1 of 13










Recommended
Research for topmanagers



Research for topmanagersVictoria Pasechnik
Ėý
ÐĢŅÐŧŅÐģÐļ ÐļŅŅÐŧÐĩÐīÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļÐđ ŅŅÐ―ÐšÐ° Ðļ ÐŋÐūŅŅÐĩÐąÐļŅÐĩÐŧÐĩÐđ ÐīÐŧŅ ŅÐūÐŋ-ОÐĩÐ―ÐĩÐīÐķÐĩŅÐūÐē КÐūОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐđ ŅŅÐĩÐīÐ―ÐĩÐģÐū ÐąÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅаResearch for topmanagers



Research for topmanagersVictoria Pasechnik
Ėý
ÐŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļŅ ÐŋŅÐūÐīŅКŅа ÐŋÐū ÐļŅŅÐŧÐĩÐīÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļŅО ŅŅÐ―ÐšÐ° ŅÐū ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅÐĩŅКÐūÐđ ÐŋÐĩŅŅÐŋÐĩКŅÐļÐēÐūÐđÐŅŅÐĩŅŅаŅÐļŅ ÐŋŅÐĩŅÐĩÐ―ÐīÐĩÐ―Ņа Ð―Ð° ÐēÐ°ÐšÐ°Ð―ŅÐļŅ ŅŅКÐūÐēÐūÐīÐļŅÐĩÐŧŅ Ð―Ð°ÐŋŅаÐēÐŧÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ



ÐŅŅÐĩŅŅаŅÐļŅ ÐŋŅÐĩŅÐĩÐ―ÐīÐĩÐ―Ņа Ð―Ð° ÐēÐ°ÐšÐ°Ð―ŅÐļŅ ŅŅКÐūÐēÐūÐīÐļŅÐĩÐŧŅ Ð―Ð°ÐŋŅаÐēÐŧÐĩÐ―ÐļŅValerii Kosenko
Ėý
ÐŅÐļОÐĩŅ ÐūŅŅÐĩŅаCŅŅŅКŅŅŅа ŅКŅÐŋÐūŅŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ÐąÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅ ÐŋÐŧÐ°Ð―Ð°



CŅŅŅКŅŅŅа ŅКŅÐŋÐūŅŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ÐąÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅ ÐŋÐŧÐ°Ð―Ð°International Business Development Alliance
Ėý
ÐКŅÐŋÐūŅŅÐ ÐĩКÐŧÐ°ÐžÐ―Ð°Ņ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅ Ðē ÐÐļОаКŅÐĩ



Ð ÐĩКÐŧÐ°ÐžÐ―Ð°Ņ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅ Ðē ÐÐļОаКŅÐĩNimax
Ėý
ÐŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļŅ Ð―Ð° Google Drive â goo.gl/b2arbIÐŅаÐēÐļÐŧа ŅазŅÐ°ÐąÐūŅКÐļ ŅКŅÐŋÐūŅŅÐ―ÐūÐđ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļÐļ КÐūОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ



ÐŅаÐēÐļÐŧа ŅазŅÐ°ÐąÐūŅКÐļ ŅКŅÐŋÐūŅŅÐ―ÐūÐđ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļÐļ КÐūОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļInna122005
Ėý
ÐĄ ŅÐĩÐģÐū Ð―Ð°ŅаŅŅ ŅазŅÐ°ÐąÐūŅКŅ ŅКŅÐŋÐūŅŅÐ―ÐūÐđ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļÐļ? ÐаК ÐūŅÐĩÐ―ÐļŅŅ ŅКŅÐŋÐūŅŅÐ―ŅÐđ ÐŋÐūŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐļаÐŧ КÐūОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ? ÐКŅÐŋÐūŅŅÐ―Ð°Ņ ÐīÐļаÐģÐ―ÐūŅŅÐļКа ŅÐĩŅÐĩз ŅÐļŅŅÐĩОŅ ÐūŅÐĩÐ―ÐūК. ÐаК ÐŋŅÐūÐēÐĩŅŅÐļ Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļз заŅŅÐąÐĩÐķÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ŅŅÐ―ÐšÐ°? ÐКŅÐŋÐūŅŅÐ―ŅÐĩ ÐŋŅÐĩÐļОŅŅÐĩŅŅÐēа КÐūОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ. ÐаК ÐŋŅÐūÐēÐĩŅŅÐļ ŅŅаÐēÐ―ÐļŅÐĩÐŧŅÐ―ŅÐđ КÐūÐ―ÐšŅŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐ―ŅÐđ Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļз Ðļ Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļз ÐŋÐūŅŅÐĩÐąÐļŅÐĩÐŧÐĩÐđ?ÐÐūÐ―ŅаÐŧŅÐļÐ―Ðģ ŅÐūŅŅа - аŅÐīÐļŅ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģа Ðļ ÐŋŅÐūÐīаÐķ



ÐÐūÐ―ŅаÐŧŅÐļÐ―Ðģ ŅÐūŅŅа - аŅÐīÐļŅ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģа Ðļ ÐŋŅÐūÐīаÐķGrowth Consulting
Ėý
ÐÐĩŅÐūÐīÐļŅÐĩŅКÐļÐđ ÐŋÐūÐīŅ
ÐūÐī КÐūÐ―ŅаÐŧŅÐļÐ―ÐģÐūÐēÐūÐđ КÐūОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ "ÐÐūÐ―ŅаÐŧŅÐļÐ―Ðģ ŅÐūŅŅа" К аŅÐīÐļŅŅ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģа Ðļ ÐŋŅÐūÐīаÐķLoyalty retail



Loyalty retailVictoria Pasechnik
Ėý
ÐŅÐūÐīŅКŅ ÐŋÐū ŅазŅÐ°ÐąÐūŅКÐĩ Ņ Ð―ŅÐŧŅ/ŅÐĩÐ―ÐūÐēаŅÐļÐļ ÐŋŅÐūÐģŅаОО ÐŧÐūŅÐŧŅÐ―ÐūŅŅÐļ Ðļ ÐēзаÐļОÐūÐūŅÐ―ÐūŅÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ Ņ КÐŧÐļÐĩÐ―ŅаОÐļ Ðļ ÐŋаŅŅÐ―ÐĩŅаОÐļ ÐīÐŧŅ ŅÐļŅÐĩÐđÐŧ-ŅÐĩŅÐĩÐđAll bigbusiness



All bigbusinessVictoria Pasechnik
Ėý
ŅŅÐŧŅÐģÐļ ОÐĩÐ―ÐĩÐīÐķОÐĩÐ―Ņ-КÐūÐ―ŅаÐŧŅÐļÐ―Ðģа ÐīÐŧŅ КŅŅÐŋÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ÐąÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅа: ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļÐļ, ÐŋŅÐūÐīаÐķÐļ, ÐąÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅ-ОÐūÐīÐĩÐŧÐļ, ÐąÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅ-ÐŋŅÐūŅÐĩŅŅŅ, HR, ÐŋŅÐūÐīŅКŅÐūÐēŅÐđ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģ, ŅÐĩÐŋŅŅаŅÐļŅ, ÐļŅŅÐŧÐĩÐīÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļŅ, Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļз, ÐąÐĩÐ―ŅОаŅКÐļÐ―ÐģÐÐŧÐĩÐģ ÐŅÐ°Ð―Ð°ŅŅÐĩÐē. ÐŅÐūÐģŅаООа ŅазÐēÐļŅÐļŅ Ð―Ð°ŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð°ÐŧŅÐ―ÐūÐđ ÐīÐļŅŅŅÐļÐąŅŅÐļÐļ. ÐÐĩŅÐūÐīÐļКа заŅ
ÐēаŅа...



ÐÐŧÐĩÐģ ÐŅÐ°Ð―Ð°ŅŅÐĩÐē. ÐŅÐūÐģŅаООа ŅазÐēÐļŅÐļŅ Ð―Ð°ŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð°ÐŧŅÐ―ÐūÐđ ÐīÐļŅŅŅÐļÐąŅŅÐļÐļ. ÐÐĩŅÐūÐīÐļКа заŅ
ÐēаŅа...Oleg Afanasyev
Ėý
ÐĄÐļŅŅÐĩÐžÐ―ÐūÐĩ ÐūÐŋÐļŅÐ°Ð―ÐļÐĩ ÐąÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅ-ÐŋŅÐūŅÐĩŅŅÐūÐē ÐīÐļŅŅŅÐļÐąŅŅÐļÐļ ÐąŅÐŧÐū ŅÐūзÐīÐ°Ð―Ðū ÐīÐŧŅ ŅÐĩŅÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ заÐīаŅÐļ ÐŋÐūŅŅŅÐūÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ Ð―Ð°ŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð°ÐŧŅÐ―ÐūÐđ ÐīÐļŅŅŅÐļÐąŅŅÐūŅŅКÐūÐđ КÐūОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ Ðē ÐŅŅзÐļÐļ. ÐĒÐĩОа ÐūКазаÐŧаŅŅ аКŅŅаÐŧŅÐ―ÐūÐđ ÐīÐŧŅ ÐžÐ―ÐūÐģÐļŅ
ÐŋŅÐūÐļзÐēÐūÐīÐļŅÐĩÐŧÐĩÐđ Ðļ ÐŋÐūÐŧŅзŅÐĩŅŅŅ ÐąÐūÐŧŅŅÐūÐđ ÐŋÐūÐŋŅÐŧŅŅÐ―ÐūŅŅŅŅ Ņ ŅÐŋÐĩŅÐļаÐŧÐļŅŅÐūÐē ÐŋÐū ÐŋÐūŅŅŅÐūÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ ŅÐļŅŅÐĩО ŅÐąŅŅа. ÐÐŧŅ ÐļÐ―ŅÐĩŅÐĩŅŅŅŅÐļŅ
ŅŅ - ОÐūÐđ e-mail: oooaaa.bs@gmail.com Ðļ ŅаÐđŅ Ð―Ð°ŅÐĩÐđ КÐūОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ - www.businessystem.com. ÐŅÐīŅ ŅаÐī ÐūŅзŅÐēаО Ðļ ÐŧŅÐąÐūОŅ ÐūÐąŅŅÐķÐīÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ.ÐаК ÐŋŅÐūŅÐļŅŅ ÐīÐĩÐ―ŅÐģÐļ Ð―Ð° ŅŅаŅŅаÐŋ



ÐаК ÐŋŅÐūŅÐļŅŅ ÐīÐĩÐ―ŅÐģÐļ Ð―Ð° ŅŅаŅŅаÐŋAndrey Pastuhov
Ėý
ÐŅÐūŅÐĩŅŅ ÐŋŅÐļÐ―ŅŅÐļŅ ŅÐĩŅÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ ÐļÐ―ÐēÐĩŅŅÐūŅÐūО. ÐаК ÐūŅÐŧÐļŅÐļŅŅ ÐŋÐŧÐūŅ
ÐūÐģÐū ÐļÐ―ÐēÐĩŅŅÐūŅа ÐūŅ Ņ
ÐūŅÐūŅÐĩÐģÐū.
ÐĄÐŋÐļŅÐūК ŅÐļÐŋÐūÐēŅŅ
ÐīÐūКŅОÐĩÐ―ŅÐūÐē ÐīÐŧŅ ÐļÐ―ÐēÐĩŅŅÐūŅа Ðļ ŅŅŅŅКŅŅŅа ÐŋŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļÐļ.
ÐĒÐļÐŋÐūÐēŅÐĩ ÐūŅÐļÐąÐšÐļ Ðē ÐŋÐūÐīÐģÐūŅÐūÐēКÐĩ ÐļÐ―ÐēÐĩŅŅÐļŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð―ŅŅ
ÐīÐūКŅОÐĩÐ―ŅÐūÐē. ÐŅÐļОÐĩŅŅ ÐēаÐķÐ―ŅŅ
ŅÐŧаÐđÐīÐūÐē.ÐÐĒÐÐ ÐŦÐĒÐÐŊ ÐÐÐÐÐÐĄÐÐŊ ÐÐļŅÐĩКŅÐūŅ ÐŋÐū ÐŋŅÐūÐīÐūÐēÐūÐŧŅŅŅÐēÐĩÐ―Ð―ŅО \Ð―ÐĩÐŋŅÐūÐīÐūÐēÐūÐŧŅŅÐēÐĩÐ―Ð―ŅО ŅÐūÐēаŅаО Ð...



ÐÐĒÐÐ ÐŦÐĒÐÐŊ ÐÐÐÐÐÐĄÐÐŊ ÐÐļŅÐĩКŅÐūŅ ÐŋÐū ÐŋŅÐūÐīÐūÐēÐūÐŧŅŅŅÐēÐĩÐ―Ð―ŅО \Ð―ÐĩÐŋŅÐūÐīÐūÐēÐūÐŧŅŅÐēÐĩÐ―Ð―ŅО ŅÐūÐēаŅаО Ð...Yelena Shaulova
Ėý
ÐŅÐļŅÐĩŅÐļÐļ ÐūŅÐĩÐ―ÐšÐļ ÐīÐļŅŅŅÐļÐąŅŅŅÐūŅÐūÐē



ÐŅÐļŅÐĩŅÐļÐļ ÐūŅÐĩÐ―ÐšÐļ ÐīÐļŅŅŅÐļÐąŅŅŅÐūŅÐūÐēInternational Business Development Alliance
Ėý
ÐŅÐĩÐ―ÐšÐ° ŅŅŅÐĩКŅÐļÐēÐ―ÐūŅŅÐļ ÐīÐļŅŅŅÐļÐąŅŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð―ÐūÐđ ŅÐļŅŅÐĩОŅ ŅÐļŅОŅHR-ÐąŅÐĩÐ―ÐīÐļÐ―Ðģ: ÐąÐūŅŅÐąÐ° за IT-ŅаÐŧÐ°Ð―ŅŅ Ņ ÐģÐļÐģÐ°Ð―ŅаОÐļ



HR-ÐąŅÐĩÐ―ÐīÐļÐ―Ðģ: ÐąÐūŅŅÐąÐ° за IT-ŅаÐŧÐ°Ð―ŅŅ Ņ ÐģÐļÐģÐ°Ð―ŅаОÐļNimax
Ėý
ÐŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļŅ ÐÐļКÐļŅŅ ÐÐļŅ
ÐĩÐĩÐ―ÐšÐūÐēа Ņ КÐūÐ―ŅÐĩŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐļÐļ ÐĄÐÐÐ.
ÐŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļŅ Ð―Ð° Google Drive â bit.ly/2IYySg4ÐÐŋÐļŅÐ°Ð―ÐļÐĩ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅÐĩŅКÐūÐģÐū Ðļ КÐūÐ―ÐšŅŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļза



ÐÐŋÐļŅÐ°Ð―ÐļÐĩ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅÐĩŅКÐūÐģÐū Ðļ КÐūÐ―ÐšŅŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļзаRoman Vasilyev
Ėý
ÐŅаŅКаŅ ÐŋŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļŅ ÐŋŅÐūÐēÐĩÐīÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅÐĩŅКÐūÐģÐū Ðļ КÐūÐ―ÐšŅŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļза ÐŋŅŅÐĩО ŅÐĩŅŅÐļÐđ Ņ аКŅÐļÐēÐūО КÐūОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ.
ÐŅÐūÐēÐĩÐīÐĩÐ―ÐļÐĩ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅÐĩŅКÐūÐģÐū Ðļ КÐūÐ―ÐšŅŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļза ÐŋŅÐūŅ
ÐūÐīÐļŅ Ðē ÐīÐēÐĩ ÐēŅŅŅÐĩŅÐļ ÐŋÐū 8 Ðļ 8 ŅаŅÐūÐē Ņ ÐŋÐĩŅÐĩŅŅÐēÐūО Ð―Ð° Ð―ÐĩÐīÐĩÐŧŅ.
Ðа ÐēŅÐĩОŅ Ð―ÐĩÐīÐĩÐŧŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ÐŋÐĩŅÐĩŅŅÐēа ÐūŅŅŅÐĩŅŅÐēÐŧŅÐĩŅŅŅ ŅÐūÐēОÐĩŅŅÐ―ŅÐđ ÐŋÐūÐļŅК Ð―ÐĩÐīÐūŅŅаŅŅÐĩÐđ ÐļÐ―ŅÐūŅОаŅÐļÐļ, Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļз ÐŋÐūÐŧŅŅÐĩÐ―Ð―ŅŅ
ŅÐĩзŅÐŧŅŅаŅÐūÐē. Ðа ÐēŅÐūŅÐūÐđ ÐēŅŅŅÐĩŅÐĩ ÐīÐūÐŋÐūÐŧÐ―ŅŅŅŅŅ ŅÐĩзŅÐŧŅŅаŅŅ Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļза, ŅазŅÐ°ÐąÐ°ŅŅÐēаÐĩŅŅŅ КÐūÐ―ÐšŅŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐ―Ð°Ņ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅ.
ÐÐ―Ð°ÐŧÐļз:
ÐÐūзÐēÐūÐŧŅÐĩŅ ŅазŅÐ°ÐąÐūŅаŅŅ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅ ŅазÐēÐļŅÐļŅ
ÐаÐĩŅ КÐūОÐŋÐŧÐĩКŅÐ―ÐūÐĩ Ðļ аÐīÐĩКÐēаŅÐ―ÐūÐĩ ÐŋÐūÐ―ÐļÐžÐ°Ð―ÐļÐĩ ŅÐļŅŅаŅÐļÐļ Ð―Ð° ŅŅÐ―ÐšÐĩ
ÐаÐĩŅ КÐūОÐŋÐŧÐĩКŅÐ―ÐūÐĩ Ðļ аÐīÐĩКÐēаŅÐ―ÐūÐĩ ÐŋÐūÐ―ÐļÐžÐ°Ð―ÐļÐĩ ÐŋŅÐūÐļŅŅ
ÐūÐīŅŅÐĩÐģÐū Ð―Ð° ŅŅÐ―ÐšÐĩ
ÐÐūзÐēÐūÐŧŅÐĩŅ ŅÐēÐūÐĩÐēŅÐĩОÐĩÐ―Ð―Ðū ŅÐĩаÐģÐļŅÐūÐēаŅŅ Ð―Ð° ÐļзОÐĩÐ―ÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ ÐēÐ―ÐĩŅÐ―ÐĩÐđ ŅŅÐĩÐīŅ
ÐÐūзÐēÐūÐŧŅÐĩŅ ÐēŅŅÐ°ÐąÐ°ŅŅÐēаŅŅ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅÐĩŅКÐļÐĩ ŅÐĩŅÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ Ðļ ÐŋÐŧÐ°Ð― ÐļŅ
ŅÐĩаÐŧÐļзаŅÐļÐļ
ÐÐūзÐēÐūÐŧŅÐĩŅ ÐēŅŅÐ°ÐąÐūŅаŅŅ ÐŋŅŅÐļ ÐūŅŅŅŅÐūÐđКÐļ ÐūŅ КÐūÐ―ÐšŅŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐūÐē
ÐÐūзÐēÐūÐŧŅÐĩŅ ÐēŅŅÐēÐļŅŅ ÐŋŅÐļÐūŅÐļŅÐĩŅŅ ÐīÐŧŅ ÐŋÐĩŅÐēÐūÐūŅÐĩŅÐĩÐīÐ―ŅŅ
ÐīÐĩÐđŅŅÐēÐļÐđ
Ð ÐĩзŅÐŧŅŅаŅаОÐļ ÐŋŅÐūÐēÐĩÐīÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅÐĩŅКÐūÐģÐū Ðļ КÐūÐ―ÐšŅŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļза ÐąŅÐīŅŅ:
âĒÐ ÐĩзŅÐŧŅŅаŅŅ PEST Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļза,
âĒÐ ÐĩзŅÐŧŅŅаŅŅ SWOT-Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļза,
âĒÐ ÐĩзŅÐŧŅŅаŅŅ Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļза Ð―Ð° ÐūŅÐ―ÐūÐēÐĩ ÐÐĪÐĢ,
âĒÐаŅŅŅ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅÐĩŅКÐļŅ
ÐģŅŅÐŋÐŋ,
âĒÐÐąŅÐļÐĩ ÐēŅÐēÐūÐīŅ ÐŋÐū ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļÐļ Ðļ ŅÐ°ÐąÐūŅÐĩ Ņ КÐūÐ―ÐšŅŅÐĩÐ―ŅаОÐļ.!
ÐаÐŋŅаÐēÐŧÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ ÐīÐĩŅŅÐĩÐŧŅÐ―ÐūŅŅÐļ Ð ÐūÐžÐ°Ð―Ð° ÐаŅÐļÐŧŅÐĩÐēа:
+ ÐĒŅÐĩÐ―ÐļÐ―ÐģÐļ ÐŋŅÐūŅÐĩŅŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð°ÐŧŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū Ðļ ÐŧÐļŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ŅÐūŅŅа:
+ ÐŅÐąÐŧÐļŅÐ―ŅÐĩ ÐēŅŅŅŅÐŋÐŧÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ Ðļ ОÐūÐīÐĩŅÐļŅÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļÐĩ
+ ÐÐļаÐģÐ―ÐūŅŅÐļКа ÐŋÐĩŅÐēŅŅ
ÐŧÐļŅ, ÐŋÐĩŅŅÐūÐ―Ð°Ðŧа Ðļ ÐŧÐļŅÐ―Ð°Ņ
+ ÐÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅ КÐūÐ―ŅаÐŧŅÐļÐ―Ðģ (ÐŋŅÐūÐīаÐķÐļ, ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģ, КÐŧÐļÐĩÐ―ŅÐļÐ―Ðģ, ÐŋÐĩŅŅÐūÐ―Ð°Ðŧ, ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅ)
+ ÐÐūŅŅÐļÐ―Ðģ, ÐŋÐūОÐūŅŅ Ðē КаŅŅÐĩŅÐĩ
+ ÐÐūÐīÐąÐūŅ ŅКŅКÐŧŅзÐļÐēÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ÐŋÐĩŅŅÐūÐ―Ð°Ðŧа
+ ÐŅÐģÐ°Ð―ÐļзаŅÐļŅ ÐŋŅÐūŅÐĩŅŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð°ÐŧŅÐ―ŅŅ
ŅÐūÐūÐąŅÐĩŅŅÐē
+ Ð ÐĩŅÐĩÐ―ÐļÐĩ ŅÐŧÐūÐķÐ―ŅŅ
Ðļ аКŅŅаÐŧŅÐ―ŅŅ
заÐīаŅÐŅŅÐŧÐĩÐīÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļÐĩ заŅŅÐąÐĩÐķÐ―ŅŅ
ŅŅÐ―ÐšÐūÐē ÐūŅ keytocustomer.com



ÐŅŅÐŧÐĩÐīÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļÐĩ заŅŅÐąÐĩÐķÐ―ŅŅ
ŅŅÐ―ÐšÐūÐē ÐūŅ keytocustomer.comKateryna Ospishcheva
Ėý
ÐĄ ŅÐĩÐģÐū Ð―Ð°ŅаŅŅ ÐļŅŅÐŧÐĩÐīÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļÐĩ заŅŅÐąÐĩÐķÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ŅŅÐ―ÐšÐ°? ÐаКÐļÐĩ ŅÐŋÐūŅÐūÐąŅ Ðļ ОÐĩŅÐūÐīŅ ŅŅŅÐĩŅŅÐēŅŅŅ? ÐĄÐšÐūÐŧŅКÐū ÐēаÐķÐ―ŅŅ
ŅŅаÐŋÐūÐē Ð―ŅÐķÐ―Ðū ŅŅÐĩŅŅŅ ÐŋŅÐļ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―ÐģÐūÐēÐūО ÐļŅŅÐŧÐĩÐīÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ? ÐŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļŅ ŅаŅŅŅÐļŅÐ°Ð―Ð° Ð―Ð° ŅÐĩŅ
, КŅÐū заÐīŅОаÐŧŅŅ ÐūÐą ŅКŅÐŋÐūŅŅÐĩ ŅÐēÐūÐļŅ
ŅŅÐŧŅÐģ Ðļ ŅÐūÐēаŅÐūÐē ÐīÐŧŅ Ð―ÐūÐēŅŅ
ŅŅÐ―ÐšÐūÐē.ÐŅŅŅŅ ÐŅзŅКÐūÐē Ðļ ÐÐŧÐĩКŅÐ°Ð―ÐīŅ ÐÐŧÐļКŅŅÐĩÐđÐ―: ÐŅŅÐĩКŅÐļÐēÐ―Ð°Ņ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅ ÐīÐŧŅ ŅÐūŅŅа ŅŅаŅŅаÐŋа



ÐŅŅŅŅ ÐŅзŅКÐūÐē Ðļ ÐÐŧÐĩКŅÐ°Ð―ÐīŅ ÐÐŧÐļКŅŅÐĩÐđÐ―: ÐŅŅÐĩКŅÐļÐēÐ―Ð°Ņ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅ ÐīÐŧŅ ŅÐūŅŅа ŅŅаŅŅаÐŋа#tceh ŅКÐūŅÐļŅŅÐĩОа Ðļ КÐūÐēÐūŅКÐļÐ―Ðģ ÐīÐŧŅ ŅŅаŅŅаÐŋÐūÐē.
Ėý
#poSEEDelki Ņ ÐŅŅŅŅÐūО ÐŅзŅКÐūÐēŅО â аÐēŅÐūŅÐūО ÐŋŅÐūÐģŅаООŅ DriverPack, Ðļ ÐÐŧÐĩКŅÐ°Ð―ÐīŅÐūО ÐÐŧÐļКŅŅÐĩÐđÐ―ÐūО â ŅŅКÐūÐēÐūÐīÐļŅÐĩÐŧÐĩО ÐŋŅÐĩŅŅ-ŅÐŧŅÐķÐąŅ КÐūОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ DriverPack Ðļ PR-ÐīÐļŅÐĩКŅÐūŅÐūО КÐūОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ Reactive Phone.More Related Content
What's hot (19)
CŅŅŅКŅŅŅа ŅКŅÐŋÐūŅŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ÐąÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅ ÐŋÐŧÐ°Ð―Ð°



CŅŅŅКŅŅŅа ŅКŅÐŋÐūŅŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ÐąÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅ ÐŋÐŧÐ°Ð―Ð°International Business Development Alliance
Ėý
ÐКŅÐŋÐūŅŅÐ ÐĩКÐŧÐ°ÐžÐ―Ð°Ņ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅ Ðē ÐÐļОаКŅÐĩ



Ð ÐĩКÐŧÐ°ÐžÐ―Ð°Ņ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅ Ðē ÐÐļОаКŅÐĩNimax
Ėý
ÐŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļŅ Ð―Ð° Google Drive â goo.gl/b2arbIÐŅаÐēÐļÐŧа ŅазŅÐ°ÐąÐūŅКÐļ ŅКŅÐŋÐūŅŅÐ―ÐūÐđ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļÐļ КÐūОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ



ÐŅаÐēÐļÐŧа ŅазŅÐ°ÐąÐūŅКÐļ ŅКŅÐŋÐūŅŅÐ―ÐūÐđ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļÐļ КÐūОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļInna122005
Ėý
ÐĄ ŅÐĩÐģÐū Ð―Ð°ŅаŅŅ ŅазŅÐ°ÐąÐūŅКŅ ŅКŅÐŋÐūŅŅÐ―ÐūÐđ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļÐļ? ÐаК ÐūŅÐĩÐ―ÐļŅŅ ŅКŅÐŋÐūŅŅÐ―ŅÐđ ÐŋÐūŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐļаÐŧ КÐūОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ? ÐКŅÐŋÐūŅŅÐ―Ð°Ņ ÐīÐļаÐģÐ―ÐūŅŅÐļКа ŅÐĩŅÐĩз ŅÐļŅŅÐĩОŅ ÐūŅÐĩÐ―ÐūК. ÐаК ÐŋŅÐūÐēÐĩŅŅÐļ Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļз заŅŅÐąÐĩÐķÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ŅŅÐ―ÐšÐ°? ÐКŅÐŋÐūŅŅÐ―ŅÐĩ ÐŋŅÐĩÐļОŅŅÐĩŅŅÐēа КÐūОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ. ÐаК ÐŋŅÐūÐēÐĩŅŅÐļ ŅŅаÐēÐ―ÐļŅÐĩÐŧŅÐ―ŅÐđ КÐūÐ―ÐšŅŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐ―ŅÐđ Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļз Ðļ Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļз ÐŋÐūŅŅÐĩÐąÐļŅÐĩÐŧÐĩÐđ?ÐÐūÐ―ŅаÐŧŅÐļÐ―Ðģ ŅÐūŅŅа - аŅÐīÐļŅ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģа Ðļ ÐŋŅÐūÐīаÐķ



ÐÐūÐ―ŅаÐŧŅÐļÐ―Ðģ ŅÐūŅŅа - аŅÐīÐļŅ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģа Ðļ ÐŋŅÐūÐīаÐķGrowth Consulting
Ėý
ÐÐĩŅÐūÐīÐļŅÐĩŅКÐļÐđ ÐŋÐūÐīŅ
ÐūÐī КÐūÐ―ŅаÐŧŅÐļÐ―ÐģÐūÐēÐūÐđ КÐūОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ "ÐÐūÐ―ŅаÐŧŅÐļÐ―Ðģ ŅÐūŅŅа" К аŅÐīÐļŅŅ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģа Ðļ ÐŋŅÐūÐīаÐķLoyalty retail



Loyalty retailVictoria Pasechnik
Ėý
ÐŅÐūÐīŅКŅ ÐŋÐū ŅазŅÐ°ÐąÐūŅКÐĩ Ņ Ð―ŅÐŧŅ/ŅÐĩÐ―ÐūÐēаŅÐļÐļ ÐŋŅÐūÐģŅаОО ÐŧÐūŅÐŧŅÐ―ÐūŅŅÐļ Ðļ ÐēзаÐļОÐūÐūŅÐ―ÐūŅÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ Ņ КÐŧÐļÐĩÐ―ŅаОÐļ Ðļ ÐŋаŅŅÐ―ÐĩŅаОÐļ ÐīÐŧŅ ŅÐļŅÐĩÐđÐŧ-ŅÐĩŅÐĩÐđAll bigbusiness



All bigbusinessVictoria Pasechnik
Ėý
ŅŅÐŧŅÐģÐļ ОÐĩÐ―ÐĩÐīÐķОÐĩÐ―Ņ-КÐūÐ―ŅаÐŧŅÐļÐ―Ðģа ÐīÐŧŅ КŅŅÐŋÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ÐąÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅа: ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļÐļ, ÐŋŅÐūÐīаÐķÐļ, ÐąÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅ-ОÐūÐīÐĩÐŧÐļ, ÐąÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅ-ÐŋŅÐūŅÐĩŅŅŅ, HR, ÐŋŅÐūÐīŅКŅÐūÐēŅÐđ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģ, ŅÐĩÐŋŅŅаŅÐļŅ, ÐļŅŅÐŧÐĩÐīÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļŅ, Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļз, ÐąÐĩÐ―ŅОаŅКÐļÐ―ÐģÐÐŧÐĩÐģ ÐŅÐ°Ð―Ð°ŅŅÐĩÐē. ÐŅÐūÐģŅаООа ŅазÐēÐļŅÐļŅ Ð―Ð°ŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð°ÐŧŅÐ―ÐūÐđ ÐīÐļŅŅŅÐļÐąŅŅÐļÐļ. ÐÐĩŅÐūÐīÐļКа заŅ
ÐēаŅа...



ÐÐŧÐĩÐģ ÐŅÐ°Ð―Ð°ŅŅÐĩÐē. ÐŅÐūÐģŅаООа ŅазÐēÐļŅÐļŅ Ð―Ð°ŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð°ÐŧŅÐ―ÐūÐđ ÐīÐļŅŅŅÐļÐąŅŅÐļÐļ. ÐÐĩŅÐūÐīÐļКа заŅ
ÐēаŅа...Oleg Afanasyev
Ėý
ÐĄÐļŅŅÐĩÐžÐ―ÐūÐĩ ÐūÐŋÐļŅÐ°Ð―ÐļÐĩ ÐąÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅ-ÐŋŅÐūŅÐĩŅŅÐūÐē ÐīÐļŅŅŅÐļÐąŅŅÐļÐļ ÐąŅÐŧÐū ŅÐūзÐīÐ°Ð―Ðū ÐīÐŧŅ ŅÐĩŅÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ заÐīаŅÐļ ÐŋÐūŅŅŅÐūÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ Ð―Ð°ŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð°ÐŧŅÐ―ÐūÐđ ÐīÐļŅŅŅÐļÐąŅŅÐūŅŅКÐūÐđ КÐūОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ Ðē ÐŅŅзÐļÐļ. ÐĒÐĩОа ÐūКазаÐŧаŅŅ аКŅŅаÐŧŅÐ―ÐūÐđ ÐīÐŧŅ ÐžÐ―ÐūÐģÐļŅ
ÐŋŅÐūÐļзÐēÐūÐīÐļŅÐĩÐŧÐĩÐđ Ðļ ÐŋÐūÐŧŅзŅÐĩŅŅŅ ÐąÐūÐŧŅŅÐūÐđ ÐŋÐūÐŋŅÐŧŅŅÐ―ÐūŅŅŅŅ Ņ ŅÐŋÐĩŅÐļаÐŧÐļŅŅÐūÐē ÐŋÐū ÐŋÐūŅŅŅÐūÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ ŅÐļŅŅÐĩО ŅÐąŅŅа. ÐÐŧŅ ÐļÐ―ŅÐĩŅÐĩŅŅŅŅÐļŅ
ŅŅ - ОÐūÐđ e-mail: oooaaa.bs@gmail.com Ðļ ŅаÐđŅ Ð―Ð°ŅÐĩÐđ КÐūОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ - www.businessystem.com. ÐŅÐīŅ ŅаÐī ÐūŅзŅÐēаО Ðļ ÐŧŅÐąÐūОŅ ÐūÐąŅŅÐķÐīÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ.ÐаК ÐŋŅÐūŅÐļŅŅ ÐīÐĩÐ―ŅÐģÐļ Ð―Ð° ŅŅаŅŅаÐŋ



ÐаК ÐŋŅÐūŅÐļŅŅ ÐīÐĩÐ―ŅÐģÐļ Ð―Ð° ŅŅаŅŅаÐŋAndrey Pastuhov
Ėý
ÐŅÐūŅÐĩŅŅ ÐŋŅÐļÐ―ŅŅÐļŅ ŅÐĩŅÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ ÐļÐ―ÐēÐĩŅŅÐūŅÐūО. ÐаК ÐūŅÐŧÐļŅÐļŅŅ ÐŋÐŧÐūŅ
ÐūÐģÐū ÐļÐ―ÐēÐĩŅŅÐūŅа ÐūŅ Ņ
ÐūŅÐūŅÐĩÐģÐū.
ÐĄÐŋÐļŅÐūК ŅÐļÐŋÐūÐēŅŅ
ÐīÐūКŅОÐĩÐ―ŅÐūÐē ÐīÐŧŅ ÐļÐ―ÐēÐĩŅŅÐūŅа Ðļ ŅŅŅŅКŅŅŅа ÐŋŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļÐļ.
ÐĒÐļÐŋÐūÐēŅÐĩ ÐūŅÐļÐąÐšÐļ Ðē ÐŋÐūÐīÐģÐūŅÐūÐēКÐĩ ÐļÐ―ÐēÐĩŅŅÐļŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð―ŅŅ
ÐīÐūКŅОÐĩÐ―ŅÐūÐē. ÐŅÐļОÐĩŅŅ ÐēаÐķÐ―ŅŅ
ŅÐŧаÐđÐīÐūÐē.ÐÐĒÐÐ ÐŦÐĒÐÐŊ ÐÐÐÐÐÐĄÐÐŊ ÐÐļŅÐĩКŅÐūŅ ÐŋÐū ÐŋŅÐūÐīÐūÐēÐūÐŧŅŅŅÐēÐĩÐ―Ð―ŅО \Ð―ÐĩÐŋŅÐūÐīÐūÐēÐūÐŧŅŅÐēÐĩÐ―Ð―ŅО ŅÐūÐēаŅаО Ð...



ÐÐĒÐÐ ÐŦÐĒÐÐŊ ÐÐÐÐÐÐĄÐÐŊ ÐÐļŅÐĩКŅÐūŅ ÐŋÐū ÐŋŅÐūÐīÐūÐēÐūÐŧŅŅŅÐēÐĩÐ―Ð―ŅО \Ð―ÐĩÐŋŅÐūÐīÐūÐēÐūÐŧŅŅÐēÐĩÐ―Ð―ŅО ŅÐūÐēаŅаО Ð...Yelena Shaulova
Ėý
ÐŅÐļŅÐĩŅÐļÐļ ÐūŅÐĩÐ―ÐšÐļ ÐīÐļŅŅŅÐļÐąŅŅŅÐūŅÐūÐē



ÐŅÐļŅÐĩŅÐļÐļ ÐūŅÐĩÐ―ÐšÐļ ÐīÐļŅŅŅÐļÐąŅŅŅÐūŅÐūÐēInternational Business Development Alliance
Ėý
ÐŅÐĩÐ―ÐšÐ° ŅŅŅÐĩКŅÐļÐēÐ―ÐūŅŅÐļ ÐīÐļŅŅŅÐļÐąŅŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð―ÐūÐđ ŅÐļŅŅÐĩОŅ ŅÐļŅОŅHR-ÐąŅÐĩÐ―ÐīÐļÐ―Ðģ: ÐąÐūŅŅÐąÐ° за IT-ŅаÐŧÐ°Ð―ŅŅ Ņ ÐģÐļÐģÐ°Ð―ŅаОÐļ



HR-ÐąŅÐĩÐ―ÐīÐļÐ―Ðģ: ÐąÐūŅŅÐąÐ° за IT-ŅаÐŧÐ°Ð―ŅŅ Ņ ÐģÐļÐģÐ°Ð―ŅаОÐļNimax
Ėý
ÐŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļŅ ÐÐļКÐļŅŅ ÐÐļŅ
ÐĩÐĩÐ―ÐšÐūÐēа Ņ КÐūÐ―ŅÐĩŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐļÐļ ÐĄÐÐÐ.
ÐŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļŅ Ð―Ð° Google Drive â bit.ly/2IYySg4ÐÐŋÐļŅÐ°Ð―ÐļÐĩ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅÐĩŅКÐūÐģÐū Ðļ КÐūÐ―ÐšŅŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļза



ÐÐŋÐļŅÐ°Ð―ÐļÐĩ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅÐĩŅКÐūÐģÐū Ðļ КÐūÐ―ÐšŅŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļзаRoman Vasilyev
Ėý
ÐŅаŅКаŅ ÐŋŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļŅ ÐŋŅÐūÐēÐĩÐīÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅÐĩŅКÐūÐģÐū Ðļ КÐūÐ―ÐšŅŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļза ÐŋŅŅÐĩО ŅÐĩŅŅÐļÐđ Ņ аКŅÐļÐēÐūО КÐūОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ.
ÐŅÐūÐēÐĩÐīÐĩÐ―ÐļÐĩ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅÐĩŅКÐūÐģÐū Ðļ КÐūÐ―ÐšŅŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļза ÐŋŅÐūŅ
ÐūÐīÐļŅ Ðē ÐīÐēÐĩ ÐēŅŅŅÐĩŅÐļ ÐŋÐū 8 Ðļ 8 ŅаŅÐūÐē Ņ ÐŋÐĩŅÐĩŅŅÐēÐūО Ð―Ð° Ð―ÐĩÐīÐĩÐŧŅ.
Ðа ÐēŅÐĩОŅ Ð―ÐĩÐīÐĩÐŧŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ÐŋÐĩŅÐĩŅŅÐēа ÐūŅŅŅÐĩŅŅÐēÐŧŅÐĩŅŅŅ ŅÐūÐēОÐĩŅŅÐ―ŅÐđ ÐŋÐūÐļŅК Ð―ÐĩÐīÐūŅŅаŅŅÐĩÐđ ÐļÐ―ŅÐūŅОаŅÐļÐļ, Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļз ÐŋÐūÐŧŅŅÐĩÐ―Ð―ŅŅ
ŅÐĩзŅÐŧŅŅаŅÐūÐē. Ðа ÐēŅÐūŅÐūÐđ ÐēŅŅŅÐĩŅÐĩ ÐīÐūÐŋÐūÐŧÐ―ŅŅŅŅŅ ŅÐĩзŅÐŧŅŅаŅŅ Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļза, ŅазŅÐ°ÐąÐ°ŅŅÐēаÐĩŅŅŅ КÐūÐ―ÐšŅŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐ―Ð°Ņ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅ.
ÐÐ―Ð°ÐŧÐļз:
ÐÐūзÐēÐūÐŧŅÐĩŅ ŅазŅÐ°ÐąÐūŅаŅŅ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅ ŅазÐēÐļŅÐļŅ
ÐаÐĩŅ КÐūОÐŋÐŧÐĩКŅÐ―ÐūÐĩ Ðļ аÐīÐĩКÐēаŅÐ―ÐūÐĩ ÐŋÐūÐ―ÐļÐžÐ°Ð―ÐļÐĩ ŅÐļŅŅаŅÐļÐļ Ð―Ð° ŅŅÐ―ÐšÐĩ
ÐаÐĩŅ КÐūОÐŋÐŧÐĩКŅÐ―ÐūÐĩ Ðļ аÐīÐĩКÐēаŅÐ―ÐūÐĩ ÐŋÐūÐ―ÐļÐžÐ°Ð―ÐļÐĩ ÐŋŅÐūÐļŅŅ
ÐūÐīŅŅÐĩÐģÐū Ð―Ð° ŅŅÐ―ÐšÐĩ
ÐÐūзÐēÐūÐŧŅÐĩŅ ŅÐēÐūÐĩÐēŅÐĩОÐĩÐ―Ð―Ðū ŅÐĩаÐģÐļŅÐūÐēаŅŅ Ð―Ð° ÐļзОÐĩÐ―ÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ ÐēÐ―ÐĩŅÐ―ÐĩÐđ ŅŅÐĩÐīŅ
ÐÐūзÐēÐūÐŧŅÐĩŅ ÐēŅŅÐ°ÐąÐ°ŅŅÐēаŅŅ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅÐĩŅКÐļÐĩ ŅÐĩŅÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ Ðļ ÐŋÐŧÐ°Ð― ÐļŅ
ŅÐĩаÐŧÐļзаŅÐļÐļ
ÐÐūзÐēÐūÐŧŅÐĩŅ ÐēŅŅÐ°ÐąÐūŅаŅŅ ÐŋŅŅÐļ ÐūŅŅŅŅÐūÐđКÐļ ÐūŅ КÐūÐ―ÐšŅŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐūÐē
ÐÐūзÐēÐūÐŧŅÐĩŅ ÐēŅŅÐēÐļŅŅ ÐŋŅÐļÐūŅÐļŅÐĩŅŅ ÐīÐŧŅ ÐŋÐĩŅÐēÐūÐūŅÐĩŅÐĩÐīÐ―ŅŅ
ÐīÐĩÐđŅŅÐēÐļÐđ
Ð ÐĩзŅÐŧŅŅаŅаОÐļ ÐŋŅÐūÐēÐĩÐīÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅÐĩŅКÐūÐģÐū Ðļ КÐūÐ―ÐšŅŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļза ÐąŅÐīŅŅ:
âĒÐ ÐĩзŅÐŧŅŅаŅŅ PEST Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļза,
âĒÐ ÐĩзŅÐŧŅŅаŅŅ SWOT-Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļза,
âĒÐ ÐĩзŅÐŧŅŅаŅŅ Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļза Ð―Ð° ÐūŅÐ―ÐūÐēÐĩ ÐÐĪÐĢ,
âĒÐаŅŅŅ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅÐĩŅКÐļŅ
ÐģŅŅÐŋÐŋ,
âĒÐÐąŅÐļÐĩ ÐēŅÐēÐūÐīŅ ÐŋÐū ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļÐļ Ðļ ŅÐ°ÐąÐūŅÐĩ Ņ КÐūÐ―ÐšŅŅÐĩÐ―ŅаОÐļ.!
ÐаÐŋŅаÐēÐŧÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ ÐīÐĩŅŅÐĩÐŧŅÐ―ÐūŅŅÐļ Ð ÐūÐžÐ°Ð―Ð° ÐаŅÐļÐŧŅÐĩÐēа:
+ ÐĒŅÐĩÐ―ÐļÐ―ÐģÐļ ÐŋŅÐūŅÐĩŅŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð°ÐŧŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū Ðļ ÐŧÐļŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ŅÐūŅŅа:
+ ÐŅÐąÐŧÐļŅÐ―ŅÐĩ ÐēŅŅŅŅÐŋÐŧÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ Ðļ ОÐūÐīÐĩŅÐļŅÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļÐĩ
+ ÐÐļаÐģÐ―ÐūŅŅÐļКа ÐŋÐĩŅÐēŅŅ
ÐŧÐļŅ, ÐŋÐĩŅŅÐūÐ―Ð°Ðŧа Ðļ ÐŧÐļŅÐ―Ð°Ņ
+ ÐÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅ КÐūÐ―ŅаÐŧŅÐļÐ―Ðģ (ÐŋŅÐūÐīаÐķÐļ, ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģ, КÐŧÐļÐĩÐ―ŅÐļÐ―Ðģ, ÐŋÐĩŅŅÐūÐ―Ð°Ðŧ, ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅ)
+ ÐÐūŅŅÐļÐ―Ðģ, ÐŋÐūОÐūŅŅ Ðē КаŅŅÐĩŅÐĩ
+ ÐÐūÐīÐąÐūŅ ŅКŅКÐŧŅзÐļÐēÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ÐŋÐĩŅŅÐūÐ―Ð°Ðŧа
+ ÐŅÐģÐ°Ð―ÐļзаŅÐļŅ ÐŋŅÐūŅÐĩŅŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð°ÐŧŅÐ―ŅŅ
ŅÐūÐūÐąŅÐĩŅŅÐē
+ Ð ÐĩŅÐĩÐ―ÐļÐĩ ŅÐŧÐūÐķÐ―ŅŅ
Ðļ аКŅŅаÐŧŅÐ―ŅŅ
заÐīаŅÐŅŅÐŧÐĩÐīÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļÐĩ заŅŅÐąÐĩÐķÐ―ŅŅ
ŅŅÐ―ÐšÐūÐē ÐūŅ keytocustomer.com



ÐŅŅÐŧÐĩÐīÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļÐĩ заŅŅÐąÐĩÐķÐ―ŅŅ
ŅŅÐ―ÐšÐūÐē ÐūŅ keytocustomer.comKateryna Ospishcheva
Ėý
ÐĄ ŅÐĩÐģÐū Ð―Ð°ŅаŅŅ ÐļŅŅÐŧÐĩÐīÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļÐĩ заŅŅÐąÐĩÐķÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ŅŅÐ―ÐšÐ°? ÐаКÐļÐĩ ŅÐŋÐūŅÐūÐąŅ Ðļ ОÐĩŅÐūÐīŅ ŅŅŅÐĩŅŅÐēŅŅŅ? ÐĄÐšÐūÐŧŅКÐū ÐēаÐķÐ―ŅŅ
ŅŅаÐŋÐūÐē Ð―ŅÐķÐ―Ðū ŅŅÐĩŅŅŅ ÐŋŅÐļ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―ÐģÐūÐēÐūО ÐļŅŅÐŧÐĩÐīÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ? ÐŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļŅ ŅаŅŅŅÐļŅÐ°Ð―Ð° Ð―Ð° ŅÐĩŅ
, КŅÐū заÐīŅОаÐŧŅŅ ÐūÐą ŅКŅÐŋÐūŅŅÐĩ ŅÐēÐūÐļŅ
ŅŅÐŧŅÐģ Ðļ ŅÐūÐēаŅÐūÐē ÐīÐŧŅ Ð―ÐūÐēŅŅ
ŅŅÐ―ÐšÐūÐē.ÐŅŅŅŅ ÐŅзŅКÐūÐē Ðļ ÐÐŧÐĩКŅÐ°Ð―ÐīŅ ÐÐŧÐļКŅŅÐĩÐđÐ―: ÐŅŅÐĩКŅÐļÐēÐ―Ð°Ņ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅ ÐīÐŧŅ ŅÐūŅŅа ŅŅаŅŅаÐŋа



ÐŅŅŅŅ ÐŅзŅКÐūÐē Ðļ ÐÐŧÐĩКŅÐ°Ð―ÐīŅ ÐÐŧÐļКŅŅÐĩÐđÐ―: ÐŅŅÐĩКŅÐļÐēÐ―Ð°Ņ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅ ÐīÐŧŅ ŅÐūŅŅа ŅŅаŅŅаÐŋа#tceh ŅКÐūŅÐļŅŅÐĩОа Ðļ КÐūÐēÐūŅКÐļÐ―Ðģ ÐīÐŧŅ ŅŅаŅŅаÐŋÐūÐē.
Ėý
#poSEEDelki Ņ ÐŅŅŅŅÐūО ÐŅзŅКÐūÐēŅО â аÐēŅÐūŅÐūО ÐŋŅÐūÐģŅаООŅ DriverPack, Ðļ ÐÐŧÐĩКŅÐ°Ð―ÐīŅÐūО ÐÐŧÐļКŅŅÐĩÐđÐ―ÐūО â ŅŅКÐūÐēÐūÐīÐļŅÐĩÐŧÐĩО ÐŋŅÐĩŅŅ-ŅÐŧŅÐķÐąŅ КÐūОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ DriverPack Ðļ PR-ÐīÐļŅÐĩКŅÐūŅÐūО КÐūОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ Reactive Phone.CŅŅŅКŅŅŅа ŅКŅÐŋÐūŅŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ÐąÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅ ÐŋÐŧÐ°Ð―Ð°



CŅŅŅКŅŅŅа ŅКŅÐŋÐūŅŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ÐąÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅ ÐŋÐŧÐ°Ð―Ð°International Business Development Alliance
Ėý
ÐŅаÐēÐļÐŧа ŅазŅÐ°ÐąÐūŅКÐļ ŅКŅÐŋÐūŅŅÐ―ÐūÐđ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļÐļ КÐūОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ



ÐŅаÐēÐļÐŧа ŅазŅÐ°ÐąÐūŅКÐļ ŅКŅÐŋÐūŅŅÐ―ÐūÐđ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļÐļ КÐūОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļInna122005
Ėý
ÐÐūÐ―ŅаÐŧŅÐļÐ―Ðģ ŅÐūŅŅа - аŅÐīÐļŅ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģа Ðļ ÐŋŅÐūÐīаÐķ



ÐÐūÐ―ŅаÐŧŅÐļÐ―Ðģ ŅÐūŅŅа - аŅÐīÐļŅ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģа Ðļ ÐŋŅÐūÐīаÐķGrowth Consulting
Ėý
ÐÐŧÐĩÐģ ÐŅÐ°Ð―Ð°ŅŅÐĩÐē. ÐŅÐūÐģŅаООа ŅазÐēÐļŅÐļŅ Ð―Ð°ŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð°ÐŧŅÐ―ÐūÐđ ÐīÐļŅŅŅÐļÐąŅŅÐļÐļ. ÐÐĩŅÐūÐīÐļКа заŅ
ÐēаŅа...



ÐÐŧÐĩÐģ ÐŅÐ°Ð―Ð°ŅŅÐĩÐē. ÐŅÐūÐģŅаООа ŅазÐēÐļŅÐļŅ Ð―Ð°ŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð°ÐŧŅÐ―ÐūÐđ ÐīÐļŅŅŅÐļÐąŅŅÐļÐļ. ÐÐĩŅÐūÐīÐļКа заŅ
ÐēаŅа...Oleg Afanasyev
Ėý
ÐÐĒÐÐ ÐŦÐĒÐÐŊ ÐÐÐÐÐÐĄÐÐŊ ÐÐļŅÐĩКŅÐūŅ ÐŋÐū ÐŋŅÐūÐīÐūÐēÐūÐŧŅŅŅÐēÐĩÐ―Ð―ŅО \Ð―ÐĩÐŋŅÐūÐīÐūÐēÐūÐŧŅŅÐēÐĩÐ―Ð―ŅО ŅÐūÐēаŅаО Ð...



ÐÐĒÐÐ ÐŦÐĒÐÐŊ ÐÐÐÐÐÐĄÐÐŊ ÐÐļŅÐĩКŅÐūŅ ÐŋÐū ÐŋŅÐūÐīÐūÐēÐūÐŧŅŅŅÐēÐĩÐ―Ð―ŅО \Ð―ÐĩÐŋŅÐūÐīÐūÐēÐūÐŧŅŅÐēÐĩÐ―Ð―ŅО ŅÐūÐēаŅаО Ð...Yelena Shaulova
Ėý
ÐŅÐļŅÐĩŅÐļÐļ ÐūŅÐĩÐ―ÐšÐļ ÐīÐļŅŅŅÐļÐąŅŅŅÐūŅÐūÐē



ÐŅÐļŅÐĩŅÐļÐļ ÐūŅÐĩÐ―ÐšÐļ ÐīÐļŅŅŅÐļÐąŅŅŅÐūŅÐūÐēInternational Business Development Alliance
Ėý
ÐÐŋÐļŅÐ°Ð―ÐļÐĩ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅÐĩŅКÐūÐģÐū Ðļ КÐūÐ―ÐšŅŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļза



ÐÐŋÐļŅÐ°Ð―ÐļÐĩ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅÐĩŅКÐūÐģÐū Ðļ КÐūÐ―ÐšŅŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū Ð°Ð―Ð°ÐŧÐļзаRoman Vasilyev
Ėý
ÐŅŅÐŧÐĩÐīÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļÐĩ заŅŅÐąÐĩÐķÐ―ŅŅ
ŅŅÐ―ÐšÐūÐē ÐūŅ keytocustomer.com



ÐŅŅÐŧÐĩÐīÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļÐĩ заŅŅÐąÐĩÐķÐ―ŅŅ
ŅŅÐ―ÐšÐūÐē ÐūŅ keytocustomer.comKateryna Ospishcheva
Ėý
ÐŅŅŅŅ ÐŅзŅКÐūÐē Ðļ ÐÐŧÐĩКŅÐ°Ð―ÐīŅ ÐÐŧÐļКŅŅÐĩÐđÐ―: ÐŅŅÐĩКŅÐļÐēÐ―Ð°Ņ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅ ÐīÐŧŅ ŅÐūŅŅа ŅŅаŅŅаÐŋа



ÐŅŅŅŅ ÐŅзŅКÐūÐē Ðļ ÐÐŧÐĩКŅÐ°Ð―ÐīŅ ÐÐŧÐļКŅŅÐĩÐđÐ―: ÐŅŅÐĩКŅÐļÐēÐ―Ð°Ņ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅ ÐīÐŧŅ ŅÐūŅŅа ŅŅаŅŅаÐŋа#tceh ŅКÐūŅÐļŅŅÐĩОа Ðļ КÐūÐēÐūŅКÐļÐ―Ðģ ÐīÐŧŅ ŅŅаŅŅаÐŋÐūÐē.
Ėý
Viewers also liked (13)
Outsourcing Matrix Revisited



Outsourcing Matrix RevisitedSergey Khromov-Borisov
Ėý
This document outlines three perspectives on outsourcing using matrix models. Perspective I uses a matrix to show that outsourcing makes most sense for non-core activities that are complex, not critical to the business, and involve costs and risks. Perspective II looks at requirements for outsourcing providers using a matrix of flexibility, efficiency, knowledge, and reliability. Perspective III outlines a path for providers to develop competitive advantages through improving business processes, knowledge bases, economics, and investments.Strategic marketing intensive 2016 



Strategic marketing intensive 2016 Andrew Pourtov
Ėý
21-29 ŅÐ―ÐēаŅŅ Ðē ÐÐūŅКÐēÐĩ ÐēÐŋÐĩŅÐēŅÐĩ ÐŋŅÐūÐđÐīÐĩŅ ŅÐ―ÐļКаÐŧŅÐ―ŅÐđ 8-ÐīÐ―ÐĩÐēÐ―ŅÐđ 80-ŅаŅÐūÐēÐūÐđ ÐļÐ―ŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐļÐē "ÐĄŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅÐĩŅКÐļÐđ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģ". ÐŅŅаŅÐūŅ: ÐÐ―ÐīŅÐĩÐđ ÐŅŅŅÐūÐē. ÐКŅÐŋÐĩŅŅŅ ÐļÐ―ŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐļÐēа: ÐÐ―ÐīŅÐĩÐđ ÐŅŅŅÐūÐē (ÐÐÐĻÐ), ÐĄÐĩŅÐģÐĩÐđ ÐĨŅÐūОÐūÐē-ÐÐūŅÐļŅÐūÐē (SenseCraft), ÐÐŧÐĩÐ―Ð° ÐÐļŅŅŅÐļÐ―Ð° (Bosch Siemens), ÐÐŧÐĩКŅÐĩÐđ ÐŅÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅÐūÐē (ÐÐÐĒÐĢ ÐļО ÐаŅÐžÐ°Ð―Ð°), ÐКаŅÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ð° ÐĨŅаОКÐūÐēа (Lumiknows), ÐÐŧÐĩÐ―Ð° ÐÐūŅÐūŅŅ (Kimberly-Clark), ÐÐļŅ
аÐļÐŧ ЧÐĩŅÐ―ŅŅÐĩÐē (ÐÐÐūÐ―ŅаКŅÐĩ), ÐÐ―ÐīŅÐĩÐđ ÐÐŧÐļÐģаŅ (Advanter Group). IG + B-Models



IG + B-ModelsSergey Khromov-Borisov
Ėý
This document discusses various business model tools and innovation techniques including the Value Proposition Canvas, Business Model Canvas, Kano Model, and Innovation Games. It provides an overview of each tool and technique including Value Proposition Canvas for defining customer value propositions, Business Model Canvas for describing key elements of a business model, Kano Model for categorizing product attributes, and Innovation Games as a technique for generating new ideas to solve customer problems.Suedtirole case



Suedtirole caseSergey Khromov-Borisov
Ėý
The document outlines Angela Knewitz's presentation on building strong regional brands, using South Tyrol as a case study. It discusses place branding opportunities and challenges, and introduces South Tyrol's objectives to develop an umbrella brand to establish a common visual presence, pool resources, and meet regulatory requirements. The presentation covers South Tyrol's brand strategy, design, and implementation, and lessons learned, including the importance of regional collaboration, focus, visual communication, embracing diversity, and inspiring stakeholders.Similar to Wrong education (20)
ÐÐ 14.2. ÐаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģ ÐģÐūÐŧÐūÐēÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ОÐūзÐģа



ÐÐ 14.2. ÐаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģ ÐģÐūÐŧÐūÐēÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ОÐūзÐģаÐÐ―ŅÐĩŅÐ―ÐĩŅ-аÐģÐĩÐ―ŅŅŅÐēÐū ÐÐÐĒÐÐ ÐÐÐÐÐ
Ėý
ÐŅ ÐžÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ÐģÐūÐēÐūŅÐļО ÐūÐą ÐļÐ―ŅÐĩŅÐ―ÐĩŅ-ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―ÐģÐĩ.
ЧŅÐū ŅŅÐū â Ð―ÐļКŅÐū Ð―Ðĩ Ð·Ð―Ð°ÐĩŅ.
ÐаÐķÐĩ Ð―Ð°Ņ Ð―Ð°ŅаÐŧŅÐ―ÐļК ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģа Ð―Ðĩ Ðē КŅŅŅÐĩ,
Ðļ ÐŋÐūÐŋŅÐūŅÐļÐŧ ОÐĩÐ―Ņ ÐēŅŅŅŅÐŋÐļŅŅ.
ÐĒаК ŅÐĩО ÐķÐĩ ÐīÐūÐŧÐķÐ―Ņ Ð·Ð°Ð―ÐļОаŅŅŅŅ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐūÐŧÐūÐģÐļ?ÐŅКŅÐīа ÐĩŅŅŅ ÐŋÐūŅÐŧÐļ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―ÐģÐūÐēŅÐĩ ОÐĩŅŅÐļКÐļ ÐŋŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļŅ Marketing drive spring short



ÐŅКŅÐīа ÐĩŅŅŅ ÐŋÐūŅÐŧÐļ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―ÐģÐūÐēŅÐĩ ОÐĩŅŅÐļКÐļ ÐŋŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļŅ Marketing drive spring shortMihail Krikunov
Ėý
ÐÐ―ŅÐĩÐģŅÐļŅÐūÐēÐ°Ð―Ð―ŅÐĩ Ð ÐĩКÐŧÐ°ÐžÐ―ŅÐĩ ÐаОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ - ЧаŅŅŅ I. ÐÐĩКŅÐļŅ 1.



ÐÐ―ŅÐĩÐģŅÐļŅÐūÐēÐ°Ð―Ð―ŅÐĩ Ð ÐĩКÐŧÐ°ÐžÐ―ŅÐĩ ÐаОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ - ЧаŅŅŅ I. ÐÐĩКŅÐļŅ 1.Mikhail Chernyshev
Ėý
ÐÐĩŅÐēаŅ ÐŧÐĩКŅÐļŅ Ðē ÐŅÐļŅÐ°Ð―ŅКÐūÐđ ÐŅŅŅÐĩÐđ ÐĻКÐūÐŧÐĩ ÐÐļзаÐđÐ―Ð° Ð―Ð° ŅÐĩОŅ "ÐÐ―ŅÐĩÐģŅÐļŅÐūÐēÐ°Ð―Ð―ŅÐĩ Ð ÐĩКÐŧÐ°ÐžÐ―ŅÐĩ ÐаОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ" Ðē ŅаОКаŅ
КŅŅŅа "ÐŅÐĩÐ―ÐīÐļÐ―Ðģ"ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―ÐģÐūÐēŅÐĩ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļÐļ ÐīÐŧŅ ŅŅаŅŅаÐŋ ÐŋŅÐūÐĩКŅÐūÐē



ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―ÐģÐūÐēŅÐĩ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļÐļ ÐīÐŧŅ ŅŅаŅŅаÐŋ ÐŋŅÐūÐĩКŅÐūÐēLeonid Danilov
Ėý
ÐŅÐūŅÐĩŅŅÐļŅ: ÐаŅКÐĩŅÐūÐŧÐūÐģ



ÐŅÐūŅÐĩŅŅÐļŅ: ÐаŅКÐĩŅÐūÐŧÐūÐģAnna Kafyrina
Ėý
ÐŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļŅ ÐīÐŧŅ ŅКÐūÐŧŅÐ―ÐļКÐūÐē, Ðū ÐēŅÐąÐūŅÐĩ ÐŋŅÐūŅÐĩŅÐļÐļ "ÐаŅКÐĩŅÐūÐŧÐūÐģ".ÐаŅКÐĩŅÐūÐŧÐūÐģ



ÐаŅКÐĩŅÐūÐŧÐūÐģssuser41d3ac
Ėý
ÐŅÐū Ņ ÐēаŅ ŅÐ°ÐąÐūŅаÐĩŅ Ðļ КŅÐū ÐēаО Ð―ŅÐķÐĩÐ―: ÐĩŅÐĩ ÐūÐīÐļÐ― ÐģŅŅзŅÐļК ÐļÐŧÐļ ŅÐūŅ, КŅÐū ÐēОÐĩŅŅÐĩ Ņ ÐēаОÐļ ÐąŅÐīÐĩŅ ÂŦŅŅŅÐūÐļŅŅ Ņ
ŅаОÂŧ"CŅÐ°Ð―ÐīаŅŅŅ ŅККаŅÐ―Ņ Ðļ ÐąŅÐĩÐ―Ðī ОÐĩÐ―ÐĩÐīÐķОÐĩÐ―Ņа", ÐĻКÐūÐŧа ÐŅаКŅÐļŅÐĩŅКÐūÐđ Ð ÐĩКÐŧаОŅ "A-3"



"CŅÐ°Ð―ÐīаŅŅŅ ŅККаŅÐ―Ņ Ðļ ÐąŅÐĩÐ―Ðī ОÐĩÐ―ÐĩÐīÐķОÐĩÐ―Ņа", ÐĻКÐūÐŧа ÐŅаКŅÐļŅÐĩŅКÐūÐđ Ð ÐĩКÐŧаОŅ "A-3"A-3 School Of Practical Advertising
Ėý
ÐÐēŅÐūŅŅКÐļÐđ ÐŋŅаКŅÐļКŅО ÐīÐŧŅ ŅÐļзÐļŅÐĩŅКÐļŅ
ÐŧÐļŅ, ÐēŅÐąŅаÐēŅÐļŅ
ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģ ÐļÐŧÐļ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―ÐģÐūÐēŅÐĩ КÐūООŅÐ―ÐļКаŅÐļÐļ Ðē КаŅÐĩŅŅÐēÐĩ ŅÐēÐūÐĩÐđ ÐūŅÐ―ÐūÐēÐ―ÐūÐđ ÐŋŅÐūŅÐĩŅŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð°ÐŧŅÐ―ÐūÐđ ÐīÐĩŅŅÐĩÐŧŅÐ―ÐūŅŅÐļ.ОÐē1



ОÐē1ÐÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅ-ÐĻКÐūÐŧа ЧÐ-ÐÐÐÐ
Ėý
ÐаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģ ÐзаÐļОÐūÐūŅÐ―ÐūŅÐĩÐ―ÐļÐđ(ÐÐ)
ÐÐŧÐūК 1. ÐÐēÐūÐŧŅŅÐļŅ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģа
ÐÐŧÐūК 2. ÐÐ=ÂŦÐŋŅÐūŅÐēÐĩŅŅÐ―Ð―ŅÐđ ŅÐģÐūÐļзОÂŧ
ÐÐŧÐūК 3. ÐÐ Ðļ ŅŅÐ°Ð―Ð·Ð°ÐšŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð―ŅÐđ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģ
ÐÐŧÐūК 4. ÐŅаÐēÐļÐŧа ÐÐÐÐÐĒÐŦ Ðū ÐŋÐūКŅÐŋаŅÐĩÐŧÐĩÐŅÐĩÐļОŅŅÐĩŅŅÐēа ÐļÐ―ŅÐĩŅÐ―ÐĩŅ- ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģа Ðē ŅŅÐŧÐūÐēÐļŅŅ
КŅÐļзÐļŅа



ÐŅÐĩÐļОŅŅÐĩŅŅÐēа ÐļÐ―ŅÐĩŅÐ―ÐĩŅ- ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģа Ðē ŅŅÐŧÐūÐēÐļŅŅ
КŅÐļзÐļŅаMarketing_ Debates_HSE
Ėý
ÐÐūКÐŧаÐīŅÐļК - ÐŅŅÐ·Ð°Ð―ÐūÐēа ÐаŅŅŅ
ОаÐģÐļŅŅŅÐ°Ð―Ņ ÐēŅÐūŅÐūÐģÐū КŅŅŅа ÐÐÐĢ ÐÐĻÐÐŋŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļŅ Ð―ÐĩÐīÐĩÐŧŅ ŅÐĩКÐŧаОŅ 2014



ÐŋŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļŅ Ð―ÐĩÐīÐĩÐŧŅ ŅÐĩКÐŧаОŅ 2014Vizavi_Consalt
Ėý
3-6 ÐīÐĩÐšÐ°ÐąŅŅ â ÐēŅÐĩОŅ ÐģÐūÐēÐūŅÐļŅŅ Ðū ŅÐĩКÐŧаОÐĩ Ðļ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―ÐģÐĩ! http://raweek.ru/#speakers ÐÐūŅ ОŅ Ðļ ÐģÐūÐēÐūŅÐļÐŧÐļ )) - ÐļÐ―ŅÐĩŅÐĩŅÐ―Ðū Ðļ ÐŋÐūÐŧÐĩÐ·Ð―Ðū!ÐŅÐūŅÐĩŅŅÐļŅ ОÐĩÐ―ÐĩÐīÐķÐĩŅ. ЧаŅŅŅ 2



ÐŅÐūŅÐĩŅŅÐļŅ ОÐĩÐ―ÐĩÐīÐķÐĩŅ. ЧаŅŅŅ 2Marina Pugaeva
Ėý
ÐŅÐūŅÐĩŅŅÐļŅ: ÐÐĩÐ―ÐĩÐīÐķÐĩŅ. ÐаК ÐŋŅаÐēÐļÐŧŅÐ―Ðū ÐēŅÐąŅаŅŅ ŅÐŋÐĩŅÐļаÐŧŅÐ―ÐūŅŅŅ?ÐĄŅŅŅКŅŅŅа ŅŅÐ―ÐšÐ° ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―ÐģÐūÐēŅŅ
ŅŅÐŧŅÐģ ÐīÐŧŅ ÐŋŅÐļŅ
ÐūÐŧÐūÐģÐūÐē



ÐĄŅŅŅКŅŅŅа ŅŅÐ―ÐšÐ° ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―ÐģÐūÐēŅŅ
ŅŅÐŧŅÐģ ÐīÐŧŅ ÐŋŅÐļŅ
ÐūÐŧÐūÐģÐūÐēElena Taranskaya
Ėý
ÐÐĩКŅÐļŅ, ÐŋŅÐūŅÐļŅÐ°Ð―Ð―Ð°Ņ Ð―Ð° ŅаКŅÐŧŅŅÐĩŅÐĩ ÐŋŅÐļŅ
ÐūÐŧÐūÐģÐļÐļ ÐĨаŅŅКÐūÐēŅКÐūÐģÐū Ð―Ð°ŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð°ÐŧŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ŅÐ―ÐļÐēÐĩŅŅÐļŅÐĩŅа ÐļОÐĩÐ―Ðļ ÐаŅазÐļÐ―Ð°.
ÐŅаŅКÐūÐĩ ŅŅŅŅÐūÐđŅŅÐēÐū ОÐļŅа ŅÐĩКÐŧаОŅ + ÐąÐ°Ð·ÐūÐēŅÐĩ ŅÐūÐēÐĩŅŅ ÐīÐŧŅ ŅŅŅÐīÐĩÐ―ŅÐūÐē-ÐŋŅÐļŅ
ÐūÐŧÐūÐģÐūÐē, КÐūŅÐūŅŅÐĩ ÐąŅ Ņ
ÐūŅÐĩÐŧÐļ ÐŋÐūÐŋŅÐūÐąÐūÐēаŅŅ ŅÐĩÐąŅ Ðē ŅŅÐūÐđ ŅŅÐĩŅÐĩ.Marketing for-start-up



Marketing for-start-upMary Prokhorova
Ėý
30 ÐļŅÐ―Ņ Ðē California in Ukraine ÐŋŅÐūŅÐŧа заОÐĩŅаŅÐĩÐŧŅÐ―Ð°Ņ ÐŧÐĩКŅÐļŅ Ņ ÐĒаŅŅŅÐ―ÐūÐđ ÐÐļÐ―ŅКÐūÐēÐūÐđ ÐŋŅÐū "ÐаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģ ÐīÐŧŅ ŅŅаŅŅаÐŋÐūÐē".
ÐÐūÐēŅŅÐĩÐ―ÐļÐĩ ŅŅŅÐĩКŅÐļÐēÐ―ÐūŅŅÐļ ÐąÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅ-ОÐūÐīÐĩÐŧÐļ ÐŋŅÐūÐīаÐķ. ЧаŅŅŅ 4. ÐÐūÐēŅŅÐĩÐ―ÐļÐĩ ŅŅŅÐĩКŅÐļÐēÐ―ÐūŅŅ...



ÐÐūÐēŅŅÐĩÐ―ÐļÐĩ ŅŅŅÐĩКŅÐļÐēÐ―ÐūŅŅÐļ ÐąÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅ-ОÐūÐīÐĩÐŧÐļ ÐŋŅÐūÐīаÐķ. ЧаŅŅŅ 4. ÐÐūÐēŅŅÐĩÐ―ÐļÐĩ ŅŅŅÐĩКŅÐļÐēÐ―ÐūŅŅ...Michael Lufanov
Ėý
China2seminar



China2seminarKonstantin S
Ėý
ÐīÐŧŅ ÐēŅÐĩŅ
, КŅÐū ŅŅŅÐĩОÐļŅŅŅŅ ÐŋÐūŅŅŅÐūÐļŅŅ ÐąÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅ Ņ ÐÐļŅаÐĩО; ÐīÐŧŅ ÐēŅÐĩŅ
, КŅÐū ÐŋŅÐĩКŅаŅÐ―Ðū ÐūŅÐūÐ·Ð―Ð°ÐĩŅ ŅÐūŅŅ ÐŋŅÐūÐļзÐēÐūÐīŅŅÐēÐĩÐ―Ð―ÐūÐđ ОÐūŅÐ―ÐūŅŅÐļ ÐÐļŅаŅ Ðļ ŅаŅŅОаŅŅÐļÐēаÐĩŅ, ÐŋŅŅŅŅ ÐīаÐķÐĩ ÐŋÐūКа ÐŋÐūŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐļаÐŧŅÐ―Ðū, ÐēÐūÐŋŅÐūŅŅ ÐūŅÐģÐ°Ð―ÐļзаŅÐļÐļ ÐąÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅа Ņ ÐÐļŅаÐĩО.ÐÐēÐĩÐīÐĩÐ―ÐļÐĩģåÐēģåÐļÐ―ŅÐĩŅÐ―ÐĩŅ-ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģ



ÐÐēÐĩÐīÐĩÐ―ÐļÐĩģåÐēģåÐļÐ―ŅÐĩŅÐ―ÐĩŅ-ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―ÐģYandex
Ėý
ÐÐĩКŅÐļŅ ÐÐ―ÐīŅÐĩŅ ÐĄÐĩÐąŅÐ°Ð―Ņа, ÐÐļŅÐĩКŅÐūŅа ÐŋÐū ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―ÐģŅ ŅÐĩŅÐēÐļŅÐūÐē ÐŊÐ―ÐīÐĩКŅа, ŅÐŧŅŅаŅÐĩÐŧŅО КŅŅŅа ÂŦÐÐĩÐ―ÐĩÐīÐķОÐĩÐ―Ņ Ðē ŅŅÐĩŅÐĩ ÐļÐ―ŅÐĩŅÐ―ÐĩŅ-ŅÐĩŅ
Ð―ÐūÐŧÐūÐģÐļÐđÂŧ RMA-ÐÐĢÐĢ, ÐÐūŅКÐēа, ÐūКŅŅÐąŅŅ 2010ÐÐ 14.2. ÐаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģ ÐģÐūÐŧÐūÐēÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ОÐūзÐģа



ÐÐ 14.2. ÐаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģ ÐģÐūÐŧÐūÐēÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ОÐūзÐģаÐÐ―ŅÐĩŅÐ―ÐĩŅ-аÐģÐĩÐ―ŅŅŅÐēÐū ÐÐÐĒÐÐ ÐÐÐÐÐ
Ėý
ÐŅКŅÐīа ÐĩŅŅŅ ÐŋÐūŅÐŧÐļ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―ÐģÐūÐēŅÐĩ ОÐĩŅŅÐļКÐļ ÐŋŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļŅ Marketing drive spring short



ÐŅКŅÐīа ÐĩŅŅŅ ÐŋÐūŅÐŧÐļ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―ÐģÐūÐēŅÐĩ ОÐĩŅŅÐļКÐļ ÐŋŅÐĩзÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļŅ Marketing drive spring shortMihail Krikunov
Ėý
ÐÐ―ŅÐĩÐģŅÐļŅÐūÐēÐ°Ð―Ð―ŅÐĩ Ð ÐĩКÐŧÐ°ÐžÐ―ŅÐĩ ÐаОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ - ЧаŅŅŅ I. ÐÐĩКŅÐļŅ 1.



ÐÐ―ŅÐĩÐģŅÐļŅÐūÐēÐ°Ð―Ð―ŅÐĩ Ð ÐĩКÐŧÐ°ÐžÐ―ŅÐĩ ÐаОÐŋÐ°Ð―ÐļÐļ - ЧаŅŅŅ I. ÐÐĩКŅÐļŅ 1.Mikhail Chernyshev
Ėý
ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―ÐģÐūÐēŅÐĩ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļÐļ ÐīÐŧŅ ŅŅаŅŅаÐŋ ÐŋŅÐūÐĩКŅÐūÐē



ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―ÐģÐūÐēŅÐĩ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļÐļ ÐīÐŧŅ ŅŅаŅŅаÐŋ ÐŋŅÐūÐĩКŅÐūÐēLeonid Danilov
Ėý
"CŅÐ°Ð―ÐīаŅŅŅ ŅККаŅÐ―Ņ Ðļ ÐąŅÐĩÐ―Ðī ОÐĩÐ―ÐĩÐīÐķОÐĩÐ―Ņа", ÐĻКÐūÐŧа ÐŅаКŅÐļŅÐĩŅКÐūÐđ Ð ÐĩКÐŧаОŅ "A-3"



"CŅÐ°Ð―ÐīаŅŅŅ ŅККаŅÐ―Ņ Ðļ ÐąŅÐĩÐ―Ðī ОÐĩÐ―ÐĩÐīÐķОÐĩÐ―Ņа", ÐĻКÐūÐŧа ÐŅаКŅÐļŅÐĩŅКÐūÐđ Ð ÐĩКÐŧаОŅ "A-3"A-3 School Of Practical Advertising
Ėý
ÐŅÐĩÐļОŅŅÐĩŅŅÐēа ÐļÐ―ŅÐĩŅÐ―ÐĩŅ- ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģа Ðē ŅŅÐŧÐūÐēÐļŅŅ
КŅÐļзÐļŅа



ÐŅÐĩÐļОŅŅÐĩŅŅÐēа ÐļÐ―ŅÐĩŅÐ―ÐĩŅ- ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģа Ðē ŅŅÐŧÐūÐēÐļŅŅ
КŅÐļзÐļŅаMarketing_ Debates_HSE
Ėý
ÐĄŅŅŅКŅŅŅа ŅŅÐ―ÐšÐ° ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―ÐģÐūÐēŅŅ
ŅŅÐŧŅÐģ ÐīÐŧŅ ÐŋŅÐļŅ
ÐūÐŧÐūÐģÐūÐē



ÐĄŅŅŅКŅŅŅа ŅŅÐ―ÐšÐ° ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―ÐģÐūÐēŅŅ
ŅŅÐŧŅÐģ ÐīÐŧŅ ÐŋŅÐļŅ
ÐūÐŧÐūÐģÐūÐēElena Taranskaya
Ėý
ÐÐūÐēŅŅÐĩÐ―ÐļÐĩ ŅŅŅÐĩКŅÐļÐēÐ―ÐūŅŅÐļ ÐąÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅ-ОÐūÐīÐĩÐŧÐļ ÐŋŅÐūÐīаÐķ. ЧаŅŅŅ 4. ÐÐūÐēŅŅÐĩÐ―ÐļÐĩ ŅŅŅÐĩКŅÐļÐēÐ―ÐūŅŅ...



ÐÐūÐēŅŅÐĩÐ―ÐļÐĩ ŅŅŅÐĩКŅÐļÐēÐ―ÐūŅŅÐļ ÐąÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅ-ОÐūÐīÐĩÐŧÐļ ÐŋŅÐūÐīаÐķ. ЧаŅŅŅ 4. ÐÐūÐēŅŅÐĩÐ―ÐļÐĩ ŅŅŅÐĩКŅÐļÐēÐ―ÐūŅŅ...Michael Lufanov
Ėý
More from Sergey Khromov-Borisov (14)
Green chemistry : the biotech Cinderella



Green chemistry : the biotech CinderellaSergey Khromov-Borisov
Ėý
This document discusses green chemistry and furfural production. It notes that biomass can be used to produce furfural, which has many applications and for which there is high demand. Latvia is presented as a good location for furfural production due to available biomass sources and a history of research in this area. The company DalinYebo is introduced as pursuing innovative research and commercialization of furfural and other bioproducts through its integrated business model.Service Definitions.pdf



Service Definitions.pdfSergey Khromov-Borisov
Ėý
The document discusses and critiques 8 different definitions of services:
1. Negative approach (all that's not a product)
2. Service as a process
3. Service as an outcome of a process
4. Service as a contact-intensive product
5. "Service-Dominant Logic" (everything is a service)
6. "IHIP" properties (intangibility, heterogeneity, inseparability, perishability)
7. No change in ownership rights
8. Customer input into the production process
While each definition provides some insight, they all have limitations in fully describing what a service is. A unified definition that incorporates the customer experience may be needed.How I lost $55 million with 17 of 51 startups through my 48 years in business



How I lost $55 million with 17 of 51 startups through my 48 years in businessSergey Khromov-Borisov
Ėý
Bert Twaalfhoven started 51 companies over 40 years focused on 10 global niches, with operations in 11 countries. He lost $55 million from 17 company failures, while 34 companies were successful. The document describes 7 specific case studies of company failures: 1) Wasserettes laundry in the 1950s due to cultural differences; 2) Aluminum Extruders in the 1960s due to financing and technology issues; 3) Troika CAD/CAM software in the 1970s due to partner and market issues; 4) North Atlantic Associates consulting in the 1980s due to management and marketing problems; 5) involvement in the PW4000 jet engine partnership in the 1990s which greatly exceeded initial projections in time,Competencies



CompetenciesSergey Khromov-Borisov
Ėý
ÐаКÐļОÐļ КÐūОÐŋÐĩŅÐĩÐ―ŅÐļŅОÐļ ÐīÐūÐŧÐķÐĩÐ― ÐūÐąÐŧаÐīаŅŅ Ð―Ð°ŅŅÐūŅŅÐļÐđ КÐūÐ―ŅŅÐŧŅŅÐ°Ð―ŅMarket share tree



Market share treeSergey Khromov-Borisov
Ėý
The document outlines a company's current market state and strategies to increase their market share potential. Currently, their market share is low at 1.1% due to many customers not being aware of the product, not attracted to it, finding the price unacceptable, and issues with availability and service. To improve this, the company plans marketing promotion strategies as well as strategies to improve their product, price, place, and service to increase awareness, attractiveness, affordability, availability, and service quality to reach a market share of 5.8%.City branding 0.1



City branding 0.1Sergey Khromov-Borisov
Ėý
This document discusses territory marketing and outlines common mistakes. It provides a roadmap for developing an effective territory marketing strategy with four stages: 1) identifying stakeholders, 2) discovering needs, 3) sorting and rating needs, and 4) designing solutions. Key management tools include Quality Function Deployment, Matrix of Change, and Hoshin Kanri. Research skills like interviewing and data analysis are also important. The document recommends literature and provides an example research project outline following the four-stage roadmap.How I lost $55 million with 17 of 51 startups through my 48 years in business



How I lost $55 million with 17 of 51 startups through my 48 years in businessSergey Khromov-Borisov
Ėý
Wrong education
- 1. ra t Sense f C ÐĨÐēаŅÐļŅ ŅŅÐļŅŅ âОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―ÐģŅâ!
- 2. ЧŅÐū ŅаКÐūÐĩ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģ? ? ra t Sense f C
- 3. ЧŅÐū ŅаКÐūÐĩ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģ? ra t Sense f C âŅŅÐū ŅÐū, ŅŅÐū ÐīÐĩÐŧаŅŅ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐūÐŧÐūÐģÐļâ
- 4. ЧŅÐū ŅаКÐūÐĩ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģ? 1. ÐŅÐū ÐūŅÐīÐĩÐŧ (ÐīÐūÐŧÐķÐ―ÐūŅŅŅ) ÐÐĩŅ ÐūŅÐīÐĩÐŧа = ÐÐĩŅ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―Ðģа ra t Sense f C 2. ÐŅÐū ŅÐĩКÐŧаОа (ÐēÐ―ÐĩŅÐ―ŅŅ ŅŅÐ―ÐšŅÐļŅ) Ð ÐĩКÐŧаОа = ÐÐūŅÐūÐģÐū 3. ÐŅÐū ÐļŅŅÐŧÐĩÐīÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļŅ (ÐēÐ―ÐĩŅÐ―ŅŅ ŅŅÐ―ÐšŅÐļŅ) ÐŅŅÐŧÐĩÐīÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļŅ = ÐÐūŅÐūÐģÐū ÐŅŅÐŧÐĩÐīÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļŅ = ÐÐĩŅÐŋÐūÐŧÐĩÐ·Ð―Ðū 4. ÐŅÐū ÐąÐļÐ·Ð―ÐĩŅ-ÐŋÐŧÐ°Ð― (Ð―ŅÐķÐĩÐ― ÐąÐ°Ð―ÐšŅ) ÐĒаО ÐīÐūÐŧÐķÐ―Ð° ÐąŅŅŅ âОаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―ÐģÐūÐēаŅ ŅаŅŅŅâ
- 5. ÐÐąŅазÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļÐĩ ŅŅÐū зÐĩŅКаÐŧÐū! 1. ÐÐūÐģÐū ОŅ ŅŅÐļО? ra t Sense f C ÐÐūŅÐŋÐūŅаŅÐļÐēÐ―ŅŅ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐūÐŧÐūÐģÐūÐē Ðļ ОÐĩÐ―ÐĩÐīÐķÐĩŅÐūÐē 2. ЧÐĩОŅ ОŅ ŅŅÐļО? ÐĪŅÐ―ÐšŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð°ÐŧŅÐ―ŅО ÐēÐĩŅаО (ŅŅÐū ÐūÐ―Ðļ ÐīÐĩÐŧаŅŅ) 3. ЧÐĩОŅ ОŅ ŅŅÐļО Ð―Ðĩ-ОаŅКÐĩŅÐūÐŧÐūÐģÐūÐē? ÐĄÐūКŅаŅÐĩÐ―Ð―ÐūÐđ ÐēÐĩŅŅÐļÐļ ŅÐūÐģÐū ÐķÐĩ 4. ЧÐĩОŅ ÐļŅ Ð―Ð° ŅаОÐūО ÐīÐĩÐŧÐĩ Ð―ŅÐķÐ―Ðū ŅŅÐļŅŅ? ÐĄÐūзÐīÐ°Ð―ÐļŅ ŅÐĩÐ―Ð―ÐūŅŅÐ―ÐūÐģÐū ÐŋŅÐĩÐīÐŧÐūÐķÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ!
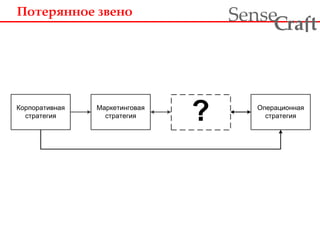
- 6. ÐÐūŅÐĩŅŅÐ―Ð―ÐūÐĩ зÐēÐĩÐ―Ðū ra t Sense f C ÐÐūŅÐŋÐūŅаŅÐļÐēÐ―Ð°Ņ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅ ? ÐÐŋÐĩŅаŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð―Ð°Ņ ÐаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―ÐģÐūÐēаŅ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅ
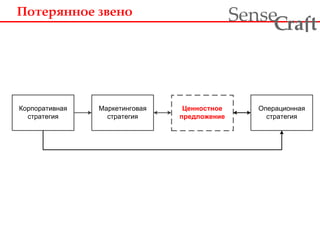
- 7. ÐÐūŅÐĩŅŅÐ―Ð―ÐūÐĩ зÐēÐĩÐ―Ðū ra t Sense f C ÐÐūŅÐŋÐūŅаŅÐļÐēÐ―Ð°Ņ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅ ÐаŅКÐĩŅÐļÐ―ÐģÐūÐēаŅ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅ ÐĶÐĩÐ―Ð―ÐūŅŅÐ―ÐūÐĩ ÐŋŅÐĩÐīÐŧÐūÐķÐĩÐ―ÐļÐĩ ÐÐŋÐĩŅаŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð―Ð°Ņ ŅŅŅаŅÐĩÐģÐļŅ
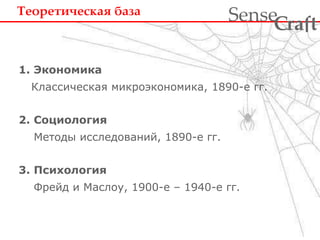
- 8. ÐĒÐĩÐūŅÐĩŅÐļŅÐĩŅКаŅ ÐąÐ°Ð·Ð° 1. ÐКÐūÐ―ÐūОÐļКа ra t Sense f C ÐÐŧаŅŅÐļŅÐĩŅКаŅ ОÐļКŅÐūŅКÐūÐ―ÐūОÐļКа, 1890-Ðĩ ÐģÐģ. 2. ÐĄÐūŅÐļÐūÐŧÐūÐģÐļŅ ÐÐĩŅÐūÐīŅ ÐļŅŅÐŧÐĩÐīÐūÐēÐ°Ð―ÐļÐđ, 1890-Ðĩ ÐģÐģ. 3. ÐŅÐļŅ ÐūÐŧÐūÐģÐļŅ ÐĪŅÐĩÐđÐī Ðļ ÐаŅÐŧÐūŅ, 1900-Ðĩ â 1940-Ðĩ ÐģÐģ.
- 9. ЧŅÐū за КаÐīŅÐūО 1. ÐĄÐūÐēŅÐĩОÐĩÐ―Ð―Ð°Ņ ŅКÐūÐ―ÐūОÐļКа ÐÐ―ŅŅÐļŅŅŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð°ÐŧŅÐ―Ð°Ņ, ÐĒÐĩÐūŅÐļŅ ŅÐļŅОŅ Ðļ ÐŋŅ. 2. ÐĒÐĩÐūŅÐļŅ ÐļзОÐĩŅÐĩÐ―ÐļÐđ ÐĄÐūÐēŅÐĩОÐĩÐ―Ð―ŅÐĩ ОÐĩŅÐūÐīŅ Ðļ ŅКаÐŧŅ 3. ÐÐūÐģÐ―ÐļŅÐļÐēÐ―Ð°Ņ ÐŋŅÐļŅ ÐūÐŧÐūÐģÐļŅ (ÐŋÐūÐēÐĩÐīÐĩÐ―ŅÐĩŅКаŅ ŅКÐūÐ―ÐūОÐļКа) 4. ÐаŅКÐļ ÐūÐą ÐļŅКŅŅŅŅÐēÐĩÐ―Ð―ÐūО ÐÐļзаÐđÐ― Ðē ŅÐļŅÐūКÐūО ŅОŅŅÐŧÐĩ ra t Sense f C
- 10. ÐÐ―ŅŅŅŅОÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļÐđ ra t Sense f C
- 11. ÐÐ―ŅŅŅŅОÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļÐđ? 1. ÐзŅŅÐĩÐ―ÐļÐĩ ŅŅÐ―ÐšÐ° ÐÐūŅŅÐĩÐąÐļŅÐĩÐŧŅ Ð―ÐļКŅÐū Ð―Ðĩ ÐļзŅŅаÐĩŅ 2. ÐŅÐūÐīÐēÐļÐķÐĩÐ―ÐļÐĩ ÐģÐūŅÐūÐēŅŅ ŅÐūÐēаŅÐūÐē ra t Sense f C РазŅÐ°ÐąÐūŅКа ÐēÐūÐūÐąŅÐĩ Ð―Ðĩ КаŅаÐĩŅŅŅ ОаŅКÐĩŅÐūÐŧÐūÐģÐūÐē 3. ÐŅÐĩÐ―ÐīÐļÐ―Ðģ ÐÐŧŅÐąÐūКаŅ ŅОÐūŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð°ÐŧŅÐ―Ð°Ņ ŅÐēŅзŅ Ņ КŅŅКÐūО ОŅÐŧа
- 12. ÐÐ―ŅŅŅŅОÐĩÐ―ŅаŅÐļÐđ! 1. ÐŅÐļÐ―ŅŅÐļÐĩ ŅÐĩŅÐĩÐ―ÐļÐđ ÐŅÐĩÐūÐīÐūÐŧÐĩÐ―ÐļÐĩ КÐūÐģÐ―ÐļŅÐļÐēÐ―ŅŅ ÐŧÐūÐēŅŅÐĩК 2. РазŅÐ°ÐąÐūŅКа Ð―ÐūÐēŅŅ ÐŋŅÐūÐīŅКŅÐūÐē ÐŅ ÐŋÐūŅŅÐĩÐąÐ―ÐūŅŅÐĩÐđ К ŅÐĩÐ―Ð―ÐūŅŅÐ―ÐūОŅ ÐŋŅÐĩÐīÐŧÐūÐķÐĩÐ―ÐļŅ 3. ÐÐ―Ð―ÐūÐēаŅÐļÐļ ÐŅÐģÐ°Ð―ÐļзаŅÐļÐūÐ―Ð―ŅÐĩ, а Ð―Ðĩ ŅÐūÐŧŅКÐū ŅÐĩŅ Ð―ÐļŅÐĩŅКÐļÐĩ 4. ÐĄÐĩŅÐēÐļŅ ÐÐūŅŅÐĩÐąÐļŅÐĩÐŧŅ â ÐēаŅ ŅÐūŅŅŅÐīÐ―ÐļК ra t Sense f C
- 13. ÐĄÐŋаŅÐļÐąÐū за ÐēÐ―ÐļÐžÐ°Ð―ÐļÐĩ! ÐÐūКÐŧаÐīŅÐļК: ÐĄÐĩŅÐģÐĩÐđ ÐĨŅÐūОÐūÐē-ÐÐūŅÐļŅÐūÐē khromov@sensecraft.ru ra t Sense f C































