The Do‚Äôs and ∂Ŕī«≤‘‚Äôt≤ű of Equity in a Start-Up
- 1. The DO’s and DON’Ts of Equity in a Start UpScott Kaplowitch, CPAJonathan Gorski, CPA, MBAPartnerssbk@edelsteincpa.comjpg@edelsteincpa.comBoston, MA 02110617-227-6161
- 3. Review of commonly used equity oriented compensation plans
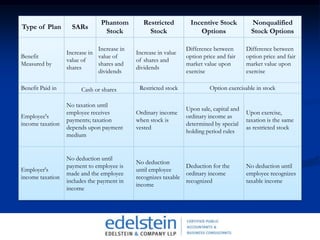
- 4. Incentive Stock Options (Īű≥ßįŅ‚Äôs)
- 5. Nonqualified Stock Options (Ī∑≤Ō≥ßįŅ‚Äôs)
- 8. Common Do‚Äôs and ∂Ŕī«≤‘‚Äôt≤ű
- 9. Other equity based compensation plansTerminologyStock Option ‚Äď a contractual right granted to an employee to purchase shares of the employer‚Äôs stock in the future in accordance with a specified plan.Grant Date ‚Äď the date on which an employee receives a stock option.Vesting Date ‚Äď date on which an employee has the right of ownership for the stock option.Exercise Date ‚Äď the date shares are purchased.Exercise Price ‚Äď The price at which the stock option may be purchased for.Sales Date ‚Äď The date when exercised options are soldExpiration Date- The date when the option will expire.IRC Sec. 83b ‚Äď election, which the recipient of restricted stock may elect, to include in his gross income the FMV of the shares on the date of grant. IRC 409 A - Adopts a broad definition of nonqualified compensation.
- 10. Incentive Stock Options RequirementsThe option is granted pursuant to a plan.The option is granted within 10 years of adoption or shareholder approval.The exercise price equals or exceeds the fair market value at the time the option is granted.The option is nontransferable The option is granted to an employee who owns no more than 10% of the Corporation.
- 11. Incentive Stock Options Requirements (continued)The total FMV of options first exercisable by any grantee during a calendar year does not exceed $100,000.The option must be granted to an employee of: (1) the granting corporation(2) a parent or subsidiary of the granting corporation(3) a corporation that assumes the options pursuant to a merger, consolidation, acquisition or property or stock, reorganization or liquidation, under Section 424(a) of the Internal Revenue Code.
- 12. Nonqualified Stock OptionsA stock option that does not meet the requirements of an incentive stock option.The employee is taxed when the option is exercised.
- 13. Planning for Income Recognition upon Receipt of NSQO’s4-Step Analysis:Consider the tax impact at the Grant DateTax substantially vested stock at the Exercise DateDefer tax on Restricted Stock until Substantially VestedConsider aSection 83(b) Election on Restricted Stock upon exercise date
- 14. Stock Option ExampleISO:An employee is granted an ISO on March 1st 2010 to purchase 1,000 shares in his/her company for $10/share, the current market price of the stock. The option is redeemable one year from the grant date and expires March 1st 2020NQSO:Same as above, however the NQSO is granted at a discounted rate of $8/share.For both examples assume the employee exercises his/her option for all 1,000 shares on July 1, 2011 when the shares are trading at $15/share.
- 15. Stock Option Example (continued)
- 16. Restricted StockA grant of company stock in which the recipient’s rights in the stock are restricted until the shares vest. (i.e. restricted stock are subject to forfeiture risk)The Company can transfer its stock at no cost to its employees. Consider Section 83(b) election
- 17. Section 83(b) ElectionDefinition: When an employee receives restricted stock, a decision must be made on whether to pay taxes on the restricted stock at its current value in the year in which the stock was received, rather than when it vests. This election must be made within 30 days of receiving the stock.
- 18. 83(b) Election (continued)YES ‚Äď election for 83(b): The employee recognizes income on the date of receipt and pays tax on the compensation amount of the stock received. He/she then pays capital gains tax on the stock when it is sold.NO ‚Äď election against 83(b): The employee will pay tax at ordinary income tax rates on the date the time restrictions lapse. This tax will be higher assuming that the stock has appreciated.
- 19. 83(b) Election - ExampleIn return for services, you receive 5,000 shares of restricted stock in a startup company when the shares are worth $1.00. Shortly thereafter the company goes public and is extremely successful. When the shares vest three years from now, they are trading at $60.If you chose not to elect 83(b), you report nothing when you receive the shares, but report $300,000 of ordinary income (not capital gain) when the shares vest. You may pay close to $120,000 in federal income tax as a result.If you elect to take 83(b), you would report $5,000 of ordinary income when you make the election. You do not report income at the time the stock vests. If you sell the stock for $300,000 after holding the it for more than a year you'll report $295,000 of long-term capital gain and be taxed at a much lower rate saving you approximately $80,000 in taxes.
- 20. 83(b) Election SummaryThe section 83(b) election makes sense in the following situations:The amount of income you’ll report when you make the election is small and the potential for growth in value of the stock is greatYou expect reasonable growth in the value of the stock and the likelihood of a forfeiture is very smallConversely, you should avoid the section 83(b) election where a forfeiture is likely or where you’ll pay a great deal of tax at the time of the election with only modest prospects of growth in the stock’s value
- 21. Sample of an 83(b) Election form:
- 22. Common Do‚Äôs and ∂Ŕī«≤‘‚Äôt≤űRecord KeepingStock for ServiceReporting & RecordingAMT tax preference item upon exercising ISOUnderstanding the Deferred Compensation Plan DocumentDilutionDifferent Classes of Stock
- 23. Other Executive Compensation:Options that do not Dilute OwnershipEquity oriented plans paid in cashStock Appreciation RightsPhantom Stock PlansEmployee Stock Purchase Plans
- 25. Thank you!We are Edelstein & Company LLP, a certified public accounting & consulting firm based in downtown Boston, MA, providing accounting, tax, business consulting, and financial planning services to individuals and companies.Scott Kaplowitch, CPAJonathan Gorski, CPA, MBAPartnerssbk@edelsteincpa.comjpg@edelsteincpa.comEdelstein & Company LLP160 Federal StreetBoston, MA 02110617-227-6161
Editor's Notes
- #2: 600ŐżŐżŐżŐżŐżIntroduction600.1 Family businesses are always looking for nontaxable and tax-deferred compensation planning techniques to maximize the effectiveness of their compensation packages for shareholder-employees and key executives. 600.2 Fringe benefits (Chapter 4) and qualified retirement plans (Chapter 5) provide only minimal help in this effort because of limits on the size of employer contributions, nondiscrimination requirements, or both. This chapter focuses on nonqualified deferred compensation (cash and stock-based) and nonqualified retirement programs that are typically the most effective supplements to the salary and bonuses of a shareholder-employee or key executive.600.3 Deferred compensation is a cash payment made in one period for services performed in an earlier period. In a nonqualified deferred cash compensation plan (for simplicity, the term deferred compensation plan is used in this chapter), the employee defers the receipt of cash compensation to a future year. Deferred compensation plans can be effective planning tools for deferring tax on cash salary and credited earnings, to take advantage of lower tax rates in later years, or to achieve personal financial planning and retirement goals.600.4 Equity-oriented plans determine compensation by the value of the company's stock and may involve cash, actual stock, or stockoptions. Several types of plans exist for each category and the employee's tax treatment depends on the form of payment.
- #4: What Is a Stock Option?603.11 A stock option is a contractual right granted to an executive to purchase shares of the company's stock in accordance with a specified plan. The plan normally specifies how many options may be granted, the executives who may participate, the option price, the form of payment, the periods for exercising options and making payment, and other matters. The company's shareholders usually must vote to approve the option plan. The purchase price, sometimes called the strike price, is usually the stock's FMV on the day the executive is granted the option. The plan may, however, set the option price different from the market value. The plan may specify the strike price be paid in cash or with employer stock the executive already owns. 603.12 Stock options fit into two broad categories: a. Incentive Stock Options (ISOs). Qualified stock options, more commonly known as incentive stock options, must meet certain statutory requirements outlined in IRC Sec. 422. ISOs are covered in sections 606 and 608.b. Nonqualified Stock Options (NQSOs). These include those not meeting the requirements of an ISO, or an option stating it is an NQSO. See sections 607 and 608 for coverage of NQSOs.Stock Options as a Risk-free Equity Vehicle603.13 A stock option program allows the executive an opportunity to participate in equity growth of the company. The option fixes the purchase price that executives must pay to exercise the option and buy stock. The better the company performs, the more the options are worth because of the increase in the value of the underlying stock. 603.14 Stock options generally are granted to the executive at no cost. Therefore, the executive gets in with minimal or no up-front capital and without significant downside investment risk if the company stock declines in value before the executive exercises the option. If the price of company stock drops below the exercise price, the executive does not incur a loss. He or she simply chooses not to exercise the option.603.15 Since the purpose of the option is to allow the executive to share in the company's growth, option programs are built around the assumption that the company's stock will increase in value. However, the ability of the option holder to participate in the company's equity growth without any upfront capital risk is a significant benefit.
- #11: 605ŐżŐżŐżŐżŐżRestrictedStock Plans605.1 In a typical restrictedstock plan, an executive receives company stock subject to certain restrictions. Often, the stock is transferred at no cost to the executive. The shares are subject to forfeiture if the executive fails to fulfill the terms of the restrictedstock program. For example, a common restriction is that the executive will forfeit the shares if he terminates employment within a certain number of years. 605.2 When restrictedstock (i.e., subject to a forfeiture risk) is transferred to the executive for payment of services, the executive's income and the employer's deductions are not recognized until vesting occurs (i.e., the stock is no longer restricted), unless the executive makes an election to recognize the income at the date of receipt.605.3ŐżNote: When unrestricted vested stock is transferred in payment for services, the executive recognizes ordinary (compensation) income equal to the stock's value less any amount paid for the stock on the transfer date [IRC Sec. 83(a)]. Here, little or no planning can be done to reduce or minimize taxes; however, with vested stock, the executive also avoids the risk of losing his stock investment. 605.4 Appendix 6H is a sample restrictedstock plan agreement that can be used to assist the client's legal counsel. Appendix 6I is a checklist for evaluating a restrictedstock program.
- #17: AMTTax Treatment of ISOs606.4 The tax benefits of an ISO are heavily weighted in the executive's favor. Generally, the executive recognizes no taxable income for regular tax purposes on either the grant or exercise of an ISO [IRC Sec. 421(a)(1)]. However, upon exercise, the executive does have a tax preference item for the alternative minimum tax (AMT). The preference is the difference between the stock'soption price and its market value at exercise [IRC Sec. 56(b)(3)]. The employer receives no deduction. 606.5 Upon exercise, the basis of the stock for regular tax purposes will be the exercise price. For AMT purposes, however, it will be the exercise price plus the positive alternative minimum taxable income (AMTI) adjustment item (i.e., the excess of the FMV at the time of exercise over the option price) recognized upon the exercise of the ISO. An offsetting negative AMT adjustment item occurs when the stock is sold. Therefore, if the executive disposes of the stock in the same year as the exercise, the two adjustments will offset. However, if the executive does not dispose of the stock in the same year as the exercise (e.g., because the stock price declines substantially after exercise) the executive may incur an unexpected AMT liability.