実环境下におけるサイレント音声通话の実现に向けた雑音环境変动に顽健な非可聴つぶやき强调
0 likes1,085 views
第3回 サイレント音声認識ワークショップ 学生奨励賞(受賞者:田尻 祐介) 田尻 祐介,亀岡 弘和,戸田 智基 :実环境下におけるサイレント音声通话の実现に向けた雑音环境変动に顽健な非可聴つぶやき强调,Oct 2016 名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室
1 of 16


![非可聴つぶやき(NAM)マイク
2017/05/25 3
?非常に微弱なささやき声を体表から収録
[Nakajima et al., 2006]
声道内の
空気振動
筋肉 皮膚
骨
口腔 振動センサ
遮音カバー
軟シリコン
?使用時のイメージ
ボソボソ
ゲイン調整
or
音声強調
もしもし!
音声に近い信号を扱うため、音声情報の抽出が比較的容易](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ssrw20161014namtajiri-170525091722/85/-3-320.jpg)
![0
1
2
3
4
5
works in silence
works for
laryngectomy
non-invasive
low cost
market ready
works in noise
メリット: ①小型で安価に製造可能
? 次世代の標準的な音声インタフェースにしたい!
他のインタフェースとの比較
2017/05/25 4
?未完成の技術であり、認識精度等での比較は困難
? 適用性や潜在的な可能性をスコア付け
[Denby et al., 2010]
NAM 超音波画像/口唇画像 顔面筋電位
0
1
2
3
4
5
0
1
2
3
4
5
①②
見や目や装着性は改善済
デメリット: ①発声が必要、②外部雑音の問題が未解決
①](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ssrw20161014namtajiri-170525091722/85/-4-320.jpg)
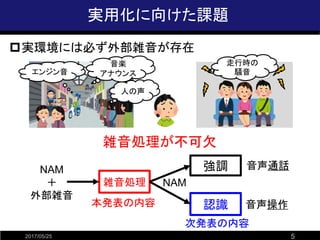
![空気伝導マイクによる外部雑音モニタリング
2017/05/25 6
? 放射される音声の微弱性に着目
? 空気伝導マイクをNAMマイク付近に配置
1) NAM信号の漏れ込みを抑制
2) NAMマイクに混入するものと近い雑音を収録
? 空気伝導信号を雑音の参照信号として使用
空気伝導信号=空気伝導NAM+空気伝導外部雑音
≈ 空気伝導外部雑音
NAM
マイク
空気伝導
マイク
体内伝導信号=体内伝導NAM+体内伝導外部雑音
非常に微弱
空気/体内伝導信号間の特性を補正するフィルタを推定
[Tajiri et al., 2016]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ssrw20161014namtajiri-170525091722/85/-6-320.jpg)
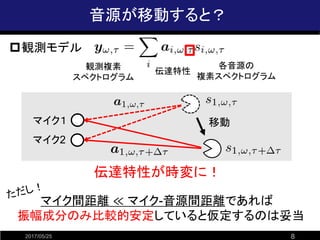
![振幅情報のみを用いた音源分離法の例
2017/05/25 9
?非負値行列因子分解(NMF)
? 振幅(or パワー)スペクトルに加法性を仮定
※複素スペクトルではないため厳密には不成立
? 観測行列(非負)を低ランク行列(非負)の積で近似
=
観測行列
(音源数=2)
係数行列基底行列
音源2に対応
音源1に対応
スペクトル距離最小化によるパラメータ推定は
観測データの背後に特定の分布を仮定し、最尤推定することに相当
[Lee and Seung, 2001]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ssrw20161014namtajiri-170525091722/85/-9-320.jpg)
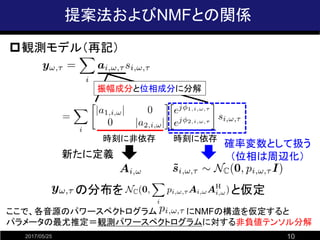

![処理前後のSN比(防音室収録の場合)
2017/05/25 13
?雑音源が一つかつ固定されていればSemi-BSSが有効
雑音の種類
SN比[dB]
-5
0
5
10
15
crowd60dB booth70dB station80dB
未処理 Semi-BSS NMF NTF
悪い
良い
補正フィルタの時不変性が
成立するため!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ssrw20161014namtajiri-170525091722/85/-13-320.jpg)
![処理前後のSN比(実環境収録の場合)
2017/05/25 14
?全ての雑音に対してNTFが最も有効
?外部雑音情報の活用により、NMF<NTF
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
crowd_in5dB traffic5dB restaurant0dB station0dB
未処理 Semi-BSS NMF NTF
雑音の種類
SN比[dB]
悪い
良い 推定すべきフィルタが時不変のため](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ssrw20161014namtajiri-170525091722/85/-14-320.jpg)

Ad
Recommended
音学シンポジウム2025「ニューラルボコーダ概説:生成モデルと実用性の観点から」
音学シンポジウム2025「ニューラルボコーダ概説:生成モデルと実用性の観点から」NU_I_TODALAB
?
音学シンポジウム2025
第156回音声言語情報処理研究発表会
招待講演
米山 怜於:ニューラルボコーダ概説:生成モデルと実用性の観点から,2025年6月
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室2025年3月音楽情报科学研究会「大局的构造生成のための小节特徴量系列モデリングに基づく阶层的自动作曲」
2025年3月音楽情报科学研究会「大局的构造生成のための小节特徴量系列モデリングに基づく阶层的自动作曲」NU_I_TODALAB
?
音楽情報科学研究会
澤田 桂都,Wen-Chin Huang,戸田 智基:大局的構造生成のための小節特徴量系列モデリングに基づく階層的自動作曲,2025年3月
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室2025年5月応用音响研究会「滨颁础厂厂笔2025における音楽情报処理の动向」
2025年5月応用音响研究会「滨颁础厂厂笔2025における音楽情报処理の动向」NU_I_TODALAB
?
応用音響研究会
橋爪 優果:ICASSP2025における音楽情報処理の動向,2025年5月
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室2025年5月応用音响研究会「滨颁础厂厂笔2025における异常音検知の动向」
2025年5月応用音响研究会「滨颁础厂厂笔2025における异常音検知の动向」NU_I_TODALAB
?
応用音響研究会
藤村 拓弥:ICASSP2025における異常音検知の動向,2025年5月
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室Automatic Quality Assessment for Speech and Beyond
Automatic Quality Assessment for Speech and BeyondNU_I_TODALAB
?
Mila Conversational AI reading group
Wen-Chin Huang:Automatic Quality Assessment for Speech and Beyond,May 2025
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室异常音検知に対する深层学习适用事例
异常音検知に対する深层学习适用事例NU_I_TODALAB
?
第144回ロボット工学セミナー「ロボットのための音声?音響処理技術」日本ロボット学会
戸田 智基:异常音検知に対する深层学习适用事例,Nov. 2022
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室深层生成モデルに基づく音声合成技术
深层生成モデルに基づく音声合成技术NU_I_TODALAB
?
第21回情報科学技術フォーラム(FIT2022)
招待講演
戸田 智基:深层生成モデルに基づく音声合成技术,Sep. 2022
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室信号の独立性に基づく多チャンネル音源分离
信号の独立性に基づく多チャンネル音源分离NU_I_TODALAB
?
令和四年度 電気?電子?情報関係学会 東海支部連合大会
招待講演
李 莉:信号の独立性に基づく多チャンネル音源分离,Aug. 2022
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室
The VoiceMOS Challenge 2022
The VoiceMOS Challenge 2022NU_I_TODALAB
?
The VoiceMOS Challenge 2022 aimed to encourage research in automatic prediction of mean opinion scores (MOS) for speech quality. It featured two tracks evaluating systems' ability to predict MOS ratings from a large existing dataset or a separate listening test. 21 teams participated in the main track and 15 in the out-of-domain track. Several teams outperformed the best baseline, which fine-tuned a self-supervised model, though the top-performing approaches generally involved ensembling or multi-task learning. While unseen systems were predictable, unseen listeners and speakers remained a difficulty, especially for generalizing to a new test. The challenge highlighted progress in MOS prediction but also the need for metrics reflecting both ranking and absolute accuracy敌対的学习による统合型ソースフィルタネットワーク
敌対的学习による统合型ソースフィルタネットワークNU_I_TODALAB
?
日本音響学会 2021年秋季研究発表会
米山 怜於, Yi-Chiao Wu, 戸田 智基:敌対的学习による统合型ソースフィルタネットワーク,Sep. 2021
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室距离学习を导入した二値分类モデルによる异常音検知
距离学习を导入した二値分类モデルによる异常音検知NU_I_TODALAB
?
日本音響学会 2021年秋季研究発表会
畔栁 伊吹, 林 知樹, 武田 一哉, 戸田 智基:距离学习を导入した二値分类モデルによる异常音検知,Sep. 2021
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室Investigation of Text-to-Speech based Synthetic Parallel Data for Sequence-to...
Investigation of Text-to-Speech based Synthetic Parallel Data for Sequence-to...NU_I_TODALAB
?
This document investigates the use of synthetic parallel data (SPD) to enhance non-parallel voice conversion (VC) through sequence-to-sequence modeling. The study evaluates the feasibility and influence of SPD on VC performance, analyzing various training pairs and the effectiveness of semiparallel datasets. Findings indicate that SPD is viable for VC, but its success depends on the training data quality and the size of the dataset used.Interactive voice conversion for augmented speech production
Interactive voice conversion for augmented speech productionNU_I_TODALAB
?
This document discusses recent progress in interactive voice conversion techniques for augmenting speech production. It begins by explaining the physical limitations of normal speech production and how voice conversion can augment speech by controlling more information. It then discusses how interactive voice conversion allows for quick response times, better controllability through real-time feedback, and understanding user intent from multimodal behavior signals. Recent advances discussed include low-latency voice conversion networks, controllable waveform generation respecting the source-filter model of speech, and expression control using signals like arm movements. The goal is to develop cooperatively augmented speech that can help users with lost speech abilities.颁搁贰厂罢「共生インタラクション」共创型音メディア机能拡张プロジェクト
颁搁贰厂罢「共生インタラクション」共创型音メディア机能拡张プロジェクトNU_I_TODALAB
?
第135回音声言語情報処理研究会
招待講演
戸田 智基:颁搁贰厂罢「共生インタラクション」共创型音メディア机能拡张プロジェクト,Feb. 2021
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室Recent progress on voice conversion: What is next?
Recent progress on voice conversion: What is next?NU_I_TODALAB
?
The document discusses recent advancements in voice conversion (VC) techniques, emphasizing the importance of preserving linguistic content while modifying non-linguistic features. It outlines the Voice Conversion Challenges (VCC) from 2016 to 2020, highlighting different training methods and the role of neural vocoders. The paper also suggests future directions for VC research, focusing on improving performance, developing interactive applications, and exploring higher-level feature conversions.Weakly-Supervised Sound Event Detection with Self-Attention
Weakly-Supervised Sound Event Detection with Self-AttentionNU_I_TODALAB
?
This document presents a weakly-supervised sound event detection method using self-attention, aiming to enhance detection performance through the utilization of weak label data. The proposed approach introduces a special tag token for weak label handling and employs a transformer encoder for improved sequence modeling, achieving performance improvements from a baseline CRNN model. Experimental results indicate a notable increase in sound event detection accuracy, with the new method outperforming the baseline in various evaluation metrics.Statistical voice conversion with direct waveform modeling
Statistical voice conversion with direct waveform modelingNU_I_TODALAB
?
This document provides an outline for a tutorial on voice conversion techniques. It begins with an introduction to the goal of the tutorial, which is to help participants grasp the basics and recent progress of VC, develop a baseline VC system, and develop a more sophisticated system using a neural vocoder. The tutorial will include an overview of VC techniques, introduction of freely available software for building a VC system, and breaks between sessions. The first session will cover the basics of VC, improvements to VC techniques, and an overview of recent progress in direct waveform modeling. The second session will demonstrate how to develop a VC system using the WaveNet vocoder with freely available tools.音素事后确率を利用した表现学习に基づく発话感情认识
音素事后确率を利用した表现学习に基づく発话感情认识NU_I_TODALAB
?
日本音響学会 2019年春季研究発表会
岡田 慎太郎,安藤 厚志,戸田 智基:音素事后确率を利用した表现学习に基づく発话感情认识,Mar. 2019
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室 楽曲中歌声加工における声质変换精度向上のための歌声?伴奏分离法
楽曲中歌声加工における声质変换精度向上のための歌声?伴奏分离法NU_I_TODALAB
?
第33回信号処理シンポジウム
山田 智也,関 翔悟,小林 和弘,戸田 智基:楽曲中歌声加工における声质変换精度向上のための歌声?伴奏分离法,Nov. 2018.
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室End-to-End音声認識ためのMulti-Head Decoderネットワーク
End-to-End音声認識ためのMulti-Head DecoderネットワークNU_I_TODALAB
?
日本音響学会 2018年秋季研究発表会
林 知樹,渡部 晋治,戸田 智基,武田 一哉:End-to-End音声認識ためのMulti-Head Decoderネットワーク,Sep. 2018.
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室空気/体内伝导マイクロフォンを用いた雑音环境下における自己発声音强调/抑圧法
空気/体内伝导マイクロフォンを用いた雑音环境下における自己発声音强调/抑圧法NU_I_TODALAB
?
日本音響学会 2018年秋季研究発表会
高田 萌絵,関 翔悟,戸田 智基:空気/体内伝导マイクロフォンを用いた雑音环境下における自己発声音强调/抑圧法,Sep. 2018
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室时间领域低ランクスペクトログラム近似法に基づくマスキング音声の欠损成分復元
时间领域低ランクスペクトログラム近似法に基づくマスキング音声の欠损成分復元NU_I_TODALAB
?
日本音響学会 2017年春季研究発表会
関 翔悟,亀岡 弘和,戸田 智基,武田 一哉:时间领域低ランクスペクトログラム近似法に基づくマスキング音声の欠损成分復元,Mar. 2017
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室Hands on Voice Conversion
Hands on Voice ConversionNU_I_TODALAB
?
The document outlines a hands-on workshop for developing voice conversion (VC) systems using open-source software called Sprocket, created by Nagoya University. It details the process of building a traditional GMM-based VC and includes instructions for installing the software, preparing datasets, and configuring the system for speaker conversion. The overall goal is to provide participants with the knowledge and tools needed to initiate their own VC research and development.Advanced Voice Conversion
Advanced Voice ConversionNU_I_TODALAB
?
The document discusses advancements in voice conversion (VC) techniques, focusing on its definition, necessity, methodologies, and research progress. VC is a method for altering speech to convey desired characteristics while retaining the linguistic content. It highlights various models, comparisons of techniques, training improvements, and applications in real-time communication and character voice modulation.Deep Neural Networkに基づく日常生活行動認識における適応手法
Deep Neural Networkに基づく日常生活行動認識における適応手法NU_I_TODALAB
?
2016年8月 音声研究会
オーガナイズドセッション「あらゆる音を対象とした情報処理の実現に向けて」
林 知樹,北岡 教英, 戸田 智基, 武田 一哉:Deep Neural Networkに基づく日常行動認識における適応手法,Aug. 2016
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室颁罢颁に基づく音响イベントからの拟音语表现への変换
颁罢颁に基づく音响イベントからの拟音语表现への変换NU_I_TODALAB
?
日本音響学会 2017年秋季研究発表会
第16回日本音響学会学生優秀発表賞(受賞者:宮崎 晃一)
宮崎 晃一,林 知樹,戸田 智基,武田 一哉:颁罢颁に基づく音响イベントからの拟音语表现への変换,Sep. 2017
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室奥补惫别狈别迟が音声合成研究に与える影响
奥补惫别狈别迟が音声合成研究に与える影响NU_I_TODALAB
?
2018年1月 音声研究会
オーガナイズドセッション「新たな音声モデルによる音声合成?音声生成―深層学習による音声波形モデルWaveNet―」(招待講演)
戸田 智基:奥补惫别狈别迟が音声合成研究に与える影响,Jan. 2018
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室Missing Component Restoration for Masked Speech Signals based on Time-Domain ...
Missing Component Restoration for Masked Speech Signals based on Time-Domain ...NU_I_TODALAB
?
The document discusses a method for restoring masked speech signals using time-domain spectrogram factorization, addressing challenges caused by aggressive noise suppression that leads to sparse spectrograms. It evaluates various strategies for enhancing speech features by utilizing low-rank structures, the redundancy of spectrograms, and distributions of clean speech features through Gaussian Mixture Models (GMM). Experimental results indicate that the proposed time-domain signal factorization (TSF) method outperforms conventional Non-negative Matrix Factorization (NMF) approaches in terms of restoration quality.More Related Content
More from NU_I_TODALAB (20)
The VoiceMOS Challenge 2022
The VoiceMOS Challenge 2022NU_I_TODALAB
?
The VoiceMOS Challenge 2022 aimed to encourage research in automatic prediction of mean opinion scores (MOS) for speech quality. It featured two tracks evaluating systems' ability to predict MOS ratings from a large existing dataset or a separate listening test. 21 teams participated in the main track and 15 in the out-of-domain track. Several teams outperformed the best baseline, which fine-tuned a self-supervised model, though the top-performing approaches generally involved ensembling or multi-task learning. While unseen systems were predictable, unseen listeners and speakers remained a difficulty, especially for generalizing to a new test. The challenge highlighted progress in MOS prediction but also the need for metrics reflecting both ranking and absolute accuracy敌対的学习による统合型ソースフィルタネットワーク
敌対的学习による统合型ソースフィルタネットワークNU_I_TODALAB
?
日本音響学会 2021年秋季研究発表会
米山 怜於, Yi-Chiao Wu, 戸田 智基:敌対的学习による统合型ソースフィルタネットワーク,Sep. 2021
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室距离学习を导入した二値分类モデルによる异常音検知
距离学习を导入した二値分类モデルによる异常音検知NU_I_TODALAB
?
日本音響学会 2021年秋季研究発表会
畔栁 伊吹, 林 知樹, 武田 一哉, 戸田 智基:距离学习を导入した二値分类モデルによる异常音検知,Sep. 2021
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室Investigation of Text-to-Speech based Synthetic Parallel Data for Sequence-to...
Investigation of Text-to-Speech based Synthetic Parallel Data for Sequence-to...NU_I_TODALAB
?
This document investigates the use of synthetic parallel data (SPD) to enhance non-parallel voice conversion (VC) through sequence-to-sequence modeling. The study evaluates the feasibility and influence of SPD on VC performance, analyzing various training pairs and the effectiveness of semiparallel datasets. Findings indicate that SPD is viable for VC, but its success depends on the training data quality and the size of the dataset used.Interactive voice conversion for augmented speech production
Interactive voice conversion for augmented speech productionNU_I_TODALAB
?
This document discusses recent progress in interactive voice conversion techniques for augmenting speech production. It begins by explaining the physical limitations of normal speech production and how voice conversion can augment speech by controlling more information. It then discusses how interactive voice conversion allows for quick response times, better controllability through real-time feedback, and understanding user intent from multimodal behavior signals. Recent advances discussed include low-latency voice conversion networks, controllable waveform generation respecting the source-filter model of speech, and expression control using signals like arm movements. The goal is to develop cooperatively augmented speech that can help users with lost speech abilities.颁搁贰厂罢「共生インタラクション」共创型音メディア机能拡张プロジェクト
颁搁贰厂罢「共生インタラクション」共创型音メディア机能拡张プロジェクトNU_I_TODALAB
?
第135回音声言語情報処理研究会
招待講演
戸田 智基:颁搁贰厂罢「共生インタラクション」共创型音メディア机能拡张プロジェクト,Feb. 2021
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室Recent progress on voice conversion: What is next?
Recent progress on voice conversion: What is next?NU_I_TODALAB
?
The document discusses recent advancements in voice conversion (VC) techniques, emphasizing the importance of preserving linguistic content while modifying non-linguistic features. It outlines the Voice Conversion Challenges (VCC) from 2016 to 2020, highlighting different training methods and the role of neural vocoders. The paper also suggests future directions for VC research, focusing on improving performance, developing interactive applications, and exploring higher-level feature conversions.Weakly-Supervised Sound Event Detection with Self-Attention
Weakly-Supervised Sound Event Detection with Self-AttentionNU_I_TODALAB
?
This document presents a weakly-supervised sound event detection method using self-attention, aiming to enhance detection performance through the utilization of weak label data. The proposed approach introduces a special tag token for weak label handling and employs a transformer encoder for improved sequence modeling, achieving performance improvements from a baseline CRNN model. Experimental results indicate a notable increase in sound event detection accuracy, with the new method outperforming the baseline in various evaluation metrics.Statistical voice conversion with direct waveform modeling
Statistical voice conversion with direct waveform modelingNU_I_TODALAB
?
This document provides an outline for a tutorial on voice conversion techniques. It begins with an introduction to the goal of the tutorial, which is to help participants grasp the basics and recent progress of VC, develop a baseline VC system, and develop a more sophisticated system using a neural vocoder. The tutorial will include an overview of VC techniques, introduction of freely available software for building a VC system, and breaks between sessions. The first session will cover the basics of VC, improvements to VC techniques, and an overview of recent progress in direct waveform modeling. The second session will demonstrate how to develop a VC system using the WaveNet vocoder with freely available tools.音素事后确率を利用した表现学习に基づく発话感情认识
音素事后确率を利用した表现学习に基づく発话感情认识NU_I_TODALAB
?
日本音響学会 2019年春季研究発表会
岡田 慎太郎,安藤 厚志,戸田 智基:音素事后确率を利用した表现学习に基づく発话感情认识,Mar. 2019
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室 楽曲中歌声加工における声质変换精度向上のための歌声?伴奏分离法
楽曲中歌声加工における声质変换精度向上のための歌声?伴奏分离法NU_I_TODALAB
?
第33回信号処理シンポジウム
山田 智也,関 翔悟,小林 和弘,戸田 智基:楽曲中歌声加工における声质変换精度向上のための歌声?伴奏分离法,Nov. 2018.
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室End-to-End音声認識ためのMulti-Head Decoderネットワーク
End-to-End音声認識ためのMulti-Head DecoderネットワークNU_I_TODALAB
?
日本音響学会 2018年秋季研究発表会
林 知樹,渡部 晋治,戸田 智基,武田 一哉:End-to-End音声認識ためのMulti-Head Decoderネットワーク,Sep. 2018.
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室空気/体内伝导マイクロフォンを用いた雑音环境下における自己発声音强调/抑圧法
空気/体内伝导マイクロフォンを用いた雑音环境下における自己発声音强调/抑圧法NU_I_TODALAB
?
日本音響学会 2018年秋季研究発表会
高田 萌絵,関 翔悟,戸田 智基:空気/体内伝导マイクロフォンを用いた雑音环境下における自己発声音强调/抑圧法,Sep. 2018
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室时间领域低ランクスペクトログラム近似法に基づくマスキング音声の欠损成分復元
时间领域低ランクスペクトログラム近似法に基づくマスキング音声の欠损成分復元NU_I_TODALAB
?
日本音響学会 2017年春季研究発表会
関 翔悟,亀岡 弘和,戸田 智基,武田 一哉:时间领域低ランクスペクトログラム近似法に基づくマスキング音声の欠损成分復元,Mar. 2017
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室Hands on Voice Conversion
Hands on Voice ConversionNU_I_TODALAB
?
The document outlines a hands-on workshop for developing voice conversion (VC) systems using open-source software called Sprocket, created by Nagoya University. It details the process of building a traditional GMM-based VC and includes instructions for installing the software, preparing datasets, and configuring the system for speaker conversion. The overall goal is to provide participants with the knowledge and tools needed to initiate their own VC research and development.Advanced Voice Conversion
Advanced Voice ConversionNU_I_TODALAB
?
The document discusses advancements in voice conversion (VC) techniques, focusing on its definition, necessity, methodologies, and research progress. VC is a method for altering speech to convey desired characteristics while retaining the linguistic content. It highlights various models, comparisons of techniques, training improvements, and applications in real-time communication and character voice modulation.Deep Neural Networkに基づく日常生活行動認識における適応手法
Deep Neural Networkに基づく日常生活行動認識における適応手法NU_I_TODALAB
?
2016年8月 音声研究会
オーガナイズドセッション「あらゆる音を対象とした情報処理の実現に向けて」
林 知樹,北岡 教英, 戸田 智基, 武田 一哉:Deep Neural Networkに基づく日常行動認識における適応手法,Aug. 2016
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室颁罢颁に基づく音响イベントからの拟音语表现への変换
颁罢颁に基づく音响イベントからの拟音语表现への変换NU_I_TODALAB
?
日本音響学会 2017年秋季研究発表会
第16回日本音響学会学生優秀発表賞(受賞者:宮崎 晃一)
宮崎 晃一,林 知樹,戸田 智基,武田 一哉:颁罢颁に基づく音响イベントからの拟音语表现への変换,Sep. 2017
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室奥补惫别狈别迟が音声合成研究に与える影响
奥补惫别狈别迟が音声合成研究に与える影响NU_I_TODALAB
?
2018年1月 音声研究会
オーガナイズドセッション「新たな音声モデルによる音声合成?音声生成―深層学習による音声波形モデルWaveNet―」(招待講演)
戸田 智基:奥补惫别狈别迟が音声合成研究に与える影响,Jan. 2018
名古屋大学 情報学研究科 知能システム学専攻 戸田研究室Missing Component Restoration for Masked Speech Signals based on Time-Domain ...
Missing Component Restoration for Masked Speech Signals based on Time-Domain ...NU_I_TODALAB
?
The document discusses a method for restoring masked speech signals using time-domain spectrogram factorization, addressing challenges caused by aggressive noise suppression that leads to sparse spectrograms. It evaluates various strategies for enhancing speech features by utilizing low-rank structures, the redundancy of spectrograms, and distributions of clean speech features through Gaussian Mixture Models (GMM). Experimental results indicate that the proposed time-domain signal factorization (TSF) method outperforms conventional Non-negative Matrix Factorization (NMF) approaches in terms of restoration quality.実环境下におけるサイレント音声通话の実现に向けた雑音环境変动に顽健な非可聴つぶやき强调
- 1. 2017/05/25 実環境下におけるサイレント音声通話の実現に向けた 雑音環境変動に頑健な非可聴つぶやき強調 第3回 サイレント音声認識ワークショップ 10月14日 セッションA 13:45~14:00 ○田尻祐介1,亀岡弘和2 ,戸田智基1 1 名古屋大学,2 NTTコミュニケーション科学基礎研究所 空気/体内伝導マイク 実環境収録 in 梅田駅
- 2. サイレント音声インタフェースが描く未来 2017/05/25 2 ?音声コミュニケーションの問題点 発声を躊躇するような場面が存在 ? 人混みの中 ? 秘匿性の高い会話は困難 ? 公共スペース ? 周囲にとって迷惑 ?サイレント音声インタフェースの登場 周囲に内容を知られることなく音声を入力 いつでも、どこででも音声通話や音声操作が可能に!
- 3. 非可聴つぶやき(NAM)マイク 2017/05/25 3 ?非常に微弱なささやき声を体表から収録 [Nakajima et al., 2006] 声道内の 空気振動 筋肉 皮膚 骨 口腔 振動センサ 遮音カバー 軟シリコン ?使用時のイメージ ボソボソ ゲイン調整 or 音声強調 もしもし! 音声に近い信号を扱うため、音声情報の抽出が比較的容易
- 4. 0 1 2 3 4 5 works in silence works for laryngectomy non-invasive low cost market ready works in noise メリット: ①小型で安価に製造可能 ? 次世代の標準的な音声インタフェースにしたい! 他のインタフェースとの比較 2017/05/25 4 ?未完成の技術であり、認識精度等での比較は困難 ? 適用性や潜在的な可能性をスコア付け [Denby et al., 2010] NAM 超音波画像/口唇画像 顔面筋電位 0 1 2 3 4 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 ①② 見や目や装着性は改善済 デメリット: ①発声が必要、②外部雑音の問題が未解決 ①
- 6. 空気伝導マイクによる外部雑音モニタリング 2017/05/25 6 ? 放射される音声の微弱性に着目 ? 空気伝導マイクをNAMマイク付近に配置 1) NAM信号の漏れ込みを抑制 2) NAMマイクに混入するものと近い雑音を収録 ? 空気伝導信号を雑音の参照信号として使用 空気伝導信号=空気伝導NAM+空気伝導外部雑音 ≈ 空気伝導外部雑音 NAM マイク 空気伝導 マイク 体内伝導信号=体内伝導NAM+体内伝導外部雑音 非常に微弱 空気/体内伝導信号間の特性を補正するフィルタを推定 [Tajiri et al., 2016]
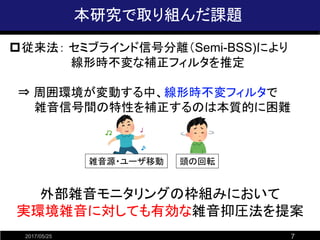
- 7. 本研究で取り組んだ課題 2017/05/25 7 ?従来法: セミブラインド信号分離(Semi-BSS)により 線形時不変な補正フィルタを推定 ? 周囲環境が変動する中、線形時不変フィルタで 雑音信号間の特性を補正するのは本質的に困難 外部雑音モニタリングの枠組みにおいて 実環境雑音に対しても有効な雑音抑圧法を提案 頭の回転雑音源?ユーザ移動
- 8. 音源が移動すると? 2017/05/25 8 ?観測モデル 観測複素 スペクトログラム 各音源の 複素スペクトログラム 伝達特性 マイク1 マイク2 移動 マイク間距離 ? マイク-音源間距離であれば 振幅成分のみ比較的安定していると仮定するのは妥当 伝達特性が時変に!
- 9. 振幅情報のみを用いた音源分離法の例 2017/05/25 9 ?非負値行列因子分解(NMF) ? 振幅(or パワー)スペクトルに加法性を仮定 ※複素スペクトルではないため厳密には不成立 ? 観測行列(非負)を低ランク行列(非負)の積で近似 = 観測行列 (音源数=2) 係数行列基底行列 音源2に対応 音源1に対応 スペクトル距離最小化によるパラメータ推定は 観測データの背後に特定の分布を仮定し、最尤推定することに相当 [Lee and Seung, 2001]
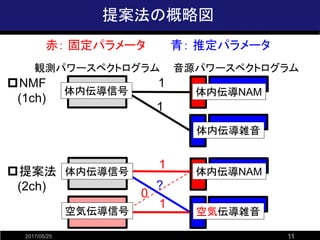
- 10. 提案法およびNMFとの関係 2017/05/25 10 ?観測モデル(再記) 時刻に非依存 時刻に依存 振幅成分と位相成分に分解 確率変数として扱う (位相は周辺化)新たに定義 ここで、各音源のパワースペクトログラム にNMFの構造を仮定すると パラメータの最尤推定=観測パワースペクトログラムに対する非負値テンソル分解 の分布を と仮定
- 11. 提案法の概略図 2017/05/25 11 観測パワースペクトログラム 音源パワースペクトログラム ?NMF (1ch) 1 1 体内伝導雑音 体内伝導NAM体内伝導信号 ?提案法 (2ch) 1 ? 空気伝導雑音 体内伝導NAM 1 0 体内伝導信号 空気伝導信号 赤: 固定パラメータ 青: 推定パラメータ
- 12. 実験的評価 2017/05/25 12 ? 男性話者1名のNAM(50文)を防音室で収録 ? 3種類の雑音を防音室で収録 ※雑音は固定した1台のスピーカーから提示 ? crowd60dB: 60 dBAの人混み雑音 ? booth70dB: 70 dBAの展示場の雑音 ? station80dB: 80 dBAの駅構内の雑音 ? 4種類の雑音を実環境で収録 ? crowd5dB_SNR: 人混み雑音を5 dBで重畳 ? traffic5dB_SNR: 高架下の雑音を5 dBで重畳 ? restaurant0dB_SNR: 飲食店の雑音を0 dBで重畳 ? station0dB_SNR: 駅構内の雑音を0 dBで重畳 ? 評価対象 ? Semi-BSS (自然勾配法を使用) ? NMF ? 提案法(NTF) 処理前後のSN比を比較 NAM基底は事前に学習(1個抜き交差検証) 板倉齋藤擬距離規準 各音源の基底数20、更新回数50
- 13. 処理前後のSN比(防音室収録の場合) 2017/05/25 13 ?雑音源が一つかつ固定されていればSemi-BSSが有効 雑音の種類 SN比[dB] -5 0 5 10 15 crowd60dB booth70dB station80dB 未処理 Semi-BSS NMF NTF 悪い 良い 補正フィルタの時不変性が 成立するため!
- 14. 処理前後のSN比(実環境収録の場合) 2017/05/25 14 ?全ての雑音に対してNTFが最も有効 ?外部雑音情報の活用により、NMF<NTF 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 crowd_in5dB traffic5dB restaurant0dB station0dB 未処理 Semi-BSS NMF NTF 雑音の種類 SN比[dB] 悪い 良い 推定すべきフィルタが時不変のため
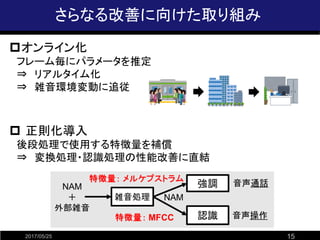
- 15. さらなる改善に向けた取り組み 2017/05/25 15 ?オンライン化 フレーム毎にパラメータを推定 ? リアルタイム化 ? 雑音環境変動に追従 ? 正則化導入 後段処理で使用する特徴量を補償 ? 変換処理?認識処理の性能改善に直結
- 16. まとめ 2017/05/25 16 ?目的 雑音環境変動に対して頑健な雑音抑圧処理の実現 ? 提案法 伝達特性の位相成分を周辺化した観測モデル 観測パワースペクトログラムに対するNTF ? 実験的評価結果 提案法は実環境収録雑音に対しても有効 ? 今後の展望 オンライン化、後段処理を考慮した正則化の導入