Touchstone 4 el 701 sem9
- 1. Touchstone 4 EL 701 Seminar 9 Reported speech Reported questions
- 2. When you report the things people say, the verb tense often âshifts back.â
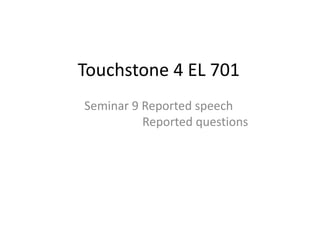
- 3. Tense Direct Speech Reported Speech present simple I like ice cream. She said (that) she liked ice cream. present continuous I am living in London. She said she was living in London. past simple I bought a car. She said she had bought a car OR She said she bought a car.
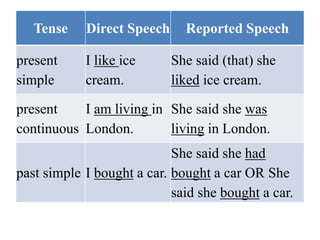
- 4. past continuous I was walking along the street. She said she had been walking along the street. present perfect I haven't seen Julie. She said she hadn't seen Julie. past perfect* I had taken English lessons before. She said she had take English lessons before. will I'll see you later. She said she would see me later.
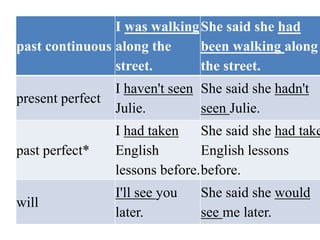
- 5. would* I would help, but.. She said she would help but... can I can speak perfect English. She said she could speak perfect English. could* I could swim when I was four. She said she could swim when she was four. shall I shall come later. She said she would come later.
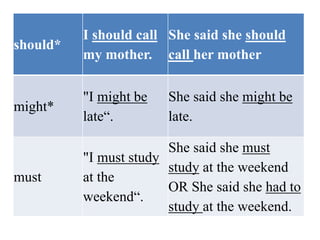
- 6. should* I should call my mother. She said she should call her mother might* "I might be lateâ. She said she might be late. must "I must study at the weekendâ. She said she must study at the weekend OR She said she had to study at the weekend.
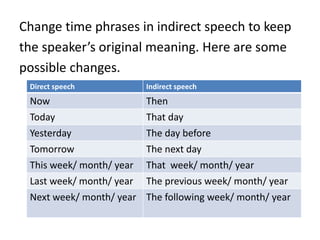
- 7. Change time phrases in indirect speech to keep the speakerâs original meaning. Here are some possible changes. Direct speech Indirect speech Now Then Today That day Yesterday The day before Tomorrow The next day This week/ month/ year That week/ month/ year Last week/ month/ year The previous week/ month/ year Next week/ month/ year The following week/ month/ year
- 8. Example: Sam: I just got home yesterday. Iâll start cleaning up tomorrow. Kate: He said that he had just gotten home the day before. He said he would start cleaning up the next day.
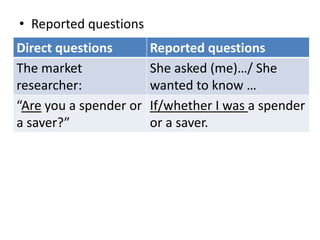
- 9. âĒ Reported questions Direct questions Reported questions The market researcher: She asked (me)âĶ/ She wanted to know âĶ âAre you a spender or a saver?â If/whether I was a spender or a saver.
- 10. âHow do you usually pay for things?â How I usually paid for things. âHow many times have you used a credit card?â How many times Iâd used a credit card. âCan one of your parents sign the application? â If/whether one of my parents could sign it.
- 11. Reported speech - simple statements â Exercise 1 Finish the sentences using Reported speech. Always change the tense, although it is sometimes not necessary. 1) John:"Mandy is at home." John said that Mandy was at home. 2) Max:"Frank often reads a book." Max told me that Frank often read a book. 3) Susan:"I'm watching TV." Susan said to me that she was watching TV.
- 12. 4) Simon:"David was ill." Simon said that David had been ill. 5) Peggy:"The girls helped in the house." Peggy told me that the girls had helped in the house. 6) Richard:"I am going to ride a skateboard." Richard said to me that he was going to ride a skateboard.
- 13. 7) Stephen and Claire:"We have cleaned the windows." Stephen and Claire told me that they had cleaned the windows. 8) Charles:"I didn't have time to do my homework." Charles remarked that he hadn't had time to do his homework. 9) Mrs Jones:"My mother will be 50 years old." Mrs Jones told me that her mother would be 50 years old. 10) Jean:"The boss must sign the letter." Jean said that the boss had to sign the letter.
- 14. Exercise on Reported Speech Questions - Exercise 2 Complete the sentences in reported speech. Note the change of pronouns and tenses. 1. "Where is my umbrella?" she asked. â She asked where her umbrella was. 2. "How are you?" Martin asked us. â Martin asked us how we were. 3. He asked, "Do I have to do it?" â He asked if he had to do it. 4. "Where have you been?" the mother asked her daughter. â The mother asked her daughter where she had been. 5. "Which dress do you like best?" she asked her boyfriend. â She asked her boyfriend which dress he liked best.
- 15. 6. "What are they doing?" she asked. â She wanted to know what they were doing. 7. "Are you going to the cinema?" he asked me. â He wanted to know if I was going to the cinema. 8. The teacher asked, "Who speaks English?" â The teacher wanted to know who spoke English. 9. "How do you know that?" she asked me. â She asked me how I knew that. 10. "Has Caron talked to Kevin?" my friend asked me. â My friend asked me if Caron had talked to Kevin.
- 16. Exercise 3 1. Mary "I love chocolate." Jill: "Mary said (that) she ___ chocolate.â a. loved b. loves c. loving 2. Mary: "I went skiing." Jill: "Mary said (that) she ___ skiing." a. went b. had gone c. have gone 3. Mary: "I will eat steak for dinner." Jill: "Mary said (that) she ___ eat steak for dinner." a. willing b. will c. would 4. Mary: "I have been to Sydney." Jill: "Mary said (that) she ___ to Sydney." a. had been b. has been c. was being
- 17. 5. Mary: "I have had three cars." Jill: "Mary said (that) she ___ three cars. a. has b. has had c. had had 6. Mary: "I'm going to go to Long Beach." Jill: "Mary said (that) she ___ going to go to Long Beach." a. is b. was c. went 7. Mary: "I don't like spinach." Jill: "Mary said (that) she ___ like spinach." a. doesn't b. don't c. didn't 8. Mary: "I have never been to London." Jill: "Mary said (that) she ___ never been to London." a. had b. has c. have
- 18. 9. Mary: "I was swimming." Jill: "Mary said (that) she ___ swimming. a. has been b. had been c. have been 10. Mary: "I had a cat." Jill: Mary said (that) she had ___ a cat." a. have b. has c. had 11. Mary: "I can't swim." Jill: "Mary said (that) she ___ swim." a. can't b. couldn't c. can not 12. Mary: "I won't buy a new car." Jill: "Mary said (that) she ___ by a new car." a. won't b. will c. wouldn't 13. Mary: "I have to do my laundry." Jill: "Mary said (that) she ___ to do her laundry." a. had b. has c. have