Table 1
Download as DOC, PDF0 likes27 views
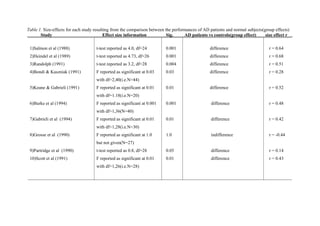
The document reports the results of 17 studies comparing the performance of Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients to normal subjects on various cognitive tests. For each study, it provides information on the statistical analysis conducted to evaluate the significance of differences in performance between AD patients and controls. Across the studies, t-tests and ANOVAs consistently showed significant performance differences, with large effect sizes in many cases.
1 of 2
Download to read offline

Recommended


ąĘąð°ųīÚūąąôģåĩþąðēÔąðīÚūąģĶūąÃĄ°ųūąīĮēõģåĩþēđēÔģĶīĮģåŧåąðģåīĄąôūąģūąðēÔģŲīĮģåģ§ēđēÔģŲīĮģåīĄēÔŧå°ųÃĐDaniel Veras, PhD
Ėý
Este documento fornece um perfil socioeconÃīmico das 4.036 famÃlias beneficiÃĄrias do Programa Banco de Alimentos em Santo AndrÃĐ que estÃĢo cadastradas no Cadastro Ãnico. Mostra que a maioria dessas famÃlias sÃĢo chefiadas por mulheres, negras, com renda muito baixa e alta dependÊncia. Muitos trabalhadores dessas famÃlias atuam na informalidade.Instalacion de windows server 2008 en Virtual Box



Instalacion de windows server 2008 en Virtual Boxsyed usman ali shah
Ėý
como instalar windows server 2009 en virtualboxAutomatski - Asset Management Solution



Automatski - Asset Management Solutionautomatskicorporation
Ėý
Automatski Corporation provides an asset management solution to track, maintain, and operate assets for organizations. The solution involves commissioning assets, performing diagnostics and maintenance, tracking supplies and consumables, and remotely managing assets. It also includes data analysis, categorizing assets, budgeting, and decommissioning assets. The solution utilizes a management portal, QR codes, NFC tags, and mobile apps. Automatski also offers consulting services, IoT solutions, and IoT training related to asset management and other domains like smart cities.Jentry stoddard portfolio



Jentry stoddard portfolioJentry Stoddard
Ėý
This document provides a design portfolio for Jentry Stoddard containing descriptions of various design projects completed for a COMM 130 visual media course. The portfolio includes summaries of 14 projects involving magazine covers, website mockups, brochures, business cards, letterheads, Prezi presentations, infographics, photos, and HTML coding. For each project, the design problem, date, software used, objectives, and design process are summarized.10361



10361ivanov15666688
Ėý
ÐаŅÐĩÐ―Ņ Ð―Ð° ÐŋÐūÐŧÐĩÐ·Ð―ŅŅ ОÐūÐīÐĩÐŧŅ Ð ÐĩŅÐŋŅÐąÐŧÐļКÐļ ÐÐĩÐŧаŅŅŅŅworth-the-wait-report



worth-the-wait-reportSophia Papastavrou
Ėý
This document provides an introduction and overview of reflections on Canada's National Action Plan on Women, Peace and Security (C-NAP) and the government's first two progress reports covering 2011-2012 and 2012-2013. It summarizes the goals and pillars of the C-NAP, notes the delay in releasing the first progress report, and introduces a collection of reflections and analysis from Canadian civil society organizations on implementing the C-NAP and improving accountability. The reflections aim to further discussion on how Canada can better uphold its commitments to UN Security Council resolutions on women, peace and security.

Livro_Mulheres_SA_FINAL (1)Daniel Veras, PhD
Ėý
1) O documento apresenta um perfil socioeconÃīmico das mulheres de Santo AndrÃĐ e um mapeamento da violÊncia contra mulheres no municÃpio.
2) A primeira parte traz dados sobre a condiçÃĢo socioeconÃīmica das mulheres incluindo educaçÃĢo, trabalho e renda, enquanto a segunda parte analisa os Ãndices de violÊncia como homicÃdios, estupros e violÊncia domÃĐstica.
3) O prefeito Carlos Grana destaca a importÃĒncia do documento para auxiliar na formulaçÃĢo de polÃticas pÚblicas voltadas para as mulheresGrupos de Usuarios y Plantillas



Grupos de Usuarios y Plantillassyed usman ali shah
Ėý
aqui podreis mirar que como se configura los usuarios y las plantillas, ,etcc, dominio , active directory, etc...The Book of Liberty



The Book of LibertyDavid Turner
Ėý
The greatest book of liberty is not a document or a declaration. The greatest book of liberty is the Bible. The bible presents the Gospel, the good news that sets me free. Thanksgiving, An Attitude of Gratitude.



Thanksgiving, An Attitude of Gratitude.David Turner
Ėý
For the Christian, thanksgiving is not an option. We are commanded to give thanks. When we don't give thanks we forget out blessings and become bitter. In all things, Give Thanks!Wrestling In A Dark World John 15:18-16:4 and Ephesians 6:12-13



Wrestling In A Dark World John 15:18-16:4 and Ephesians 6:12-13David Turner
Ėý
As believers in Jesus Christ we are fighting against the Principalities and Powers of this world. We cannot fight with the methods of the world. We must wrestle in the manner in which Christ wrestled, in the power of the Spirit. BIOSIMILARS - Regulation and Market Trends 



BIOSIMILARS - Regulation and Market Trends Joseph Pategou
Ėý
Nowadays patients and physicians can have access to three types of drugs: a originators, a generic or a biosimilar.
Those drugs have different regulatory systems that apply in Europe; moreover the biosimilars regulation is evolving and may change. Regulation is an important factor that can give more confidence to patients and healthcare professionals. As a consequence, biosimilaires will grow.
Area solv



Area solvSnehasish dutta
Ėý
The document contains information about geometric shapes such as circles, triangles, squares, rectangles, and parallelograms. It provides definitions and formulas for calculating properties of these shapes such as circumference, area, perimeter, and ratios of corresponding sides. It also includes examples of geometry problems and their step-by-step solutions.5 Hiring and Onboarding Practices That Create Engaged Employees



5 Hiring and Onboarding Practices That Create Engaged EmployeesQualtrics
Ėý
Many companies tackle employee engagement through reactionary programs. The best companies take a more proactive approach. In this session you'll learn five hiring and onboarding practices LinkedIn is using to unlock the power of employee engagement.
table 2



table 2Despina Ioannidou
Ėý
This table summarizes 7 studies that examined priming effects in Alzheimer's disease patients by comparing test scores on studied words versus unstudied words. It reports the effect size information and statistical significance from t-tests or F-tests conducted in each study, with most finding significant priming effects at the 0.05 level or better. The table also includes the corresponding effect size r calculated for each study, ranging from 0.54 to 0.71.Superficial bladder cancer



Superficial bladder cancerFouad Abdelshaheed
Ėý
This document summarizes a study on T1G3 superficial bladder cancers from the Egyptian experience. The study reviewed 100 cases of superficial bladder cancer, finding that 22% were T1G3 tumors. T1G3 cancers had high recurrence rates within 6 months and often progressed to muscle invasion within 2-36 months. Based on these findings, the study concluded that T1G3 tumors represent a high-risk group that may require early radical cystectomy rather than adjuvant therapy alone. Clear follow-up and treatment protocols are needed for managing T1G3 superficial bladder cancers.Epidemiological Exercises on case control studies



Epidemiological Exercises on case control studiesJayaramachandran S
Ėý
This document discusses case-control study design and calculating odds ratios. It provides examples of 3 case-control studies examining suspected risk factors for cervical cancer, lung cancer, and esophageal cancer. For each study, it constructs a 2x2 contingency table and calculates the odds ratio to assess the strength of association between the disease and suspected risk factor. Odds ratios greater than 1 indicate the exposure increases disease risk.Carcinogenicity of Glyphosate A Systematic Review of the Available Evidence



Carcinogenicity of Glyphosate A Systematic Review of the Available EvidenceAsociaciÃģn ToxicolÃģgica Argentina
Ėý
This document summarizes recent cancer assessments of glyphosate and epidemiological studies and animal carcinogenicity studies on glyphosate. It notes that IARC and Portier et al. classified glyphosate as a probable human carcinogen while EFSA, FAO/WHO JMPR, and draft EPA assessments found it unlikely to pose a carcinogenic risk. Meta-analyses of epidemiological studies found a statistically significant increased risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Animal studies found increased incidences of renal tumors, malignant lymphomas, and hemangiosarcomas in male mice, with statistical significance. Rat studies had mixed or inadequate findings.NFL 2013 Combine Data Multivariate Analysis



NFL 2013 Combine Data Multivariate AnalysisJohn Michael Croft
Ėý
This analysis examines differences in physical attributes between NFL player positions using data from the 2013 NFL Combine. Multivariate analysis of variance finds significant differences between four groups of positions across variables like vertical jump, bench press, and hand size. The most significant differences are between defensive backs/wide receivers and offensive linemen/defensive tackles, with the former jumping higher and having better bench press scores on average. The largest difference is between running backs and offensive linemen/defensive tackles, with the former being shorter on average. The analysis provides evidence that positions requiring more athleticism differ physically from those emphasizing stamina and stability.Sample size in general



Sample size in generalMmedsc Hahm
Ėý
This document discusses sample size calculations for clinical trials. It covers the key requirements for determining sample size such as power, significance level, variability, and smallest effect size. Methods for calculating sample size are presented, including formulas, software, tables, and nomograms. Considerations for adjustments to the sample size due to factors like dropout rates and unequal group sizes are also described. Examples of sample size calculations for comparing means and proportions in independent groups using t-tests and chi-squared tests are provided.New Epidemiologic Measures in Multilevel Study: Median Risk Ratio, Median Haz...



New Epidemiologic Measures in Multilevel Study: Median Risk Ratio, Median Haz...Jinseob Kim
Ėý
This document introduces new epidemiological measures for multilevel studies, including the median risk ratio, median hazard ratio, and median beta. It begins with an introduction and overview of intraclass correlation coefficients and variance partition coefficients. It then provides formulas for calculating the new measures based on binomial, Poisson, and Cox proportional hazards multilevel models. Examples are shown using real data on breast cancer and families to demonstrate how to compute and interpret the median odds ratio, median risk ratio, and median hazard ratio. The document concludes by discussing applications of the new measures to other data types like count and survival data.New perspectives in the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis - Profe...



New perspectives in the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis - Profe...WAidid
Ėý
The slideset offers an overview of MDR-TB: the epidemiology, the efficacy of the available treatments, and the new perspectives in the management of the pathology.
The slideset underlines, moreover, the existence of a free cost online instrument developed by ERS together with WHO to help clinician from all Europe to manage difficult-to-treat TB cases: TB Consilium. More Related Content
Viewers also liked (7)
Grupos de Usuarios y Plantillas



Grupos de Usuarios y Plantillassyed usman ali shah
Ėý
aqui podreis mirar que como se configura los usuarios y las plantillas, ,etcc, dominio , active directory, etc...The Book of Liberty



The Book of LibertyDavid Turner
Ėý
The greatest book of liberty is not a document or a declaration. The greatest book of liberty is the Bible. The bible presents the Gospel, the good news that sets me free. Thanksgiving, An Attitude of Gratitude.



Thanksgiving, An Attitude of Gratitude.David Turner
Ėý
For the Christian, thanksgiving is not an option. We are commanded to give thanks. When we don't give thanks we forget out blessings and become bitter. In all things, Give Thanks!Wrestling In A Dark World John 15:18-16:4 and Ephesians 6:12-13



Wrestling In A Dark World John 15:18-16:4 and Ephesians 6:12-13David Turner
Ėý
As believers in Jesus Christ we are fighting against the Principalities and Powers of this world. We cannot fight with the methods of the world. We must wrestle in the manner in which Christ wrestled, in the power of the Spirit. BIOSIMILARS - Regulation and Market Trends 



BIOSIMILARS - Regulation and Market Trends Joseph Pategou
Ėý
Nowadays patients and physicians can have access to three types of drugs: a originators, a generic or a biosimilar.
Those drugs have different regulatory systems that apply in Europe; moreover the biosimilars regulation is evolving and may change. Regulation is an important factor that can give more confidence to patients and healthcare professionals. As a consequence, biosimilaires will grow.
Area solv



Area solvSnehasish dutta
Ėý
The document contains information about geometric shapes such as circles, triangles, squares, rectangles, and parallelograms. It provides definitions and formulas for calculating properties of these shapes such as circumference, area, perimeter, and ratios of corresponding sides. It also includes examples of geometry problems and their step-by-step solutions.5 Hiring and Onboarding Practices That Create Engaged Employees



5 Hiring and Onboarding Practices That Create Engaged EmployeesQualtrics
Ėý
Many companies tackle employee engagement through reactionary programs. The best companies take a more proactive approach. In this session you'll learn five hiring and onboarding practices LinkedIn is using to unlock the power of employee engagement.
Similar to Table 1 (8)
table 2



table 2Despina Ioannidou
Ėý
This table summarizes 7 studies that examined priming effects in Alzheimer's disease patients by comparing test scores on studied words versus unstudied words. It reports the effect size information and statistical significance from t-tests or F-tests conducted in each study, with most finding significant priming effects at the 0.05 level or better. The table also includes the corresponding effect size r calculated for each study, ranging from 0.54 to 0.71.Superficial bladder cancer



Superficial bladder cancerFouad Abdelshaheed
Ėý
This document summarizes a study on T1G3 superficial bladder cancers from the Egyptian experience. The study reviewed 100 cases of superficial bladder cancer, finding that 22% were T1G3 tumors. T1G3 cancers had high recurrence rates within 6 months and often progressed to muscle invasion within 2-36 months. Based on these findings, the study concluded that T1G3 tumors represent a high-risk group that may require early radical cystectomy rather than adjuvant therapy alone. Clear follow-up and treatment protocols are needed for managing T1G3 superficial bladder cancers.Epidemiological Exercises on case control studies



Epidemiological Exercises on case control studiesJayaramachandran S
Ėý
This document discusses case-control study design and calculating odds ratios. It provides examples of 3 case-control studies examining suspected risk factors for cervical cancer, lung cancer, and esophageal cancer. For each study, it constructs a 2x2 contingency table and calculates the odds ratio to assess the strength of association between the disease and suspected risk factor. Odds ratios greater than 1 indicate the exposure increases disease risk.Carcinogenicity of Glyphosate A Systematic Review of the Available Evidence



Carcinogenicity of Glyphosate A Systematic Review of the Available EvidenceAsociaciÃģn ToxicolÃģgica Argentina
Ėý
This document summarizes recent cancer assessments of glyphosate and epidemiological studies and animal carcinogenicity studies on glyphosate. It notes that IARC and Portier et al. classified glyphosate as a probable human carcinogen while EFSA, FAO/WHO JMPR, and draft EPA assessments found it unlikely to pose a carcinogenic risk. Meta-analyses of epidemiological studies found a statistically significant increased risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Animal studies found increased incidences of renal tumors, malignant lymphomas, and hemangiosarcomas in male mice, with statistical significance. Rat studies had mixed or inadequate findings.NFL 2013 Combine Data Multivariate Analysis



NFL 2013 Combine Data Multivariate AnalysisJohn Michael Croft
Ėý
This analysis examines differences in physical attributes between NFL player positions using data from the 2013 NFL Combine. Multivariate analysis of variance finds significant differences between four groups of positions across variables like vertical jump, bench press, and hand size. The most significant differences are between defensive backs/wide receivers and offensive linemen/defensive tackles, with the former jumping higher and having better bench press scores on average. The largest difference is between running backs and offensive linemen/defensive tackles, with the former being shorter on average. The analysis provides evidence that positions requiring more athleticism differ physically from those emphasizing stamina and stability.Sample size in general



Sample size in generalMmedsc Hahm
Ėý
This document discusses sample size calculations for clinical trials. It covers the key requirements for determining sample size such as power, significance level, variability, and smallest effect size. Methods for calculating sample size are presented, including formulas, software, tables, and nomograms. Considerations for adjustments to the sample size due to factors like dropout rates and unequal group sizes are also described. Examples of sample size calculations for comparing means and proportions in independent groups using t-tests and chi-squared tests are provided.New Epidemiologic Measures in Multilevel Study: Median Risk Ratio, Median Haz...



New Epidemiologic Measures in Multilevel Study: Median Risk Ratio, Median Haz...Jinseob Kim
Ėý
This document introduces new epidemiological measures for multilevel studies, including the median risk ratio, median hazard ratio, and median beta. It begins with an introduction and overview of intraclass correlation coefficients and variance partition coefficients. It then provides formulas for calculating the new measures based on binomial, Poisson, and Cox proportional hazards multilevel models. Examples are shown using real data on breast cancer and families to demonstrate how to compute and interpret the median odds ratio, median risk ratio, and median hazard ratio. The document concludes by discussing applications of the new measures to other data types like count and survival data.New perspectives in the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis - Profe...



New perspectives in the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis - Profe...WAidid
Ėý
The slideset offers an overview of MDR-TB: the epidemiology, the efficacy of the available treatments, and the new perspectives in the management of the pathology.
The slideset underlines, moreover, the existence of a free cost online instrument developed by ERS together with WHO to help clinician from all Europe to manage difficult-to-treat TB cases: TB Consilium. Carcinogenicity of Glyphosate A Systematic Review of the Available Evidence



Carcinogenicity of Glyphosate A Systematic Review of the Available EvidenceAsociaciÃģn ToxicolÃģgica Argentina
Ėý
Table 1
- 1. Table 1. Size-effects for each study resulting from the comparison between the performances of AD patients and normal subjects(group effects) Study Effect size information Sig. AD patients vs controls(group effect) size effect r . 1)Salmon et al (1988) 2)Heindel et al (1989) 3)Randolph (1991) 4)Bondi & Kaszniak (1991) 5)Keane & Gabrieli (1991) 6)Burke et al (1994) 7)Gabrieli et al (1994) 8)Grosse et al (1990) 9)Partridge et al (1990) 10)Scott et al (1991) t-test reported as 4.0, df=24 t-test reported as 4.73, df=26 t-test reported as 3.2, df=28 F reported as significant at 0.03 with df=2,40(i.e.N=44) F reported as significant at 0.01 with df=1.18(i.e.N=20) F reported as significant at 0.001 with df=1,36(N=40) F reported as significant at 0.01 with df=1,28(i.e.N=30) F reported as significant at 1.0 but not given(N=27) t-test reported as 0.8, df=28 F reported as significant at 0.01 with df=1,26(i.e.N=28) 0.001 0.001 0.004 0.03 0.01 0.001 0.01 1.0 0.05 0.01 difference difference difference difference difference difference difference indifference difference difference r = 0.64 r = 0.68 r = 0.51 r = 0.28 r = 0.52 r = 0.48 r = 0.42 r = -0.44 r = 0.14 r = 0.43
- 2. 11)Russo & Spinler (1994) 12) Huberman & Moscovitch (1994) 13)Fleischman et al (1997) 14) Park et al(1998) 15)Christensen et al (1992) 16)Randolph et al (1995) 17)Downes et al (1996) exp 1 exp 2 F reported as significant at 1.0 but not given(N=24) F reported as significant at 0.25 with df=3,51(i.e.N=55) F reported as significant at 0.28 but not given (N=52) F reported as significant at 1.0 but not given (N=32) given F reported as significant at 0.01 under two conditions, N=42 F reported as significant at 0.01 with df=1,12 (N=14) F reported as significant at 0.05 N=28 1.0 0.25 0.28 1.0 0.193 0.01 0.01 0.05 indifference indifference indifference indifference indifference difference difference indifference r = -0.47 r = 0.09 r = 0.08 r = -0.41 r = 0.15 from d=0.30 r = 0.35 r = 0.62 r = 0.31
