Romatoid Artrit
- 1. ROMATO─░D ARTR─░T DR.GAMZE G├£L │ę├£│óĘĪ├ć
- 2. ’éó RA tipik bulgular─▒n─▒ en ├¦ok periferik sinoviyal eklemlerde g├Čsteren kronik,progresif ve sistemik bir hastal─▒kt─▒r. ’éó Toplumun %1 ini etkiler. ’éó Y─▒ll─▒k maliyeti ABD de 30 milyon dolar ’éó K/E:3:1 ’éó En s─▒k 40- 60 ya┼¤ aras─▒nda g├Čr├╝l├╝r.
- 3. KONU ALT BA┼×LIKLARI ’éó PATOGENEZ ’éó EKLEM BULBULARI ’éó S─░STEM─░K BULGULAR ’éó MED─░KAL TEDAV─░
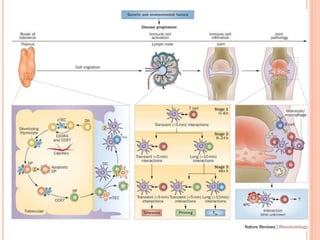
- 5. EKLEMLER NEDEN BU HALE GELIYOR?
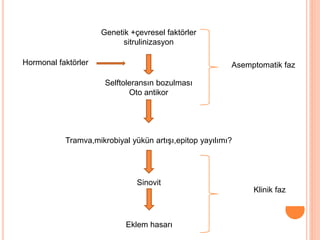
- 6. Genetik +├¦evresel fakt├Črler sitrulinizasyon Selftolerans─▒n bozulmas─▒ Oto antikor Tramva,mikrobiyal y├╝k├╝n art─▒┼¤─▒,epitop yay─▒l─▒m─▒? Sinovit Eklem hasar─▒ Asemptomatik faz Klinik faz Hormonal fakt├Črler
- 7. ŌĆó ├ćevresel fakt├Črlerde ├Čnemli ŌĆó Mikro┼¤imerizm ŌĆó Epigenetik MONOZIGOT IKIZLERDE RA KONKORDANSI ’éó HLA DR pozitif ise,%21 ’éó SE +(homozigot) pozitif ise,%26 ’éó Dizigotik ikizlerde,%3.5 ’éó Neden monozigot ikizlerde %100 de─¤il?
- 8. ’éó RA i├¦in en g├╝├¦l├╝ genetik risk MHC allelleri ile ta┼¤─▒nmaktad─▒r. HLA-DR1 ve DR4 allellerinin varl─▒─¤─▒ ile RA prevalans─▒ artar.
- 9. ORTAK EPITOP ’éó HLA s─▒n─▒f DR antijenlerinin 3. hipervariable b├Člgesinde 70-74. aa diziliminde de─¤i┼¤iklik ’éó Seropozitif RA i├¦in genetik riskin %30 unu olu┼¤turur. ’éó Ortak EpitopŌĆÖun hastada bulunmas─▒ hem hastal─▒─¤─▒n riskini artt─▒r─▒r hem de a─¤─▒r seyretmesine neden olur.
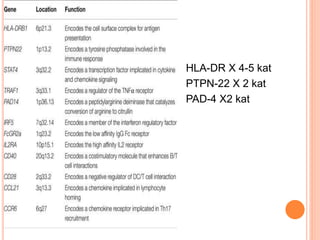
- 10. HLA-DR X 4-5 kat PTPN-22 X 2 kat PAD-4 X2 kat
- 11. ├ćEVRESEL FAKT├¢RLER ’éó G─▒da K─▒rm─▒z─▒ et Kahve? Protein ’éó Y├╝ksek do─¤um a─¤─▒rl─▒─¤─▒ ’éó Obezite ’éó Kan transf├╝zyonlar─▒ ’éó Bak─▒r,selenyum eksikli─¤i ’éó Post tramvatik stres bozuklu─¤u ’éó E─¤itim seviyesinin d├╝┼¤├╝k olmas─▒ ’éó Toksik maddeler Trafik kirlili─¤i End├╝strile┼¤me Asbest Slika Mineral ya─¤─▒ ’éó Meslek A─¤a├¦ i┼¤iyle u─¤ra┼¤ma Elektrik i┼¤i A─¤─▒r i┼¤ ’éó ─░nfeksiyoz ajanlara maruz kalmak
- 12. GENETIK VE ├ćEVRESEL RISK FAKT├¢RLERI ETKILE┼×IMI ’éó En iyi bilinen ├¦evresel risk fakt├Čr├╝ sigarad─▒r. ’éó Sigara+ ortak epitop x 1.5 kat ’éó Sigara + homozigot epitop x 21 kat RA geli┼¤im riskini artt─▒r─▒r.
- 16. HASTALIK SINOVYADA DE─×IL MUKOZADA Ą■┤ĪĮó│ó┤ĪĖķ.
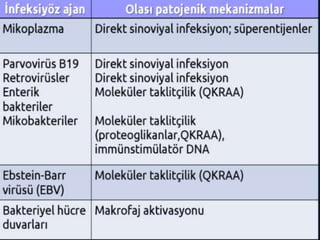
- 17. ŌĆó Romatoid Artritte Olas─▒ Otoantijenler ŌĆó 1) Kartilaj antijenleri ŌĆō ŌĆö Tip II kollajen ŌĆō ŌĆö Gp39 (glikoprotein tip39) ŌĆō ŌĆö Kartilaj ba─¤lay─▒c─▒ protein ŌĆō ŌĆö Proteoglikanlar ŌĆō ŌĆö Aggregan ŌĆó 2) Sitr├╝line edilmi┼¤ peptidler ŌĆó 3) Glukoz-6-fosfoizomeraz ŌĆó 4) HLA-DR(QKRAA) ŌĆó 5) Is─▒-┼¤ok Proteinleri ŌĆó 6) A─¤─▒r-zincir Ba─¤lay─▒c─▒ protein(B─░P) ŌĆó 7) HnRNP-A2 ŌĆó 8) ─░mmunglobulinler
- 18. HORMONAL DISREGULASYON ’éó ├¢strojenler immunmodulatuar ’ā╝ B h├╝crelerini apoptoza diren├¦li hale getirir. ’ā╝ T supres├Črleri inhibe Th yi aktive eder. ’ā╝ FLS MMP sal─▒n─▒m─▒ ’ā╝ Makrofajlardan TNF sal─▒n─▒m─▒ RA prevalans─▒n─▒n kad─▒nlarda y├╝ksek olmas─▒, gebelik s├╝recinde g├Čzlenen dramatik iyile┼¤me ya da postpartum s├╝re├¦te alevlenme patogenezde hormonal disreg├╝lasyonun katk─▒s─▒ olabilece─¤ini d├╝┼¤├╝nd├╝rmektedir.
- 19. RA GELI┼×ME RISKINI AZALTAN FAKT├¢RLER ’éóAlkol ’éóBal─▒k ya─¤─▒ ’éóZeytinya─¤─▒ ’éóD vitamini? ’éóC vitamini
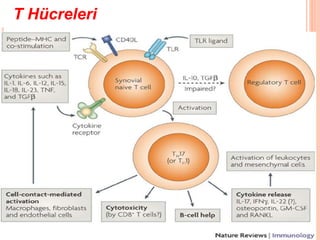
- 20. T H├╝creleri
- 22. RF AND ANTI CCP ’éó B lenfositlere plazma h├╝crelerine prolifere olarak RF ve anti CCP antikorlar─▒n─▒ olu┼¤turur. ’éó RF: IgG nin Fc k─▒sm─▒na kar┼¤─▒ olu┼¤an Ig M tipi antikorlar─▒ g├Čsterir. RA hastalar─▒n─▒n %70 inde RF + dir. ’éó Romatoid fakt├Čr seronegatif spondiloartropatiler hari├¦ her t├╝rl├╝ hastal─▒kta pozitif olabilir. Hastal─▒k spesifik de─¤ildir. ’éó Y├╝ksek RF titresi olan hastalarda s├╝bkutan nod├╝ller ve vaskulit daha fazla g├Čr├╝l├╝r. ’éó Anti-CCP antikoru(anti siklik sitrulinli peptid antikoru): RA n─▒n erken tan─▒s─▒nda ├Čnemlidir. ’éó Laboratuvar tan─▒s─▒nda y├╝ksek sensitivite ve spesifite g├Čsterir. RF SENS─░T─░V─░TE:%80 SPES─░F─░TE:%78 A-CCP SENS─░T─░V─░TE:%72 SPES─░F─░TE:%92
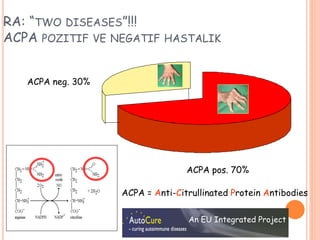
- 23. RA: ŌĆ£TWO DISEASESŌĆØ!!! ACPA POZITIF VE NEGATIF HASTALIK ACPA pos. 70% ACPA neg. 30% ACPA = Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibodies An EU Integrated Project
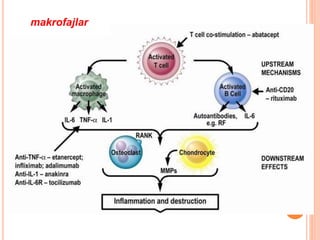
- 24. makrofajlar
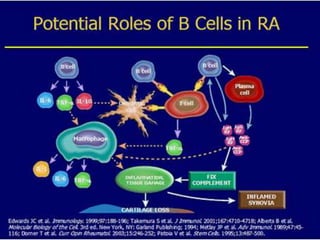
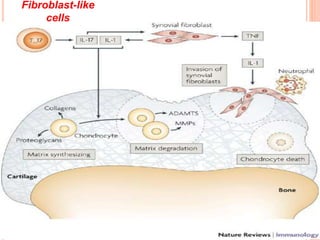
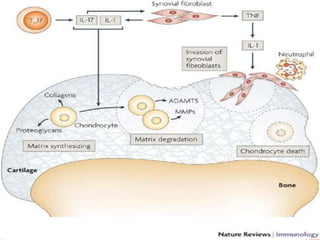
- 25. FIBROBLAST BENZERI H├£CRELER(FLS) ’éó Tip B sinovisitler ’éó IL-1 ve TNF-a,TLR arac─▒l─▒g─▒yla uyar─▒l─▒r. ’éó MMP-13(Kollejenaz 13) salg─▒larlar. ve adenozin deaminaz etkinlikleri vard─▒r. ’éó Anti inflamatuar olan adenozinin etkinli─¤ini bask─▒larlar.
- 27. MAST H├£CRELERI ’éó Mast h├╝creleri insanda RA sinoviyumunda ├¦ok fazla miktarda bulunurlar ve onlar─▒n varl─▒─¤─▒ hastal─▒k progresyonuyla koreledir. ’éó Inflamatuar sitokinlerin sal─▒n─▒m─▒ndan sorumludur.
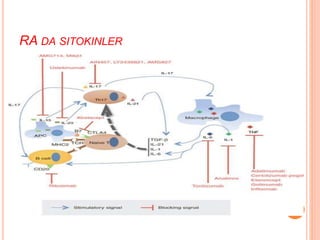
- 28. RA DA SITOKINLER
- 29. ’éó Kompleman aktivasyonu: artm─▒┼¤t─▒r. Sinovyada C1q- C4komp. ’éó Anjiogenez: sinovya b├╝y├╝mesi i├¦in gerekli ’éó Doku k├╝tlesi ├¦ok ’éó Oksijen t├╝ketimi ├¦ok ’éó Ef├╝zyon bas─▒ yapar ’éó Adhezyon molek├╝lleri sinoviyal proliferasyon i├¦in gerekli; ICAM,VCAM, E-selektin,P-selektinŌĆ” ’éó Apoptoz inhibisyonu iskemi HIF 1 Gen transkripsiyonu (vegf,vegf resept├Čr├╝,..)
- 30. RA DA SINYAL MEKANIZMALARI ’éó Sitokinlerin yap─▒m─▒ i├¦in gerekli genleri uyaran sinyal yolaklar─▒: NfKB MAP kinaz Jak (tofasitinib) AP-1 Syk
- 31. RA DA DI─×ER INFLAMATUAR MEDYAT├¢RLER ’éó Substance-P ’éó IL-l, IL-6, TNF-╬▒' n─▒n monositlerden sal─▒n─▒m─▒n─▒ art─▒ran substans-P, RAŌĆÖl─▒ hastalar─▒n sinovyal s─▒v─▒lar─▒nda y├╝ksek d├╝zeyde saptanm─▒┼¤ ve simetrik tutulumda etkisi olabilece─¤i d├╝┼¤├╝n├╝lm├╝┼¤t├╝r. ’éó RAŌĆÖdeki en ├Čnemli semptom olan a─¤r─▒da rol oynar.
- 32. RA DA DI─×ER INFLAMATUAR MEDYAT├¢RLER ’éó N├Čropeptit Y; ’éó P─▒ht─▒la┼¤ma fakt├Črleri ve fibrinoliz ’éó Trombin sinovyal h├╝creler i├¦in mitojeniktir. ’éó Fibrin pannus b├╝y├╝mesi ve adezyonu artt─▒r─▒r. ’éó Plazmin MMP lar─▒n─▒ artt─▒r─▒r. ’éó Fibrinoliz inhibisyonu deneysel olarak ├╝mit verici sonu├¦lar vermi┼¤.
- 33. RA VE OKSIDATIF STRESS
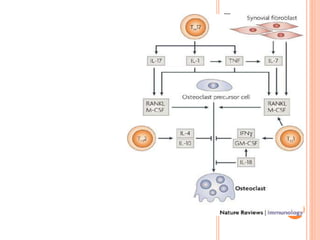
- 35. KEMIKYIKIMI
- 38. KLINIK BULGULAR
- 39. KLINIK BULGULAR ’éó Eklem bulgular─▒: RA da eklem tutulumu poliartik├╝ler, simetrik ve deformasyon yap─▒c─▒d─▒r. Tuttu─¤u eklemde a─¤r─▒, en az 30-45 dk s├╝ren sabah tutuklu─¤u, ┼¤i┼¤lik, s─▒cakl─▒k art─▒┼¤─▒ ve fonksiyon kayb─▒na neden olur.
- 40. KLINIK BULGULAR Ba┼¤lang─▒├¦ ┼¤ekilleri: ’éó Sinsi ba┼¤lang─▒├¦: (%50) haftalar ve aylar i├¦erisinde, k├╝├¦├╝k periferik eklemlerde,simetrik olarak, halsizlik yorgunluk gibi sistemik semptomlarla birlikte g├Čr├╝l├╝r. ’éó Yava┼¤ monoartrit: omuz/diz ’éó Akut poliartrit: ya┼¤l─▒larda s─▒k ’éó Akut monoartrit: diz, omuz,kal├¦a etkilenir ,nadir,septik artrit, gut ve pseudoguttan ay─▒rt edilmeli
- 41. ’éó Farkl─▒ ba┼¤lang─▒├¦l─▒ bir form adult ba┼¤layan Still hastal─▒─¤─▒d─▒r. Genellikle 3 ve 4. dekada g├Čr├╝l├╝r. .Kad─▒n=Erkek. RF ve ANA (-) dir. Ferritin artm─▒┼¤,kompleman N/artm─▒┼¤ Subkutan nod├╝ller g├Čr├╝lmez. Servikal omurga tutulumu vard─▒r. ’éó ├ćo─¤unlukla ate┼¤le ba┼¤vururlar.Ate┼¤li d├Čnemde somomn rengi mak├╝ler d├Čk├╝nt├╝ g├Čr├╝lebilir ’éó Hastal─▒─¤─▒n ba┼¤lang─▒c─▒ndan sonraki 10 y─▒l i├¦inde amiloidozis geli┼¤me insidans─▒ % 30. ’éó Tedavi agresif olmal─▒d─▒r.
- 42. ’éó Bir di─¤er akut ba┼¤lang─▒├¦l─▒ tablo palindromik romatizmad─▒r. Eklemlerde birka├¦ saat ile birka├¦ g├╝n devam eden, spontan gerileyen ve iz b─▒rakmayan artritle karakterizedir. Bu olgular─▒n en az 1/3 ├╝ RA ya d├Čn├╝┼¤├╝r. ’éó Antimalaryaller ile tedavi s─▒ras─▒nda ataklar─▒n s─▒kl─▒─¤─▒nda ve s├╝resinde anlaml─▒ d├╝zelme oldu─¤u bildirilmi┼¤tir.
- 43. RA HASTALI─×IN KLINIK AKTIVITESINE G├¢RE ERKEN VE GE├ć HASTALIK OLARAK SINIFLANDIRILIR. ’éó Erken RA ’éó Hen├╝z eklem hasar─▒na ba─¤l─▒ klinik bulgular yoktur ve Radyolojik olarak kemik erozyonlar─▒ ve Kartilaj kayb─▒ yoktur. ’éó Hastal─▒─¤─▒ bu evrede yakalamak ├Čnemlidir ├¦├╝nk├╝ erken evrede inflamasyon yo─¤undur. ’éó Kemik erozyon olu┼¤um h─▒z─▒ fazlad─▒r. ’éó Remisyon bu d├Čnemde daha ├¦ok olu┼¤ur.
- 44. ’éó Ge├¦ RA ’éó 60 ya┼¤ ├╝st├╝nde genellikle erkeklerde g├Čr├╝len bir tablodur. ’éó RF pozitivite oran─▒ d├╝┼¤├╝kt├╝r. ’éó Ba┼¤lang─▒├¦ yava┼¤t─▒r fakat tutukluk fonksiyon kayb─▒na neden olacak kadar belirgindir. ’éó NSAI etkili de─¤ildir. ’éó D├╝┼¤├╝k doz kortikosteroid yararl─▒ olur. ’éó Tekrar eden aktivite ataklar─▒ nedeni ile hastan─▒n GYA ve fonksiyonel kapasitesinde azalma meydana gelir
- 46. ’éó Torakolomber, sakroiliak ve DIP eklem tutulumu RA da ├¦ok nadirdir.
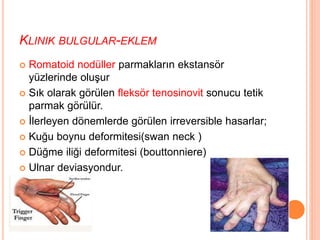
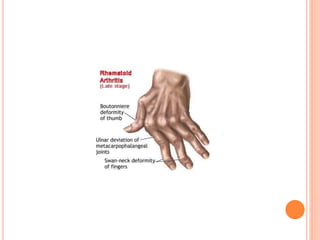
- 47. KLINIK BULGULAR-EKLEM ’éó Romatoid nod├╝ller parmaklar─▒n ekstans├Čr y├╝zlerinde olu┼¤ur ’éó S─▒k olarak g├Čr├╝len fleks├Čr tenosinovit sonucu tetik parmak g├Čr├╝l├╝r. ’éó ─░lerleyen d├Čnemlerde g├Čr├╝len irreversible hasarlar; ’éó Ku─¤u boynu deformitesi(swan neck ) ’éó D├╝─¤me ili─¤i deformitesi (bouttonniere) ’éó Ulnar deviasyondur.
- 49. KLINIK BULGULAR-EKLEM ’éó El bile─¤inde ulnar stiloid ├¦evresinde sinoviyal proliferasyon radyoulnar ligamentin laksitesine yol a├¦ar ve piyano anahtar─▒ deformitesine neden olur. Ulnar stiloide ba┼¤ parmakla bask─▒ yap─▒ld─▒─¤─▒nda yukar─▒ a┼¤a─¤─▒ hareket eder. ’éó Bilateral karpal t├╝nel sendromu olduk├¦a s─▒k g├Čr├╝l├╝r. ’éó El bile─¤inde dorsal ┼¤i┼¤lik hastal─▒─¤─▒n erken bulgular─▒ndan birisidir:eksternal carpi ulnar─▒s ve external digitorium kommunis tendonlar─▒n─▒n tutulumu
- 50. KLINIK BULGULAR-EKLEM ’éó Omuz da pad i┼¤areti; glenohumeral eff├╝zyon sonucu olu┼¤ur. Bursalar ve rotator man┼¤on da etkilenir. Sternoklavik├╝ler eklemde a─¤r─▒ ve ┼¤i┼¤lik g├Čr├╝lebilir. ’éó Dirsekte tam ekstansiyon kayb─▒ ve romatoid nod├╝ller g├Čr├╝l├╝r.
- 51. KLINIK BULGULAR-EKLEM ’éó Kal├¦a tutulumu;(%50) uzun s├╝re steroid kullan─▒m─▒na ba─¤l─▒ avask├╝ler nekrozla kar─▒┼¤─▒r. ’éó Diz tutulumu: ekstansiyon kayb─▒ ve quadriceps atrofisi, baker kisti ’éó Ayak bile─¤i nadir tutulur pronasyon ve eversiyon deformitesi g├Čr├╝l├╝r. MTF hastal─▒k ba┼¤lang─▒c─▒ndan itibaren tutulabilir. ’éó A┼¤il tendonunda romatoid nod├╝llerin geli┼¤mesi tendonun spontan r├╝pt├╝r├╝ne neden olabilir.
- 52. KLINIK BULGULAR-EKLEM ’éó Temporomandibuler eklem hastal─▒─¤─▒n seyrinde s─▒kl─▒kla g├Čr├╝l├╝r. RA l─▒ hastalar─▒n muayenesinde palpasyonla hassasiyet aranmal─▒d─▒r. ’éó Sternoklavik├╝ler ve manubriosternal eklemler de RA da s─▒kl─▒kla tutulur ’éó Spinal tutulum servikal b├Člgeyle s─▒n─▒rl─▒. %30-50 hastada g├Čr├╝l├╝r. ’éó ├¢zellikle C1-C2 aras─▒ tutulum ├Čnemlidir. Anterior subluksasyon servikal tutulumu olan hastalar─▒n %50 sinde g├Čr├╝l├╝r.
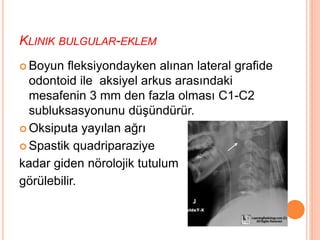
- 53. KLINIK BULGULAR-EKLEM ’éó Boyun fleksiyondayken al─▒nan lateral grafide odontoid ile aksiyel arkus aras─▒ndaki mesafenin 3 mm den fazla olmas─▒ C1-C2 subluksasyonunu d├╝┼¤├╝nd├╝r├╝r. ’éó Oksiputa yay─▒lan a─¤r─▒ ’éó Spastik quadriparaziye kadar giden n├Črolojik tutulum g├Čr├╝lebilir.
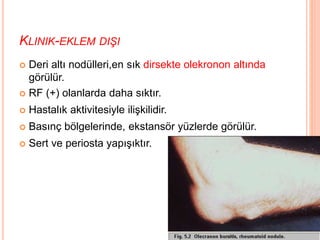
- 54. KLINIK-EKLEM DI┼×I ’éó Deri alt─▒ nod├╝lleri,en s─▒k dirsekte olekronon alt─▒nda g├Čr├╝l├╝r. ’éó RF (+) olanlarda daha s─▒kt─▒r. ’éó Hastal─▒k aktivitesiyle ili┼¤kilidir. ’éó Bas─▒n├¦ b├Člgelerinde, ekstans├Čr y├╝zlerde g├Čr├╝l├╝r. ’éó Sert ve periosta yap─▒┼¤─▒kt─▒r.
- 55. KLINIK-EKLEM DI┼×I Hematolojik ’éó Anemi:hastal─▒k aktivitesiyle korele ’éó Trombositoz:sinovitli eklem say─▒s─▒ ile korele ’éó Lenfadenopati ’éó Eozinofili Vaskulit ’éó Y├╝ksek RF titresi,romatoid nod├╝lleri olan hastalarda ’éó PAN gibi k├╝├¦├╝k ve orta ├¦apl─▒ arterleri etkiler,b├Čbrekleri asla tutmaz. ’éó Vazavazorum ve digital arterlerin t─▒kanmas─▒na ba─¤l─▒ olarak periferik n├Čropati,├╝lser ve gangren ortaya ├¦─▒kabilir. ’éó Palpabl purpura
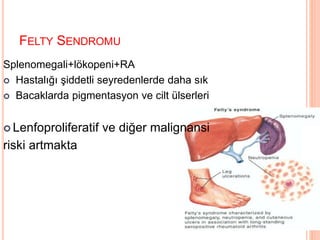
- 56. FELTY SENDROMU Splenomegali+l├Čkopeni+RA ’éó Hastal─▒─¤─▒ ┼¤iddetli seyredenlerde daha s─▒k ’éó Bacaklarda pigmentasyon ve cilt ├╝lserleri ’éó Lenfoproliferatif ve di─¤er malignansi riski artmakta
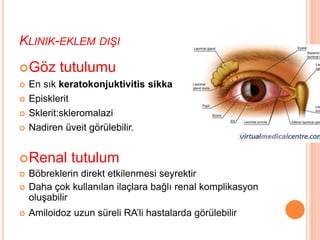
- 57. KLINIK-EKLEM DI┼×I ’éóG├Čz tutulumu ’éó En s─▒k keratokonjuktivitis sikka ’éó Episklerit ’éó Sklerit:skleromalazi ’éó Nadiren ├╝veit g├Čr├╝lebilir. ’éóRenal tutulum ’éó B├Čbreklerin direkt etkilenmesi seyrektir ’éó Daha ├¦ok kullan─▒lan ila├¦lara ba─¤l─▒ renal komplikasyon olu┼¤abilir ’éó Amiloidoz uzun s├╝reli RAŌĆÖli hastalarda g├Čr├╝lebilir
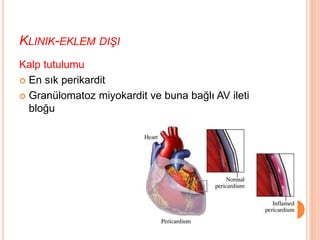
- 58. KLINIK-EKLEM DI┼×I Kalp tutulumu ’éó En s─▒k perikardit ’éó Gran├╝lomatoz miyokardit ve buna ba─¤l─▒ AV ileti blo─¤u
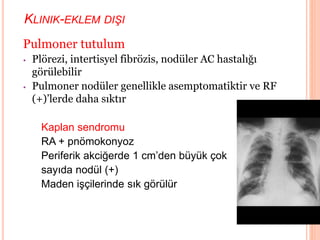
- 59. KLINIK-EKLEM DI┼×I Pulmoner tutulum ŌĆó Pl├Črezi, intertisyel fibr├Čzis, nod├╝ler AC hastal─▒─¤─▒ g├Čr├╝lebilir ŌĆó Pulmoner nod├╝ler genellikle asemptomatiktir ve RF (+)ŌĆÖlerde daha s─▒kt─▒r Kaplan sendromu RA + pn├Čmokonyoz Periferik akci─¤erde 1 cmŌĆÖden b├╝y├╝k ├¦ok say─▒da nod├╝l (+) Maden i┼¤├¦ilerinde s─▒k g├Čr├╝l├╝r
- 60. RA HASTASI NEFES DARLI─×INDAN ┼×IKAYET EDIYOR VE BAZALDE RALLER DUYULUYORSA HRCT ENDIKASYONU VARDIR. ─░NTERSTISYEL TUTULUM?
- 61. ŌĆó N├Črolojik tutulum ŌĆó En s─▒k tuzak n├Čropatileri Ō¢½ Karpal t├╝nel sendromu, tarsal t├╝nel sendrom ŌĆó Atlantoaksiyel eklem subluksasyonuna ba─¤l─▒ servikal miyelopati ŌĆó Musk├╝ler tutulum ŌĆó Sekonder kas atrofileri ŌĆó ─░laca ba─¤l─▒ miyopati
- 62. TANI
- 63. 2010 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria for RA JOINT DISTRIBUTION (0-5) 1 large joint 0 2-10 large joints 1 1-3 small joints (large joints not counted) 2 4-10 small joints (large joints not counted) 3 >10 joints (at least one small joint) 5 SEROLOGY (0-3) Negative RF AND negative ACPA 0 Low positive RF OR low positive ACPA 2 High positive RF OR high positive ACPA 3 SYMPTOM DURATION (0-1) <6 weeks 0 Ōēź6 weeks 1 ACUTE PHASE REACTANTS (0-1) Normal CRP AND normal ESR 0 Abnormal CRP OR abnormal ESR 1 Ōēź6 = definite RA Eklem de─¤erlendirilmesi A─¤r─▒l─▒ veya ┼¤i┼¤ eklem say─▒s─▒ DIF, 1. KMKF, 1.MTF eklemi de─¤erlendirmeye al─▒nmaz B├╝y├╝k eklem: Omuz, dirsek, kal├¦a, diz, ayak bile─¤i K├╝├¦├╝k eklem: PIF, MKF, el bilek, 2-4 MTF, ayak 1.IF eklem Tan─▒mlanmam─▒┼¤ t├╝m eklemler toplam eklem say─▒s─▒ i├¦in kullan─▒l─▒r (├Črnek:temporamandibular veya sternoklavikular eklem)
- 64. Konnektif doku hastal─▒klar─▒ (Lupus, Sjogren) Non erozif artrit Poliartik├╝ler gut Eklemler s─▒kl─▒kla eritemat├Čz, ├¦ok a─¤r─▒l─▒d─▒r. Seronegatif spondilartrit Asimetrik, alt ekstremitelerde oligoartrit ve omurga tutulumu Ps├Čriazis, ReiterŌĆÖs sendromu, inflamatuvar barsak hastal─▒klar─▒ sorgulanmal─▒ Still hastal─▒─¤─▒ Ate┼¤, l├Čkositoz, bo─¤az a─¤r─▒s─▒, splenomegali, karaci─¤er disfonksiyonu ve/veya d├Čk├╝nt├╝ Hemokromatozis Demir d├╝zeyleri, cilt de─¤i┼¤ikli─¤i ─░nfektif endokardit ├£f├╝r├╝m, y├╝ksek ate┼¤, intraven├Čz ila├¦ kullan─▒m─▒ Reaktif artrit Enfeksiyon sonras─▒ olabilir, cinsel yolla veya gastrointestinal enfeksiyon sonras─▒ Viral artrit Parvovirus, hepatit B Polimiyaljia romatika Romatoid artrit PMRŌĆÖye ├¦ok benzemez, nadiren proksimallerde a─¤r─▒ Akut romatizmal ate┼¤ Migratuar artrit Sarkoidoz Granulomalar, hiperkalsemi ve akci─¤er grafisi Romatoid artrit ay─▒r─▒c─▒ tan─▒s─▒
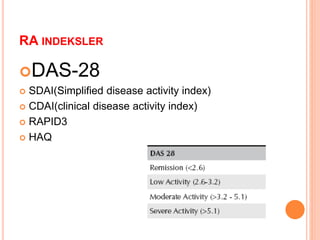
- 65. RA INDEKSLER ’éóDAS-28 ’éó SDAI(Simplified disease activity index) ’éó CDAI(clinical disease activity index) ’éó RAPID3 ’éó HAQ
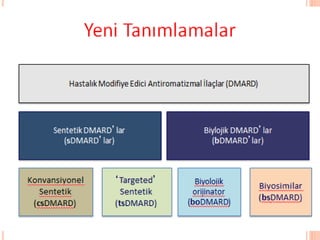
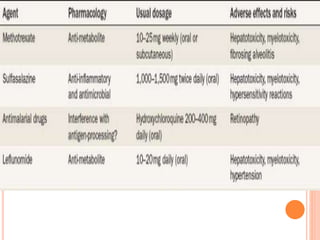
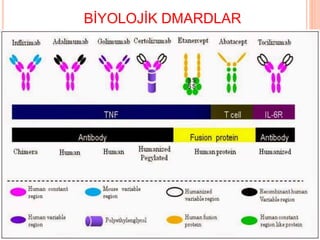
- 68. SENTETIK DMARDLAR ’éóMethotreksat : tedavide ilk se├¦enek ’éóLeflunomide: MTX KE oldu─¤unda,ya da kombinasyon tedavisinde ’éóKlorokin/hidroksiklorokin:DMARD ├Čzelli─¤i zay─▒ft─▒r. Radyografik progresyonu ├Čnlemezler. Bu nedenle monoterapi olarak kullan─▒m─▒ ├Čnerilmez. ’éóSulfasalazin:Gebelikte kullan─▒labilir. Oligospermi yapar ’éó Bu ila├¦lar─▒n ortak ├Čzelli─¤i hastal─▒─¤─▒n seyrinde de─¤i┼¤iklik yapmalar─▒, etkilerinin yava┼¤ ortaya ├¦─▒kmas─▒ ve inflamasyonun de─¤i┼¤ik basamaklar─▒nda etkili olmalar─▒
- 74. EULAR ├¢NER─░LER─░ ├¢neri 1 ’é¦RA tan─▒s─▒ konar konmaz derhal DMARDŌĆÖlar ile tedaviye ba┼¤lanmal─▒d─▒r Eklem tutulumu (0-5) 1 b├╝y├╝k eklem 2-10 b├╝y├╝k eklem 1-3 k├╝├¦├╝k eklem 4-10 k├╝├¦├╝k eklem >10 eklem ( en az 1 k├╝├¦├╝k eklem) 0 1 2 3 5 Seroloji (0-3) RF (-) VE ACPA (-) D├╝┼¤├╝k titrede (+) RF VEYA d├╝┼¤├╝k titrede ACPA Y├╝ksek titrede (+) RF VEYA y├╝ksek titrede ACPA 0 2 3 Semptom s├╝resi (0-1) < 6 hafta > 6 hafta 0 1 Akut Faz Reaktanlar─▒ (0-1) Normal CRP VE normal ESH Anormal CRP VEYA anormal ESH 0 1
- 75. EULAR ├¢NER─░LER─░ ├¢neri 2 ’é¦RA tedavisinde hedef ; her hastada remisyon veya d├╝┼¤├╝k hastal─▒k aktivitesi olmal─▒ Fonksiyonel d├╝zelme Yap─▒sal hasar─▒n ├Čnlenmesi
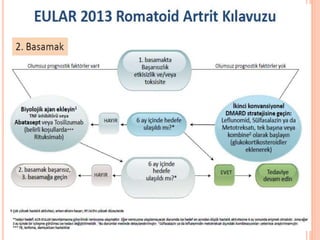
- 76. EULAR ├¢NER─░LER─░ ├¢neri 3 ’é¦Moniterizasyon aktif hastal─▒kta s─▒k (1-3 ayda bir) ’é¦E─¤er tedavinin ba┼¤lang─▒c─▒ndan itibaren 3. ayda hi├¦ bir iyile┼¤me yoksa VEYA 6. ayda hedefe ula┼¤─▒lamam─▒┼¤sa tedavi yeniden d├╝zenlenmelidir.
- 77. Tedavi Stratejileri B─░R─░NC─░ BASAMAK ░šĘĪČ┘┤Ī│š─░│óĘĪĖķ
- 78. EULAR ├¢NER─░LER─░ ’é¦ ├¢neri 4: Aktif RAŌĆÖl─▒ hastalarda METOTREKSAT ilk basamak tedavi stratejisinin bir par├¦as─▒ olmal─▒d─▒r ’é¦ ├¢neri 5: MTX kontrendikasyonunda (veya erken intoleransda) s├╝lfasalazin veya leflunomid (ilk) tedavi stratejisinde d├╝┼¤├╝n├╝lmelidir ’é¦ MTX monoterapisi ile DMARD naif hastada 6-12 ayda %25-50 LDA. ’é¦ GC veya di─¤er DMARDŌĆÖlar ile kombine edilebilir ’é¦ Aktif Hastal─▒k: CDAI>10, DAS28>3.2, SDAI> 11 ’é¦ Optimal doz, folik asit, 8 hafta ’é¦ SSP (3-4 g/g├╝n), LEF 20 mg/ g├╝n klinik etkinlik, fonksiyonel ve yap─▒sal hasara etki bak─▒m─▒ndan MTXŌĆÖe benzer
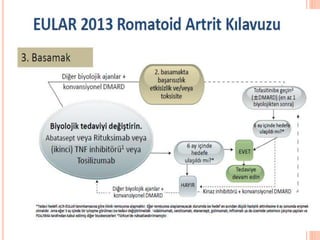
- 79. EULAR ├¢NER─░LER─░ 2013 G├£NCELLEME ├¢neri 6: DMARD naiv hastalarda monoterapi VEYA kombine olarak csDMARDŌĆÖlar kullan─▒lmal─▒d─▒r (steroid eklenmesinden ba─¤─▒ms─▒z olarak) Kombinasyon daha iyi tREACH-2013 Ard─▒┼¤─▒k monoterapi vs kombine ayn─▒ DeJong 2013 Monoterapiden biyolojik ajana step up kombinasyondan daha iyi BeST, Klarenbeek 2011
- 80. EULAR ├¢NER─░LER─░ ├¢neri 7 Mono veya kombine csDMARDŌĆÖlar ile birlikte d├╝┼¤├╝k doz glukokortikoid tedavisi 6. aya kadar ba┼¤lang─▒├¦ tedavisinin bir par├¦as─▒ olarak d├╝┼¤├╝n├╝lmelidir, ancak klinik olarak m├╝mk├╝n olan en k─▒sa s├╝rede azalt─▒lmal─▒d─▒r De Jong PH. ARD 2013,72:72-8 Bakker MF. Ann Intern Med 2012;156:329-39
- 81. DMARD D─░REN├ćL─░ HASTADA B─░YOLOJ─░KLERE M─░ YOKSA 3ŌĆÖL├£ TEDAV─░YE M─░ GE├ćEL─░M?
- 82. EULAR ├¢NER─░LER─░ ├¢neri 8 ─░lk DMARD stratejisi ile hedefe ula┼¤─▒lamam─▒┼¤sa; ’é¦ K├Čt├╝ prognostik fakt├Črler yoksa ; ba┼¤ka bir csDMARD tedavi stratejisi d├╝┼¤├╝n├╝lebilir ’é¦ K├Čt├╝ prognostik fakt├Črler varsa ; bir biyolojik DMARD eklenmesi d├╝┼¤├╝n├╝lmelidir Y├╝ksek hastal─▒k aktivitesi RF ve/veya CCP pozitifli─¤i Erken eklem hasar─▒SWEFOT- van Vollenhoven RACAT-OŌĆÖDell 2013 TEAR- Moreland 2012
- 83. DMARD SONRASI HANG─░ B─░YOLOJ─░K? B─░YOLOJ─░K MONOTERAP─░S─░ M─░, DMARD ─░LE KOMB─░NASYONU MU?
- 84. EULAR ├¢NER─░LER─░ ├¢neri 9 ’é¦MTX ve/veya di─¤er konvansiyonel sentetik DMARD stratejilerine yetersiz yan─▒t veren hastalarda, glukokortikoid olsun olmas─▒n, biyolojik DMARDŌĆÖlar ( antiTNFŌĆÖler, abatacept veya tocilizumab, ve baz─▒ ko┼¤ullarda rituximab) MTX ile beraber ba┼¤lanmal─▒d─▒r
- 85. Tedavi Stratejileri B─░YOLOJ─░KLER─░ DMARDŌĆÖLAR ─░LE KOMB─░NE ETMEL─░ M─░Y─░Z?
- 87. EULAR ├¢NER─░LER─░- G├£NCELLENME ├¢neri 10 ’éó─░lk biyolojik DMARDŌĆÖa yan─▒t vermeyenlerde ba┼¤ka bir biyolojik DMARD kullan─▒lmal─▒d─▒r; ilk antiTNFŌĆÖe yan─▒t vermeyenlerde ikinci biyolojik ba┼¤ka bir antiTNF veya ba┼¤ka etki mekanizmal─▒ bir biyolojik olabilir.
- 88. EULAR ├¢NER─░LER─░- G├£NCELLENME ├¢neri 11 ’éóBiyolojik tedaviye yan─▒t yoksa tofacitinib kullan─▒labilir
- 90. EULAR ├¢NER─░LER─░- G├£NCELLENME ├¢neri 12 ’éóE─¤er glukokortikoidler kesildikten sonra da kal─▒c─▒ remisyon devam ediyorsa, bDMARDŌĆÖlar─▒n azalt─▒lmas─▒ d├╝┼¤├╝n├╝lebilir; ├Čzellikle de csDMARD ile kombinasyon varsa
- 91. EULAR ├¢NER─░LER─░- G├£NCELLENME ├¢neri 13 ’éóKal─▒c─▒ uzus├╝reli remisyonda, hasta ve hekimin ortak karar─▒ ile, csDMARD dozunun da dikketli azalt─▒m─▒ d├╝┼¤├╝nebilir.
- 92. EULAR ├¢NER─░LER─░- G├£NCELLENME ├¢neri 14 ’éóTedavinin yeniden ayarlanmas─▒ gerekti─¤inde hastal─▒k aktivitesinden ba┼¤ka fakt├Črler de ├Črn; yap─▒sal hasar─▒n progresyonu, ko-morbiditeler ve g├╝venlik konular─▒ g├Čz ├Čn├╝nde tutulmal─▒d─▒r
- 97. HEDEFE Y├¢NELIK SENTETIK DMARDLAR ’éó 2013 g├╝ncellemesindeki mevcut verilerin aksine tofasitinib veritaban─▒, yeni g├╝venlik sorunlar─▒ ortaya ├¦─▒karmayan uzun s├╝reli uzatma ├¦al─▒┼¤malar─▒ ile geni┼¤letilmi┼¤tir. Ayr─▒ca ba┼¤ka bir Jak inhibit├Čr├╝ olan baritisinib, faz 3 ├¦al─▒┼¤malar─▒n─▒ tamamlad─▒ ve yeni g├╝venlik sorunlar─▒ olmaks─▒z─▒n ├Čnemli etkinli─¤i oldu─¤u g├Čsterildi.(bir TNF-inhibit├Čr├╝ ile kar┼¤─▒la┼¤t─▒r─▒ld─▒─¤─▒nda) ’éó T├╝m bMARD'lerin csDMARD'lar, ├Čzellikle MTX ile kombine edildi─¤inde daha iyi klinik, fonksiyonel ve yap─▒sal sonu├¦lar verdi─¤ini g├Čsteren g├╝├¦l├╝ kan─▒tlar vard─▒r, Jak inhibit├Črleri i├¦in bu ge├¦erli olmayabilir.
- 98. SONU├ć ’éó RAŌĆÖn─▒n ba┼¤ar─▒l─▒ tedavisi i├¦in stratejiler gereklidir ’éó Hedef; kal─▒c─▒ remisyon veya d├╝┼¤├╝k hastal─▒k aktivitesi ’éó MTX monoterapi ilk basamak tedavidir. ’éó ─░lk basamakta biyolojikler ile kombinasyon ├Čnerilmemektedir ’éó Biyolojikler genellikle DMARDŌĆÖlarla beraber kullan─▒lmal─▒d─▒r .
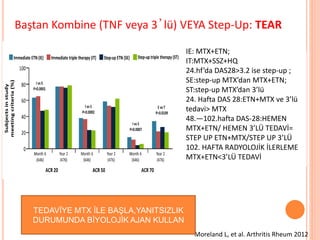
- 100. Ba┼¤tan Kombine (TNF veya 3ŌĆÖl├╝) VEYA Step-Up: TEAR Moreland L, et al. Arthritis Rheum 2012 IE: MTX+ETN; IT:MTX+SSZ+HQ 24.hfŌĆÖda DAS28>3.2 ise step-up ; SE:step-up MTXŌĆÖdan MTX+ETN; ST:step-up MTXŌĆÖdan 3ŌĆÖl├╝ 24. Hafta DAS 28:ETN+MTX ve 3ŌĆÖl├╝ tedavi> MTX 48.ŌĆö102.hafta DAS-28:HEMEN MTX+ETN/ HEMEN 3ŌĆÖL├£ TEDAV─░= STEP UP ETN+MTX/STEP UP 3ŌĆÖL├£ 102. HAFTA RADYOLOJ─░K ─░LERLEME MTX+ETN<3ŌĆÖL├£ TEDAV─░ TEDAV─░YE MTX ─░LE BA┼×LA,YANITSIZLIK DURUMUNDA B─░YOLOJ─░K AJAN KULLAN
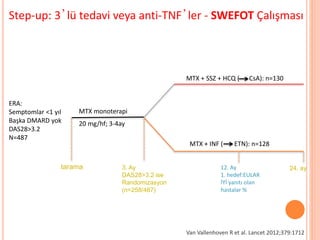
- 101. Step-up: 3ŌĆÖl├╝ tedavi veya anti-TNFŌĆÖler - SWEFOT ├ćal─▒┼¤mas─▒ ERA: Semptomlar <1 y─▒l Ba┼¤ka DMARD yok DAS28>3.2 N=487 MTX monoterapi 20 mg/hf; 3-4ay tarama 3. Ay DAS28>3.2 ise Randomizasyon (n=258/487) 12. Ay 1. hedef:EULAR ─░Y─░ yan─▒t─▒ olan hastalar % 24. ay MTX + SSZ + HCQ ( CsA): n=130 MTX + INF ( ETN): n=128 Van Vallenhoven R et al. Lancet 2012;379:1712
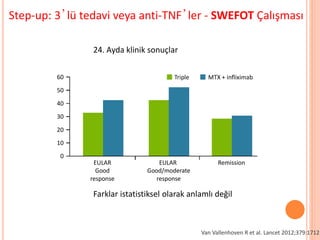
- 102. Step-up: 3ŌĆÖl├╝ tedavi veya anti-TNFŌĆÖler - SWEFOT ├ćal─▒┼¤mas─▒ Van Vallenhoven R et al. Lancet 2012;379:1712 van Vollenhoven RF, et al. Lancet 2012. Triple MTX + infliximab60 50 40 30 20 10 0 EULAR Good response EULAR Good/moderate response Remission Differences not statistically significant Clinical results at 24 months Step up to Triple Therapy or to TNF Inhibitors? The SWEFOT Trial 24. Ayda klinik sonu├¦lar Farklar istatistiksel olarak anlaml─▒ de─¤il
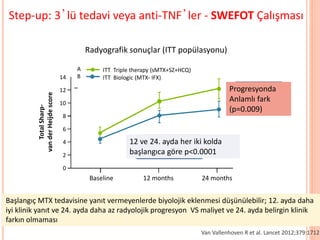
- 103. Step-up: 3ŌĆÖl├╝ tedavi veya anti-TNFŌĆÖler - SWEFOT ├ćal─▒┼¤mas─▒ Van Vallenhoven R et al. Lancet 2012;379:1712 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 Baseline 12 months 24 months TotalSharp vanderHeijdescore ITT Triple therapy (sMTX+SZ+HCQ) ITT Biologic (MTX IFX) van Vollenhoven RF, et al. ACR 2009, Philadelphia, LB6 A B van Vollenhoven RF, et al. Lancet 2012. p<0.0001 vs baseline for both arms at 12 and 24 months Significant difference in progression (p=0.009) Radiographic outcomes (ITT population) Step up to Triple Therapy or to TNF Inhibitors? The SWEFOT Trial Radyografik sonu├¦lar (ITT pop├╝lasyonu) Progresyonda Anlaml─▒ fark (p=0.009) 12 ve 24. ayda her iki kolda ba┼¤lang─▒ca g├Čre p<0.0001 Ba┼¤lang─▒├¦ MTX tedavisine yan─▒t vermeyenlerde biyolojik eklenmesi d├╝┼¤├╝n├╝lebilir; 12. ayda daha iyi klinik yan─▒t ve 24. ayda daha az radyolojik progresyon VS maliyet ve 24. ayda belirgin klinik fark─▒n olmamas─▒
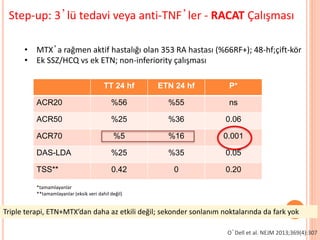
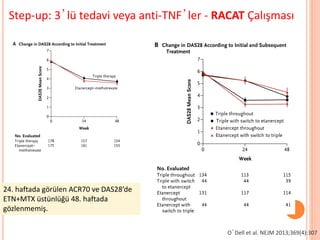
- 104. Step-up: 3ŌĆÖl├╝ tedavi veya anti-TNFŌĆÖler - RACAT ├ćal─▒┼¤mas─▒ TT 24 hf ETN 24 hf P* ACR20 %56 %55 ns ACR50 %25 %36 0.06 ACR70 %5 %16 0.001 DAS-LDA %25 %35 0.05 TSS** 0.42 0 0.20 ŌĆó MTXŌĆÖa ra─¤men aktif hastal─▒─¤─▒ olan 353 RA hastas─▒ (%66RF+); 48-hf;├¦ift-k├Čr ŌĆó Ek SSZ/HCQ vs ek ETN; non-inferiority ├¦al─▒┼¤mas─▒ *tamamlayanlar **tamamlayanlar (eksik veri dahil de─¤il) OŌĆÖDell et al. NEJM 2013;369(4):307 Triple terapi, ETN+MTXŌĆÖdan daha az etkili de─¤il; sekonder sonlan─▒m noktalar─▒nda da fark yok
- 105. Step-up: 3ŌĆÖl├╝ tedavi veya anti-TNFŌĆÖler - RACAT ├ćal─▒┼¤mas─▒ OŌĆÖDell et al. NEJM 2013;369(4):307 24. haftada g├Čr├╝len ACR70 ve DAS28ŌĆÖde ETN+MTX ├╝st├╝nl├╝─¤├╝ 48. haftada g├Čzlenmemi┼¤.
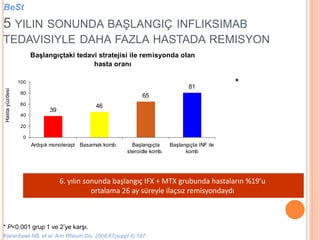
- 106. Ba┼¤lang─▒├¦taki tedavi stratejisi ile remisyonda olan hasta oran─▒ 39 46 65 81 0 20 40 60 80 100 Ard─▒┼¤─▒k monoterapi Basamak komb. Ba┼¤lang─▒├¦ta steroidle komb. Ba┼¤lang─▒├¦ta INF ile komb Hastay├╝zdesi 5 YILIN SONUNDA BA┼×LANGI├ć INFLIKSIMAB TEDAVISIYLE DAHA FAZLA HASTADA REMISYON * * P<0.001 grup 1 ve 2ŌĆÖye kar┼¤─▒. Klarenbeek NB, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67(suppl II):187. BeSt 6. y─▒l─▒n sonunda ba┼¤lang─▒├¦ IFX + MTX grubunda hastalar─▒n %19ŌĆÖu ortalama 26 ay s├╝reyle ila├¦s─▒z remisyondayd─▒
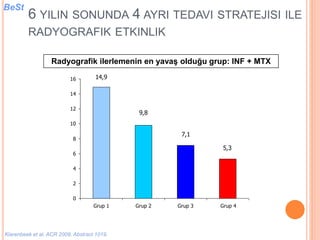
- 107. 6 YILIN SONUNDA 4 AYRI TEDAVI STRATEJISI ILE RADYOGRAFIK ETKINLIK Radyografik ilerlemenin en yava┼¤ oldu─¤u grup: INF + MTX 5,3 7,1 14,9 9,8 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 Grup 1 Grup 2 Grup 3 Grup 4 Klarenbeek et al. ACR 2009. Abstract 1019. BeSt
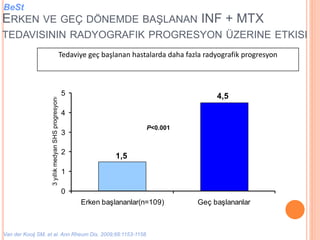
- 108. Tedaviye ge├¦ ba┼¤lanan hastalarda daha fazla radyografik progresyon 1,5 4,5 0 1 2 3 4 5 Erken ba┼¤lananlar(n=109) Ge├¦ ba┼¤lananlar 3y─▒ll─▒kmedyanSHSprogresyonu P<0.001 Van der Kooij SM, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68:1153-1158. ERKEN VE GE├ć D├¢NEMDE BA┼×LANAN INF + MTX TEDAVISININ RADYOGRAFIK PROGRESYON ├£ZERINE ETKISI BeSt
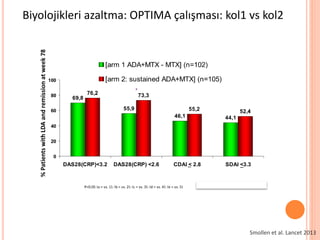
- 109. Biyolojikleri azaltma: OPTIMA ├¦al─▒┼¤mas─▒: kol1 vs kol2 Smollen et al. Lancet 2013
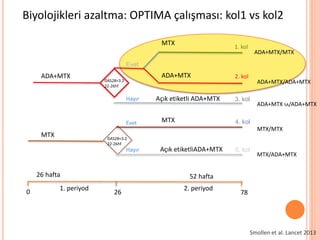
- 110. Biyolojikleri azaltma: OPTIMA ├¦al─▒┼¤mas─▒: kol1 vs kol2 ADA+MTX MTX ADA+MTX Evet Hay─▒r Evet Hay─▒r MTX 26 hafta 0 26 78 1. periyod 2. periyod A├¦─▒k etiketli ADA+MTX A├¦─▒k etiketliADA+MTX MTX 52 hafta DAS28<3.2 22-26hf DAS28<3.2 22-26hf 1. kol 2. kol 3. kol 4. kol 5. kol ADA+MTX/MTX ADA+MTX/ADA+MTX ADA+MTX SA/ADA+MTX MTX/MTX MTX/ADA+MTX Smollen et al. Lancet 2013
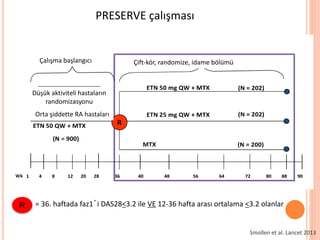
- 111. PRESERVE ├¦al─▒┼¤mas─▒ Smollen et al. Lancet 2013 ├ćal─▒┼¤ma ba┼¤lang─▒c─▒ ├ćift-k├Čr, randomize, idame b├Čl├╝m├╝ D├╝┼¤├╝k aktiviteli hastalar─▒n randomizasyonu Orta ┼¤iddette RA hastalar─▒ R = 36. haftada faz1ŌĆÖi DAS28<3.2 ile VE 12-36 hafta aras─▒ ortalama <3.2 olanlar
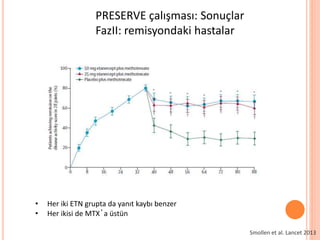
- 112. PRESERVE ├¦al─▒┼¤mas─▒: Sonu├¦lar FazII: remisyondaki hastalar Smollen et al. Lancet 2013 ŌĆó Her iki ETN grupta da yan─▒t kayb─▒ benzer ŌĆó Her ikisi de MTXŌĆÖa ├╝st├╝n