Telecom industry copy
- 1. By: Saurbh Kumar Tribhuvan Saini Vipul Aanad Telecom Industry
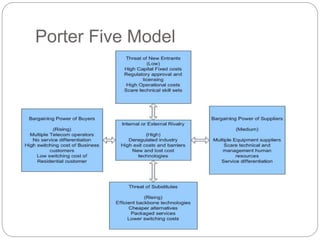
- 2. Contents ’éŚ Introduction ’éŚ History ’éŚ Telecom Facts ’éŚ Major Players ’éŚ SWOT Analysis ’éŚ PEST Analysis ’éŚ PORTERŌĆÖS Analysis ’éŚ Government Initiatives ’éŚ Future Prospectus
- 3. Introduction ’éŚ Indian Telecom market is one of the fastest growing markets in the world. Indian telecom network has about 1.05 billion connections as on 31 December 2015. ’éŚ With 1.05 billion wireless connections, Indian telecom has become the second largest wireless network surpassing US in the world after China. ’éŚ About 15 million connections are being added every month. Wireless telephones are increasing at faster rate. ’éŚ Telecom Industry contribute more than 6% in the GDP ’éŚ The share of private sector in total telephone is about 82.33%.
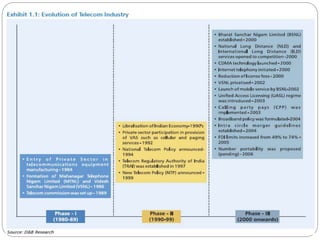
- 4. History of Indian Telecommunications ’éŚ Year 1851 First operational land lines were laid by the government near Calcutta (seat of British power) ’éŚ 1881 Telephone service introduced in India ’éŚ 1883 Merger with the postal system ’éŚ 1947 Nationalization of all foreign telecommunication companies to form the Posts, Telephone and Telegraph (PTT), a monopoly run by the governmentŌĆÖs Ministry of Communications ’éŚ 1985 Department of Telecommunications (DOT) established, an exclusive provider of domestic and long-distance service that would be its own regulator (separate from the postal system) ’éŚ 1986 Conversion of DOT into two wholly government-owned companies: the Videsh Sanchar Nigam Limited (VSNL) for international telecommunications and Mahanagar Telephone Nigam Limited (MTNL) for service in metropolitan areas. ’éŚ 1997 Telecom Regulatory Authority of India created ’éŚ 1999 Cellular Services are launched in India. New National Telecom Policy is adopted ’éŚ 2000 DoT becomes a corporation, BSNL
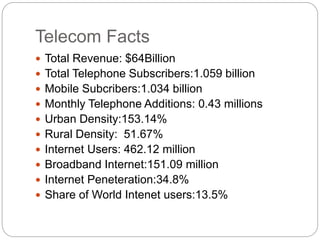
- 5. Telecom Facts ’éŚ Total Revenue: $64Billion ’éŚ Total Telephone Subscribers:1.059 billion ’éŚ Mobile Subcribers:1.034 billion ’éŚ Monthly Telephone Additions: 0.43 millions ’éŚ Urban Density:153.14% ’éŚ Rural Density: 51.67% ’éŚ Internet Users: 462.12 million ’éŚ Broadband Internet:151.09 million ’éŚ Internet Peneteration:34.8% ’éŚ Share of World Intenet users:13.5%
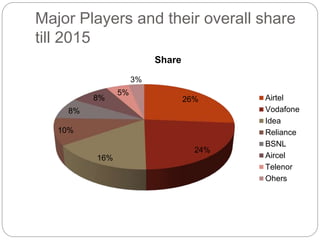
- 6. Major Players and their overall share till 2015 26% 24% 16% 10% 8% 8% 5% 3% Share Airtel Vodafone Idea Reliance BSNL Aircel Telenor Ohers
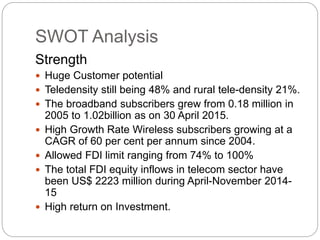
- 7. SWOT Analysis Strength ’éŚ Huge Customer potential ’éŚ Teledensity still being 48% and rural tele-density 21%. ’éŚ The broadband subscribers grew from 0.18 million in 2005 to 1.02billion as on 30 April 2015. ’éŚ High Growth Rate Wireless subscribers growing at a CAGR of 60 per cent per annum since 2004. ’éŚ Allowed FDI limit ranging from 74% to 100% ’éŚ The total FDI equity inflows in telecom sector have been US$ 2223 million during April-November 2014- 15 ’éŚ High return on Investment.
- 8. Weakness ’éŚ Poor Telecommunication Infrastructure ’éŚ Large number of call drops. ’éŚ Late adopters of New Technology India is among the last countries in the world to get access to 3G technology. Some estimates suggest that nearly 132 countries across the world already have 3G technology and mobile services in one form or the other. ’éŚ Most competitive market ,10 to 12 companies offer mobile services in most parts of India, globally, the average is 4. ’éŚ A market strongly regulated by Government. ’éŚ Difficult to enter because of requirement of huge financial resources. E.g Auction of 3G license has reached Rs 15814.15 crores.
- 9. Opportunities ’éŚ Entry Into other consumer segments leveraging the present channels E.g. DTH service like Reliance BIG TV, Tata SKY, Airtel digital TV by telecom majors like Reliance, Tata and Airtel Respectively. ’éŚ Other examples : Airtel website builder Providing fibre Connectivity to 2,50,000 village panchayat by 2016. ’éŚ More scope in content related services, since, the consumer is influenced by local culture.
- 10. Threats ’éŚ Increase in competition from different players creates huge losses. ’éŚ The telecom infrastructure equipment, majority of which is imported annually into the country at 5 percent customs duty. Whereas, duties are levied (10ŌĆō30 percent) on inputs that go into the manufacturing of this equipment, ’éŚ price wars like per-second billing which is deflating revenues and making sure the ŌĆśsurvival of the fittestŌĆÖ ’éŚ Partiality on the part of the Govt, E.g.Allowing 3G service in a PSU (MTNL,BSNL) before auctioning to Private Sector
- 11. PEST Analysis Political Analysis ’éŚ The Government of India plans to cut license fees by up to 33 per cent for operators. ’éŚ The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) has recommended a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model for BharatNet, the central governmentŌĆÖs ambitious project to set up a broadband network in rural India, and has also envisaged central and state governments to become the main clients in this project. Econmical Analysis: The Indian Telecom industry has been playing an important role in the world economy and global revenues. ’éŚ In 2017, there were USD 4 trillion, expected to grow at a steep 11% p.a. CAGR over the next 2 years. ’éŚ Output per annum - Ōé╣ 136,833 crores per annum & Increasing 20% for every month.
- 12. Social Analysis: ’éŚ Growing young population. ’éŚ Change in Lifestyle. ’éŚ Increment in services which includes digital television, voice and high-speed internet services and various social application. ’éŚ Building awareness and connecting people. Technological Analysis: ’éŚ Total government spending on research and devlopment ’éŚ Total indutry spending on research and devlopment ’éŚ New and upgraded devices and applications
- 14. Government Initiatives The Government has taken many proactive initiatives which has provided a framework for the rapid growth of the telecom industry. ’éŚ The Government of India has cleared India's biggest spectrum auction across seven bands, which is expected to generate revenue of Rs 5.66 trillion (US$ 83.9 billion). ’éŚ 100 per cent FDI is permitted in telecom equipment manufacturing through the automatic route. ’éŚ The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has amended the Unified Licence for telecom operations which will allow sharing of active telecom infrastructure like antenna, feeder cable and transmission systems between operators, thereby lowering the costs of operations and leading to faster rollout of networks ’éŚ Establishment of an independent regulator - the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI)-for the telecom sector. ’éŚ Introduction of a Unified access licensing regime for telecom services on a pan-India basis.
- 15. Future Prospectus ’éŚ The Indian telecommunication services market will likely grow by 10.3 per cent year-on-year to reach US$ 103.9 billion by 2020#. ’éŚ Driven by strong adoption of data consumption on handheld devices, the total mobile services market revenue in India is expected to touch US$ 37 billion in 2017. ’éŚ The broadband services user-base in India is expected to grow to 250 million connections by 2017, according to GSMA. ’éŚ Overall expenditure on mobile services in India is expected to increase to US$ 21.4 billion in 2015, led by 15 per cent growth in data services expenditure. ’éŚ The Indian telecom sector is expected to generate four million direct and indirect jobs over the next five years according to estimates by Randstad India.