ý§Öý§®ý•çý§® ý§Üý§£ý§ø ý§Öý§®ý•çý§®ý§æý§öý•á ý§∞ý§ïý•çý§∑ý§£
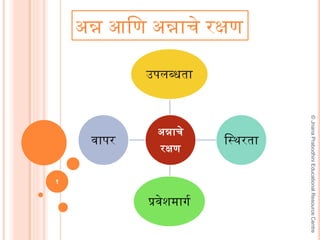
- 1. ý§Öý§®ý•çý§® ý§Üý§£ý§ø ý§Öý§®ý•çý§®ý§æý§öý•á ý§ïý•çý§∑ý§£ý§ø ¬©JnanaPrabodhiniEducationalResourceCentre 1 ý§Öý§®ý•çý§®ý§æý§öý•á ý§ïý•çý§∑ý§£ý§ø ý§âý§™ý§≤ý§¨ý•çý§ßý§§ý§æ ý§™ý•çý§∞ý§µý•áý§∂ý§Æý§æý§∞ý•çý§ó ý§£ý§•ý§øý§ïý§§ý§æý§µý§æý§™ý§ï
- 2. ý§∏ý§úý•Äý§µý§æý§æý§Çý§®ý§æ ý§µý§æý§¢ý•Äý§∏ý§æý§Ýý•Ä, ý§∂ý§ïý•Äý§ïý§æý§§ý•Äý§≤ ý§úý•Äý§µý§®ý§ïý•çý§∞ý§øý§Øý§æý§æý§Çý§∏ý§æý§Ýý•Ä, ý§∂ý§ïý•Äý§ïý§æý§öý•Ä ý§ùý•Äý§ú ý§≠ý§∞ý•Çý§® ý§ïý§æý§¢ý§£ý•çý§Øý§æý§∏ý§æý§Ýý•Ä, ý§Üý§£ý§ø ý§£ý§®ý§ïý§£ý§®ý§ïý§æý§≥ý•Ä ý§ïý§æý§Æý•á ý§ïý§ïý§£ý•çý§Øý§æý§∏ý§æý§Ýý•Ä ý§âý§úý•áý§öý•Ä ý§∞ý•çý§ïý§ú ý§Öý§∏ý§§ý•á. ý§πý•Ä ý§äý§úý§æý§ó ý§Üý§™ý§≤ý•çý§Øý§æý§≤ý§æ ý§Öý§®ý•çý§®ý§æý§§ý•Çý§® ý§£ý§Æý§≥ý§§ý•á. ý§£ý§™ý§∑ý•çý§üý§Æý§Ø ý§™ý§¶ý§æý§øý§ó (ý§ïý§∞ý•çý§¨ý•ãý§¶ý§ïý•á ), ý§™ý•çý§∞ý§£ý§øý§®ý•á, ý§£ý§øý§óý•çý§ßý§™ý§¶ý§æý§øý§ó, ý§öý•ãý§øý§æý§Øý•Åý§ïý•çý§§ ý§™ý§¶ý§æý§øý§ó, ý§úý•Äý§µý§®ý§∏ý§§ý•çý§§ý•çý§µý•á ý§Üý§£ý§ø ý§™ý§æý§øý•Ä ý§πý•á ý§Öý§®ý•çý§®ý§æý§öý•á ý§™ý•çý§∞ý§Æý•Åý§ñ ý§òý§üý§ï ý§Üý§πý•áý§§. ¬©JnanaPrabodhiniEducationalResourceCentre 2
- 3. ý§ïý§∂ý§æý§§ ý§Öý§∏ý§§ý•ã ý§ïý§æý§Øý§ó ý•ß) ý§£ý§™ý§∑ý•çý§üý§Æý§Ø ý§™ý§¶ý§æý§øý§ó (ý§ïý§∞ý•çý§¨ý•ãý§¶ý§ïý•á) ý§£ý§™ý§Ýý•Çý§≥ ý§™ý§¶ý§æý§øý§ó, ý§™ý•Äý§Ý, ý§£ý§µý§£ý§µý§ß ý§∂ý§ïý§óý§ïý§æ, ý§∞ý•çý§πý•Ç, ý§§ý§æý§æý§Çý§¶ý•Çý§≥, ý§úý•çý§µý§æý§ïý•Ä,ý§∞ý•çý§¨ý§æý§úý§ïý•Ä, ý§Æý§ïý§æ ý§πý•Ä ý§§ý•Éý§øý§ßý§æý§®ý•çý§Ø ý§´ý•çý§∞ý•Åý§ïý•çý§üý•ãý§ú, ý§∏ý•Åý§øý•ãý§ú, ý§óý•çý§≤ý•Åý§ïý•ãý§ú, ý§≤ý•Öý§ïý•çý§üý•ãý§ú ý§Øý§æ ý§§ý•Éý§øý§ßý§æý§®ý•çý§Øý§æý§æý§Çý§Æý§ßý•Äý§≤ ý§∂ý§ïý§óý§ïý§æ ý§∂ý§ïý•Äý§ïý§æý§§ý•Äý§≤ ý§äý§úý•áý§öý§æ ý§Æý•Åý§ñý•çý§Ø ý§∏ý•çý§§ý•çý§∞ý•ãý§§ ý•®) ý§™ý•çý§∞ý§£ý§øý§®ý•á (ý§®ý§æý§Øý§üý•çý§∞ý•ãý§úý§®ý§Øý•Åý§ïý•çý§§ ý§ïý§æý§∞ý•çý§¨ý§óý§®ý•Ä ý§™ý§¶ý§æý§øý§ó) ý§πý§ïý§≠ý§ïý§æ, ý§µý§æý§üý§øý§æ, ý§öý§µý§≥ý•Ä, ý§Æý•Çý§∞ý•ç, ý§Æý§üý§ïý•Ä, ý§§ý•Çý§ï ý§Öý§∂ý•Ä ý§ïý§°ý§ßý§æý§®ý•çý§Øý•á. ý§Öý§æý§Çý§°ý•Ä, ý§Æý§æý§æý§Çý§∏, ý§Æý§æý§∏ý•á ý§£ý§µý§£ý§µý§ß ý§úý•àý§£ý§µý§ï ý§ïý§æý§∏ý§æý§Øý§£ý§®ý§ï ý§Öý§£ý§≠ý§ïý•çý§∞ý§øý§Øý§æ ý§òý§°ý§µý•Çý§® ý§Üý§øý§øý•á, ý§Öý§®ý•Åý§µý§æý§æý§Çý§£ý§∂ý§ï ý§∞ý•çý•Åý§øý§ßý§Æý§æý§óý§öý•á ý§£ý§®ý§Øý•ãý§úý§® ý§ïý§ïý§øý•á ý•©) ý§£ý§øý§óý•çý§ßý§™ý§¶ý§æý§øý§ó ý§≤ý•ãý§øý•Ä, ý§§ý•Çý§™, ý§£ý§µý§£ý§µý§ß ý§£ý§∞ý•çý§¨ý§Øý§æý§æý§Çý§öý•Ä ý§§ý•áý§≤ý•á ý§äý§úý§æý§ó ý§£ý§®ý§∞ý•çý§Æý§óý§§ý•Ä ý•™) ý§öý•ãý§øý§æý§Øý•Åý§ïý•çý§§ ý§™ý§¶ý§æý§øý§ó (ý§∏ý•áý§≤ý•çý§Øý•Åý§≤ý•ãý§ú ý§πý§æ ý§§ý§æý§Çý§§ý•Åý§Æý§Ø ý§™ý§¶ý§æý§øý§ó ) ý§™ý§æý§≤ý•áý§≠ý§æý§úý•çý§Øý§æ, ý§´ý§≥ý•á, ý§≠ý§æý§úý•çý§Øý§æý§æý§Çý§öý•çý§Øý§æ ý§∏ý§æý§≤ý•Ä, ý§∞ý•çý§µý•çý§πý§æý§öý§æ ý§ïý•ãý§Çý§°ý§æ ý§Æý§≤ý§∞ý•çý§¨ý§æý§æý§Çý§ßý§øý•Ä ý•´) ý§úý•Äý§µý§®ý§∏ý§§ý•çý§§ý•çý§µý•á ý§´ý§≥ý•á, ý§≠ý§æý§úý•çý§Øý§æ ý§úý•Äý§µý§®ý§ïý•çý§∞ý§øý§Øý§æ ý§∏ý•Åý§ïý§≥ý•Äý§§ ý§∏ý•Åý§∞ý•Å ý§Ýý•áý§µý§øý•á ¬©JnanaPrabodhiniEducationalResourceCentre 3 ý§Öý§®ý•çý§®ý§æý§§ý•Äý§≤ ý§òý§üý§ï
- 4. ý§úý•Äý§µý§®ý§∏ý§§ý•çý§§ý•çý§µ ý§∏ý•çý§§ý•çý§∞ý•ãý§§ ý§ïý§æý§Øý§ó ý§Öý§≠ý§æý§µý§æý§öý§æ ý§™ý§∞ý§ïý§øý§æý§Æ ý•ß) ý§è ý§™ý§æý§≤ý•áý§≠ý§æý§úý•çý§Øý§æ, ý§∞ý•çý§æý§úý§ï, ý§™ý§™ý§à, ý§¶ý•Çý§ß ý§πý§æý§°ý§æý§æý§Çý§öý•Ä ý§µý§æý§¢ ý§∏ý•Åý§Øý•ãý§óý•çý§Ø ý§¶ý•Éý§∑ý•çý§üý•Ä ý§ïý§æý§§ý§æý§æý§Çý§ßý§≥ý•áý§™ý§øý§æ ý•®) ý§∞ý•çý§¨ý•Ä ý§°ý§æý§≥ý•Ä, ý§™ý§æý§≤ý•áý§≠ý§æý§úý•çý§Øý§æ, ý§¶ý•Çý§ß ý§úý•Äý§≠ ý§≤ý§æý§≤, ý§§ý•çý§µý§öý§æ ý§ñý§ïý§ñý§ïý•Äý§§ ý•©) ý§∏ý•Ä ý§Üý§µý§≥ý§æ, ý§≤ý§≤ý§æý§Çý§∞ý•çý§¨ý•Ç, ý§∏ý§æý§Çý§§ý•çý§∞ý•á, ý§Æý•ãý§°ý§æý§öý•Ä ý§ïý§°ý§ßý§æý§®ý•çý§Ø ý§£ý§πý§ïý§°ý•çý§Øý§æý§§ý•Çý§® ý§ïý§ïý•çý§§ ý§Øý•áý§§ý•á, ý§•ý§ïý§µý•çý§πý•Ä ý•™) ý§°ý•Ä ý§ïý•ãý§µý§≥ý§æ ý§∏ý•Çý§Øý§óý§™ý•çý§∞ý§ïý§æý§∂, ý§ïý•âý§° ý§£ý§≤ý§µý•çý§πý§ï ý§ìý§àý§≤, ý§∂ý§æý§ïý§ó ý§£ý§≤ý§µý•çý§πý§ï ý§ìý§àý§≤ ý§™ý§æý§Øý§æý§æý§Çý§öý•Ä ý§πý§æý§°ý•á ý§µý§æý§ïý§§ý§æý§§, ý§™ý§æý§Ýý•Äý§≤ý§æ ý§∞ý•çý§¨ý§æý§ï ý§Øý•áý§§ý•ã, ý§Æý•Åý§°ý§¶ý•Çý§∏ ¬©JnanaPrabodhiniEducationalResourceCentre 4 ý§úý•Äý§µý§®ý§∏ý§§ý•çý§§ý•çý§µ
- 5. ý§£ý§µý§£ý§∂ý§∑ý•çý§ü ý§ßý§æý§®ý•çý§Ø, ý§´ý§≥ý•á, ý§≠ý§æý§úý•çý§Øý§æ ý§Ýý§ïý§æý§£ý§µý§ï ý§ãý§§ý•Çý§æý§Çý§§ ý§£ý§™ý§ïý§§ý§æý§§. ý§™ý§ïý§æý§Çý§§ý•Å ý§§ý•çý§Øý§æý§§ý•Äý§≤ ý§âý§™ý§Øý•Åý§ïý•çý§§ ý§Öý§®ý•çý§®ý§òý§üý§ï ý§µý§∞ý•çý§óý§≠ý§ï ý§âý§™ý§≤ý§¨ý•çý§ß ý§µý•çý§πý§æý§µý•áý§§ ý§Æý•çý§πý§øý•Çý§® ý§Öý§®ý•çý§®ý§™ý§¶ý§æý§øý§ó ý§∏ý§æý§Ýý§µý•Çý§® ý§Ýý•áý§µý§≤ý•á ý§úý§æý§§ý§æý§§. ý§∏ý§µý§ó ý§Öý§®ý•çý§®ý§™ý§¶ý§æý§øý§ó ý§∞ý§üý§ïý§æý§ä ý§Öý§∏ý§§ý§æý§§ý§ö ý§Öý§∏ý•á ý§®ý§æý§πý•Ä. ý§§ý•á ý§∏ý§æý§Ýý§µý•Çý§® ý§Ýý•áý§µý§§ý§æý§®ý§æ ý§§ý•çý§Øý§æý§æý§Çý§öý•Ä ý§ïý§æý§≥ý§úý•Ä ý§òý•áý§øý•á ý§Æý•çý§πý§øý§úý•á ý§Öý§®ý•çý§®ý§ïý•çý§∑ý§£ý§ø. ý§Öý§®ý•çý§® ý§ïý•çý§∑ý§£ý§ø ý§ïý§ïý§§ý§æý§®ý§æ ý§Öý§®ý•çý§®ý§æý§öý•Ä ý§∞ý•çý•Åý§øý§µý§§ý•çý§§ý§æ ý§∞ý§üý§ïý§µý§øý•á ý§Üý§µý§∂ý•çý§Øý§ï ý§Öý§∏ý§§ý•á. ¬©JnanaPrabodhiniEducationalResourceCentre 5
- 6. ý§Öý§®ý•çý§® ý§∏ý§æý§Çý§ïý•çý§∑ý§£ý§øý§æý§öý•çý§Øý§æ ý§™ý§¶ý•çý§ßý§§ý•Ä : ý§ßý§æý§®ý•çý§Ø ý§∏ý§æý§Ýý§µý§§ý§æý§®ý§æ ý§§ý•çý§Øý§æý§§ ý§™ý§æý§£ý•çý§Øý§æý§öý§æ ý§Öý§æý§Çý§∂ ý§Öý§∏ý•áý§≤ ý§§ý§ï ý§ßý§æý§®ý•çý§Øý§æý§∏ ý§∞ý•çý§¨ý•Åý§ïý§∂ý•Ä ý§Øý•áý§§ý•á. ý§Öý§∏ý•á ý§πý•ãý§ä ý§®ý§Øý•á ý§Æý•çý§πý§øý•Çý§® ý§ßý§æý§®ý•çý§Ø ý§âý§®ý•çý§πý§æý§§ ý§µý§æý§≥ý§µý•Çý§® ý§ïý•ãý§ïý§°ý§Øý§æ ý§úý§æý§∞ý•çý•Ä ý§∏ý§æý§Ýý§£ý§µý§§ý§æý§§. ý§∏ý§æý§Ýý§µý§øý•Äý§öý•çý§Øý§æ ý§∞ý§Ýý§ïý§æý§øý•Ä ý§âý§æý§Çý§¶ý•Äý§ï,ý§òý•Åý§∂ý•Ä ý§ßý§æý§®ý•çý§Øý§æý§öý•Ä ý§®ý§æý§∏ý§æý§°ý•Ä ý§ïý§ïý§øý§æý§ï ý§®ý§æý§πý•Äý§§ ý§Øý§æý§öý•Ä ý§ïý§æý§≥ý§úý•Ä ý§òý•çý§Øý§æý§µý•Ä ý§≤ý§æý§∞ý•çý§§ý•á. ý§ßý§®ý•çý§Øý§æý§≤ý§æ ý§ïý•Äý§° ý§≤ý§æý§∞ý•çý•Ç ý§®ý§Øý•á ý§Æý•çý§πý§øý•Çý§® ý§ïý§°ý•Çý§≤ý§≤ý§æý§Çý§∞ý•çý§¨ý§æý§öý§æ ý§™ý§æý§≤ý§æ, ý§∏ý§æý§Çý§ïý•çý§∑ý§£ý§ï ý§ïý§∏ý§æý§Øý§®ý•á ý§Øý§æý§æý§Çý§öý§æ ý§µý§æý§™ý§ï ý§ïý§ïý§§ý§æý§§. ¬©JnanaPrabodhiniEducationalResourceCentre 6
- 7. ý§£ý§∂ý§úý§≤ý•áý§≤ý•çý§Øý§æ ý§Öý§®ý•çý§®ý§æý§§ ý§∏ý•Åý§•ý§Æý§úý•Äý§µý§æý§æý§Çý§öý•Ä ý§µý§æý§¢ ý§≤ý§µý§ïý§ï ý§πý•ãý§äý§® ý§Öý§®ý•çý§®ý§æý§öý•Ä ý§®ý§æý§∏ý§æý§°ý•Ä ý§πý•ãý§§ý•á. ý§Öý§∂ý§æ ý§Öý§®ý•çý§®ý§æý§öý•Ä ý§öý§µ, ý§ïý§æý§Çý§∞ý•ç, ý§µý§æý§∏ ý§Üý§£ý§ø ý§™ý•ãý§§ ( ý§πý§æý§§ý§æý§≤ý§æ ý§úý§æý§øý§µý§øý§æý§ïý§æ ý§•ý§™ý§∂ý§ó ) ý§∞ý•çý§¨ý§¶ý§≤ý§§ý§æý§§. ý§Öý§∏ý•á ý§πý•ãý§ä ý§®ý§Øý•á ý§Æý•çý§πý§øý•Çý§® ý§¶ý•Çý§ß, ý§Üý§Æý§üý•Ä, ý§∏ý§æý§ï ý§Öý§∏ý•á ý§¶ý•çý§∞ý§µý•çý§Øý§™ý§¶ý§æý§øý§ó ý§µý§æý§ïý§æý§Çý§µý§æý§ï ý§âý§ïý§≥ý§§ý§æý§§. ¬©JnanaPrabodhiniEducationalResourceCentre 7
- 8. ý§£ý§∂ý§úý§µý§≤ý•áý§≤ý•á ý§™ý§¶ý§æý§øý§ó ý§øý•ãý§°ý§Øý§æ ý§ïý§æý§≥ý§æý§∏ý§æý§Ýý•Ä ý§∏ý§æý§Ýý§µý§æý§Øý§öý•á ý§Öý§∏ý§≤ý•çý§Øý§æý§∏ ý§∂ý•Äý§§ý§ïý§™ý§æý§üý§æý§§ ( ý§ïý•áý§ïý•çý§∞ý§´ý•çý§∞ý§úý§ïý•áý§üý§ï ) ý§Ýý•áý§µý§§ý§æý§§. ý§™ý§æý§≤ý•áý§≠ý§æý§úý•çý§Øý§æ, ý§´ý§≥ý•á, ý§Æý§æý§æý§Çý§∏, ý§Æý§æý§∏ý•á ý§Öý§∏ý•á ý§Öý§®ý•áý§ï ý§®ý§æý§∂ý§µý§æý§Çý§§ ý§ïý§öý•çý§öý•á ý§™ý§¶ý§æý§øý§ó ý§∂ý•Äý§§ ý§∞ý•çý•Éý§πý§æý§§ ý§Ýý•áý§µý§§ý§æý§§. ý§ïý§æý§πý•Ä ý§™ý§¶ý§æý§øý§ó ý§ñý§æý§ïý§µý•Çý§® ý§µý§æý§≥ý§µý§≤ý•çý§Øý§æý§∏ ý§§ý•á ý§∞ý§üý§ïý§§ý§æý§§. ý§âý§¶ý§æ ; ý§Üý§Æý§∏ý•Åý§≤ý•á, ý§ïý•àý§ïý•Ä, ý§Üý§µý§≥ý§æ ý§Øý§æý§æý§Çý§öý•çý§Øý§æ ý§´ý•ãý§°ý•Ä, ý§ïý§æý§πý•Ä ý§£ý§µý§£ý§∂ý§∑ý•çý§ü ý§™ý•çý§∞ý§ïý§æý§ïý§öý•á ý§Æý§æý§∏ý•á ý§á. ¬©JnanaPrabodhiniEducationalResourceCentre 8
- 9. ý§∞ý•çý§¨ý§üý§æý§üý•á, ý§ïý§æý§æý§Çý§¶ý•á ý§Øý§æý§æý§Çý§∏ý§æý§ïý§ñý•çý§Øý§æ ý§≠ý§æý§úý•çý§Øý§æý§æý§Çý§®ý§æ ý§ïý•ãý§Çý§∞ý•çý§¨ ý§Øý•áý§äý§® ý§§ý•çý§Øý§æ ý§µý§æý§Øý§æ ý§úý§æý§ä ý§®ý§Øý•áý§§ ý§Æý•çý§πý§øý•Çý§® ý§§ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§ï ý§∞ý•çý•Öý§Æý§æ ý§ïý•çý§∞ý§ïý§ïý§øý§æý§æý§Çý§öý§æ ý§Æý§æý§ïý§æ ý§ïý§ïý§§ý§æý§§. ý§¶ý•Çý§ß ý§∞ý§üý§ïý§£ý§µý§£ý•çý§Øý§æý§∏ý§æý§Ýý•Ä ý§§ý•á ý§™ý•çý§∞ý§øý§Æ 80¬∞ ý§∏ý•á. ý§§ý§æý§™ý§Æý§æý§®ý§æý§™ý§Øý§Çý§§ ý§§ý§æý§™ý§µý•Çý§® ý§≤ý§∞ý•çý•áý§ö ý§øý§æý§Çý§° ý§ïý•áý§≤ý•á ý§úý§æý§§ý•á. ý§Øý§æ ý§™ý§¶ý•çý§ßý§§ý•Äý§≤ý§æ ý§™ý§æý§∂ý•çý§öý§ïý§æý§Øý§ùý•áý§∂ý§® ý§Æý•çý§πý§øý§§ý§æý§§. ý§ïý§æý§πý•Ä ý§≠ý§æý§úý•çý§Øý§æ, ý§´ý§≥ý•á ý§Ýý§ïý§æý§£ý§µý§ï ý§πý§æý§Çý§∞ý•çý§æý§Æý§æý§§ ý§£ý§™ý§ïý§§ý§æý§§.ý§§ý•Ä ý§µý§∞ý•çý§óý§≠ý§ï ý§âý§™ý§≤ý§¨ý•çý§ß ý§µý•çý§πý§æý§µý•Äý§§ ý§§ý§∏ý•áý§ö ý§úý§æý§•ý§§ý•Ä ý§™ý•çý§∞ý§Æý§æý§øý§æý§§ ý§Üý§≤ý•áý§≤ý•á ý§™ý•Äý§ï ý§µý§æý§Øý§æ ý§úý§æý§ä ý§®ý§Øý•á ý§Æý•çý§πý§øý•Çý§® ý§≤ý•ãý§øý§öý•Ä, ý§Æý•ãý§ïý§æý§æý§Çý§∞ý•çý§¨ý•á ý§∞ý•çý§¨ý§®ý§µý•Çý§® ý§Æý§∏ý§æý§≤ý•çý§Øý§æý§æý§Çý§öý§æ ý§µý§æý§™ý§ï ý§ïý§∞ý•Çý§® ý§™ý§¶ý§æý§øý§ó ý§∞ý§üý§ïý§µý§≤ý•á ý§úý§æý§§ý§æý§§. ¬©JnanaPrabodhiniEducationalResourceCentre 9
- 10. ý§Æý•Äý§Ý, ý§Æý§∏ý§æý§≤ý•á, ý§§ý•áý§≤, ý§∏ý§æý§ñý§ï ý§Øý§æý§æý§Çý§öý§æ ý§µý§æý§™ý§ï ý§Öý§®ý•çý§® ý§∞ý§üý§ïý§µý§£ý•çý§Øý§æý§∏ý§æý§Ýý•Ä, ý§Öý§®ý•çý§®ý§æý§öý•á ý§ïý•çý§∑ý§£ý§ø ý§ïý§ïý§£ý•çý§Øý§æý§∏ý§æý§Ýý•Ä ý§ïý§ïý§§ý§æý§§.ý§§ý•çý§Øý§æý§æý§Çý§®ý§æ ý§®ý•àý§∏ý§∞ý•çý§∞ý•çý§óý§ï ý§™ý§∞ý§ïý§ïý•çý§∑ý§£ý§ï ý§Æý•çý§πý§øý§§ý§æý§§.ý§™ý§∞ý§ïý§ïý•çý§∑ý§£ý§ï ý§òý§æý§§ý§≤ý•áý§≤ý•á ý§™ý§¶ý§æý§øý§ó ý§∂ý•Äý§§ý§ïý§™ý§æý§§ ý§Ýý•áý§µý§£ý•çý§Øý§æý§öý•Ä ý§Üý§µý§∂ý•çý§Øý§ïý§§ý§æ ý§®ý§∏ý§§ý•á. ý§ïý§æý§∏ý§æý§Øý§£ý§®ý§ï ý§™ý§ïý•Äý•çý§∑ý§£ý§ïý§æý§æý§Çý§öý§æ ý§µý§æý§™ý§ï ý§ïý§∞ý•Çý§® ý§∏ý•âý§∏, ý§úý•Öý§Æ ý§Øý§æý§æý§Çý§∏ý§æý§ïý§ñý•á ý§™ý§¶ý§æý§øý§ó ý§∞ý•çý§¨ý§®ý§µý§≤ý•á ý§úý§æý§§ý§æý§§. ý§∏ý•ãý§£ý§°ý§Øý§Æ ý§Æý•áý§üý§æ ý§∞ý•çý§¨ý§æý§Øý§∏ý§≤ý•çý§´ý•áý§ü, ý§∏ý§æý§Øý§∞ý§üý•çý§∞ý§ï ý§Üý§Æý•çý§≤, ý§∞ý•çý§¨ý•ãý§∞ý§ïý§ï ý§Üý§Æý•çý§≤, ý§Öý•Öý§∏ý•áý§∞ý§üý§ï ý§Öý•Öý§£ý§∏ý§°ý§πý•Ä ý§ïý§æý§∏ý§æý§Øý§£ý§®ý§ï ý§Öý§®ý•çý§®ý§æý§™ý§ïý•Äý•çý§∑ý§£ý§ïý•á ý§Üý§πý•áý§§. ¬©JnanaPrabodhiniEducationalResourceCentre 10
- 11. ý§≠ý•áý§∏ý§≥ ý§Øý•Åý§ïý•çý§§ ý§Öý§®ý•çý§® ý§ñý§æý§≤ý•çý§Øý§æý§Æý•Åý§≥ý•á ý§∞ý•çý§æý§Çý§≠ý•Äý§ï ý§Üý§úý§æý§ï ý§πý•ãý§ä ý§∂ý§ïý§§ý§æý§§. ý§Öý§®ý•çý§®ý§™ý§¶ý§æý§øý§æý§óý§§ ý§≠ý•áý§∏ý§≥ ý§ïý§ïý§øý•á ý§πý§æ ý§ïý§æý§Øý§¶ý•çý§Øý§æý§®ý•á ý§∞ý•çý•Åý§®ý•çý§πý§æ ý§Üý§πý•á. ý§Öý§®ý•çý§®ý§æý§§ý•Äý§≤ ý§≠ý•áý§∏ý§≥ ý§ïý•ãý§ñý§£ý•çý§Øý§æý§∏ý§æý§Ýý•Ä ý§∏ý§ïý§ïý§æý§ïý•Ä ‚Äòý§Öý§®ý•çý§® ý§µ ý§îý§∞ý•çý§ßý•á‚Äô ý§™ý•çý§∞ý§∂ý§æý§∏ý§® ý§ñý§æý§§ý•çý§Øý§æý§Æý§æý§´ý§ó ý§§ ý§Öý§®ý•çý§®ý§æý§öý•Ä ý§§ý§™ý§æý§∏ý§øý•Ä ý§ïý•áý§≤ý•Ä ý§úý§æý§§ý•á. ý§Öý§®ý•çý§®ý§™ý§¶ý§æý§øý§æý§óý§öý•Ä ý§ñý§ïý•áý§¶ý•Ä ý§ïý§ïý§§ý§æý§®ý§æ ý§Üý§™ý§øý§πý•Ä ý§ïý§æý§≥ý§úý•Ä ý§òý•áý§§ý§≤ý•Ä ý§™ý§æý§£ý§πý§úý•á. ý§âý§¶ý§æ; ý§¶ý•Åý§ßý§æý§Æý§ßý•çý§Øý•á ý§™ý§æý§øý•Ä ý§£ý§Æý§∏ý§≥ý§øý•á, ý§ïý§æý§≥ý•çý§Øý§æ ý§£ý§Æý§ïý•Äý§Æý§ßý•çý§Øý•á ý§™ý§™ý§àý§öý•çý§Øý§æ ý§£ý§∞ý•çý§¨ý§Øý§æ ý§£ý§Æý§∏ý§≥ý§øý•á, ý§öý§æý§æý§Çý§∞ý•çý§≤ý•çý§Øý§æ ý§§ý•áý§≤ ý§µ ý§§ý•Åý§™ý§æý§Æý§ßý•çý§Øý•á ý§ïý§Æý•Ä ý§™ý•çý§∞ý§§ý•Äý§öý•á ý§§ý•áý§≤ ý§µ ý§§ý•Çý§™ ý§£ý§Æý§∏ý§≥ý§øý•á ý§á. ¬©JnanaPrabodhiniEducationalResourceCentre 11
- 12. ý§Üý§™ý§≤ý•çý§Øý§æý§≤ý§æ ý§äý§úý§æý§ó ý§¶ý•áý§øý§æý§ïý•á ý§Öý§®ý•çý§® ý§∂ý•Åý§¶ý•çý§ß ý§Öý§∏ý§æý§Øý§≤ý§æ ý§πý§µý•á. ý§™ý§ø ý§ïý§æý§πý•Äý§µý•áý§≥ý§æ ý§§ý•çý§Øý§æý§§ ý§ïý§Æý•Ä ý§¶ý§úý§æý§óý§öý•á ý§™ý§¶ý§æý§øý§ó ý§ïý§ïý§æý§Çý§µý§æ ý§áý§§ý§ï ý§Öý§∂ý•Åý§¶ý•çý§ßý•Ä ý§£ý§Æý§∏ý§≥ý§≤ý•çý§Øý§æ ý§úý§æý§§ý§æý§§. ý§Öý§®ý•çý§®ý§æý§öý§æ ý§¶ý§úý§æý§ó ý§ïý§Æý•Ä ý§ïý§ïý§øý§æý§±ý•çý§Øý§æ ý§Öý§∂ý§æ ý§™ý§¶ý§æý§øý§æý§Çý§®ý§æ ý§≠ý•áý§∏ý§≥ ý§Æý•çý§πý§øý§§ý§æý§§. ¬©JnanaPrabodhiniEducationalResourceCentre 12