1 of 7
Download to read offline





Ad
Recommended
G pub
G pubHCPC: ±±º£µÀ´óѧ¸¼¼¥×¥í¥°¥é¥ß¥ó¥°¥µ©`¥¯¥ë
?
This document discusses an algorithm for determining if one permutation contains another as a pattern by examining runs (increasing or decreasing subsequences) in the permutations. It presents the concept of representing permutations as permutation matrices and comparing the runs within them. The algorithm runs in linear time by using dynamic programming to check for matching runs between the permutations p and q when the lengths of their longest common increasing subsequences are equal to |p| or |q|.F pub
F pubHCPC: ±±º£µÀ´óѧ¸¼¼¥×¥í¥°¥é¥ß¥ó¥°¥µ©`¥¯¥ë
?
The document contains a series of symbols, numbers, and characters with no discernible meaning or context. It includes repeating patterns of 10s, 1s, and 0s as well as other random numbers and characters. The formatting includes boxes and lines that do not provide any additional clarity to the content. Overall, the document is nonsensical and provides no clear information to summarize.D pub
D pubHCPC: ±±º£µÀ´óѧ¸¼¼¥×¥í¥°¥é¥ß¥ó¥°¥µ©`¥¯¥ë
?
This document appears to be notes from March 24, 2017 related to programming competitions and algorithms. It includes sections labeled with numbers and dates that seem to contain brief descriptions of coding challenges, with some mentioning specific algorithms like SPFA and languages like C++. Overall topics discussed include competitive programming, algorithms, and coding challenges from that date.B pub
B pubHCPC: ±±º£µÀ´óѧ¸¼¼¥×¥í¥°¥é¥ß¥ó¥°¥µ©`¥¯¥ë
?
The document discusses algorithms for three problems:
1. Finding the maximum value of a function of N variables in O(NlogN) time.
2. Finding the first index where a value exceeds a threshold in O(N) time.
3. Sorting N numbers in O(NlogN) time.
It also provides the time complexities of different solutions to related problems and statistics on code submissions for a programming challenge.E pub
E pubHCPC: ±±º£µÀ´óѧ¸¼¼¥×¥í¥°¥é¥ß¥ó¥°¥µ©`¥¯¥ë
?
The document contains a binary sequence recorded over 8 days from March 24 to March 31, 2017. Each day contains a number from 1 to 8, suggesting it was part of a longer term experiment or study where binary data was collected over that period.Deposited Ranges
Deposited RangesTakumi Yamashita
?
Plasma ¤Ç×Ó¥Á¥§©`¥óÉϤÎNFT¤ò¹ÜÀí¤¹¤ë¤¿¤á¤Î¥Ç©`¥¿Ôì DepositedRanges ¤Ë¤Ä¤¤¤Æ¤Î¥á¥âMore Related Content
Viewers also liked (14)
G pub
G pubHCPC: ±±º£µÀ´óѧ¸¼¼¥×¥í¥°¥é¥ß¥ó¥°¥µ©`¥¯¥ë
?
This document discusses an algorithm for determining if one permutation contains another as a pattern by examining runs (increasing or decreasing subsequences) in the permutations. It presents the concept of representing permutations as permutation matrices and comparing the runs within them. The algorithm runs in linear time by using dynamic programming to check for matching runs between the permutations p and q when the lengths of their longest common increasing subsequences are equal to |p| or |q|.F pub
F pubHCPC: ±±º£µÀ´óѧ¸¼¼¥×¥í¥°¥é¥ß¥ó¥°¥µ©`¥¯¥ë
?
The document contains a series of symbols, numbers, and characters with no discernible meaning or context. It includes repeating patterns of 10s, 1s, and 0s as well as other random numbers and characters. The formatting includes boxes and lines that do not provide any additional clarity to the content. Overall, the document is nonsensical and provides no clear information to summarize.D pub
D pubHCPC: ±±º£µÀ´óѧ¸¼¼¥×¥í¥°¥é¥ß¥ó¥°¥µ©`¥¯¥ë
?
This document appears to be notes from March 24, 2017 related to programming competitions and algorithms. It includes sections labeled with numbers and dates that seem to contain brief descriptions of coding challenges, with some mentioning specific algorithms like SPFA and languages like C++. Overall topics discussed include competitive programming, algorithms, and coding challenges from that date.B pub
B pubHCPC: ±±º£µÀ´óѧ¸¼¼¥×¥í¥°¥é¥ß¥ó¥°¥µ©`¥¯¥ë
?
The document discusses algorithms for three problems:
1. Finding the maximum value of a function of N variables in O(NlogN) time.
2. Finding the first index where a value exceeds a threshold in O(N) time.
3. Sorting N numbers in O(NlogN) time.
It also provides the time complexities of different solutions to related problems and statistics on code submissions for a programming challenge.E pub
E pubHCPC: ±±º£µÀ´óѧ¸¼¼¥×¥í¥°¥é¥ß¥ó¥°¥µ©`¥¯¥ë
?
The document contains a binary sequence recorded over 8 days from March 24 to March 31, 2017. Each day contains a number from 1 to 8, suggesting it was part of a longer term experiment or study where binary data was collected over that period.More from Takumi Yamashita (15)
Deposited Ranges
Deposited RangesTakumi Yamashita
?
Plasma ¤Ç×Ó¥Á¥§©`¥óÉϤÎNFT¤ò¹ÜÀí¤¹¤ë¤¿¤á¤Î¥Ç©`¥¿Ôì DepositedRanges ¤Ë¤Ä¤¤¤Æ¤Î¥á¥âAd
Recently uploaded (7)
Vibe Coding¤òʼ¤á¤è¤¦ ?Cursor¤òÀı¤Ë¡¢¥Î©`¥³©`¥É¤Ç¤Î¥×¥í¥°¥é¥ß¥ó¥°ÌåòY?
Vibe Coding¤òʼ¤á¤è¤¦ ?Cursor¤òÀı¤Ë¡¢¥Î©`¥³©`¥É¤Ç¤Î¥×¥í¥°¥é¥ß¥ó¥°ÌåòY?iPride Co., Ltd.
?
2025/06/20¤ÎÃãÇ¿»á¤Ç°k±í¤µ¤ì¤¿¤â¤Î¤Ç¤¹¡£PGConf.dev 2025 ²Î¼Ó¥ì¥İ©`¥È (JPUG¾t»áãÔO¥»¥ß¥Ê©`2025 °k±íÙYÁÏ)
PGConf.dev 2025 ²Î¼Ó¥ì¥İ©`¥È (JPUG¾t»áãÔO¥»¥ß¥Ê©`2025 °k±íÙYÁÏ)NTT DATA Technology & Innovation
?
PGConf.dev 2025 ²Î¼Ó¥ì¥İ©`¥È
(JPUG¾t»áãÔO¥»¥ß¥Ê©`2025 °k±íÙYÁÏ)
2025Äê6ÔÂ14ÈÕ(ÍÁ)
NTT¥Ç©`¥¿
OSS¥Ó¥¸¥Í¥¹ÍÆßMÊÒ
غë Ì©İo¡¢³ØÌï ÁİÌ«ÀÉ´¡±õ¼¼Êõ¹²ÓĞ»á2025-06-05³å¶Ù±ğ±ğ±è¸é±ğ²õ±ğ²¹°ù³¦³ó¤ÎÀí½â¤Èg¼ù.±è»å´Ú
´¡±õ¼¼Êõ¹²ÓĞ»á2025-06-05³å¶Ù±ğ±ğ±è¸é±ğ²õ±ğ²¹°ù³¦³ó¤ÎÀí½â¤Èg¼ù.±è»å´ÚTakuma Oda
?
Deep Research¤Î¼¼Ğg¸ÅÒª¤ä»îÓÃÀı¤Ê¤É¤Ë¤Ä¤¤¤Æ½B½éÃã»á_¥¿©`¥ß¥Ê¥ë¥³¥Ş¥ó¥È?ÈëÁ¦Ñ¸ËÙ»¯_20250620. pptx. .
Ãã»á_¥¿©`¥ß¥Ê¥ë¥³¥Ş¥ó¥È?ÈëÁ¦Ñ¸ËÙ»¯_20250620. pptx. .iPride Co., Ltd.
?
2025/06/20¤ÎÃãÇ¿»á¤Ç°k±í¤µ¤ì¤¿¤â¤Î¤Ç¤¹¡£Forguncy 10 ÑuÆ·¸ÅÒªÙYÁÏ - ¥Î©`¥³©`¥ÉWeb¥¢¥×¥êé_°k¥×¥é¥Ã¥È¥Õ¥©©`¥à
Forguncy 10 ÑuÆ·¸ÅÒªÙYÁÏ - ¥Î©`¥³©`¥ÉWeb¥¢¥×¥êé_°k¥×¥é¥Ã¥È¥Õ¥©©`¥à¥Õ¥©©`¥¬¥ó¥·©`
?
¥á¥·¥¦¥¹Öêʽ»áÉç¤ÎÑuÆ·¹ó´Ç°ù²µ³Ü²Ô³¦²â¤ÎÑuÆ·×ÊÁϤǤ¹¡£Protect Your IoT Data with UbiBot's Private Platform.pptx
Protect Your IoT Data with UbiBot's Private Platform.pptx¥æ¥Ó¥Ü¥Ã¥È Öêʽ»áÉç
?
Our on-premise IoT platform offers a secure and scalable solution for businesses, with features such as real-time monitoring, customizable alerts and open API support, and can be deployed on your own servers to ensure complete data privacy and control.Ad
¸é±«±Ê°ä2017:°½âÕh
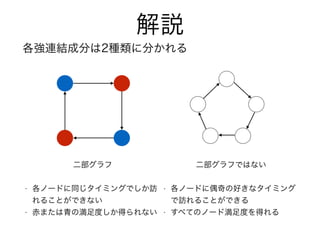
- 2. î}¸ÅÒª ? ¸÷½Ö¤ÏÓĞÏòŞx¤Ç¿¤¬¤ì¤Æ¤¤¤ë ? ½Ö0¤«¤é¥¹¥¿©`¥È¤·¡¢¸÷½Ö¤Ë³õ¤á¤ÆżÊı¥¹¥Æ¥Ã¥×Ä¿ ¤ËÔL¤ì¤¿r¤Ëº×ã¶È¤òµÃ¤é¤ì¤ë ? ×îÊʤËÒƶ¯¤·¤¿Ê±¤Îº×ã¶È¤ÎºÏ¼Æ¤Î×î´ó¤òÇó¤á¤è
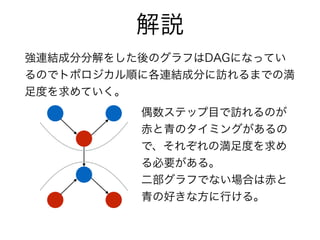
- 4. ½âÕh ¸÷ßB½Y³É·Ö¤Ï2·Nî¤Ë·Ö¤«¤ì¤ë ¶ş²¿¥°¥é¥Õ¤Ç¤Ï¤Ê¤¤ ? ¸÷¥Î©`¥É¤ËżÆæ¤ÎºÃ¤¤Ê¥¿¥¤¥ß¥ó¥° ¤ÇÔL¤ì¤ë¤³¤È¤¬¤Ç¤¤ë ? ¤¹¤Ù¤Æ¤Î¥Î©`¥Éº×ã¶È¤òµÃ¤ì¤ë ¶ş²¿¥°¥é¥Õ ? ¸÷¥Î©`¥É¤Ëͬ¤¸¥¿¥¤¥ß¥ó¥°¤Ç¤·¤«ÔL ¤ì¤ë¤³¤È¤¬¤Ç¤¤Ê¤¤ ? ³à¤Ş¤¿¤ÏÇà¤Îº×ã¶È¤·¤«µÃ¤é¤ì¤Ê¤¤
- 6. ¥¸¥ã¥Ã¥¸½â ? kzyKT?C++?135ĞĞ ? haji?C++?135ĞĞ ? sate?C++?144ĞĞ ? uku?C++?205ĞĞ
- 7. ½Y¹û ? First Submission ??On-site: ca?e 4h11min ??Online: btklatte 2h40min ? First Accepted ??On-site: ??Online: btklatte 2h40min ? Success Rate: 6.67% (1/15)
