Tablet Coating, Types and Their Compositions.
- 1. TABLET COATING, TYPES, COATING MATERIAL & COATING PANS SUBMITTED BY: RAJ KUMAR MANDAL B. PHARM VTH SEM. 3RD YEAR SUBJECT: INDUSTRIAL PHARMACY-I (BP502T) SUBMITTED TO: MR. RAHUL PAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR*, DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACEUTICS ISF COLLEGE OF PHARMACY, MOGA Pharmaceutics, Industrial Pharmacy-Ist Theory {BP502T}
- 2. INTRODUCTION ’éĪ In Pharmaceutical Science there are many different doses form which includes tablets, pills, bend, pallets, etc. in which tablet is the most common pharmaceutical doses form. ’éĪ Coating is a covering that is applied to the surface of any object here the coating term is used in the tablet mean the covering of a thin layer over a surface of a tablet. ’éĪ Coating is a unique technique through which tablet are covered by a material on its outer surface. After coating material is applied to a batch of tablet into the coating pen resulting on this surface tablet become cover with an extra layer. Spray pattern, nozzle spacing, size of droplets, etc. are some parameters which depends on the coating technique.
- 3. PURPOSE OF COATING ’éĪ # To masking taste order colour ’éĪ # To insure the physical and chemical protection from the outer environment like oxygen moisture light and other form . ’éĪ # Protection of drug from the gastric environment and other factor . ’éĪ # Enhance Patient Compliance and Improves tablet appearance and brand differentiation ’éĪ # Prevent tablet sticking and enhancement of self-life of the drug ’éĪ # Making too easy for swelling or large dose form ’éĪ # Prevent the losing of volatile ingredient . ’éĪ # Follows fine contours of embossed logo. ’éĪ Can be used for tablet printing. ’éĪ # Modification in the rate of drug release like sustained repeated and delay released and rrevention of drug incompatibility ’éĪ # Making increase the physical strength also increase the packaging rate
- 4. DEFECTS IN TABLET COATING 1. Tablet Picking and Sticking ’éĪ Cause: This occurs when tablets stick together, resulting in portions of the tablet being torn off. It is usually caused by over-wetting of the tablets due to an excessive spray rate or insufficient drying. ’éĪ Solution: Reduce the spray rate or increase the drying temperature or airflow to evaporate the solvent more quickly. 2. Orange Peel Effect ’éĪ Cause: An uneven or rough coating surface (resembling the texture of an orange peel) is often caused by high viscosity of the coating solution or rapid drying before the coating can level out. ’éĪ Solution: Adjust the viscosity of the coating solution by reducing the concentration or modifying the spray conditions.
- 5. CONTŌĆ” 3. Cracking ’éĪ Cause: Cracks can form in the coating due to improper drying conditions or over-application of the coating material, leading to internal stress in the film. ’éĪ Solution: Adjust the drying temperature to ensure the coating dries gradually and uniformly. Also, check the amount of plasticizer in the coating solution to improve flexibility. 4. Bridging ’éĪ Cause: Bridging occurs when the coating solution covers the tabletŌĆÖs logo, scoreline, or any embossed markings, making them less visible. ’éĪ Solution: Use a more fluid coating solution or adjust the spray pattern and rate to ensure that fine details remain intact.
- 6. CONTŌĆ” 5. Colour Variation ’éĪ Cause: Uneven distribution of the colorant in the coating solution or improper mixing can result in inconsistent colouring of the tablets. ’éĪ Solution: Ensure uniform dispersion of colorants in the solution and optimize the spray pattern to cover all tablets uniformly. 6. Chipping ’éĪ Cause: Chipping is when parts of the coating break off during handling or packaging. It can be caused by an overly brittle coating, excessive mechanical stress, or insufficient plasticizer in the formula. ’éĪ Solution: Increase the plasticizer content to enhance coating flexibility or reduce mechanical stress during tablet handling.
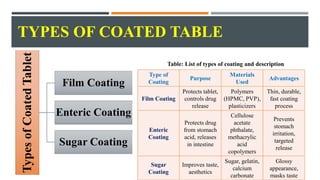
- 7. TYPES OF COATED TABLE Type of Coating Purpose Materials Used Advantages Film Coating Protects tablet, controls drug release Polymers (HPMC, PVP), plasticizers Thin, durable, fast coating process Enteric Coating Protects drug from stomach acid, releases in intestine Cellulose acetate phthalate, methacrylic acid copolymers Prevents stomach irritation, targeted release Sugar Coating Improves taste, aesthetics Sugar, gelatin, calcium carbonate Glossy appearance, masks taste Table: List of types of coating and description
- 8. (I) ENTERIC COATING ’éĪ It is a modification to the conventional approach of drug to dissolve the dosage form in gastric or stomach & release the drug in GIT. ’éĪ It may improve or prevent the degradation of drug through gastric ph. ’éĪ Enteric coating also improves bioavailability of drug. ’éĪ In this coat a layer of polymer that prevents disintegration in the gastric environment which makes the drug Gastro resistant. ’éĪ It may also cause the delay in action of the drug. ’éĪ Technique involved in enteric coating is to protect the tablet core from disintegration in acidic environment and on the other hand helps to solubilize in response to an increased pH (6-8) of intestine. ’éĪ It prevents acid labile drug from gastric or acidic pH & gastric enzymes.
- 9. CONTŌĆ” Many polymers can be used for enteric coating they are divided into 2 types: (A) Natural: Shellac (B) Synthetic: CAP (cellulose acetate phthalate), PVAP (poly vinyl acetate phthalate), HPMCP (Hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose phthalate) ’éĪ HPMCP is mostly used polymer for enteric coating as it is easily soluble in organic solvent & it is not hygroscopic as CAP, hence provide more stability. ’éĪ These polymers are insoluble in lower pH (2.5-4.5) and release the tablet in higher pH between (5-7) ’éĪ Plasticizers: Triethyl citrate & diethyl phthalate .
- 10. (II) FILM COATING ’éĪ It is process to apply a thin layer of polymer to a tablet ’éĪ It is used to prevent the oxidation with environment and helps to improve the shell life of drug ’éĪ Thickness of film is approximately (25-100 um ). ’éĪ Polymers are non-toxic with no pharmacological action. ’éĪ Provide strength and prevent cracking ’éĪ Those types of film coating based on coating material (1) Organic film coating (2) Aqua film coating
- 11. Sr. No. Class Example 1. Cellulose Cellulose HPMC, HPC, HEC, Methyl HEC methylcellulose EC CMC Sodium 2. Vinyls PVC 3. Glycol PEG 4. Acrylates Ethyl acrylate, methyl mrthylate copolymers
- 12. (III) SUGAR COATING This type of coating, we cover the tablet with sugar syrup /sucrose solution. ’éĪ It masks the taste & make it easy to swallow. ’éĪ It may be colored or may be uncolored. ’éĪ Mostly used for pediatric and geriatric patients. ’éĪ Shape of sugar-coated tablets are deeply convex core with minimal edges. ’éĪ Sugar coating enhances the weight of tablet by 50-100% Key pointes to be noted during sugar coating: (1) Quantity of sugar solution to be added for coating as coating material. (2) Rate of pouring of solution. (3) speed of tumbling of pan and application of air dryer.
- 13. CONTŌĆ” Steps involved in Sugar Coating: (i) Sealing: it is done to prevent moisture damage or to water proofing of the tablet. (ii) Sub coating: it is done to round off the edges of tablet (iii) Syruping: layer of sugar syrup / sucrose solution is added with some binder such as acacia, gelatin along with coating material such as calcium carbonate, titanium dioxide along with drying. (iv) Finishing: it may include an outer covering to cover rough surface & to increase bulk of tablet also it includes the coloring of the of the rough sugar-coated tablet as required. (v) Polishing: It gives a shining / glossy outer appearance which make the tablet attractive, polishing is done by using bees wax, & candelilla wax mixture.
- 14. COATING PANS
- 15. 1. CONVENTIONAL COATING PANS ’éĪ It is also known as a standard coating pan. ’éĪ Circular metal pan which are inclined with the 40 degree angle. ’éĪ Having 8 to 60 inch diameter ’éĪ Rotated on its horizontal axis by a motor. ’éĪ Heated air is supplied by the inlet hair supply in order to prevent from sticking. ’éĪ Exhaust by means of dusts. ’éĪ Coating solution are applied to the tablet by landing or spring ’éĪ Use of atomizing system to produce event distribution of coating solution.
- 16. CONTŌĆ” i) PELLIGRINI COATING PAN ’éĪ They are available from the range of 10 to 1000 kg batch. They are suitable for the sugar coated tablets but not for the film coated due to the limitation in the drawing comparability. Coating buffet Pan and diffuser that distributes the drying air uniformly ’éĪ Limitation was overcome by installing Glatt impression sword air handling system to improve drying efficiency. ii) GLATT IMPRESSION SWORD COATING PAN ’éĪ In this type of coating instruments two systems are followed ’éĪ a) PLG SYSTEM ’éĪ In this the hot air inlet by a sword and exhaust air by plenum ’éĪ b) in this the hot air inlet by a plenum and exhaust by 2- perforated swords. iii) IMMERSION TUBE COATING PAN ’éĪ This type of putting Pan have a long tube with a spring nozzle at its tip. Hot air gets into through the tube into tablet bed. The dried air flow upward and exhausted by the conventional dust ’éĪ On the same time rapid processing have been reported for both film and sugar coating within the system.
- 17. 2. PERFORATED COATING PANS ’éĪ An another type of coating pan. ’éĪ It consist of partial or full perforated drum that rotate on its horizontal axis ’éĪ On the same time the entire system remains in closed in a seal housing. ’éĪ Tablets are in the perforated pan enhancing drying efficiency. The coating solution is a sprayed while warm air circulate through the perforation insuring event coating and effective drying. ’éĪ They are ideal for film and enteric coating that provide a better control over coating quality and drawing if you can see compare to the traditional pans
- 18. CONTŌĆ” i) ACCELA COAT PAN ’éĪ This type of pants are fully perforated, contains mixing blades. Inlet air is by a plenum in contact with the top of the pan. Air is exhausted by the plenum located below the pan. ii)DUMMOULIN IDA.X. COATING EQUIPMENT ’éĪ 1) Fully perforated cylindrical central section. ’éĪ 2) The two air plenums that function as both inlet or exhaust air systems are located in contact with the outside of the pan. ’éĪ 3) A third plenum, connected to a slotted tube located inside the pan and above the cascading product bed allows inlet air only to be directed onto the surface of product being coated. ’éĪ 4) Air flows, single flow, reversed single flow, double flow and direct double flow iii) GLATT PAN-COATING EQUIPMENT ’éĪ 1) Similar to that of Accela Cota. ’éĪ 2) A divided air plenum located beneath the moving tablet bed enables air to be blown into or exhausted from the pan through either or both of the two sections ’éĪ 3) In addition, another air plenum, connected to an opening above the door (similar to that in a HI coater also allows air to be blown into exhausted from the pan and quite expensive.
- 19. CONTŌĆ” iv) HI- COATER PAN ’éĪ It's consists of 4 perforated segments which are perpendicular to each other and each of these perforations acts as an opening for air outlet which is fixed to the exterior of the pan surface and drying air is introduced into pan through an opening located on inside periphery of top of the pan. v) DRIA COATER ’éĪ Introduces drying air through hallow perforated baffles located on inside periphery of drum and exhaust is from back of the pan. ’éĪ Different air flows ’éĪ a)direct flow: air in at the top and exhausted through baffles located beneath tablet bed. ’éĪ b)reverse flow A: air in through baffles located beneath, tablet bed and exhausted via baffle top of pan. ’éĪ c)reverse flow B: air in through baffles located beneath tablet bed, and exhausted via plenum connected to opening at back of pan. vi) HUTTLIN BUTTERFLY PAN ’éĪ It has a series of large, angled, slotted opening in, the pan wall at the junction of the cylindrical portion with each of the front or back panels. These openings permit air to be exhausted from the pan and drying air is applied to the surface of the bed of the product being coated by Mear tube. ’éĪ Front and back of the pan can be disconnected from the cylindrical, central section and hinged down.
- 20. 3. FLUIDIZED BED COATING PANS ’éĪ In this type of coating pan Fluidization technique is used. Air is used to suspend, and floor dies the tablet or granules which create a uniform bed. The coating solution is sprayed on to the particle as they move in the air stream, that ensuring even coating distribution . ’éĪ While the coating solution is sprayed, hot dryer the particle in real time which prevent agglomeration and allowing for effective coating. ’éĪ A fluidized bed coating pan is a type of equipment used in the pharmaceutical, chemical, and food industries for coating particles such as granules, pellets, or powders. The process uses a combination of fluidization and spray coating, making it ideal for applications like controlled-release drug formulations or the application of protective coatings.
- 21. CONTŌĆ” Principle of Operation: ’éĪ Fluidization: Particles to be coated are suspended in an air stream, which causes them to behave like a fluid. This ensures that each particle is evenly exposed to the coating solution. ’éĪ Spraying: While the particles are suspended, a coating solution (often a polymer dissolved in a solvent or water) is sprayed into the bed. The solution adheres to the particles. ’éĪ Drying: The hot air used for fluidization also evaporates the solvent or moisture in the coating solution, leaving behind a uniform layer on the particle surface. Types of Fluidized Bed Coating Processes: ’éĪ Top-Spray Coating: The spray nozzle is positioned above the fluidized particles. This is often used for granulation and coating processes. ’éĪ Bottom-Spray Coating: The spray nozzle is placed at the bottom, and coating is applied as particles are pushed upwards by the air stream. This is common for controlled-release coatings. ’éĪ Tangential Spray: Used for applying high-load coatings, the nozzle is positioned at an angle to the bed.
- 22. CONCLUSION ’éĪ Tablet coating is a crucial process in pharmaceutical manufacturing that enhances the stability, aesthetics, and functionality of tablets by applying a thin layer of coating material. The main types of tablet coatings include sugar coating, film coating, and enteric coating. ’éĪ Sugar coatings improve taste and appearance, while film coatings, using polymers like HPMC, offer protection and control drug release. Enteric coatings protect drugs from stomach acid and ensure release in the intestines. Common coating materials include polymers, plasticizers, and colorants. Coating pans, such as conventional coating pans, perforated coating pans, and fluidized bed coaters, are used to achieve uniform coating application through processes like spraying, drying, and mixing.
- 23. REFERENCES 1. Pandey, Prachi & Pal, Rahul & Singh, Sudhanshu & Gupta, Himangi & Batham, Aryan & Kumar, Narendra & Sharma, Arushi. (2023). The Current Status In Mucosal drug Delivery System (MDDS)and Future Prospectus In delivery: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Medicine. 8. 76-106. 10.47760/ijpsm.2023.v08i10.007. 2. Pal, Rahul & Pandey, Prachi & Nogai, Lipi & Sharma, Arushi & Mishra, Riya & Koli, Manju & Thakur, Shiva. (2023). The Advanced Approach in The Development of Targeted Drug Delivery (TDD) With Their Bio-Medical Applications: A Descriptive Review. International Neurourology Journal. 27. 40-58. 10.5123/inj.2023.4.inj6. 3. Pal, Rahul & Pandey, Prachi & Sharma, Arushi & Saxena, Archita & Thakur, Shiva. (2023). The Pharmaceutical Polymer's; A Current Status In Drug Delivery: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Survey in Fisheries Sciences. 10. 3682-3692. 10.53555/sfs.v10i1.1648. 4. Pal, Rahul & Pandey, Prachi & Nogai, Lipi & Sharma, Arushi & Anand, Amit & Suthar, Pallavi & Keskar, Madhuri & Kumar, Vikash. (2023). The Future Perspectives And Novel Approach On Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) With Current State. Journal of Population Therapeutics and Clinical Pharmacology. 30. 594-613. 10.53555/jptcp.v30i17.2852.
- 24. CONTŌĆ” 5. Pal, Rahul & Pandey, Prachi & Koli, Manju & Saxena, Archita & Rizwan, Mohammad. (2023). Chitosan: As Highly Potential Biopolymer Obtainable In Several Advance Drug Delivery Systems Including Biomedical Applications. European Chemical Bulletin. 12. 322-344. 10.48047/ecb/2023.12.si10.0036. 6. Pal, Rahul & Pandey, Prachi & Saxena, Archita & Koli, Manju & Thakur, Shiva. (2023). ØÉōØÉ×ØÉ▒ØÉŁØÉøØÉ©ØÉ©ØÉż: PHARMACEUTICS- I [Diploma in Pharmacy], Ist Year. 7. Pandey, Prachi & Pal, Rahul & Thakur, Shiva. (2023). A Text Book of Pharmaceutics-1" B. Pharm 1st sem. (Ist Year) PCI Syllabus. 8. Pal, Rahul & Pandey, Prachi. (2023). A Text Book of "Pharmaceutics Practical-1" M. Pharm (Pharmaceutics) Ist Sem.. 9. Pal, Rahul & Pandey, Prachi & Thakur, Shiva & Chanana, Arsh & Singh, Ravindra. (2023). Biodegradable PolymerŌĆÖs Enhancing Drug Delivery Activity In Different Novel Drug Delivery System. World Journal Of Pharmacy And Pharmaceutical Sciences. 12. 2046-2069. 10.20959/wjpps2023.






















![CONTŌĆ”
5. Pal, Rahul & Pandey, Prachi & Koli, Manju & Saxena, Archita & Rizwan, Mohammad. (2023). Chitosan: As Highly
Potential Biopolymer Obtainable In Several Advance Drug Delivery Systems Including Biomedical Applications.
European Chemical Bulletin. 12. 322-344. 10.48047/ecb/2023.12.si10.0036.
6. Pal, Rahul & Pandey, Prachi & Saxena, Archita & Koli, Manju & Thakur, Shiva. (2023). ØÉōØÉ×ØÉ▒ØÉŁØÉøØÉ©ØÉ©ØÉż:
PHARMACEUTICS- I [Diploma in Pharmacy], Ist Year.
7. Pandey, Prachi & Pal, Rahul & Thakur, Shiva. (2023). A Text Book of Pharmaceutics-1" B. Pharm 1st sem. (Ist Year)
PCI Syllabus.
8. Pal, Rahul & Pandey, Prachi. (2023). A Text Book of "Pharmaceutics Practical-1" M. Pharm (Pharmaceutics) Ist Sem..
9. Pal, Rahul & Pandey, Prachi & Thakur, Shiva & Chanana, Arsh & Singh, Ravindra. (2023). Biodegradable PolymerŌĆÖs
Enhancing Drug Delivery Activity In Different Novel Drug Delivery System. World Journal Of Pharmacy And
Pharmaceutical Sciences. 12. 2046-2069. 10.20959/wjpps2023.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coatingtabletppt-241001112452-9eebf48a/85/Tablet-Coating-Types-and-Their-Compositions-24-320.jpg)






















































