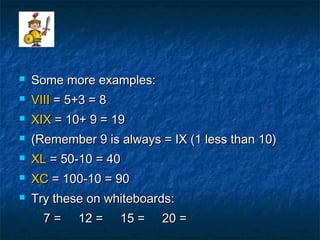ROMAN EMPIRE
- 2. A Brief History of Roman NumeralsA Brief History of Roman Numerals ’ü« Roman numerals originated in ancient Rome.Roman numerals originated in ancient Rome. This ancient counting system is believed to haveThis ancient counting system is believed to have started with the ancient Etruscans.started with the ancient Etruscans. ’ü« The symbol forThe symbol for oneone in the roman numeralin the roman numeral system probably represented a single tally marksystem probably represented a single tally mark which people would notch into wood or dirt towhich people would notch into wood or dirt to keep track of items or events they werekeep track of items or events they were counting. It would also be easy to write on a waxcounting. It would also be easy to write on a wax tablet.tablet.
- 3. How to convert Arabic numbers toHow to convert Arabic numbers to Roman NumeralsRoman Numerals ’ü« Roman numerals are written asRoman numerals are written as combinations ofcombinations of seven lettersseven letters.. I = 1 V = 5 X = 10 L = 50I = 1 V = 5 X = 10 L = 50 C = 100 D =500 M = 1000C = 100 D =500 M = 1000 ’ü« The letters can be written as capital (XVI)The letters can be written as capital (XVI) or lower-case letters (xvi).or lower-case letters (xvi). ╠²╠²
- 4. As a general guideAs a general guide ’ü« Roman Numerals are made up by addingRoman Numerals are made up by adding or subtracting numbers like this:-or subtracting numbers like this:- ’ü« 11=10+111=10+1 = XI= XI 9 = 10 ŌĆō 19 = 10 ŌĆō 1 = IX= IX ’ü« 40 = 50 ŌĆō1040 = 50 ŌĆō10 == XLXL ’ü« If you want to sayIf you want to say 1,1001,100 in Romanin Roman Numerals, you would sayNumerals, you would say MM forfor 10001000 andand then put athen put a CC after it forafter it for 100100;; 1,1001,100 = MC= MC ’ü« 900900 =1000 ŌĆō 100=1000 ŌĆō 100 soso the C comes before M = CMthe C comes before M = CM
- 5. ’ü« Some more examples:Some more examples: ’ü« VIIIVIII = 5+3 = 8= 5+3 = 8 ’ü« XIXXIX = 10+ 9 = 19= 10+ 9 = 19 ’ü« (Remember 9 is always = IX (1 less than 10)(Remember 9 is always = IX (1 less than 10) ’ü« XLXL = 50-10 = 40= 50-10 = 40 ’ü« XCXC = 100-10 = 90= 100-10 = 90 ’ü« Try these on whiteboards:Try these on whiteboards: 7 = 12 = 15 = 20 =7 = 12 = 15 = 20 =
- 6. Check your answers.Check your answers. 7 =7 = VIIVII 12 =12 = XIIXII 15 =15 = XVXV 20 =20 = XXXX
- 7. Can you convert these numbers toCan you convert these numbers to Roman Numerals?Roman Numerals? ’ü« Work in pairs, answer in the back ofWork in pairs, answer in the back of books ŌĆōbooks ŌĆō ’ü« 17 = 22 = 26 = 29 = 30 =17 = 22 = 26 = 29 = 30 = ’ü« 32 = 35 = 50 = so 40 =32 = 35 = 50 = so 40 = ’ü« 44 = 49 = 58 = 60 =44 = 49 = 58 = 60 =
- 8. Were you correct?Were you correct? ’ü« 17=17=XVIIXVII 22=22=XXIIXXII 26=26=XXVIXXVI 29=29=XXIXXXIX ’ü« 30=30=XXXXXX 32=32=XXXIIXXXII 35=35=XXXVXXXV ’ü« 50=50=LL so 40=so 40=XLXL ’ü« 44=44=XLIVXLIV 49=49=XLIXXLIX 58=58=LVIIILVIII 60=60=LXLX
- 9. Try these.Try these. ’ü« 70 = 80 = 83 = 88 =70 = 80 = 83 = 88 = ’ü« 89 = 100 = so 90 =89 = 100 = so 90 = ’ü« 120 = 150 = 200 =120 = 150 = 200 = ’ü« 300 = 500 = so 400 =300 = 500 = so 400 =
- 10. How well did you do?How well did you do? ’ü« 70 =70 = LXXLXX 80 =80 = LXXXLXXX 83 =83 =LXXXIIILXXXIII ’ü« 88 =88 = LXXXV111LXXXV111 89 =89 =LXXXIXLXXXIX ’ü« 100 =100 = CC so 90 =so 90 =XCXC ’ü« 120 =120 =CXXCXX 150 =150 =CLCL 200 =200 = CCCC ’ü« 300 =300 = CCCCCC 500 =500 = DD so 400 =so 400 = CDCD
- 11. Some more large numbers to try.Some more large numbers to try. ’ü« 600 = 700 = 800 =600 = 700 = 800 = ’ü« 1000 = so 900 =1000 = so 900 = ’ü« 1600 = 1700 = 1900 =1600 = 1700 = 1900 = ’ü« 2000 =2000 =
- 12. Check your answers.Check your answers. ’ü« 600 =600 = DCDC 700 =700 = DCCDCC 800 =800 = DCCCDCCC ’ü« 1000 =1000 = MM so 900 =so 900 = CMCM ’ü« 1600 =1600 =MDCMDC 1700 =1700 =MDCCMDCC ’ü« 1900 =1900 = MCMMCM 2000 =2000 =MMMM
- 13. Last one.Last one. ’ü« Can you convert 2010?Can you convert 2010? ’ü« MMXMMX Now try to write todayŌĆÖs date.Now try to write todayŌĆÖs date. Day / Month / YearDay / Month / Year ’ü« Well done. You are a Roman NumeralWell done. You are a Roman Numeral Converter!Converter!