Transcription and translation
Download as ppt, pdf3 likes158 views
This document provides an overview of transcription and translation. It discusses how DNA is transcribed into mRNA, which is then translated into proteins. Transcription occurs in the nucleus and involves RNA polymerase making a complementary mRNA copy of a DNA sequence. The mRNA then undergoes processing before being exported to the cytoplasm. Translation takes place on ribosomes, where tRNA brings amino acids specified by mRNA codons to form a polypeptide chain. The genetic code maps codons to their corresponding amino acids.
1 of 31
Downloaded 11 times











Ad
Recommended
Unit B7 8 Protein Synthesis
Unit B7 8 Protein Synthesissciencechris
╠²
The document provides information about protein synthesis, including:
1. Protein synthesis involves transcription of DNA into mRNA in the nucleus, and translation of mRNA into proteins at ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
2. Key molecules involved include DNA, mRNA, tRNA, ribosomes, and amino acids. DNA contains the genetic code. mRNA carries the code to the ribosomes. tRNA brings amino acids and pairs with mRNA codons.
3. Transcription and translation involve initiation, elongation, and termination steps. During transcription, RNA polymerase copies DNA onto mRNA. During translation, ribosomes read mRNA and link amino acids using tRNA.Rna and protein synthesis
Rna and protein synthesisMuhmmad Asif
╠²
1. The document describes the three main steps in protein synthesis: transcription, RNA processing, and translation.
2. Transcription involves copying a segment of DNA into a complementary mRNA molecule. RNA processing removes introns from pre-mRNA, joining exons to create mature mRNA.
3. Translation uses the mRNA to sequence amino acids via tRNA molecules on ribosomes, forming proteins according to the genetic code.Protein synthesis with turning point
Protein synthesis with turning pointtas11244
╠²
DNA contains genes that code for proteins. Proteins are made of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. There are 20 different amino acids. An amino acid chain is called a polypeptide. DNA is found in the nucleus, while proteins are made in the cytoplasm of cells by ribosomes. The process of protein synthesis begins with transcription of DNA into mRNA, which is then translated by ribosomes into a polypeptide chain. There are three main types of RNA involved in protein synthesis: mRNA carries the genetic code to ribosomes, rRNA makes up ribosomes, and tRNA transfers amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain.Transcription and translation
Transcription and translationsikojp
╠²
The document discusses gene regulation and the central dogma of biology. It explains that genes can be switched on or off, with some genes used by cells and others not. A gene has an operator region that binds a repressor protein, preventing RNA polymerase from initiating transcription when the repressor is bound (gene is off). When the repressor is not bound, RNA polymerase can initiate transcription (gene is on). The central dogma holds that DNA is transcribed into RNA which is translated into protein.Rna And Protein Synthesis Ss
Rna And Protein Synthesis SsLeslie Smith
╠²
This document summarizes RNA and protein synthesis. It describes that DNA is made of nucleotides and has a double helix structure. During transcription, RNA polymerase builds an RNA strand that is complementary to DNA. The RNA can be messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), or ribosomal RNA (rRNA). mRNA carries the genetic code from the nucleus to the ribosome. During translation, mRNA matches up with tRNA to add amino acids together and form a protein according to the mRNA's code.Central dogma and transcription slides
Central dogma and transcription slidesQuanina Quan
╠²
The document discusses the central dogma of molecular biology and transcription, specifically describing the process of transcription which involves DNA being used as a template to produce a complementary RNA copy. It explains transcription occurs differently in eukaryotes versus prokaryotes, with the main steps being initiation, elongation, and termination for both, though eukaryotes have additional post-transcriptional modification steps.Transcription
TranscriptionDr.M.Prasad Naidu
╠²
This document provides information about transcription in prokaryotes. It defines transcription as the synthesis of RNA using single-stranded DNA as a template. It describes the basic requirements for transcription including the template, enzyme, regulatory proteins, ribonucleoside triphosphates, and energy. It then explains the three main steps of transcription - initiation, elongation, and termination - and provides details about each step. The document also discusses transcription regulation and inhibitors like rifampicin and actinomycin D.Protein synthesis
Protein synthesis jmpettis10
╠²
This document discusses RNA and protein synthesis. It describes the three main types of RNA - mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA - and their functions. mRNA carries instructions from DNA to the cytoplasm, rRNA binds to mRNA and helps assemble amino acids, and tRNA supplies amino acids. The document then explains how RNA is made, compares RNA and DNA structures, and outlines the process of transcription of DNA to mRNA and translation of mRNA to proteins with the help of tRNA and rRNA.Translation
TranslationMicrobiology
╠²
Translation, transcription, and transduction are processes involved in gene expression and DNA transfer. Translation is the process by which messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded by ribosomes to produce a polypeptide. Transcription is the process where DNA is copied into mRNA by RNA polymerase. Transduction is the transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another mediated by bacteriophages through generalized or specialized transduction. These processes play important roles in protein production and genetic exchange.Protein syntheisis 2016
Protein syntheisis 2016Calleva912
╠²
DNA is transcribed into mRNA which carries the genetic code from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules match up with mRNA codons through complementary base pairing and bring the corresponding amino acids. The mRNA attaches to a ribosome where tRNA molecules deliver amino acids in the correct order for protein assembly as the ribosome moves along the mRNA. This process of protein synthesis translates the genetic code into proteins that carry out the functions specified by the DNA.Translation mutation ppt
Translation mutation pptlvilleDrFox
╠²
No, not all mutations are passed on to the next generation. Mutations that occur in somatic (non-reproductive) cells are not passed on, while mutations in germline (reproductive) cells have the potential to be inherited by offspring.Biology trancription translation
Biology trancription translationroufieh
╠²
Transcription is the process of copying a section of DNA into a complementary strand of mRNA. Translation is the decoding of an mRNA message into a polypeptide chain by a ribosome, starting at a START codon and stopping at a STOP codon. The document provides an overview of transcription and translation and encourages practicing replicating DNA, mRNA, tRNA, and protein sequences.12.3 DNA - RNA - Amino Acid - Protein
12.3 DNA - RNA - Amino Acid - Proteinsbcvmi06
╠²
RNA and protein synthesis involves two main steps: transcription and translation. During transcription, DNA is used as a template to produce mRNA through the enzymatic action of RNA polymerase. The mRNA then leaves the nucleus and binds to ribosomes for translation. During translation, tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosome according to the mRNA codon sequence. The amino acids are linked together to form a polypeptide or protein chain. Translation stops when a stop codon is reached.Gene Expression/ Protein Synthesis
Gene Expression/ Protein SynthesisRobin Seamon
╠²
1. DNA contains the genetic code and instructions for making proteins, which it stores in the cell nucleus. 2. During transcription, RNA polymerase copies DNA into messenger RNA (mRNA) which carries the code to the cytoplasm. 3. In translation, ribosomes use mRNA to produce proteins according to the genetic code by linking amino acids specified by mRNA codons. 4. Newly formed proteins travel to the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi body for processing and packaging before use in the cell.Protein Syntesis
Protein SyntesisAlvaro Lafuente
╠²
The document explains the process of protein synthesis, detailing the roles of DNA, mRNA, and tRNA. It describes how mRNA carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes, where ribosomes synthesize proteins by assembling amino acids in the correct order based on the mRNA sequence. The document highlights the importance of tRNA as an adapter molecule during translation, linking amino acids to the mRNA template.Gene expression/ RNA & Protein Synthesis
Gene expression/ RNA & Protein SynthesisRobin Seamon
╠²
1. DNA contains the genetic instructions and is located in the nucleus.
2. During transcription, DNA is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA) by RNA polymerase.
3. The mRNA carries the genetic message to the cytoplasm where protein synthesis occurs through translation.
4. During translation, transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomes in the cytoplasm work together to assemble amino acids into proteins based on the mRNA instructions.Protein Syntheis
Protein Syntheisallyjer
╠²
A gene is selected for protein production and RNA polymerase unwinds the DNA at that gene. It uses one DNA strand as a template to produce mRNA through transcription. The primary mRNA transcript is processed to remove introns, leaving exons that are spliced together. The mature mRNA then binds to ribosomes for translation, where tRNA matches its anticodon to mRNA codons and carries the corresponding amino acids. The ribosome catalyzes peptide bond formation between amino acids specified by mRNA to produce the protein.Transcription and Translation PowerPoint
Transcription and Translation PowerPointBiologyIB
╠²
Transcription is the process of making mRNA from DNA. It involves RNA polymerase making an mRNA complementary copy of the DNA strand. Translation is the process of using the mRNA to produce a polypeptide by linking amino acids specified by the mRNA codons. During transcription, introns are removed from pre-mRNA and exons are joined to form mature mRNA. If the parent DNA strand is A A T G C A G T, the complementary mRNA strand will be U U A C G U C A.Protein Synthesis
Protein Synthesisncvpselise
╠²
The document discusses how genetic information passes from DNA to proteins. It explains that the DNA code is transcribed into mRNA, which is then translated by ribosomes into proteins. During translation, the mRNA codons bind to complementary tRNA anticodons, which bring amino acids. The amino acids are linked together to form a polypeptide chain, which then folds into a functional protein that carries out the genetic trait specified by the DNA.Protein synthesis
Protein synthesisAftab Badshah
╠²
The document summarizes the process of protein synthesis which occurs in two main steps: transcription and translation. During transcription, DNA is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA) in the cell nucleus. The mRNA then transports the genetic code to the cytoplasm where ribosomes read the mRNA during translation and assemble amino acids to make a protein based on the code. Transfer RNA molecules deliver amino acids to the ribosome and assemble them into a protein chain based on the mRNA codons.Protein synthesis
Protein synthesisnidhiinjbp
╠²
The document summarizes the process of protein synthesis in three main steps: transcription, translation, and termination. During transcription, RNA polymerase makes an mRNA copy of a DNA sequence. Translation then uses the mRNA to assemble a polypeptide chain via tRNAs and ribosomes. Termination occurs when a stop codon signals the release of the completed protein chain. The central dogma of biology is demonstrated as DNA is transcribed to mRNA which is then translated to protein.AP Bio Ch 17 part 1 translation
AP Bio Ch 17 part 1 translationStephanie Beck
╠²
This document provides an overview of transcription in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. It discusses how DNA serves as a template for RNA production. The three main stages of transcription are initiation, elongation, and termination. In eukaryotes, the pre-mRNA undergoes processing including 5' capping, poly-A tail addition, and splicing of introns before becoming a functional mRNA that can be translated into a protein.Rna protein-synthesis
Rna protein-synthesislegoscience
╠²
This document discusses RNA, ribosomes, and protein synthesis. It explains that DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA, which directs the process of translation where transfer RNA and ribosomes work together to assemble amino acids into proteins according to the genetic code stored in DNA. The central dogma of molecular biology is that DNA makes RNA makes protein, with three types of RNA - messenger RNA, transfer RNA, and ribosomal RNA - all playing important roles in the transfer of genetic information from DNA to protein.12.3 dna, rna, and protein
12.3 dna, rna, and proteinkathy_lambert
╠²
This document explains how DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA and then translated into proteins. It begins by establishing that DNA contains the genetic instructions, which are passed to RNA and then proteins. It then describes transcription, where DNA is copied into messenger RNA in the nucleus. The document explains how messenger RNA carries the genetic code to the cytoplasm to be translated by ribosomes into proteins, using transfer RNA to match mRNA codons to amino acids. In summary, it outlines the central dogma of molecular biology - that DNA is transcribed into RNA and then translated into functional proteins.AP Bio Ch 17 part 2 translation
AP Bio Ch 17 part 2 translationStephanie Beck
╠²
The document summarizes key concepts about translation - the process by which the genetic code is translated into proteins. It discusses how the genetic code uses triplets of nucleotides (codons) to specify 20 different amino acids. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules carry specific amino acids and interpret the codons by base-pairing between the tRNA's anticodon and the mRNA codon. Ribosomes facilitate the assembly of amino acids into a polypeptide chain according to the mRNA sequence. The stages of translation include initiation, elongation through multiple cycles of codon recognition and peptide bond formation, and termination when a stop codon is reached. Point mutations can cause substitutions, insertions or deletions of nucleotides and affect protein structure.Rna and protein synthesis
Rna and protein synthesisWenny Wang Wu
╠²
RNA plays an essential role in protein synthesis by carrying copies of DNA's instructions from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. There are three main types of RNA: messenger RNA carries copies of genes to ribosomes for protein assembly, ribosomal RNA is a component of ribosomes, and transfer RNA transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis. The process of protein synthesis involves transcription of DNA to mRNA in the nucleus, followed by translation of mRNA's codons into amino acids on ribosomes in the cytoplasm.Wtk apbi och17genetoprotein
Wtk apbi och17genetoproteinsbarkanic
╠²
This document summarizes the central dogma of molecular biology - that DNA is transcribed into RNA which is then translated into proteins. It describes the three types of RNA (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA) and their roles in protein synthesis. The process of transcription in the nucleus and translation on ribosomes in the cytoplasm is explained in detail, including the key steps of initiation, elongation and termination. The roles of various enzymes and molecular players like RNA polymerase, spliceosomes, and signal recognition particles are outlined. Finally, it briefly discusses post-translational modification of proteins and types of mutations that can occur.Biology lecture 5
Biology lecture 5Etugen
╠²
The document discusses protein synthesis which involves two main phases - transcription and translation. Transcription occurs in the nucleus and involves the DNA being used as a template to produce mRNA. The mRNA then undergoes processing before being exported to the cytoplasm where translation occurs, involving ribosomes and tRNA to link amino acids together using the mRNA as a template to produce a protein.Transcriptionand translation
Transcriptionand translationAmy Allen
╠²
Transcription is the process of copying information from DNA to mRNA. Translation is the process of using the mRNA code to assemble a protein. The genetic code links codons, which are three nucleotide sequences in mRNA, to specific amino acids. tRNA molecules match codons to their corresponding amino acids and deliver them to the ribosome for protein assembly.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Translation
TranslationMicrobiology
╠²
Translation, transcription, and transduction are processes involved in gene expression and DNA transfer. Translation is the process by which messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded by ribosomes to produce a polypeptide. Transcription is the process where DNA is copied into mRNA by RNA polymerase. Transduction is the transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another mediated by bacteriophages through generalized or specialized transduction. These processes play important roles in protein production and genetic exchange.Protein syntheisis 2016
Protein syntheisis 2016Calleva912
╠²
DNA is transcribed into mRNA which carries the genetic code from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules match up with mRNA codons through complementary base pairing and bring the corresponding amino acids. The mRNA attaches to a ribosome where tRNA molecules deliver amino acids in the correct order for protein assembly as the ribosome moves along the mRNA. This process of protein synthesis translates the genetic code into proteins that carry out the functions specified by the DNA.Translation mutation ppt
Translation mutation pptlvilleDrFox
╠²
No, not all mutations are passed on to the next generation. Mutations that occur in somatic (non-reproductive) cells are not passed on, while mutations in germline (reproductive) cells have the potential to be inherited by offspring.Biology trancription translation
Biology trancription translationroufieh
╠²
Transcription is the process of copying a section of DNA into a complementary strand of mRNA. Translation is the decoding of an mRNA message into a polypeptide chain by a ribosome, starting at a START codon and stopping at a STOP codon. The document provides an overview of transcription and translation and encourages practicing replicating DNA, mRNA, tRNA, and protein sequences.12.3 DNA - RNA - Amino Acid - Protein
12.3 DNA - RNA - Amino Acid - Proteinsbcvmi06
╠²
RNA and protein synthesis involves two main steps: transcription and translation. During transcription, DNA is used as a template to produce mRNA through the enzymatic action of RNA polymerase. The mRNA then leaves the nucleus and binds to ribosomes for translation. During translation, tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosome according to the mRNA codon sequence. The amino acids are linked together to form a polypeptide or protein chain. Translation stops when a stop codon is reached.Gene Expression/ Protein Synthesis
Gene Expression/ Protein SynthesisRobin Seamon
╠²
1. DNA contains the genetic code and instructions for making proteins, which it stores in the cell nucleus. 2. During transcription, RNA polymerase copies DNA into messenger RNA (mRNA) which carries the code to the cytoplasm. 3. In translation, ribosomes use mRNA to produce proteins according to the genetic code by linking amino acids specified by mRNA codons. 4. Newly formed proteins travel to the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi body for processing and packaging before use in the cell.Protein Syntesis
Protein SyntesisAlvaro Lafuente
╠²
The document explains the process of protein synthesis, detailing the roles of DNA, mRNA, and tRNA. It describes how mRNA carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes, where ribosomes synthesize proteins by assembling amino acids in the correct order based on the mRNA sequence. The document highlights the importance of tRNA as an adapter molecule during translation, linking amino acids to the mRNA template.Gene expression/ RNA & Protein Synthesis
Gene expression/ RNA & Protein SynthesisRobin Seamon
╠²
1. DNA contains the genetic instructions and is located in the nucleus.
2. During transcription, DNA is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA) by RNA polymerase.
3. The mRNA carries the genetic message to the cytoplasm where protein synthesis occurs through translation.
4. During translation, transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomes in the cytoplasm work together to assemble amino acids into proteins based on the mRNA instructions.Protein Syntheis
Protein Syntheisallyjer
╠²
A gene is selected for protein production and RNA polymerase unwinds the DNA at that gene. It uses one DNA strand as a template to produce mRNA through transcription. The primary mRNA transcript is processed to remove introns, leaving exons that are spliced together. The mature mRNA then binds to ribosomes for translation, where tRNA matches its anticodon to mRNA codons and carries the corresponding amino acids. The ribosome catalyzes peptide bond formation between amino acids specified by mRNA to produce the protein.Transcription and Translation PowerPoint
Transcription and Translation PowerPointBiologyIB
╠²
Transcription is the process of making mRNA from DNA. It involves RNA polymerase making an mRNA complementary copy of the DNA strand. Translation is the process of using the mRNA to produce a polypeptide by linking amino acids specified by the mRNA codons. During transcription, introns are removed from pre-mRNA and exons are joined to form mature mRNA. If the parent DNA strand is A A T G C A G T, the complementary mRNA strand will be U U A C G U C A.Protein Synthesis
Protein Synthesisncvpselise
╠²
The document discusses how genetic information passes from DNA to proteins. It explains that the DNA code is transcribed into mRNA, which is then translated by ribosomes into proteins. During translation, the mRNA codons bind to complementary tRNA anticodons, which bring amino acids. The amino acids are linked together to form a polypeptide chain, which then folds into a functional protein that carries out the genetic trait specified by the DNA.Protein synthesis
Protein synthesisAftab Badshah
╠²
The document summarizes the process of protein synthesis which occurs in two main steps: transcription and translation. During transcription, DNA is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA) in the cell nucleus. The mRNA then transports the genetic code to the cytoplasm where ribosomes read the mRNA during translation and assemble amino acids to make a protein based on the code. Transfer RNA molecules deliver amino acids to the ribosome and assemble them into a protein chain based on the mRNA codons.Protein synthesis
Protein synthesisnidhiinjbp
╠²
The document summarizes the process of protein synthesis in three main steps: transcription, translation, and termination. During transcription, RNA polymerase makes an mRNA copy of a DNA sequence. Translation then uses the mRNA to assemble a polypeptide chain via tRNAs and ribosomes. Termination occurs when a stop codon signals the release of the completed protein chain. The central dogma of biology is demonstrated as DNA is transcribed to mRNA which is then translated to protein.AP Bio Ch 17 part 1 translation
AP Bio Ch 17 part 1 translationStephanie Beck
╠²
This document provides an overview of transcription in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. It discusses how DNA serves as a template for RNA production. The three main stages of transcription are initiation, elongation, and termination. In eukaryotes, the pre-mRNA undergoes processing including 5' capping, poly-A tail addition, and splicing of introns before becoming a functional mRNA that can be translated into a protein.Rna protein-synthesis
Rna protein-synthesislegoscience
╠²
This document discusses RNA, ribosomes, and protein synthesis. It explains that DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA, which directs the process of translation where transfer RNA and ribosomes work together to assemble amino acids into proteins according to the genetic code stored in DNA. The central dogma of molecular biology is that DNA makes RNA makes protein, with three types of RNA - messenger RNA, transfer RNA, and ribosomal RNA - all playing important roles in the transfer of genetic information from DNA to protein.12.3 dna, rna, and protein
12.3 dna, rna, and proteinkathy_lambert
╠²
This document explains how DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA and then translated into proteins. It begins by establishing that DNA contains the genetic instructions, which are passed to RNA and then proteins. It then describes transcription, where DNA is copied into messenger RNA in the nucleus. The document explains how messenger RNA carries the genetic code to the cytoplasm to be translated by ribosomes into proteins, using transfer RNA to match mRNA codons to amino acids. In summary, it outlines the central dogma of molecular biology - that DNA is transcribed into RNA and then translated into functional proteins.AP Bio Ch 17 part 2 translation
AP Bio Ch 17 part 2 translationStephanie Beck
╠²
The document summarizes key concepts about translation - the process by which the genetic code is translated into proteins. It discusses how the genetic code uses triplets of nucleotides (codons) to specify 20 different amino acids. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules carry specific amino acids and interpret the codons by base-pairing between the tRNA's anticodon and the mRNA codon. Ribosomes facilitate the assembly of amino acids into a polypeptide chain according to the mRNA sequence. The stages of translation include initiation, elongation through multiple cycles of codon recognition and peptide bond formation, and termination when a stop codon is reached. Point mutations can cause substitutions, insertions or deletions of nucleotides and affect protein structure.Rna and protein synthesis
Rna and protein synthesisWenny Wang Wu
╠²
RNA plays an essential role in protein synthesis by carrying copies of DNA's instructions from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. There are three main types of RNA: messenger RNA carries copies of genes to ribosomes for protein assembly, ribosomal RNA is a component of ribosomes, and transfer RNA transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis. The process of protein synthesis involves transcription of DNA to mRNA in the nucleus, followed by translation of mRNA's codons into amino acids on ribosomes in the cytoplasm.Wtk apbi och17genetoprotein
Wtk apbi och17genetoproteinsbarkanic
╠²
This document summarizes the central dogma of molecular biology - that DNA is transcribed into RNA which is then translated into proteins. It describes the three types of RNA (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA) and their roles in protein synthesis. The process of transcription in the nucleus and translation on ribosomes in the cytoplasm is explained in detail, including the key steps of initiation, elongation and termination. The roles of various enzymes and molecular players like RNA polymerase, spliceosomes, and signal recognition particles are outlined. Finally, it briefly discusses post-translational modification of proteins and types of mutations that can occur.Biology lecture 5
Biology lecture 5Etugen
╠²
The document discusses protein synthesis which involves two main phases - transcription and translation. Transcription occurs in the nucleus and involves the DNA being used as a template to produce mRNA. The mRNA then undergoes processing before being exported to the cytoplasm where translation occurs, involving ribosomes and tRNA to link amino acids together using the mRNA as a template to produce a protein.Similar to Transcription and translation (20)
Transcriptionand translation
Transcriptionand translationAmy Allen
╠²
Transcription is the process of copying information from DNA to mRNA. Translation is the process of using the mRNA code to assemble a protein. The genetic code links codons, which are three nucleotide sequences in mRNA, to specific amino acids. tRNA molecules match codons to their corresponding amino acids and deliver them to the ribosome for protein assembly.Protein Synthesis Worksheet for Grade 10
Protein Synthesis Worksheet for Grade 10MichelleBaguio6
╠²
The document provides an overview of protein synthesis, explaining the roles of proteins, the functions of DNA and RNA, and the stages of transcription and translation in protein production. It details the structures of DNA and RNA, their nucleotide components, and the genetic codes involved in forming amino acids. Additionally, it includes activities and assessments to reinforce understanding of the processes and terminology associated with protein synthesis.Molec cellextracredit
Molec cellextracreditbabbileo
╠²
DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA) in the cell nucleus. The mRNA is then transported out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm, where it is translated into a protein with the help of transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomes. Transcription and translation are the two main steps by which the genetic code stored in DNA is used to synthesize proteins according to the DNA instructions.Transcription and Translation _ Biology
Transcription and Translation _ BiologyConnorEngland5
╠²
This document discusses the processes of transcription and translation. It begins by explaining that DNA contains the genetic template for proteins and is located in the nucleus, while protein synthesis occurs in the cytoplasm. It then describes the two main processes:
1. Transcription - the genetic template on DNA is copied and carried out of the nucleus to the cytoplasm in the form of mRNA.
2. Translation - the mRNA template serves as a series of codes that specifies the amino acid sequence of the protein. tRNAs bring amino acids to the ribosome based on complementary base pairing between the mRNA codon and the tRNA anticodon. Enzymes link the amino acids together to form the protein chain.Transcription and Translation
Transcription and TranslationReginald V. Finley Sr. M.Ed.
╠²
The document explains the processes of transcription and translation in the context of DNA and RNA. It details how DNA is transcribed into mRNA by RNA polymerase, which then travels to the ribosome for translation into proteins via tRNA bringing amino acids. Key distinctions between DNA and RNA, and the roles of different types of RNA are also highlighted.Central Dogma of DNA ANDRES
Central Dogma of DNA ANDRESLeha Andres
╠²
This document explains the process of protein synthesis, detailing how DNA codes for proteins through the intermediary steps of transcription and translation. It describes the roles of various types of RNA, including messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer RNA, as well as the structure of amino acids and the genetic code that translates nucleotide sequences into protein. The document provides a comprehensive overview of how proteins are built from polypeptides and the necessary processes involved in these cellular functions.Protein Synthesis.pptx
Protein Synthesis.pptxFarawahidaAZaharin
╠²
DNA contains genes that code for proteins. During transcription, mRNA is synthesized using DNA as a template. mRNA then directs protein synthesis during translation. Translation occurs in the ribosome and involves tRNA, rRNA, and amino acids. The mRNA codons are read three bases at a time by tRNA which brings the corresponding amino acids. The amino acids are linked together to form a polypeptide chain until a stop codon is reached, terminating translation.Protein Synthesis ppt. Genes DNA explained
Protein Synthesis ppt. Genes DNA explainedbmuhindo
╠²
The document outlines the process of protein synthesis, explaining how DNA contains genes that are transcribed into mRNA, which then translates to proteins in the cytoplasm. It details roles of RNA types, including mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA, and describes transcription and translation as key phases in protein formation. Additionally, it emphasizes the genetic code's role in determining amino acid sequences and the importance of mRNA processing.Transcription-and-Translation Science 10.pptx
Transcription-and-Translation Science 10.pptxHglainidLynAntolinEs
╠²
The document explains the process of protein synthesis, detailing how DNA in the nucleus is transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA) before being translated into proteins at the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. It outlines the steps of transcription, including initiation, elongation, and termination, as well as the subsequent translation process where mRNA codons correspond to specific amino acids. Additionally, the document compares DNA and RNA, highlighting their structural differences and the role of various types of RNA in the synthesis process.Gene expression---(Biochem)
Gene expression---(Biochem)Soft-Learners
╠²
Gene expression involves two main steps - transcription and translation. During transcription, DNA is copied into mRNA with the help of RNA polymerase. Translation then uses the mRNA to assemble amino acids into proteins with the help of tRNA and rRNA. Though genes code for traits, there is not a simple one-to-one relationship due to various regulatory factors.transcription and rna
transcription and rna Dr-HAMDAN
╠²
The document discusses transcription and protein synthesis. It explains that DNA contains the genetic code to make proteins, and transcription is the process of copying this code from DNA to mRNA in the nucleus. Translation then uses the mRNA code to assemble amino acids in the cytoplasm. The key steps are: 1) DNA unzips and mRNA nucleotides pair with the DNA template, 2) mRNA exits the nucleus where ribosomes read its code 3) Transfer RNA delivers amino acids to the ribosome based on mRNA codons to form a polypeptide chain. Mutations can occur during transcription or DNA replication and result in substitutions, deletions or insertions of genetic code.Molecular Genetics: Protein Synthesis
Molecular Genetics: Protein Synthesisvjcummins
╠²
DNA contains genes that code for proteins. During protein synthesis, the DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA) in the cell nucleus. The mRNA then transports the protein coding instructions to the cytoplasm where ribosomes read the mRNA to produce proteins. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules match to the mRNA codons and bring the corresponding amino acids. The amino acids are linked together on the ribosome to form the protein chain according to the mRNA instructions.Chapter 7 - DNA to Protein.ppt
Chapter 7 - DNA to Protein.pptahmedisseali
╠²
DNA acts as a template for protein production. It is transcribed into mRNA which is then translated into protein with the help of tRNA and ribosomes. Transcription occurs in the nucleus and copies DNA into RNA. Translation occurs in the cytoplasm and uses mRNA to assemble amino acids into a protein chain based on the genetic code. Gene expression can be regulated at the transcriptional or translational level to control the amount of protein produced.gene expression.ppt
gene expression.pptMedical Knowledge
╠²
Gene expression involves two main steps - transcription and translation. During transcription, DNA is copied into mRNA with the help of RNA polymerase. Translation then uses the mRNA to assemble amino acids into proteins with the help of tRNA and rRNA. The genetic code uses three-letter codons in DNA and mRNA to specify each amino acid. However, the relationship between genes and traits is complex as multiple factors influence gene expression.Transcription and Translation part 2.ppt
Transcription and Translation part 2.pptmikeebio1
╠²
Protein synthesis involves two main processes - transcription and translation. In transcription, the DNA message is converted into mRNA in the nucleus. In translation, the mRNA message is used to assemble amino acids into a protein chain. Key elements that aid these processes include RNA polymerase which synthesizes mRNA, transfer RNA (tRNA) which translates mRNA codons into amino acids, and ribosomes which are the sites of protein synthesis in the cell.Transcription and Translation part 2.ppt
Transcription and Translation part 2.pptmikeebio1
╠²
Protein synthesis involves two main processes - transcription and translation. In transcription, the DNA message is converted into mRNA in the nucleus. In translation, the mRNA message is used to assemble amino acids into a protein chain. Key elements that aid these processes include RNA polymerase which synthesizes mRNA, transfer RNA (tRNA) which translates mRNA codons into amino acids, and ribosomes which are the sites of protein synthesis in the cell.Q3 W3 Ppt 4.1 Protein Synthesis-1.pdf
Q3 W3 Ppt 4.1 Protein Synthesis-1.pdfxeniavi
╠²
The document discusses protein synthesis, which involves transcription and translation. Transcription occurs in the nucleus and involves RNA polymerase making an mRNA copy of a gene from DNA. The mRNA then undergoes processing and modification before being exported to the cytoplasm. Translation happens in the cytoplasm using ribosomes, where the mRNA sequence is read to create a polypeptide chain according to the genetic code. The genetic code is carried by DNA to RNA to proteins, which give organisms their unique traits.Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Primary and Secondary immune modulation.pptx
Primary and Secondary immune modulation.pptxdevikasanalkumar35
╠²
Primary and secondary immune modulation
International Journal of Pharmacological Sciences (IJPS)
International Journal of Pharmacological Sciences (IJPS)journalijps98
╠²
Call for Research Articles.!!!
FREE PUBLICATION CHARGES
International Journal of Pharmacological Sciences (IJPS)
Webpage URL : https://www.wireilla.com/medical/IJPS/index.html
Wikicfp Url:http://www.wikicfp.com/cfp/servlet/event.showcfp?eventid=181292©ownerid=33993
Authors are invited to submit papers through the Journal Submission System
http://allcfps.com/wireilla/submission/index.php
Submission Deadline : June 17, 2025
Contact Us
Here's where you can reach us : journalijps98@gmail.com or ijpsjournal@wireilla.comIntroductory Material for Markov-chain Description of Abzymes Catalysis
Introductory Material for Markov-chain Description of Abzymes CatalysisOrchidea Maria Lecian
╠²
speaker: Orchidea Maria Lecian
Authors: Orchidea Maria Lecian, seergey Suchkov
Title: Introductory Material for
Markov-chain Description of Abzymes Catalysis
Talk presented at the International Symposium on
Public Health and Epidemiology and
Immunology Research
12-13 June 2025, Rome, Italy on 13 June 2025.GBSN_ Unit 1 - Introduction to Microbiology
GBSN_ Unit 1 - Introduction to MicrobiologyAreesha Ahmad
╠²
Microbiology for Nursing students - According to New PNC course curriculum - 2025CULTIVATION - HARVESTING - PROCESSING - STORAGE -.pdf
CULTIVATION - HARVESTING - PROCESSING - STORAGE -.pdfNistarini College, Purulia (W.B) India
╠²
This presentation offers a brief idea about the cultivation, processing, storage and marketing of medicinal plants for the health care practices in sustainable health. The role of different factors has been assessed for the same.Cloud Collaboration Market Challenges, Drivers, Trends, and Forecast by 2031
Cloud Collaboration Market Challenges, Drivers, Trends, and Forecast by 2031moresonali406
╠²
The report is segmented by Component (Solution, Service); Deployment (Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Hybrid Cloud); Organization Size (Large Enterprises, Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)); Vertical (BFSI, Consumer Goods And Retail, Education, Government and Public Sector, Healthcare and Life Sciences, Manufacturing, Media and Entertainment, Telecommunication and ITES, Others). The global analysis is further broken-down at regional level and major countries. The report offers the value in USD for the above analysis and segmentsIntroduction to Microbiology and Microscope
Introduction to Microbiology and Microscopevaishrawan1
╠²
This presentation describe about the types of microscope, history and development of microscope and microbiology. Especially focus on Structure & Morphology of BacteriaPathophysiology_Unit1_BPharm CELL INJURY
Pathophysiology_Unit1_BPharm CELL INJURYKRUTIKA CHANNE
╠²
Basic principles of Cell injury and Adaptation:
Introduction, definitions, Homeostasis, Components and Types of Feedback systems, Causes of cellular injury, Pathogenesis (Cell membrane damage, Mitochondrial damage, Ribosome damage, Nuclear damage), Morphology of cell injury ŌĆō Adaptive changes (Atrophy, Hypertrophy, hyperplasia, Metaplasia, Dysplasia), Cell swelling, Intra cellular accumulation, Calcification, Enzyme leakage and Cell Death, Acidosis &Alkalosis, Electrolyte imbalance
Science 8 Quarter 4 first quiz digestive system.docx
Science 8 Quarter 4 first quiz digestive system.docxjunefermunez
╠²
Quiz for the topic Digestive System. 4th QaurterMatt Ridley: Economic Evolution and Ideas that have Sex
Matt Ridley: Economic Evolution and Ideas that have SexConservative Institute / Konzervat├Łvny in┼Ītit├║t M. R. ┼Ātef├Īnika
╠²
Matt Ridley is a British independent science popularizer, journalist, entrepreneur, and author of several bestselling books, for which he has received numerous awards. He focuses primarily on the economic, biological, and environmental dimensions of the spontaneous functioning and advancement of human society. GBSN__Unit 2 - Control of Microorganisms
GBSN__Unit 2 - Control of MicroorganismsAreesha Ahmad
╠²
Microbiology for Nursing students - According to New PNC course curriculum - 2025
Matt Ridley: Economic Evolution and Ideas that have Sex
Matt Ridley: Economic Evolution and Ideas that have SexConservative Institute / Konzervat├Łvny in┼Ītit├║t M. R. ┼Ātef├Īnika
╠²
Ad
Transcription and translation
- 1. Transcription and Translation Copying DNA Translating RNA into Proteins
- 2. Questions to be answered today ’éĪ How do we get from the bases found in DNA to amino acids? ’éĪ How do we get from a bunch of amino acids to proteins? DNA Amino Acids Proteins?
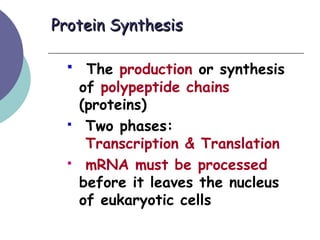
- 3. Protein SynthesisProtein Synthesis ’é¦ The production or synthesis of polypeptide chains (proteins) ’é¦ Two phases: Transcription & Translation ’é¦ mRNA must be processed before it leaves the nucleus of eukaryotic cells
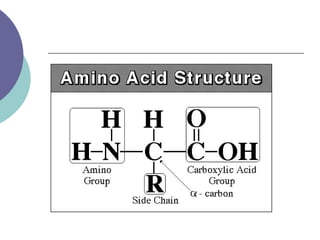
- 4. Protein Structure ’éĪ Made up of amino acids ’éĪ Polypeptide- string of amino acids ’éĪ 20 amino acids are arranged in different orders to make a variety of proteins ’éĪ Assembled on a ribosome
- 6. Replication Review ŌĆóDNA double helix unwinds ŌĆóDNA now single-stranded ŌĆóNew DNA strand forms using complementary base pairing (A-T, C-G) ŌĆóUsed to prepare DNA for cell division ŌĆóWhole genome copied/replicated
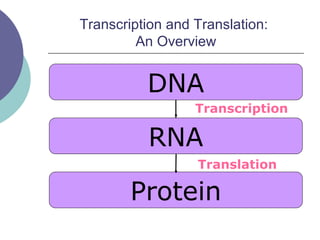
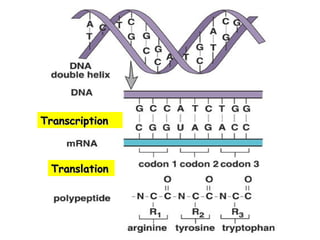
- 7. Transcription and Translation: An Overview DNA RNA Protein Transcription Translation
- 8. Roles of RNA and DNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan ’éĪ Transcription and Translation - PBS
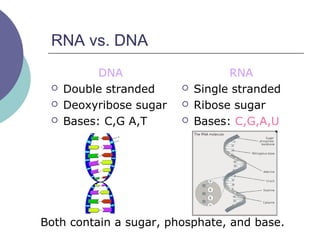
- 9. RNA vs. DNA DNA ’éĪ Double stranded ’éĪ Deoxyribose sugar ’éĪ Bases: C,G A,T RNA ’éĪ Single stranded ’éĪ Ribose sugar ’éĪ Bases: C,G,A,U Both contain a sugar, phosphate, and base.
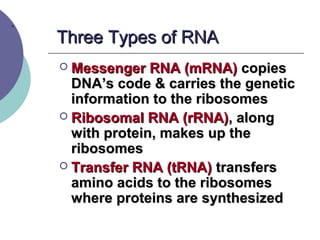
- 10. . Three Types of RNAThree Types of RNA ’éĪ Messenger RNA (mRNA)Messenger RNA (mRNA) copiescopies DNAŌĆÖs code & carries the geneticDNAŌĆÖs code & carries the genetic information to the ribosomesinformation to the ribosomes ’éĪ Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)Ribosomal RNA (rRNA), along, along with protein, makes up thewith protein, makes up the ribosomesribosomes ’éĪ Transfer RNA (tRNA)Transfer RNA (tRNA) transferstransfers amino acids to the ribosomesamino acids to the ribosomes where proteins are synthesizedwhere proteins are synthesized
- 11. Three Types of RNAThree Types of RNA ’éĪ How do you remember the 3 types?
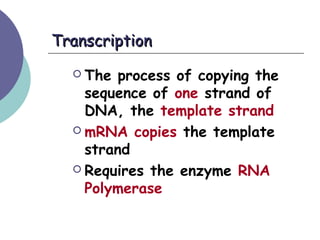
- 12. TranscriptionTranscription ’éĪ The process of copying the sequence of one strand of DNA, the template strand ’éĪ mRNA copies the template strand ’éĪ Requires the enzyme RNA Polymerase
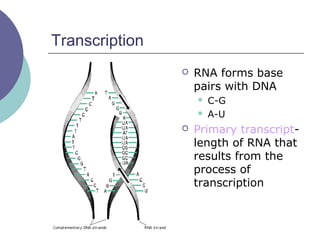
- 13. Transcription ’éĪ RNA forms base pairs with DNA ’ü¼ C-G ’ü¼ A-U ’éĪ Primary transcript- length of RNA that results from the process of transcription
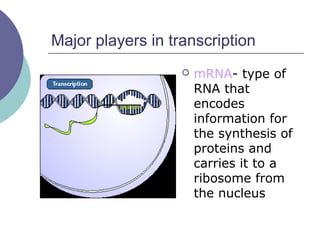
- 15. Major players in transcription ’éĪ mRNA- type of RNA that encodes information for the synthesis of proteins and carries it to a ribosome from the nucleus
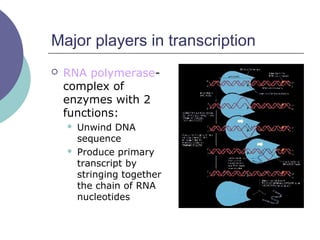
- 16. Major players in transcription ’éĪ RNA polymerase- complex of enzymes with 2 functions: ’ü¼ Unwind DNA sequence ’ü¼ Produce primary transcript by stringing together the chain of RNA nucleotides
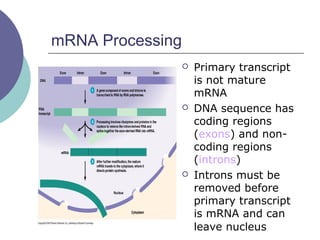
- 17. mRNA Processing ’éĪ Primary transcript is not mature mRNA ’éĪ DNA sequence has coding regions (exons) and non- coding regions (introns) ’éĪ Introns must be removed before primary transcript is mRNA and can leave nucleus
- 18. Transcription Review ’éĪ Go to http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/
- 19. Transcription is doneŌĆ”what now? Now we have mature mRNA transcribed from the cellŌĆÖs DNA. It is leaving the nucleus through a nuclear pore. Once in the cytoplasm, it finds a ribosome so that translation can begin. We know how mRNA is made, but how do we ŌĆ£readŌĆØ the code?
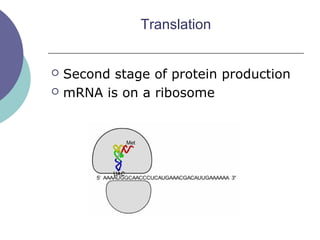
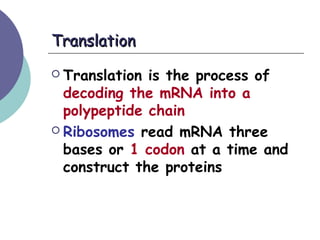
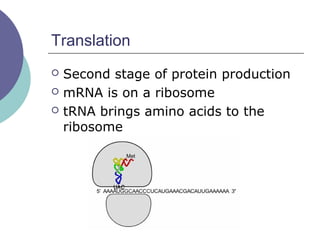
- 20. Translation ’éĪ Second stage of protein production ’éĪ mRNA is on a ribosome
- 21. TranslationTranslation ’éĪ Translation is the process of decoding the mRNA into a polypeptide chain ’éĪ Ribosomes read mRNA three bases or 1 codon at a time and construct the proteins
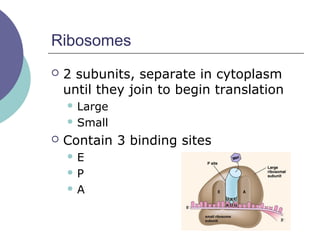
- 22. Ribosomes ’éĪ 2 subunits, separate in cytoplasm until they join to begin translation ’ü¼ Large ’ü¼ Small ’éĪ Contain 3 binding sites ’ü¼ E ’ü¼ P ’ü¼ A
- 23. Translation ’éĪ Second stage of protein production ’éĪ mRNA is on a ribosome ’éĪ tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosome
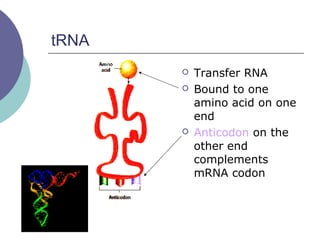
- 24. tRNA ’éĪ Transfer RNA ’éĪ Bound to one amino acid on one end ’éĪ Anticodon on the other end complements mRNA codon
- 25. tRNA Function ’éĪ Amino acids must be in the correct order for the protein to function correctly ’éĪ tRNA lines up amino acids using mRNA code
- 26. Reading the DNA code ’éĪ Every 3 DNA bases pairs with 3 mRNA bases ’éĪ Every group of 3 mRNA bases encodes a single amino acid ’éĪ Codon- coding triplet of mRNA bases
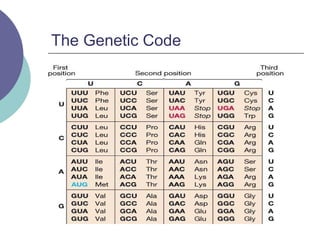
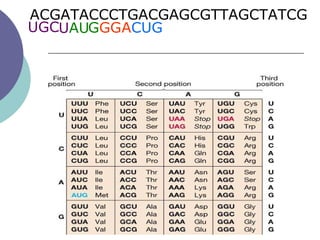
- 27. The Genetic Code
- 29. Which codons code for which amino acids? ’éĪ Genetic code- inventory of linkages between nucleotide triplets and the amino acids they code for ’éĪ A gene is a segment of RNA that brings about transcription of a protein (eventually)
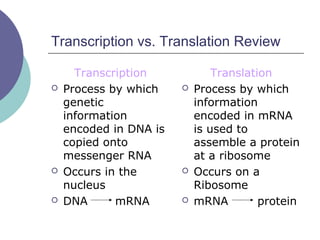
- 30. Transcription vs. Translation Review Transcription ’éĪ Process by which genetic information encoded in DNA is copied onto messenger RNA ’éĪ Occurs in the nucleus ’éĪ DNA mRNA Translation ’éĪ Process by which information encoded in mRNA is used to assemble a protein at a ribosome ’éĪ Occurs on a Ribosome ’éĪ mRNA protein
Editor's Notes
- #32: Transcription occurs when DNA acts as a template for mRNA synthesis. Translation occurs when the sequence of the mRNA codons determines the sequence of amino acids in a protein.