Social Dialect
Download as PPTX, PDF10 likes6,746 views
This document discusses social dialects and how they differ from regional dialects. It defines dialect as a variety of a language that signals where a person comes from and is influenced by their social background. Social dialect, also called sociolinguistics, refers to variations in language based on social factors like ethnicity, gender, age, and social class. Regional dialect depends more on the geographical area where a language is spoken. While both reflect social variations in language use, social dialects are influenced more by social barriers between groups rather than geographical distance.
1 of 11
Downloaded 102 times




Recommended
Social dialect



Social dialectaliaJaafar2
Ã˝
Language, Culture and Society
Social dialects
Social variation
Regional variation
Group members
Nik Nur Amalia Bt Wan Anuar Shaipu'din
Alia Atikah Bt Jaafar
Nur Ain Batrisyia Bt Mohd Zaini
SOCIAL DIALECT



SOCIAL DIALECTComilla University, Bangladesh
Ã˝
Definition....differences...Factors....how does language vary....kinds of social dialect....sociolect in England and Bangladesh..... importance of social class in social dialect.....Meeting 4 language attitude



Meeting 4 language attitudeSchool
Ã˝
This document discusses language attitudes and related concepts. It defines language attitude as inferences about people based on how they speak. People have attitudes toward their own and other languages. Attitudes are demonstrated through behavior. The document also discusses semantics shift, derogation, linguistic relativism, perceptual dialectology, social identity theory, and communication accommodation theory as they relate to language attitudes. It provides examples to illustrate key concepts.Introduction to sociolinguistics



Introduction to sociolinguisticsLusya Liann
Ã˝
1) Sociolinguistics is the study of the relationship between language and society. It examines how social factors such as context, status, and function influence language variation and use.
2) People code switch and use different linguistic varieties depending on social context, including the participants, setting, topic, and function of the interaction. Formal contexts like religion or education use high varieties while informal settings use low varieties.
3) Languages shift when their speakers abandon them for a dominant language due to economic, social, or demographic factors. This can lead to language loss or even death when no one speaks it anymore.SOCIAL DIALECT



SOCIAL DIALECTComilla University, Bangladesh
Ã˝
Definition.types.factors.differences.examples from England and Bangladesh....importance of social classSociolinguistics



SociolinguisticsJunaid Amjed
Ã˝
This document discusses sociolinguistics and the varieties of language. It defines sociolinguistics as the study of language in relation to society, including how social aspects influence language use and how language impacts society. It then discusses that there is no single set of rules for a language like English, and that language varies between individuals and social groups. Specifically, it outlines that language exists in idiolects unique to individuals, dialects specific to regions, registers for certain purposes, diglossia where separate varieties are used in formal vs informal contexts, and sociolects associated with social groups.SOCIOLINGUISTIC about LANGUAGE AND CULTURE



SOCIOLINGUISTIC about LANGUAGE AND CULTUREAnisa Asharie
Ã˝
The document discusses the relationship between language and culture in three main points:
1) Language is closely tied to the culture of its speech community, as a community's culture consists of what members have to know to operate acceptably.
2) While communities can share similar cultures but different languages, the close relationship between language and culture has long been studied. A language reflects the values of its speakers' culture.
3) Approaching foreign language teaching with an understanding of the target culture can help address issues of misunderstanding that may arise from cultural differences in word meanings.Social variation (SLT)



Social variation (SLT)H. R. Marasabessy
Ã˝
This document discusses social variation in language, focusing on African American Vernacular English (AAVE). It covers the following key points:
1) AAVE has distinct phonological and grammatical features that developed from its creole origins and divergence over time from other English dialects.
2) Teachers often have negative attitudes toward students who speak AAVE, which can negatively impact these students' academic performance. Understanding students' and communities' attitudes toward AAVE is important for teaching.
3) Recognizing AAVE as a valid dialect that developed naturally, rather than from ignorance, can help teachers incorporate the dialect into their language arts pedagogy through exercises like translation drills between AAVE and standard English.Language and ethnic group



Language and ethnic groupLampung University
Ã˝
1) Language is closely intertwined with ethnic identity and group membership. Members of ethnic groups often learn the linguistic varieties associated with that group.
2) In the United States, differences exist between the English spoken by white and black Americans, and ethnicity can often be identified based on language alone. However, these linguistic differences result from learned behavior within communities rather than innate qualities.
3) The situation in former Yugoslavia demonstrates how ethnic identities and linguistic varieties can change over time and in response to political situations. Serbo-Croatian was once considered a single language but is now considered separate Serbian and Croatian languages.Language Loss



Language Lossdrfaithpolk
Ã˝
This document discusses language loss in bilingual children and strategies to promote balanced bilingualism. It notes that language loss occurs when a minority language is no longer used proficiently due to increased exposure to a dominant language like English. This can lead to incomplete learning or forgetting of the home language over time. The document recommends that teachers recognize this as a temporary developmental phase and that families provide opportunities to use and maintain the home language through exposure to speakers and social contexts that support both languages.Language Planning



Language PlanningAyesha Mir
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of language planning. It defines language planning as efforts to influence and modify a language's structure and function. It discusses key aspects of language planning including its goals, processes, types (status and corpus planning), ideologies, and issues. The summary focuses on language planning's aim to alter a language's role and how it is implemented through selection, codification, elaboration, and acceptance of a standardized variety.Linguistics imperialism



Linguistics imperialismSajid Ali Lashari
Ã˝
The causes, effects, start, and the way its going, what are the roles, what are the agencies through which linguistics imperialism is spreading. Sociolinguistic terms



Sociolinguistic termsFatmawati Khodijah
Ã˝
This document defines and explains various sociolinguistic terms related to language, dialects, and language varieties. It provides definitions for 50 terms, including language, dialect, patois, standardization, standard English, vitality, historicity, autonomy, reduction, mixture, de facto norm, regional dialect, received pronunciation, dialect geography, dialect boundary, isogloss, accent, style, register, competence, performance, non-standard variety, variety, sociolect, creole, lingua franca, pidgin, norms, class, prestige, caste, ethnicity, vernacular, idiolect, social dialect, social network, homogeneous, bilingual, and multilingual. The document was created by students andAccommodation Theory



Accommodation TheoryIrsalina Viramdani
Ã˝
Communication Accommodation Theory (CAT) proposes that people change their speech patterns, vocal characteristics, and gestures when communicating with others in order to be better understood. Developed by Howard Giles in 1973, CAT suggests that speakers may converge their speech towards another person's patterns or diverge from them. Convergence can occur downward from higher to lower social classes, upward from lower to higher classes, or mutually as both speakers adjust towards each other. The goal of accommodation is effective communication across differences in language, age, or other barriers.language and social variation



language and social variationhojjat namdaran
Ã˝
This document discusses language variation based on social factors. It covers the topics of sociolinguistics, social dialects, education and occupation, social markers, and speech style/style-shifting. Sociolinguistics examines the relationship between language and society, investigating how languages function in communication and the structure of language. Social dialects, or sociolects, are language varieties that differ based on a speaker's social status or group, such as social class, religion, or ethnicity. Features like pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar are used to analyze social dialects. Education level and occupation also influence one's speech patterns and style.Language and Gender by Muhammad Ahmad



Language and Gender by Muhammad AhmadAhmadSadequain
Ã˝
Complete Description of the Relationships between Language and Gender - how men and women speak differently? Personality differences in genders? gender discrimination? Authentic sources....Style Register and Dialect



Style Register and DialectSidra Shahid
Ã˝
Language varieties refer to different forms of a language influenced by social factors such as situation, occupation, age, geography, education, gender, social status, and ethnicity. There are several types of language varieties including dialects, registers, pidgins, and creoles. A dialect is a variety of a language used in a specific region or social class. Registers are varieties used in different situations based on formality. A pidgin is a simplified mixed language with reduced vocabulary and grammar used for communication between speakers of different languages, while a creole develops when a pidgin becomes the primary language of a group and acquires more complex grammar.Language and social variation



Language and social variationluzfernndez9
Ã˝
This document discusses language variation and the relationship between language and society. It introduces key concepts such as speech communities, sociolinguistics, social dialects, linguistic variables, and registers. Social factors like class, education, occupation, and context can influence the way people speak. The document also discusses concepts like convergence, divergence, prestige, jargon, slang, vernacular languages, and provides examples of linguistic features in African American Vernacular English. Applied Linguistics & Language Teaching



Applied Linguistics & Language TeachingFarhad Mohammad
Ã˝
This document discusses the relationship between applied linguistics and language teaching. It defines applied linguistics as the theoretical and empirical investigation of real-world language problems. It explores how applied linguistics can positively impact language teachers by informing areas like teaching methods, materials development, and testing. The document also examines how linguistics, applied linguistics, and language teaching are interrelated and how descriptions of language can improve teaching.Language,dialect and variation, sociolinguistic



Language,dialect and variation, sociolinguisticPurnama Ratna Sari Dewi
Ã˝
This document discusses sociolinguistic concepts related to language variation, including:
- Varieties include languages, dialects, accents, registers, and styles of a language. Variation occurs at the lexical level through slang and levels of formality.
- Dialects are regional or social varieties of a language characterized by their own phonological, syntactic, and lexical properties. They can also be associated with ethnic groups or socioeconomic classes.
- Registers or styles are varieties of language used in particular social settings defined by levels of formality or social events like baby talk.
- An idiolect is the unique language use of an individual person influenced by various dialects, registers, and languagesSpeech Communities



Speech CommunitiesMary Joy Jagonia
Ã˝
The document discusses key concepts relating to speech communities. It defines a speech community as a group of people who interact through shared use of language and participation in common norms. While some definitions require all members to use the same language or dialect, most acknowledge that communities can be multilingual. Characteristics like shared social networks, values and beliefs help define communities more than sole reliance on linguistic criteria. Urban areas in particular may contain overlapping and intersecting speech communities with blurred boundaries.Full summary an_introduction_to_sociolinguistics



Full summary an_introduction_to_sociolinguisticsLutfan Adli
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of Chapter One from Janet Holmes' book "An Introduction to Sociolinguistics". It discusses key topics that sociolinguists study such as how social factors influence language varieties and how sociolinguists define terms like variety. Sociolinguists are interested in explaining why people speak differently in different social contexts and how social factors like social distance, status, age and gender impact language varieties and convey social meanings.Language and age



Language and ageGraciela Bortoluzzi
Ã˝
The document discusses how language variation allows people to construct identities based on age and social dimensions. It examines how language is used differently across three life stages: young children, teenagers, and the elderly. Specific examples are given of "baby talk" used with young children, texting language in conversations between teenagers, and the phenomenon of "elderspeak" which is commonly used but can be harmful by implying incompetence in older adults.What is sociolinguistics,



What is sociolinguistics,Purnama Ratna Sari Dewi
Ã˝
Sociolinguistics is the study of how social factors such as ethnicity, gender, age, and socioeconomic class influence language. It examines how language differs between social groups and how these differences can categorize individuals. Sociolinguists study how grammar, vocabulary, and other language aspects vary depending on social context, in contrast to dialectology which focuses on language's effect on society. Key concepts in sociolinguistics include speech communities, prestige varieties, social networks, and differences in language according to class, age, gender, geography, and politeness.Dialectology



DialectologyAsmaSaifUllah
Ã˝
This document discusses the topic of dialectology, which is the scientific study of linguistic dialects. It defines dialect as a specific form of a language that is peculiar to a certain region or social group. Dialectology studies variations in language based on geographic distribution and associated features. To distinguish between dialects of the same language, speakers must be able to understand each other. The document outlines levels of dialect analysis including geography, ethnicity, and social class. It also discusses the need to study dialects from both linguistic and social perspectives.Gander and age



Gander and ageMaulidifi
Ã˝
This document discusses gender and age related differences in speech. It notes that while women and men share a language, there are often small differences in features like pronunciation or morphology. Research has shown women tend to use more standard forms while men use more vernacular forms. Social class also influences speech, with women across classes using more standard forms than men. The document explores various explanations for why women's speech patterns differ, and discusses how age can influence language use, with vernacular forms highest in youth and old age when social pressures are lower.Sapir and Whorf



Sapir and WhorfIka Hentihu
Ã˝
This document discusses the Sapir-Whorf hypothesis, which was first proposed by Edward Sapir and later expanded upon by Benjamin Lee Whorf. It presents the key figures and their backgrounds, including Sapir's work in linguistics and Whorf's study of the Hopi language. The hypothesis is introduced as having both a strong version, that language determines thought, and a weak version, that language influences thought. While heavily criticized, most linguists now accept the weak version to some degree. Examples are given of how language can reflect cultural differences in areas like kinship terminology. The conclusion is that while the extreme versions have been disproven, most agree there is some influence of language on thought.Teaching of Vocabulary



Teaching of VocabularyDr. Bhavin Chauhan
Ã˝
Words are very essential for effective communication. The teaching Vocabulary helps the students to develop the word vocab as well as fluency.Varities in sociolinguistics



Varities in sociolinguisticsShehnaz Mehboob
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of linguistic variation and key concepts related to dialects and registers. It discusses the differences between language and dialect, and notes that all speakers use some dialect. Dialects can be divided into regional dialects, which vary based on geography, and social dialects, which are influenced by factors like occupation, age, education, and gender. The document also examines concepts like standard vs. non-standard dialects, speech communities, linguistic styles and registers, which refer to context-specific variations in language use. Key terms discussed include idiolect, isogloss, diglossia, and the prestige often afforded to standard dialects over non-standard varieties.Introduction to Soicolinguistics



Introduction to SoicolinguisticsFarjana Ela
Ã˝
The document discusses sociolinguistics and language variation. It defines sociolinguistics as the systematic study of language in society, focusing on how individuals and groups use language in social contexts. There are three main perspectives in sociolinguistics: geographic, examining regional dialects; anthropological, studying the relationship between language, culture and thought; and sociological, analyzing the link between social relations and language varieties. Speech communities are groups that share the same or similar language varieties. Varieties include dialects, sociolects, and idiolects, which differ by region, social class, gender, age, and ethnicity at the lexical, phonological and syntactic levels. Pidgins are simplified mixed languages for basic communication betweenMore Related Content
What's hot (20)
Language and ethnic group



Language and ethnic groupLampung University
Ã˝
1) Language is closely intertwined with ethnic identity and group membership. Members of ethnic groups often learn the linguistic varieties associated with that group.
2) In the United States, differences exist between the English spoken by white and black Americans, and ethnicity can often be identified based on language alone. However, these linguistic differences result from learned behavior within communities rather than innate qualities.
3) The situation in former Yugoslavia demonstrates how ethnic identities and linguistic varieties can change over time and in response to political situations. Serbo-Croatian was once considered a single language but is now considered separate Serbian and Croatian languages.Language Loss



Language Lossdrfaithpolk
Ã˝
This document discusses language loss in bilingual children and strategies to promote balanced bilingualism. It notes that language loss occurs when a minority language is no longer used proficiently due to increased exposure to a dominant language like English. This can lead to incomplete learning or forgetting of the home language over time. The document recommends that teachers recognize this as a temporary developmental phase and that families provide opportunities to use and maintain the home language through exposure to speakers and social contexts that support both languages.Language Planning



Language PlanningAyesha Mir
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of language planning. It defines language planning as efforts to influence and modify a language's structure and function. It discusses key aspects of language planning including its goals, processes, types (status and corpus planning), ideologies, and issues. The summary focuses on language planning's aim to alter a language's role and how it is implemented through selection, codification, elaboration, and acceptance of a standardized variety.Linguistics imperialism



Linguistics imperialismSajid Ali Lashari
Ã˝
The causes, effects, start, and the way its going, what are the roles, what are the agencies through which linguistics imperialism is spreading. Sociolinguistic terms



Sociolinguistic termsFatmawati Khodijah
Ã˝
This document defines and explains various sociolinguistic terms related to language, dialects, and language varieties. It provides definitions for 50 terms, including language, dialect, patois, standardization, standard English, vitality, historicity, autonomy, reduction, mixture, de facto norm, regional dialect, received pronunciation, dialect geography, dialect boundary, isogloss, accent, style, register, competence, performance, non-standard variety, variety, sociolect, creole, lingua franca, pidgin, norms, class, prestige, caste, ethnicity, vernacular, idiolect, social dialect, social network, homogeneous, bilingual, and multilingual. The document was created by students andAccommodation Theory



Accommodation TheoryIrsalina Viramdani
Ã˝
Communication Accommodation Theory (CAT) proposes that people change their speech patterns, vocal characteristics, and gestures when communicating with others in order to be better understood. Developed by Howard Giles in 1973, CAT suggests that speakers may converge their speech towards another person's patterns or diverge from them. Convergence can occur downward from higher to lower social classes, upward from lower to higher classes, or mutually as both speakers adjust towards each other. The goal of accommodation is effective communication across differences in language, age, or other barriers.language and social variation



language and social variationhojjat namdaran
Ã˝
This document discusses language variation based on social factors. It covers the topics of sociolinguistics, social dialects, education and occupation, social markers, and speech style/style-shifting. Sociolinguistics examines the relationship between language and society, investigating how languages function in communication and the structure of language. Social dialects, or sociolects, are language varieties that differ based on a speaker's social status or group, such as social class, religion, or ethnicity. Features like pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar are used to analyze social dialects. Education level and occupation also influence one's speech patterns and style.Language and Gender by Muhammad Ahmad



Language and Gender by Muhammad AhmadAhmadSadequain
Ã˝
Complete Description of the Relationships between Language and Gender - how men and women speak differently? Personality differences in genders? gender discrimination? Authentic sources....Style Register and Dialect



Style Register and DialectSidra Shahid
Ã˝
Language varieties refer to different forms of a language influenced by social factors such as situation, occupation, age, geography, education, gender, social status, and ethnicity. There are several types of language varieties including dialects, registers, pidgins, and creoles. A dialect is a variety of a language used in a specific region or social class. Registers are varieties used in different situations based on formality. A pidgin is a simplified mixed language with reduced vocabulary and grammar used for communication between speakers of different languages, while a creole develops when a pidgin becomes the primary language of a group and acquires more complex grammar.Language and social variation



Language and social variationluzfernndez9
Ã˝
This document discusses language variation and the relationship between language and society. It introduces key concepts such as speech communities, sociolinguistics, social dialects, linguistic variables, and registers. Social factors like class, education, occupation, and context can influence the way people speak. The document also discusses concepts like convergence, divergence, prestige, jargon, slang, vernacular languages, and provides examples of linguistic features in African American Vernacular English. Applied Linguistics & Language Teaching



Applied Linguistics & Language TeachingFarhad Mohammad
Ã˝
This document discusses the relationship between applied linguistics and language teaching. It defines applied linguistics as the theoretical and empirical investigation of real-world language problems. It explores how applied linguistics can positively impact language teachers by informing areas like teaching methods, materials development, and testing. The document also examines how linguistics, applied linguistics, and language teaching are interrelated and how descriptions of language can improve teaching.Language,dialect and variation, sociolinguistic



Language,dialect and variation, sociolinguisticPurnama Ratna Sari Dewi
Ã˝
This document discusses sociolinguistic concepts related to language variation, including:
- Varieties include languages, dialects, accents, registers, and styles of a language. Variation occurs at the lexical level through slang and levels of formality.
- Dialects are regional or social varieties of a language characterized by their own phonological, syntactic, and lexical properties. They can also be associated with ethnic groups or socioeconomic classes.
- Registers or styles are varieties of language used in particular social settings defined by levels of formality or social events like baby talk.
- An idiolect is the unique language use of an individual person influenced by various dialects, registers, and languagesSpeech Communities



Speech CommunitiesMary Joy Jagonia
Ã˝
The document discusses key concepts relating to speech communities. It defines a speech community as a group of people who interact through shared use of language and participation in common norms. While some definitions require all members to use the same language or dialect, most acknowledge that communities can be multilingual. Characteristics like shared social networks, values and beliefs help define communities more than sole reliance on linguistic criteria. Urban areas in particular may contain overlapping and intersecting speech communities with blurred boundaries.Full summary an_introduction_to_sociolinguistics



Full summary an_introduction_to_sociolinguisticsLutfan Adli
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of Chapter One from Janet Holmes' book "An Introduction to Sociolinguistics". It discusses key topics that sociolinguists study such as how social factors influence language varieties and how sociolinguists define terms like variety. Sociolinguists are interested in explaining why people speak differently in different social contexts and how social factors like social distance, status, age and gender impact language varieties and convey social meanings.Language and age



Language and ageGraciela Bortoluzzi
Ã˝
The document discusses how language variation allows people to construct identities based on age and social dimensions. It examines how language is used differently across three life stages: young children, teenagers, and the elderly. Specific examples are given of "baby talk" used with young children, texting language in conversations between teenagers, and the phenomenon of "elderspeak" which is commonly used but can be harmful by implying incompetence in older adults.What is sociolinguistics,



What is sociolinguistics,Purnama Ratna Sari Dewi
Ã˝
Sociolinguistics is the study of how social factors such as ethnicity, gender, age, and socioeconomic class influence language. It examines how language differs between social groups and how these differences can categorize individuals. Sociolinguists study how grammar, vocabulary, and other language aspects vary depending on social context, in contrast to dialectology which focuses on language's effect on society. Key concepts in sociolinguistics include speech communities, prestige varieties, social networks, and differences in language according to class, age, gender, geography, and politeness.Dialectology



DialectologyAsmaSaifUllah
Ã˝
This document discusses the topic of dialectology, which is the scientific study of linguistic dialects. It defines dialect as a specific form of a language that is peculiar to a certain region or social group. Dialectology studies variations in language based on geographic distribution and associated features. To distinguish between dialects of the same language, speakers must be able to understand each other. The document outlines levels of dialect analysis including geography, ethnicity, and social class. It also discusses the need to study dialects from both linguistic and social perspectives.Gander and age



Gander and ageMaulidifi
Ã˝
This document discusses gender and age related differences in speech. It notes that while women and men share a language, there are often small differences in features like pronunciation or morphology. Research has shown women tend to use more standard forms while men use more vernacular forms. Social class also influences speech, with women across classes using more standard forms than men. The document explores various explanations for why women's speech patterns differ, and discusses how age can influence language use, with vernacular forms highest in youth and old age when social pressures are lower.Sapir and Whorf



Sapir and WhorfIka Hentihu
Ã˝
This document discusses the Sapir-Whorf hypothesis, which was first proposed by Edward Sapir and later expanded upon by Benjamin Lee Whorf. It presents the key figures and their backgrounds, including Sapir's work in linguistics and Whorf's study of the Hopi language. The hypothesis is introduced as having both a strong version, that language determines thought, and a weak version, that language influences thought. While heavily criticized, most linguists now accept the weak version to some degree. Examples are given of how language can reflect cultural differences in areas like kinship terminology. The conclusion is that while the extreme versions have been disproven, most agree there is some influence of language on thought.Teaching of Vocabulary



Teaching of VocabularyDr. Bhavin Chauhan
Ã˝
Words are very essential for effective communication. The teaching Vocabulary helps the students to develop the word vocab as well as fluency.Similar to Social Dialect (20)
Varities in sociolinguistics



Varities in sociolinguisticsShehnaz Mehboob
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of linguistic variation and key concepts related to dialects and registers. It discusses the differences between language and dialect, and notes that all speakers use some dialect. Dialects can be divided into regional dialects, which vary based on geography, and social dialects, which are influenced by factors like occupation, age, education, and gender. The document also examines concepts like standard vs. non-standard dialects, speech communities, linguistic styles and registers, which refer to context-specific variations in language use. Key terms discussed include idiolect, isogloss, diglossia, and the prestige often afforded to standard dialects over non-standard varieties.Introduction to Soicolinguistics



Introduction to SoicolinguisticsFarjana Ela
Ã˝
The document discusses sociolinguistics and language variation. It defines sociolinguistics as the systematic study of language in society, focusing on how individuals and groups use language in social contexts. There are three main perspectives in sociolinguistics: geographic, examining regional dialects; anthropological, studying the relationship between language, culture and thought; and sociological, analyzing the link between social relations and language varieties. Speech communities are groups that share the same or similar language varieties. Varieties include dialects, sociolects, and idiolects, which differ by region, social class, gender, age, and ethnicity at the lexical, phonological and syntactic levels. Pidgins are simplified mixed languages for basic communication between Language, Dialect and Accent.pptx



Language, Dialect and Accent.pptxIvaMutmainah
Ã˝
This document discusses language variation and dialects. It defines language varieties as forms of language that change based on social factors like region, social class, individual, and situation. A dialect is a language variety spoken by a speech community that is distinguished by systematic phonological, lexical and grammatical features from other varieties of the same language. An idiolect refers to the speech variety of an individual speaker. Dialects can be regional, based on geographical area, temporal based on historical stage, or social/sociolects based on social class. Factors like social situation, occupation, age, geography, education, gender, social status, and ethnicity can contribute to language variation. All languages have dialects and everyone speaks at least oneLanguage, dialect, and varieties



Language, dialect, and varietiesSari Kusumaningrum
Ã˝
This document discusses language variation and varieties. It defines key terms such as language, dialect, and varieties. Some main points:
- No two speakers speak exactly the same way and an individual's speech varies across situations.
- Language varieties refer to different forms of language influenced by social factors like region, social class, individual, and situation.
- A dialect is a language variety spoken by a community that has distinguishing phonological, lexical, and grammatical features.
- Varieties refer to sets of linguistic items associated with external social factors like a geographical area and social group.
- Dialects are influenced by various social factors and everyone speaks at least one dialect. Standard dialects have more prestige than others dueLanguage, dialect, and varieties



Language, dialect, and varietiesSari Kusumaningrum
Ã˝
This document discusses language variation and the different varieties of language. It defines key terms like dialect, idiolect, and varieties. A dialect is a language variety spoken by a speech community that is distinguished by systematic features. An idiolect refers to the speech variety of an individual speaker. Varieties refer to forms of language associated with social factors like region, social class, situation, and individual. Dialects and varieties differ based on factors like geography, occupation, age, education, gender, and ethnicity. While some dialects have more prestige than others due to historical and social factors, all languages consist of dialects and everyone speaks at least one dialect.UQROO Sociolinguistics terms1



UQROO Sociolinguistics terms1maggmiss
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of key concepts in sociolinguistics. It defines sociolinguistics as the study of the relationship between language and social function. Some key topics covered include dialects, registers, speech communities, pidgins, creoles, bilingualism, lingua francas, and quantitative and qualitative research approaches. Examples are given to illustrate concepts like dialects, jargon, mutual intelligibility, and types of bilingualism.Sociolinguistics 1.pdf



Sociolinguistics 1.pdffatimazahraSoulaiman2
Ã˝
This syllabus outlines the topics to be covered in a sociolinguistics course, including introducing the field of sociolinguistics, varieties of language, linguistic phenomena influenced by social factors, and language contact. The course will examine the relationship between language and society, differences between social dialects, and concepts such as diglossia, code-switching, and language change through borrowing and creoles.sociolinguistics



sociolinguisticsMubarak Khan
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of sociolinguistics and psycholinguistics. It defines language and discusses how it is used to communicate information and establish social relationships. It also examines how language reveals aspects of a speaker's identity. The document then discusses sociolinguistics as the study of language in relation to society. It explores the relationship between language and society, including how language reflects social and physical environments. The document also defines and compares standard languages, dialects, registers, pidgins and creoles. It examines how gender and age can influence language use.Speech_communities_,social_&rejional_variation



Speech_communities_,social_&rejional_variationzahraa Aamir Kamil
Ã˝
This document discusses speech communities and language variation. It defines a speech community as a group that shares language practices and norms. Speech communities can be defined geographically, socioeconomically, ethnically/culturally, by age, or gender. The document also discusses that all languages exhibit variation in aspects like pronunciation, grammar and vocabulary. This variation can be regional, based on social factors like class, education, or the formality of the situation. Studies of language variation provide insights into how languages change over time.Phonetics: Varieties of English Language



Phonetics: Varieties of English LanguageYamileth Urriola
Ã˝
Language can be defined as a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used by a social group to communicate and express ideas, identities, and emotions. There are many variations within and across languages, including dialects, registers, sociolects, and ethnolects that vary by region, social group, ethnicity, gender, and even individual. Some key types of linguistic variations include dialects, which can differ in vocabulary, grammar and pronunciation depending on geography; sociolects, which vary based on social factors like education and class; and idiolects, an individual's unique way of speaking. Languages exist on spectrums and can be classified based on various social and historical contexts.Language, dialect and accent



Language, dialect and accentMuslimah Alg
Ã˝
This document discusses the nature of language, dialect, and accent. It defines language and dialect, noting that dialects are varieties of a language that are mutually intelligible. Dialects differ based on region or social factors rather than linguistic ones. Accent refers to differences in pronunciation between varieties. Dialect continuum is used to show how dialects gradually change between geographic areas. Linguistic variables are linguistic items that have variant forms based on non-linguistic factors like age, status, or situation.English language teaching



English language teachingPrakruti Bhatt
Ã˝
Dialects refer to regional variations in vocabulary and grammar within a language, whereas accents refer to differences in pronunciation influenced by an individual's mother tongue. A dialect is influenced more by historical factors and is specific to a region, while an accent is specific to an individual. In language teaching, a learner's dialect can pose barriers that teachers aim to help students overcome to acquire the target language, while accents develop later once basic communication is established.6. Aftermath of language variation.pptx



6. Aftermath of language variation.pptxMemonMemon4
Ã˝
The document discusses different types of language varieties that emerge from natural variation in language, including dialects, registers, pidgins, creoles, jargon, and more. It provides definitions and examples of each. Key varieties discussed are:
- Dialects emerge from regional, social, or ethnic differences in vocabulary, grammar and pronunciation. Examples include Southern American English.
- Registers vary based on social context or formality, like casual conversation versus formal writing.
- Pidgins develop for communication between speakers of different languages but become more standardized over time.
- Creoles emerge when a pidgin becomes a community's native language over generations with its own grammar.
- JargonSOCIOLINGUISTICS_15 (1).pptx



SOCIOLINGUISTICS_15 (1).pptxislamelzainy1
Ã˝
Sociolinguistics is the study of language in social contexts. It analyzes how language varies based on social factors like geographical location, age, gender, occupation, and situation. Language varies across speech communities and registers. It changes over time through processes like dialect formation. Sociolinguistic analysis uses methods like ethnography, variationist analysis, and discourse analysis to study language variation and how it relates to power dynamics in society.Standard language.



Standard language.zahraa Aamir Kamil
Ã˝
This document provides an outline and overview of sociolinguistics concepts related to standard language and dialects. It discusses how a standard language is selected and codified through processes like selection, codification, elaboration of functions, and acceptance. It notes that a standard language gains prestige and becomes a symbol of independence. The document also explores the differences between dialects and languages, noting they are ambiguous terms without universal criteria. Dialects can be regional, relating to a geographical area, or social, relating to factors like class, religion, occupation.Language in social context revised 2012



Language in social context revised 2012Kristel Cacha
Ã˝
This document discusses speech communities and speech varieties. A speech community is defined as a group that shares a language or language variety and whose members interact frequently. There are four main types of speech varieties: standard languages, social dialects, regional varieties, and registers. Standard languages are promoted varieties, while social dialects are defined by social attributes. Regional varieties are defined geographically and registers are defined by social context or situation. The document also discusses social differentiation of language and how socioeconomic status can correlate with differences in language use.Basic notions; language variation and levels



Basic notions; language variation and levelsAmna Malik
Ã˝
These slides are very clear to learn about why there are different varieties of English language, and features that make English plural 'Englishes'Language Variation



Language VariationDr. Cupid Lucid
Ã˝
This document discusses various types of language variation including dialects, sociolects, idiolects, registers, pidgins, and creoles. It notes that dialects are varieties of a language used by a particular group that share non-linguistic characteristics. Pidgins develop for communication between groups that don't share a common language, while creoles emerge when a pidgin becomes a community's native language.Language Variation



Language VariationDr. Cupid Lucid
Ã˝
This document discusses various types of language variation including dialects, sociolects, idiolects, registers, pidgins, and creoles. It notes that dialects are varieties of a language used by a specific group that share non-linguistic characteristics. Pidgins develop for communication between groups that don't share a common language, while creoles emerge when a pidgin becomes a community's native language.Sociolinguistics_April 15th, 2019



Sociolinguistics_April 15th, 2019ilhamseptian02
Ã˝
The results of our group discussion on sociolinguistics. We take this material from several book references. We uploaded this presentation with the aim that we can learn together especially sociolinguistics. We hope that readers can understand the contents of the material. There are many mistakes please forgive us. Thank you.Recently uploaded (20)
Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ã˝
Finals of Rass MELAI : a Music, Entertainment, Literature, Arts and Internet Culture Quiz organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
Ã˝
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
-Autonomy, Teams and Tension: Projects under stress
-Tim Lyons
-The neurological levels of
team-working: Harmony and tensions
With a background in projects spanning more than 40 years, Tim Lyons specialised in the delivery of large, complex, multi-disciplinary programmes for clients including Crossrail, Network Rail, ExxonMobil, Siemens and in patent development. His first career was in broadcasting, where he designed and built commercial radio station studios in Manchester, Cardiff and Bristol, also working as a presenter and programme producer. Tim now writes and presents extensively on matters relating to the human and neurological aspects of projects, including communication, ethics and coaching. He holds a Master’s degree in NLP, is an NLP Master Practitioner and International Coach. He is the Deputy Lead for APM’s People Interest Network.
Session | The Neurological Levels of Team-working: Harmony and Tensions
Understanding how teams really work at conscious and unconscious levels is critical to a harmonious workplace. This session uncovers what those levels are, how to use them to detect and avoid tensions and how to smooth the management of change by checking you have considered all of them.How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 Employee



How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 EmployeeCeline George
Ã˝
In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to configure flexible working schedule in Odoo 18 Employee module. In Odoo 18, the Employee module offers powerful tools to configure and manage flexible working schedules tailored to your organization's needs.APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...Association for Project Management
Ã˝
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
- Autonomy, Teams and Tension
- Oliver Randall & David Bovis
- Own Your Autonomy
Oliver Randall
Consultant, Tribe365
Oliver is a career project professional since 2011 and started volunteering with APM in 2016 and has since chaired the People Interest Network and the North East Regional Network. Oliver has been consulting in culture, leadership and behaviours since 2019 and co-developed HPTM® an off the shelf high performance framework for teams and organisations and is currently working with SAS (Stellenbosch Academy for Sport) developing the culture, leadership and behaviours framework for future elite sportspeople whilst also holding down work as a project manager in the NHS at North Tees and Hartlepool Foundation Trust.
David Bovis
Consultant, Duxinaroe
A Leadership and Culture Change expert, David is the originator of BTFA‚Ñ¢ and The Dux Model.
With a Masters in Applied Neuroscience from the Institute of Organisational Neuroscience, he is widely regarded as the ‘Go-To’ expert in the field, recognised as an inspiring keynote speaker and change strategist.
He has an industrial engineering background, majoring in TPS / Lean. David worked his way up from his apprenticeship to earn his seat at the C-suite table. His career spans several industries, including Automotive, Aerospace, Defence, Space, Heavy Industries and Elec-Mech / polymer contract manufacture.
Published in London’s Evening Standard quarterly business supplement, James Caan’s ‘Your business’ Magazine, ‘Quality World’, the Lean Management Journal and Cambridge Universities ‘PMA’, he works as comfortably with leaders from FTSE and Fortune 100 companies as he does owner-managers in SME’s. He is passionate about helping leaders understand the neurological root cause of a high-performance culture and sustainable change, in business.
Session | Own Your Autonomy – The Importance of Autonomy in Project Management
#OwnYourAutonomy is aiming to be a global APM initiative to position everyone to take a more conscious role in their decision making process leading to increased outcomes for everyone and contribute to “a world in which all projects succeed”.
We want everyone to join the journey.
#OwnYourAutonomy is the culmination of 3 years of collaborative exploration within the Leadership Focus Group which is part of the APM People Interest Network. The work has been pulled together using the 5 HPTM® Systems and the BTFA neuroscience leadership programme.
https://www.linkedin.com/showcase/apm-people-network/about/Research & Research Methods: Basic Concepts and Types.pptx



Research & Research Methods: Basic Concepts and Types.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
Ã˝
This ppt has been made for the students pursuing PG in social science and humanities like M.Ed., M.A. (Education), Ph.D. Scholars. It will be also beneficial for the teachers and other faculty members interested in research and teaching research concepts.FESTIVAL: SINULOG & THINGYAN-LESSON 4.pptx



FESTIVAL: SINULOG & THINGYAN-LESSON 4.pptxDanmarieMuli1
Ã˝
Sinulog Festival of Cebu City, and Thingyan Festival of Myanmar.EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdf



EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdfLiz Walsh-Trevino
Ã˝
EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdfSOCIAL CHANGE(a change in the institutional and normative structure of societ...



SOCIAL CHANGE(a change in the institutional and normative structure of societ...DrNidhiAgarwal
Ã˝
This PPT is showing the effect of social changes in human life and it is very understandable to the students with easy language.in this contents are Itroduction, definition,Factors affecting social changes ,Main technological factors, Social change and stress , what is eustress and how social changes give impact of the human's life.QuickBooks Desktop to QuickBooks Online How to Make the Move



QuickBooks Desktop to QuickBooks Online How to Make the MoveTechSoup
Ã˝
If you use QuickBooks Desktop and are stressing about moving to QuickBooks Online, in this webinar, get your questions answered and learn tips and tricks to make the process easier for you.
Key Questions:
* When is the best time to make the shift to QuickBooks Online?
* Will my current version of QuickBooks Desktop stop working?
* I have a really old version of QuickBooks. What should I do?
* I run my payroll in QuickBooks Desktop now. How is that affected?
*Does it bring over all my historical data? Are there things that don't come over?
* What are the main differences between QuickBooks Desktop and QuickBooks Online?
* And moreEssentials of a Good PMO, presented by Aalok Sonawala



Essentials of a Good PMO, presented by Aalok SonawalaAssociation for Project Management
Ã˝
APM event hosted by the South Wales and West of England Network (SWWE Network)
Speaker: Aalok Sonawala
The SWWE Regional Network were very pleased to welcome Aalok Sonawala, Head of PMO, National Programmes, Rider Levett Bucknall on 26 February, to BAWA for our first face to face event of 2025. Aalok is a member of APM’s Thames Valley Regional Network and also speaks to members of APM’s PMO Interest Network, which aims to facilitate collaboration and learning, offer unbiased advice and guidance.
Tonight, Aalok planned to discuss the importance of a PMO within project-based organisations, the different types of PMO and their key elements, PMO governance and centres of excellence.
PMO’s within an organisation can be centralised, hub and spoke with a central PMO with satellite PMOs globally, or embedded within projects. The appropriate structure will be determined by the specific business needs of the organisation. The PMO sits above PM delivery and the supply chain delivery teams.
For further information about the event please click here.Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding || Boby Basnet



Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding || Boby BasnetBoby Basnet
Ã˝
Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding Full Note
|| Assistant Professor Boby Basnet ||IAAS || AFU || PU || FUMate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptx



Mate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptxLiny Jenifer
Ã˝
A powerpoint presentation on the short story Mate by Kate Greenville. This presentation provides information on Kate Greenville, a character list, plot summary and critical analysis of the short story.Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo ∫›∫›fl£s



Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo ∫›∫›fl£sCeline George
Ã˝
In this slide we’ll discuss on the useful environment methods in Odoo 18. In Odoo 18, environment methods play a crucial role in simplifying model interactions and enhancing data processing within the ORM framework.Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ã˝
Prelims of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. Eng7-Q4-Lesson 1 Part 1 Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and T...



Eng7-Q4-Lesson 1 Part 1 Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and T...sandynavergas1
Ã˝
Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and Technical TermsRass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ã˝
APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
Ã˝
APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...Association for Project Management
Ã˝
Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ã˝
Social Dialect
- 1. LANGUAGE, CULTURE AND SOCIETY TSL1044 TOPIC : SOCIAL DIALECT BY : ATHIRA NABILA BINTI JASMAN1
- 2. • Commonly uses language variety • cover term for overlapping subcategories of language Linguistics 2
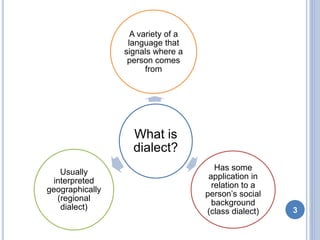
- 3. What is dialect? A variety of a language that signals where a person comes from Has some application in relation to a person’s social background (class dialect) Usually interpreted geographically (regional dialect) 3
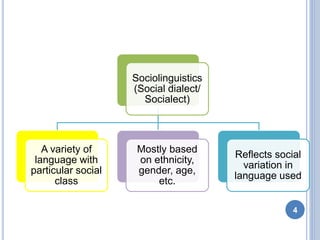
- 4. Sociolinguistics (Social dialect/ Socialect) A variety of language with particular social class Mostly based on ethnicity, gender, age, etc. Reflects social variation in language used 4
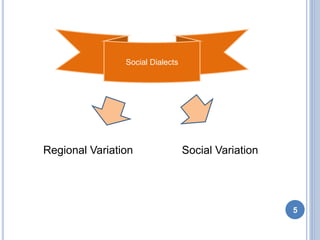
- 5. Social Dialects Social VariationRegional Variation 5
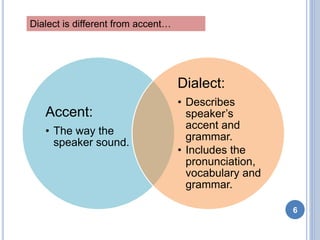
- 6. Dialect is different from accent… Accent: • The way the speaker sound. Dialect: • Describes speaker’s accent and grammar. • Includes the pronunciation, vocabulary and grammar. 6
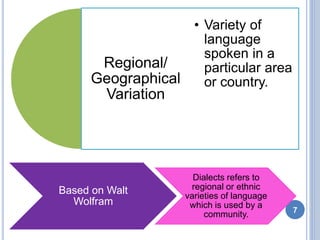
- 7. Regional/ Geographical Variation • Variety of language spoken in a particular area or country. Based on Walt Wolfram Dialects refers to regional or ethnic varieties of language which is used by a community. 7
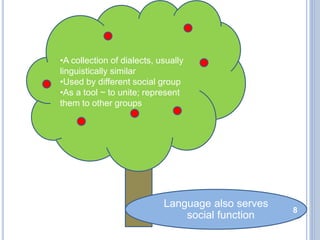
- 8. •A collection of dialects, usually linguistically similar •Used by different social group •As a tool ~ to unite; represent them to other groups Language also serves social function 8
- 9. • Connected to social classes, educational, or both. • Called as Sociolinguistics • More concerned with social variation • Considered from different perspective between the speakers in; • Age • Social class • Race • Ethnicity • Gender Social Variation 9
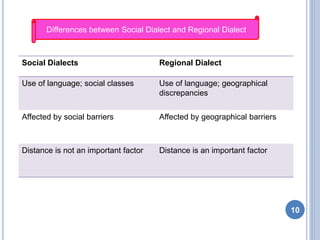
- 10. Social Dialects Regional Dialect Use of language; social classes Use of language; geographical discrepancies Affected by social barriers Affected by geographical barriers Distance is not an important factor Distance is an important factor Differences between Social Dialect and Regional Dialect 10
- 11. Thank You 11





