutions which can be easily implemented Summarize your results and restate their educational value Stage 8