中国古代房内考(高罗佩)图文版
0 likes4,791 views
七喜下载站提供多种精品软件下载服务,用户可以访问 www.7xdown.com 获取所需软件。该网站的信息重复出现,强调了其在软件下载领域的显著存在。
1 of 623
Downloaded 58 times











































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































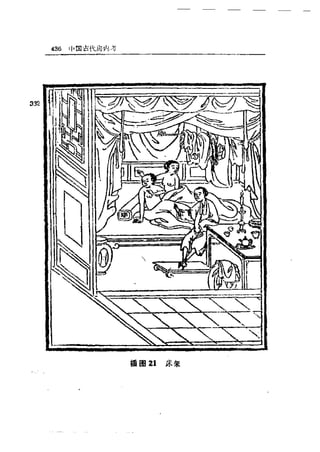














































































































Ad
Recommended
HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS 12032019 TUESDAY pptx
HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS 12032019 TUESDAY pptxPulkitMittal54
?
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) causes contagious infections that establish lifelong latent infections. HSV-1 typically causes oral infections while HSV-2 typically causes genital infections. Both viruses enter the body through mucous membranes or skin and travel to sensory neurons where they remain latent, occasionally reactivating and traveling back to the original site of infection to cause lesions. Transmission occurs through direct contact with infected secretions or lesions. While there is no vaccine, antiviral treatment can reduce symptoms and transmission can be prevented through safe sexual practices and avoiding contact with active lesions.Epidemiology of leprosy
Epidemiology of leprosyNamita Batra
?
This document provides information on Hansen's disease (leprosy), including:
- It is caused by Mycobacterium leprae and affects peripheral nerves, manifesting as lepromatous or tuberculoid forms.
- Diagnosis involves clinical examination of skin and nerves as well as bacteriological examination of skin and nasal smears.
- Treatment is multidrug therapy administered over 6-12 months depending on classification as paucibacillary or multibacillary.
- Control efforts include early detection, treatment, surveillance, immunoprophylaxis, health education and rehabilitation to prevent disabilities.CNS infections
CNS infectionsTarika Sharma, Lecturer, CON, ILBS, New Delhi
?
Albendazole or praziquantel
b) Inflammatory phase
Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
c) Seizures
Antiepileptic drugs
Surgical
For cysts causing mass effect or hydrocephalus
Prevention
Improved sanitation, pork inspection, health educationOsteomyelitis
OsteomyelitisPratikDhabalia
?
1) Osteomyelitis is an inflammation of bone caused by an infecting organism that may remain localized or spread through the bone.
2) Staphylococcus aureus is the most common infecting organism and can remain dormant in bone for years.
3) Chronic osteomyelitis is characterized by infected dead bone surrounded by avascular tissue, making systemic antibiotics ineffective. Surgical debridement is usually required.Leprosy
Leprosypavithra vinayak
?
This document summarizes leprosy (Hansen's disease), caused by Mycobacterium leprae. It has an incubation period of 2-20 years and primarily affects the nerves, skin, eyes, and respiratory tract. Transmission occurs through direct contact with untreated patients or infected soil. Leprosy is classified into tuberculoid, lepromatous, borderline, and indeterminate forms based on symptoms and immune response. Tuberculoid leprosy causes localized skin lesions and nerve damage, while lepromatous leprosy results in widespread skin nodules and organ involvement. Diagnosis involves skin smears and biopsies examined microscopically. Treatment consists of multidCorona virus
Corona virus Searchable Design
?
Coronaviruses are a large family of viruses that can cause illness in humans and animals. COVID-19 is a new strain caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus that was first identified in Wuhan, China in late 2019 and has since spread globally. It causes respiratory symptoms ranging from mild to severe and can lead to pneumonia, multi-organ failure, and death in some cases. Prevention focuses on hand washing, social distancing, and self-isolation for those exhibiting symptoms or testing positive. There is no vaccine and treatment is focused on relief of symptoms.Chikungunya
ChikungunyaKULDEEP VYAS
?
(1) Chikungunya is a viral illness transmitted through mosquito bites that causes fever and severe joint pain.
(2) It was first documented in an outbreak in Tanzania and has since spread throughout Africa and parts of Asia.
(3) There is no vaccine or specific treatment, so prevention through mosquito control and protection from bites is the primary strategy to control the disease.Septic arthritis
Septic arthritisNur Izzatul Najwa
?
Septic arthritis is caused by pyogenic organisms invading the joint space. Staphylococcus aureus is the most common causative organism. Risk factors include poor hygiene, diabetes, immunosuppression, and intravenous drug use. Symptoms include acute painful swelling of one or more joints. Diagnosis involves joint aspiration and examination of fluid. Treatment requires antibiotics, drainage of purulent fluid, and splinting of the affected joint. Complications can include joint damage, deformity, and ankylosis if left untreated.Meningitis
MeningitisDarya Daoud
?
Meningitis is an inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or certain drugs. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and neck stiffness. Diagnosis involves examining cerebrospinal fluid obtained via lumbar puncture. Treatment involves immediate antibiotics, steroids, and other drugs depending on the cause. Complications can include brain damage, hearing loss, and death if not treated promptly.Arterial arterial occlusion
Arterial arterial occlusionRaafi Ul Zargar
?
The document discusses chronic arterial occlusion, including aorto-iliac and femoro-popliteal occlusions, their symptoms, clinical features, and various treatment options such as medical therapy, surgical interventions like bypass grafting, and endarterectomy. It emphasizes the importance of patient-specific factors in determining treatment approaches and outlines the consequences of acute arterial occlusion, including symptoms and emergency management strategies. The text also references standard surgical textbooks for further reading.Leprosy (Hansen's Disease)
Leprosy (Hansen's Disease) KULDEEP VYAS
?
Leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease, is a chronic infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium leprae. It primarily affects the skin and peripheral nerves. Leprosy has been recognized throughout history in many ancient civilizations. It is transmitted via droplets from the nose and mouth during close contact with untreated cases. While not highly infectious, untreated leprosy can cause permanent damage to skin, nerves, limbs, and eyes. Diagnosis is based on clinical signs and symptoms, and confirmation is through skin smears or biopsy. Treatment involves multidrug therapy with dapsone, rifampicin, and clofazimine.Projectile motion
Projectile motionLiwayway Memije-Cruz
?
The document discusses projectile motion, defining it as the motion of objects influenced only by gravity. It provides examples, various trajectories, and formulas to calculate the maximum height, total flight time, horizontal range, and final velocity of a projectile launched at specific angles. Additionally, it includes problems to apply the concepts of projectile motion and their corresponding calculations.CNS Infections
CNS InfectionsSuprakash Das
?
The document discusses central nervous system (CNS) infections, including viral and bacterial meningitis and viral encephalitis. It describes the anatomy of the CNS and how it is protected. It then explains how the CNS can be infected by various agents like viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and helminths. It provides details on the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of acute bacterial meningitis, acute viral meningitis, and viral encephalitis.Fracture - Types, complications and management
Fracture - Types, complications and managementSachin Chauhan
?
The document discusses fractures, including defining fractures and related terms. It describes the typical causes and symptoms of fractures and classifies fractures according to type, including transverse, oblique, spiral, and stress fractures. The management of fractures is outlined, focusing on initial first aid, transport, assessment, reduction, immobilization, and rehabilitation. Factors that influence fracture healing and potential complications are also reviewed. The terms dislocation and subluxation are defined as the displacement of bones in a joint.Coronavirus disease (COVID-19)
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19)Mohammed Musa
?
The document provides a comprehensive overview of COVID-19, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, including its transmission, clinical features, diagnosis, management, and prevention strategies. It highlights the variation in the severity of cases and the lack of specific antiviral treatments currently available, emphasizing the importance of support and infection control measures. Additionally, it details the risk factors for severe outcomes and recommends preventive practices to limit spread.Chicken pox
Chicken poxMEEQAT HOSPITAL
?
Varicella, commonly known as chickenpox, is a highly contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It presents with an itchy rash that goes through several phases from raised bumps to fluid-filled blisters to crusts and scabs. While usually mild and self-limiting, it can develop into more serious complications in babies, pregnant women, and those with weak immune systems. The virus is transmitted through direct contact or respiratory droplets. Vaccination with two doses is recommended to prevent infection. Complications may include bacterial skin infections, pneumonia, or inflammation of the brain or bloodstream. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and allowing the immune system to suppress the virus.Orthopaedic history taking ugpg
Orthopaedic history taking ugpgKishore Vemula
?
This document provides guidance on taking a thorough musculoskeletal history. It emphasizes that history taking is the most important part of making a diagnosis, as a clinician is 60% closer to a diagnosis with a thorough history compared to 40% from physical examination and investigations alone. It outlines the key components of a musculoskeletal history, including chief complaint, history of present illness, functional assessment, review of systems, past medical and surgical history, medications, social history, and specific questions for common conditions like pain, swelling, instability, and loss of function. Examination techniques like inspection, palpation, and active and passive range of motion testing are also summarized. The goal is to educate clinicians on how to take a comprehensive history for the major musculoskeletalLeprosy
LeprosyGajendrayadav35
?
Here are some possible responses to the questions:
1. The higher incidence and prevalence of leprosy in males compared to females could be due to various socio-cultural factors. Males may have greater exposure and mobility which increases their risk of contracting the disease. There could also be under-reporting of cases in females due to lack of access to healthcare and social stigma.
2. To reduce stigma and discrimination against leprosy affected persons and their families, sustained awareness programs targeting the general public as well as affected communities are needed. Educating people about the modes of transmission and that leprosy is curable can help reduce misconceptions. Involving affected persons in advocacy can also help normalize the condition and empower those慢性胃炎的中医特色疗法(郭海英)
慢性胃炎的中医特色疗法(郭海英)yct.Ken Chang
?
《慢性胃炎的中医特色疗法》由郭海英和汪悦编着,谢建群和郑林赟翻译,出版于2004年9月,涵盖259页内容。该书探讨了中医在慢性胃炎治疗中的特色疗法。诊治胃食管反流病经验(李乾构教授)
诊治胃食管反流病经验(李乾构教授)yct.Ken Chang
?
李乾构教授的诊治经验提供了对胃食管反流病(骋贰搁顿)的中医理解,认为其可用“胸痞”来命名,并分析了病机及治疗方法。该病的病因主要是由于肝气郁结与脾胃功能失调导致胃气上逆,伴随相应症状。治疗建议包括疏肝和胃、调理饮食和情绪,以促进病症恢复。养胃全书
养胃全书yct.Ken Chang
?
该文档提供了养胃的建议,包括易消化的早餐食物如粥类、鸡蛋和蔬菜,以及多种有益的食疗和按摩方法,还强调了改善生活习惯的重要性。推荐的养胃食物包括小米、南瓜等,而瑜伽姿势则有助于促进消化。最后,提供了清晨饮食的禁忌和养胃的小偏方,以帮助人们更好地保护胃部健康。脾胃学真詮
脾胃学真詮yct.Ken Chang
?
《脾胃学真诠》由刘炳凡着,详述脾胃学的理论基础、病理变化及相关医家研究成就,涵盖脾胃与其他脏腑的关系。书中探讨脾胃学的应用原则、机理与方法,并涉及急症治疗和常见疑难病的诊疗。此书为中医学脾胃学领域的重要参考文献。成功有约—高效会计手册
成功有约—高效会计手册yct.Ken Chang
?
《管理精英宣言》强调追求非凡生活和积极冒险的公司家精神,而《成功有约——高效会议手册》则探讨了会议的意义和功能,指出提高会议效率的重要性。文档分析了会议的多种类型和具体应用,旨在加强公司内部沟通和决策效果。整体内容围绕更高效的管理实践及团队合作展开。诞生(狈补迟颈惫颈迟别蝉)yct.Ken Chang
?
Le document énumère divers artistes et peintres importants de l'histoire de l'art, en mentionnant leurs dates et contributions. Il met l'accent sur des figures telles que Giovanni Francesco da Rimini, Botticelli et Fra Angelico. La liste reflète la richesse de la peinture à différentes époques et styles.性传播疾病础
性传播疾病础yct.Ken Chang
?
本文讨论了性传播疾病(厂罢顿)的不同病原体及相关疾病,包括淋病和梅毒的症状、传播途径、诊断和治疗方法。淋病由淋病奈瑟菌引起,是世界上发病率最高的性传播疾病,而梅毒由梅毒螺旋体引起,分为不同的阶段,具高度的传染性。针对这些疾病的治疗方案包括使用青霉素、四环素及其他抗生素。More Related Content
What's hot (10)
Meningitis
MeningitisDarya Daoud
?
Meningitis is an inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or certain drugs. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and neck stiffness. Diagnosis involves examining cerebrospinal fluid obtained via lumbar puncture. Treatment involves immediate antibiotics, steroids, and other drugs depending on the cause. Complications can include brain damage, hearing loss, and death if not treated promptly.Arterial arterial occlusion
Arterial arterial occlusionRaafi Ul Zargar
?
The document discusses chronic arterial occlusion, including aorto-iliac and femoro-popliteal occlusions, their symptoms, clinical features, and various treatment options such as medical therapy, surgical interventions like bypass grafting, and endarterectomy. It emphasizes the importance of patient-specific factors in determining treatment approaches and outlines the consequences of acute arterial occlusion, including symptoms and emergency management strategies. The text also references standard surgical textbooks for further reading.Leprosy (Hansen's Disease)
Leprosy (Hansen's Disease) KULDEEP VYAS
?
Leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease, is a chronic infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium leprae. It primarily affects the skin and peripheral nerves. Leprosy has been recognized throughout history in many ancient civilizations. It is transmitted via droplets from the nose and mouth during close contact with untreated cases. While not highly infectious, untreated leprosy can cause permanent damage to skin, nerves, limbs, and eyes. Diagnosis is based on clinical signs and symptoms, and confirmation is through skin smears or biopsy. Treatment involves multidrug therapy with dapsone, rifampicin, and clofazimine.Projectile motion
Projectile motionLiwayway Memije-Cruz
?
The document discusses projectile motion, defining it as the motion of objects influenced only by gravity. It provides examples, various trajectories, and formulas to calculate the maximum height, total flight time, horizontal range, and final velocity of a projectile launched at specific angles. Additionally, it includes problems to apply the concepts of projectile motion and their corresponding calculations.CNS Infections
CNS InfectionsSuprakash Das
?
The document discusses central nervous system (CNS) infections, including viral and bacterial meningitis and viral encephalitis. It describes the anatomy of the CNS and how it is protected. It then explains how the CNS can be infected by various agents like viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and helminths. It provides details on the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of acute bacterial meningitis, acute viral meningitis, and viral encephalitis.Fracture - Types, complications and management
Fracture - Types, complications and managementSachin Chauhan
?
The document discusses fractures, including defining fractures and related terms. It describes the typical causes and symptoms of fractures and classifies fractures according to type, including transverse, oblique, spiral, and stress fractures. The management of fractures is outlined, focusing on initial first aid, transport, assessment, reduction, immobilization, and rehabilitation. Factors that influence fracture healing and potential complications are also reviewed. The terms dislocation and subluxation are defined as the displacement of bones in a joint.Coronavirus disease (COVID-19)
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19)Mohammed Musa
?
The document provides a comprehensive overview of COVID-19, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, including its transmission, clinical features, diagnosis, management, and prevention strategies. It highlights the variation in the severity of cases and the lack of specific antiviral treatments currently available, emphasizing the importance of support and infection control measures. Additionally, it details the risk factors for severe outcomes and recommends preventive practices to limit spread.Chicken pox
Chicken poxMEEQAT HOSPITAL
?
Varicella, commonly known as chickenpox, is a highly contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It presents with an itchy rash that goes through several phases from raised bumps to fluid-filled blisters to crusts and scabs. While usually mild and self-limiting, it can develop into more serious complications in babies, pregnant women, and those with weak immune systems. The virus is transmitted through direct contact or respiratory droplets. Vaccination with two doses is recommended to prevent infection. Complications may include bacterial skin infections, pneumonia, or inflammation of the brain or bloodstream. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and allowing the immune system to suppress the virus.Orthopaedic history taking ugpg
Orthopaedic history taking ugpgKishore Vemula
?
This document provides guidance on taking a thorough musculoskeletal history. It emphasizes that history taking is the most important part of making a diagnosis, as a clinician is 60% closer to a diagnosis with a thorough history compared to 40% from physical examination and investigations alone. It outlines the key components of a musculoskeletal history, including chief complaint, history of present illness, functional assessment, review of systems, past medical and surgical history, medications, social history, and specific questions for common conditions like pain, swelling, instability, and loss of function. Examination techniques like inspection, palpation, and active and passive range of motion testing are also summarized. The goal is to educate clinicians on how to take a comprehensive history for the major musculoskeletalLeprosy
LeprosyGajendrayadav35
?
Here are some possible responses to the questions:
1. The higher incidence and prevalence of leprosy in males compared to females could be due to various socio-cultural factors. Males may have greater exposure and mobility which increases their risk of contracting the disease. There could also be under-reporting of cases in females due to lack of access to healthcare and social stigma.
2. To reduce stigma and discrimination against leprosy affected persons and their families, sustained awareness programs targeting the general public as well as affected communities are needed. Educating people about the modes of transmission and that leprosy is curable can help reduce misconceptions. Involving affected persons in advocacy can also help normalize the condition and empower thoseMore from yct.Ken Chang (20)
慢性胃炎的中医特色疗法(郭海英)
慢性胃炎的中医特色疗法(郭海英)yct.Ken Chang
?
《慢性胃炎的中医特色疗法》由郭海英和汪悦编着,谢建群和郑林赟翻译,出版于2004年9月,涵盖259页内容。该书探讨了中医在慢性胃炎治疗中的特色疗法。诊治胃食管反流病经验(李乾构教授)
诊治胃食管反流病经验(李乾构教授)yct.Ken Chang
?
李乾构教授的诊治经验提供了对胃食管反流病(骋贰搁顿)的中医理解,认为其可用“胸痞”来命名,并分析了病机及治疗方法。该病的病因主要是由于肝气郁结与脾胃功能失调导致胃气上逆,伴随相应症状。治疗建议包括疏肝和胃、调理饮食和情绪,以促进病症恢复。养胃全书
养胃全书yct.Ken Chang
?
该文档提供了养胃的建议,包括易消化的早餐食物如粥类、鸡蛋和蔬菜,以及多种有益的食疗和按摩方法,还强调了改善生活习惯的重要性。推荐的养胃食物包括小米、南瓜等,而瑜伽姿势则有助于促进消化。最后,提供了清晨饮食的禁忌和养胃的小偏方,以帮助人们更好地保护胃部健康。脾胃学真詮
脾胃学真詮yct.Ken Chang
?
《脾胃学真诠》由刘炳凡着,详述脾胃学的理论基础、病理变化及相关医家研究成就,涵盖脾胃与其他脏腑的关系。书中探讨脾胃学的应用原则、机理与方法,并涉及急症治疗和常见疑难病的诊疗。此书为中医学脾胃学领域的重要参考文献。成功有约—高效会计手册
成功有约—高效会计手册yct.Ken Chang
?
《管理精英宣言》强调追求非凡生活和积极冒险的公司家精神,而《成功有约——高效会议手册》则探讨了会议的意义和功能,指出提高会议效率的重要性。文档分析了会议的多种类型和具体应用,旨在加强公司内部沟通和决策效果。整体内容围绕更高效的管理实践及团队合作展开。诞生(狈补迟颈惫颈迟别蝉)yct.Ken Chang
?
Le document énumère divers artistes et peintres importants de l'histoire de l'art, en mentionnant leurs dates et contributions. Il met l'accent sur des figures telles que Giovanni Francesco da Rimini, Botticelli et Fra Angelico. La liste reflète la richesse de la peinture à différentes époques et styles.性传播疾病础
性传播疾病础yct.Ken Chang
?
本文讨论了性传播疾病(厂罢顿)的不同病原体及相关疾病,包括淋病和梅毒的症状、传播途径、诊断和治疗方法。淋病由淋病奈瑟菌引起,是世界上发病率最高的性传播疾病,而梅毒由梅毒螺旋体引起,分为不同的阶段,具高度的传染性。针对这些疾病的治疗方案包括使用青霉素、四环素及其他抗生素。内科名家严苍山学术经验集(笔345)
内科名家严苍山学术经验集(笔345)yct.Ken Chang
?
This document is a demonstration of A-PDF Merger, a software that allows users to merge multiple PDF documents into a single file. The document contains repetitive text and symbols across many pages, demonstrating the program's ability to combine different PDFs while maintaining the content of each original file. It shows how A-PDF Merger can merge PDF documents with just a few clicks.内科名家黄文东学术经验集
内科名家黄文东学术经验集yct.Ken Chang
?
This document is a demonstration of A-PDF Merger, a software that allows users to merge multiple PDF documents into a single file. The document shows the interface of the software and its ability to add, rearrange, and delete pages from different PDFs to customize the merged output file.内科名家陈道隆学术经验集
内科名家陈道隆学术经验集yct.Ken Chang
?
This document is a demonstration of A-PDF Merger, a software that allows users to merge multiple PDF documents into a single file. The document consists of the text "A-PDF MERGER DEMO" repeated across multiple lines, serving as a placeholder to represent example PDF pages that could be merged. It demonstrates the basic capabilities of A-PDF Merger without providing any substantial information about the software or merged document contents.蚂蚁的故事础苍迟.濒别蝉蝉辞苍(管理学)
蚂蚁的故事础苍迟.濒别蝉蝉辞苍(管理学)yct.Ken Chang
?
An ant works hard without supervision and is very productive. A lion in charge is impressed and hires a cockroach supervisor who implements excessive paperwork and meetings. This decreases the ant's productivity and morale. More managers are hired, expanding costs. An audit finds the department is overstaffed and the ant is fired for a bad attitude, though she was the original high performer. The fable warns about over-management reducing effectiveness.螞蟻的一課 (Ant.lesson)
螞蟻的一課 (Ant.lesson)yct.Ken Chang
?
An ant works hard without supervision and is very productive. A lion notices this and thinks she could produce even more with oversight. He hires a cockroach supervisor who implements extensive paperwork and meetings. This decreases the ant's productivity. More managers are hired, further reducing productivity until an audit reveals the department is overstaffed. The ant is fired for a poor attitude. The fable warns about over-management decreasing efficiency.寓言分享...蚂蚁的故事
寓言分享...蚂蚁的故事yct.Ken Chang
?
An ant works hard without supervision and is very productive. A lion in charge is impressed and hires more managers to oversee the ant, including a cockroach, spider, and fly. This leads to excessive meetings and paperwork that reduce the ant's productivity. More managers are hired, including a cicada and owl consultant. Ultimately, an audit finds productivity has declined due to overstaffing, and the ant is fired for lack of motivation despite being the original high performer. The story is an allegory for how over-management can negatively impact productivity.《清明上河图》(第叁版)
《清明上河图》(第叁版)yct.Ken Chang
?
《清明上河图》是北宋画家张择端创作的风俗画,属于中国十大传世名画之一。文档包含清乾隆时期的临摹本和对于作品的介绍,描绘了繁忙的河汴码头和市区街道的景象。该文档涉及放映模式选择和观赏信息。Ad
