1 of 26
Download to read offline
























Ad
Recommended
Georgia ppt 06 08
Georgia ppt 06 08Naniko Khouskivadze
╠²
The document summarizes Thomson Reuters solutions for scientific research, focusing on their ISI Web of Knowledge platform and Web of Science database. It discusses the comprehensive coverage and citation searching capabilities provided over 100 years of data from over 10,000 journals, as well as the rigorous editorial evaluation process.Multimedia For Cultural Learning
Multimedia For Cultural LearningSanjay Goel
╠²
Sanjay Goel discusses the role of multimedia in cultural documentation and learning, emphasizing the integration of technology in understanding nature, society, and knowledge creation. He outlines the complexities of multimedia content, including its creation, quality, and the importance of cognitive mapping and categorization. The document also highlights the potential of digital libraries for cultural heritage, stressing the need for digitization and preservation of artifacts while facilitating research and dissemination.Final presentation
Final presentationHaran Sivakumar
╠²
This document summarizes the goals and process of creating an online educational resource by the Southern California Library focused on their collections related to the blacklisting of teachers in LA during the McCarthy era. The project aimed to increase accessibility of the library's resources using multimedia to reduce intimidation. Key steps included selecting a collection, designing an intuitive website with layered information and minimizing scrolling, integrating interfaces like timelines and document previews, and connecting elements while maintaining usability. Challenges included technical issues, and the site was launched at http://socallib.org/blacklistedTeachers to inspire future digital initiatives.Multimedia, undergrads and the library
Multimedia, undergrads and the libraryVic Divecha
╠²
The document discusses the role of multimedia and the library in undergraduate education. It notes that today's undergraduates are consumers and generators of multimedia content through their use of mobile devices. The library can play an important role by supporting multimedia production on campus through expertise, spaces, and training. The future role of the library is to identify disruptive technologies, embrace them, make them available to students, and help shape how they are used in education.Newman Library Multimedia Portal
Newman Library Multimedia Portalllrath5
╠²
The document discusses creating a portal to aggregate and share library-related instructional multimedia content such as tutorials, PDFs, videos, and Captivate files. The portal could be used for on-demand instruction, reinforcing classroom lessons, and integrating media into tutorials. Content may include tutorials on research strategies, interviews with library/college faculty and students, and marketing materials. The portal would be created in LibGuides and any librarian could add or share content. Potential issues include staff time, different file formats, and length of media.The interactive and multimedia library
The interactive and multimedia libraryHelMet-kirjasto
╠²
The document discusses plans for an interactive and multimedia library called the New Central Library in Helsinki, Finland. Some key points:
- The library will be 10,000 square meters and a hub of knowledge, skills, and stories, with 5,000 daily visitors and 1.5 million annual visitors.
- It will have a variety of spaces like events areas, meeting rooms, learning spaces, creative spaces, and studios.
- The library aims to be open and accessible to all, with some areas open 24/7. It will have a collection of 200,000 items both physical and electronic.
- Construction is estimated to begin in 2014 at a cost of around 69.9 million euros, withImportance of Multimedia
Importance of MultimediaSa├Łful ├Źslam
╠²
This presentation discusses the importance of multimedia, outlining its uses in various fields such as business, education, entertainment, home, and public places. Multimedia can benefit business through sales/marketing presentations, trade show production, staff training, and company kiosks. In education, multimedia is useful for courseware/simulations, e-learning, distance learning, and information searching. The presentation concludes by stating that as multimedia increasingly permeates various domains, it will become even more integral to the future world.Multimedia approach
Multimedia approachRahul Reghu
╠²
Multimedia is an important innovation in educational technology that can improve teaching and learning. It involves using various media like text, pictures, sound, animation and video together in a program. Multimedia approaches can be classified in different ways, such as by instructional methods, auto-instructional techniques, mass communication tools, audiovisual materials, experiential learning, and teaching resources. Implementing multimedia approaches requires changes to organizational structures, infrastructure, teacher training, and attitudes. It provides benefits like making learning more engaging, individualized, and memorable for students.Chapter 3 The Role of Multimedia in Education
Chapter 3 The Role of Multimedia in EducationSalina Saharudin
╠²
This document discusses the role of multimedia in education. It defines multimedia as communicating in multiple ways using elements like text, audio, video, graphics, animation, and interactivity. Multimedia can enhance teaching by allowing annotations during live lectures, freeing teachers from blackboards, and facilitating collaboration. It also reviews types of multimedia presentations and considers criteria for creating presentations in PowerPoint. The document outlines the four basic functions of the Internet in education: searching for and receiving information, publishing and providing information, communicating, and collaborating. It discusses best practices for multimedia development and the standard phases of multimedia production.Advantage and Disadvantages of MULTIMEDIA
Advantage and Disadvantages of MULTIMEDIAjopin_5
╠²
Technology and multimedia applications are becoming increasingly integrated into the academic and personal lives of students. This document discusses how technology is now part of daily life both in and out of school. The technological revolution will significantly impact how students learn, with curriculum emphasizing higher-order thinking skills, authentic tasks, and collaborative work rather than isolated skill-building. Multimedia activities can provide learning opportunities for students to develop real-world technology skills while expressing their knowledge.Importance of multimedia
Importance of multimediaOnline
╠²
Multimedia has many uses across several fields including business, education, entertainment, home, and public places. It can be used for sales presentations, staff training, course materials, games, movies, television, information kiosks, and more. As multimedia technologies continue to advance, they will become more integrated into more aspects of life and work.Introduction to multimedia
Introduction to multimediaZurina Yasak
╠²
This document introduces multimedia and its applications. It defines multimedia as a combination of text, graphics, sound, animation and video to effectively communicate ideas. It discusses two types of multimedia presentations: linear, which progresses without user control, and non-linear, which offers interactivity. It provides examples of linear and non-linear multimedia. It also outlines several applications of multimedia such as in creative industries, commerce, entertainment, engineering, science, medicine, education and more.ßāĪßāÉßā¼ßāÉßāĢßāÜßāØ ßā×ßāĀßāØßāößāźßāóßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāößāÆßāøßāśßāĪ ßā©ßāÉßāæßāÜßāØßā£ßāś(Bolo variant)
ßāĪßāÉßā¼ßāÉßāĢßāÜßāØ ßā×ßāĀßāØßāößāźßāóßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāößāÆßāøßāśßāĪ ßā©ßāÉßāæßāÜßāØßā£ßāś(Bolo variant)lomadze70
╠²
ßāĪßāÉßā¼ßāÉßāĢßāÜßāØ ßā×ßāĀßāØßāößāźßāóßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāößāÆßāøßāśßāĪ ßā©ßāÉßāæßāÜßāØßā£ßāś(Bolo variant)
ßāĪßāÉßā¼ßāÉßāĢßāÜßāØ ßā×ßāĀßāØßāößāźßāóßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāößāÆßāøßāśßāĪ ßā©ßāÉßāæßāÜßāØßā£ßāś(Bolo variant)lomadze70
╠²
Nazi Dvalishvili
Nazi Dvalishvilinazidvalishvili
╠²
ßā©ßāößāøßāÉßā»ßāÉßāøßāößāæßāößāÜßāś ßāÆßāÉßāÖßāĢßāößāŚßāśßāÜßāś ßāøßāÉßāŚßāößāøßāÉßāŚßāśßāÖßāÉßā©ßāś.
II ßāÖßāÜßāÉßāĪßāś.
2011 ßā¼.ßāÖßāśßāößāĢßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāØßāößāŚßāößāĪ ßāśßā£ßāĪßāóßāśßāóßāŻßāóßā©ßāś ßā®ßāÉßāóßāÉßāĀßāößāæßāŻßāÜßāś ßāĪßāößāøßāśßā£ßāÉßāĀßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāÉßā£ßā«ßāśßāÜßāĢßāÉ
ßāÖßāśßāößāĢßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāØßāößāŚßāößāĪ ßāśßā£ßāĪßāóßāśßāóßāŻßāóßā©ßāś ßā®ßāÉßāóßāÉßāĀßāößāæßāŻßāÜßāś ßāĪßāößāøßāśßā£ßāÉßāĀßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāÉßā£ßā«ßāśßāÜßāĢßāÉNational Parliamentary Library of Georgia
╠²
11 ßāøßāÉßāĀßāóßāĪ, ßāĪßāÉßāźßāÉßāĀßāŚßāĢßāößāÜßāØßāĪ ßā×ßāÉßāĀßāÜßāÉßāøßāößā£ßāóßāśßāĪ ßāößāĀßāØßāĢßā£ßāŻßāÜßāś ßāæßāśßāæßāÜßāśßāØßāŚßāößāÖßāśßāĪ ßāĪßāÉßāÖßāØßā£ßāżßāößāĀßāößā£ßā¬ßāśßāØ ßāōßāÉßāĀßāæßāÉßā¢ßā©ßāś ßā¬ßāśßāżßāĀßāŻßāÜßāś ßāæßāśßāæßāÜßāśßāØßāŚßāößāÖßāÉ ŌĆ×ßāśßāĢßāößāĀßāśßāößāÜßāśßāĪ" ßā«ßāößāÜßāøßā½ßā”ßāĢßāÉßā£ßāößāÜßāøßāÉ ßāĀßāŻßāĪßāŻßāōßāÉßā£ ßāÉßāĪßāÉßāŚßāśßāÉßā£ßāøßāÉ ßā¼ßāÉßāĀßāøßāØßāÉßāōßāÆßāśßā£ßāÉ ßāøßāØßā«ßāĪßāößā£ßāößāæßāÉ ŌĆ×ßāśßā£ßāżßāØßāĀßāøßāÉßā¬ßāśßāśßāĪ ßāōßāśßāÆßāśßāóßāÉßāÜßāśßā¢ßāÉßā¬ßāśßāśßāĪ ßāŚßāÉßā£ßāÉßāøßāößāōßāĀßāØßāĢßāö ßāóßāößāźßā£ßāØßāÜßāØßāÆßāśßāößāæßāś ßāōßāÉ ßāøßāÉßāŚßāś ßāÆßāÉßāøßāØßā¦ßāößā£ßāößāæßāÉ". ßāøßāØßā«ßāĪßāößā£ßāößāæßāśßāĪ ßā©ßāößāøßāōßāößāÆ ßāÆßāÉßāśßāøßāÉßāĀßāŚßāÉ ßāōßāśßāĪßāÖßāŻßāĪßāśßāÉ.
ßāÉßā”ßā£ßāśßā©ßā£ßāŻßāÜßāś ßāøßāØßā«ßāĪßāößā£ßāößāæßāÉ ßā¼ßāÉßāĀßāøßāØßāÉßāōßāÆßāößā£ßāĪ 2013 ßā¼ßāÜßāśßāĪ 25-26 ßāŚßāößāæßāößāĀßāĢßāÉßāÜßāĪ ßāÖßāśßāößāĢßāśßāĪ (ßāŻßāÖßāĀßāÉßāśßā£ßāÉ) ßāÆßāØßāößāŚßāößāĪ ßāśßā£ßāĪßāóßāśßāóßāŻßāóßāśßāĪßāÉ ßāōßāÉ ßāŻßāÖßāĀßāÉßāśßā£ßāśßāĪ ßāĪßāÉßāæßāśßāæßāÜßāśßāØßāŚßāößāÖßāØ ßāÉßāĪßāØßā¬ßāśßāÉßā¬ßāśßāśßāĪ ßāößāĀßāŚßāØßāæßāÜßāśßāĢßāś ßāØßāĀßāÆßāÉßā£ßāśßā¢ßāößāæßāśßāŚ ßāÆßāÉßāøßāÉßāĀßāŚßāŻßāÜßāś ßāĪßāößāøßāśßā£ßāÉßāĀßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāÉßā£ßā«ßāśßāÜßāĢßāÉßāĪ.
ßāĪßāÉßāøßāÖßāśßāŚßā«ßāĢßāößāÜßāØ ßāōßāÉßāĀßāæßāÉßā¢ßāößāæßāśßāŚ ßāøßāØßāøßāĪßāÉßā«ßāŻßāĀßāößāæßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāÉßā£ßā¦ßāØßāżßāśßāÜßāößāæßāśßāĪ 2014 ßā¼ßāÜßāśßāĪ ßāÉßā£ßāÆßāÉßāĀßāśßā©ßāś
ßāĪßāÉßāøßāÖßāśßāŚßā«ßāĢßāößāÜßāØ ßāōßāÉßāĀßāæßāÉßā¢ßāößāæßāśßāŚ ßāøßāØßāøßāĪßāÉßā«ßāŻßāĀßāößāæßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāÉßā£ßā¦ßāØßāżßāśßāÜßāößāæßāśßāĪ 2014 ßā¼ßāÜßāśßāĪ ßāÉßā£ßāÆßāÉßāĀßāśßā©ßāśNational Parliamentary Library of Georgia
╠²
ßāößāĀßāØßāĢßā£ßāŻßāÜßāś ßāæßāśßāæßāÜßāśßāØßāŚßāößāÖßāśßāĪ ßāĪßāÉßāøßāÖßāśßāŚßā«ßāĢßāößāÜßāØ ßāōßāÉßāĀßāæßāÉßā¢ßāößāæßāśßāŚ ßāøßāØßāøßāĪßāÉßā«ßāŻßāĀßāößāæßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāÉßā£ßā¦ßāØßāżßāśßāÜßāößāæßāśßāĪ 2014 ßā¼ßāÜßāśßāĪ ßāÉßā£ßāÆßāÉßāĀßāśßā©ßāś - ßā×ßāĀßāößā¢ßāößā£ßāóßāÉßā¬ßāśßāÉMore Related Content
Viewers also liked (12)
Multimedia For Cultural Learning
Multimedia For Cultural LearningSanjay Goel
╠²
Sanjay Goel discusses the role of multimedia in cultural documentation and learning, emphasizing the integration of technology in understanding nature, society, and knowledge creation. He outlines the complexities of multimedia content, including its creation, quality, and the importance of cognitive mapping and categorization. The document also highlights the potential of digital libraries for cultural heritage, stressing the need for digitization and preservation of artifacts while facilitating research and dissemination.Final presentation
Final presentationHaran Sivakumar
╠²
This document summarizes the goals and process of creating an online educational resource by the Southern California Library focused on their collections related to the blacklisting of teachers in LA during the McCarthy era. The project aimed to increase accessibility of the library's resources using multimedia to reduce intimidation. Key steps included selecting a collection, designing an intuitive website with layered information and minimizing scrolling, integrating interfaces like timelines and document previews, and connecting elements while maintaining usability. Challenges included technical issues, and the site was launched at http://socallib.org/blacklistedTeachers to inspire future digital initiatives.Multimedia, undergrads and the library
Multimedia, undergrads and the libraryVic Divecha
╠²
The document discusses the role of multimedia and the library in undergraduate education. It notes that today's undergraduates are consumers and generators of multimedia content through their use of mobile devices. The library can play an important role by supporting multimedia production on campus through expertise, spaces, and training. The future role of the library is to identify disruptive technologies, embrace them, make them available to students, and help shape how they are used in education.Newman Library Multimedia Portal
Newman Library Multimedia Portalllrath5
╠²
The document discusses creating a portal to aggregate and share library-related instructional multimedia content such as tutorials, PDFs, videos, and Captivate files. The portal could be used for on-demand instruction, reinforcing classroom lessons, and integrating media into tutorials. Content may include tutorials on research strategies, interviews with library/college faculty and students, and marketing materials. The portal would be created in LibGuides and any librarian could add or share content. Potential issues include staff time, different file formats, and length of media.The interactive and multimedia library
The interactive and multimedia libraryHelMet-kirjasto
╠²
The document discusses plans for an interactive and multimedia library called the New Central Library in Helsinki, Finland. Some key points:
- The library will be 10,000 square meters and a hub of knowledge, skills, and stories, with 5,000 daily visitors and 1.5 million annual visitors.
- It will have a variety of spaces like events areas, meeting rooms, learning spaces, creative spaces, and studios.
- The library aims to be open and accessible to all, with some areas open 24/7. It will have a collection of 200,000 items both physical and electronic.
- Construction is estimated to begin in 2014 at a cost of around 69.9 million euros, withImportance of Multimedia
Importance of MultimediaSa├Łful ├Źslam
╠²
This presentation discusses the importance of multimedia, outlining its uses in various fields such as business, education, entertainment, home, and public places. Multimedia can benefit business through sales/marketing presentations, trade show production, staff training, and company kiosks. In education, multimedia is useful for courseware/simulations, e-learning, distance learning, and information searching. The presentation concludes by stating that as multimedia increasingly permeates various domains, it will become even more integral to the future world.Multimedia approach
Multimedia approachRahul Reghu
╠²
Multimedia is an important innovation in educational technology that can improve teaching and learning. It involves using various media like text, pictures, sound, animation and video together in a program. Multimedia approaches can be classified in different ways, such as by instructional methods, auto-instructional techniques, mass communication tools, audiovisual materials, experiential learning, and teaching resources. Implementing multimedia approaches requires changes to organizational structures, infrastructure, teacher training, and attitudes. It provides benefits like making learning more engaging, individualized, and memorable for students.Chapter 3 The Role of Multimedia in Education
Chapter 3 The Role of Multimedia in EducationSalina Saharudin
╠²
This document discusses the role of multimedia in education. It defines multimedia as communicating in multiple ways using elements like text, audio, video, graphics, animation, and interactivity. Multimedia can enhance teaching by allowing annotations during live lectures, freeing teachers from blackboards, and facilitating collaboration. It also reviews types of multimedia presentations and considers criteria for creating presentations in PowerPoint. The document outlines the four basic functions of the Internet in education: searching for and receiving information, publishing and providing information, communicating, and collaborating. It discusses best practices for multimedia development and the standard phases of multimedia production.Advantage and Disadvantages of MULTIMEDIA
Advantage and Disadvantages of MULTIMEDIAjopin_5
╠²
Technology and multimedia applications are becoming increasingly integrated into the academic and personal lives of students. This document discusses how technology is now part of daily life both in and out of school. The technological revolution will significantly impact how students learn, with curriculum emphasizing higher-order thinking skills, authentic tasks, and collaborative work rather than isolated skill-building. Multimedia activities can provide learning opportunities for students to develop real-world technology skills while expressing their knowledge.Importance of multimedia
Importance of multimediaOnline
╠²
Multimedia has many uses across several fields including business, education, entertainment, home, and public places. It can be used for sales presentations, staff training, course materials, games, movies, television, information kiosks, and more. As multimedia technologies continue to advance, they will become more integrated into more aspects of life and work.Introduction to multimedia
Introduction to multimediaZurina Yasak
╠²
This document introduces multimedia and its applications. It defines multimedia as a combination of text, graphics, sound, animation and video to effectively communicate ideas. It discusses two types of multimedia presentations: linear, which progresses without user control, and non-linear, which offers interactivity. It provides examples of linear and non-linear multimedia. It also outlines several applications of multimedia such as in creative industries, commerce, entertainment, engineering, science, medicine, education and more.Similar to Multimedia Library (20)
ßāĪßāÉßā¼ßāÉßāĢßāÜßāØ ßā×ßāĀßāØßāößāźßāóßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāößāÆßāøßāśßāĪ ßā©ßāÉßāæßāÜßāØßā£ßāś(Bolo variant)
ßāĪßāÉßā¼ßāÉßāĢßāÜßāØ ßā×ßāĀßāØßāößāźßāóßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāößāÆßāøßāśßāĪ ßā©ßāÉßāæßāÜßāØßā£ßāś(Bolo variant)lomadze70
╠²
ßāĪßāÉßā¼ßāÉßāĢßāÜßāØ ßā×ßāĀßāØßāößāźßāóßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāößāÆßāøßāśßāĪ ßā©ßāÉßāæßāÜßāØßā£ßāś(Bolo variant)
ßāĪßāÉßā¼ßāÉßāĢßāÜßāØ ßā×ßāĀßāØßāößāźßāóßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāößāÆßāøßāśßāĪ ßā©ßāÉßāæßāÜßāØßā£ßāś(Bolo variant)lomadze70
╠²
Nazi Dvalishvili
Nazi Dvalishvilinazidvalishvili
╠²
ßā©ßāößāøßāÉßā»ßāÉßāøßāößāæßāößāÜßāś ßāÆßāÉßāÖßāĢßāößāŚßāśßāÜßāś ßāøßāÉßāŚßāößāøßāÉßāŚßāśßāÖßāÉßā©ßāś.
II ßāÖßāÜßāÉßāĪßāś.
2011 ßā¼.ßāÖßāśßāößāĢßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāØßāößāŚßāößāĪ ßāśßā£ßāĪßāóßāśßāóßāŻßāóßā©ßāś ßā®ßāÉßāóßāÉßāĀßāößāæßāŻßāÜßāś ßāĪßāößāøßāśßā£ßāÉßāĀßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāÉßā£ßā«ßāśßāÜßāĢßāÉ
ßāÖßāśßāößāĢßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāØßāößāŚßāößāĪ ßāśßā£ßāĪßāóßāśßāóßāŻßāóßā©ßāś ßā®ßāÉßāóßāÉßāĀßāößāæßāŻßāÜßāś ßāĪßāößāøßāśßā£ßāÉßāĀßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāÉßā£ßā«ßāśßāÜßāĢßāÉNational Parliamentary Library of Georgia
╠²
11 ßāøßāÉßāĀßāóßāĪ, ßāĪßāÉßāźßāÉßāĀßāŚßāĢßāößāÜßāØßāĪ ßā×ßāÉßāĀßāÜßāÉßāøßāößā£ßāóßāśßāĪ ßāößāĀßāØßāĢßā£ßāŻßāÜßāś ßāæßāśßāæßāÜßāśßāØßāŚßāößāÖßāśßāĪ ßāĪßāÉßāÖßāØßā£ßāżßāößāĀßāößā£ßā¬ßāśßāØ ßāōßāÉßāĀßāæßāÉßā¢ßā©ßāś ßā¬ßāśßāżßāĀßāŻßāÜßāś ßāæßāśßāæßāÜßāśßāØßāŚßāößāÖßāÉ ŌĆ×ßāśßāĢßāößāĀßāśßāößāÜßāśßāĪ" ßā«ßāößāÜßāøßā½ßā”ßāĢßāÉßā£ßāößāÜßāøßāÉ ßāĀßāŻßāĪßāŻßāōßāÉßā£ ßāÉßāĪßāÉßāŚßāśßāÉßā£ßāøßāÉ ßā¼ßāÉßāĀßāøßāØßāÉßāōßāÆßāśßā£ßāÉ ßāøßāØßā«ßāĪßāößā£ßāößāæßāÉ ŌĆ×ßāśßā£ßāżßāØßāĀßāøßāÉßā¬ßāśßāśßāĪ ßāōßāśßāÆßāśßāóßāÉßāÜßāśßā¢ßāÉßā¬ßāśßāśßāĪ ßāŚßāÉßā£ßāÉßāøßāößāōßāĀßāØßāĢßāö ßāóßāößāźßā£ßāØßāÜßāØßāÆßāśßāößāæßāś ßāōßāÉ ßāøßāÉßāŚßāś ßāÆßāÉßāøßāØßā¦ßāößā£ßāößāæßāÉ". ßāøßāØßā«ßāĪßāößā£ßāößāæßāśßāĪ ßā©ßāößāøßāōßāößāÆ ßāÆßāÉßāśßāøßāÉßāĀßāŚßāÉ ßāōßāśßāĪßāÖßāŻßāĪßāśßāÉ.
ßāÉßā”ßā£ßāśßā©ßā£ßāŻßāÜßāś ßāøßāØßā«ßāĪßāößā£ßāößāæßāÉ ßā¼ßāÉßāĀßāøßāØßāÉßāōßāÆßāößā£ßāĪ 2013 ßā¼ßāÜßāśßāĪ 25-26 ßāŚßāößāæßāößāĀßāĢßāÉßāÜßāĪ ßāÖßāśßāößāĢßāśßāĪ (ßāŻßāÖßāĀßāÉßāśßā£ßāÉ) ßāÆßāØßāößāŚßāößāĪ ßāśßā£ßāĪßāóßāśßāóßāŻßāóßāśßāĪßāÉ ßāōßāÉ ßāŻßāÖßāĀßāÉßāśßā£ßāśßāĪ ßāĪßāÉßāæßāśßāæßāÜßāśßāØßāŚßāößāÖßāØ ßāÉßāĪßāØßā¬ßāśßāÉßā¬ßāśßāśßāĪ ßāößāĀßāŚßāØßāæßāÜßāśßāĢßāś ßāØßāĀßāÆßāÉßā£ßāśßā¢ßāößāæßāśßāŚ ßāÆßāÉßāøßāÉßāĀßāŚßāŻßāÜßāś ßāĪßāößāøßāśßā£ßāÉßāĀßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāÉßā£ßā«ßāśßāÜßāĢßāÉßāĪ.
ßāĪßāÉßāøßāÖßāśßāŚßā«ßāĢßāößāÜßāØ ßāōßāÉßāĀßāæßāÉßā¢ßāößāæßāśßāŚ ßāøßāØßāøßāĪßāÉßā«ßāŻßāĀßāößāæßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāÉßā£ßā¦ßāØßāżßāśßāÜßāößāæßāśßāĪ 2014 ßā¼ßāÜßāśßāĪ ßāÉßā£ßāÆßāÉßāĀßāśßā©ßāś
ßāĪßāÉßāøßāÖßāśßāŚßā«ßāĢßāößāÜßāØ ßāōßāÉßāĀßāæßāÉßā¢ßāößāæßāśßāŚ ßāøßāØßāøßāĪßāÉßā«ßāŻßāĀßāößāæßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāÉßā£ßā¦ßāØßāżßāśßāÜßāößāæßāśßāĪ 2014 ßā¼ßāÜßāśßāĪ ßāÉßā£ßāÆßāÉßāĀßāśßā©ßāśNational Parliamentary Library of Georgia
╠²
ßāößāĀßāØßāĢßā£ßāŻßāÜßāś ßāæßāśßāæßāÜßāśßāØßāŚßāößāÖßāśßāĪ ßāĪßāÉßāøßāÖßāśßāŚßā«ßāĢßāößāÜßāØ ßāōßāÉßāĀßāæßāÉßā¢ßāößāæßāśßāŚ ßāøßāØßāøßāĪßāÉßā«ßāŻßāĀßāößāæßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāÉßā£ßā¦ßāØßāżßāśßāÜßāößāæßāśßāĪ 2014 ßā¼ßāÜßāśßāĪ ßāÉßā£ßāÆßāÉßāĀßāśßā©ßāś - ßā×ßāĀßāößā¢ßāößā£ßāóßāÉßā¬ßāśßāÉßāĪßāÉßā¼ßāÉßāĢßāÜßāØ ßā×ßāĀßāØßāößāźßāóßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāößāÆßāøßāśßāĪ ßā©ßāÉßāæßāÜßāØßā£ßāś(Bolo variant)
ßāĪßāÉßā¼ßāÉßāĢßāÜßāØ ßā×ßāĀßāØßāößāźßāóßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāößāÆßāøßāśßāĪ ßā©ßāÉßāæßāÜßāØßā£ßāś(Bolo variant)lomadze70
╠²
ßāĪßāÉßā¼ßāÉßāĢßāÜßāØ ßā×ßāĀßāØßāößāźßāóßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāößāÆßāøßāśßāĪ ßā©ßāÉßāæßāÜßāØßā£ßāś(Bolo variant)
ßāĪßāÉßā¼ßāÉßāĢßāÜßāØ ßā×ßāĀßāØßāößāźßāóßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāößāÆßāøßāśßāĪ ßā©ßāÉßāæßāÜßāØßā£ßāś(Bolo variant)lomadze70
╠²
ßāÖßāśßāößāĢßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāØßāößāŚßāößāĪ ßāśßā£ßāĪßāóßāśßāóßāŻßāóßā©ßāś ßā®ßāÉßāóßāÉßāĀßāößāæßāŻßāÜßāś ßāĪßāößāøßāśßā£ßāÉßāĀßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāÉßā£ßā«ßāśßāÜßāĢßāÉ
ßāÖßāśßāößāĢßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāØßāößāŚßāößāĪ ßāśßā£ßāĪßāóßāśßāóßāŻßāóßā©ßāś ßā®ßāÉßāóßāÉßāĀßāößāæßāŻßāÜßāś ßāĪßāößāøßāśßā£ßāÉßāĀßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāÉßā£ßā«ßāśßāÜßāĢßāÉNational Parliamentary Library of Georgia
╠²
ßāĪßāÉßāøßāÖßāśßāŚßā«ßāĢßāößāÜßāØ ßāōßāÉßāĀßāæßāÉßā¢ßāößāæßāśßāŚ ßāøßāØßāøßāĪßāÉßā«ßāŻßāĀßāößāæßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāÉßā£ßā¦ßāØßāżßāśßāÜßāößāæßāśßāĪ 2014 ßā¼ßāÜßāśßāĪ ßāÉßā£ßāÆßāÉßāĀßāśßā©ßāś
ßāĪßāÉßāøßāÖßāśßāŚßā«ßāĢßāößāÜßāØ ßāōßāÉßāĀßāæßāÉßā¢ßāößāæßāśßāŚ ßāøßāØßāøßāĪßāÉßā«ßāŻßāĀßāößāæßāśßāĪ ßāÆßāÉßā£ßā¦ßāØßāżßāśßāÜßāößāæßāśßāĪ 2014 ßā¼ßāÜßāśßāĪ ßāÉßā£ßāÆßāÉßāĀßāśßā©ßāśNational Parliamentary Library of Georgia
╠²
Ad
More from Naniko Khouskivadze (7)
'ßāĀßāśßāōßāößāĀßāößāæßāśßāĪ' ßāōßāÉßāøßā¢ßāÉßāōßāößāæßāśßāĪ ßāÉßā£ßāÆßāÉßāĀßāśßā©ßāś
'ßāĀßāśßāōßāößāĀßāößāæßāśßāĪ' ßāōßāÉßāøßā¢ßāÉßāōßāößāæßāśßāĪ ßāÉßā£ßāÆßāÉßāĀßāśßā©ßāśNaniko Khouskivadze
╠²
Tr georgia 05 2010
Tr georgia 05 2010Naniko Khouskivadze
╠²
The document discusses various tools from Thomson Reuters for research evaluation, including Web of Science for analyzing scholarly literature and citations, EndNote Web for managing references and citations, and ResearcherID for identifying individual researchers and analyzing their impact, collaboration networks, and publications. It provides demonstrations of these tools' capabilities for analyzing research at the journal, institution, and individual researcher levels.'ßāĀßāśßāōßāößāĀßāößāæßāśßāĪ' ßāōßāÉßāøßā¢ßāÉßāōßāößāæßāśßāĪ ßāÉßā£ßāÆßāÉßāĀßāśßā©ßāś
'ßāĀßāśßāōßāößāĀßāößāæßāśßāĪ' ßāōßāÉßāøßā¢ßāÉßāōßāößāæßāśßāĪ ßāÉßā£ßāÆßāÉßāĀßāśßā©ßāśNaniko Khouskivadze
╠²
Ad
Multimedia Library
- 1. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >> ßāøßāŻßāÜßāóßāśßāøßāößāōßāśßāÉ ßāæßāśßāæßāÜßāśßāØßāŚßāößāÖßāÉ ßāśßāÜßāśßāÉßāĪ ßāĪßāÉßā«ßāößāÜßāøßā¼ßāśßāżßāØ ßāŻßā£ßāśßāĢßāößāĀßāĪßāśßāóßāößāóßāś
- 2. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >> 8
- 3. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >> 7
- 4. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >> 6
- 5. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >> 5
- 6. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >> 4
- 7. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >> 3
- 8. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >>
- 9. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >> PICTURE START
- 10. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >>
- 11. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >>
- 12. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >>
- 13. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >> - 2009ßāśßāōßāößāÉ ŌĆó ßāøßāÉßāĀßāśßā£ßāÉ ßāÉßāōßāÉßāøßāśßāÉ ŌĆó ßāæßāśßāæßāÜßāśßāØßāŚßāößāÖßāÉ
- 14. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >> ßāōßāØßā£ßāØßāĀßāś ŌĆó ßāĪßāÉßāøßā«ßāĀßāößāŚ ßāÖßāÉßāĢßāÖßāÉßāĪßāśßāÉßā©ßāś ßā©ßāĢßāößāśßā¬ßāÉßāĀßāśßāśßāĪ ßāŚßāÉßā£ßāÉßāøßā©ßāĀßāØßāøßāÜßāØßāæßāśßāĪ ßāØßāżßāśßāĪßāś
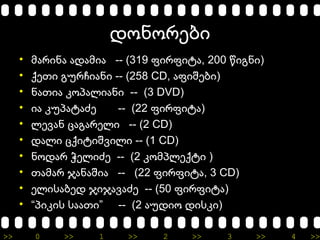
- 15. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >> ßāōßāØßā£ßāØßāĀßāößāæßāś ŌĆó -- (319 , 200 )ßāøßāÉßāĀßāśßā£ßāÉ ßāÉßāōßāÉßāøßāśßāÉ ßāżßāśßāĀßāżßāśßāóßāÉ ßā¼ßāśßāÆßā£ßāś ŌĆó -- (258ßāźßāößāŚßāś ßāÆßāŻßāĀßā®ßāśßāÉßā£ßāś CD, )ßāÉßāżßāśßā©ßāößāæßāś ŌĆó -- (3ßā£ßāÉßāŚßāśßāÉ ßāÖßāØßā×ßāÉßāÜßāśßāÉßā£ßāś DVD) ŌĆó -- (22 )ßāśßāÉ ßāÖßāŻßā×ßāÉßāóßāÉßā½ßāö ßāżßāśßāĀßāżßāśßāóßāÉ ŌĆó -- (2ßāÜßāößāĢßāÉßā£ ßā¬ßāÉßāÆßāÉßāĀßāößāÜßāś CD) ŌĆó -- (1ßāōßāÉßāÜßāś ßā¬ßāźßāśßāóßāśßā©ßāĢßāśßāÜßāś CD) ŌĆó -- (2 )ßā£ßāØßāōßāÉßāĀ ßāŁßāößāÜßāśßā½ßāö ßāÖßāØßāøßā×ßāÜßāößāźßāóßāś ŌĆó -- (22 , 3ßāŚßāÉßāøßāÉßāĀ ßā»ßāÉßā£ßāÉßā©ßāśßāÉ ßāżßāśßāĀßāżßāśßāóßāÉ CD) ŌĆó ßāößāÜßāśßāĪßāÉßāæßāößāō ßā»ßāśßā»ßāÉßāĢßāÉßā½ßāö -- (50 ßāżßāśßāĀßāżßāśßāóßāÉ) ŌĆó ŌĆ£ ŌĆØ -- (2 )ßā×ßāśßāÖßāśßāĪ ßāĪßāÉßāÉßāŚßāś ßāÉßāŻßāōßāśßāØ ßāōßāśßāĪßāÖßāś
- 16. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >> ßāóßāößāźßā£ßāśßāÖßāŻßāĀßāś ßāśßā£ßāżßāĀßāÉßāĪßāóßāĀßāŻßāźßāóßāŻßāĀßāÉ ŌĆó 4 (ßāÖßāØßāøßā×ßāśßāŻßāóßāößāĀßāś ąĪD/DVD) ŌĆó +ßāżßāśßāĀßāĪßāÉßāÖßāĀßāÉßāĢßāś ßāÆßāÉßāøßāÉßā½ßāÜßāśßāößāĀßāößāæßāößāÜßāś ŌĆó 5 ßā¦ßāŻßāĀßāĪßāÉßāĪßāøßāößā£ßāś
- 17. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >> ßāøßāŻßāĪßāśßāÖßāÉßāÜßāŻßāĀßāś ßāÖßāØßāÜßāößāźßā¬ßāśßāÉ
- 18. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >> ßāżßāśßāĀßāżßāśßāóßāößāæßāś 400 ßāößāĀßāŚßāößāŻßāÜßāś ßāōßāśßāĪßāÖßāößāæßāś 265 ßāößāĀßāŚßāößāŻßāÜßāś
- 19. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >> ßāÖßāśßā£ßāØ ßāÖßāØßāÜßāößāźßā¬ßāśßāÉ
- 20. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >> 35ßāŻßā£ßāśßāÖßāśßā£ßāØßāĪ ßāżßāśßāÜßāøßāś
- 21. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >> ßā¼ßāśßāÆßā£ßāÉßāōßāś ßāżßāØßā£ßāōßāś ßā¼ßāśßāÆßā£ßāößāæßāś - 80 ßāößāĀßāŚßāößāŻßāÜßāś - 50ßā£ßāØßāóßāößāæßāś ßāößāĀßāŚßāößāŻßāÜßāś
- 22. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >> ßāĀßāØßāÆßāØßāĀ ßāĢßāśßā×ßāØßāĢßāØßāŚ ßāĪßāÉßāĪßāŻßāĀßāĢßāößāÜßāś /ßāżßāśßāĀßāżßāśßāóßāÉ CD/DVD/ ?ßā¼ßāśßāÆßā£ßāś ßāößāÜßāößāźßāóßāĀßāØßā£ßāŻßāÜßāś ßāÖßāÉßāóßāÉßāÜßāØßāÆßāś opac.iliauni.edu.ge
- 23. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >> ßāĪßāÉßāøßāŻßā©ßāÉßāØ ßāĪßāÉßāÉßāŚßāößāæßāś ßāĪßāÉßāøßāŻßā©ßāÉßāØ ßāōßā”ßāößāößāæßāś ŌĆó ßāØßāĀßā©ßāÉßāæßāÉßāŚßāś ŌĆó ßāĪßāÉßāøßā©ßāÉßāæßāÉßāŚßāś ŌĆó ßāØßāŚßā«ßā©ßāÉßāæßāÉßāŚßāś ŌĆó ßā«ßāŻßāŚßā©ßāÉßāæßāÉßāŚßāś ŌĆó ßā×ßāÉßāĀßāÉßāĪßāÖßāößāĢßāś ŌĆó ßā©ßāÉßāæßāÉßāŚßāś ŌĆó ßāÖßāĢßāśßāĀßāÉ ßāĪßāÉßāøßāŻßā©ßāÉßāØ ßāĪßāÉßāÉßāŚßāößāæßāś ŌĆó 9.00 ŌĆō 21.00 ŌĆó 9.00 ŌĆō 21.00 ŌĆó 9.00 ŌĆō 21.00 ŌĆó 9.00 ŌĆō 21.00 ŌĆó 9.00 ŌĆō 21.00 ŌĆó 10.00 ŌĆō 18.00 ŌĆó 10.00 ŌĆō 18.00
- 24. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >> ßāøßāØßā«ßāøßāÉßāĀßāößāæßāśßāĪ ßā×ßāśßāĀßāØßāæßāößāæßāś ŌĆó ßāĀßāößāÆßāśßāĪßāóßāĀßāÉßā¬ßāśßāÉ ’āś ßāśßā£ßāóßāößāĀßā£ßāößāóßāśßāŚ ’āś ßāøßāØßāÖßāÜßāö ßāóßāößāźßāĪßāóßāŻßāĀßāś ßā©ßāößāóßā¦ßāØßāæßāśßā£ßāößāæßāśßāŚ ’āś ßāÉßāōßāÆßāśßāÜßā¢ßāö
- 25. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >> .... +1ßāōßāÉ ßāæßāØßāÜßāØßāĪ ßāÉßāźßā¬ßāśßāÉ
- 26. >> 0 >> 1 >> 2 >> 3 >> 4 >> ßāÆßāøßāÉßāōßāÜßāØßāæßāŚ ßā¦ßāŻßāĀßāÉßāōßā”ßāößāæßāśßāĪßāÉßāŚßāĢßāśßāĪ ’üŖ
