?? Visual SLAM 14? - 2? Introduction to slam
- 1. 190531 ??? Introduction to SLAM ?? : ???, Introduction to SLAM, SLAM KR, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_i8PaekcguA
- 2. Introduction 2 - Example : Pepper robot - ??? ??? ???? ???? ? ?? ?? ?? ?? - ??? ???? ??? ? ??? ?? ??? ???? ?? - ??? ??? ???? ???? ? ?? ?? ?? ?? - ??? ???? ???? ? ??? ?? ?? ??? ? - Localization - Mapping
- 3. Simultaneous Localization and Mapping 3 - Visual localization - ??? ??? ???? ?? (?? ?? x) - GPS? ? ???? ?? ?? - Ex) - Mapping - ??? ?? ?? ????? ?? ?? ???? ? ?? ?? - ?? ??? ?? ??? ?? - Ex) Indoor environment Private area Downtown Disaster area Cesar Cadena, Past, Present, and Future of Simultaneous Localization And Mapping: Towards the Robust-Perception Age, IEEE Transactions on Robotics 32 (6) pp 1309-1332, 2016
- 4. Earlier Inspirations 4 - Bayesian Filtering based SLAM - prototype of traditional Bayesian filtering based SLAM framework emerged in 1900s. - ex) EKF SLAM, FastSLAM - Visual Odometry - The process of estimating the ego-motion of a robot using only the input of a single or multiple cameras attached to it - ex) stereo VO, monocular VO - Structure from motion - Investigating the problem of recovering relative camera poses and 3D structure from a set of camera images - Off-line version of visual SLAM
- 5. ??? ?? ?? ?? 5 - ??? ??, QR ??, GPS ?? - ???? ??? ??, QR??? ?? ? ?? ??? ????) - GPS ??? ? ?? ?? ?? ?? ( ??, ?? ??, ?? ?? ?) - ??? ? ??? ????? ?? - ???? ??? ?? - ???? ?? ??? ?? ?? - ?? ???, ?? ???, ?? ??? - ??? ? ???, ???, ???, IMU ?? - ??? ?? ???? ???? ?? - ??? ?? ???? ?? ?? ?? ?? - ???? ??? ?? - Visual SLAM - ??? ??? ?? ??? ?? ?? ? ?? ?? ??
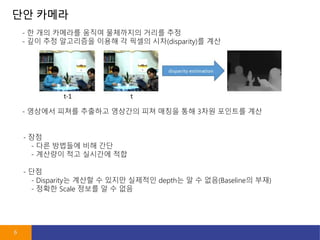
- 6. ?? ??? 6 - ? ?? ???? ??? ????? ??? ?? - ?? ?? ????? ??? ? ??? ??(disparity)? ?? - ?? - ?? ???? ?? ?? - ???? ?? ???? ?? - ???? ??? ???? ???? ?? ??? ?? 3?? ???? ?? - ?? - Disparity? ??? ? ??? ???? depth? ? ? ??(Baseline? ??) - ??? Scale ??? ? ? ??
- 7. ?? ??? 7 - ??? ??? ? ?? ???? ???? ????? ??? ?? - ??? ?? ?? ??? ?? - ?? - ?? ??? ?? ?? ??? ?? ?? ?? - Dense? ? ?? ?? - Baseline : ? ??? ??? ??? ?? - ?????? ??? ? ??? ?? ?? - ?? - ???? ?? ????? ??? ?? - ?? ??? ??
- 8. ?? ??? 8 - ??? ??? ?? ?? ??? ??? ????? ??? ?? ?? - ?? - ??? ??? ?? ? ??? ?? - Dense? ? ?? - ?? ????? ???? ?? ??? - Kinect V1, Kinect V2 - Xtion Pro Live - Intel RealSense - Google Tango - ?? - ?? ?? ?? - ?? ??? - ??, ??? ??? ?? ?? ?? ?? - ?? ?? ???? ???
- 9. Lidar ?? 9 - ??? ??? ????? ??? ??? ?? - ?? ?? ?? ? ?? ???? ?? - ?? - 2D ???/3D ??? - Spinning/Solide-state - ?? ?? - Velodyne - Robosense - Ouster - SOSLab
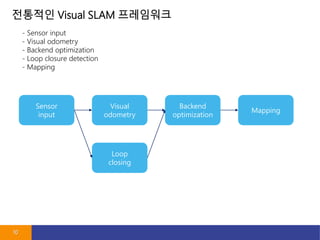
- 10. ???? Visual SLAM ????? 10 - Sensor input - Visual odometry - Backend optimization - Loop closure detection - Mapping Sensor input Visual odometry Loop closing Backend optimization Mapping
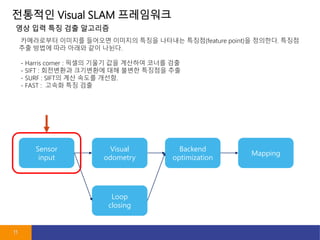
- 11. ???? Visual SLAM ????? 11 Sensor input Visual odometry Loop closing Backend optimization Mapping ?????? ???? ???? ???? ??? ???? ???(feature point)? ????. ??? ?? ??? ?? ??? ?? ???. - Harris corner : ??? ??? ?? ???? ??? ?? - SIFT : ????? ????? ?? ??? ???? ?? - SURF : SIFT? ?? ??? ???. - FAST : ??? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? ????
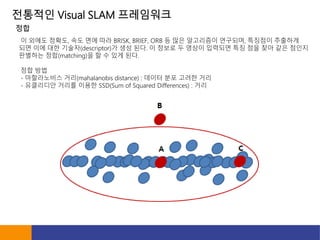
- 12. ???? Visual SLAM ????? ? ??? ???, ?? ?? ?? BRISK, BRIEF, ORB ? ?? ????? ????, ???? ???? ?? ?? ?? ???(descriptor)? ?? ??. ? ??? ? ??? ???? ?? ?? ?? ?? ??? ???? ??(matching)? ? ? ?? ??. ?? ?? - ?????? ??(mahalanobis distance) : ??? ?? ??? ?? - ????? ??? ??? SSD(Sum of Squared Differences) : ?? ??
- 13. ???? Visual SLAM ????? ???? ?? ?????? ???(outlier)? ????. ???? ???? ? ???? ??? ????? ??? ?? ? ? ??. ??? ?? ???? - RANSAC(RANdom Sample Consensus) - MSAC(M-estimator Sample And Consensus) ??? ?? ??? ??? ??? ?? RANSAC ??
- 14. Visual Odometry 14 - Frontend - ??? ??? ??? ??? ??? - ???? ??? ?? ???? ??? ?? - ?? ? ?? - ???? 3?? ?? ? ??? ???? ??? ?? - Drift error - Visual odometry?? ???? ??? ???? ??? ??? - ??? - Backend optimization? loop closure detection
- 15. Backend Optimization 15 - Sensor noise - ??? ???? ???? ?? ?? - ??? ??? ?? ??? ? - ?? ??? ???? ??? ??? ?? - Backend ??? - ???? ?? ?????? ?? ???? ??? ???? ??(state estimation) - Frontend?? ??? Drift ??? ?? - Frontend??? Backend? ??? ? ???? ???? ?? ?? ?? - Backend ???? ?? - ?? ??(Kalman filter, particle filter) - ??? ??? ??(bundle adjustment, pose graph optimization)
- 16. Loop Closure Detection 16 - ?? ??? ??? ??? ???? ?? - QR ?? ?? - ???? ??? ?? - ??? ??? ?? - ??? ?? ???? ?? - Backend??? ?? ??? ?? ??? ??? ?? ??? ?? ??? ?? - Drift ??? ???? ????? ??? ?? ?? T. Sattler, Ī░Benchmarking 6DOF Outdoor Visual Localization in Changing Conditions,Ī▒ 2017.
- 17. Mapping 17 - ?? ?? ??? ?? - ?? ????? ?? ??? ?? - ?? ?? ?? - 2?? ??? ?? - ???? ?? - 6DOF??? 3?? ??? ?? - Map representation - Pointcloud - Voxel - Surfel - Occupancy grid map - ? ?? ??? ?? ?? - Sparse, dense, semi-dense map
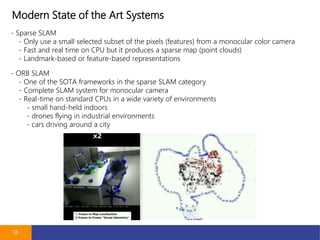
- 18. Modern State of the Art Systems 18 - Sparse SLAM - Only use a small selected subset of the pixels (features) from a monocular color camera - Fast and real time on CPU but it produces a sparse map (point clouds) - Landmark-based or feature-based representations - ORB SLAM - One of the SOTA frameworks in the sparse SLAM category - Complete SLAM system for monocular camera - Real-time on standard CPUs in a wide variety of environments - small hand-held indoors - drones flying in industrial environments - cars driving around a city
- 19. Modern State of the Art Systems 19 - Dense SLAM - Use most or all of the pixels in each received frame - Or use depth images from a depth camera - It produces a dense map but GPU acceleration is necessary from the real-time operation - Volumetric model or surfel(Surface Element)-based representations - InfiniTam - One of the SOTA frameworks in the Dense SLAM category - Multi-platform framework for real-time, large-scale depth fusion and tracking - Densely reconstructed 3D scene
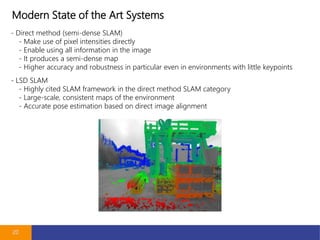
- 20. Modern State of the Art Systems 20 - Direct method (semi-dense SLAM) - Make use of pixel intensities directly - Enable using all information in the image - It produces a semi-dense map - Higher accuracy and robustness in particular even in environments with little keypoints - LSD SLAM - Highly cited SLAM framework in the direct method SLAM category - Large-scale, consistent maps of the environment - Accurate pose estimation based on direct image alignment
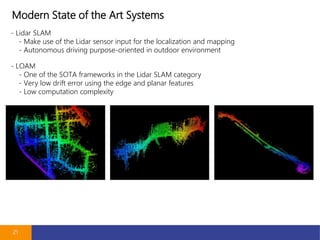
- 21. Modern State of the Art Systems 21 - Lidar SLAM - Make use of the Lidar sensor input for the localization and mapping - Autonomous driving purpose-oriented in outdoor environment - LOAM - One of the SOTA frameworks in the Lidar SLAM category - Very low drift error using the edge and planar features - Low computation complexity
- 22. SLAM ??? ??? ?? 22 - Motion model - ??? ??? ??? ????? ?? - Sensor model - ????? ???? ??? ?????? ??
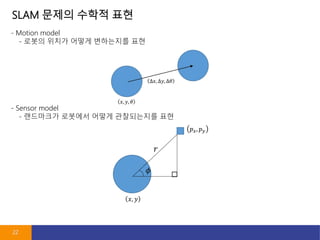
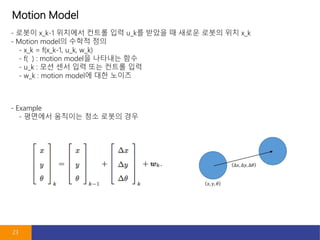
- 23. Motion Model 23 - ??? x_k-1 ???? ??? ?? u_k? ??? ? ??? ??? ?? x_k - Motion model? ??? ?? - x_k = f(x_k-1, u_k, w_k) - f( ) : motion model? ???? ?? - u_k : ?? ?? ?? ?? ??? ?? - w_k : motion model? ?? ??? - Example - ???? ???? ?? ??? ??
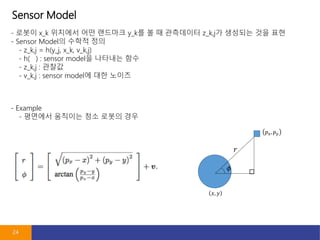
- 24. Sensor Model 24 - ??? x_k ???? ?? ???? y_k? ? ? ????? z_k,j? ???? ?? ?? - Sensor Model? ??? ?? - z_k,j = h(y_j, x_k, v_k,j) - h( ) : sensor model? ???? ?? - z_k,j : ??? - v_k,j : sensor model? ?? ??? - Example - ???? ???? ?? ??? ??
- 25. SLAM? ?? ?? ?? 25 - ?? ??? ?? ?? - x_k = f(x_k-1, u_k, w_k) - z_k,j = h(y_j, x_k, v_k,j) - ???? ?????? - ?? SLAM ??? Extended Kalman filter? ?? - EKF SLAM? ?? - ??? ????? ?? - ??? ??, ??? ??? ??? ???? ?? - Graph ??? SLAM ??? ??? ?? - Large scale? ?? H. Strasdat, Ī░Visual SLAM: Why Filter?,Ī▒ 2012.
- 26. ????? 26