Router y?nlendi?rme protokolleri? ve algori?tmalari(9.grup)
- 1. ROUTER Y?NLEND?RME PROTOKOLLER? VE ALGOR?TMALARI 11310134093 Feriha SE?EN 11310134092 Hatice S???TL? 11310131019 Havva Nur TOTAN 13310131097 Zeliha BALEMEN 11310131056 Arife UYU 12310131073 G¨¹ls¨¹m ??P??
- 2. Y?NLEND?R?C?LER(ROUTER) ? A?lar aras? (LAN-LAN,LAN-WAN,WAN-WAN) haberle?menin yap?labilmesi i?in ara ba?lant?y? sa?lar. ? Gelen paketin ba?l???ndan ve y?nlendirme tablosu bilgilerinden yararlanarak y?nlendirme kararlar?n? verme yetene?ine sahiptir.
- 3. ? Routerin bir RAM, CPU ve ¨¹zerinde bir i?letim sistemi IOS (Internal Operating System) vard?r. ? Y?nlendiricilerin as?l vazifesi ald??? paketi hedef adresine g?ndermektir. ? Y?nlendiriciler farkl? ?l?ekteki a?lara g?re farkl? kapasitelerde ¨¹retilirler.
- 4. ? Y?nlendirici al?rken; 1.Hangi a? aray¨¹zlerini desteklemektedir? Her y?nlendirici her ba?lant? ?eklini desteklemez. Ethernet ya da Fastethernet portu hemen t¨¹m y?nlendiricilerin ¨¹zerinde bulunur. Di?er portlar ihtiyaca g?re sonradan tak?labilir. 2.Y?nlenricilerin ayn? anda ?evirebilecekleri paket oran? (switchfabric) bilinmelidir. Y?nlendiricilerin ayn? anda i?leyebilecekleri paket miktar? k?s?tl?d?r. Al?nacak y?nlendiricinin switchfabric de?eri y?nlendiricinin ¨¹zerinden akacak toplam trafik miktar?na g?re belirlenmelidir.
- 5. Y?nlendiriciler Merkez Y?nlendiriciler: ? Daha fazla porta ve h?zl? bir a? eri?imine sahiptir. ? A??n merkezinde bulunduklar?ndan hatas?z ve s¨¹rekli ?al??mas? gerekir. Kenar Y?nlendiriciler: ? Yerel a?? geni? alana ba?lamakta kullan?l?r.
- 7. Y?nlendirme (Routing) Nedir? ? Bir networkten di?erine ge?i? i?in bir yol haritas?d?r. ? Bu yol haritalar? routerlar?m?za dinamik olarak ba?ka bir router taraf?ndan yada statik olarak bir admin taraf?ndan haz?rlanm?? olabilirler.
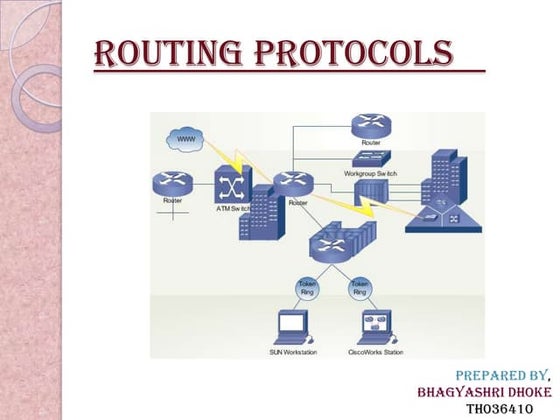
- 8. Y?nlendirici Kullanan Geni? Bir A? Yap?s?
- 9. Y?nlendirme Algoritmalar? ? Y?nlendirme algoritmalar? y?nlendirme tablolar?n? haz?rlamak i?in izlenen yollar olarak tan?mlanmaktad?r.
- 10. Algoritma ?e?itleri Sabit Y?ntem: ? Tablo, y?nlendirme i?lemleri boyunca sabit olarak kullan?l?r ve a?daki trafik farkl?la?malar?na ra?men de?i?tirilmez. ? ?ki nokta aras?nda verinin ilerleyece?i yol ?nceden belli olmaktad?r.
- 11. Algoritma ?e?itleri Sabit Algoritman?n Dezavantajlar? ? A? ¨¹zerinde belli yollarda t?kan?kl??a neden olabilmektedir. ? Ba?ka bir olumsuz noktas? ise ba?lant?larda meydana gelebilecek kopmalar?n tablolarda g¨¹ncelleme yap?lmad???ndan dolay? y?nlendirme i?lemine olumsuz yans?mas?d?r.
- 12. Algoritma ?e?itleri Dinamik ( Dynamic ) Y?ntem: ? Tablolar?n a??n trafi?ine g?re s¨¹rekli g¨¹ncellenmesi yap?lmaktad?r. ? ?ki nokta aras?nda iletilen veri her seferinde farkl? yollar? kullanabilmektedir. ? Daha karma??k algoritmalara sahiptir. ? A?da olu?abilecek trafik de?i?imleri ve ba?lant? kopmalar?nda farkl? yollar kullanabilmektedir.
- 13. Y?nlendirme ?e?itleri Merkezi Y?nlendirme ? Paketin g?nderilmesi s?ras?nda ¨¹zerinden ge?ece?i y?nlendiriciler g?nderildi?i y?nlendirici taraf?ndan belirlenmektedir. ? Y?nlendirme i?lemi veri yolculu?una ??karken belirlenmi? olmaktad?r.
- 14. Y?nlendirme ?e?itleri Da??n?k Y?nlendirme: ? Paketin ula?t??? her y?nlendirici hedef ?P adresi baz alarak elindeki bilgiler ile paketi bir sonraki y?nlendiriciye iletmektedir. ? Paketin yolu ba?lang??ta de?il s¨¹re? i?erisinde belirlenmektedir.
- 15. Y?nlendirme Algoritmalar? ? Temel amac? bir graf ¨¹zerindeki iki nokta aras?nda en k?sa yolun bulunmas?d?r. ? Y?nlendirme algoritmalar?n?n atas? olarak da kabul edilmektedir. a. Dijkstra En K?sa Yol Algoritmas?
- 16. Y?nlendirme Algoritmalar? ? Dijkstra algoritmas? sonu? olarak A d¨¹?¨¹m¨¹nden di?er d¨¹?¨¹mlere giden en k?sa yollar? verecektir. a. Dijkstra En K?sa Yol Algoritmas?
- 17. Y?nlendirme Algoritmalar? ? Bu algoritma sabit y?nlendirme algoritmas? s?n?f?na dahildir. ?¨¹nk¨¹ bu algoritma taraf?ndan olu?turulan y?nlendirme tablosu, y?nlendirme i?lemleri boyunca sabit olarak kullan?l?r ve a?daki trafik farkl?la?malar?na ra?men de?i?tirilmez. a. Dijkstra En K?sa Yol Algoritmas?
- 18. Y?nlendirme Algoritmalar? ? Bellman-Frord algoritmas? Dijkstra algoritmas?na g?re daha kapsaml? bir algoritmad?r. ? Bu Algoritma temel olarak d¨¹?¨¹mlerin kaynaktan olan uzakl?klar?na g?re (ge?ilecek d¨¹?¨¹m say?s?-hop) i?lemektedir. b. Bellman-Ford En K?sa Yol Algoritmas?
- 19. Y?nlendirme Algoritmalar? ? ?lk olarak kaynak d¨¹?¨¹mden (A d¨¹?¨¹m¨¹) bir atlamayla gidilecek olan B ve D d¨¹?¨¹mleri belirlenir ve de?erleri i?lenir. b. Bellman-Ford En K?sa Yol Algoritmas?
- 20. Y?nlendirme Algoritmalar? ? Ge?ilecek d¨¹?¨¹m say?s? s?ras?yla 2-3 ve 4 olarak belirlenip her atlamada gidilecek d¨¹?¨¹mler belirlenerek algoritma sonunda kaynak d¨¹?¨¹mden di?er t¨¹m d¨¹?¨¹mlere gidilecek en k?sa yollar belirlenmi? olur. b. Bellman-Ford En K?sa Yol Algoritmas?
- 21. Y?nlendirme Algoritmalar? ? Su bask?n? y?nteminde bir d¨¹?¨¹me gelen paketin kopyalar? paketin geldi?i d¨¹?¨¹m hari? t¨¹m kom?ular?na g?nderilme prensibine dayanmaktad?r. ? Bu y?ntemin dezavantaj? her d¨¹?¨¹mde paketin kopyalar? olu?turuldu?undan dolay? trafi?in a??r? derecede yo?unla?mas?d?r. c. Su Bask?n? (Flooding) Algoritmas?
- 22. Y?nlendirme Algoritmalar? ? Su bask?n? y?nteminin dezavantajlar? olmas?na ra?men bir?ok da avantaj? bulunmaktad?r. ? Bu avantajlar, d¨¹?¨¹mlerde hi?bir hesaplaman?n yap?lmamas? ve paketin ne olursa olsun bir yolunu bulup hedefe ula?mas? ?eklinde s?ralanabilir. c. Su Bask?n? (Flooding) Algoritmas?
- 23. d. Rastgele (Random) Y?nlendirme Algoritmas? ? D¨¹?¨¹me gelen paket tamamen rastsal bir bi?imde se?ilen kom?ulardan birine g?nderilmektedir. ? Bu y?ntemde d¨¹?¨¹me paketin geldi?i d¨¹?¨¹m hari? 4 yol varsa paketin herhangi bir yola g?nderilme olas?l??? 1/4 olmaktad?r. ? Bu y?ntemdeki rastsal se?im i?in belli bir ?l?¨¹t koyularak geli?mi? bir modele d?nd¨¹r¨¹lebilmektedir. Bu ?l?¨¹t genelde d¨¹?¨¹me ba?l? hatlar?n veri h?z? olarak kullan?lmaktad?r. ? Bu sayede paketin daha h?zl? olan bir hatta g?nderilme olas?l??? artt?r?lmaktad?r. Y?nlendirme Algoritmalar?
- 24. e. Uzakl?k Vekt?r¨¹ Algoritmas? ? Dinamik bir y?nlendirme algoritmas?d?r. ? Her bir d¨¹?¨¹m a??n geneli hakk?nda bir y?nlendirme tablosu tutmaktad?r. ? Bu tabloda hedef d¨¹?¨¹m¨¹n uzakl??? ve hedef d¨¹?¨¹me ula?abilmek i?in y?nlendirilmesi gereken bir sonraki d¨¹?¨¹m bilgisi tutulmaktad?r. ? Bu tablolara uzakl?k vekt?r¨¹ ad? verilmektedir. Y?nlendirme Algoritmalar?
- 25. e. Uzakl?k Vekt?r¨¹ Algoritmas? ? D¨¹?¨¹mler ellerinde bulunan vekt?rleri belli zaman aral?klar?nda kom?ula- r?na g?ndermekte ve kom?ular?ndan gelen bilgileri almaktad?rlar. ? Her d¨¹?¨¹m kendine gelen vekt?rlerdeki verileri kullanarak tuttu?u vekt?r¨¹ g¨¹ncellemektedir. ? Bu sayede d¨¹?¨¹m kendine kom?u olmayan d¨¹?¨¹mlere ula?ma yollar?n? da ??renmi? olmaktad?r. Y?nlendirme Algoritmalar?
- 26. ? Sistem ilk ?al??maya ba?lad???nda b¨¹t¨¹n d¨¹?¨¹mlerdeki bo? olan tablolar, d¨¹?¨¹m¨¹n kom?ular?na olan uzakl?klar?n? ??renmesi ile doldurulmaktad?r. Bu durumda sadece kom?ular?na olan uzakl?k yer almaktad?r.
- 27. f. Ba?lant? Durumu Algoritmas? ? Ba?lant? durumu y?nlendirme (Link State) algoritmas? Dijkstra en k?sa yol algoritmas?n? kullanmaktad?r. Fakat bu algoritmalardan en b¨¹y¨¹k fark? sabit de?il a??n durumuna g?re de?i?en (dinamik) bir y?ntem olmas?d?r. ? Bu y?ntem 1979'da uzakl?k vekt?r¨¹ algoritmas?n?n temel iki problemine alternatif olarak geli?tirilmi?tir. ? Bu iki problemden ilki uzakl?k vekt?r¨¹ algoritmas?n?n sonuca ula?mas?n?n fazla zaman almas?d?r. ?kincisi ise uzakl?k vekt?r¨¹ algoritmas?n?n ba?lant?lar?n kapasitelerinin g?z ?n¨¹nde bulundurulmamas?d?r. Y?nlendirme Algoritmalar?
- 28. Y?nlendirme Protokolleri ? ?nterneti olu?turan a?lar birbirlerine a? ge?idi ile ba?lanmaktad?r. ? ?nterneti olu?turan ve kendi i?erisinde ortak bir y?netime sahip a? yap?lar?na otonom sistemler (Autonomous systems) denir. ? Y?nlendirme Protokoller; 1) Otonom sistemlerin i?erisinde ?al??an dahili y?nlendirme protokolleri (Inte- rior Routing Protokol-IRP) 2) Otonom sistemler aras?nda y?nlendirme sa?layan harici y?nlendirme protokolleri (Exterior Routing Protokol-ERP)
- 29. Otonom sistemlerin i?erisinde ?al??an dahili y?nlendirme protokolleri (Inte- rior Routing Protokol-IRP) Y?nlendirme Protokolleri
- 30. Otonom sistemler aras?nda y?nlendirme sa?layan harici y?nlendirme protokolleri (Exterior Routing Protokol-ERP) Y?nlendirme Protokolleri
- 31. ? Dahili y?nlendirme protokolleri kulland?klar? algoritmalara g?re iki alt kategoriye ayr?lmaktad?r. Y?nlendirme Protokolleri Uzakl?k vekt?r¨¹ algoritmas? Ba?lant? durumu algoritmas?
- 32. ? Dahili y?nlendirme protokolleri: ? Y?nlendirme bilgi protokol¨¹ (Routing Information Protocol-RIP), ? En k?sa a??k yol protokol¨¹ (Open shortest path first protokol-OSPF), ? Dahili a? ge?idi y?nlendirme protokol¨¹ (Interior Gatevvay Routing Protocol-IGRP), ? Geli?tirilmi? dahili a? ge?idi y?nlendirme protokol¨¹d¨¹r (Enhanced In- terior Gateway Routing Protocol-E?GRP). Y?nlendirme Protokolleri
- 33. ? Harici y?nlendirme protokolleri: ? Harici a? ge?idi protokol¨¹ (Exterior Gateway Protocol-EGP), ? S?n?r a? ge?idi protokol¨¹ (Border Gateway Protokol-BGP), ? En k?sa s?n?rlan dirilmi? yol protokol¨¹d¨¹r (Constrained Shortest Path First- CSPF). Y?nlendirme Protokolleri
- 34. Y?nlendirme Protokolleri A.RIP ? Dahili y?nlendirme protokol¨¹ olan y?nlendirme bilgi protokol¨¹ (Rou ting Information Protocol-RIP). ? TCP/IP a??ndaki y?nlendiricilerin birbirini otomatik olarak tan?mas?nda ve kendi y?nlendirme tablolar?n? olu?turmas?nda kullan?lan protokold¨¹r. ? Uzakl?k vekt?r¨¹ algoritmas?n? kuIlan?r. ? RIP bu algoritmay? kullan?rken kaynak ve hedef aras?ndaki mesafeyi ge?ilecek d¨¹?¨¹m say?s? olarak kabul etmektedir. ? Uzakl?k vekt?r¨¹ algoritmas?nda ortaya ??kan sonsuza sayma probleminin ??z¨¹m¨¹ i?in RIP, iki nokta aras?ndaki yolun maksimum 15 d¨¹?¨¹m say?s? kabul etmektedir.
- 35. ? B.OSPF ? En k?sa a??k yol protokol¨¹ (OPSF-Open Shortest Path First). ? A? katman?nda ?al??an, TCP/IP protokol¨¹ a?lar? ¨¹zerinde y?nlendirme yapan dahili y?nlendirme protokol¨¹d¨¹r. ? Ba?lant? durumu algoritmas?n? kullanmakta dolay?s? ile Dijkstra algoritmas? temelinde ?al??maktad?r. ? OSPF'nin en b¨¹y¨¹k avantaj? b¨¹y¨¹k a?lar ¨¹zerinde bile maliyeti ?ok d¨¹?¨¹k tutarak verimlili?i artt?rmas?d?r. ? En b¨¹y¨¹k dezavantaj? ise karma??k bir yap?ya sahip olmas?d?r. ? Her bir y?nlendirici ba?l? bulundu?u otonom sistem i?erisinde yer alan t¨¹m yol bilgisini bir tabloda tutmakta ve en k?sa yolu bu tabloyu kullanarak hesaplamaktad?r. Y?nlendirme Protokolleri
- 37. ? C.IGRP ? Dahili a? ge?idi y?nlendirme protokol¨¹ (Dahili a? ge?idi y?nlendirme prolokol¨¹- IGRP) ? IGRP, RIP i?erisinde bulunan s?n?rl?l?klar? (iki d¨¹?¨¹m aras? maksimum d¨¹?¨¹m say?s?) ortadan kald?rmak amac? ile geli?tirilmi?tir. ? IGRP'de maksimum d¨¹?¨¹m say?s? varsay?lan olarak 100 ile belirlense de 255'e kadar ??kart?labilmektedir. ? Yol se?iminde atlama say?s? yerine be? adet ?l?¨¹t kullan?lmaktad?r: bant geni?li?i, y¨¹k, gecikme, g¨¹venilirlik ve iletilen maksimum birim. ? Uzakl?k vekt?r¨¹ algoritmas?n? kullanan IGRP yol bilgisine ait veri de?i?imi 90 saniyede ger?ekle?tirirken, a?daki de?i?ikliklerin bildirilmesini hemen yapmaktad?r. Y?nlendirme Protokolleri
- 38. ? D.EIGRP ? Geli?tirilmi? dahili a? ge?idi y?nlendirme protokol¨¹ (Enhanced inter- rior gateway routing protocol-EIGRP) ? IGRP'nin yetersiz kalmas? ile geli?tirilmi? bir protokold¨¹r. ? EIGRP temel olarak hem bir uzakl?k vekt?r¨¹ ve ba?lant? durum vekt?r¨¹ algoritmas?n?n iyi y?nlerini alarak geli?tirilmi?tir. Y?nlendirme Protokolleri
- 39. ? D.EIGRP ? EIGRP ¨¹zerinde ?al??an y?nlendiriciler, veri al??veri?i amac? ile 5 farkl? paket kullanmaktad?r: ? Selam (Hello), ? G¨¹ncelleme (Update), ? Sorgu (Query), ? Yan?t (Reply) ? Onay (Acknovvledgement) ? Sisteme yeni dahil olan veya sistemden ??kar?lan bir y?nlendiricinin belirlenmesi sorgu, selam ve onay mesajlar? ile tespit edilmektedir. ? A? da ger?ekle?en de?i?iklikler g¨¹ncelleme paketleri ile kom?ulara sunulur. Y?nlendirme Protokolleri
- 40. ? E.EGP ? Harici a? ge?idi protokol¨¹ (Exterior Gatevvay Protocol-EGP) ? Otonom sistemler aras?nda yol belirlemede kullan?l?r. ? EGP temel olarak a? ge?itleri i?erisinde bulunan y?nlendirme tab- lolar?n?n kurulmas? ve g¨¹ncellenmesini sa?lamaktad?r. ? EGP ile ?al??an bir a? ge?idi kom?ular?n? belirlemekte, kom?ular?na bilgi mesajlar? g?ndermekte ve onlar?n ?al???r durumda olduklar?m test etmektedir. Y?nlendirme Protokolleri
- 41. ?ekil- IGP ve EGP¡¯nin Kullan?m Yeri
- 42. ? F.BGP ? S?n?r a? ge?idi protokol¨¹ (Border gatevvay protocol-BGP) ? EGP protokol¨¹n¨¹n yerine geli?tirilen merkezi olmayan bir y?nlendirme protokol¨¹d¨¹r. ? ?rnek olarak i?erisinde OSPF protokol¨¹ kullanan otonom sistemler bu protokol yard?m? ile birbirlerine ba?lanabilmektedirler. Bu yap?s? ile BGP ?nternet'in en ?nemli protokollerinden birisidir. ? BGP a? yap?s?nda ger?ekle?ebilecek de?i?imleri anlayabilmek amac? ile duyuru (anouncement) paketlerini kullanmaktad?r. ? Bu y?ntemde her kenar a? ge?idi belli s¨¹re aral?klar?nda ?al???r durumda oldu?unu kom?ular?na duyurmaktad?r. Y?nlendirme Protokolleri
- 43. ? Herhangi bir nedenden ?t¨¹r¨¹ a? ge?idi ?al??amaz hale gelirse kom?u cihaz, bu paketi alamayacakt?r. ? Bu durumda a? ge?idi ?al???r durumda olmayan a? ge?idinin bilgilerini tespit etmekte ve bunlar? silmektedir. ? BGP di?er bir?ok y?nlendirme protokol¨¹nden farkl? olarak TCP protokol¨¹n¨¹ kullanmaktad?r. ? BGP¡¯yi kullanan bir y?nlendirici her 60 saniyede bir 19 byte paketleri kom?ular?na g?ndermektedir. ? ?nemli fonksiyonlar?ndan biri y?nlendirmede ger?ekle?ebilecek d?ng¨¹lerin yakalanmas?d?r. ? BGP, otonom sistemleri birbirlerine ba?lamas?n?n d???nda, otonom sistem i?erisinde de kullan?labilmektedir. Y?nlendirme Protokolleri
- 44. Kaynak?a ? http://www.cozumpark.com/blogs/network/archive/2013/02/03/dinamik- yonlendirme-ve-rip-konfigurasyonu.aspx ? http://cagataykartal.net/Pages/Dinamikyonlendirme.aspx ? http://tr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Y%C3%B6nlendirme_protokolleri ? http://bilgisayarokulumuz.com/?tag=statik-yonlendirme