Robobat - Projektowanie przyszłości
•
0 likes•760 views
Projektowanie przyszłości 2014
1 of 14
Download to read offline













Recommended
Wojciech gawinowski vostok design



Wojciech gawinowski vostok designHanna Wincenciak
Ěý
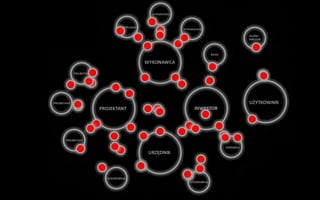
The document discusses algorithm-assisted design (AAD), where computer algorithms are used to describe relationships and interactions between design elements. AAD allows for complex, dynamic systems and structures to be created that enable unprecedented design effects. Early examples of analog algorithms include pyramids and Gaudi's works, while early digital algorithms include the Eden Project and British Museum Court. AAD is now used for facades, structures, form-finding, simulation, and as part of open BIM workflows.Strusoft - BIM in structural design



Strusoft - BIM in structural designthyforhtian
Ěý
The document discusses BIM and structural design software. It summarizes StruSoft, a producer of structural design software including FEM-Design. FEM-Design allows accurate and effective structural analysis with features like automatic mesh generation and element design. The document focuses on connecting FEM-Design with Revit through a StruXML add-in. The add-in allows exporting Revit models to FEM-Design for analysis and updating models between the programs. Issues in BIM workflows are recognized, such as inconsistencies between physical and analytical models.Mott MacDonald



Mott MacDonaldthyforhtian
Ěý
This document discusses how BIM can be used across all stages of a construction project lifecycle, from planning and design through construction and asset management. It provides examples of projects where BIM delivered benefits like reduced costs, improved coordination and clash detection. BIM was used for tasks like 4D construction planning, 5D cost estimation, design optimization and prefabrication. Asset information from BIM models can also be used to support long-term facility management.More Related Content
More from thyforhtian (9)
Strusoft - BIM in structural design



Strusoft - BIM in structural designthyforhtian
Ěý
The document discusses BIM and structural design software. It summarizes StruSoft, a producer of structural design software including FEM-Design. FEM-Design allows accurate and effective structural analysis with features like automatic mesh generation and element design. The document focuses on connecting FEM-Design with Revit through a StruXML add-in. The add-in allows exporting Revit models to FEM-Design for analysis and updating models between the programs. Issues in BIM workflows are recognized, such as inconsistencies between physical and analytical models.Mott MacDonald



Mott MacDonaldthyforhtian
Ěý
This document discusses how BIM can be used across all stages of a construction project lifecycle, from planning and design through construction and asset management. It provides examples of projects where BIM delivered benefits like reduced costs, improved coordination and clash detection. BIM was used for tasks like 4D construction planning, 5D cost estimation, design optimization and prefabrication. Asset information from BIM models can also be used to support long-term facility management.












