VIRAL DISEASES OF RICE TRASMITTED BY VECTORS
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes42 views
VIRAL DISEASES OF RICE TRASMITTED BY VECTORS
1 of 31
Download to read offline






























Recommended
COCONUT (Cocos nucifera).pptx



COCONUT (Cocos nucifera).pptxDR. RAJIB KUMAR DE, ICAR-CRIJAF, BARRACKPORE, KOLKATA, INDIA
╠²
The document provides information on maintaining healthy coconut plantations. It discusses planting materials, spacing, irrigation, integrated nutrient management, and control of diseases. Key recommendations include using good quality seedlings and mother plants, spacing palms 7.5-9 meters apart, irrigating with 45 liters every 4 days, applying organic and chemical fertilizers, controlling pests and diseases through proper sanitation and spraying, and removing diseased or unproductive palms. The main diseases discussed are root wilt caused by a phytoplasma and transmitted by insects, and bud/fruit rot caused by Phytophthora fungi.pests of groundnut



pests of groundnutVAKALIYA MUSTUFA
╠²
This document provides information on the major and minor pests that affect groundnut crops. It describes 10 major pests, including aphids, leafhoppers, thrips, and red hairy caterpillars. For each major pest, it provides details on identification, life cycle, damage symptoms, and integrated pest management strategies involving cultural, mechanical, biological and chemical controls. The document also briefly mentions two minor groundnut pests and concludes with descriptions of the aphid pest and its management.plp-02m-2018hemrajpantrice-190721094630.pdf



plp-02m-2018hemrajpantrice-190721094630.pdfDawitGetahun6
╠²
This document discusses diseases of rice and their management. It provides details on several major rice diseases caused by fungi, including rice blast caused by Magnaporthe grisea, brown spot caused by Bipolaris oryzae, sheath blight caused by Rhizoctinia solani, sheath rot caused by Sarocladium oryzae, and false smut caused by Ustilaginoidea virens. For each disease, it describes the causal organism, symptoms, disease cycle, predisposing factors, and recommendations for management. The document emphasizes the importance of host plant resistance, cultural practices, and fungicide applications in integrated disease management.Major diseases of Rice and their management in Nepal 



Major diseases of Rice and their management in Nepal Hem Raj Pant
╠²
This document discusses diseases of rice and their management. It provides details on several major rice diseases caused by fungi, including rice blast caused by Magnaporthe grisea, brown spot caused by Bipolaris oryzae, sheath blight caused by Rhizoctonia solani, sheath rot caused by Sarocladium oryzae, and false smut caused by Ustilaginoidea virens. For each disease, it describes the causal organism, symptoms, disease cycle, predisposing factors, and recommendations for management. The document emphasizes the importance of host plant resistance, cultural practices, and fungicide applications in integrated disease management.Insect vector transmitted plant diseases



Insect vector transmitted plant diseasesKamalraj Ganesan
╠²
This document discusses various insect vectors and the plant diseases they transmit. It provides examples of different insect vectors like green leafhopper, brown plant hopper, bean aphid, leaf hopper, whitefly, thrips, brown leafhopper, green peach aphid, and banana aphid. For each vector, it describes the disease(s) they transmit, associated symptoms in plants, and potential management strategies. Insects can transmit viruses, bacteria, fungi, or phytoplasmas, with viruses being the most common type of plant pathogen transmitted by insect vectors.insect pest management in cotton crop



insect pest management in cotton cropAryan Vats
╠²
This document discusses several major insect pests that affect cotton crops and their management. It describes the leafhopper (Amrasca biguttula biguttula) which damages cotton leaves causing them to curl and turn colors. It also discusses the cotton aphid (Aphis gossypii) which sucks sap from leaves and excretes honeydew, the thrips (Thrips tabaci) which feeds on leaves causing them to curl and silvering, the whitefly (Bemisia tabaci) which sucks sap and transmits viruses, and the mealybug (Phenacoccus solani) which feeds on plant tissues and excretes honeydew. The document provides details on thePests of cotton and their management



Pests of cotton and their managementRAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
This document discusses several major pests that affect cotton crops in India, including the leafhopper (Amrasca biguttula biguttula), cotton aphid (Aphis gossypii), thrips (Thrips tabaci), whitefly (Bemisia tabaci), and mealy bug (Phenacoccus solani). For each pest, it describes key details like appearance, life cycle, damage symptoms, and management strategies. It emphasizes the importance of integrated pest management using cultural, biological, and chemical controls to minimize pest impacts on cotton crops.Insect pests of cotton Gossypium hirsutum



Insect pests of cotton Gossypium hirsutumInformationSource1
╠²
This document discusses various sucking insect pests that damage cotton crops, including whiteflies, dusky cotton bugs, mealybugs, jassids, and thrips. It describes the nature of damage caused by each pest, as well as symptoms of infestation. The document also covers breeding strategies in cotton to develop resistance, such as the use of nectariless, hairy, Bt, and high gossypol varieties. Finally, it lists important natural enemies used in biological control, including lacewing, ladybird beetle, syrphid fly, spiders, big-eyed bugs, and damsel bugs.Plant Diseases



Plant Diseasesguest807eec1
╠²
Rust is a fungal disease that infects a wide range of plant species. It has a complex life cycle involving 5 spore-producing stages and usually requires two different host plants. Common rust symptoms include yellow or rust-colored spores produced in pustules on leaves and stems. Disease management focuses on using resistant varieties and fungicide application when needed.DISEASES OF SUNFLOWER AND CASTOR



DISEASES OF SUNFLOWER AND CASTORSivaK66
╠²
This document discusses several fungal, bacterial, and viral diseases that affect sunflower crops. It describes the key symptoms and impact of major diseases like Alternaria leaf blight, downy mildew, rust, Sclerotinia wilt and rot, charcoal rot, and powdery mildew. It provides details on the causal organisms, disease development and spread, and recommends management practices like crop rotation, seed treatment, and fungicide application to control sunflower diseases.Rice diseases part_3_zahid



Rice diseases part_3_zahidSyed Zahid Hasan
╠²
The document discusses several rice diseases that affect Bangladesh, including leaf scald, bacterial leaf blight, bacterial leaf streak, tungro virus, and grassy stunt virus. Leaf scald causes scalded lesions on rice leaves and can result in 20-30% yield losses. Bacterial leaf blight forms water-soaked lesions that enlarge to cause yellow stripes, and it is one of the most serious rice diseases, capable of 70% yield loss. Tungro virus stunts rice plants, causes discolored leaves, and sterile panicles, resulting in complete yield loss in severe cases. Control methods for these diseases include removing weeds, crop residues, and infected plants, using resistant varieties, seed treatment, and targetedNematode damage symptoms in crop plants



Nematode damage symptoms in crop plantsJSA College of Agriculture and Technology
╠²
The document summarizes nematode damage symptoms in several crops. In rice, the white tip nematode causes whitening and necrosis of leaf tips and twisted leaf tips. The rice root nematode causes arrested growth, poor tillering, and reddish brown discoloration of leaves. The rice root knot nematode causes swellings and galls on roots. In maize, the lesion nematode causes small lesions on roots and necrosis that can lead to secondary infections. Several nematodes are also described that cause symptoms in pulses, oilseeds, cotton, fruits, and vegetables.Disease of Sorghum



Disease of SorghumAvikalp Mishra
╠²
This document lists 9 common diseases that affect sorghum, providing the causal organism, symptoms, disease cycle, and management for each. The diseases discussed are: 1) anthracnose, 2) rust, 3) ergot, 4) head mould, 5) leaf blight, 6) grain smut, 7) charcoal rot, 8) downy mildew, and 9) witch weed. For each disease, the summary highlights the causal organism, key symptoms, and recommendations for management.diseaseofsorghum-120711180411-phpapp01.pdf



diseaseofsorghum-120711180411-phpapp01.pdfdawitg2
╠²
This document lists 9 common diseases that affect sorghum crops, providing the causal organism, symptoms, and management strategies for each disease. The diseases discussed are: anthracnose, rust, ergot, head mould, leaf blight, grain smut, charcoal rot, downy mildew, and phanerogamic parasites. For each disease, the summary provides the causal organism, brief overview of symptoms, and 1-2 management strategies.Lec. 7 rkp pcgm_sugarcane



Lec. 7 rkp pcgm_sugarcaneRajuPanse
╠²
This document discusses several major insect pests that affect sugarcane crops. It describes 24 insect pests that can cause heavy losses in sugarcane yields and quality. Some of the key pests covered include the Chilo infuscatellus borer, Scirpophaga nivella borer, Holotrichia serrata beetle, Odontotermes obesus termite, Melanapis glomerata scale, and Ripersia sacchari mealybug. For each pest, the document discusses their scientific classification, life cycle, symptoms of damage caused, and integrated pest management strategies that can be used for control.Group1(alva,bablu,fiva) 6th semester presentation



Group1(alva,bablu,fiva) 6th semester presentationBABLUHRANGKHAWL
╠²
This presentation summarizes several major viral diseases affecting field crops in Meghalaya, India, including their causative agents, symptoms, economic impact, and management practices. It covers Potato Leaf Roll Virus in potatoes, Mungbean Yellow Mosaic Virus in mungbeans, Citrus Tristeza Virus in citrus, Urdbean Leaf Crinkle Virus in blackgram, Papaya Ring Spot Virus in papaya, and Potato Virus Y in potatoes. For each disease, it discusses the virus classification, transmission method, characteristic symptoms, and integrated management approaches focusing on prevention and control.Rice disease



Rice diseaseAminul Haque
╠²
The document discusses common rice diseases found in Bangladesh. It identifies 31 total rice diseases, with 10 considered major. These major diseases include bacterial blight, bacterial leaf streak, sheath blight, blast, brown spot, narrow brown leaf spot, false smut, and rice tungro viral disease. For each disease, the document discusses the causal pathogen, symptoms, and management recommendations. Key management strategies include using resistant varieties, crop rotation, proper fertilization and irrigation, and fungicide application.Sugarcane diseases



Sugarcane diseasesSyed Zahid Hasan
╠²
This document summarizes major diseases that affect pulse crops in Bangladesh. It lists the main pulse crops grown in the country and provides details on several fungal, bacterial, and viral diseases. For each disease, it describes the symptoms, life cycle, predisposing factors, and recommended management practices. The diseases discussed include foot and root rot caused by Fusarium oxysporum and Rhizoctonia solani, Cercospora leaf spot, Ascochyta blight of chickpea, Leptosphaerulina leaf blight, bean common mosaic virus, rust diseases, powdery mildew, and wilt diseases caused by various pathogens.Types of Oil Seeds Pest 



Types of Oil Seeds Pest AnishaCutie
╠²
This document provides information on insect pests that affect various oilseed crops. It discusses the major pests that impact sunflower, groundnut, and safflower crops. For sunflower, the major pests listed are the leaf hopper and capitulum borer. The document outlines the damage symptoms and lifecycles of these pests. For groundnuts, major pests discussed include aphids, leaf hoppers, thrips, and various caterpillar species. The management strategies provided for the pests include the use of insecticides as well as cultural practices like intercropping and trap cropping. The document concludes by listing references used to compile the pest information.TYPES OF OILSEEDS PEST



TYPES OF OILSEEDS PESTAnishaCutie
╠²
This document provides information on insect pests that affect various oilseed crops. It discusses the major pests that impact sunflower, groundnut, and safflower crops. For sunflower, the major pests listed are the leaf hopper and capitulum borer. The document outlines the damage symptoms and lifecycles of these pests. For groundnuts, major pests discussed include aphids, leaf hoppers, thrips, and various caterpillar species. The management strategies suggested for various pests include intercropping, use of resistant varieties, light traps, and insecticide applications. The document concludes by listing some references used to compile the information on oilseed pest management.Integrated disease management Maize diseases 



Integrated disease management Maize diseases hema latha
╠²
This document discusses several diseases that affect maize crops. It begins by introducing maize as a major cereal crop in India and its economic importance. It then describes the major and sporadic diseases that affect maize, when they typically occur, and their potential yield losses. Several diseases are explained in more detail, including their symptoms, disease cycle, distribution, and management strategies. These include turcicum leaf blight, sorghum downy mildew, crazy top of corn, brown stripe downy mildew, and others. Management involves practices like using resistant varieties, crop rotation, removing debris, and fungicide application.INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT FOR INSECT PESTS OF PULSES 



INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT FOR INSECT PESTS OF PULSES RAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
This document provides an overview of integrated pest management for insect pests that affect pulse crops. It discusses 12 major insect pests that cause significant damage to pulses, including the pod borer (Helicoverpa armigera), legume pod borer (Maruca vitrata), pod-sucking bugs, and beanfly (Ophiomyia phaseoli). It also covers several minor pests such as aphids, thrips, whitefly, and jassids. The document emphasizes the importance of using integrated pest management strategies like host plant resistance, biological control, and targeted use of pesticides to control pests while minimizing environmental impacts.Web blight of mungbean



Web blight of mungbeanRinkuBhaskar
╠²
This document provides an overview of a seminar presentation on web blight, a devastating disease of mungbean. Some key points:
- Mungbean is an important crop originating from India that provides protein and nutrients. Web blight, caused by the fungus Rhizoctonia solani, infects all above-ground plant parts and can cause up to 40% yield losses.
- Symptoms include circular brown leaf spots that enlarge and collapse, forming a white fungal growth on the underside resembling a spider web, giving the disease its name. Lesions also form on stems, petioles and pods.
- The fungus survives in soil, seeds and crop debris as sclerotiaPests of tomato1



Pests of tomato1Dinesh Dalvaniya
╠²
This document provides information on 4 major pests of tomato crops: 1) Fruit borer (Helicoverpa armigera), 2) Defoliator (Spodoptera litura), 3) Serpentine leaf miner (Liriomyza trifolii), and 4) Whiteflies (Bemisia tabaci). It describes the identification, life cycle, damage caused, and management strategies for each pest. Common natural enemies are also listed. The management approaches emphasized include cultural controls, use of tolerant varieties, pheromone traps, biological control agents, and targeted application of chemical pesticides when needed.Insect pests of paddy



Insect pests of paddyNavneet Mahant
╠²
This document summarizes key insect pests that affect rice crops in India. It describes several major borer pests, sucking pests, and defoliator pests. For each pest, it provides details on identification, lifecycle, nature of damage, and symptoms caused. Management strategies are also outlined, such as removing crop residue, using biological or chemical controls, monitoring economic thresholds, and following integrated pest management practices. The document aims to educate readers on the major rice crop insects and their effective management.pests of Cashew nut .



pests of Cashew nut .Loki Horti
╠²
This document discusses the major pests that affect cashew plants in India. It focuses on describing four major pests in detail: the tea mosquito bug, cashew stem and root borer, apple and nut borer, and thrips. For the tea mosquito bug and cashew stem and root borer, it provides information on symptoms, biology, seasonal incidence, and management strategies to control these pests. Red ants are highlighted as a potential biocontrol agent for tea mosquito bugs. The document also includes pictures to illustrate pest damage.Diseases of turmeric and management



Diseases of turmeric and managementAshwwine Uppuluri
╠²
The document discusses several important diseases that affect turmeric plants, including rhizome root rot caused by Pythium fungi, dry rot caused by Rhizoctonia batalicola, and four foliar diseases: leaf blotch caused by Taphrina maculans, Colletotrichum leaf spot caused by Colletotrichum capsici, cercospora leaf spot, and leaf blight caused by Rhizoctonia solani. These diseases can affect turmeric plants at all stages and reduce rhizome yields considerably.Resistance Management Strategies in transgenic crops.pptx



Resistance Management Strategies in transgenic crops.pptxRAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
Resistance Management Strategies in transgenic crops.pptxIdentification, symptoms and nature of damage: white grub, mole cricket and ants



Identification, symptoms and nature of damage: white grub, mole cricket and antsRAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
Identification, symptoms and nature of damage: white grub, mole cricket and ants
More Related Content
Similar to VIRAL DISEASES OF RICE TRASMITTED BY VECTORS (20)
Insect pests of cotton Gossypium hirsutum



Insect pests of cotton Gossypium hirsutumInformationSource1
╠²
This document discusses various sucking insect pests that damage cotton crops, including whiteflies, dusky cotton bugs, mealybugs, jassids, and thrips. It describes the nature of damage caused by each pest, as well as symptoms of infestation. The document also covers breeding strategies in cotton to develop resistance, such as the use of nectariless, hairy, Bt, and high gossypol varieties. Finally, it lists important natural enemies used in biological control, including lacewing, ladybird beetle, syrphid fly, spiders, big-eyed bugs, and damsel bugs.Plant Diseases



Plant Diseasesguest807eec1
╠²
Rust is a fungal disease that infects a wide range of plant species. It has a complex life cycle involving 5 spore-producing stages and usually requires two different host plants. Common rust symptoms include yellow or rust-colored spores produced in pustules on leaves and stems. Disease management focuses on using resistant varieties and fungicide application when needed.DISEASES OF SUNFLOWER AND CASTOR



DISEASES OF SUNFLOWER AND CASTORSivaK66
╠²
This document discusses several fungal, bacterial, and viral diseases that affect sunflower crops. It describes the key symptoms and impact of major diseases like Alternaria leaf blight, downy mildew, rust, Sclerotinia wilt and rot, charcoal rot, and powdery mildew. It provides details on the causal organisms, disease development and spread, and recommends management practices like crop rotation, seed treatment, and fungicide application to control sunflower diseases.Rice diseases part_3_zahid



Rice diseases part_3_zahidSyed Zahid Hasan
╠²
The document discusses several rice diseases that affect Bangladesh, including leaf scald, bacterial leaf blight, bacterial leaf streak, tungro virus, and grassy stunt virus. Leaf scald causes scalded lesions on rice leaves and can result in 20-30% yield losses. Bacterial leaf blight forms water-soaked lesions that enlarge to cause yellow stripes, and it is one of the most serious rice diseases, capable of 70% yield loss. Tungro virus stunts rice plants, causes discolored leaves, and sterile panicles, resulting in complete yield loss in severe cases. Control methods for these diseases include removing weeds, crop residues, and infected plants, using resistant varieties, seed treatment, and targetedNematode damage symptoms in crop plants



Nematode damage symptoms in crop plantsJSA College of Agriculture and Technology
╠²
The document summarizes nematode damage symptoms in several crops. In rice, the white tip nematode causes whitening and necrosis of leaf tips and twisted leaf tips. The rice root nematode causes arrested growth, poor tillering, and reddish brown discoloration of leaves. The rice root knot nematode causes swellings and galls on roots. In maize, the lesion nematode causes small lesions on roots and necrosis that can lead to secondary infections. Several nematodes are also described that cause symptoms in pulses, oilseeds, cotton, fruits, and vegetables.Disease of Sorghum



Disease of SorghumAvikalp Mishra
╠²
This document lists 9 common diseases that affect sorghum, providing the causal organism, symptoms, disease cycle, and management for each. The diseases discussed are: 1) anthracnose, 2) rust, 3) ergot, 4) head mould, 5) leaf blight, 6) grain smut, 7) charcoal rot, 8) downy mildew, and 9) witch weed. For each disease, the summary highlights the causal organism, key symptoms, and recommendations for management.diseaseofsorghum-120711180411-phpapp01.pdf



diseaseofsorghum-120711180411-phpapp01.pdfdawitg2
╠²
This document lists 9 common diseases that affect sorghum crops, providing the causal organism, symptoms, and management strategies for each disease. The diseases discussed are: anthracnose, rust, ergot, head mould, leaf blight, grain smut, charcoal rot, downy mildew, and phanerogamic parasites. For each disease, the summary provides the causal organism, brief overview of symptoms, and 1-2 management strategies.Lec. 7 rkp pcgm_sugarcane



Lec. 7 rkp pcgm_sugarcaneRajuPanse
╠²
This document discusses several major insect pests that affect sugarcane crops. It describes 24 insect pests that can cause heavy losses in sugarcane yields and quality. Some of the key pests covered include the Chilo infuscatellus borer, Scirpophaga nivella borer, Holotrichia serrata beetle, Odontotermes obesus termite, Melanapis glomerata scale, and Ripersia sacchari mealybug. For each pest, the document discusses their scientific classification, life cycle, symptoms of damage caused, and integrated pest management strategies that can be used for control.Group1(alva,bablu,fiva) 6th semester presentation



Group1(alva,bablu,fiva) 6th semester presentationBABLUHRANGKHAWL
╠²
This presentation summarizes several major viral diseases affecting field crops in Meghalaya, India, including their causative agents, symptoms, economic impact, and management practices. It covers Potato Leaf Roll Virus in potatoes, Mungbean Yellow Mosaic Virus in mungbeans, Citrus Tristeza Virus in citrus, Urdbean Leaf Crinkle Virus in blackgram, Papaya Ring Spot Virus in papaya, and Potato Virus Y in potatoes. For each disease, it discusses the virus classification, transmission method, characteristic symptoms, and integrated management approaches focusing on prevention and control.Rice disease



Rice diseaseAminul Haque
╠²
The document discusses common rice diseases found in Bangladesh. It identifies 31 total rice diseases, with 10 considered major. These major diseases include bacterial blight, bacterial leaf streak, sheath blight, blast, brown spot, narrow brown leaf spot, false smut, and rice tungro viral disease. For each disease, the document discusses the causal pathogen, symptoms, and management recommendations. Key management strategies include using resistant varieties, crop rotation, proper fertilization and irrigation, and fungicide application.Sugarcane diseases



Sugarcane diseasesSyed Zahid Hasan
╠²
This document summarizes major diseases that affect pulse crops in Bangladesh. It lists the main pulse crops grown in the country and provides details on several fungal, bacterial, and viral diseases. For each disease, it describes the symptoms, life cycle, predisposing factors, and recommended management practices. The diseases discussed include foot and root rot caused by Fusarium oxysporum and Rhizoctonia solani, Cercospora leaf spot, Ascochyta blight of chickpea, Leptosphaerulina leaf blight, bean common mosaic virus, rust diseases, powdery mildew, and wilt diseases caused by various pathogens.Types of Oil Seeds Pest 



Types of Oil Seeds Pest AnishaCutie
╠²
This document provides information on insect pests that affect various oilseed crops. It discusses the major pests that impact sunflower, groundnut, and safflower crops. For sunflower, the major pests listed are the leaf hopper and capitulum borer. The document outlines the damage symptoms and lifecycles of these pests. For groundnuts, major pests discussed include aphids, leaf hoppers, thrips, and various caterpillar species. The management strategies provided for the pests include the use of insecticides as well as cultural practices like intercropping and trap cropping. The document concludes by listing references used to compile the pest information.TYPES OF OILSEEDS PEST



TYPES OF OILSEEDS PESTAnishaCutie
╠²
This document provides information on insect pests that affect various oilseed crops. It discusses the major pests that impact sunflower, groundnut, and safflower crops. For sunflower, the major pests listed are the leaf hopper and capitulum borer. The document outlines the damage symptoms and lifecycles of these pests. For groundnuts, major pests discussed include aphids, leaf hoppers, thrips, and various caterpillar species. The management strategies suggested for various pests include intercropping, use of resistant varieties, light traps, and insecticide applications. The document concludes by listing some references used to compile the information on oilseed pest management.Integrated disease management Maize diseases 



Integrated disease management Maize diseases hema latha
╠²
This document discusses several diseases that affect maize crops. It begins by introducing maize as a major cereal crop in India and its economic importance. It then describes the major and sporadic diseases that affect maize, when they typically occur, and their potential yield losses. Several diseases are explained in more detail, including their symptoms, disease cycle, distribution, and management strategies. These include turcicum leaf blight, sorghum downy mildew, crazy top of corn, brown stripe downy mildew, and others. Management involves practices like using resistant varieties, crop rotation, removing debris, and fungicide application.INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT FOR INSECT PESTS OF PULSES 



INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT FOR INSECT PESTS OF PULSES RAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
This document provides an overview of integrated pest management for insect pests that affect pulse crops. It discusses 12 major insect pests that cause significant damage to pulses, including the pod borer (Helicoverpa armigera), legume pod borer (Maruca vitrata), pod-sucking bugs, and beanfly (Ophiomyia phaseoli). It also covers several minor pests such as aphids, thrips, whitefly, and jassids. The document emphasizes the importance of using integrated pest management strategies like host plant resistance, biological control, and targeted use of pesticides to control pests while minimizing environmental impacts.Web blight of mungbean



Web blight of mungbeanRinkuBhaskar
╠²
This document provides an overview of a seminar presentation on web blight, a devastating disease of mungbean. Some key points:
- Mungbean is an important crop originating from India that provides protein and nutrients. Web blight, caused by the fungus Rhizoctonia solani, infects all above-ground plant parts and can cause up to 40% yield losses.
- Symptoms include circular brown leaf spots that enlarge and collapse, forming a white fungal growth on the underside resembling a spider web, giving the disease its name. Lesions also form on stems, petioles and pods.
- The fungus survives in soil, seeds and crop debris as sclerotiaPests of tomato1



Pests of tomato1Dinesh Dalvaniya
╠²
This document provides information on 4 major pests of tomato crops: 1) Fruit borer (Helicoverpa armigera), 2) Defoliator (Spodoptera litura), 3) Serpentine leaf miner (Liriomyza trifolii), and 4) Whiteflies (Bemisia tabaci). It describes the identification, life cycle, damage caused, and management strategies for each pest. Common natural enemies are also listed. The management approaches emphasized include cultural controls, use of tolerant varieties, pheromone traps, biological control agents, and targeted application of chemical pesticides when needed.Insect pests of paddy



Insect pests of paddyNavneet Mahant
╠²
This document summarizes key insect pests that affect rice crops in India. It describes several major borer pests, sucking pests, and defoliator pests. For each pest, it provides details on identification, lifecycle, nature of damage, and symptoms caused. Management strategies are also outlined, such as removing crop residue, using biological or chemical controls, monitoring economic thresholds, and following integrated pest management practices. The document aims to educate readers on the major rice crop insects and their effective management.pests of Cashew nut .



pests of Cashew nut .Loki Horti
╠²
This document discusses the major pests that affect cashew plants in India. It focuses on describing four major pests in detail: the tea mosquito bug, cashew stem and root borer, apple and nut borer, and thrips. For the tea mosquito bug and cashew stem and root borer, it provides information on symptoms, biology, seasonal incidence, and management strategies to control these pests. Red ants are highlighted as a potential biocontrol agent for tea mosquito bugs. The document also includes pictures to illustrate pest damage.Diseases of turmeric and management



Diseases of turmeric and managementAshwwine Uppuluri
╠²
The document discusses several important diseases that affect turmeric plants, including rhizome root rot caused by Pythium fungi, dry rot caused by Rhizoctonia batalicola, and four foliar diseases: leaf blotch caused by Taphrina maculans, Colletotrichum leaf spot caused by Colletotrichum capsici, cercospora leaf spot, and leaf blight caused by Rhizoctonia solani. These diseases can affect turmeric plants at all stages and reduce rhizome yields considerably.More from RAKESH KUMAR MEENA (20)
Resistance Management Strategies in transgenic crops.pptx



Resistance Management Strategies in transgenic crops.pptxRAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
Resistance Management Strategies in transgenic crops.pptxIdentification, symptoms and nature of damage: white grub, mole cricket and ants



Identification, symptoms and nature of damage: white grub, mole cricket and antsRAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
Identification, symptoms and nature of damage: white grub, mole cricket and ants
Sustainable AgricultureGreen/Sustainable Agriculture.pptx



Sustainable AgricultureGreen/Sustainable Agriculture.pptxRAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
Sustainable AgricultureÓż¤Óż┐ÓżĪÓźŹŌĆīÓżĪÓźĆ Óż¬ÓźŹÓż░Óż¼ÓżéÓż¦Óż© : ÓżĄÓż░ÓźŹÓżżÓż«ÓżŠÓż© ÓżĖÓźŹÓżźÓż┐ÓżżÓż┐ ÓżöÓż░ ÓżŁÓżĄÓż┐ÓżĘÓźŹÓż» ÓżĢÓźĆ Óż░ÓżŻÓż©ÓźĆÓżżÓż┐



Óż¤Óż┐ÓżĪÓźŹŌĆīÓżĪÓźĆ Óż¬ÓźŹÓż░Óż¼ÓżéÓż¦Óż© : ÓżĄÓż░ÓźŹÓżżÓż«ÓżŠÓż© ÓżĖÓźŹÓżźÓż┐ÓżżÓż┐ ÓżöÓż░ ÓżŁÓżĄÓż┐ÓżĘÓźŹÓż» ÓżĢÓźĆ Óż░ÓżŻÓż©ÓźĆÓżżÓż┐RAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
Óż¤Óż┐ÓżĪÓźŹŌĆīÓżĪÓźĆ Óż¬ÓźŹÓż░Óż¼ÓżéÓż¦Óż© : ÓżĄÓż░ÓźŹÓżżÓż«ÓżŠÓż© ÓżĖÓźŹÓżźÓż┐ÓżżÓż┐ ÓżöÓż░ ÓżŁÓżĄÓż┐ÓżĘÓźŹÓż» ÓżĢÓźĆ Óż░ÓżŻÓż©ÓźĆÓżżÓż┐VARIOUS GROWTH INHIBITORS AND RETARDANTS THEIR ROLE IN YIELD AND QUALITY OF V...



VARIOUS GROWTH INHIBITORS AND RETARDANTS THEIR ROLE IN YIELD AND QUALITY OF V...RAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
VARIOUS GROWTH INHIBITORS AND RETARDANTS THEIR ROLE IN YIELD AND QUALITY OF VEGETABLE CROPS
VIRUS DISEASES OF SANDALWOOD /VIRUS DISEASES OF SANDALWOOD



VIRUS DISEASES OF SANDALWOOD /VIRUS DISEASES OF SANDALWOODRAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
VIRUS DISEASES OF SANDALWOOD /VIRUS DISEASES OF SANDALWOOD NEW ALL DEFINITIONS AND ABBREVIATIONS RAKESH (1).pptx



NEW ALL DEFINITIONS AND ABBREVIATIONS RAKESH (1).pptxRAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
DEFINITIONS AND ABBREVIATIONSSymptomatic diagnosis and other techniques to detect pest / pathogen infestat...



Symptomatic diagnosis and other techniques to detect pest / pathogen infestat...RAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
Symptomatic diagnosis and other techniques to detect pest / pathogen infestations
EXPORT ,IMPORT &RELEASE OF BIOCONTROL AGENTS



EXPORT ,IMPORT &RELEASE OF BIOCONTROL AGENTSRAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
EXPORT ,IMPORT &RELEASE OF BIOCONTROL AGENTSPest risk analysis-Pest risk analysis (PRA)



Pest risk analysis-Pest risk analysis (PRA)RAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
Pest risk analysis (PRA) is ŌĆ£the process of evaluating biological or other scientific and economic evidence to determine whether an organism is a pest, whether it should be regulated, and the strength of any phytosanitary measures to be taken against itŌĆØ (IPPC, 2012).
The Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (AP...



The Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (AP...RAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
The Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) COLONIZATION OF NATURAL ENEMIES



COLONIZATION OF NATURAL ENEMIESRAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
This document summarizes techniques for evaluating the effectiveness of releasing natural enemies for biological control of pests. It describes four main techniques:
1) Correlation of pest and natural enemy populations to show control.
2) Experimental addition, exclusion, and interference methods to directly measure control. Exclusion involves removing natural enemies from plots while addition entails introducing them.
3) Specific interference techniques include using insecticides, hand removal, manipulating other species, and traps.
4) Population modeling can also demonstrate control by mathematically modeling pest and natural enemy interactions.MASS MULTIPLICATION OF Corcyra cephalonia PPT



MASS MULTIPLICATION OF Corcyra cephalonia PPTRAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
This document provides information on mass production techniques for Trichogramma and nuclear polyhedrosis viruses (NPVs). It describes the steps for rearing the rice grain moth Corcyra cephalonica which is used as a host for producing Trichogramma. The techniques for mass rearing Trichogramma including parasitizing Corcyra eggs and storing the parasitized eggs are summarized. It also outlines the basic steps for mass producing NPVs which involve rearing host insects like Helicoverpa armigera on artificial diet, infecting the larvae with viruses, harvesting and purifying the viruses. Field application doses of different NPVs for crops are also mentioned.Recent Advances in Integrated Pest Management of Sorghum



Recent Advances in Integrated Pest Management of SorghumRAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
This document describes 12 insect pests that affect sorghum crops. It provides details on the appearance, lifecycle and damage caused by each pest, which includes stem borers, shoot flies, caterpillars, aphids, beetles and others. It also discusses integrated pest management strategies for sorghum like cultural, mechanical, nutrient and host plant resistance methods.Role of biological control agent in crop protection



Role of biological control agent in crop protectionRAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
This document discusses the role of biological control agents in crop protection. It defines biological control as using natural enemies like parasites, predators, and pathogens to suppress pest populations. The three main techniques of biological control are classical, augmentative, and conservation biological control. Examples are provided of important insect pests and their corresponding natural enemies, including parasitoid wasps, green lacewings, fungi, bacteria like Bt, viruses, nematodes, and protozoa.Shoot and fruit borer of brinjal 



Shoot and fruit borer of brinjal RAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
This document discusses the shoot and fruit borer pest of brinjal plants. It begins with an introduction to brinjal and then focuses on the shoot and fruit borer pest, including its scientific classification, importance as an agricultural pest as it reduces brinjal yields, life cycle of egg to adult, and methods of management. Cultural, biological and chemical controls are outlined as well as the use of Bt brinjal, a genetically modified variety that is resistant to the borer pest through expression of a Cry protein. The document concludes that integrated pest management using selective biological controls is the most effective approach to control the pest while preserving beneficial insect populations.Identification, symptoms and nature of damage: white grub, mole cricket and ants



Identification, symptoms and nature of damage: white grub, mole cricket and antsRAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
Óż¤Óż┐ÓżĪÓźŹŌĆīÓżĪÓźĆ Óż¬ÓźŹÓż░Óż¼ÓżéÓż¦Óż© : ÓżĄÓż░ÓźŹÓżżÓż«ÓżŠÓż© ÓżĖÓźŹÓżźÓż┐ÓżżÓż┐ ÓżöÓż░ ÓżŁÓżĄÓż┐ÓżĘÓźŹÓż» ÓżĢÓźĆ Óż░ÓżŻÓż©ÓźĆÓżżÓż┐



Óż¤Óż┐ÓżĪÓźŹŌĆīÓżĪÓźĆ Óż¬ÓźŹÓż░Óż¼ÓżéÓż¦Óż© : ÓżĄÓż░ÓźŹÓżżÓż«ÓżŠÓż© ÓżĖÓźŹÓżźÓż┐ÓżżÓż┐ ÓżöÓż░ ÓżŁÓżĄÓż┐ÓżĘÓźŹÓż» ÓżĢÓźĆ Óż░ÓżŻÓż©ÓźĆÓżżÓż┐RAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
VARIOUS GROWTH INHIBITORS AND RETARDANTS THEIR ROLE IN YIELD AND QUALITY OF V...



VARIOUS GROWTH INHIBITORS AND RETARDANTS THEIR ROLE IN YIELD AND QUALITY OF V...RAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
Symptomatic diagnosis and other techniques to detect pest / pathogen infestat...



Symptomatic diagnosis and other techniques to detect pest / pathogen infestat...RAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
The Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (AP...



The Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (AP...RAKESH KUMAR MEENA
╠²
Recently uploaded (20)
Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Prelims of Rass MELAI : a Music, Entertainment, Literature, Arts and Internet Culture Quiz organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...



South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...History of Stoke Newington
╠²
Presented at the 24th Stoke Newington History Talks event on 27th Feb 2025
https://stokenewingtonhistory.com/stoke-newington-history-talks/The Battle of Belgrade Road: A WW1 Street Renaming Saga by Amir Dotan



The Battle of Belgrade Road: A WW1 Street Renaming Saga by Amir DotanHistory of Stoke Newington
╠²
Presented at the 24th Stoke Newington History Talks event on 27th Feb 2025
https://stokenewingtonhistory.com/stoke-newington-history-talks/The Story Behind the Abney Park Restoration Project by Tom Walker



The Story Behind the Abney Park Restoration Project by Tom WalkerHistory of Stoke Newington
╠²
Presented at the 24th Stoke Newington History Talks event on 27th Feb 2025
https://stokenewingtonhistory.com/stoke-newington-history-talks/QuickBooks Desktop to QuickBooks Online How to Make the Move



QuickBooks Desktop to QuickBooks Online How to Make the MoveTechSoup
╠²
If you use QuickBooks Desktop and are stressing about moving to QuickBooks Online, in this webinar, get your questions answered and learn tips and tricks to make the process easier for you.
Key Questions:
* When is the best time to make the shift to QuickBooks Online?
* Will my current version of QuickBooks Desktop stop working?
* I have a really old version of QuickBooks. What should I do?
* I run my payroll in QuickBooks Desktop now. How is that affected?
*Does it bring over all my historical data? Are there things that don't come over?
* What are the main differences between QuickBooks Desktop and QuickBooks Online?
* And moreYear 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptx



Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxmansk2
╠²
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxAdventure Activities Final By H R Gohil Sir



Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil SirGUJARATCOMMERCECOLLE
╠²
Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil SirHow to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 Employee



How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 EmployeeCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to configure flexible working schedule in Odoo 18 Employee module. In Odoo 18, the Employee module offers powerful tools to configure and manage flexible working schedules tailored to your organization's needs.EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdf



EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdfLiz Walsh-Trevino
╠²
EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdfA PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...



A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...Beena E S
╠²
A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by Aaron ShepardUseful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In this slide weŌĆÖll discuss on the useful environment methods in Odoo 18. In Odoo 18, environment methods play a crucial role in simplifying model interactions and enhancing data processing within the ORM framework.Reordering Rules in Odoo 17 Inventory - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



Reordering Rules in Odoo 17 Inventory - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In Odoo 17, the Inventory module allows us to set up reordering rules to ensure that our stock levels are maintained, preventing stockouts. Let's explore how this feature works.Eng7-Q4-Lesson 1 Part 1 Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and T...



Eng7-Q4-Lesson 1 Part 1 Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and T...sandynavergas1
╠²
Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and Technical TermsAPM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...Association for Project Management
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
- Autonomy, Teams and Tension
- Oliver Randall & David Bovis
- Own Your Autonomy
Oliver Randall
Consultant, Tribe365
Oliver is a career project professional since 2011 and started volunteering with APM in 2016 and has since chaired the People Interest Network and the North East Regional Network. Oliver has been consulting in culture, leadership and behaviours since 2019 and co-developed HPTM┬«ŌĆ»an off the shelf high performance framework for teams and organisations and is currently working with SAS (Stellenbosch Academy for Sport) developing the culture, leadership and behaviours framework for future elite sportspeople whilst also holding down work as a project manager in the NHS at North Tees and Hartlepool Foundation Trust.
David Bovis
Consultant, Duxinaroe
A Leadership and Culture Change expert, David is the originator of BTFAŌäó and The Dux Model.
With a Masters in Applied Neuroscience from the Institute of Organisational Neuroscience, he is widely regarded as the ŌĆśGo-ToŌĆÖ expert in the field, recognised as an inspiring keynote speaker and change strategist.
He has an industrial engineering background, majoring in TPS / Lean. David worked his way up from his apprenticeship to earn his seat at the C-suite table. His career spans several industries, including Automotive, Aerospace, Defence, Space, Heavy Industries and Elec-Mech / polymer contract manufacture.
Published in LondonŌĆÖs Evening Standard quarterly business supplement, James CaanŌĆÖs ŌĆśYour businessŌĆÖ Magazine, ŌĆśQuality WorldŌĆÖ, the Lean Management Journal and Cambridge Universities ŌĆśPMAŌĆÖ, he works as comfortably with leaders from FTSE and Fortune 100 companies as he does owner-managers in SMEŌĆÖs. He is passionate about helping leaders understand the neurological root cause of a high-performance culture and sustainable change, in business.
Session | Own Your Autonomy ŌĆō The Importance of Autonomy in Project Management
#OwnYourAutonomy is aiming to be a global APM initiative to position everyone to take a more conscious role in their decision making process leading to increased outcomes for everyone and contribute to ŌĆ£a world in which all projects succeedŌĆØ.
We want everyone to join the journey.
#OwnYourAutonomy is the culmination of 3 years of collaborative exploration within the Leadership Focus Group which is part of the APM People Interest Network. The work has been pulled together using the 5 HPTM® Systems and the BTFA neuroscience leadership programme.
https://www.linkedin.com/showcase/apm-people-network/about/Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding || Boby Basnet



Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding || Boby BasnetBoby Basnet
╠²
Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding Full Note
|| Assistant Professor Boby Basnet ||IAAS || AFU || PU || FUDigital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptx



Digital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
╠²
This ppt is useful for not only for B.Ed., M.Ed., M.A. (Education) or any other PG level students or Ph.D. scholars but also for the school, college and university teachers who are interested to prepare an e-content with AI for their students and others.Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...



South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...History of Stoke Newington
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...Association for Project Management
╠²
VIRAL DISEASES OF RICE TRASMITTED BY VECTORS
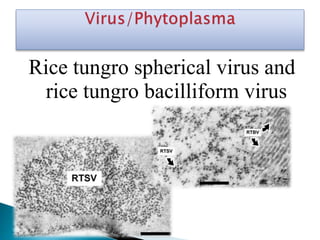
- 2. Rice tungro spherical virus and rice tungro bacilliform virus
- 3. ’üĮ Severe stuntung ’üĮ Reduced tillering ’üĮ Yellow to orange discolouration ’üĮ Interveinal chlorosis ’üĮ Twisting of leaf tip
- 4. ’üĮ 1966 ŌĆōtill today ’üĮ Raychaudhuri et al 1967 ’üĮ Green leaf hopper ’üĮ Nephotettix nigropictus
- 5. ’üĮ Rice ragged stunt virus
- 6. ’üĮ stunting, ’üĮ abnormal leaves with serrated edges ’üĮ twisted leaf tips, ’üĮ vein swelling or galls on the underside of the leaf blades
- 7. ’üĮ Gosh 1979 ’üĮ Brown planthopper ’üĮ Nilaparvata lugens
- 8. ’üĮ Rice grassy stunt virus
- 9. ’üĮ severe stunting ’üĮ profuse tillering. ’üĮ leaves are stiff and narrow ’üĮ interveinal chlorosis & bronzing.
- 10. ’üĮ 1972-84 ’üĮ Kulshreshtha et al 1974 ’üĮ Mariyappan et al 1984 ’üĮ Green leaf hopper ’üĮ Nephotettix virescens
- 11. ’üĮRice necrosis mosaic virus
- 12. ’üĮ Stunting with reduced tillering ’üĮ Mosaic mottling on the upper leaves ’üĮ Necrotic lesions on the basal parts of the stems and sheaths
- 13. ’üĮ 1979 ’üĮ (Ghosh 1979) ’āśMechanical and Soil transmission
- 14. ’üĮ Rice yellow dwarf (Candidatus Phytoplasma oryza
- 15. ’üĮ Yellowing of the newly formed leaves ’üĮ Stunted plant ’üĮ Increased tillering ’üĮ Conspcuous on the ratoon crop
- 16. ’üĮ 1976 ’üĮ (Muniyappa and Ramakrishna 1976) ’āś Green leafhopper ’üĮ Nephotettix virescens ’üĮ N. nigropictus
- 17. ’āś Judicious application of fertilizer is practiced to manage leaf folder pest ’āś Puddling and grass on field to check the population of rice mealy bug ’āś Passing of rope over crop flied in rice case worm ’āś Baiting with zinc phosphide
- 18. ’üĮRice case worm (Nymphula depunctalis)
- 19. ’üĮ Leaf case hanging from rice leaf ’üĮ cut leaf bits floting in water ’üĮ Leaves with papery upper epidermis that were fed on ’üĮ Skeletonized leaf tissues usually appear ladder-like
- 20. ’üĮ RICE CASE WORM
- 21. ’üĮ Use of correct fertilizer application. ’üĮ Plant early and use wider spacing (30 ├Ś 20 mm). ’üĮ Drain the field. ’üĮ Transplant older seedlings. Sparse planting can also reduce the damage. ’üĮ Grow a ratoon. ’üĮ Encourage biological control agents: snails (feed on eggs), hydrophilid and dytiscid water beetles (feed on larvae), spiders, dragonflies, and birds (feed on adults), nuclear polyhedrosis virus (a potential control agent) ’üĮ Use foliar treatments of carbamate insecticides; avoid pyrethroids.
- 23. IRRI: Planning Breeding Programs for Impact ’üĮ Reduction in photosynthetic area ’üĮ Reduction in 1000 grain weight ’üĮ Empty grains ’üĮ 20 ŌĆō 50% yield loss reported
- 24. IRRI: Planning Breeding Programs for Impact ŌĆśPale yellowŌĆÖ leaf ŌĆśKresekŌĆÖ or wilting ŌĆśLeaf blightŌĆÖ phase
- 25. ’üĮ Water soaked lesions move from tip downwards on the edges of leaves. ’üĮ ŌĆó Gradually symptoms turn into yellow and straw coloured stripes with wavy margins. ’üĮ ŌĆó In early morning in humid areas yellowish, opaque, turbid drops of bacterial ooze may be seen. ’üĮ ŌĆó In Kresek (wilt) phase, leaves roll completely, droop and plants die completely.
- 26. ’üĮ Spray fresh cowdung extract 20% twice (starting from initial appearance of the disease and another at fortnightly interval) ’üĮ Neem oil 60 EC 3% (or) NSKE 5% is recommended for the control of sheath rot, sheath blight, grain discolouration and bacterial blight
- 28. ’üĮ M. grisea is an ascomycete fungus. It is an extremely effective plant pathogen as it can reproduce both sexually and asexually to produce specialized infectious structures known as appressoria that infect aerial tissues and hyphae that can infect root tissues.
- 29. IRRI: Planning Breeding Programs for Impact Neck blast Leaf blast Node blast Collar blast Yield losses up to 50-85% reported
- 30. ’üĮ The fungus has been able to establish resistance to both chemical treatments and genetic resistance in some types of rice developed by plant breeders. It is thought that the fungus can achieve this by genetic change through mutation. In order to most effectively control infection by M. grisea, an integrated management program should be implemented to avoid overuse of a single control method and fight against genetic resistance.









