X rayBY sushil kumar
Download as pptx, pdf0 likes716 views
X-rays are high-energy electromagnetic radiation produced by decelerating electrons or electronic transitions in atoms. X-ray spectrometry uses components like x-ray sources, filters, monochromators, sample holders, and detectors to analyze materials. Monochromators restrict the wavelength range of incident radiation by absorbing certain wavelengths. Diffraction of x-rays from crystalline materials enables high specificity analysis using Bragg's law. Common detectors like gas detectors, scintillators, and semiconductors convert x-ray photons into electrical signals for analysis.
1 of 18
Download to read offline











Ad
Recommended
Radiation detection and measurement
Radiation detection and measurement Shahid Younas
╠²
This document discusses semi-conductor detectors and their use in radiation detection. It describes the basic structure of atoms and different types of bonds between atoms. It explains that in crystalline materials like semiconductors, electrons exist in energy bands separated by gaps. In semiconductors and insulators, the valence band is full while the conduction band is empty, allowing electrons to move if given enough energy to cross the band gap. Semiconductors can be "doped" with impurities to create p-type or n-type materials and function as radiation detectors by generating electron-hole pairs when ionizing radiation transfers electrons to the conduction band.Chapter 3 detection devices
Chapter 3 detection devicesROBERT ESHUN
╠²
This document discusses various types of radiation detection devices, including film badges, ionization chambers, Geiger-Muller counters, proportional counters, scintillation counters, photographic plates, electroscopes, bubble chambers, solid-state detectors, cloud chambers, and spark counters. Each detection method works by using different processes like ionization, fluorescence, or track visualization to detect and sometimes quantify radiation levels or particle energy. Regular monitoring of radiation is important for safety when working with radioactive materials.Nuclear radiation detector
Nuclear radiation detectorsiddharth gupta
╠²
Nuclear radiation detectors detect nuclear particles and radiation. They work by exciting or ionizing the atoms in the material they pass through. There are different types of radiation including charged particles like alpha and beta particles, uncharged neutrons, and electromagnetic gamma rays and x-rays. Detection methods are based on the radiation interacting with the detector's base material, often ionizing or exciting its atoms. Detectors are classified as gas filled, ionization chambers, Geiger-Muller counters, semiconductors, Wilson cloud chambers or bubble chambers. Their workings exploit the properties of ionization, fluorescence, or exposing photographic plates.Radiation detectors
Radiation detectorsjmocherman
╠²
This document discusses various methods for detecting radiation. It outlines passive detectors like photographic film, electroscopes, dosimeters, and thermoluminescent dosimeters (TLDs) which do not require a power source. Active detectors mentioned include Geiger-Muller tubes and scintillation detectors, which need a constant energy supply. Both types detect radiation indirectly by ionizing matter and detecting the ions produced, though active detectors provide more information about the radiation type and energy.Scintillation Counter and Semiconductor Detector
Scintillation Counter and Semiconductor DetectorSri Ramakrishna Mission Vidyalaya College of Arts and Science,Coimbatore-20.
╠²
The document provides an overview of scintillation counters, including their historical invention and operational principles for detecting ionizing radiation. It details various types of scintillators and semiconductor detectors, explaining their compositions and mechanisms for radiation detection. Additionally, it discusses advantages of semiconductor detectors in detecting alpha and beta particles with high resolution and efficiency.Active methods of neutron detection
Active methods of neutron detectionleishare
╠²
This document provides an overview of active methods for neutron detection, including gas filled detectors like ionization chambers and proportional counters, scintillation detectors using materials like lithium iodide and organic scintillators, and semiconductor detectors. It describes the basic detection mechanisms, advantages and disadvantages of different methods, and their typical applications in neutron dosimetry and spectrometry.nuclear radiation detector unit V
nuclear radiation detector unit VDr. Vishal Jain
╠²
This document provides information about nuclear radiation detectors. It discusses three main types of gaseous ionization detectors: ionization chambers, proportional counters, and Geiger-M├╝ller tubes. Ionization chambers detect radiation by collecting all ion pairs created through gas ionization when radiation passes through. Proportional counters can measure radiation energy by producing output proportional to radiation energy through gas amplification of ion pairs. Geiger-M├╝ller tubes operate at very high voltages where any initial ionization causes a self-sustaining discharge and produces a standard pulse height independent of radiation type.Radiation detection and measurement
Radiation detection and measurement Shahid Younas
╠²
This document discusses different types of gas-filled and scintillation radiation detectors. It provides information on GM counters, proportional counters, scintillators, photomultiplier tubes, and thermoluminescent dosimeters. Key points include: how GM counters differ from proportional counters in their avalanche chain reactions; common scintillator materials like NaI(Tl) and BGO; how photomultiplier tubes convert light photons to electrical signals and amplify signals through dynode multiplication; and applications of different detector types in nuclear medicine imaging. The document is in a question-answer format where various concepts are explained in response to questions.Gm counter
Gm counterAvinashAvi110
╠²
The document summarizes a seminar on the Geiger-Muller (G-M) counter. It describes the G-M counter as a device invented in 1928 that uses a gas-filled tube to detect alpha, beta, and gamma radiation. When radiation enters the tube, it ionizes the gas molecules, producing a pulse of current between electrodes that is counted. The document discusses the construction, working principle, advantages, and applications of the G-M counter.Nmr instrumentation
Nmr instrumentationShivam Sharma
╠²
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is an analytical technique that uses radio waves and strong magnetic fields to characterize organic molecules. The key components of an NMR spectrometer include a sample holder, permanent magnet, magnetic coil, radio frequency generator and receiver, and readout system. The magnet provides a strong and uniform magnetic field, the generator produces radio waves to excite the nuclei, and the receiver and readout system detect and display the resonance signals to identify the molecules.Atomic emission spectroscopy
Atomic emission spectroscopyWasla Anum
╠²
Atomic emission spectroscopy is a standard method for metal analysis where a sample is vaporized to form free atoms that are excited to higher energy states. When the atoms return to lower states, they emit photons of radiation. Modern instruments use non-combustion plasma sources like inductively coupled plasma. An atomic emission spectrometer consists of a sample atomizer, monochromator, and detector. The sample is vaporized and excited, then the emitted light is dispersed and measured to identify elemental composition. Atomic emission spectroscopy is used for applications like pharmaceutical and metals analysis, and determining mineral composition in materials.Detection of Gamma Radiation
Detection of Gamma Radiation@Saudi_nmc
╠²
Detection of gamma radiation is used to study properties of atomic nuclei. Two common detectors are scintillation detectors and semiconductor detectors. Scintillation detectors use scintillation materials that emit visible light when struck by gamma rays, while semiconductor detectors use depletion regions in germanium crystals. Both detectors require amplification and signal processing electronics to analyze the energy deposited by gamma rays. Key measurements involve determining the energy spectrum of gamma ray sources and identifying peaks and edges that reveal information about nuclear properties and interactions.25 -radiation_detection_&_measurement_i
25 -radiation_detection_&_measurement_imurty61
╠²
There are three main types of radiation detectors: gas-filled detectors which use a gas between electrodes, scintillation detectors which use materials that produce light when irradiated, and semiconductor detectors made of purified crystalline materials. Detectors can also be classified by the type of information they provide, such as counting interactions, measuring energy, or indicating dose. The main challenges for detectors are dead time at high interaction rates and maintaining good energy resolution and detection efficiency.Gamma ray spectrum by using na i(tl)detector ..
Gamma ray spectrum by using na i(tl)detector ..Hemn Rahman
╠²
The document discusses the study of gamma-ray spectrum using scintillation detectors and single channel analyzers, highlighting the nature of radioactive decay and transmutation. It explains different types of decay, including gamma decay, and delves into interactions of gamma radiation with matter, such as the photoelectric effect and Compton scattering. Additionally, it describes the properties and functioning of scintillation detectors, particularly thallium-activated sodium iodide (NaI(Tl)).Geiger muller counter
Geiger muller counterAvi Dhawal
╠²
The document is a presentation about the Geiger-Muller counter given by Avinash Dhawal to Mr. Sudhir Bhardhwaj. It discusses the history, development, principle, and applications of the Geiger-Muller counter. The Geiger-Muller counter detects ionizing radiation such as alpha, beta, and gamma rays using ionization produced in a Geiger-Muller tube. It was originally developed in 1908 and an advanced model capable of detecting all radiation types was developed in 1928 by Geiger and Muller.Nmr spectroscopy
Nmr spectroscopyAnubhav Gupta
╠²
NMR spectroscopy is a technique that uses radio waves and strong magnetic fields to analyze atomic nuclei and their magnetic properties. It provides information about the molecular structure of compounds. The document discusses the basic principles of NMR spectroscopy including nuclear spin, chemical shifts, spin-spin coupling, and instrumentation. It also provides an example 1H NMR spectrum of ethanol to demonstrate how peaks are split based on neighboring hydrogen atoms.Analytical biochemistry
Analytical biochemistryMonika Uma Shankar
╠²
1) A Geiger-Muller counter detects ionizing radiation by measuring the pulses produced when radiation particles pass through a gas-filled tube and cause ionization.
2) It consists of a copper cylinder containing an inert gas at low pressure, with electrodes to collect ions produced and measure the resulting pulse.
3) Geiger counters are useful for detecting beta particles and low-energy photons, and have applications in radiation dosimetry, health physics, and other fields where radiation detection is needed.Radiation detectors
Radiation detectors Jonathan Lalrinmawia
╠²
This document provides an overview of radiation detectors. It discusses why radiation detection is important, how radiation interacts with matter, common types of detectors like ionization chambers, proportional counters, and GM counters, and how detectors work to detect different types of radiation. Specific examples are given around using an ion chamber survey meter to detect x-rays. Key factors around detector selection, specifications, and operating principles are summarized.Geiger muller counter
Geiger muller counterBritto Samuel
╠²
The document summarizes the Geiger-M├╝ller counter, an instrument used to detect ionizing radiation such as alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays. It describes the history and development of the counter, from its original detection principle discovered in 1908 to its modern form using a Geiger-M├╝ller tube. The operating principle is explained, where ionization events in an inert gas-filled tube produce electrical pulses that are counted and displayed. Different readout types including counts per second and absorbed dose are discussed. Applications include detection of radioactive materials and environmental monitoring for radiation levels.Basics of NMR
Basics of NMRrajkchem
╠²
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is a technique that studies molecules by observing their interaction with radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation in a strong magnetic field. The document outlines the key components of NMR instrumentation, including the sample holder, magnetic coils, and various detectors, which work together to analyze the energy transitions of nuclei. Additionally, it explains the fundamental principle of NMR involving chemical shifts and energy transfer during the excitation of nuclei.Nuclear i nstrumentation
Nuclear i nstrumentationshalet kochumuttath Shaji
╠²
Nuclear radiation detectors function by detecting nuclear particles or radiation using two main principles: ionization and excitation of atoms. There are two main types of radiation detectors: gas-filled detectors like ionization chambers which measure ionization produced in a gas, and scintillation counters which use a scintillator material to produce light pulses from incident radiation that are then converted to electrical signals. Common radiation detectors include Geiger-Muller tubes, which use a gas-filled tube and high voltage to produce a cascade of ion pairs to detect radiation, and scintillation counters, which use a scintillator and photomultiplier tube to convert radiation interactions into light and then an electrical signal.Ionization chamber - INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE
Ionization chamber - INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGEAnas Yess
╠²
Radiation detection uses two main methods: ionization and excitation. There are two types of radiation detection in nuclear medicine: gas-filled detectors used for non-imaging and scintillator detectors used for imaging. Gas-filled detectors like ionization chambers function by measuring the ionization produced in the gas when radiation passes through. Ionization chambers are the simplest gas-filled detectors and are widely used to detect x-rays, gamma rays, and beta particles by collecting the ion pairs created through ionization in the gas using an electric field.Proportional counter
Proportional counterHarish kumawat
╠²
The document describes the proportional counter, which is a gaseous state particle detector used to detect nuclear particles and radiation. It consists of a cylindrical metal tube filled with argon and methane gas and a thin metal wire running down the center as an anode. When radiation enters the tube, it ionizes the gas, producing electron-ion pairs. An applied voltage between the wire and tube causes gas amplification through avalanching, resulting in a pulse signal. The proportional counter can be used for particle counting and energy determination, and has advantages like low-energy detection but requires stable applied voltages.Mass spectrometry by m. usama shabbir
Mass spectrometry by m. usama shabbirMian Usama
╠²
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that separates sample components based on their mass-to-charge ratio using a mass spectrometer. The process involves sample vaporization, ionization, acceleration through electric fields, and detection after moving through a magnetic field. Applications include determining molecular masses, characterizing organic compounds, analyzing isotopic ratios, and conducting pharmaceutical analysis.Ionization chamber
Ionization chamberAnas Yess
╠²
The document discusses different types of radiation detection, focusing on gas-filled detectors and ionization chambers. There are two main effects of radiation: ionization and excitation. Gas-filled detectors measure ionization produced in gas. Ionization chambers are the simplest gas-filled detectors and work by collecting ion pairs created through gas ionization using an electric field to measure radiation. Ionization chambers are useful for radiation measurement and medical applications like dose calibration.Radiation/Particle Detectors
Radiation/Particle DetectorsErich Wanzek
╠²
The document discusses different types of particle detectors, focusing on gaseous ionization detectors and scintillating detectors. Gaseous ionization detectors like ion chambers, proportional counters, and Geiger tubes use gases to detect ionizing radiation via ionization. Ion chambers simply collect charges, while proportional counters and Geiger tubes produce proportional and amplified signals via gas multiplication. Scintillating detectors use scintillator materials to convert radiation into light, which is then detected by photomultiplier tubes. Scintillating detectors include organic/inorganic crystals and plastics, and can measure radiation intensity and energy.Basic dosimetric principle and dosimeters
Basic dosimetric principle and dosimetersVinay Desai
╠²
The document outlines basic dosimetric principles, dosimeters, and their applications in radiation physics, with a focus on the measurement of radiation exposure and absorbed dose. It covers various types of dosimeters, their properties, and operation modes including gas-filled detectors, scintillation detectors, and solid state detectors, along with the hierarchy of dosimetric regulation. Key dosimetric quantities such as activity, exposure, and absorbed dose are also defined and explained.Geiger muller counting system
Geiger muller counting systemGaurav Bhati
╠²
A Geiger-Muller counter consists of a gas-filled tube that detects ionizing radiation such as alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays. When radiation enters the tube, it ionizes the gas and produces a pulse of current that is counted by a scaler. To prevent additional pulses from a single radiation event, a small amount of quenching gas is added which absorbs excess energy and prevents further ionization of the main gas. The Geiger-Muller counter has a dead time after each detection where it cannot detect additional radiation as it re-establishes the electric field inside the tube.Erosion in indian currency
Erosion in indian currencyAshish Bhardwaj
╠²
A deficit in India's trade balance and lower foreign investment inflows put downward pressure on the Indian rupee in 2014-2015. A Chinese devaluation of the yuan further weakened the rupee by making Chinese exports more competitive. Additionally, fears over slower Indian economic growth and declines in foreign institutional investment out of Indian markets exacerbated pressure on the currency. Offloading of Indian assets by foreign investors increased demand for U.S. dollars and contributed to the rupee's decline.iros02print
iros02printSong You (??)
╠²
This document discusses modeling haptic forces and moments during interactions between virtual objects. It presents an efficient method to model haptic effects in real-time by taking into account factors like friction, gravity, contact state, and prior motion. The key ideas are to analytically solve for contact friction forces and moments based on the contact configuration type and prior motion type, after obtaining a contact normal force based on a spring model. The method was tested in a virtual assembly environment where haptic feedback was calculated at 2kHz, producing stable, smooth forces that felt realistic to the user.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Gm counter
Gm counterAvinashAvi110
╠²
The document summarizes a seminar on the Geiger-Muller (G-M) counter. It describes the G-M counter as a device invented in 1928 that uses a gas-filled tube to detect alpha, beta, and gamma radiation. When radiation enters the tube, it ionizes the gas molecules, producing a pulse of current between electrodes that is counted. The document discusses the construction, working principle, advantages, and applications of the G-M counter.Nmr instrumentation
Nmr instrumentationShivam Sharma
╠²
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is an analytical technique that uses radio waves and strong magnetic fields to characterize organic molecules. The key components of an NMR spectrometer include a sample holder, permanent magnet, magnetic coil, radio frequency generator and receiver, and readout system. The magnet provides a strong and uniform magnetic field, the generator produces radio waves to excite the nuclei, and the receiver and readout system detect and display the resonance signals to identify the molecules.Atomic emission spectroscopy
Atomic emission spectroscopyWasla Anum
╠²
Atomic emission spectroscopy is a standard method for metal analysis where a sample is vaporized to form free atoms that are excited to higher energy states. When the atoms return to lower states, they emit photons of radiation. Modern instruments use non-combustion plasma sources like inductively coupled plasma. An atomic emission spectrometer consists of a sample atomizer, monochromator, and detector. The sample is vaporized and excited, then the emitted light is dispersed and measured to identify elemental composition. Atomic emission spectroscopy is used for applications like pharmaceutical and metals analysis, and determining mineral composition in materials.Detection of Gamma Radiation
Detection of Gamma Radiation@Saudi_nmc
╠²
Detection of gamma radiation is used to study properties of atomic nuclei. Two common detectors are scintillation detectors and semiconductor detectors. Scintillation detectors use scintillation materials that emit visible light when struck by gamma rays, while semiconductor detectors use depletion regions in germanium crystals. Both detectors require amplification and signal processing electronics to analyze the energy deposited by gamma rays. Key measurements involve determining the energy spectrum of gamma ray sources and identifying peaks and edges that reveal information about nuclear properties and interactions.25 -radiation_detection_&_measurement_i
25 -radiation_detection_&_measurement_imurty61
╠²
There are three main types of radiation detectors: gas-filled detectors which use a gas between electrodes, scintillation detectors which use materials that produce light when irradiated, and semiconductor detectors made of purified crystalline materials. Detectors can also be classified by the type of information they provide, such as counting interactions, measuring energy, or indicating dose. The main challenges for detectors are dead time at high interaction rates and maintaining good energy resolution and detection efficiency.Gamma ray spectrum by using na i(tl)detector ..
Gamma ray spectrum by using na i(tl)detector ..Hemn Rahman
╠²
The document discusses the study of gamma-ray spectrum using scintillation detectors and single channel analyzers, highlighting the nature of radioactive decay and transmutation. It explains different types of decay, including gamma decay, and delves into interactions of gamma radiation with matter, such as the photoelectric effect and Compton scattering. Additionally, it describes the properties and functioning of scintillation detectors, particularly thallium-activated sodium iodide (NaI(Tl)).Geiger muller counter
Geiger muller counterAvi Dhawal
╠²
The document is a presentation about the Geiger-Muller counter given by Avinash Dhawal to Mr. Sudhir Bhardhwaj. It discusses the history, development, principle, and applications of the Geiger-Muller counter. The Geiger-Muller counter detects ionizing radiation such as alpha, beta, and gamma rays using ionization produced in a Geiger-Muller tube. It was originally developed in 1908 and an advanced model capable of detecting all radiation types was developed in 1928 by Geiger and Muller.Nmr spectroscopy
Nmr spectroscopyAnubhav Gupta
╠²
NMR spectroscopy is a technique that uses radio waves and strong magnetic fields to analyze atomic nuclei and their magnetic properties. It provides information about the molecular structure of compounds. The document discusses the basic principles of NMR spectroscopy including nuclear spin, chemical shifts, spin-spin coupling, and instrumentation. It also provides an example 1H NMR spectrum of ethanol to demonstrate how peaks are split based on neighboring hydrogen atoms.Analytical biochemistry
Analytical biochemistryMonika Uma Shankar
╠²
1) A Geiger-Muller counter detects ionizing radiation by measuring the pulses produced when radiation particles pass through a gas-filled tube and cause ionization.
2) It consists of a copper cylinder containing an inert gas at low pressure, with electrodes to collect ions produced and measure the resulting pulse.
3) Geiger counters are useful for detecting beta particles and low-energy photons, and have applications in radiation dosimetry, health physics, and other fields where radiation detection is needed.Radiation detectors
Radiation detectors Jonathan Lalrinmawia
╠²
This document provides an overview of radiation detectors. It discusses why radiation detection is important, how radiation interacts with matter, common types of detectors like ionization chambers, proportional counters, and GM counters, and how detectors work to detect different types of radiation. Specific examples are given around using an ion chamber survey meter to detect x-rays. Key factors around detector selection, specifications, and operating principles are summarized.Geiger muller counter
Geiger muller counterBritto Samuel
╠²
The document summarizes the Geiger-M├╝ller counter, an instrument used to detect ionizing radiation such as alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays. It describes the history and development of the counter, from its original detection principle discovered in 1908 to its modern form using a Geiger-M├╝ller tube. The operating principle is explained, where ionization events in an inert gas-filled tube produce electrical pulses that are counted and displayed. Different readout types including counts per second and absorbed dose are discussed. Applications include detection of radioactive materials and environmental monitoring for radiation levels.Basics of NMR
Basics of NMRrajkchem
╠²
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is a technique that studies molecules by observing their interaction with radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation in a strong magnetic field. The document outlines the key components of NMR instrumentation, including the sample holder, magnetic coils, and various detectors, which work together to analyze the energy transitions of nuclei. Additionally, it explains the fundamental principle of NMR involving chemical shifts and energy transfer during the excitation of nuclei.Nuclear i nstrumentation
Nuclear i nstrumentationshalet kochumuttath Shaji
╠²
Nuclear radiation detectors function by detecting nuclear particles or radiation using two main principles: ionization and excitation of atoms. There are two main types of radiation detectors: gas-filled detectors like ionization chambers which measure ionization produced in a gas, and scintillation counters which use a scintillator material to produce light pulses from incident radiation that are then converted to electrical signals. Common radiation detectors include Geiger-Muller tubes, which use a gas-filled tube and high voltage to produce a cascade of ion pairs to detect radiation, and scintillation counters, which use a scintillator and photomultiplier tube to convert radiation interactions into light and then an electrical signal.Ionization chamber - INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE
Ionization chamber - INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGEAnas Yess
╠²
Radiation detection uses two main methods: ionization and excitation. There are two types of radiation detection in nuclear medicine: gas-filled detectors used for non-imaging and scintillator detectors used for imaging. Gas-filled detectors like ionization chambers function by measuring the ionization produced in the gas when radiation passes through. Ionization chambers are the simplest gas-filled detectors and are widely used to detect x-rays, gamma rays, and beta particles by collecting the ion pairs created through ionization in the gas using an electric field.Proportional counter
Proportional counterHarish kumawat
╠²
The document describes the proportional counter, which is a gaseous state particle detector used to detect nuclear particles and radiation. It consists of a cylindrical metal tube filled with argon and methane gas and a thin metal wire running down the center as an anode. When radiation enters the tube, it ionizes the gas, producing electron-ion pairs. An applied voltage between the wire and tube causes gas amplification through avalanching, resulting in a pulse signal. The proportional counter can be used for particle counting and energy determination, and has advantages like low-energy detection but requires stable applied voltages.Mass spectrometry by m. usama shabbir
Mass spectrometry by m. usama shabbirMian Usama
╠²
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that separates sample components based on their mass-to-charge ratio using a mass spectrometer. The process involves sample vaporization, ionization, acceleration through electric fields, and detection after moving through a magnetic field. Applications include determining molecular masses, characterizing organic compounds, analyzing isotopic ratios, and conducting pharmaceutical analysis.Ionization chamber
Ionization chamberAnas Yess
╠²
The document discusses different types of radiation detection, focusing on gas-filled detectors and ionization chambers. There are two main effects of radiation: ionization and excitation. Gas-filled detectors measure ionization produced in gas. Ionization chambers are the simplest gas-filled detectors and work by collecting ion pairs created through gas ionization using an electric field to measure radiation. Ionization chambers are useful for radiation measurement and medical applications like dose calibration.Radiation/Particle Detectors
Radiation/Particle DetectorsErich Wanzek
╠²
The document discusses different types of particle detectors, focusing on gaseous ionization detectors and scintillating detectors. Gaseous ionization detectors like ion chambers, proportional counters, and Geiger tubes use gases to detect ionizing radiation via ionization. Ion chambers simply collect charges, while proportional counters and Geiger tubes produce proportional and amplified signals via gas multiplication. Scintillating detectors use scintillator materials to convert radiation into light, which is then detected by photomultiplier tubes. Scintillating detectors include organic/inorganic crystals and plastics, and can measure radiation intensity and energy.Basic dosimetric principle and dosimeters
Basic dosimetric principle and dosimetersVinay Desai
╠²
The document outlines basic dosimetric principles, dosimeters, and their applications in radiation physics, with a focus on the measurement of radiation exposure and absorbed dose. It covers various types of dosimeters, their properties, and operation modes including gas-filled detectors, scintillation detectors, and solid state detectors, along with the hierarchy of dosimetric regulation. Key dosimetric quantities such as activity, exposure, and absorbed dose are also defined and explained.Geiger muller counting system
Geiger muller counting systemGaurav Bhati
╠²
A Geiger-Muller counter consists of a gas-filled tube that detects ionizing radiation such as alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays. When radiation enters the tube, it ionizes the gas and produces a pulse of current that is counted by a scaler. To prevent additional pulses from a single radiation event, a small amount of quenching gas is added which absorbs excess energy and prevents further ionization of the main gas. The Geiger-Muller counter has a dead time after each detection where it cannot detect additional radiation as it re-establishes the electric field inside the tube.Viewers also liked (15)
Erosion in indian currency
Erosion in indian currencyAshish Bhardwaj
╠²
A deficit in India's trade balance and lower foreign investment inflows put downward pressure on the Indian rupee in 2014-2015. A Chinese devaluation of the yuan further weakened the rupee by making Chinese exports more competitive. Additionally, fears over slower Indian economic growth and declines in foreign institutional investment out of Indian markets exacerbated pressure on the currency. Offloading of Indian assets by foreign investors increased demand for U.S. dollars and contributed to the rupee's decline.iros02print
iros02printSong You (??)
╠²
This document discusses modeling haptic forces and moments during interactions between virtual objects. It presents an efficient method to model haptic effects in real-time by taking into account factors like friction, gravity, contact state, and prior motion. The key ideas are to analytically solve for contact friction forces and moments based on the contact configuration type and prior motion type, after obtaining a contact normal force based on a spring model. The method was tested in a virtual assembly environment where haptic feedback was calculated at 2kHz, producing stable, smooth forces that felt realistic to the user.Ðçð░ÐüÐï1
Ðçð░ÐüÐï1Anna2434
╠²
ðƒÐÇðÁðÀðÁð¢Ðéð░Ðåð©ÐÅ ð┐ð¥Ðüð▓ÐÅÐëðÁð¢ð░ ð┐ð¥ðÀð¢ð░ð▓ð░ÐéðÁð╗Ðîð¢ð¥ð╝Ðâ ÐÇð░ðÀð▓ð©Ðéð©ÐÄ ð┤ðÁÐéðÁð╣ ÐüÐéð░ÐÇÐêðÁð│ð¥ ð┤ð¥Ðêð║ð¥ð╗Ðîð¢ð¥ð│ð¥ ð▓ð¥ðÀÐÇð░ÐüÐéð░. ð×ð¢ð░ ð▓ð║ð╗ÐÄÐçð░ðÁÐé ð▓ ÐüðÁð▒ÐÅ ÐéðÁð╝Ðï, Ðüð▓ÐÅðÀð░ð¢ð¢ÐïðÁ Ðü ð▓ð¥Ðüð┐ÐÇð©ÐÅÐéð©ðÁð╝ ð▓ÐÇðÁð╝ðÁð¢ð©, ð©ðÀÐâÐçðÁð¢ð©ðÁð╝ Ðçð░Ðüð¥ð▓ÐïÐà ð╝ðÁÐàð░ð¢ð©ðÀð╝ð¥ð▓ ð© ð©Ðà ÐÇð¥ð╗ð© ð▓ ð▒ÐïÐéÐâ. ð×Ðüð¢ð¥ð▓ð¢ð¥ðÁ ð▓ð¢ð©ð╝ð░ð¢ð©ðÁ Ðâð┤ðÁð╗ÐÅðÁÐéÐüÐÅ ÐÇð░ðÀð╗ð©Ðçð¢Ðïð╝ Ðéð©ð┐ð░ð╝ Ðçð░Ðüð¥ð▓ ð© ð©Ðà ÐäÐâð¢ð║Ðåð©ð¥ð¢ð©ÐÇð¥ð▓ð░ð¢ð©ÐÄ.Erosion in indian currency
Erosion in indian currencyAshish Bhardwaj
╠²
A trade deficit, lower foreign investment, and concerns over economic growth put downward pressure on the Indian rupee in 2014-2015. A Chinese yuan devaluation and foreign investors offloading Indian assets exacerbated the rupee's decline. Lower foreign reserves and a higher demand for dollars to pay for imports further weakened the currency.International student presentation
International student presentationKaitlin Hurley
╠²
The document discusses international students at St. John's University and includes country profiles of Australia, China, and India. It asks what concerns international students may have living on campus and lists three potential concerns. It then provides profiles of three international students - Sophia, Liu, and Vijay - and divides groups to discuss residence halls and activities, dining facilities, and food options. The document proposes solutions for these areas and references theories of ethnic identity development and Maslow's hierarchy of needs.Chß╗»a trß╗ï chß╗®ng sa s├║t tr├¡ tuß╗ç, Alzheimer, tho├íi h├│a thß║ºn kinh
Chß╗»a trß╗ï chß╗®ng sa s├║t tr├¡ tuß╗ç, Alzheimer, tho├íi h├│a thß║ºn kinhmarlena178
╠²
Sa s├║t tr├¡ tuß╗ç l├á t├¼nh trß║íng suy giß║úm chß╗®c n─âng tr├¡ tuß╗ç ß║únh hã░ß╗ƒng ─æß║┐n ngã░ß╗Øi cao tuß╗òi, vß╗øi tß╗À lß╗ç mß║»c bß╗çnh ã░ß╗øc t├¡nh 3,9% ß╗ƒ lß╗®a tuß╗òi tß╗½ 60 trß╗ƒ l├¬n. C├íc yß║┐u tß╗æ nguy cãí bao gß╗ôm huyß║┐t ├íp cao, b├®o ph├¼, bß╗çnh tiß╗âu ─æã░ß╗Øng, v├á lß╗æi sß╗æng kh├┤ng l├ánh mß║ính, trong khi triß╗üu chß╗®ng ch├¡nh bao gß╗ôm giß║úm tr├¡ nhß╗ø v├á kh├│ kh─ân trong sinh hoß║ít h├áng ng├áy. Hiß╗çn chã░a c├│ phã░ãíng ph├íp ─æiß╗üu trß╗ï ─æß║Àc hiß╗çu, chß╗ë c├│ thß╗â kiß╗âm so├ít triß╗çu chß╗®ng v├á khuyß║┐n kh├¡ch ph├▓ng ngß╗½a bß║▒ng c├ích quß║ún l├¢ c├íc yß║┐u tß╗æ nguy cãí.Resumes Magic- Presentation
Resumes Magic- PresentationMax Infosoft
╠²
ResumesMagic.com provides resume writing and design services. They offer suitable cover letters, deliverables in common file formats, and prioritize facts according to job profiles to create standout resumes. The company has an award-winning management team and experienced content writers and designers with diverse business expertise and decades of industry experience. Sample resumes are available on their website. Contact and address information is also provided.Patch antenna
Patch antenna Ayush Bansal
╠²
This document provides an overview of microstrip patch antennas, also known as patch antennas. It defines patch antennas as consisting of a metal patch on top of a grounded dielectric substrate, which are useful at microwave frequencies above 1 GHz. The document discusses the geometry, advantages, disadvantages, feeding techniques, basic properties including resonance frequency and bandwidth, radiation pattern, and applications of microstrip patch antennas. The main applications mentioned are in mobiles, satellites, GPS, WiMAX, medical devices, and radar.xray tubes
xray tubesaugpax
╠²
This document discusses the components and operation of different types of x-ray tubes, including Crookes tubes, Coolidge tubes, rotating anode tubes, mammography tubes, and rotating envelope tubes. It describes the glass envelope, anode assembly, cathode assembly, and principles of each tube. The key components are the cathode, which emits electrons, and the anode, made of materials like tungsten, which produces x-rays upon electron bombardment. More advanced tubes use rotating or magnetic components to improve heat dissipation and image quality. Proper care and operation within rating charts is important to maximize tube lifespan.PHARMACOGNOSY GLYCOSIDES, B PHARM SECOND YEAR, RCPIPER
PHARMACOGNOSY GLYCOSIDES, B PHARM SECOND YEAR, RCPIPERMAHAJAN DHANRAJ,R C PATEL INSTITUTE OF PHARMACEUTICAL EDUCATION AND RESEARCH, SHIRPUR
╠²
This document discusses glycosides, which are organic natural compounds found in many plants and some animals. Glycosides are composed of a sugar (glycone) and non-sugar (aglycone) moiety linked together by a glycosidic linkage. The sugar is often glucose but can also be other sugars. Glycosides have therapeutic effects when the aglycone is released upon hydrolysis. The document further classifies and discusses the properties, extraction, uses and examples of various types of glycosides including saponins, liquorice roots, brahmi, dioscorea, ginseng, and sarsaparilla.The x ray tube
The x ray tubeairwave12
╠²
The x-ray tube is a key component of x-ray imaging systems. It contains a cathode that emits electrons and an anode that produces x-rays. The tube is housed in a protective enclosure to allow positioning while shielding against radiation leakage. Modern tubes use rotating anodes to dissipate heat and produce a line-focused beam from the angled target, forming a small, effective focal spot. This design provides good resolution but can cause non-uniform intensity and extrafocal radiation from electrons missing the target.X ray tube
X ray tubeRad Tech
╠²
The document discusses the components and functioning of an X-ray tube. The key components are the glass envelope, cathode, and anode. Electrons are emitted from the cathode filament and accelerated toward the anode, where their impact produces X-rays. The rotating anode allows for greater heat dissipation to enable higher exposures. Factors like focal spot size and the anode heel effect determine the quality and characteristics of the emitted X-rays. Proper cooling and protective housing are also important for safe tube operation.Zayed journalis
Zayed journalisZayed Abu Snaineh
╠²
Zayed Salman Noman Abu Snaineh is a Jordanian sports teacher and journalist seeking work. He holds a Master's degree in journalism and new media from Jordan University and a Bachelor's degree in physical education. His work experience includes teaching sports in Jordan and Dubai, and working as a recreational therapist in Saudi Arabia. He is fluent in English and Arabic with computer skills and qualifications. His interests include football, reading, and social relationships.Volatile oils mahajan
Volatile oils mahajanMAHAJAN DHANRAJ,R C PATEL INSTITUTE OF PHARMACEUTICAL EDUCATION AND RESEARCH, SHIRPUR
╠²
This document provides information about the botanical source, geographical source, cultivation, collection, macroscopic and microscopic characteristics, chemical constituents, uses, and substitutes/adulterants of several herbal drugs including Fennel fruit, Coriander fruit, Cassia bark, Clove bud, Cinnamon, Dill, Caraway, Ajowan, Cardamom, and Nutmeg. It discusses the plant species, parts used, chemical profiles and typical applications of these medicinal herbs.PHARMACOGNOSY GLYCOSIDES, B PHARM SECOND YEAR, RCPIPER
PHARMACOGNOSY GLYCOSIDES, B PHARM SECOND YEAR, RCPIPERMAHAJAN DHANRAJ,R C PATEL INSTITUTE OF PHARMACEUTICAL EDUCATION AND RESEARCH, SHIRPUR
╠²
Ad
Similar to X rayBY sushil kumar (20)
XRF and its types
XRF and its typesHamza Suharwardi
╠²
X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectrometry is a technique used for elemental analysis. There are two main types of XRF spectrometers: energy-dispersive (ED) and wavelength-dispersive (WD). ED spectrometers use a detector to measure the energy of emitted X-rays, producing a spectrum. WD spectrometers use crystals to diffract and measure wavelengths of emitted X-rays. XRF can be used to identify elements in materials like metals, glass, ceramics, and paintings.xray diffraction instrumentation
xray diffraction instrumentationBindu Kshtriya
╠²
This document describes the key components and functioning of instrumentation used in x-ray diffraction. The main components are a radiation source like an x-ray tube, a collimator to narrow the beam, a monochromator to remove unwanted radiation, detectors like photographic film or counters, and associated electronics. X-ray tubes generate x-rays via the impact of electrons on a metal target. Collimators and monochromators shape and refine the x-ray beam before it interacts with the sample. Detectors then measure the diffraction pattern, with options including film, Geiger-Muller tubes, proportional counters, scintillators, and semiconductors.X-Ray Spectroscopy.pptx
X-Ray Spectroscopy.pptxKarismaDash1
╠²
The document provides an extensive overview of x-ray spectroscopy, including its principles, instrumentation, and various techniques such as x-ray fluorescence and diffraction methods. It discusses the generation of x-rays, types, applications in both medical and industrial fields, and highlights key contributions by notable physicists like Wilhelm Roentgen and Max von Laue. The conclusion emphasizes the utility of x-ray diffraction as a non-destructive analytical tool for various materials.UV-Visible Spectrophotometer
UV-Visible SpectrophotometerLEKSHMI M R
╠²
The document summarizes the principles and components of a UV-Visible spectrophotometer. It discusses how Isaac Newton and Joseph von Fraunhofer made early contributions to spectroscopy. The key components of a UV-Vis spectrophotometer include a light source, monochromator, sample holder, detector, and signal processor. The monochromator separates light into wavelengths and the detector measures light intensity. UV-Vis spectroscopy provides information on functional groups and chemical structure by measuring absorption of light across wavelengths.UV SPECTROSCOPY ppt.pptx
UV SPECTROSCOPY ppt.pptxAshish Hingnekar
╠²
This document provides an overview of UV-Visible spectroscopy. It discusses the basic principles including electromagnetic radiation, spectroscopy, absorption of UV-Visible light, and Beer-Lambert's law. It describes the instrumentation of UV-Visible spectroscopy including light sources, wavelength selectors, sample compartments, detectors and basic components. It also discusses electronic transitions, shifts in absorption, and applications of UV-Visible spectroscopy in qualitative and quantitative analysis.UV SPECTROSCOPY ppt.pptx
UV SPECTROSCOPY ppt.pptxAshishHingnekar1
╠²
The document presents an overview of UV-Visible spectroscopy, covering its principles, instrumentation, and applications in analyzing the interaction of light with matter. Key concepts include Beer-Lambert's law, electronic transitions, and the roles of chromophores and auxochromes. Additionally, it discusses various components of UV spectrophotometers and methods for multicomponent analysis.Spectrophotometry basics and principle.pptx
Spectrophotometry basics and principle.pptxpgbiochem2023
╠²
The document discusses spectrophotometry, detailing the principles of light interaction with matter, including Planck's formula, Beer-Lambert law, and the components of a single beam spectrophotometer. It highlights the importance of wavelength accuracy, detector response consistency, and quality control checks in spectrophotometric measurements. Various sources of radiant energy, wavelength selectors, and detector types are also detailed, emphasizing their specific applications and limitations.Uv visiblr spectroscopy
Uv visiblr spectroscopyGovernment Pharmacy College Sajong, Government of Sikkim
╠²
This document provides an overview of UV-visible spectroscopy and chromophores. It discusses electromagnetic radiation and its wave and particle properties. UV-visible spectroscopy utilizes absorption of radiation in the ultraviolet and visible wavelength ranges by chromophores in molecules. Chromophores are functional groups that absorb specific wavelengths, while auxochromes modify this absorption. Beer's law describes the relationship between absorption and concentration. Instrumentation for UV-visible spectroscopy includes sources of radiation, monochromators, sample cells, and detectors. Applications involve quantitative analysis, structure elucidation, and more.x ray crystallography & diffraction
x ray crystallography & diffractionArman Dalal
╠²
X-ray crystallography is a technique for determining the atomic and molecular structure of crystals by analyzing the diffraction patterns of X-rays as they interact with electrons in a crystallized molecule. The method relies on the precision of crystal formation to provide clear data, and uses Bragg's law to establish a relationship between the diffraction angle, wavelength, and distance between crystal planes. Various detection methods, including photographic and counter methods, are employed to measure the properties of X-rays and analyze crystallized structures.B.Tech sem I Engineering Physics U-IV Chapter 2-X-Rays
B.Tech sem I Engineering Physics U-IV Chapter 2-X-RaysAbhi Hirpara
╠²
This document discusses X-rays, including their discovery, production, properties, diffraction, absorption, and applications. X-rays were discovered in 1895 by R├Ântgen during experiments with cathode ray tubes. They are generated when high-speed electrons strike a metal target in an X-ray tube. X-rays have various wavelengths and are used in fields like medicine, science research, and industry for applications such as medical imaging, defect detection, and crystal structure analysis.X ray diffraction
X ray diffractionhdghcfgfgftf
╠²
X-Ray Diffraction is a technique used to analyze crystalline structures. It involves using X-rays that are scattered by crystals in a specific pattern determined by Bragg's Law. The document discusses the instrumentation of XRD including the X-ray source, collimator, monochromator, and various detectors. It also covers different XRD methods like Laue, Bragg spectrometer, rotating crystal, and powder crystal methods. Finally, applications of XRD are presented such as determining crystal structures, polymer characterization, and soil classification.x-rays.pdf
x-rays.pdfchandankumar745043
╠²
X-ray Lab, Room 117 documents properties of x-rays including their electromagnetic nature, short wavelengths, and ability to be considered as both waves and particles. It describes how x-rays are produced via electron bombardment in an x-ray tube, and the continuous and characteristic spectra that result. Key safety aspects of x-ray sources like filtration, shielding, and interlocks are covered. Radiation safety depends on proper procedures to prevent accidental exposures from improperly configured equipment, equipment manipulation when energized, or failure to follow safety protocols.X ray generation Radiology information by rahul ppt 2
X ray generation Radiology information by rahul ppt 2Rahul Midha
╠²
X-rays are generated when high-energy electrons collide with a metal target in an X-ray tube. This produces both a continuous spectrum and characteristic peaks corresponding to the target material. Various techniques can be used to produce nearly monochromatic X-rays for diffraction experiments, including ╬▓ filters to remove unwanted wavelengths, pulse-height discrimination with detectors, and diffraction from monochromator crystals which selectively pass the desired wavelength.XRF Theory and Application
XRF Theory and ApplicationSirwan Hasan
╠²
The document discusses X-ray fluorescence (XRF) theory and applications. XRF involves bombarding a sample with X-rays, which causes fluorescent X-rays to be emitted from the sample that are characteristic of its elemental composition. This allows for both qualitative and quantitative elemental analysis. Key advantages of XRF include rapid, nondestructive analysis of major and trace elements in various materials. Common applications include analysis of soils, minerals, metals, and more in fields like geology, archaeology, and environmental analysis.X ray crystallography
X ray crystallographyROHIT PAL
╠²
X-ray crystallography is a technique that uses X-rays to determine the atomic and molecular structure of crystals. When X-rays hit a crystal, they cause the crystal to diffract the X-rays into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a three-dimensional picture of electron density within the crystal can be determined, revealing information about atomic positions and chemical bonds. Bragg's law describes the diffraction conditions of X-rays by crystals and is used to analyze diffraction patterns to determine crystal structures. Common techniques for X-ray crystallography include Laue photography, powder diffraction, and rotating crystal methods.U.V Spectroscopy.
U.V Spectroscopy.Ali Allana College Of Pharmacy
╠²
This document discusses the principles, instrumentation, and applications of UV spectroscopy. It begins with an introduction to UV spectroscopy and its uses in qualitative and quantitative analysis. It then covers the underlying principles of UV absorption, including Lambert's law and Beer's law. The key components of a UV spectrophotometer are described, including radiation sources, monochromators, sample containers, detectors, and recording systems. Finally, common applications of UV spectroscopy are outlined, such as determining functional groups, conjugation, and reaction monitoring."X ray crystallography" - Tathagata Pradhan , Department of Pharmaceutical Ch...
"X ray crystallography" - Tathagata Pradhan , Department of Pharmaceutical Ch...Tathagata Pradhan, Indo Soviet Friendship College of Pharmacy, Moga, Punjab
╠²
X-ray crystallography uses X-rays to determine the atomic structure of crystals. When X-rays hit a crystal, they cause the electrons in the crystal to diffract the X-rays into specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted X-rays, a three-dimensional picture of electron density within the crystal can be produced to determine the positions of atoms and their bonds. Bragg's law describes X-ray diffraction from crystals and states that diffraction occurs when the path length difference between X-rays reflected from successive crystal planes is an integer multiple of the wavelength. X-ray crystallography has numerous applications including determining crystal structures, identifying impurities, and analyzing chemical composition.B.tech sem i engineering physics u iv chapter 2-x-rays
B.tech sem i engineering physics u iv chapter 2-x-raysRai University
╠²
This document provides an overview of X-rays, including their discovery, production, properties, diffraction, absorption, and applications. It discusses how X-rays are generated via the bombardment of a metal target by electrons in an X-ray tube. Key points covered include Bragg's law of diffraction, Moseley's law relating atomic number to X-ray wavelength, the continuous and characteristic spectra produced, and common medical and scientific uses of X-rays.Analytical Chemistry
Analytical ChemistrySidra Javed
╠²
The document discusses various techniques in analytical chemistry, primarily focusing on spectroscopy, including infrared, UV-visible, atomic emission, and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. It details how these methods involve the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter to analyze molecular structures and identify compounds based on their absorption or emission spectra. Additionally, it explains the principles and applications of mass spectrometry for measuring the mass and abundance of ions produced from samples.ir spectroscopy
ir spectroscopykomal shinde
╠²
This document discusses infrared spectroscopy and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). It provides information on:
1. The basic theory and principles of infrared spectroscopy, including how molecular vibrations and rotations can be detected via infrared light absorption.
2. An overview of FTIR instrumentation, including how an interferometer is used to collect infrared absorption data in the time domain that is then converted to the frequency domain via a Fourier transform.
3. Performance characteristics and advantages of FTIR, such as its ability to collect an entire infrared spectrum simultaneously with high signal-to-noise ratio compared to dispersive instruments."X ray crystallography" - Tathagata Pradhan , Department of Pharmaceutical Ch...
"X ray crystallography" - Tathagata Pradhan , Department of Pharmaceutical Ch...Tathagata Pradhan, Indo Soviet Friendship College of Pharmacy, Moga, Punjab
╠²
Ad
X rayBY sushil kumar
- 1. By PRACHI
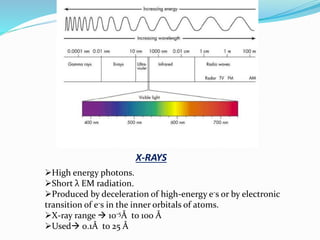
- 2. X-RAYS ´âÿHigh energy photons. ´âÿShort ╬╗ EM radiation. ´âÿProduced by deceleration of high-energy e-s or by electronic transition of e-s in the inner orbitals of atoms. ´âÿX-ray range ´âá 10-5├à to 100 ├à ´âÿUsed´âá 0.1├à to 25 ├à
- 3. Characteristics of X-rays ´âÿAbsorption of X-rays give information about the absorbing material. ´âÿFluorescence emission of X-rays enables to identify & measure heavy elements in the presence of each other & in any matrix. ´âÿDiffraction of X-rays enables analysis of crystalline materials with a high degree of specificity & accuracy.
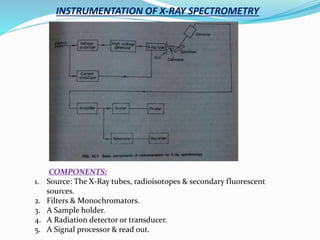
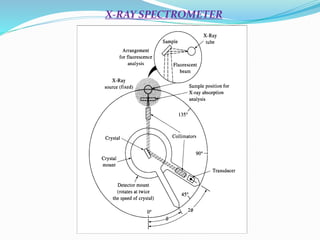
- 4. INSTRUMENTATION OF X-RAY SPECTROMETRY COMPONENTS: 1. Source: The X-Ray tubes, radioisotopes & secondary fluorescent sources. 2. Filters & Monochromators. 3. A Sample holder. 4. A Radiation detector or transducer. 5. A Signal processor & read out.
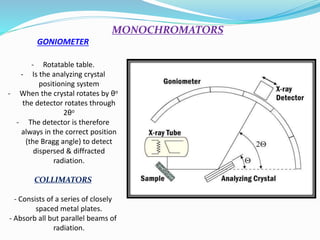
- 7. MONOCHROMATORS ÔÇóUsed for restricting the wavelength range of incident radiation. ÔÇóUsed to absorb certain ╬╗s but permit desired ╬╗s. ÔÇó Consists of a pair of beam collimators & a dispersing element. ÔÇóIs placed between the X-ray source & the sample. ÔÇó Only one type of radiation is however desired.
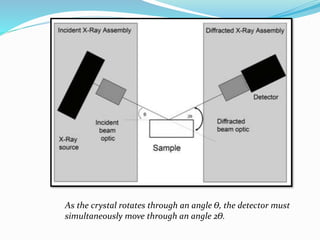
- 8. GONIOMETER - Rotatable table. - Is the analyzing crystal positioning system - When the crystal rotates by ╬©o the detector rotates through 2╬©o - The detector is therefore always in the correct position (the Bragg angle) to detect dispersed & diffracted radiation. COLLIMATORS - Consists of a series of closely spaced metal plates. - Absorb all but parallel beams of radiation. MONOCHROMATORS
- 9. BRAGG EQUATION where D spacing of the analyzing crystal Ë¿ half the angle between the detector & the sample n order of diffraction d2 n sin ´ü¼ ´ü▒ ´Ç¢ MONOCHROMATORS ÔÇóA Single crystal mounted on a goniometer that permits variation & precise determination of angle Ë¿ between crystal face & collimated incident beam. ÔÇóBy Bragg equation, for any given angular setting of the goniometer, only a few wavelengths are diffracted.
- 10. As the crystal rotates through an angle Ë¿, the detector must simultaneously move through an angle 2Ë¿.
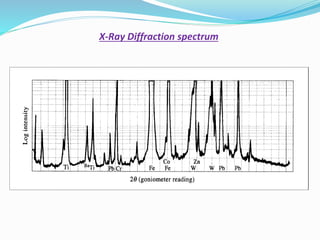
- 12. DETECTORS - Transform photon energy into electrical pulses. - The pulses (photons) are recorded as counts per second (known as count rate). - Count rate is a measure of the intensity of the X-ray beam. Three classes of X-ray detectors - Gas-filled detectors - Scintillation detectors - Semiconductor detectors
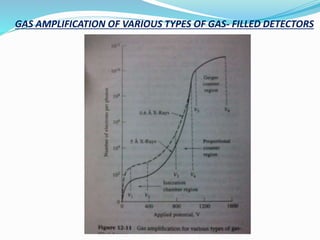
- 13. Gas-Filled Detectors - Filled with inert gas. - Gas is ionized by X-ray photons to produce Gaseous+ ions and e- - Under the influence of an applied potential, e- move to central wire anode & are detected; While slower moving cations attracted towards metal cathode. DETECTORS
- 14. Gas-Filled Detectors - Three types Ionization Chambers - Number of electrons reaching the anode is reasonably constant. Proportional Counters - Number of electrons increases rapidly with applied voltage. Geiger Muller Tubes - Enormous amplification of the electrical pulse. DETECTORS
- 15. GAS AMPLIFICATION OF VARIOUS TYPES OF GAS- FILLED DETECTORS
- 16. THE GEIGER TUBE ÔÇóOperated in the voltage region V5 & V6. ÔÇóTubes are filled with Ar. ÔÇóAmplification of electrical pulse is enormous in this region. ÔÇóGas amplification > 10^9. ÔÇóEach photon produces an avalance of electrons & cations. ÔÇóConduction of electricity is not continuous.
- 17. THE GEIGER TUBE LIMITATIONS: ÔÇó Lacks the large counting range of other detectors. ÔÇó Has long dead time. ÔÇó Its use in X-ray spectrometers is limited by this factor. ÔÇó Quantitative applications have decreased.
- 18. THANK YOU