Ξ±ΞΔΞι©` ÷’
- 1. ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛΈΫιΉoΛρΛΖΛΤΛΛΛκΛΔΛ ΛΩΛΈΛΩΛαΛΈ “Μ “Μ Γω Γω Γω Γω ©` ΓΪ ? Γω Γω Γω Γω “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ Γω I Γω Γω Γω “Μ “Μ ©` ©` “Μ Γω Γω Γω Γω ©` ΓΪ “ΜΓωΓωΓωΓω'ΓωΓωΓωΓωΓωΓωΓωΓω©`ΓωΓωΓωΓω©` ΓΔ ΞΔΞι©` ÷éΛ Γε Θ… Θ… Θλ Θλ Θλ Θλ Θλ Θλ Θλ Θλ Θλ Θ… Θ… Θ… Θλ Θλ Θλ Θλ Θλ Θλ Θλ Θλ Θλ Θλ Θλ Θλ Θλ Θλ Θ± Θ± ΓΔ Θ± Θ± Θλ Θ… Θ… Θ… Θ… Θλ Θ± Θ… Θ… Θ… Θ… Θ… Θ… Θ… Θλ Θλ Θ… Θλ Θλ Θ… Θ… Θ… Θλ Θ… Θ… Θ… Θ… Θ… Θξ Ξ±ΞΔΞι©` ÷’ “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ ¥σ«–Λ »ΥΛρΫιΉoΛΖΛΤΛΛΛκ ΛΔΛ ΛΩΛβ ¥σ«–Λ “Μ»ΥΛ«ΛΙΓΘ Αk––»’ 2014Ρξ3‘¬20»’ Αk –– …œ ΓΨ“ΜΑψ…γ΅βτΡ»Υ»’±ΨΞ±ΞΔΞι©`ΏBΟΥΘί ®™160-0022•|Ψ©ΕΦ–¬Υό«χ–¬Υό1-25-3ήηΞΜΞκΞ≥©`Ξ»302 TEL:03-3355-8028(Υ°?Ϋπ13:00ΓΪ17:00) FAX:03-5368-1956 nail:info@carersiapan.comWebΞΒΞΛΞ»:carersjapan.comE-mail: ΓΨΙΪ“φ…γ΅βΖ®»Υ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛ»Φ“ΉεΛΈΜαêέ÷Σ±h÷ßδz ®™477-0034êέ÷Σ±h•|ΚΘ –πBΗΗν°±±ήΞ°x58?1 TEL:0562-33-7048FAX;0562-33-7102 Γώ’J÷Σ÷ΔΫιΉoœύ’³Θ®‘¬ΓΪΫπ10ïrΓΪ16ïr)TEL:0562-31-1911 E-mail:rara2@ma.medias.ne.ip WebΞΒΞΛΞ»:http://www.hearttoheart.or.ip/kazoku/ “ΜΑψ…γ΅βΖ®»Υ ?±ΨΞ±ΞΔΞι©`ΏBΟΥ ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛ»Φ“ΉεΛΈΜαêέ÷Σ±h÷ß≤ΩΙΪ“φ…γ΅βΖ®»Υ ΓΔ “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ Γ®? Γω Γω Γω Γω “Μ“Μ ? U Γω Γω 1 ? ΘΫ q _ Λ« ? Ξω - p “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ L ?? ? ? Γω “Μ
- 2. ΞΔΞι©` ÷éΛΛρ ÷ΛΥΛΒΛλΛΩΖΫΛΊ Λ≥ΛΈ ÷éΛΛœΓΔ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛρΫιΉoΛΖΛΤΛΛΛκΞ±ΞΔΞι©`Λρ÷ß‘°ΛΙ ΛκΛΩΛαΛΥΛΡΛ·ΛιΛλΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘΞ±ΞΔΞι©`Λ»Ξ±ΞΔΞι©`ΛΈΛΩΛαΛΈΞΒ©` Ξ”ΞΙΛδΞΒΞί©`Ξ»ΛρΛΡΛ ΛΑΛ≥Λ»ΛρΤΎ¥ΐΛΖΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ ΓώΗςΞΎ©`ΞΗΛΈάϊ”ΟΛΈΞίΞΛΞσΞ»Λ«ΛΙΓΘ ±όüoΈ`κÖ÷ζë½ζêΚ\Υ_Λ≠ΛΛΓ≠ΘΫ??Γζ Ω±û{’τâ÷»Ί―‘ΗwΤ·»Ύϊê ΜσκÉΒΫΉRΛΊάΏκÉλFΝRœΔ–ήœΔσ@Λ·Γ± γRΚ\ρnΝήώ{θé―‘-δzΓ≠Γ≠ ΉoΉjΩéΙQάΏ’τΚ\ρTΊûΝLΗ² Μυ±ΨΒΡΛ ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ÷ΣΉRΛδΛΝΛγΛΟΛ»ΛΖΛΩΫιΉoΛΈ κy¬ö±ΠΛ Λ≥Λ≥άΏ≈κ÷îΡΐ»οκL’èίίΌû Ω±ΛΔΛ ΛΩΛΈΛΩΛαΛΈΨV’³ΖôΩΎάΏ«ΌϊêΦ»Ην»οc≤θ®Q Ω±ΛβΛΖΛβΛΥ²δ÷ΨΖΨΩéùïΚ\ΣïΩ½“Αy―© ??Θ© ι΅ΛΔΛ ΛΩΛρ÷ßΛ®ΛκΒΊ”ρ??????Λ§ΛΔΛξΛόΛΙ ΒΊ”ρΑϋά®÷ß‘°ΞΜΞσΞΩ©` ±Θ ΫΓ éü ? …γ Μα ΗΘ λμ Ω ? ÷ς »Έ Ξ±ΞΔΞόΞΆΞΗΞψ©`Β»Λ§ΗΏΐh’ΏΛδ Φ“ΉεΛΈœύ’³ΛΥ ÷ß‘°Λρ––ΛΛΛό ¹\ΛξΓΔΨtΚœΒΡΛ Θ· “Ϋ·üôCιv?±ΘΫΓΥυ ≤Γ‘ΚΛ«ΛΈ‘\·ü?‘LÜ•‘\·üΓΘ ‘LÜ•Ω¥Ήo?ΫΓΩΒΙήάμΛ Λ…Λρ ΛΖ Λό ΛΙ ΞΈ Οώ…ζΈ·ÜT άßΛξΛ¥Λ»Λδ…ζΜν ²SôCιvΛ»ΛΈΛΡΛ Ή¥ ¦r ΛΈ œύ ’³ ιv Λ°“έΛρΛΖΛό ΛΙ ΫιΉo±Θξ™ ¬‰IΥυ Ξ«ΞΛΞΒ©`Ξ”ΞΙ?‘LÜ•ΫιΉoΘ°??? ΞΖΞγ©`Ξ»ΞΙΞΤΞΛΛ Λ…ΫιΉo±Θξ™ ΞΒ©`Ξ”ΞΙΛρΧαΙ©ΛΖΛΤΛ·ΛλΛόΛΙ I NPO?ΞήΞιΞσΞΤΞΘΞΔ “Τ³”ΞΒ©`Ξ”ΞΙΛδ≈δ ≥ΞΒ©`Ξ”ΞΙ Λ Λ……ζΜν‘°÷ζΞΒ©`Ξ”ΞΙΛρ¨g © ΛΖΓΔΙΪΒΡΞΒ©`Ξ”ΞΙΛ§ΫλΛ≠Θϋ ΛΛ≤ΩΖ÷ΛρΒΘΛΟΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙ Γω Λ≥ΛΑ ΓΔ ΛΙ Ή‘÷ΈΜα »’ Λ¥ Λμ ΛΈ …υ ΛΪ Λ± Λδ Ψo Φ± ïr ΛΈ ÷ ÷ζ Λ± Λρ ΛΖ ΛΤ Λ· Λλ Λό ΛΙ Ω…?Γώ Θ· ΓΔ –«χν°¥ε“έàω ΗΏΐh’ΏΛδΫιΉo±Θξ™ΛΈΞΜΞ·ΞΖΞγ ΞσΛ Λ…Λ§ΒΊ”ρΛΈΗΘλμΞΒ©`Ξ”ΞΙ ΛρΒΘΒ±ΛΖΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙ I …γΜαΗΘλμÖfΉhΜα ΗΏΐh’ΏΛδ’œΛ§ΛΛ’ΏΓΔΫιΉo’ΏΛΈ ΛΩ Λα ΛΈ ΛΒ Λό ΛΕ Λό Λ ΉΓ Οώ ΗΘ λμ ΞΒ©`Ξ”ΞΙΛδœύ’³ΛΥ¹\ΛΟΛΤΛΛΛό ΛΙ ΫιΉo’ΏΛΈΜα ΫιΉo’ΏΛ…ΛΠΛΖΛ§’ZΛξΛΔΛΠàωΛ« ΛΙΓΘΑ≤–ΡΛΖΛΤΓΔΛ ΛσΛ«Λβ‘£ΛΜ ΛόΛΙΓΘöίΛ≈Λ≠Λ»«ιàσΫΜ™QΛΈàω Λ« Λβ ΛΔ Λξ Λό ΛΙ ΞΈ Ξ±ΞΔΞι©`ΞΚΞΪΞ’Ξß Ξ±ΞΓΞι©`Λ§ΓΔΒΊ”ρΛ«ΛέΛΟΛ»Λ« Λ≠ΛκΩ’ιgΘ®Ψ”àωΥυΘ©Λ«ΛΙΓΘ÷Ό ιgΛ§ΛΛΛΤΓΔ«ιàσΛ§ΛΔΛξΛό ΛΙ Γώ?ΫιΉo’ΏΛΈΜαΓΙΓΗΞ±ΞΔΞι©`ΞΚΞΪΞ’ΞßΓΙΛ Λ…ΛΈàωΥυΛδι_¥Ώ»’ïrΛρ”¦»κΛΖΛΤΛΣΛ≠ΛόΛΖΛηΛΠΓΘ ΓΨ ΓΩ 25
- 3. 42 ΓΔ ΛβΛΖΛβΛΥ²δΛ®ΛΤ ΓώΡΩ¥ΈΘ°ΛοΛΩΛΖΛΈ”¦εhΓ≠Γ≠?Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠?Γ≠Γ≠?Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠PI Γώ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛΈΫιΉoΛρΛΖΛΤΛΛΛκΛΔΛ ΛΩΛΊΓ≠Γ≠Γ≠?Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠?Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠?Γ≠P.2 ΓώΛΔΛ ΛΩΛΈöί≥÷ΛΝΛρ¬½ΛΛΛΤΛ·ΛλΛκ»ΥΛ§ΛΛΛόΛΙΓ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠P3ΓΪ7 Γώöί≥÷ΛΝΛ§…ρΛύ»’ΛΥΞ±ΞΔΞι©`ΛΈΛΔΛ ΛΩΛΊΓ≠.Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠?Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠?Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠P8ΓΪ9 Γώ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛΈΦ“ΉεΫιΉo’ΏΛœ?ΛέΛ»ΛσΛ…Λ§?…ζΜνΛ§ΛΖΛ≈ΛιΛ·Λ ΛΟΛΩ?Λ»¥πΛ®ΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓ≠P10ΓΪII ΓώΉ‘Ζ÷Λρ¥σ«–ΛΥΛΙΛκΛΩΛαΛΥΓώΛΔΛ ΛΩΉ‘…μΛΈΫΓΩΒΞαΞβ?Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠P12ΓΪ13 ΓώΫΓΩΒΞΝΞßΞΟΞ·ΞξΞΙΞ»Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠?Γ≠Γ≠ΓΑΓ≠P14ΓΪ15 Γώ ÷Σ ΛΟ ΛΤ ΛΣ Λ≥ ΛΠ ’J ÷Σ ÷Δ ΛΈ Λ≥ Λσ Λ Λ≥ Λ» Γώ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΥΛ ΛκΛ»Λ≥ΛσΛ Λ≥Λ»Λ§ΛΣΛ≥ΛξΛόΛΙΓ≠Γ≠Γ≠P16ΓΪ18 Γώ’J÷Σ÷ΔΫιΉoΛΈΛ≥Λ≥ΛμΛ§ΛόΛ®Γ≠?Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Θ°Θ°Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠P19 ΓώΛ ΛκΛέΛ…1’J÷Σ÷ΔΫιΉoΛΈΛ“Λ»ΙΛΖρΓ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠P20ΓΪ21 ΓώΛΔΛ ΛΩΛΈΛΩΛαΛΈœύ’³ΖôΩΎΓ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠?Γ≠Γ≠?Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠?Γ≠?Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠?Γ≠P22ΓΪ23 ΓώΛβΛΖΛβΛΥ²δΛ®ΛΤΓ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠.Γ≠.Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠?Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠?Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠P24 ΓώΛΔΛ ΛΩΛρ÷ßΛ®ΛκΒΊ”ρΞΆΞΟΞ»Ξο©`Ξ·Λ§ΛΔΛξΛόΛΙΘ°Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠?Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠P25 ΒΊ’π?ΜπûΡΛ Λ…ΛΪΛι¥σ«–Λ Φ“ΉεΛρ ΊΛκΛΩΛαΛΥ ΓτûΡΚΠΛ§ΤπΛ≠ΛΩΛ»Λ≠ΛœΓτ ûΡ ΚΠ ïr ΓΔ ΉR Ώ[ ΛΈ »Υ Λœ ΚΈ ΛΪ ΛΣ Λ≥ ΛΟ ΛΩ ΛΪ άμ Ϋβ Λ« Λ≠ Ϋ ΞΈ f ΞΥ ΞΟ Ξ· ΛΥ Λ ΛΟ ΛΩ Λξ ≤Μ;Α≤Λ«¬δΛΝΛΡΛΪΛ Λ·Λ ΛΟΛΩΛξΛΖΛό ΫΛΔΛοΛΤΛ ΛΛΛ«ΓΔΑ≤–ΡΛΙΛκΛηΛΠΛΥ…υΛρ ΛΪ/ΛΩΛξΞΙΞ≠ΞσΞΖΞΟΞ÷ΛΙΛκΛ Λ…Γ°Λρ–ΡΛ§Λ±ΛόΛΖΛγΛΠΓΘ ΓώΛΔΛ ΛΩΛ§νmΛξΛ«ΛΙΓΘΛΔΛοΛΤΛ ΛΛΛ«––³”ΛΖΛΤΛ·ΛάΛΒΛΛΓΘ 1Θ°ΛΔΛ ΛΩΛ»Φ“ΉεΛΈΑ≤»ΪΛρ¥_’JΛΖΛΤΛ·ΛάΛΒΛΛ 2Θ°ΜπΛΈ¥_’JΛρΛΖΛΤΛ·ΛάΛΒΛΛ 3Θ°≥ωΩΎΛΈ¥_±ΘΓΔΑ≤»ΪΛΈΛΩΛα―ΞΛρΛœΛΛΛΤΛ·ΛάΛΒΛΛ 4Θ°Φ“ΉεΛρΏBΛλ≥ωΛΜΛ ΛΛΛ»Λ≠ΛœΓΔΑ≤»ΪΛρ¥_±ΘΛΖΛΤΓΔΫϋΛ·ΛΈ»ΥΛΥ÷ζΛ±Λρ «σΛαΛΤΛ·ΛάΛΒΛΛ ΓώΤ’ΕΈΛΪΛιöίΛρΛΡΛ±ΛΩΛΛΛ≥Λ» ?Ξ±ΞΔΞι©`Λ«ΛΔΛκΛ≥Λ»ΛρΉ‘÷ΈΜαΛδΛ ΛΗΛΏΛΈΛΣΒξΛ Λ…ΛΥ÷ΣΛιΛΜΛΤΛΣΛ≠Λό ΛΖΛγΛΠ ?“Τ³” ÷ΕΈΘ®ή΅“ΈΉ”?öi––ΤςΛ Λ…Θ©Λρ¥_±ΘΛΖΛΤΛΣΛ≠ΛόΛΖΛγΛΠ ?Φ“ΨΏΛΥΛœήûΒΙΖά÷ΙΛΈΫπΨΏΛ Λ…Λρ»ΓΛξΗΕΛ±ΛΤΛΣΛ≠ΛόΛΖΛγΛΠ ?≤ΩΈίΛΈ≥ω»κΩΎΛΥΛœΛβΛΈΛρ÷ΟΛΪΛ ΛΛΛηΛΠΛΥΛΖΛόΛΖΛγΛΠ ?ΥaΘ®ΥaΛΈΟϊ≥ΤΛβΩΊΛ®ΛΤΛΣΛ·)ΓΔΛΣΛύΛΡΓΔ“¬νêΛ Λ…Λρ€ ²δΛΖΛΤΛΣΛ≠ ΛόΛΖΛγΛΠΓΘΓΗΨoΦ±ïrΑ≤–ΡΞ≠ΞΟΞ»ΓΙΛ Λ…Λβ”Ο“βΛΖΛΤΛΣΛ·Λ»±ψάϊΛ«ΛΙ ?3»’Ζ÷ΛΈΥ°? ≥ΦZΛρ€ ²δΛΖΛΤΛΣΛ≠ΛόΛΖΛηΛΠ ?ΞέΞΛΞΟΞΙΞκΛδë·÷–κäΒΤΛ Λ…ΛρΞΌΞΟΞ…ΛΈ²»ΛΥΛΣΛΛΛΤΛΣΛ≠ΛόΛΖΛγΛΠ ΛοΛΩΛΖΛΈ”¦εh ΥΫΛΈ±ήκyΥυΛœ ΓΨ Θ± Οφ “Ϋ·üôCιvΟϊ?“ΫéüΟϊ?ΉΓΥυκä‘£Ζ§Κ≈Λ Λ… <ΥaΛΈΞαΞβΘΨ “Μ ΓΔ 24 œ Οϊ …ζ Ρξ ‘¬ »’ ΉΓ Υυ ΨoΦ±ΏBΫjœ»¬ϊ Ψo Φ± ΏB Ϋj œ» 2 ΛΪ ΛΪ Λξ ΛΡ Λ± “Ϋ Ος ÷Έ ? ¥σ ’ΐ ? ’― ΚΆ ΤΫ ≥… Ρξ ‘¬ 9 (κä‘£Ζ§Κ≈ΓΖ (κä‘£Ζ§Κ≈ΘΜ ΔΌ ?ώR”ξ“Μ“Μ(κä‘£Ζ§Κ≈Θ© ΔΎ ΨA±ζ
- 4. ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛΈΫιΉoΛρΛΖΛΤΛΛΛκΛΔΛ ΛΩΛΊ “Μ ? Υ] ? ? ΘΚ ? ? Θι ΛΈΙΪ“φ…γ΅βΖ®»Υ≥…Ρξαα“äΞΜΞσΞΩ©`?Ξξ©`Ξ§ΞκΞΒΞή©`Ξ»÷ß≤Ω ΩΎ“Μ”EΓΨhttps://www.legal-support.or.jp/ΓΩI¬ΕΛΟΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΛΏΛσΛ Ά§ΛΗΛηΛΠΛ ¬ Λ«άß »’±ΨΥΨΖ®÷ß‘°ΞΜΞσΞΩ©`?Ζ®ΞΤΞιΞΙΓ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠ΙΎ0570-078374 ΓΨ‘¬ΓΪΫπ9ïrΓΪ21ïrΓΔΆΝ9ïrΓΪ17ïrΘ®Φά»’?ΡξΡ©Ρξ Φ–ί‰I)ΓΩΞμ 1?»ΥΛ«ΛΪΛΪΛ®Λ≥ΛόΛ ΛΛΛ«ΫιΉo÷ΌιgΛρΛΡΛ·ΛμΛΠΓΘ ΫιΉo’ΏΫΜΝςΜαΓΔκä‘£œύ’³Λ Λ…ΛρΆ®ΛΖΛΤΓΔΛέΛΪΛΈΫιΉo’ΏΛΪΛιΛΈ«ιàσΛρΒΟΛκôCΜαΛρ ΛΡΛ·ΛξΛόΛΖΛγΛΠ?ΫιΉoΛΈ÷Σê{Λ§€ΚίdΛ«ΛΙ?”ό≥’Λρ―‘Λ®Λκœύ ÷Λ§ΛΛΛκΛ≥Λ»Λβ¥σ«–Λ«ΛΙΓΘ Γώ “Ϋ ·ü ôC ιv ΛΈ ¨ù èξ ΛΥ ιv ΛΙ Λκ œύ ’³ ΘϋΛ¥άϊ”ΟΛΈ“Ϋ·üôCιvΛΈœύ’³ΖôΩΎ Ζ®»ΥΛΒΛΒΛ®ΛΔΛΛ“Ϋ·ü»Υ‰ΊΞΜΞσΞΩ©`COML(Ξ≥ΞύΞκΘ©κä‘£œύ’³ -6314-1652ΓΨ‘¬ΓΪΫπΓΩΓ¥9ïrΓΪ12ïr13ïrΓΪ17ïrΓΒΓΨΆΝΓΩΓ¥9ïrΓΪ12ïrΓΒω†2Ή‘Ζ÷ΛρΛέΛαΛΤΛΔΛ≤ΛηΛΠΓΘ ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈΫιΉoΛœΡΩΛΥ“äΛ®Λ ΛΛΩύ³ΚΛ§ΛΔΛξΛόΛΙΓΘΛ«ΛΙΛ§ΫιΉo’ΏΛΈΩύ³ΚΛœΛ ΛΪΛ ΘΚ ΛΪΛόΛοΛξΛΥάμΫβΛΖΛΤΛβΛιΛ®Λ ΛΛΛβΛΈΛ«ΛΙΓΘ‘ΣöίΛ§≥ωΛκΛηΛΠΉ‘Ζ÷Λ«Ή‘Ζ÷ΛρΛέΛαΛΤΘΜi ΛΔΛ≤ΛόΛΖΛγΛΠΓΘ 3Λ§ΛσΛ–ΛξΛΙΛ°Λ ΛΛΓΘ ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈΫιΉoΛœΓ®ΛΛΛΛΛΪΛ≤ΛσΛ§ΓΔΛΝΛγΛΠΛ…ΛΛΛΛΛΪΛ≤ΛσΓ®Λ«ΛΙΓΘΛΗΛγΛΠΛΚΛΥ ÷ΘΚ £iΛ≠ΛρΛΖΛΤœΔΛΈιLΛΛΫιΉoΛ§Λ«Λ≠ΛκΛηΛΠΓΔΫιΉoΞΒ©`Ξ”ΞΙΛράϊ”ΟΛΖΛ§ΛσΛ–ΛιΛ ΛΛΫιΉol Λρ–ΡΛ§Λ±ΛόΛΖΛγΛΠ? 4ΫΓΩΒΛΥöίΛρΛΡΛ±Ή‘Ζ÷Λρ¥σ«–ΛΥΓΘ ΫιΉo’ΏΛΔΛΟΛΤΛΈΫιΉoΛ«ΛΙΓΘΫιΉo’ΏΛ§œ»ΛΥΒΙΛλΛΤΛΖΛόΛΟΛΤΛœ‘ΣΛβΉ”ΛβΛΔΛξΛόΛΜΘΜ ΛσΓΘΛόΛΚΛœΉ‘Ζ÷Ή‘…μΛΈΛ≥Λ»ΛρΛΛΛΝΛ–Λσ¥σ«–ΛΥΛΖΛΤΓΔΉ‘Ζ÷ΛΈ»Υ…ζΛρ‰SΛΖΛύΛ≥Λ»ΛρΘΚ ΩΦΛ®ΛΤΛΛΛ≠ΛόΛΖΛγΛΠΓΘ 5ΗΙΛ§ΝΔΛΟΛΤΛΔΛΩΛξΛόΛ®ΓΘ Γ®’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛΥΛœ≈≠ΛΟΛΤΛœΛΛΛ±Λ ΛΛΓ®Λ»―‘ΛοΛλΛόΛΙΛ§ΓΔ…μΡΎΛΈΫιΉoΛ«ΛœΓΔΛΫi ΛΠΚÜÖgΛΥΛ«Λ≠ΛκΛβΛΈΛ«ΛœΛΔΛξΛόΛΜΛσΓΘ≈≠ΛιΛ ΛΛΛ«ΫιΉoΛ«Λ≠ΛκΛηΛΠΛΥΛ ΛκΛΥΛœΛάΘΜ ΛλΛ«ΛβïrιgΛ§ΛΪΛΪΛξΛόΛΙΓΘ 6÷ΣΉRΛρΛβΛ»ΛΠΓΘ ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΥ¨ùΛΙΛκ’ΐΛΖΛΛ÷ΣΉRΛρΛβΛΝΛόΛΖΛγΛΠΓΘιgΏ`ΛΟΛΩ«ιàσΛβΛΩΛ·ΛΒΛσ≥ωΛόΘΚΘΜ ΛοΛΟΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΛΈΛ«ΓΔ«ιàσΛΥ’ώΛξΛόΛοΛΒΛλΛ ΛΛΛηΛΠΛΥΓΘΫΜΝςΜαΛ««ιàσΛρΒΟΛΤΓΔii Ή‘Ζ÷Λ ΛξΛΈΫιΉoΛΈ ΥΖΫΛρ“äΛΡΛ±ΛόΛΖΛγΛΠΓΘ ΞΔ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛρκLΛΒΛ ΛΛΓΘ ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛ§ΏMΛσΛ«Λ·ΛκΛ»ΛόΛοΛξΛΈ÷ζΛ±Λ§±Ί“ΣΛΥΛ ΛκΛ≥Λ»ΛβΛΔΛξΛόΛΙΓΘ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛρκLΛΒΛ ΛΛi Λ«ΓΔ…μΫϋΛ »ΥΛΥΛœ≤ΓöίΛΈΛ≥Λ»Λρ¹ΜΛ®ΛΤΓΔάμΫβ’ΏΛδÖfΝΠ’ΏΛρΛΡΛ·ΛΟΛΤΛΣΛ≠ΛόΛΖΛγΛΠΓΘΘΚ L ? ? ©\ ? ? ? ? ? ? ≤Έ Γώ Ϋι Ήo ¬ ‰I Υυ ΛΈ ¨ù èξ ΛΥ ιv ΛΙ Λκ œύ ’³ ??ΕΨ'?”ΟΛΈΫιΉo±Θξ™ ¬‰IΥυΛΈœύ’³ΖôΩΎΓΔΞ±ΞΔΞόΞΆΞΗΞδ©`ΛΊ Γω –ν°¥εΫιΉo±Θξ™ΒΘΒ±’n ?Ης±hΛΈΙζΟώΫΓΩΒ±Θξ™΅βΧεΏBΚœΜα(ΫιΉoΞΒ©`Ξ”ΞΙΩύ«ι³IάμΒΘΒ±²l Γώ Ώ\ ήû Οβ ‘S ΛΥ ιv ΛΙ Λκ œύ ’³ ?÷ς÷Έ“ΫΛΥœύ’³ ΓωΛΣΫϋΛ·ΛΈΨ·≤λ π?Οβ‘SΞΜΞσΞΩ©` Γώ ΞΛ Ξσ ΞΩ ©` ΞΆ ΞΟ Ξ» ΛΈ «ι àσ ΞΒ ΞΛ Ξ» ?“Ϋ·üôCιvΒ»ΛΥιvΛΙΛκ«ιàσ ΛΖΙΪ“φ…γ΅βΖ®»Υ»’±ΨάœΡξΨΪ…ώ“Ϋ―ßΜα ΛΖ“ΜΑψ…γ΅βΖ®»Υ»’±Ψ’J÷Σ÷ΔΞ±ΞΔ―ßΜα ΓΨhttp;//www.rounen.orgΓΩ ΓΨhttp;//www.chihoucare.org] ?ΗΏΐh’ΏΛΈΉΓΛόΛΛΛΥιvΛΙΛκ«ιàσ Ξλ©`Αψ…γ΅βΖ®»ΥΗΏΐh’ΏΉΓ’§Ίî΅βΓΨhttp://www.kouiuuzai.or.ipΓΩ ΛΖ’§άœΥυ?ΞΑΞκ©`ΞΉΞέ©`Ξύ»ΪΙζΞΆΞΟΞ»Ξο©`Ξ· ΓΨhttp://www.clc-japan.com/takurousyo_netΓΩ ΗΘλμ?±ΘΫΓ?“Ϋ·üΛΥιvΛΙΛκΨtΚœ«ιàσ ΛΖWAMNET(ΗΘλμ±ΘΫΓ“Ϋ·ü«ιàσΞΆΞΟΞ»)[http://www.wam.go.ip]I ΓΔ©e ΓσΨΪ…ώ’œΚΠ’Ώ±ΘΫΓΗΘλμ ÷éΛΘΚ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛ§»ΓΒΟΛ«Λ≠Λκ ÷éΛ ΓσΉ‘ΝΔ÷ß‘°“Ϋ·üΌMΘΚ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛ«Ά®‘ΚΛΙΛκΌM”ΟΛΈ€pν~ Γσ²ϊ≤Γ ÷Β±?’œΚΠ’ΏΡξΫπΘΚ»τΡξ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈΖΫΛΈ»ΥΛ§άϊ”ΟΛ«Λ≠Λκ÷ΤΕ» ΓσΥυΒΟΥΑΘ®’œΚΠ’ΏΩΊ≥ΐ?“Ϋ·üΌMΩΊ≥ΐ)ΓΔΉΓΟώΥΑΘ®’œΚΠ’ΏΩΊ≥ΐΘ©ΘΚΥΑΫπΛΈ€pν~ ΓΔ ΞΈ 23
- 5. IΛΔΛ ΛΩΛΈöί≥÷ΛΝΛρ ¬½ΛΛΛΤΛ·ΛλΛκ»ΥΛ§ΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ ΫιΉoΧερY ¬άΐΦ· Γω Γω P Ϋώ P c^ΓΔΓτΛΣΉΓΛόΛΛΛΈΒΊ”ρΛΈœύ’³ΖôΩΎΛρΞαΞβΛΖΛΤΛΣΛ≠ΛόΛΖΛγΛΠΓΘ Γω – «χ ν° ¥ε ΛΈ ΗΏ ΐh ΗΘ λμ ΒΘ Β± ’n Λœ T e l : ΛΔΛ ΛΩΛΈκOΛΥΛβΞ±ΞΔΞι©`Λ§ΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘΛΏΛσΛ ΓΔΛΔΛ ΛΩΛ»Ά§ΛΗΛηΛΠΛΥ Ωύ³ΚΛΖΓΔê‰ΛΏΓΔ≈≠ΛξΛδΤΘΛλΛρΗ–ΛΗΛ Λ§ΛιΛ§ΛσΛ–ΛΟΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘΛΫΛσΛ ΛΔΛ ΛΩΛΈ ΥΦΛΛΛρ¬½ΛΛΛΤΛ·ΛλΛκ»ΥΛœΓΔ“äΛόΛοΛΜΛ–ΛΩΛ·ΛΒΛσΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘΛ“ΛγΛΟΛ»ΛΙΛκΛ»…μΫϋΛ ”―»ΥΛδ÷Σ»ΥΛβΫιΉo’ΏΛΪΛβΛΖΛλΛόΛΜΛσΓΘ ΛΫΛΈΛέΛΪΫϋΥυΛΈ»ΥΓΔΞήΞιΞσΞΤΞΛΞΔΓΔNPOΓΔΉ‘÷ΈΜαΛΈ“έÜTΓΔ––’ΰ¬öÜTΓΔΟώ…ζ Έ·ÜTΛ Λ…Γ≠ΓΘ ΓωΒΊ”ρΑϋά®÷ß‘°ΞΜΞσΞΩ©`Λœ Te Θ° –«χν°¥ε…γΜαΗΘλμÖfΉhΜαΛœ Te ι΅ΛΫΓ≠θ†’³Ζô?Γώ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΥιvΛΙΛκœύ’³ΖôΩΎ Λ≥Λ≥ΛΥΫBΫιΛΙΛκΞ±ΞΔΞι©`ΛΈΫ‘ΛΒΛσΛœΓΔΉ‘Ζ÷ΛΈ…υΛρ¬½ΛΛΛΤΛβΛιΛΟΛΩΛ≥Λ»Λ§ öί≥÷ΛΝΛΈ’ϊάμΛΥΛ ΛξΓΔ¥ΈΛΈ?öiΛΊΛΈΛ≠ΛΟΛΪΛ±ΛΥΛ ΛΟΛΩΛ»ΛΛΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘΛΔΛ ΛΩΛΈ ΥΦΛΛΛρ¬½ΛΛΛΤΛ·ΛλΛκ»ΥΛ§ΓΔΛ≠ΛΟΛ»ΛΔΛ ΛΩΛΈΫϋΛ·ΛΥΛβΛΛΛκΛœΛΚΛ«ΛΙΓΘ Γ¥’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛ»Φ“ΉεΛΈΜαêέ÷Σ±h÷ß≤ΩΘ·Ξ±ΞΔΞι©`ΏBΟΥΛΈ’{•ΥΛΪΛιΓΒ IlΛΣΫϋΛ·ΛΈ?’J÷Σ÷ΔΦ≤ΜΦ“Ϋ·üΞΜΞσΞΩ©`ΓΙΛόΛΩΛœ?ΒΊ”ρΑϋά®÷ß‘°ΞΜΞσΞΩ©`ΓΙ …γΜαΗΘλμΖ®»Υ‘ΓοLΜαΫιΉo÷ßΛ®ΚœΛΛκä‘£œύ’³ “Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠ΙΎ03-5941-1038 ΓΨ‘¬ΓΪΡΨΘ®ΉΘ»’?ΡξΡ©Ρξ ΦΛρ≥ΐΛ·)ΓΩΓ¥10ïrΓΪ15ïrΓΒ IΙΪάΉtΝψΩêΨo?≈nξéκëiΡΩ’³Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Ζô0120-294-456 »τΡξ–‘’J÷Σ÷ΔΞ≥©`ΞκΞΜΞσΞΩ©`ΓΨ‘¬ΓΪΆΝΓΩΓ¥10ïrΓΪ15ïrΓΒΓ≠Ζô0800-100-2707 »τΡξ’J÷Σ÷ΔΦ“ΉεΜα?≤ –«ΛΈΜακä‘£œύ’³Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠ΙΎ03?5919?4185 ΓΨ‘¬?Υ°?ΫπΓΩΓ¥10ïr30Ζ÷ΓΪ17ïrΓΒ JΓΨΓΙ »τΡξ’J÷Σ÷ΔΞΒΞί©`Ξ»ΞΜΞσΞΩ©`Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠ΙΎ03?5919?4186 ΓΨ‘¬?Υ°?ΫπΓΩΓ¥10ïrΓΪ17ïrΓΒΓ· Θ– κÖ Γώ≈≈≥ΊΛΥιvΛΙΛκœύ’³ »’±ΨΞ≥ΞσΞΝΞΆΞσΞΙÖfΜα≈≈≥ΊΛΈάßΛξΛ¥Λ»110Ζ§Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Ζô050-3786-1145 ΓΨ»’?ΡΨΓΩΓ¥10ïrΓΪ16ïrΓΒI »τΡξ–‘’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈΤόΛ»ΡΚΛιΛΖΛΤΛΛ ΛόΛΙΓΘΞ«ΞΛΞΒ©`Ξ”ΞΙΛΈάϊ”ΟΛρΩΦΛ® ΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΛ§ΓΔΛ…Λ≥ΛβΗΏΐhΛΈάϊ”Ο’Ώ Λ–ΛΪΛξΛ«––Λ≠ΛΩΛ§ΛξΛόΛΜΛσΓΘœΠΖΫ ΛΥΛ ΛκΛ»ΝœάμΛρΉςΛΟΛΤΛ·ΛλΛηΛΠΛ» ΛΖΛόΛΙΛ§ΓΔΆΨ÷–Λ« ÷μ‰Λ§ΛοΛΪΛιΛ Λ·Λ ΛκΛΈΛΪΆξ≥…ΛΖΛόΛΜΛσΓΘΛΫΛΈΛ· ΛΜΛοΛΩΛΖΛ§ ÷¹ΜΛΣΛΠΛ»ΛΙΛκΛ»ΛΛΛδ Λ§ Λξ Λό ΛΙ ΓΘ œ» »’ Λœ ¥Ε οà Τς ΛΈ ÷– ΛΥ ΞΤ ΞΘ ΞΟ ΞΖ Ξε Λ» Υ° Λ§ »κ ΛΟ ΛΤ ΛΛ Λκ ΛΈ Λρ “äΛΤΤϋΛ±ΛΤΛ≠ΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘΉ”Λ…ΛβΛΩΛΝ ΛœΏhΛ·ΛΥΉΓΛσΛ«ΛΛΛκΛΈΛ«ΓΔΛΛΛΝΛΛ ΛΝΡΗ”HΛΈΉ¥ëBΛρ÷ΣΛιΛΜΛκΛΈΛβΛ…ΛΠ ΛΪ Λ» ΥΦ ΛΛ ‘î ΛΖ ΛΛ Λ≥ Λ» Λœ ¹Μ Λ® ΛΤ ΛΛ Λό ΛΜΛσΓΘΤόΛ§ΛάΛσΛάΛσâδΛοΛΟΛΤΛΛΛ· ΛΈΛ§±·ΛΖΛ·ΛΤΛΖΛΪΛΩΛΔΛξΛόΛΜΛσΓΘ Γώ © ‘O ΛΥ ιv ΛΙ Λκ œύ ’³ ?»ΪΙζ”–Νœάœ»ΥΞέ©`ΞύÖfΜαΓ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠ΙΎ03-3272-3781Θ®¥ζ±μΓΖ Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠ΙΎ03-3548-1077Θ®»κΨ”œύ’³ΓΖ ΓΨ‘¬ΓΪΫπΘ®ΉΘ»’ΓΔΡξΡ©Ρξ ΦΛρ≥ΐΛ·)ΓΩΓ¥10ïrΓΪ17ïrΓΒ Γώ ΗΏ ΐh ’Ώ ΛΊ ΛΈ ≈Α ¥ΐ ΛΥ ιv ΛΙ Λκ œύ ’³ Γω –«χν°¥ε?ΗΏΐhΗΘλμΒΘΒ±ΓΙΛόΛΩΛœΛΣΫϋΛ·ΛΈΓΗΒΊ”ρΑϋά®÷ß‘°ΞΜΞσΞΩ©`_ΘΚ Γώ≥…Ρξαα“ä÷ΤΕ»ΛΥιvΛΙΛκœύ’³ ¬Ε:ΧΟ‘¨±ΨέΆΉo ΩΏBΚœΜα)[http://www.nichibenrΓ≠Ϋ≠ 22
- 6. ΓΚΞ«ΞΛΞΒ©`Ξ”ΞΙΛΈ άϊ”ΟΛρΕœΛιΛλΛόΛΖΛΩΓΜ Ο½―ΣΙή–‘’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈΝxΡΗΛρΫιΉoΛΙΛκ50¥ζ≈°–‘ Ο½―ΣΙή–‘’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈΝxΡΗΛΈΫιΉoΛρ ΛΖΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘΝxΡΗΛœöίΛΥ»κΛιΛ ΛΛ Λ≥Λ»Λ§ΛΔΛκΛ»≈≠χQΛΟΛΩΛΝΠΛρΛ’ ΛκΛΟΛΩΛξΛΙΛκΛΈΛ«ΓΔΞ«ΞΛΞΒ©`Ξ”ΞΙ ΛΈάϊ”ΟΛρΕœΛιΛλΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘœ»»’ΛβΛέ ΛΪΛΈάϊ”Ο’ΏΛΒΛσΛρΏΒΛΛΛΤΛΖΛόΛΟΛΩ ΛηΛΠΛ«ΛΙΓΘöi––Λ§≤ΜΑ≤Ε®Λ ΛΈΛΥΉ‘ “ôΛ§Λ Λ·ΓΔΛΡΛΛöiΛ≥ΛΠΛ»ΛΖΛΤήûΒΙ ΛΈΛΣΛΫΛλΛ§ΛΔΛκΛ≥Λ»ΛβΨ¥ΏhΛΒΛλΛκ άμ”…ΛΈΛηΛΠΛ«ΛΙΓΘΞ±ΞΔΞόΞΆΞΗΞδ©` ΛΒΛσΛΥœύ’³ΛΖΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΛ§ΓΗΛΖΛΪΛΩ Λ ΛΛΛΆΛ®ΓΙΛ»―‘ΛοΛλΛκΛάΛ±Λ«Λ…ΛΠ ΛΖΛΤΛΛΛΛΛΪΛοΛΪΛξΛόΛΜΛσΓΘΦ“ΉεΛά Λ±Λ«ΛœΫιΉoΛΖΛ≠ΛλΛ ΛΛΛΪΛιΞΒ©`Ξ” ΞΙ Λρ άϊ ”Ο ΛΖ ΛΩ ΛΛ ΛΈ ΛΥ ΓΘ Λ≥ Λλ Λό Λ« Λβ ΦόΙΟΛΈΗπΧΌΛ§ΛΔΛξΓΔΛβΛΠΝxΡΗΛΈνÜ Λβ“äΛΩΛ·Λ ΛΛöί≥÷ΛΝΛ«ΛΙΓΘ ?ΫιΉoΛΈΛΩΛαΛΥ Υ ¬Λρ¥«ΛαΛόΛΖΛΩ ΞΔΞκΞΡΞœΞΛΞό©`ΛΈΗΗΛ»ΡΩΛΈêôΛΛΡΗΛΈ¹I”HΛρ ΫιΉoΛΙΛκΕά…μΛΈ40¥ζΡ–'–‘ 82örΛΈΗΗΓΔ80örΛΈΡΗΛ»Ά§Ψ”ΛΖ ΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘΗΗΛœ3Ρξ«ΑΛΪΛιΞΔΞκΞΡ ΞœΞΛΞό©`ΛΈ÷ΔΉ¥Λ§≥ωΛΤΓΔ“Μ»’÷–Ά§ ΛΗΛ≥Λ»Λρ―‘ΛΟΛΩΛξ¨ΛΛΆΛΩΛξΛΖΛΤΛΛ ΛόΛΙΓΘΚ°Λ·Λ ΛΟΛΤΛΪΛιΛœΞ»ΞΛΞλΛΈ ßîΓΛβâàΛ®ΛΤΛ≠ΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘ“Σ÷ß‘°1 Λ«ΏL1ΜΊΞ«ΞΛΞΒ©`Ξ”ΞΙΛράϊ”ΟΛΖΛΤ ΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘΡΗΛœ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛ«ΛœΛΔΛξΛόΛΜ ΛσΛ§ΡΩΛ§êôΛΛΛΈΛ«ΓΔΦ“ ¬Λ»ΫιΉo?Λό ΛοΛΩΛΖΛ§ΛΜΛΕΛκΛρΒΟΛΚΓΔΉρΡξ Υ ¬ Λρ¥«ΛαΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘΉ‘Ζ÷ΛΈ”HΛ ΛΈΛάΛΪ Λι ά ‘£ Λρ ΛΙ Λκ ΛΈ Λœ ΛΔ ΛΩ Λξ Λό Λ® Λ» ΥΦΛΟΛΤΛΛΛόΛΖΛΩΛ§ΓΔ…γΜαΛ»ΛΈΛΡΛ Λ§ΛξΛ§Λ Λ·Λ ΛΟΛΩΛηΛΠΛ öίΛ§ΛΖΛΤΓΔ Ι¬ΝΔΗ–ΓΔ·EΆβΗ–ΛρΗ–ΛΗΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ Λ≥ΛΈœ»ΫU€gΒΡΛΥΛβ≤ΜΑ≤Λ«ΛΙΓΘ ΥΤ 1 ΓΘΓώôCœ”Λ§êôΛΛΛ»Λ≠Γ≠ …Ό ?ΛμΛΛΛμΛ»―‘ΛΟΛΤΛβΞάΞαΛ ΛΈ Λ«ΓΔΡφΛΥΏ`ΛΠ≤ΩΈίΛΥΧ”Λ≤ΛΤΖ≈ΛΟΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ…ΌΛΖïr ιgΛ§ΛΩΛΟΛΤΛΪΛιΓΔΓΗΛΣω†ν^ ≥ΛΌΛκΘΩΓΙΛ»ΛΪΓΗΛΣ≤η ΛΈΛύΘΩΓΙΛ»œ≤Λ”ΛΫΛΠΛ Λ≥Λ»Λ«…υΛρΛΪΛ±ΛκΛ»ΛΒΛΟΛ≠ ΛΈΛ≥Λ»ΛœΛΙΛΟΛΪΛξΆϋΛλΛΤΛΛΛκΛΈΛ«ΓΔôCœ”ΛηΛ·Ώ^Λ¥ ΛΖΛΤΛ·ΛλΛόΛΙΓΘ ¥γΈ`»AΥ¬ Ξί©`ΞΩΞ÷ΞκΞ»ΞΛΞλΛρ ΙΛΟΛΤΛΛΛκΛ±Λ…ΓΔ Λ… ΛΠ ΛΖ ΛΤ Λβ Άβ ΛΥ ¬© Λλ ΛΤ ¦A Λλ ΛΤ ΛΖ Λό ΛΠ ΛΈ Λ« ΓΔ »° ΛΈ ΛΣ ΛΖ ΛΟ Λ≥ Ξό ΞΟ Ξ» Λρ œ¬ ΛΥ Ζσ ΛΛ ΛΤ ΓΔ ¦A Λλ ΛΩ Λι ΛΙ ΛΑ ΛΥ £Έ ΛΤ ΛΤ £Ώ ≥ΐ Λ§ ‰SΛ ΛηΛΠΛΥΛΖΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ Γΐ Ρρ≥τΛ Λ…ΛΥΓΗΟ®ΛΈ…ΑΘ®ΦàΛΈΛβΛΈ)ΓΙΛρ »κΛλΛκΛ»ΓΔ≥τΛΛΛ§Λ»ΛλΛόΛΙΓΘ Γΐ “Ι ΛΈ Ξ» ΞΛ Ξλ ΛΈ ΛΩ Λα ΓΔ ≤Ω Έί ΛΪ Λι Ξ» ΞΛ Ξλ ΛόΛ«ΛΈιgΛΥ100É“ΞΖΞγΞΟΞΉΛ«≥Θ“ΙΒΤ ΛΈ Λη ΛΠ Λ Λβ ΛΈ Λρ ΐ ²Ä ΌI ΛΟ ΛΤ ΓΔ ¹K ΛΌ ΛΤ ’T¨ßΛΖΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘ Θ°ΓώΌΫ²ÄΛΈΛ»Λ≠ΛΈΛΩΛαΛΈΞΔΞΟΞΉΞξΞ±Ήςëι Γΐ öίΛΥ»κΛΟΛΤΛΛΛκ―σΖΰΛΥΓΔΟϊ«ΑΛρΛΪΛΩΛ…ΛΟΛΩ ΞΔΞΟΞΉΞξΞ±ΛρΩpΛΛΛΡΛ±ΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ ΛΛ ΛΩ Λκ Υυ ΛΥ Ξα Ξβ Λρ ΌN ΛΟ ΛΤ ΛΣ Λ≠ Λό ΛΙ Εΰ ≥θΤΎΓΪ÷–ΤΎΛΈ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈΛ»Λ≠ΛœΓΔΡΩΛΈ «ΑΛΥΛΔΛκ«ιàσΛœ’JΉRΛ«Λ≠ΛκΛΈΛ«ΓΔΞα ΞβΛΥΚΈΛ«ΛβïχΛΛΛΤΌNΛκΛ Λ…ΛΖΛΤΓΔ≤Μ Α≤ΛδΜ묓ΛρΖάΛΛΛ«ΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ ."θéΓ≠ΞΈΞ… κyΙγ’I³κ/Ξ’ΞΖΝςΛΖΛΤΛΣΛ≠ΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘΚΈΛ»Λ Λ·¬³ΛΛΛΤΛΛΛκΓΔ “äΛΤΛΛΛκΛηΛΠΛ«ΓΔΑ≤–ΡΛΖΛΤκxΛλΛκΛ≥Λ»Λ§ Λ«Λ≠ΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘ ZΞγ ?¨O?Λ“¨OΛΣ÷ζΛ±ξ† Γΐ kΓΔ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈΉφΗΗΡΗΛΥ¨ùΛΖ
- 7. ΓΔ Λ ΛκΛέΛ…ΘΓ’J÷Σ÷ΔΫιΉoΛΈΛ“Λ»ΙΛΖρ ΫιΉo’ΏΛΈΜαΛΈΓΗΛ≥ΛσΛ Λ»Λ≠ΓΔΛ≥ΛσΛ Λ’ΛΠΛΥΛΖΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙ Λ»ΛΛΛΠ‘£ΛΪΛι ΔέΓώ≥·ΓΔΛ ΛΪΛ ΛΪΤπΛ≠ΛΤΛ·ΛλΛ ΛΛ?? Γΐ ≥·ΓΔΤπΛ≥ΛΙΛΩΛαΛΥΞ≥©`Ξ“ Λρ€ωΛλΛόΛΙΓΘ³ωΛΛΛ«ΛΡΛι ΤπΛ≠ΛΤΛ·ΛκΛ≥Λ»ΛβΓΘ ΔΎΓώΞ«ΞΛΞΒ©`Ξ”ΞΙΛρΛΛΛδΛ§ΛκΓ≠ Γΐ Φ“ΉεΛΈνÜΛρ“äΛκΛ»ΓΗΛΛΛδΛάΓΙΛ»―‘ΛΟΛΤ≥ω ΛΪ Λ± ΛΤ Λ· Λλ Λ ΛΛ ΛΈ Λ« ΓΔ Ϋι Ήo ±Θ ξ™ Λ« ΞΊ Ξκ Ξ―©`ΛΒΛσΛΥά¥ΛΤΛβΛιΛΟΛΤΞ«ΞΛΞΒ©`Ξ”ΞΙΛΈ ΥΆΛξ≥ωΛΖΛ»€ ²δΛρΛΣνäΛΛΛΖΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘΥϊ »ΥΛΈ«ΑΛ«ΛœΛΖΛΟΛΪΛξΛΙΛκΛΈΛ«ΓΔΞΊΞκΞ―©` ΛΒΛσΛάΛ»ΛΛΛδΛ§ΛιΛΚΛΥΞΥΞ≥ΞΥΞ≥ΛΖΛΤΞ«ΞΛ ΞΒ©`Ξ”ΞΙΛΥ––ΛΟΛΤΛ·ΛλΛόΛΙΓΘ Γΐ Ξ«ΞΛΞΒ©`Ξ”ΞΙΛΈ¬öÜTΛΈ»ΥΛ»ΞΥΞ≥ΞΥΞ≥νÜΛ« Ξ‘©`ΞΙΛΖΛΩ–¥’φΛρΛΛΛΟΛΖΛγΛΥ¥ιΛΟΛΤΛβΛι ΛΛΓΔ––Λ·ΛΈΛρ€iΛΟΛΤΛΛΛκΛ»Λ≠ΛœΓΔ–¥’φΛρ ≥ωΛΖΛΤΓΗΛ≥ΛΈ»ΥΛΈΛ»Λ≥ΛμΛΥΏ[Λ”ΛΥΛΛΛ·Λσ ΛάΛηΓΙΛ»―‘ΛΠΛ»ΓΔΞΥΞ≥ΞΥΞ≥ΛΖΛΤΛΛΛκνÜΛρ ΛΏΛΤΓΗΛΔΛΔΛ≥ΛΈ»ΥΛΈΛ»Λ≥ΛμΛΆΓΙΛ»ôCœ”Λη Λ·ΛΣ”≠Λ®ΛΈή΅ΛΥ¹\ΛΟΛΤΛ·ΛλΛόΛΙΓΘ 20 Θ°Γώ≤Γ‘ΚΛΈ ή‘\ΛρΛΛΛδΛ§ΛκΓ≠ Γΐ ?ΛοΛΩΛΖΛΈΧε’{Λ§êôΛΛΛΈΛ«½ •ΥΛΥΛΛΛ≠ΛΩ ΛΛΛ±Λ…–ΡΦöΛΛΛΈΛ«ΛΣΡΗΛΒΛσΛΡΛΛΛΤΛ≠ΛΤΛ· ΛλΛ ΛΛΘΩΓΙΛ»’TΛΟΛΤΓΔΛδΛΟΛ» ή‘\Λ§Λ«Λ≠ ΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘνmΛξΛΥΛΙΛκΛηΛΠΛ …υΛΪΛ±ΛρΛΙΛκ Λ»ôCœ”Λ§ΛΛΛΛΛΈΛ«ΛδΛξΛδΛΙΛΛΛ«ΛΙΓΘ Γΐ ή‘\ΛΈéΔΛξΛΥΛœ±ΊΛΚΛΣΛΛΛΖΛΛΞιΞσΞΝΛΥ–– Λ·ΛηΛΠΛΥΛΖΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘΓ®≤Γ‘ΚΛΥ––Λ·'ΓδΛΪ ΛιΓ®ΛΣΛΛΛΖΛΛΈοΛ§ ≥ΛΌΛιΛλΛκΓ®Λ»ΓΔ‰SΛΖ ΛΛ Λ≥ Λ» Λ§ ΛΔ Λκ »’ Λ» ΛΛ ΛΠ ΞΛ Ξα ©` ΞΗ Λρ Λβ ΛΟ ΛΤ ΛβΛιΛΠΛηΛΠΛΥΛΖΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ ΔΌΓ≠#Γ≠ΛηΛ·¬³Λ·Λ»ΓΔïr”΄ΛΈιLα‰Λ»ΕΧα‰Λρ’iΛΏΏ`Λ® ΛΤΛΛΛΩΛΈΛ«?ïr”΄ΛρâδΛ®ΛΩΛιΛΣΛΒΛόΛξΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘ ΔίΓώΆβ≥ωΛρΛΛΛδΛ§ΛκΓ≠ Γΐ ûsfΩê³PΩΐ ΓΚΈοΛρâ≤ΛΒΛλΛκΛΈΛ«άßΛΟΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΘΜ ΗΗ ΛΈ Ϋι Ήo Λρ ΛΖ ΛΤ ΛΛ Λό ΛΙ ΓΘ Ήν Ϋϋ ΛΈ άßΛξΛ¥Λ»ΛœΓΔκäΜ·―uΤΖΛρΛΔΛλΛ≥Λλ â≤ΛΒΛλΛκΛ≥Λ»Λ«≥ωΌMΛ§ΛΩΛΛΛΊΛσΛ« ΛΙ ΓΘ –¬ ΛΖ ΛΛ ΞΤ Ξλ Ξ” Λρ ΌI ΛΟ ΛΩ Λι ΓΔ Έτ ΛΈΛβΛΈΛ»Ώ`ΛΠΛΈΛ« ΙΛΛΖΫΛ§ΛοΛΪΛι ΛΙ ΓΔ ΛΔ Λλ Λ≥ Λλ ¥Ξ ΛΟ ΛΤ â≤ ΛΖ Λό ΛΖ ΛΩ ΓΘ Λό ΛΩ –¬ ΛΖ ΛΛ Λβ ΛΈ Λρ ΌI ΛΟ ΛΤ Λβ â≤ ΛΙ ΛΈ Λ« ΓΔ ΞΆ ΞΟ Ξ» Λ« Ι≈ ΛΛ Έτ ΛΈ –Ά ΛΈ ΞΤ Ξλ Ξ” Λρ Όè »κ ΛΖ ΛΤ ¨ù èξ ΛΖ Λό ΛΖ ΛΩ ΓΘ ¥Έ ΛΥ …» ΗΗ”HΛΈΫιΉoΛρΛΙΛκ50¥ζΡ––‘ οLôCΓΔΛ…ΛΠΛβΛ·ΛκΛ·Λκ”πΛ§ΜΊΛΟΛΤ ΛΛΛκΛΈΛ§öίΛΥΛ ΛκΛΈΛΪΓΔΞ≥©`Ξ…ΛΥ –¬ ¬³ Φà Λρ ΛΑ Λκ ΛΑ Λκ éÜ Λ≠ ΛΡ Λ± ΛΤ ΞΖΞγ©`Ξ»ΛΖΛΤ ΙΛ®Λ Λ·Λ ΛξΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘ ΛΫΛΈ¥ΈΛœΞ·©`Ξι©`ΓΔΞξΞβΞ≥ΞσΛΈ Ι ΛΛΖΫΛ§ΛοΛΪΛιΛΚ÷ΙΛαΛιΛλΛ ΛΛΛΈΛ«ΓΔ ΑτΛρΆ®οLΩΎΛΥ≤νΛΖόzΛσΛ«Ξ§ΞΝΞψΞ§ ΞΝΞδΛδΛκΛΈΛ«â≤ΛλΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘ ΓΚΛΜΛαΛΤΛΆΛ°ΛιΛΛΛΈ―‘»~Λ«ΛβΛΔΛλI ³eΨ”ΛάΛ±Λ…ΓΔ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈΡΗ”HΛρ“Μ»ΥΛ«ΫιΉoΛΙΛκ 50¥ζ≈°–‘ ΗΗ Λ§ Άω Λ· Λ ΛΟ ΛΤ ΛΪ Λι ΡΗ Λœ Εά Λξ ΡΚ ΛιΛΖΛρΛΖΛΤΛΛΛόΛΖΛΩΛ§ΓΔΑκΡξΛέΛ… «ΑΛΪΛιε¹ΛρΫΙΛ§ΛΖΛΩΛξΓΔΛΩΛ”ΛΩΛ” Ίî≤ΦΛρΛ Λ·ΛΙΛηΛΠΛΥΛ ΛΟΛΩΛΈΛ«ΓΔ Ϋϋ Υυ ΛΈ ΛΪ ΛΪ Λξ ΛΡ Λ± “Ϋ Λρ ή ‘\ ΛΖ ΛΩ Λ» Λ≥Λμ?’J÷Σ÷ΔΛάΛΆ?Λ»―‘ΛοΛλΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘ Λο Λ§ Φ“ Λœ ΡΗ ΛΈ Φ“ ΛΪ Λι ή΅ Λ« 2 0 Ζ÷ Λέ Λ… ΛΈ Ψύ κx Λ ΛΈ Λ« 1 »’ ΛΣ Λ≠ ΛΥ Λη ΛΠ ΛΙ Λρ “ä ΛΥ –– ΛΟ ΛΤ ΛΛ Λό ΛΙ Λ§ ΓΔ Ϋϋ Λ· ΛΥ ΉΓΛύΛοΛΩΛΖΛΈ–÷Ζρ΄DΛ§ΛόΛΟΛΩΛ·÷Σ ΛιΛσνÜΛΖΛΤΛΛΛκΛΈΛ«ΗΙΛ§ΝΔΛΝΛόΛΙΓΘ ΛΔΛ»Λ»ΛξœΔΉ”ΛάΛΪΛιΛ» ÷ιgΛβΛΣΫπ ΛβΛΪΛ±ΛΤ”ΐΛΤΛΤΛβΛιΛΟΛΩΛœΛΚΛ ΛΈ ΛΥΓΘΛοΛΩΛΖΛ§¨gΦ“ΛΥ≥ω»κΛξΛΙΛκΛ≥ Λ» Λρ Ζρ Λβ Ζρ ΛΈ ¹I ”H Λβ Λη Λ· ΥΦ ΛΟ ΛΤ Λ ΛΛΛΈΛ«Φγ…μΛ§œΝΛ·–ΝΛΛΛ«ΛΙΓΘ
- 8. ΛβΛ Λ·Ι¬ΝΔΛΖΛΤΛΛΛκ…œ ΞύΛΥ»κΨ”ΛΖΛΤΛΛΛκΝxΡΗΛΈΞ±ΞΔΛρ ΝxΡΗΛœΓΔΆΐœκΛδ“Ι÷–ΛΥΤπΛ≠ΛκΛ Λ… ΞΔ Ξκ ΞΡ Ξœ ΞΛ Ξό ©` –Ά ’J ÷Σ ÷Δ Λ« ΓΔ §F ‘ΎΛœ ©‘OΛΥ»κΥυΛΖΛΩΛΩΛαΓΔΛ»Λ≠Λ… Λ≠‘LÜ•ΛΖΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘΆβ≤ΩΛΈ»ΥΛρœ” ΛΛΓΔΞΊΞκΞ―©`Λβ ήΛ±ΛΡΛ±Λ ΛΛΛ≥Λ» Λ§ΛΔΛξΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘΖρΛœΡΩΛ§êôΛ·Ώ\ήû Λ«Λ≠Λ Λ·Λ ΛξΓΔΛοΛΩΛΖΉ‘…μΛβΧε’{ Λρ±άΛΖ»πœΔΓΔΞ―ΞΥΞΟΞ·ξ΅Λ§ΛΛΛρΜΦ ΛΛΆ®‘ΚΛδ»κ‘ΚΛρΛΖΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘΫϋΥυ 15ΡξΛΖΛΤΛΛΛκ60¥ζ≈°–‘ ΛΥ ”― Λά ΛΝ Λβ Λ Λ· Μα ‘£ Λβ …Ό Λ ΛΛ ΛΩ Λα Ι¬ΝΔΗ–ΛρΗ–ΛΗΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ ΝxΡΗΛΈΓΗΥάΛΧΓΙΛ»ΛΛΛΠ―‘»~Λ§ν^ ΛΪΛικxΛλΛΚΓΔΨΪ…ώΒΡΛΥΤΘΛλΓΔΛ≥Λλ ΛΪ Λι œ» Λβ Λέ ΛΪ ΛΥ Λά Λλ Λβ ΛΏ ΛΤ Λ· Λλ Λκ »Υ Λ§ ΛΛ Λ ΛΛ ΛΈ Λ« άß ΛΟ ΛΤ ΛΛ Λό ΛΙ ΓΘ Ϋι ΉoΛδΧε’{ΛΥ≤ΜΑ≤Λρ±ßΛ®ΛΤΛΛΛκ»ΥΛ§ Éûœ»ΒΡΛΥ»κΛλΛκΗΏΐh’ΏΉΓ’§Λδ ©‘O Λ§”ϊΛΖΛΛΛ«ΛΙΓΘ ΓΚöίΛ§–ίΛόΛκ»’ΛœΛ ΛΛΓΜ Ή””ΐΛΤΛ»¹I”HΛΈΞ±ΞΔΛρΛΖΛΤΛΛΛκ40¥ζ≈°–‘ Χε’{Λρ±άΛΖ“ΣΫιΉo2Λ»Λ ΛΟΛΩ¨gΗΗ Λ»ΓΔ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ’ΉΚρΛ§≥ωΛΤΛ≠ΛΩ¨gΡΗΛρ –Ρ≈δΛΖΓΔΕΦ –≤ΩΛΪΛιόr¥ε≤ΩΛΊΏL1ΓΪ 2ΜΊΆ®ΛΟΛΤΞ±ΞΔΛΖΓΔ¹I”HΛΈΆ®‘ΚΛβΥΆ ”≠ΛΖΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ¥ΚΛ≥ΛμΛΪΛιöΑΏLΆ®ΛΟ ΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΛ§ΓΔΥΦΛΠΛηΛΠΛΥΛœ––Λ±Λ ΛΛ Λ≥Λ»ΛΪΛιΓΔΜπΛœ¥σ’…ΖρΛΪΓΔΞ§ΞΙΛœΘΩ Υ°ΒάΛœ≥ωΛΖΛΟΛ―Λ ΛΖΛΥΛ ΛΟΛΤΛΛΛ ΛΛΛΪΛ Λ…ΓΔ“‘«ΑΛΥΛœΩΦΛ®ΛιΛλΛ ΛΛΛ· ΛιΛΛ–Ρ≈δΛΖΓΔöίΛ§–ίΛόΛκ»’Λ§ΛΔΛξΛό ΛΜΛσΓΘ¨gΗΗΛ»Ά§ïrΛΥ¨gΡΗΛΈ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛ§ ΏMΛΏΓΔκä‘£Λ«ΛΈΜα‘£Λ§Ά®ΛΗΛΚΓΔ§F‘Ύ ΛœΛ≥ΛόΛ¥ΛόΛ»ΛΖΛΩΏBΫjΛœΞ’ΞΓΞΟΞ·ΞΙ Λ«¹ΜΛ®ΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ ÷ήόxΛΥΛΔΛόΛξΦ“Λ§Λ ΛΛΛ»Λ≥ΛμΛ«ΡΚ ΛιΛΙΛΈΛœΛΩΛΛΛΊΛσΛ ΛΈΛ«ΓΔ –Ϋ÷ΛΥ≥ω ΛκΛΪΉ‘Ζ÷ΛΈΛΫΛ–ΛΊά¥ΛΤΛœΘΩΛ»‘£ΛΖ ΛΤΛβΓΔ¹I”HΛœΓΗ…ζΛόΛλ”ΐΛΟΛΩΛ≥ΛΈΦ“ Λ§ΛΛΛΛΓΙΛ» ήΛ±»κΛλΛηΛΠΛ»ΛΖΛόΛΜ ΛσΓΘΛ≥ΛΈΛ≥Λ»Λ§¥σΛ≠Λ ΞΙΞ»ΞλΞΙΛ» Λ ΛΟΛΤΓΗΛ ΛΦΛοΛΩΛΖΛ§Λ≥Λ≥ΛόΛ«ΛΖΛ Λ·ΛΤΛœΛ ΛιΛ ΛΛΛΈΛΪΓΙΛ»ΥΦΛΟΛΤΛΖΛό ΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘΉ‘Ζ÷Ή‘…μΛΈ…ζΜνΛβ¥σ«–Λά ΛΖΓΔΛόΛά–Γ―ß…ζΛΈΉ”Λ…ΛβΛ§ΛΛΛκΛ≥Λ» ΛΪΛιΓΔ≤¥ΛξΛ≥ΛσΛ«ΛΈΫιΉoΛœΛέΛ»ΛσΛ… Λ«Λ≠Λ ΛΛΛΈΛ«ΛΙΓΘ Ψό “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ “Μ ΓΔ rΨœ’J÷Σ÷ΔΫιΉoΛΈΛ≥Λ≥ΛμΛ§ΛόΛ®Γ·1ίXΛΛΛ»Λ≠ΛΈΛέΛΠΛ§ΛΩΛΛΛΊΛσΓΘ ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈΫιΉoΛ«ΓΔΫιΉo’ΏΛ§ΨΪ…ώΒΡΛΥΛβΛΡΛ»ΛβΛΩΛΛΛΊΛσΛ ïrΤΎΛœ≥θΤΎΛΪΛι÷–ΤΎΛ« ΛΙΓΘΛόΛάΛόΛάΛ«Λ≠ΛκΛ≥Λ»Λ§ΕύΛΛΛ»Λ≠ΛΈΛέΛΠΛ§’ώΛξΛόΛοΛΒΛλΛΤΛΖΛόΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘΏM––ΛΙ ΛκΛ» ÷ΛœΛΪΛΪΛξΛόΛΙΛ§ιvΛοΛξΛδΛΙΛ·Λ ΛΟΛΤΛ≠ΛόΛΙΓΘ 2ΡΩœ»ΛΈΛ≥Λ»ΛΥ’ώΛξΛόΛοΛΒΛλΛ ΛΛΓΘ ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛœïrιgΛΈΫUΏ^Λ»Λ»ΛβΛΥΏM––ΛΖΛΤΛΛΛ≠ΛόΛΙΓΘΫώάßΛΟΛΤΛΛΛκΛ≥Λ»ΛβïrιgΛ§ ΛΩΛΡΛ»ΛηΛΠΛΙΛ§âδΛοΛΟΛΤΛ≠ΛόΛΙΛΈΛ«ΓΔΡΩœ»ΛΈΛ≥Λ»ΛΥ’ώΛξΛόΛοΛΒΛλΛ ΛΛΛ«ΓΔ3ΛΪ ‘¬ΓΔΑκΡξΛ»…ΌΛΖιLΛΛïrιgΛ«ΛηΛΠΛΙΛΈâδΜ·Λρ“äΛόΛΖΛγΛΠΓΘ Γ·3ΓΗΛ…ΛΠΛΖΛΤΛ ΛΈΛΪΛ ?Λ»ΩΦΛ®ΛηΛΠΓΘ Θϋ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛΈ––³”ΛΥΛœ?±ΊΛΚΛΫΛΈ»ΥΛ ΛξΛΈάμ”…Λ§ΛΔΛξΛόΛΙ?ΓΗΛΔΛλ?ΓΙΛ»ΥΦ ΘϋΛΠΛ≥Λ»Λ§ΛΔΛΟΛΩΛιΓΗΛ…ΛΠΛΖΛΤΛ ΛΈΛΪΛ ?Λ»ΩΦΛ®ΛΤΛΏΛόΛΖΛγΛΠ?Ώ^»ΞΛΈΫUρYΛ Λ… ΘϋΛΫΛΈ»ΥΛΈ…ζΛ≠ΛΤΛ≠ΛΩ»Υ…ζΛΥΞ“ΞσΞ»Λ§“äΛΡΛΪΛκΛ«ΛΖΛγΛΠΓΘ Γ·4ΫώΛρ‰SΛΖΛύΛ≥Λ»Λρ–ΡΛ§Λ±ΛηΛΠΓΘ Θ§ΥaΛ«’J÷Σ÷ΔΛρ÷ΈΛΙΛ≥Λ»ΛœΛ«Λ≠ΛόΛΜΛσΓΘΛόΛΚΛœΓ®Λ…ΛΈΛηΛΠΛΥ…ζΜνΛΙΛκΛΈΛΪΓ±ΓΑΛ… Γ·ΛΈΛηΛΠΛΥΫιΉoΛΙΛκΛΈΛΪΓ®Λ§¥σ«–Λ«ΛΙΓΘΫώΛρ‰SΛΖΛύΛ≥Λ»Λρ–ΡΛ§Λ±ΛόΛΖΛγΛΠΓΘ‰SΛΖ Γ·ΛΛïrιgΛ§ΕύΛ·Λ ΛκΛ»Ή‘»ΜΛΥ÷ΔΉ¥Λ§¬δΛΝΉ≈ΛΛΛΤΛ·ΛκΛ«ΛΖΛγΛΠΓΘ Γ·5…œ ÷ΛΥ‘£ΛρΚœΛοΛΜΛηΛΠΓΘ Θ§ ’J ÷Σ ÷Δ ΛΈ »Υ Λ» ΛΈ ¨ù èξ Λœ ΛΠ ΛΫ Λβ ΖΫ ±ψ ΓΘ ‘£ ΛΈ ΡΎ »ί Λ§ ¬ ¨g Λ» Ώ` ΛΟ ΛΤ ΛΛ ΛΤ Λβ ΛΔ Λό Λξ öί ΛΥΛΖΛ ΛΛΛ«öί≥÷ΛΝΛΥΦΡΛξΧμΛΟΛΤΛΗΛγΛΠΛΚΛΥ‘£ΛρΚœΛοΛΜΛΤΛΔΛ≤ΛόΛΖΛγΛΠΓΘ’ΐΛΖΛΛ Λ≥Λ»Λρ¹ΜΛ®ΛκΛ≥Λ»Λ«ΡφΛΥν^ΛρΜ묓ΛΒΛΜΛΤΛΖΛόΛΠΛ≥Λ»ΛβΛΔΛξΛόΛΙΓΘ Γ·6??Ξ”?άϊ”ΟΛœ‘γΛαΛΥΛœΛΗΛαΛηΛΠΓΘ ΘϋΛ«Λ≠ΛκΛάΛ±‘γΛ·ΛΪΛιΞ«ΞΛΞΒ©`Ξ”ΞΙΛ Λ…Λράϊ”ΟΛΖΛΤΓΔ»ΥΛ»¥ΞΛλΚœΛΠïrιgΛρΛΡΛ· Γ·ΛξΛόΛΖΛηΛΠΓΘΛόΛάΛόΛάΛ«Λ≠ΛκΛ≥Λ»Λ§ΕύΛΛïrΤΎΛΪΛιάϊ”ΟΛΙΛκΛ≥Λ»Λ«ΓΔ…γΜα…ζΜνΛΈ ΨS≥÷Λ§Λ«Λ≠’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈΏM––”ηΖάΛΥ³ΩΙϊΒΡΛ«ΛΙΓΘ Γ·7¨ùèξΛΥάßΛΟΛΩΛ»Λ≠ΛΥΛœ‘£ν}ΛρâδΛ®ΛηΛΠΓΘ Γ·Ά§ΛΗΛ≥Λ»ΛρΚΈΕ»Λ⬳ΛΪΛλΛΩΛξΓΔΚΈΛΪΛΥΛ≥ΛάΛοΛξΛ§≥ωΛΤ¨ùèξΛΥάßΛΟΛΩΛ»Λ≠ΛΥΛœΓΔ‰SΛΖΛΛ Θϋ‘£ν}ΛρΆΕΛ≤ΛΪΛ±ΛΤΛΫΛΈàωΛΪΛιöί≥÷ΛΝΛρΛΫΛιΛΖΛόΛΖΛγΛΠ?ΛΒΛΟΛ≠ΛΈΛ≥Λ»ΛœΛΙΛΑΛΥΆϋΛλΛκΛΈ ΓΨΛ«ΓΔΞΩΞΛΞΏΞσΞΑΛρΛΚΛιΛΙΛ≥Λ»Λ«ιvΛοΛξΛδΛΙΛ·Λ ΛΟΛΤΛ≠ΛόΛΙΓΘ L ΞΈ 19
- 9. ΒΡΛ ΓΔΒάάμΛΥΚœΛοΛ ΛΛΛηΛΠΛ Λ≥Λ»ΛβΕύΛ·ΓΔΉ‘Ζ÷ΛΥ≤ΜάϊΛ Λ≥Λ»Λœ¦QΛΖΛΤ’JΛαΛη ΛΠΛ»ΛΖΛόΛΜΛσΓΘΒ±»ΜΛόΛοΛξΛΈ»ΥΛΥ¨ùΛΙΛκ≈δë]ΛœΛ«Λ≠Λ Λ·Λ ΛξΛόΛΙΓΘ ΥΫΛΩΛΝΛœΓΔΥϊ»ΥΛ»Ϋ”ΛΙΛκΛ»Λ≠ΛœΛΫΛλΛ ΛξΛΥöίΛρ ΙΛΛΓΔΉ‘’§Λ«Φ“ΉεΛ»Ώ^Λ¥ΛΖ ΛΤΛΛΛκΛ»Λ≠Λ»ΛœΏ`ΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΥΛ ΛΟΛΤΓ®Υϊ»ΥΛΈ«ΑΛ«ΛΖΛΟΛΪΛξΛΙΛκΓ®Λ»ΛΛ ΛΠΛΈΛœΓΔ≤ΓöίΛΥΛ ΛΟΛΩΛΪΛιΧΊ³eΛΥΛ«Λ≠ΛκΛΈΛ«ΛœΛ Λ·ΓΔΛάΛλΛβΛ§…γΜα…ζΜνΛρΛΗΛγ ΛΠΛΚΛΥÜ”ΛαΛκΛηΛΠΛΔΛΩΛξΛόΛ®ΛΥΛδΛΟΛΤΛ≠ΛΤΛΛΛκΛ≥Λ»Λ ΛΈΛ«ΛΙΓΘ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΥΛ ΛΟ ΛΤΛβ?ΛΔΛκ≥ΧΕ»ΏM––ΛΙΛκΛόΛ«ΛΫΛΈΝΠΛœ±ΘΛΩΛλΛόΛΙΓΘΛ«ΛΙΛΪΛιöίΛρ‘SΛΜΛκ»ΥΛΥΛœΓΔ ≤ΓöίΛΈ÷ΔΉ¥Λ§èäΛ·≥ωΛΤΛ≠ΛόΛΙΓΘΈοΒΝΛιΛλΆΐœκΛ«ΡύΑτΛ»“…ΛοΛλΛκΛΈΛœΓΔ…μΫϋΛ« ΫιΉoΛΖΛΤΛΛΛκ»ΥΛ§ΕύΛΛΛ»ΛΛΛΠΛΈΛβΛΫΛΈΛηΛΠΛ άμ”…Λ«ΛΙΓΘ ΓΔΟτΗ–ΛΥκëà@Γ≠?Λ»ΛκΦ”Έ³Γ≠ ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΥΛ ΛκΛ»―‘»~Λ§άμΫβΛ«Λ≠Λ Λ·Λ ΛΟΛΤΛ·ΛκΛΈΛ«ΓΔΛΫΛλΛρ―aΛΠΛηΛΠΛΥΓΔ ΛόΛοΛξΛΈκÉ΅λöίΛρΗ–ΛΗΛ»ΛκΝΠΛ§œ»δ³Μ·ΛΖΓΔΛόΛοΛξΛΈΛηΛΠΛΙΛΥΟτΗ–ΛΥΖ¥èξΛΙΛκ ΛηΛΠΛΥΛ ΛΟΛΤΛ≠ΛόΛΙΓΘΚΈΛβΛοΛΪΛιΛ ΛΛ–ΓΛΒΛ ≥ύΛΝΛψΛσΛ§ΛΣΡΗΛΒΛσΛ»Ώ`ΛΠ»ΥΛΥ ΛάΛΟΛ≥ΛΒΛλΛκΛ»ΤϋΛ≠≥ωΛΙΛΈΛ»Ά§ΛΗΛηΛΠΛΥΓΔΉ‘Ζ÷Λρ ΊΛκΛΩΛαΛΈ³”ΈοΒΡΛ ΝΠΛ§Κτ Λ”ΤπΛ≥ΛΒΛλΛΤΛ·ΛκΛΈΛ«ΛΙΓΘΛ«ΛΙΛΪΛιΛόΛοΛξΛ§ΛΫΛοΛΫΛοΛΖΛΤΛΛΛκΛ»ΓΔ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ »ΥΛβ¬δΛΝΉ≈ΛΪΛ Λ·Λ ΛξΓΔΫιΉo’ΏΛ§≤ΜΑ≤Λ öί≥÷ΛΝΛ«ΛΛΛκΛ»’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛΈ≤ΜΑ≤Η– ΛβèäΛ·Λ ΛΟΛΤΛ≠ΛόΛΙΓΘΫιΉo’ΏΛ»’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛœγRΛ ΛΈΛ«ΛΙΓΘ ΩΝΩΝ‘ä 18 ?±·ΛΖΛΏΛœΛ Λ·Λ ΛιΛ ΛΛΓΜ ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈΡΗΛρ1Ρξ«ΑΛΥΩ¥»ΓΛΟΛΩ60¥ζΡ––‘ 1ΡξΛέΛ…«ΑΛΥΓΔ93örΛΈΡΗΛρΆωΛ· ΛΖ Λό ΛΖ ΛΩ ΓΘ Λέ Λ» Λσ Λ… “Μ »Υ Λ« Ϋι Ήo Λρ ΛΖ ΛΤ ΛΛ Λό ΛΖ ΛΩ ΓΘ ΡΗ Λœ 6 Ρξ «Α ΛΪ Λι Φ“ ¬Λ§Λ«Λ≠Λ Λ·Λ ΛξΓΔΞΔΞκΞΡΞœΞΛΞό©` ΛΈ‘\ΕœΛρ ήΛ±ΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘ÷ΔΉ¥Λ§ΏMΛύ ΛΥΛΡΛλΓΔΡΗΛœΤ§Λ»Λ≠ΛβΛοΛΩΛΖΛΈΛΫ Λ–ΛρκxΛλΛΩΛ§ΛιΛ Λ·Λ ΛξΓΔΆβ≥ωΛβ ΛόΛόΛ ΛιΛ ΛΪΛΟΛΩΛΖΓΔ“Ι÷–ΛΥΚΈΕ» Λβ Ξ» ΞΛ Ξλ Λ« Τπ Λ≥ ΛΒ Λλ ΛΤ ΛΊ Λ» ΛΊ Λ» ΛΥ Λ ΛΟΛΤΛΛΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘ 64ΡξιgΛΚΛΟΛ»ΛΛΛΟΛΖΛγΛΥΡΚΛιΛΖ ΛΩ ΡΗ Λ« ΛΖ ΛΩ ΓΘ ΡΗ ΛΈ ¥φ ‘Ύ Λœ ΓΔ Ή‘ Ζ÷ ΛΥ Λ»ΛΟΛΤΡΗΛ«ΛΔΛκΛάΛ±Λ«Λ Λ·Ά§÷ΨΛ«ΛΔ ΛξΓΔΛΒΛιΛΥΝΒ»ΥΛΈΛηΛΠΛ ¥φ‘ΎΛ«ΛβΛΔ ΛξΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘΛβΛΟΛ»ΛβΛΟΛ»ιL…ζΛ≠ΛΖΛΤ ΛέΛΖΛΪΛΟΛΩΛΖΓΔ–“ΛΜΛΥΛ ΛΟΛΤΛέΛΖΛΛ Λ»ΥΦΛΟΛΤΛΛΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘΆωΛ·Λ ΛΟΛΩ÷±αα 1ΏLιgΛ·ΛιΛΛΛœΓΔΥάΛσΛ«ΡΗΛΈΛ»Λ≥Λμ ΛΥ––Λ≠ΛΩΛΛΛ»ΥΦΛΛΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘ §F‘ΎΛβ±·ΛΖΛΏΛœΛ Λ·Λ ΛξΛόΛΜΛσ Λ§ΓΔ…ΌΛΖΛΚΛΡ‘ΣöίΛρ»ΓΛξëχΛΖΓΔΛβ Λ»ΛβΛ»≈dΈΕΛΈΛΔΛκΖ÷“ΑΛΈ÷vΝïΜαΛΥ ≥ωΛΩΛξΓΔœΔΉ”ΫιΉo’ΏΛ§Φ·ΛόΛκΜαΛΥ ≤ΈΦ”ΛΖΛΩΛξΛΖΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ…ΌΛΖΛ«Λβ Ή‘Ζ÷ΛΈΫUρYΛ§ΛΔΛ»ΛΥΨAΛ·»ΥΛΈ“έΛΥ ΝΔΛΟΛΤΛ·ΛλΛλΛ–Λ»ΥΦΛΟΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ ΓΚ ßΛΟΛΩΛβΛΈΛœΕύΛΛΛ§Γ≠ΓΜ ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈΉφΡΗΛρ6ΡξιgΞ±ΞΔΛΖΓΔΉρΡξΩ¥»ΓΛΟΛΩ20¥ζΛΈ¨O ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈΉφΡΗΛρ6ΡξιgΫιΉoΛΖΓΔΩ¥ »ΓΛξΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘ”¦ë¦Λρ ßΛΛΓΔΆΐœκΛΥΩύ ΛΖΛΏΓΔ≤ΜΑ≤Λ«ΛήΛ·ΛΩΛΝΦ“ΉεΛΪΛικxΛλ ΛηΛΠΛ»ΛΖΛ ΛΪΛΟΛΩΉφΡΗΛΈνÜΛρΆϋΛλΛι ΛλΛόΛΜΛσΓΘΦ“ΉεΛΏΛσΛ Λ§ΩύΛΖΛΏΛόΛΖ ΛΩΓΘΛήΛ·ΛœΓΔΫιΉoΛ»“ΐΛ≠™QΛ®ΛΥΓΔ”― ΛάΛΝΓΔ―ß‰IΓΔ¬öΓΔΛΫΛΖΛΤïrιgΛρ ßΛΛ ΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘ Ω¥»ΓΛΟΛΩΛΔΛ»ΓΔ÷Σ»ΥΛΪΛιΛœΓΗΛΣΛ– ΛΔΛΝΛψΛσΛœΘ®¨OΛΥΘ©ΫιΉoΛΖΛΤΛβΛιΛΟ ΛΤ–“ΛΜΛάΛΟΛΩΛΆΓΙΛ»―‘»~ΛρΛΪΛ±ΛιΛλ ΛόΛΖΛΩΛ§ΓΔΙϊΛΩΛΖΛΤΛΫΛΠΛάΛΟΛΩΛΈΛά ΛμΛΠΛΪΛ»ΥΦΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘê{ΛόΛλΛΩ≠hΨ≥ΛΥ ΛΛΛκΛ≥Λ»Λ»ΓΗ–“ΛΜΓΙΛœιv²SΛ ΛΛΛ≥Λ» ΛάΛ»ΥΦΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘΛήΛ·Λ§ΛέΛσΛ»ΛΠΛΥΛέ ΛΖΛΪΛΟΛΩΛΈΛœΓΔΛήΛ·Ή‘…μΛΈΉ‘”…Λ …ζ ΜνΛ»ΓΔΉφΡΗΛ§–“ΛΜΛάΛ»ΥΦΛ®Λκ…ζΜνΛΈ ¹IΝΔΛ«ΛΖΛΩΓΘ
- 10. “Μ Μ≠ «“ “Μ ³J ΘΑ ΘΕ ΘΑ ΘΑ ΘΑ ΘΑ ΘΑ Γχ Γ· ΘΑ ? ΓΔΛηΛΛΛ»ïχΛ»êôΛΛΛ»―‘Λ§Γ≠Λ«ΛΣΛ≥Λκöί≥÷ΛΝΛ§…ρΛύ»’ΛΥ Ξ± ΞΔ Ξι ©` ΛΈ ΛΔ Λ ΛΩ ΛΊ ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛ§ ΦΛόΛκΛ»ΛηΛΛΛ»Λ≠Λ»êôΛΛΛ»Λ≠Λ§Μλ‘ΎΛΖΛόΛΙΓΘΉν≥θΛΈΛ≥ΛμΛœΓΔ…ζΜν ΛΈΛέΛσΛΈ“Μ≤ΩΛΥΓΗΛΔΛλΘΩΓΙΛ»ΛΛΛΠΛ≥Λ»Λ§≥ωΛΤΛ≠ΛόΛΙΛ§ΓΔ–λΓ©ΛΥΓΗΛΔΛλΘΩΘΩΓΙ Λ»ΥΦΛΠàωΟφΛ§ΕύΛ·Λ ΛΟΛΤΛ≠ΛόΛΙΓΘΛΖΛΪΛΖ≥θΤΎΛΈΛ≥ΛμΛœ»ΓΛξΛΡΛ·ΛμΛΠΝΠΛβΓΔΏm Β±ΛΥ‘£ΛρΚœΛοΛΜΛκΝΠΛβΛΔΛκΛΈΛ«ΓΔΛ…Λ≥ΛόΛ«Λ§’J÷Σ÷ΔΛ«Λ…Λ≥ΛόΛ«Λ§ΛΫΛΠΛ«Λ ΛΛ ΛΈΛΪ“äΛ≠ΛοΛαΛ§Λ»ΛΤΛβΛύΛΚΛΪΛΖΛΛΛΈΛ«ΛΙΓΘΓδ'ΡξΛΈΛΜΛΛ"Λ»öίΛ§ΛΡΛΪΛ ΛΛΛ¥Φ“Ήε ΛβΕύΛ·ΛΔΛξΛόΛΙΛ§ΓΔïrιgΛ§ΛΩΛΟΛΤΛ·ΛκΛ»ΓΔΛ«Λ≠Λ ΛΛΛ≥Λ»Λ§âàΛ®ΛΤΛ·ΛκΛΈΛ«ΓΔ ΛάΛσΛάΛσΛ»ΛηΛΛΛ»Λ≠Λ»êôΛΛΛ»Λ≠ΛΈΗνΚœΛ§ΡφήûΛΖΛΤΛ·ΛκΛηΛΠΛΥΛ ΛξΛόΛΙΓΘ ΚΈΛρΛδΛΟΛΤΛβΛΠΛόΛ·ΛΛΛΪΛ ΛΛ»’Λœ ΛάΛλΛΥΛ«ΛβΛΔΛκΛβΛΈΛ«ΛΙΓΘ ΛΔΛόΛξΉ‘Ζ÷ΛρΊüΛαΛ ΛΛΛ«ΓΘ 1 Φ“ΉεΛδ”―ΛάΛΝΛ Λ…ΓΔ ‘ΣöίΛΥΛ ΛλΛΫΛΠΛ »ΥΛ» ‘£ΛρΛΖΛΤΛΏΛόΛΖΛγΛΠ?3 ΨœΛ“Λ»ΛΡΛΈΛ≥Λ»ΛΥΛ≥ΛάΛοΛξΨAΛ±ΛκΓΘZ Ü•ν}Ϋβ¦QΛœΓΔΛΔΛΜΛιΛΚΓΔ ΛφΛΟΛ·ΛξΓΔάδΨ≤ΛΥΓΔ Λ“Λ»ΛΡΛΚΛΡΓΘ Λ“Λ»ΛΡΛΈΛ≥Λ»Λ§ΛΛΛΟΛΩΛσöίΛΥΛ Λξ ΦΛαΛκΛ»ΓΔΛΫΛΈΛ≥Λ»ΛΥàΧΉ≈ΛΖΛΤΛ≥ΛάΛοΛξ Λ§ΨAΛ≠ΛόΛΙΓΘΛ≥ΛάΛοΛξΛœΒ±Ζ÷ΨAΛ≠ΛόΛΙΛ§ΓΔΛδΛ§ΛΤΛΫΛλΛβïrιgΛΈΫUΏ^Λ»Λ»ΛβΛΥ ÖßΛόΛΟΛΤΛ≠ΛόΛΙΓΘΛΫΛΖΛΤ¥ΈΛΈΛ≥Λ»Λ§ΛιΛΥ“ΤΛΟΛΤΛΛΛ≠ΛόΛΙΓΘΛ≥ΛάΛοΛξΛΈ÷–Λ«Λβ ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ≥θΤΎΛΈΛ≥ΛμΛΥΕύΛ·≥ωΛκΛΈΛ§Γ±ΈοΒΝΛιΛλΆΐœκ"Λ«ΛΙΓΘΓΗΛΣΫπΛ§Λ ΛΛΓΙΛ» »ΥΛρ“…ΛΠΛηΛΠΛΥΛ ΛξΓΔΧΊΕ®ΛΈ»ΥΛρΡύΑτΛ»¦QΛαΛΡΛ±ΓΔàΧΩ±ΛΥΙΞ™ΡΛΙΛκΛΈΛ«Λ»ΛΤ ΛβάßΛξΛόΛΙΓΘ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛœΉ‘Ζ÷Λ§―‘ΛΟΛΤΛΛΛκΛ≥Λ»ΛœΫ~¨ù’ΐΛΖΛΛΛ»ΥΦΛΛΛ≥ΛσΛ« ΛΛΛόΛΙΛΈΛ«ΓΔΛόΛοΛξΛ«ΛΛΛ·Λι ¬¨gΛρ’hΟςΛΖΛΤΛβΛοΛΪΛΟΛΤΛœΛβΛιΛ®ΛόΛΜΛσΓΘ ΛδΛιΛ Λ±ΛλΛ–Λ ΛιΛ ΛΛΛ≥Λ»Λ§…ΫΖeΛΏΛ«ΞΠΞσΞΕ'¬σ ΛΖΛΤΛΖΛόΛΟΛΩΛιΓΔ15Ζ÷Λ»ΛΪ30Ζ÷Λ»¦QΛαΛΤΓΔ öίΛ§œρΛ·ΛόΛόΏ^Λ¥ΛΙ ?Ή‘Ζ÷ΛΈïrιgΓΙΛρΉςΛΟΛΤΛΏΛΤΛœΘΩ 4 ”ω ?Ϋώ»’ΛœüoάμΛρΛΜΛΚΏ^Λ¥ΛΖΓΔ ΛόΛΩΟς»’ΛΪΛιΛ§ΛσΛ–ΛκΓΙΛ»¦QΛαΛΤΛΖΛόΛΠ ΛΈΛβ“Μ ÷Λ«ΛΙΓΘ »ΥΛœΛάΛλΛ«ΛβΛ≥ΛλΛόΛ«…ζΛ≠ΛΤΛ≠ΛΩΉ‘–≈ΛδΞΉΞιΞΛΞ…ΛρΛβΛΟΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘΫΓΩΒΛ Λ»Λ≠ΛœΓΔ≈–ΕœΝΠ?ΥΦΩΦΝΠ?“÷÷ΤΝΠΛ«Ξ≥ΞσΞ»Ξμ©`ΞκΛΖΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΛ§ΓΔ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛ§ Φ ΛόΛκΛ»Λ≥ΛλΛιΛΈΝΠΛ§»θΛ·Λ ΛξΓΔΉ‘–≈Λ»ΞΉΞιΞΛΞ…Λ§èäΛ·±μΛΥ≥ωΛΤΛ·ΛκΛηΛΠΛΥΛ ΛκΛΩΛαΓΔ…ΌΛΖΛ«ΛβΉ‘Ζ÷ΛΈΥΦΛΛΛ…ΛΣΛξΛΥΛ ΛιΛ ΛΛΛ»ΛΙΛΑΛΥöίΖ÷ΛρΚΠΛΖΗΙΛρΝΔΛΤ ΛκΛηΛΠΛΥΛ ΛξΛόΛΙΓΘΛβΛΈΛ¥Λ»Λρμ‰–ρΝΔΛΤΛΤΩΦΛ®ΛιΛλΛ Λ·Λ ΛκΛΩΛαΓΔΉ‘ΦΚ÷––Ρ ‘ά “Μ ¨m ¨m “Μ “Μ Θ Γε Θ± Θ±
- 11. “Μ “Μ “Μ σ@ ¥π ΘΚ ÷ΣΛΟΛΤΛΣΛ≥ΛΠ ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈΛ≥ΛσΛ Λ≥Λ» Έ¬»Σ»κ‘Γ³àΛδœψΥ°Λρ»κΛλΛΩΛξΓΔ Ξ≠ΞψΞσΞ…ΞκΛρΒΤΛΖ“τ‰SΛρΛΪΛ±Λκ ΛΣöίΛΥ»κΛξΛΈ±ΨΛρ’iΛύΛ Λ…ΓΔ ΛΣοLÖΈΛ«ΞΉΞΝΌm¦gΛρΓΘ 6ΛΥΛ ΛκΛ»Λ≥ΛσΛ Λ≥Λ»Λ§ΛΣΛ≥ΛξΛόΛΙ ?Τ±Κü»ο―u"Γ≠ΛΘ …ΔöiΓΔΞηΞ§ΓΔΆΞ Υ ¬Λ Λ…ΓΔ ΞΔ…P≥mΛβ Ή‘Ζ÷Λ§ ≥ Λ»Λ«…μΧεΛρ³”ΛΪΛΖΛΤΛΏΛόΛΖΛγΛΠΘΫΉ”Λ≠Λ Λ≥ ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛœ”¦ë¦ΛΙΛκΝΠΛ§™pΛ ΛοΛλΛκΟ½ΛΈ≤ΓöίΛ«ΛΙΓΘΓΗΚΈΕ»ΛβΆ§ΛΗΛ≥Λ»ΛριgΛ·ΓΙ ?≥ωά¥ ¬Λ§ΛΔΛΟΛΩΛ≥Λ»ΛΫΛΈΛβΛΈΛρΛοΛΙΛλΛΤΛΛΛκΓΙΓΗΈτΛΈΛ≥Λ»ΛœΛηΛ·“ôΛ®ΛΤΛΛΛκΓΙ Λ»ΛΛΛΠΛηΛΠΛ Λ≥Λ»Λ§»’≥Θ…ζΜνΛ« ΦΛόΛΟΛΤΛ≠ΛόΛΙΓΘΚΈΕ»ΛβΆ§ΛΗΛ≥Λ»Λρ¬³Λ·ΛΈΛ« ?ΛΒΛΟΛ≠Λβ―‘ΛΟΛΩΛ«ΛΖΛγΛΠΓΙΛ»ΫιΉo’ΏΛœΞΛΞιΞΛΞιΛΖΛΤΛΖΛόΛΛΛόΛΙΛ§ΓΔ''–¬ΛΖΛΛΛ≥ Λ»Λρ”¦ë¦Λ«Λ≠Λ ΛΛ'Γ·ΛΈΛ«ΛΙΓΘΛΖΛΪΛΖ≤ΓöίΛΥΛ Λκ«ΑΛΈ”¦'É|Λœν^ΛΈ÷–ΛΥ≤–ΛΟΛΤΛΛ ΛόΛΙΛΈΛ«ΓΔΈτΛΈΛΣ‘£ΛœΛΖΛΟΛΪΛξΛ«Λ≠ΛόΛΙΓΘΛΩΛάΛΖ÷ΔΉ¥Λ§ΏMΛσΛ«Λ·ΛκΛ»ΈτΛΈ‘£ Λβ≥ωΛΤΛ≥Λ Λ·Λ ΛξΛόΛΙΓΘ Ή¥¦rΛ§‘SΛΙΛ ΛιΓΔΥΦΛΛΛ≠ΛΟΛΤΞΣΞΖΞψΞλΛρΛΖΛΤΓΑΛΣ≥ωΛΪΛ± ΛΙΛκΛΈΛβΛΣΛΙΛΙΛαΛ«ΛΙΓΘ ?ΛΖΛΔΛοΛΜ–ΓœδΓΙΛρΉςΛΟΛΤΛΏΛόΛΜΛσΛΪΓΘ Λ»ΛΟΛΤΛΣΛ≠ΛΈ±ΠΈοΛδΥΦΛΛ≥ωΛΈΤΖΓΔ–¥’φΓΔΚΟΈοΛΈΛΣ«ëΉ”ΓΔ ΛΣöίΛΥ»κΛξΛΈΫ}Λ Λ…ΓΔΚΟΛ≠Λ ΛβΛΈΛ–ΛΪΛξ»κΛλΛΩΓΗΛΖΛΔΛο ΛΜ–ΓœδΓΙΛρΓΔ‘ΣöίΛΥΛ ΛξΛΩΛΛΛ»Λ≠ΛΥΛœΓΔ?»ΥΛΥΛ ΛΟΛΤΓΔ ΛΫΛΟΛ»ι_Λ±ΛιΛλΛκΛηΛΠΛΥΓΘ 8 ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΥΛ ΛκΛ»”¦ë¦ΛΙΛκΝΠΛάΛ±Λ«Λ Λ·ΓΔ≈–ΕœΛΖΛΩΛξΓΔΩΦΛ®ΛΩΛξΓΔ“÷÷ΤΛΖΛΩ ΛξΛΙΛκΝΠΛ§»θΛ·Λ ΛξΓΔΛβΛΈΛ¥Λ»Λρμ‰–ρΛάΛΤΛΤ––ΛΠΛ≥Λ»ΛβΩύ ÷ΛΥΛ ΛΟΛΤΛ≠ΛόΛΙΓΘ ?önΛρΡΞΛΛΛΤΓΙΛ»önΞ÷ΞιΞΖΛρΕ…ΛΖΛΤΛβΓΔΛ…ΛΠΛΖΛΩΛιΛΛΛΛΛΈΛΪΛοΛΪΛιΛ ΛΛΛ Λ…ΓΔ ΛβΛΈΛ¥Λ»Λ§ιvΏBΛ≈ΛΪΛ ΛΛΛΈΛ«ΛΙΓΘΫώΛΈΛ≥Λ»ΛβΈτΛΈΛ≥Λ»Λβν^ΛΈ÷–Λ§Λ¥ΛΝΛδΜλΛΦ ΛΥΛ ΛΟΛΤΛ·ΛκΛΈΛ«ΓΔ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛ§ΏM––ΛΙΛκΛΥΛΡΛλΛΤΞ»ΞσΞΝΞσΞΪΞσΛ ––³”Λ§ΕύΛ·Λ ΛΟ ΛΤΛ≠ΛόΛΙΓΘ''ν^ΛΥ?ΛβΛδ?Λ§ΛΪΛΪΛΟΛΤΛΛΛκ" Λ»―‘ΛοΛλΛκΖΫΛβΛΔΛξ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΉ‘…μΛβΛ…ΛΠ ©\ ΞΝΞγΞ≥Λδ¥σΗΘΛœΓΔ»ΥΛρΞœΞΟΞ‘©`ΛΥΛΙΛκ 9‘≠Νœ»κΛξΛάΛ»ΛΪΓΘ ΛΩΛάΛΖ ≥ΛΌΏ^Λ°ΛΥΛœΓΔΛ¥ΉΔ“βΛ·ΛάΛΒΛΛΓΘ ΛΛΛΈΛΪάßΛΟΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓ°ΛΖΛΤΛΖ ?ΝΩ
- 12. Γ≠ ΛΈ ΌΚ Γ± Γ≠ ? ? ? ? Γ± ΡΎ »ί ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛΈΦ“ΉεΫιΉo’ΏΛœΓΔ ΛσΛ…Λ§ΓΗ…ζΜνΛ§ΛΖΛ≈ΛιΛ·Λ ΛΡΛά Λ®ΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙ ΛœΓΔΓΗΦ“ΉεΛ§’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΥΛ ΛΟΛΤΛΪΛι…ζΜνΛ§ΛΖΛ≈ΛιΛ· Λ ΛΟΛΩΓΙΛ»¥πΛ®ΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ ΓώΫιΉo’ΏΛΈ59ΘΞΛ§ΓΗ―ϋΛδΛ“ΛΕΛ Λ……μΧεΛΈιvΙùΛ§Ά¥ΛΛΓΙΛ»¥πΛ®ΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ ΓώΫιΉo’ΏΛΈ85ΘΞΛ§ΓΗ“β”ϊΛ§≥ωΛ ΛΛΛ»Λ≠Λ§ΛΔΛκΓΙΛ»¥πΛ®ΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ ΓώΫιΉo’ΏΛΈ80ΘΞΛ§? ÉûΛΖΛ·Λ«Λ≠Λ ΛΛΉ‘Ζ÷ΛΥœ”êôΗ–ΛρΗ–ΛΗΛκΛ»Λ≠Λ§ΛΔΛκΓΙΛ» ¥πΛ®ΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ (»Υ ΐΘ©500 ΛΥ ΫιΉo’ΏΛΈ–Ρ…μΛΈΉ¥ëBΛδ…ζΜνΛΈΛΖΛ≈ΛιΛΒ =…ζΜνΛ§ΛΖΛ≈ΛιΛ·Λ ΛΟΛΩΛ»Η–ΛΗΛκάμ”…ΘΫΘ®―} ΐΜΊ¥π«Ό400 300 200 100 ? _ ΓΙ Ξμ Γω ΏΒ ΏΒ ΓΙ _ άο ΛΫ ΛΈ Υϊ Φ“ Ήε ΛΈ ΫY χ Λ§ »θ Λ· Λ ΛΟ ΛΩ Ή” Λ… Λβ ΛΈ Λ≥ Λ» ΛΥ ÷ Λ§ Λό Λο Λι Λ ΛΛ Υ ¬ Λ§ ΛΠ Λό Λ· ΛΛ ΛΪ Λ Λ· Λ ΛΟ ΛΩ Λ¥ Ϋϋ Υυ Λ» ΛΈ ιv ²S Λ§ ΛΠ Λό Λ· ΛΛ ΛΪ Λ Λ· Λ ΛΟ ΛΩ Λό Λο Λξ ΛΈ »Υ ΛΈ ëB Ε» Λ§ âδ Λο ΛΟ ΛΩ ‘£ Λδ ”ό ≥’ Λρ ιg ΛΛ ΛΤ Λβ Λι Λ® Λκ »Υ Λ§ ΛΛ Λ ΛΛ öί ίX ΛΥ œύ ’³ Λ« Λ≠ Λκ œύ ÷ Λ§ ΛΛ Λ ΛΛ Ή‘ Ζ÷ ΛΈ Ή¥ ¦r Λρ άμ Ϋβ ΛΖ ΛΤ Λ· Λλ Λκ »Υ Λ§ ΛΛ Λ ΛΛ Φ“ Ήε Λ» ’J ÷Σ ÷Δ ΛΈ »Υ ±Ψ »Υ Λ» ΛΈ ιv ²S Λ§ êô Λ· Λ ΛΟ ΛΩ Φ“ Ήε ΛΈ ιv ²S Λ§ ΛΠ Λό Λ· ΛΛ ΛΪ Λ Λ· Λ ΛΟ ΛΩ ”H Ήε Λ» ΛΈ ιv ²S Λ§ ΛΠ Λό Λ· ΛΛ ΛΪ Λ Λ· Λ ΛΟ ΛΩ Öß »κ Λ§ €p ΛΟ ΛΩ Υ ¬ Λρ ΆΥ ¬ö ΛΖ ΛΩ Λξ ήû ¬ö ΛΖ ΛΩ Χε ’{ Λ§ êô Λ· Λ ΛΟ ΛΩ ÷ß ≥ω Λ§ âà Λ® ΛΩ Ϋώ ‘Τ Υ· ΟΏ ïr ιg Λ§ €p ΛΟ ΛΩ ΛΈ Φ“ ¬ ïr ιg Λ§ âà Φ” ΛΖ ΛΩ ΉεΦ“ ïr ιg ΛΈ Λδ Λξ Λ· Λξ Λ§ κy ΛΖ Λ· Λ ΛΟ ΛΩ Λ» Ή‘ ”… ΛΥ Ι Λ® Λκ ïr ιg Λ§ Λ Λ· Λ ΛΟ ΛΩ »ΥΛΈ ΞΙ Ξ» Ξλ ΞΙ Λδ ΤΘ ³Κ Η– Λ§ âà ΛΖ ΛΩ ÷Δ Θ’ Θν Θ» Ü ’JΡξΘΑΘ±ΘΑΘ≤ ?’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛ»Φ“ΉεΛΈΡΚΛιΛΖΛΥιvΛΙΛκΞΔΞσΞ±©`Ξ»ΓΙΛηΛξ£iΜ² Γώ’{•ΥΜΊ¥π’Ώ »ΪΙζΛΈ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛρΫιΉo÷–ΛΈΦ“ΉεΫιΉo’Ώ557ΟϊΘ®Ρ––‘143Οϊ?≈°–‘411Οϊ?üo”¦»κ3ΟϊΘ© 1άεΓ· “Μ 10 ‘¬ E ΞΝΞ®ΞΡΞ· ΩΎ ΝΦ L ΓθΛ’ΛΡΛ≠ ΩΎ êô ΛΖ Θ… Θω Μ ΓΘ Θ± Θ÷ Πύ ΞΈ ΝΦ Λ’ êô Γθ Γθ Γθ ΛΖ “Μ Ξι Θβ Πύ ΞΈ ΝΦ Λ’ êô Γθ Γθ Γθ Θ± Θ÷ Εΰ “Μ Θ± Θ÷ Πύ ΞΈ ΝΦ Λ’ êô Γθ Γθ Γθ ΩΎ ΝΦ ΛΖ ΓθΛ’ΛΡΛ≠ ΩΎ êô L ΩΎ ΝΦ L ΓθΛ’ΛΡΛ≠ ΩΎ êô ΛΖ ΩΎ ΝΦ ΛΛ ΓθΛ’ΛΡΛΠ ΩΎêôΛΘ ΩΎ ΝΦ L ΓθΛ’ΛΡΛΒ ΩΎ êô ΛΖ ΡΎ σγ
- 13. ΓώΧε’{ΛΈ????ôΎ΅βΛρ????Λρ»κΛλ?Χε’{Λ§ΛΙΛΑΛλΛ ΛΛΛ»Λ≠ΛΥΛœ ΡΎ»ίΛΈôΎΛΥΛηΛΠΛΙΛδöίΛΥΛ ΛκΛ≥Λ»Λ Λ…Λρ”¦»κΛΖΛόΛΖΛγΛΠΓΘ ΫιΉo’ΏΛ§?…ζΜνΛ§ΛΖΛ≈ΛιΛ·Λ ΛΟΛΩΛ»Η–ΛΗΛκάμ”…?Λ»ΛΖΛΤΓΔΛέΛ»ΛσΛ…ΛΈ»ΥΛ§?ΞΙΞ»ΞλΞΙΛδ ΤΘ³ΚΗ–Λ§âàΛΖΛΩ(767ΘΞ)ΓΙΛ»¥πΛ®ΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙ?’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛΈ¨ùèξΛδΛόΛοΛξΛ»ΛΈιv²SΛΥΩύë] ΛΖΓΔΓΗΥ·ΟΏïrιgΛ§€pΛΟΛΩ(42.9%)??Χε’{Λ§êôΛ·Λ ΛΟΛΩ(33.9%)ΓΙΛ»–Ρ…μΛΈΤΘΛλΛρ‘VΛ®Λκ »ΥΛ§ΛΣΛΣΛΦΛΛΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ ΛόΛΩΫιΉoΛΥΛηΛξΓΗΉ‘”…ΛΥ ΙΛ®ΛκïrιgΛ§Λ Λ·Λ ΛΟΛΩΘ®517ΘΞ)ΓΙΓΗïrιgΛΈΛδΛξΛ·ΛξΛ§κyΛΖ Λ·Λ ΛΟΛΩΘ®45.2ΘΞ)ΓΙΓΗΦ“ ¬ïrιgΛ§âàΦ”ΛΖΛΩΘ®442ΘΞ)-?Λ Λ…Ή‘Ζ÷ΛΈïrιgΛ§Ή‘”…ΛΥΞ≥ΞσΞ» Ξμ©`ΞκΛ«Λ≠Λ ΛΛΛ»ΛΛΛΟΛΩΉ¥¦rΛ§ΞΙΞ»ΞλΞΙΛρΗΏΛαΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ ΓΗ÷ß≥ωΛ§âàΛ®ΛΩΘ®39.9ΘΞ)ΓΙΓΗ Υ ¬ΛρΆΥ¬öΛΖΛΩΛξήû¬öΛΖΛΩΘ®259ΘΞ)ΓΙΓΗÖß»κΛ§€pΛΟΛΩ (239ΘΞ)?Λ»? Υ ¬ΛδΫU€gΒΡÜ•ν}ΛΊΛΈ”ΑμëΛβ¥σΛ≠Λ ΛβΛΈΛ§ΛΔΛξΛόΛΙΓΘ ΓΗ”HΉεΛ»ΛΈιv²SΛ§ΛΠΛόΛ·ΛΛΛΪΛ Λ·Λ ΛΟΛΩΘ®181ΘΞ)ΓΙΓΗΦ“ΉεΛΈιv²SΛ§ΛΠΛόΛ·ΛΛΛΪΛ Λ· Λ ΛΟΛΩ(174ΘΞ?)ΓΗΦ“ΉεΛ»’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»Υ±Ψ»ΥΛ»ΛΈιv²SΛ§êôΛ·Λ ΛΟΛΩΘ®160ΘΞ)ΓΙΛ Λ…»Υιgιv ²SΛΈÜ•ν}ΛδΓΗΉ‘Ζ÷ΛΈΉ¥¦rΛράμΫβΛΖΛΤΛ·ΛλΛκ»ΥΛ§ΛΛΛ ΛΛΘ®133ΘΞ)ΓΙΓΗöίίXΛΥ”ό≥’Λρ¬³ΛΛΛΤ ΛβΛιΛ®Λκ»ΥΛ§ΛΛΛ ΛΛ(106ΘΞ)??ΛόΛοΛξΛΈ»ΥΛΈëBΕ»Λ§âδΛοΛΟΛΩ(97ΘΞ)?Λ Λ…Ι¬ΝΔΗ–Λρ±ß Λ·»ΥΛβ…ΌΛ Λ·ΛΔΛξΛόΛΜΛσΓΘ ΓΔ ©öίΛ»Ψ£ê{Γ≠Λ®ΛκΫι÷î―‘Γ°Θ§'΅çΛάΓ≠ΛΡΛ±ΛηΓΘ ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛΈΫιΉoΛρΒΘΛΠΫιΉo’ΏΛΈ…ζΜνΛΥΛœΛΒΛόΛΕΛόΛ άßκyΛ§Λ»ΛβΛ ΛΛΛόΛΙ?ΫιΉoΛΈΊ™ ΒΘΛ§ΛΔΛόΛξΛΥΛ“Λ»ΛξΛΈΫιΉo’ΏΛΥ÷ΊΛ·ΛΈΛΖΛΪΛΪΛξΛΙΛ°ΛκΛ»–Ρ…μ÷ΔΛ Λ…≤ΓöίΛρΛ“Λ≠ΛΣΛ≥ΛΙ ¬ëBΛΥΛβΛ ΛξΛόΛΙΓΘ ΛόΛΚΓΔΫιΉo’ΏΉ‘…μΛ§”ύ‘ΘΛρΛβΛΟΛΤ…ζΜνΛρΛΙΛκΛΩΛαΛΥΛœΓΔΚΈΛ§±Ί“ΣΛ ΛΈΛΪΛρΩΦΛ®ΛκΛ≥Λ» Λ§¥σ ¬Λ«ΛΙΓΘ ≤ΓöίΛδΫιΉoΓΔΞΒΞί©`Ξ»ΛδΞΒ©`Ξ”ΞΙΛΥΛΡΛΛΛΤΛΈ÷ΣΉRΛδΦΦ–gΛρ…μΛΥΛΡΛ±ΛκΛ≥Λ»ΓΔΦ“ΉεΛδΒΊ ”ρΛ Λ…÷ή΅λΛΈ»ΥΛΈάμΫβΛδÖfΝΠΛρΒΟΛκΛ≥Λ»?ΛΫΛΖΛΤΚΈΛηΛξΛβ‘ΣöίΛ»÷Σê{ΛρΛβΛιΛ®ΛκΫιΉo’Ώ ΛΈ÷ΌιgΛΩΛΝΛρΛΏΛΡΛ±ΛκΛ≥Λ»ΛœΓΔΛΔΛ ΛΩΛΈ¥σΛ≠Λ Ίî°bΛΥΛ ΛξΛόΛΙ?ΒΊ”ρΛΈΫιΉo’ΏΛΈΦ·ΛόΛξ ΛδΫΧ “ΛΥΛβΛΦΛ“ΏMΛσΛ«≤ΈΦ”ΛΙΛκΛ≥Λ»ΛρΛΣΛΙΛΙΛαΛΖΛόΛΙΓΘ 14 1ΘΛ ‘¬ »’ Θ· Θ· Θ· Γ° Θ· Θ° ΞΝΞßΞΟΞ· ΩΎ ΝΦ ΛΛ ΓθΛ’ΛΡΛΠ ΩΎ êô ΛΛ ΩΎ ΝΦ ΛΛ ΓθΛ’ΛΡΛΠ ΩΎ êô ΛΛ ΩΎ ΝΦ ΛΛ ΓθΛ’ΛΡΛΠ ΩΎ êô ΛΛ ΩΎ ΝΦ ΛΛ ΓθΛ’ΛΡΛΠ ΩΎ êô ΛΛ ΩΎ ΝΦ ΛΛ ΓθΛ’ΛΡΛΠ ΩΎ êô ΛΛ Θ’ “Μ ΛΡ Θ’ Πύ ΞΈ ΝΦ Λ’ êô Γθ Γθ Γθ Θρ Θω Εΰ “Μ Θρ Θω Πύ ΞΈ ΝΦ Λ’ êô Γθ Γθ Γθ ΛΔ Λ ΛΩ ΛΈ Χε ’{ ΡΎ »ί ιv²S’ΏΞ≥ΞαΞσΞ»ôΎ
- 14. ΫΓ ΩΒ Ξα Ξβ ΓΔ “Μ “Μ ―‘ Θ° Λρ¥σ«–ΛΥΛΙΛκΛΩΛαΛΥ ΛΔΛ ΛΩΉ‘…μΛΈ Ξβ?ΫΓΩΒΞΝΞßΞΟΞ·ΞξΞΙΞ» 3 ΉνΫϋ?ΛΔΛ ΛΩΉ‘…μΛΈ»’Γ©ΛΈ…ζΜνΛΥΛΡΛΛΛΤ?öίΛΥΛ Λκ Λ≥Λ»ΛœΛΔΛξΛόΛΜΛσΛΪΘΩ ΛΩΛ»Λ®Λ–Γ≠ ΓθΛΖΛ–ΛιΛ·–ίπBΛΙΛκ»’Λ§Λ»ΛλΛΤΛΛΛ ΛΛ ΩΎΟΏΛλΛ ΛΛ?ΛόΛΩΛœ«όΛΡΛ±Λ ΛΛΛ»Λ≠Λ§ΛΔΛκ ΩΎΦ“Ήε“‘ΆβΛΈ»ΥΛ»ΜαΛΟΛΤΛΛΛ ΛΛ ΩΎΉ‘Ζ÷ΛΈ”ύœΨΛΈïrιgΛ§Λ ΛΛ ΩΎ±Ί“ΣΛ ÷Έ·ü?ΫΓΩΒ‘\ΕœΛ Λ…Λρ ήΛ±ΛιΛλΛΤΛΛ Λ ΛΛ ΛΔΛ ΛΩΛΈΫΓΩΒΛρΛΏΛσΛ Λ§–Ρ≈δΛΖΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙ?ΫιΉoΛΙΛκΛΔΛ ΛΩ Ή‘…μΛΈΧεΛδΓ°Λ≥ΛρΛΛΛΩΛοΛΟΛΤΛΔΛ≤ΛκΛ≥Λ»Λβ¥σ«–Λ«ΛΙΓΘ ΫΓ ΩΒ Ξα Ξβ ΓΔ ΉνΫϋ?ΛΔΛ ΛΩΉ‘…μΛΈΫΓΩΒΉ¥ëBΛΥΛΡΛΛΛΤ?öίΛΥΛ ΛκΛ≥Λ» ΛœΛΔΛξΛόΛΜΛσΛΪΘΩ 1 ? ΓΚ ? , Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω r ] , Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω ? Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω ? Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω ? ? Θ§ Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω ? ©` ©` “Μ 4ΛΔΛ ΛΩΉ‘…μΛ§ΛβΛΟΛ»ΛΖΛΤΛΏΛΩΛΛΛ≥Λ»ΛœΘΩΛΩΛ»Λ®Λ–Γ≠ ΩΎΧεΛ§ΛάΛκΛ·?ΤΘΛλΛδΛΙΛΛ ΩΎ ≥”ϊΛ§Λ ΛΛ ΩΎ―ϋΆ¥Λ§ΛΔΛκ ΩΎν^Ά¥Λ§ΛΔΛκ ΩΎΗΙΆ¥Λ§ΛΔΛκ ?ΛβΛΖïrιgΛ§ΛΔΛΟΛΩΛι?Λ≥ΛσΛ Λ≥Λ»ΛρΛΖΛΤΛΏΛΩΛΛ?Λ»ΛΛΛΠΛ≥Λ» Λœ?ΚΈΛ«ΛΖΛγΛΠΛΪΓΘ Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω . Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω I Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω ? 1 Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω I Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω ? 1 Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω I Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γ· Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω I Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω “Μ Z ΉνΫϋ?ΛΔΛ ΛΩΛœΫιΉoΛδ ά‘£ΛΥΛηΛκΞΙΞ»ΞλΞΙΛδöίΖ÷ΛΈ ¬δΛΝόzΛΏΛœΛΔΛξΛόΛΜΛσΛΪΘΩ ΛΩΛ»Λ®Λ–Γ≠ ΩΎΩΎ ΐΛ§€pΛΟΛΤΛ≠ΛΩ ΓθΛΖΛ–ΛιΛ·–ΠΛΟΛΤΛΛΛ ΛΛ ΞμΞΛΞιΞΛΞιΛΖΛΩΛξ?≤ΜΑ≤ΛΥΛ ΛκΛ≥Λ»Λ§ΕύΛΛ ΩΎöίΛ≈Λ·Λ»Ξή©`ΞΟΛ»ΛΖΛΤΛΖΛόΛΠ ΩΎ“β”ϊΛ§ΛοΛΪΛ ΛΛ ΓώΥΦΛΛΛρ―‘»~ΛΥΛΖΛΤΛΏΛόΛΖΛγΛΠ Γώ¨g§FΛ«Λ≠ΛκΛΥΛœΛ…ΛΠΛΖΛΩΛιΛηΛΛΛΪΓΔΛΔΛ ΛΩΛ»ΛΛΛΟΛΖΛγΛΥΩΦΛ® ΛΤΛ·ΛλΛκ»ΥΛ§Λ≠ΛΟΛ»ΛΛΛόΛΙ ΞΑ k “Μ ΞΏ Πύ ? Πώ “Μ Πώ ΞΥ ©` Πύ ? ΞΌ “Μ ―‘ “Μ “Μ Πη Θ± Θ±



![’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛΈΫιΉoΛρΛΖΛΤΛΛΛκΛΔΛ ΛΩΛΊ
“Μ
?
Υ]
?
?
ΘΚ
?
?
Θι
ΛΈΙΪ“φ…γ΅βΖ®»Υ≥…Ρξαα“äΞΜΞσΞΩ©`?Ξξ©`Ξ§ΞκΞΒΞή©`Ξ»÷ß≤Ω
ΩΎ“Μ”EΓΨhttps://www.legal-support.or.jp/ΓΩI¬ΕΛΟΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΛΏΛσΛ Ά§ΛΗΛηΛΠΛ ¬ Λ«άß
»’±ΨΥΨΖ®÷ß‘°ΞΜΞσΞΩ©`?Ζ®ΞΤΞιΞΙΓ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠Γ≠ΙΎ0570-078374
ΓΨ‘¬ΓΪΫπ9ïrΓΪ21ïrΓΔΆΝ9ïrΓΪ17ïrΘ®Φά»’?ΡξΡ©Ρξ Φ–ί‰I)ΓΩΞμ
1?»ΥΛ«ΛΪΛΪΛ®Λ≥ΛόΛ ΛΛΛ«ΫιΉo÷ΌιgΛρΛΡΛ·ΛμΛΠΓΘ
ΫιΉo’ΏΫΜΝςΜαΓΔκä‘£œύ’³Λ Λ…ΛρΆ®ΛΖΛΤΓΔΛέΛΪΛΈΫιΉo’ΏΛΪΛιΛΈ«ιàσΛρΒΟΛκôCΜαΛρ
ΛΡΛ·ΛξΛόΛΖΛγΛΠ?ΫιΉoΛΈ÷Σê{Λ§€ΚίdΛ«ΛΙ?”ό≥’Λρ―‘Λ®Λκœύ ÷Λ§ΛΛΛκΛ≥Λ»Λβ¥σ«–Λ«ΛΙΓΘ
Γώ “Ϋ ·ü ôC ιv ΛΈ ¨ù èξ ΛΥ ιv ΛΙ Λκ œύ ’³
ΘϋΛ¥άϊ”ΟΛΈ“Ϋ·üôCιvΛΈœύ’³ΖôΩΎ
Ζ®»ΥΛΒΛΒΛ®ΛΔΛΛ“Ϋ·ü»Υ‰ΊΞΜΞσΞΩ©`COML(Ξ≥ΞύΞκΘ©κä‘£œύ’³
-6314-1652ΓΨ‘¬ΓΪΫπΓΩΓ¥9ïrΓΪ12ïr13ïrΓΪ17ïrΓΒΓΨΆΝΓΩΓ¥9ïrΓΪ12ïrΓΒω†2Ή‘Ζ÷ΛρΛέΛαΛΤΛΔΛ≤ΛηΛΠΓΘ
’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈΫιΉoΛœΡΩΛΥ“äΛ®Λ ΛΛΩύ³ΚΛ§ΛΔΛξΛόΛΙΓΘΛ«ΛΙΛ§ΫιΉo’ΏΛΈΩύ³ΚΛœΛ ΛΪΛ ΘΚ
ΛΪΛόΛοΛξΛΥάμΫβΛΖΛΤΛβΛιΛ®Λ ΛΛΛβΛΈΛ«ΛΙΓΘ‘ΣöίΛ§≥ωΛκΛηΛΠΉ‘Ζ÷Λ«Ή‘Ζ÷ΛρΛέΛαΛΤΘΜi
ΛΔΛ≤ΛόΛΖΛγΛΠΓΘ
3Λ§ΛσΛ–ΛξΛΙΛ°Λ ΛΛΓΘ
’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈΫιΉoΛœΓ®ΛΛΛΛΛΪΛ≤ΛσΛ§ΓΔΛΝΛγΛΠΛ…ΛΛΛΛΛΪΛ≤ΛσΓ®Λ«ΛΙΓΘΛΗΛγΛΠΛΚΛΥ ÷ΘΚ
£iΛ≠ΛρΛΖΛΤœΔΛΈιLΛΛΫιΉoΛ§Λ«Λ≠ΛκΛηΛΠΓΔΫιΉoΞΒ©`Ξ”ΞΙΛράϊ”ΟΛΖΛ§ΛσΛ–ΛιΛ ΛΛΫιΉol
Λρ–ΡΛ§Λ±ΛόΛΖΛγΛΠ?
4ΫΓΩΒΛΥöίΛρΛΡΛ±Ή‘Ζ÷Λρ¥σ«–ΛΥΓΘ
ΫιΉo’ΏΛΔΛΟΛΤΛΈΫιΉoΛ«ΛΙΓΘΫιΉo’ΏΛ§œ»ΛΥΒΙΛλΛΤΛΖΛόΛΟΛΤΛœ‘ΣΛβΉ”ΛβΛΔΛξΛόΛΜΘΜ
ΛσΓΘΛόΛΚΛœΉ‘Ζ÷Ή‘…μΛΈΛ≥Λ»ΛρΛΛΛΝΛ–Λσ¥σ«–ΛΥΛΖΛΤΓΔΉ‘Ζ÷ΛΈ»Υ…ζΛρ‰SΛΖΛύΛ≥Λ»ΛρΘΚ
ΩΦΛ®ΛΤΛΛΛ≠ΛόΛΖΛγΛΠΓΘ
5ΗΙΛ§ΝΔΛΟΛΤΛΔΛΩΛξΛόΛ®ΓΘ
Γ®’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛΥΛœ≈≠ΛΟΛΤΛœΛΛΛ±Λ ΛΛΓ®Λ»―‘ΛοΛλΛόΛΙΛ§ΓΔ…μΡΎΛΈΫιΉoΛ«ΛœΓΔΛΫi
ΛΠΚÜÖgΛΥΛ«Λ≠ΛκΛβΛΈΛ«ΛœΛΔΛξΛόΛΜΛσΓΘ≈≠ΛιΛ ΛΛΛ«ΫιΉoΛ«Λ≠ΛκΛηΛΠΛΥΛ ΛκΛΥΛœΛάΘΜ
ΛλΛ«ΛβïrιgΛ§ΛΪΛΪΛξΛόΛΙΓΘ
6÷ΣΉRΛρΛβΛ»ΛΠΓΘ
’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΥ¨ùΛΙΛκ’ΐΛΖΛΛ÷ΣΉRΛρΛβΛΝΛόΛΖΛγΛΠΓΘιgΏ`ΛΟΛΩ«ιàσΛβΛΩΛ·ΛΒΛσ≥ωΛόΘΚΘΜ
ΛοΛΟΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΛΈΛ«ΓΔ«ιàσΛΥ’ώΛξΛόΛοΛΒΛλΛ ΛΛΛηΛΠΛΥΓΘΫΜΝςΜαΛ««ιàσΛρΒΟΛΤΓΔii
Ή‘Ζ÷Λ ΛξΛΈΫιΉoΛΈ ΥΖΫΛρ“äΛΡΛ±ΛόΛΖΛγΛΠΓΘ
ΞΔ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛρκLΛΒΛ ΛΛΓΘ
’J÷Σ÷ΔΛ§ΏMΛσΛ«Λ·ΛκΛ»ΛόΛοΛξΛΈ÷ζΛ±Λ§±Ί“ΣΛΥΛ ΛκΛ≥Λ»ΛβΛΔΛξΛόΛΙΓΘ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛρκLΛΒΛ ΛΛi
Λ«ΓΔ…μΫϋΛ »ΥΛΥΛœ≤ΓöίΛΈΛ≥Λ»Λρ¹ΜΛ®ΛΤΓΔάμΫβ’ΏΛδÖfΝΠ’ΏΛρΛΡΛ·ΛΟΛΤΛΣΛ≠ΛόΛΖΛγΛΠΓΘΘΚ
L ? ? ©\ ? ? ? ? ? ? ≤Έ
Γώ Ϋι Ήo ¬ ‰I Υυ ΛΈ ¨ù èξ ΛΥ ιv ΛΙ Λκ œύ ’³
??ΕΨ'?”ΟΛΈΫιΉo±Θξ™ ¬‰IΥυΛΈœύ’³ΖôΩΎΓΔΞ±ΞΔΞόΞΆΞΗΞδ©`ΛΊ
Γω –ν°¥εΫιΉo±Θξ™ΒΘΒ±’n
?Ης±hΛΈΙζΟώΫΓΩΒ±Θξ™΅βΧεΏBΚœΜα(ΫιΉoΞΒ©`Ξ”ΞΙΩύ«ι³IάμΒΘΒ±²l
Γώ Ώ\ ήû Οβ ‘S ΛΥ ιv ΛΙ Λκ œύ ’³
?÷ς÷Έ“ΫΛΥœύ’³
ΓωΛΣΫϋΛ·ΛΈΨ·≤λ π?Οβ‘SΞΜΞσΞΩ©`
Γώ ΞΛ Ξσ ΞΩ ©` ΞΆ ΞΟ Ξ» ΛΈ «ι àσ ΞΒ ΞΛ Ξ»
?“Ϋ·üôCιvΒ»ΛΥιvΛΙΛκ«ιàσ
ΛΖΙΪ“φ…γ΅βΖ®»Υ»’±ΨάœΡξΨΪ…ώ“Ϋ―ßΜα
ΛΖ“ΜΑψ…γ΅βΖ®»Υ»’±Ψ’J÷Σ÷ΔΞ±ΞΔ―ßΜα
ΓΨhttp;//www.rounen.orgΓΩ
ΓΨhttp;//www.chihoucare.org]
?ΗΏΐh’ΏΛΈΉΓΛόΛΛΛΥιvΛΙΛκ«ιàσ
Ξλ©`Αψ…γ΅βΖ®»ΥΗΏΐh’ΏΉΓ’§Ίî΅βΓΨhttp://www.kouiuuzai.or.ipΓΩ
ΛΖ’§άœΥυ?ΞΑΞκ©`ΞΉΞέ©`Ξύ»ΪΙζΞΆΞΟΞ»Ξο©`Ξ·
ΓΨhttp://www.clc-japan.com/takurousyo_netΓΩ
ΗΘλμ?±ΘΫΓ?“Ϋ·üΛΥιvΛΙΛκΨtΚœ«ιàσ
ΛΖWAMNET(ΗΘλμ±ΘΫΓ“Ϋ·ü«ιàσΞΆΞΟΞ»)[http://www.wam.go.ip]I
ΓΔ©e
ΓσΨΪ…ώ’œΚΠ’Ώ±ΘΫΓΗΘλμ ÷éΛΘΚ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛ§»ΓΒΟΛ«Λ≠Λκ ÷éΛ
ΓσΉ‘ΝΔ÷ß‘°“Ϋ·üΌMΘΚ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛ«Ά®‘ΚΛΙΛκΌM”ΟΛΈ€pν~
Γσ²ϊ≤Γ ÷Β±?’œΚΠ’ΏΡξΫπΘΚ»τΡξ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈΖΫΛΈ»ΥΛ§άϊ”ΟΛ«Λ≠Λκ÷ΤΕ»
ΓσΥυΒΟΥΑΘ®’œΚΠ’ΏΩΊ≥ΐ?“Ϋ·üΌMΩΊ≥ΐ)ΓΔΉΓΟώΥΑΘ®’œΚΠ’ΏΩΊ≥ΐΘ©ΘΚΥΑΫπΛΈ€pν~
ΓΔ ΞΈ
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/random-160620121118/85/-4-320.jpg)




![ΒΡΛ ΓΔΒάάμΛΥΚœΛοΛ ΛΛΛηΛΠΛ Λ≥Λ»ΛβΕύΛ·ΓΔΉ‘Ζ÷ΛΥ≤ΜάϊΛ Λ≥Λ»Λœ¦QΛΖΛΤ’JΛαΛη
ΛΠΛ»ΛΖΛόΛΜΛσΓΘΒ±»ΜΛόΛοΛξΛΈ»ΥΛΥ¨ùΛΙΛκ≈δë]ΛœΛ«Λ≠Λ Λ·Λ ΛξΛόΛΙΓΘ
ΥΫΛΩΛΝΛœΓΔΥϊ»ΥΛ»Ϋ”ΛΙΛκΛ»Λ≠ΛœΛΫΛλΛ ΛξΛΥöίΛρ ΙΛΛΓΔΉ‘’§Λ«Φ“ΉεΛ»Ώ^Λ¥ΛΖ
ΛΤΛΛΛκΛ»Λ≠Λ»ΛœΏ`ΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΥΛ ΛΟΛΤΓ®Υϊ»ΥΛΈ«ΑΛ«ΛΖΛΟΛΪΛξΛΙΛκΓ®Λ»ΛΛ
ΛΠΛΈΛœΓΔ≤ΓöίΛΥΛ ΛΟΛΩΛΪΛιΧΊ³eΛΥΛ«Λ≠ΛκΛΈΛ«ΛœΛ Λ·ΓΔΛάΛλΛβΛ§…γΜα…ζΜνΛρΛΗΛγ
ΛΠΛΚΛΥÜ”ΛαΛκΛηΛΠΛΔΛΩΛξΛόΛ®ΛΥΛδΛΟΛΤΛ≠ΛΤΛΛΛκΛ≥Λ»Λ ΛΈΛ«ΛΙΓΘ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΥΛ ΛΟ
ΛΤΛβ?ΛΔΛκ≥ΧΕ»ΏM––ΛΙΛκΛόΛ«ΛΫΛΈΝΠΛœ±ΘΛΩΛλΛόΛΙΓΘΛ«ΛΙΛΪΛιöίΛρ‘SΛΜΛκ»ΥΛΥΛœΓΔ
≤ΓöίΛΈ÷ΔΉ¥Λ§èäΛ·≥ωΛΤΛ≠ΛόΛΙΓΘΈοΒΝΛιΛλΆΐœκΛ«ΡύΑτΛ»“…ΛοΛλΛκΛΈΛœΓΔ…μΫϋΛ«
ΫιΉoΛΖΛΤΛΛΛκ»ΥΛ§ΕύΛΛΛ»ΛΛΛΠΛΈΛβΛΫΛΈΛηΛΠΛ άμ”…Λ«ΛΙΓΘ
ΓΔΟτΗ–ΛΥκëà@Γ≠?Λ»ΛκΦ”Έ³Γ≠
’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΥΛ ΛκΛ»―‘»~Λ§άμΫβΛ«Λ≠Λ Λ·Λ ΛΟΛΤΛ·ΛκΛΈΛ«ΓΔΛΫΛλΛρ―aΛΠΛηΛΠΛΥΓΔ
ΛόΛοΛξΛΈκÉ΅λöίΛρΗ–ΛΗΛ»ΛκΝΠΛ§œ»δ³Μ·ΛΖΓΔΛόΛοΛξΛΈΛηΛΠΛΙΛΥΟτΗ–ΛΥΖ¥èξΛΙΛκ
ΛηΛΠΛΥΛ ΛΟΛΤΛ≠ΛόΛΙΓΘΚΈΛβΛοΛΪΛιΛ ΛΛ–ΓΛΒΛ ≥ύΛΝΛψΛσΛ§ΛΣΡΗΛΒΛσΛ»Ώ`ΛΠ»ΥΛΥ
ΛάΛΟΛ≥ΛΒΛλΛκΛ»ΤϋΛ≠≥ωΛΙΛΈΛ»Ά§ΛΗΛηΛΠΛΥΓΔΉ‘Ζ÷Λρ ΊΛκΛΩΛαΛΈ³”ΈοΒΡΛ ΝΠΛ§Κτ
Λ”ΤπΛ≥ΛΒΛλΛΤΛ·ΛκΛΈΛ«ΛΙΓΘΛ«ΛΙΛΪΛιΛόΛοΛξΛ§ΛΫΛοΛΫΛοΛΖΛΤΛΛΛκΛ»ΓΔ’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ
»ΥΛβ¬δΛΝΉ≈ΛΪΛ Λ·Λ ΛξΓΔΫιΉo’ΏΛ§≤ΜΑ≤Λ öί≥÷ΛΝΛ«ΛΛΛκΛ»’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛΈ≤ΜΑ≤Η–
ΛβèäΛ·Λ ΛΟΛΤΛ≠ΛόΛΙΓΘΫιΉo’ΏΛ»’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛœγRΛ ΛΈΛ«ΛΙΓΘ
ΩΝΩΝ‘ä
18
?±·ΛΖΛΏΛœΛ Λ·Λ ΛιΛ ΛΛΓΜ
’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈΡΗΛρ1Ρξ«ΑΛΥΩ¥»ΓΛΟΛΩ60¥ζΡ––‘
1ΡξΛέΛ…«ΑΛΥΓΔ93örΛΈΡΗΛρΆωΛ·
ΛΖ Λό ΛΖ ΛΩ ΓΘ Λέ Λ» Λσ Λ… “Μ »Υ Λ« Ϋι Ήo Λρ
ΛΖ ΛΤ ΛΛ Λό ΛΖ ΛΩ ΓΘ ΡΗ Λœ 6 Ρξ «Α ΛΪ Λι Φ“
¬Λ§Λ«Λ≠Λ Λ·Λ ΛξΓΔΞΔΞκΞΡΞœΞΛΞό©`
ΛΈ‘\ΕœΛρ ήΛ±ΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘ÷ΔΉ¥Λ§ΏMΛύ
ΛΥΛΡΛλΓΔΡΗΛœΤ§Λ»Λ≠ΛβΛοΛΩΛΖΛΈΛΫ
Λ–ΛρκxΛλΛΩΛ§ΛιΛ Λ·Λ ΛξΓΔΆβ≥ωΛβ
ΛόΛόΛ ΛιΛ ΛΪΛΟΛΩΛΖΓΔ“Ι÷–ΛΥΚΈΕ»
Λβ Ξ» ΞΛ Ξλ Λ« Τπ Λ≥ ΛΒ Λλ ΛΤ ΛΊ Λ» ΛΊ Λ» ΛΥ
Λ ΛΟΛΤΛΛΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘ
64ΡξιgΛΚΛΟΛ»ΛΛΛΟΛΖΛγΛΥΡΚΛιΛΖ
ΛΩ ΡΗ Λ« ΛΖ ΛΩ ΓΘ ΡΗ ΛΈ ¥φ ‘Ύ Λœ ΓΔ Ή‘ Ζ÷ ΛΥ
Λ»ΛΟΛΤΡΗΛ«ΛΔΛκΛάΛ±Λ«Λ Λ·Ά§÷ΨΛ«ΛΔ
ΛξΓΔΛΒΛιΛΥΝΒ»ΥΛΈΛηΛΠΛ ¥φ‘ΎΛ«ΛβΛΔ
ΛξΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘΛβΛΟΛ»ΛβΛΟΛ»ιL…ζΛ≠ΛΖΛΤ
ΛέΛΖΛΪΛΟΛΩΛΖΓΔ–“ΛΜΛΥΛ ΛΟΛΤΛέΛΖΛΛ
Λ»ΥΦΛΟΛΤΛΛΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘΆωΛ·Λ ΛΟΛΩ÷±αα
1ΏLιgΛ·ΛιΛΛΛœΓΔΥάΛσΛ«ΡΗΛΈΛ»Λ≥Λμ
ΛΥ––Λ≠ΛΩΛΛΛ»ΥΦΛΛΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘ
§F‘ΎΛβ±·ΛΖΛΏΛœΛ Λ·Λ ΛξΛόΛΜΛσ
Λ§ΓΔ…ΌΛΖΛΚΛΡ‘ΣöίΛρ»ΓΛξëχΛΖΓΔΛβ
Λ»ΛβΛ»≈dΈΕΛΈΛΔΛκΖ÷“ΑΛΈ÷vΝïΜαΛΥ
≥ωΛΩΛξΓΔœΔΉ”ΫιΉo’ΏΛ§Φ·ΛόΛκΜαΛΥ
≤ΈΦ”ΛΖΛΩΛξΛΖΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ…ΌΛΖΛ«Λβ
Ή‘Ζ÷ΛΈΫUρYΛ§ΛΔΛ»ΛΥΨAΛ·»ΥΛΈ“έΛΥ
ΝΔΛΟΛΤΛ·ΛλΛλΛ–Λ»ΥΦΛΟΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ
ΓΚ ßΛΟΛΩΛβΛΈΛœΕύΛΛΛ§Γ≠ΓΜ
’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈΉφΡΗΛρ6ΡξιgΞ±ΞΔΛΖΓΔΉρΡξΩ¥»ΓΛΟΛΩ20¥ζΛΈ¨O
’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈΉφΡΗΛρ6ΡξιgΫιΉoΛΖΓΔΩ¥
»ΓΛξΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘ”¦ë¦Λρ ßΛΛΓΔΆΐœκΛΥΩύ
ΛΖΛΏΓΔ≤ΜΑ≤Λ«ΛήΛ·ΛΩΛΝΦ“ΉεΛΪΛικxΛλ
ΛηΛΠΛ»ΛΖΛ ΛΪΛΟΛΩΉφΡΗΛΈνÜΛρΆϋΛλΛι
ΛλΛόΛΜΛσΓΘΦ“ΉεΛΏΛσΛ Λ§ΩύΛΖΛΏΛόΛΖ
ΛΩΓΘΛήΛ·ΛœΓΔΫιΉoΛ»“ΐΛ≠™QΛ®ΛΥΓΔ”―
ΛάΛΝΓΔ―ß‰IΓΔ¬öΓΔΛΫΛΖΛΤïrιgΛρ ßΛΛ
ΛόΛΖΛΩΓΘ
Ω¥»ΓΛΟΛΩΛΔΛ»ΓΔ÷Σ»ΥΛΪΛιΛœΓΗΛΣΛ–
ΛΔΛΝΛψΛσΛœΘ®¨OΛΥΘ©ΫιΉoΛΖΛΤΛβΛιΛΟ
ΛΤ–“ΛΜΛάΛΟΛΩΛΆΓΙΛ»―‘»~ΛρΛΪΛ±ΛιΛλ
ΛόΛΖΛΩΛ§ΓΔΙϊΛΩΛΖΛΤΛΫΛΠΛάΛΟΛΩΛΈΛά
ΛμΛΠΛΪΛ»ΥΦΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘê{ΛόΛλΛΩ≠hΨ≥ΛΥ
ΛΛΛκΛ≥Λ»Λ»ΓΗ–“ΛΜΓΙΛœιv²SΛ ΛΛΛ≥Λ»
ΛάΛ»ΥΦΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘΛήΛ·Λ§ΛέΛσΛ»ΛΠΛΥΛέ
ΛΖΛΪΛΟΛΩΛΈΛœΓΔΛήΛ·Ή‘…μΛΈΉ‘”…Λ …ζ
ΜνΛ»ΓΔΉφΡΗΛ§–“ΛΜΛάΛ»ΥΦΛ®Λκ…ζΜνΛΈ
¹IΝΔΛ«ΛΖΛΩΓΘ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/random-160620121118/85/-9-320.jpg)


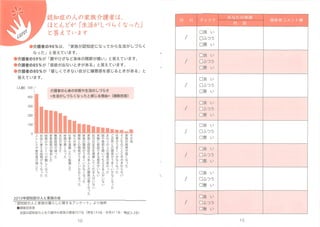
![ΓώΧε’{ΛΈ????ôΎ΅βΛρ????Λρ»κΛλ?Χε’{Λ§ΛΙΛΑΛλΛ ΛΛΛ»Λ≠ΛΥΛœ
ΡΎ»ίΛΈôΎΛΥΛηΛΠΛΙΛδöίΛΥΛ ΛκΛ≥Λ»Λ Λ…Λρ”¦»κΛΖΛόΛΖΛγΛΠΓΘ
ΫιΉo’ΏΛ§?…ζΜνΛ§ΛΖΛ≈ΛιΛ·Λ ΛΟΛΩΛ»Η–ΛΗΛκάμ”…?Λ»ΛΖΛΤΓΔΛέΛ»ΛσΛ…ΛΈ»ΥΛ§?ΞΙΞ»ΞλΞΙΛδ
ΤΘ³ΚΗ–Λ§âàΛΖΛΩ(767ΘΞ)ΓΙΛ»¥πΛ®ΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙ?’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛΈ¨ùèξΛδΛόΛοΛξΛ»ΛΈιv²SΛΥΩύë]
ΛΖΓΔΓΗΥ·ΟΏïrιgΛ§€pΛΟΛΩ(42.9%)??Χε’{Λ§êôΛ·Λ ΛΟΛΩ(33.9%)ΓΙΛ»–Ρ…μΛΈΤΘΛλΛρ‘VΛ®Λκ
»ΥΛ§ΛΣΛΣΛΦΛΛΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ
ΛόΛΩΫιΉoΛΥΛηΛξΓΗΉ‘”…ΛΥ ΙΛ®ΛκïrιgΛ§Λ Λ·Λ ΛΟΛΩΘ®517ΘΞ)ΓΙΓΗïrιgΛΈΛδΛξΛ·ΛξΛ§κyΛΖ
Λ·Λ ΛΟΛΩΘ®45.2ΘΞ)ΓΙΓΗΦ“ ¬ïrιgΛ§âàΦ”ΛΖΛΩΘ®442ΘΞ)-?Λ Λ…Ή‘Ζ÷ΛΈïrιgΛ§Ή‘”…ΛΥΞ≥ΞσΞ»
Ξμ©`ΞκΛ«Λ≠Λ ΛΛΛ»ΛΛΛΟΛΩΉ¥¦rΛ§ΞΙΞ»ΞλΞΙΛρΗΏΛαΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙΓΘ
ΓΗ÷ß≥ωΛ§âàΛ®ΛΩΘ®39.9ΘΞ)ΓΙΓΗ Υ ¬ΛρΆΥ¬öΛΖΛΩΛξήû¬öΛΖΛΩΘ®259ΘΞ)ΓΙΓΗÖß»κΛ§€pΛΟΛΩ
(239ΘΞ)?Λ»? Υ ¬ΛδΫU€gΒΡÜ•ν}ΛΊΛΈ”ΑμëΛβ¥σΛ≠Λ ΛβΛΈΛ§ΛΔΛξΛόΛΙΓΘ
ΓΗ”HΉεΛ»ΛΈιv²SΛ§ΛΠΛόΛ·ΛΛΛΪΛ Λ·Λ ΛΟΛΩΘ®181ΘΞ)ΓΙΓΗΦ“ΉεΛΈιv²SΛ§ΛΠΛόΛ·ΛΛΛΪΛ Λ·
Λ ΛΟΛΩ(174ΘΞ?)ΓΗΦ“ΉεΛ»’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»Υ±Ψ»ΥΛ»ΛΈιv²SΛ§êôΛ·Λ ΛΟΛΩΘ®160ΘΞ)ΓΙΛ Λ…»Υιgιv
²SΛΈÜ•ν}ΛδΓΗΉ‘Ζ÷ΛΈΉ¥¦rΛράμΫβΛΖΛΤΛ·ΛλΛκ»ΥΛ§ΛΛΛ ΛΛΘ®133ΘΞ)ΓΙΓΗöίίXΛΥ”ό≥’Λρ¬³ΛΛΛΤ
ΛβΛιΛ®Λκ»ΥΛ§ΛΛΛ ΛΛ(106ΘΞ)??ΛόΛοΛξΛΈ»ΥΛΈëBΕ»Λ§âδΛοΛΟΛΩ(97ΘΞ)?Λ Λ…Ι¬ΝΔΗ–Λρ±ß
Λ·»ΥΛβ…ΌΛ Λ·ΛΔΛξΛόΛΜΛσΓΘ
ΓΔ ©öίΛ»Ψ£ê{Γ≠Λ®ΛκΫι÷î―‘Γ°Θ§'΅çΛάΓ≠ΛΡΛ±ΛηΓΘ
’J÷Σ÷ΔΛΈ»ΥΛΈΫιΉoΛρΒΘΛΠΫιΉo’ΏΛΈ…ζΜνΛΥΛœΛΒΛόΛΕΛόΛ άßκyΛ§Λ»ΛβΛ ΛΛΛόΛΙ?ΫιΉoΛΈΊ™
ΒΘΛ§ΛΔΛόΛξΛΥΛ“Λ»ΛξΛΈΫιΉo’ΏΛΥ÷ΊΛ·ΛΈΛΖΛΪΛΪΛξΛΙΛ°ΛκΛ»–Ρ…μ÷ΔΛ Λ…≤ΓöίΛρΛ“Λ≠ΛΣΛ≥ΛΙ
¬ëBΛΥΛβΛ ΛξΛόΛΙΓΘ
ΛόΛΚΓΔΫιΉo’ΏΉ‘…μΛ§”ύ‘ΘΛρΛβΛΟΛΤ…ζΜνΛρΛΙΛκΛΩΛαΛΥΛœΓΔΚΈΛ§±Ί“ΣΛ ΛΈΛΪΛρΩΦΛ®ΛκΛ≥Λ»
Λ§¥σ ¬Λ«ΛΙΓΘ
≤ΓöίΛδΫιΉoΓΔΞΒΞί©`Ξ»ΛδΞΒ©`Ξ”ΞΙΛΥΛΡΛΛΛΤΛΈ÷ΣΉRΛδΦΦ–gΛρ…μΛΥΛΡΛ±ΛκΛ≥Λ»ΓΔΦ“ΉεΛδΒΊ
”ρΛ Λ…÷ή΅λΛΈ»ΥΛΈάμΫβΛδÖfΝΠΛρΒΟΛκΛ≥Λ»?ΛΫΛΖΛΤΚΈΛηΛξΛβ‘ΣöίΛ»÷Σê{ΛρΛβΛιΛ®ΛκΫιΉo’Ώ
ΛΈ÷ΌιgΛΩΛΝΛρΛΏΛΡΛ±ΛκΛ≥Λ»ΛœΓΔΛΔΛ ΛΩΛΈ¥σΛ≠Λ Ίî°bΛΥΛ ΛξΛόΛΙ?ΒΊ”ρΛΈΫιΉo’ΏΛΈΦ·ΛόΛξ
ΛδΫΧ “ΛΥΛβΛΦΛ“ΏMΛσΛ«≤ΈΦ”ΛΙΛκΛ≥Λ»ΛρΛΣΛΙΛΙΛαΛΖΛόΛΙΓΘ
14 1ΘΛ
‘¬ »’
Θ·
Θ·
Θ·
Γ°
Θ·
Θ°
ΞΝΞßΞΟΞ·
ΩΎ ΝΦ ΛΛ
ΓθΛ’ΛΡΛΠ
ΩΎ êô ΛΛ
ΩΎ ΝΦ ΛΛ
ΓθΛ’ΛΡΛΠ
ΩΎ êô ΛΛ
ΩΎ ΝΦ ΛΛ
ΓθΛ’ΛΡΛΠ
ΩΎ êô ΛΛ
ΩΎ ΝΦ ΛΛ
ΓθΛ’ΛΡΛΠ
ΩΎ êô ΛΛ
ΩΎ ΝΦ ΛΛ
ΓθΛ’ΛΡΛΠ
ΩΎ êô ΛΛ
Θ’
“Μ
ΛΡ
Θ’
Πύ
ΞΈ
ΝΦ
Λ’
êô
Γθ
Γθ
Γθ
Θρ
Θω
Εΰ
“Μ
Θρ
Θω
Πύ
ΞΈ
ΝΦ
Λ’
êô
Γθ
Γθ
Γθ
ΛΔ Λ ΛΩ ΛΈ Χε ’{
ΡΎ »ί
ιv²S’ΏΞ≥ΞαΞσΞ»ôΎ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/random-160620121118/85/-13-320.jpg)
![ΫΓ ΩΒ Ξα Ξβ
ΓΔ
“Μ
“Μ
―‘
Θ°
Λρ¥σ«–ΛΥΛΙΛκΛΩΛαΛΥ
ΛΔΛ ΛΩΉ‘…μΛΈ
Ξβ?ΫΓΩΒΞΝΞßΞΟΞ·ΞξΞΙΞ»
3 ΉνΫϋ?ΛΔΛ ΛΩΉ‘…μΛΈ»’Γ©ΛΈ…ζΜνΛΥΛΡΛΛΛΤ?öίΛΥΛ Λκ
Λ≥Λ»ΛœΛΔΛξΛόΛΜΛσΛΪΘΩ
ΛΩΛ»Λ®Λ–Γ≠
ΓθΛΖΛ–ΛιΛ·–ίπBΛΙΛκ»’Λ§Λ»ΛλΛΤΛΛΛ ΛΛ
ΩΎΟΏΛλΛ ΛΛ?ΛόΛΩΛœ«όΛΡΛ±Λ ΛΛΛ»Λ≠Λ§ΛΔΛκ
ΩΎΦ“Ήε“‘ΆβΛΈ»ΥΛ»ΜαΛΟΛΤΛΛΛ ΛΛ
ΩΎΉ‘Ζ÷ΛΈ”ύœΨΛΈïrιgΛ§Λ ΛΛ
ΩΎ±Ί“ΣΛ ÷Έ·ü?ΫΓΩΒ‘\ΕœΛ Λ…Λρ ήΛ±ΛιΛλΛΤΛΛ
Λ ΛΛ
ΛΔΛ ΛΩΛΈΫΓΩΒΛρΛΏΛσΛ Λ§–Ρ≈δΛΖΛΤΛΛΛόΛΙ?ΫιΉoΛΙΛκΛΔΛ ΛΩ
Ή‘…μΛΈΧεΛδΓ°Λ≥ΛρΛΛΛΩΛοΛΟΛΤΛΔΛ≤ΛκΛ≥Λ»Λβ¥σ«–Λ«ΛΙΓΘ
ΫΓ ΩΒ Ξα Ξβ
ΓΔ
ΉνΫϋ?ΛΔΛ ΛΩΉ‘…μΛΈΫΓΩΒΉ¥ëBΛΥΛΡΛΛΛΤ?öίΛΥΛ ΛκΛ≥Λ»
ΛœΛΔΛξΛόΛΜΛσΛΪΘΩ
1 ? ΓΚ ? , Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω r ] , Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω ? Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω ? Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω ? ? Θ§ Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω ? ©` ©` “Μ
4ΛΔΛ ΛΩΉ‘…μΛ§ΛβΛΟΛ»ΛΖΛΤΛΏΛΩΛΛΛ≥Λ»ΛœΘΩΛΩΛ»Λ®Λ–Γ≠
ΩΎΧεΛ§ΛάΛκΛ·?ΤΘΛλΛδΛΙΛΛ
ΩΎ ≥”ϊΛ§Λ ΛΛ
ΩΎ―ϋΆ¥Λ§ΛΔΛκ
ΩΎν^Ά¥Λ§ΛΔΛκ
ΩΎΗΙΆ¥Λ§ΛΔΛκ
?ΛβΛΖïrιgΛ§ΛΔΛΟΛΩΛι?Λ≥ΛσΛ Λ≥Λ»ΛρΛΖΛΤΛΏΛΩΛΛ?Λ»ΛΛΛΠΛ≥Λ»
Λœ?ΚΈΛ«ΛΖΛγΛΠΛΪΓΘ
Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω . Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω I Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω ? 1 Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω I Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω ? 1 Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω I Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γ· Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω I Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω Γω “Μ
Z ΉνΫϋ?ΛΔΛ ΛΩΛœΫιΉoΛδ ά‘£ΛΥΛηΛκΞΙΞ»ΞλΞΙΛδöίΖ÷ΛΈ
¬δΛΝόzΛΏΛœΛΔΛξΛόΛΜΛσΛΪΘΩ
ΛΩΛ»Λ®Λ–Γ≠
ΩΎΩΎ ΐΛ§€pΛΟΛΤΛ≠ΛΩ
ΓθΛΖΛ–ΛιΛ·–ΠΛΟΛΤΛΛΛ ΛΛ
ΞμΞΛΞιΞΛΞιΛΖΛΩΛξ?≤ΜΑ≤ΛΥΛ ΛκΛ≥Λ»Λ§ΕύΛΛ
ΩΎöίΛ≈Λ·Λ»Ξή©`ΞΟΛ»ΛΖΛΤΛΖΛόΛΠ
ΩΎ“β”ϊΛ§ΛοΛΪΛ ΛΛ
ΓώΥΦΛΛΛρ―‘»~ΛΥΛΖΛΤΛΏΛόΛΖΛγΛΠ
Γώ¨g§FΛ«Λ≠ΛκΛΥΛœΛ…ΛΠΛΖΛΩΛιΛηΛΛΛΪΓΔΛΔΛ ΛΩΛ»ΛΛΛΟΛΖΛγΛΥΩΦΛ®
ΛΤΛ·ΛλΛκ»ΥΛ§Λ≠ΛΟΛ»ΛΛΛόΛΙ
ΞΑ
k
“Μ
ΞΏ
Πύ
?
Πώ
“Μ
Πώ
ΞΥ
©` Πύ
?
ΞΌ
“Μ
―‘
“Μ
“Μ
Πη
Θ±
Θ±](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/random-160620121118/85/-14-320.jpg)