13
1 like977 views
Primary hilar techniques for isolation of the glissonian pedicles in major an minor liver resections
1 of 35
Downloaded 71 times


































Recommended
Qg view how it works



Qg view how it worksCorina Nikoloff
Ìę
The QuantiGene ViewRNA Assay diagram shows a process for fixing and permeabilizing cells to label RNA molecules within the cells with fluorescent probes called RNA-1 and RNA-2. The labeled RNA molecules are then detected and quantified to analyze gene expression levels.Glissonian approach for laparoscopic liver resections



Glissonian approach for laparoscopic liver resectionsMarcel Autran Machado
Ìę
Technique for intrahepatic Glissonian approach for laparoscopic right segmental liver resections is presented.
http://www.drmarcel.com.br31



31fundeni
Ìę
1) The surgical treatment of portal hypertension has evolved significantly in Egypt over the last century, driven by changes in liver pathology and the development of new techniques.
2) Initially, procedures like splenectomy were used but caused only temporary effects. Total portosystemic shunts were then introduced but were later abandoned due to high mortality and morbidity rates.
3) More selective surgeries and techniques were developed like Hassab's operation and mesocaval shunts but still had issues. The distal splenorenal shunt became more widely used as a selective shunt.29



29fundeni
Ìę
This document discusses endoscopic therapies for the management of variceal hemorrhage, specifically endoscopic sclerotherapy (EST) and endoscopic variceal ligation (EVL). It provides background on variceal bleeding and survival rates over time. It then describes the modalities and techniques of EST and EVL, including injection methods, sclerosing agents used, risks, and indications. Randomized controlled trials comparing EST and EVL are summarized, showing higher eradication rates with EVL. In conclusion, endoscopic therapies like EST and EVL are effective for controlling acute variceal bleeding and reducing recurrence when used for primary or secondary prophylaxis.25



25fundeni
Ìę
This document discusses chemotherapy options for biliary tree carcinoma. It begins by outlining the increasing mortality rates and poor prognosis of the disease. It then provides detailed information on the anatomical classification, histological classification, definition, risk factors, and problems associated with diagnosis and treatment. The document discusses surgery as the only potentially curative option but notes that most patients present with advanced, unresectable disease. It reviews several palliative chemotherapy regimens and their response rates and survival benefits, with various gemcitabine-based combinations showing the most promise. The challenges of treating this rare cancer are also summarized.22



22fundeni
Ìę
This document discusses the multimodal treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. It begins by noting that 70% of HCC occurs in patients with cirrhosis. Available treatment methods include surgical resection, liver transplantation, transarterial embolization, chemotherapy, and various ablation techniques. Surgical resection has improved and offers the best chance of cure for non-cirrhotic patients, though recurrence rates are high. Liver transplantation offers the best disease-free survival for selected cirrhotic patients meeting criteria such as tumor size and number, but organ shortage is a major limitation. Other treatments such as arterial embolization and chemotherapy have limited or debated efficacy.20



20fundeni
Ìę
This document summarizes a study comparing outcomes of surgical treatment for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) and hilar cholangiocarcinoma (Klatskin tumor). 59 patients who underwent liver resection for these tumors were analyzed. Klatskin tumors required more extensive resections and had higher postoperative morbidity. 5-year survival was similar for both tumor types at around 35%. Expression of the p27 protein was associated with lower recurrence rates and better survival outcomes. Surgical resection remains the primary treatment when possible but molecular markers may help guide future adjuvant therapies.34



34fundeni
Ìę
The document discusses the proximal splenorenal shunt procedure for patients with liver cirrhosis and portal hypertension combined with hypersplenism. The procedure involves creating a shunt from the splenic vein to the left renal vein to decompress the portal system. It is indicated for select patients as an alternative to other procedures to prevent variceal bleeding while removing the spleen. However, it carries risks of hepatic encephalopathy, worsening liver function, and is not suitable for future transplantation. The authors' experience with 17 patients who underwent this procedure is presented, along with postoperative outcomes.33



33fundeni
Ìę
The document discusses various treatment options for portal hypertension and its complications. It covers surgical procedures like devascularization operations, portosystemic shunts and splenorenal shunts that are aimed at preventing bleeding, stopping active bleeding, and preventing recurrent variceal bleeding. The choice of surgical treatment depends on factors like the severity of bleeding, liver dysfunction, and type of portal hypertension.32



32fundeni
Ìę
The document discusses different surgical treatments for portal hypertension between 1877-2003. It lists various types of shunt procedures that were developed over time to reduce portal pressure, including Eck-Pavlov-Vidal shunt in 1967, Warren shunt in 1967, and Starzl auxiliary liver transplantation in 1973. The document also discusses surgical treatments for Budd-Chiari syndrome and ascites, such as portocaval shunts, mesenterico-caval shunts, and LeVeen shunts. It concludes by providing data on the types of shunt procedures performed between 1997-2003 for portal hypertension treatment and their results.30



30fundeni
Ìę
TIPSS is a procedure that creates a permanent connection between the portal and hepatic veins to reduce portal hypertension. It has several indications including uncontrolled variceal bleeding and refractory ascites. The procedure involves catheterization of the jugular vein and placement of a stent. Complications can include thrombosis, hemorrhage, and encephalopathy. Success rates are over 80% for variceal bleeding and 50% for ascites, but secondary dysfunction occurs in 40% after 1 year often requiring revision. TIPSS provides immediate reduction in portal pressure and is less invasive than surgical shunting.28



28fundeni
Ìę
The document discusses pathogenesis and management of portal hypertension. It covers hemodynamic assessment of portal hypertension, causes of non-cirrhotic portal hypertension including nodular regenerative hyperplasia. Animal models of portal hypertension are described. The role of nitric oxide and endothelin in regulating vascular tone is discussed. Clinical consequences of cirrhotic portal hypertension include variceal bleeding. Management of acute variceal bleeding involves vasoactive drugs and endoscopic therapy. Secondary prophylaxis to prevent rebleeding involves non-selective beta-blockers or band ligation.24



24fundeni
Ìę
The document discusses guidelines for evaluating and treating hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer. It recommends investigations like CT, MRI, and ultrasound to evaluate metastases. Metastases are considered immediately resectable if the surgery is technically possible and leaves at least 40% of liver volume. Resection may be possible but risky if it requires complex procedures. Factors like number, size and location of metastases impact prognosis but are not absolute contraindications to resection. Repeat resection of recurrent metastases can provide long-term survival.23



23fundeni
Ìę
This document summarizes various radiation therapy modalities for treating hepatic malignant tumors. It discusses external beam radiotherapy techniques like conventional radiotherapy, 3D conformal radiotherapy, stereotactic radiotherapy, and proton radiotherapy. It also covers internal radiotherapy techniques like selective internal radiotherapy using yttrium microspheres, metabolic radiotherapy with iodine-131 lipiodol, and brachytherapy. The document provides details on each technique's dosimetry, efficacy, and safety considerations.21



21fundeni
Ìę
1. The document discusses the history and mechanisms of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for treating hepatic tumors. RFA uses alternating current within 200-1200 MHz to generate heat and coagulate tissue.
2. RFA can be performed percutaneously, laparoscopically, or during open surgery. Different ablation schemes and needle types are used depending on tumor size and location.
3. Complications of RFA include wound infection, bleeding, and abscesses. Studies show high rates of initial tumor necrosis but frequent recurrence within a year.19



19fundeni
Ìę
This document discusses the management of cholangiocarcinoma based on the author's experience at the Mansoura University Gastroenterology Surgical Center in Egypt. Some key points include:
- Cholangiocarcinoma is the second most common malignant liver tumor after hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Surgical resection remains the main treatment when possible but many cases are unresectable due to advanced stage at presentation.
- Of 385 patients treated between 1995-2002, 216 had central cholangiocarcinoma and most (79%) of these were unresectable.
- For unresectable cases, various palliative treatments were used with a mean survival of 5.818



18fundeni
Ìę
The document discusses classification and surgical treatment options for extrahepatic bile duct cancer. It examines preoperative biliary drainage and portal embolization. Surgical techniques discussed include laparoscopy, posterior approach, tumor resection, hepatectomy, and caudate lobe resection. Operative procedures and mortality are analyzed according to tumor location, TNM classification, and staging. Long-term survival outcomes are presented for different patient groups and surgical approaches.11



11fundeni
Ìę
1) This document discusses liver surgery for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), with a focus on techniques and outcomes in Japan.
2) The use of intraoperative ultrasound during liver surgery has enabled more limited and precise resections, such as subsegmentectomies, while preserving important vascular structures.
3) Hepatic resection for HCC has become much safer over time, with mortality rates decreasing to less than 1% at specialized centers due to techniques like intermittent inflow occlusion and precise limited resections guided by intraoperative ultrasound.8



8fundeni
Ìę
This document discusses antiviral therapy peri-liver transplantation. It provides data on primary liver disease in adult transplant recipients, with chronic hepatitis C being the most common at 20.7-40%. It also shows survival rates after transplantation by diagnosis. Therapeutic strategies for patients with HBV, HDV, and HCV undergoing liver transplantation aim to prevent recurrent infection of the graft. Recurrence of HBV infection is related to liver disease and HBV replicative status pre-transplant. Combination therapy with hepatitis B immune globulin and antiviral drugs like lamivudine is most effective for preventing HBV recurrence post-transplant according to various studies cited. Guidelines are provided for HBV prophylaxis and treatment of recurrence after6



6fundeni
Ìę
This document discusses liver transplantation for hepatitis C virus (HCV) disease. It outlines that HCV reinfection is common after transplantation, occurring in 87-97% of cases. There are different patterns of HCV recurrence post-transplant, including minimal liver injury, chronic HCV, and cholestatic HCV. Factors associated with increased rates of fibrosis post-transplant include older recipient age, bolus steroid use for rejection, induction with mycophenolic acid, and short duration of prednisone use. High pre-transplant HCV RNA levels are also associated with worse patient and graft survival outcomes.5



5fundeni
Ìę
- Liver resection (LR) and liver transplantation (LTx) are two treatment options for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This study compares outcomes of 282 patients receiving LR and 187 receiving LTx.
- Patients who received LTx had a higher perioperative mortality rate compared to LR patients (18.1% vs 4.5%), mainly due to sepsis, multiple organ failure, and vascular complications. Late mortality was higher in LR patients and mainly due to tumor recurrence.
- Recurrence rates were significantly higher after LR (47.4% vs 9%), and survival after recurrence was also lower with LR. Factors associated with recurrence and survival included tumor characteristics such as α-fetoprotein levels,8



8fundeni
Ìę
1. Antiviral therapy both before and after liver transplantation is important to prevent recurrent infection of the graft by hepatitis B and C viruses.
2. Combination therapy with hepatitis B immune globulin and antiviral drugs like lamivudine is effective at preventing HBV recurrence in most patients.
3. Recurrence of HCV infection after transplantation is very common, but antiviral treatment with interferon or pegylated interferon plus ribavirin can achieve sustained virologic response in some patients and prevent progression of liver disease.7



7fundeni
Ìę
This summarizes a case study of "domino liver transplantation" where the liver from a patient with familial hypercholesterolemia (FHC) was transplanted into a recipient with hepatocellular carcinoma. Specifically:
1) The donor liver from a woman with FHC was transplanted into a recipient with liver cirrhosis and cancer, normalizing the donor's cholesterol levels.
2) Initial results showed the recipient's liver function normalized while maintaining nearly normal cholesterol levels with treatment.
3) Further long-term follow-up is needed to monitor the recipient's cholesterol and tumor recurrence risk. The transplantation was considered a justified option given the recipient's condition and risk of future hypercholesterolemia4



4fundeni
Ìę
The document summarizes studies on using radioactive iodine-labeled lipiodol (131I lipiodol) as a neoadjuvant treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) prior to liver resection or transplantation. It found that 131I lipiodol allowed resection of larger HCC tumors (>3cm) with 3-year survival of 42%. For liver transplantation, 131I lipiodol prior to the procedure led to 5-year survival of 77% for HCC of all sizes, compared to 18% without neoadjuvant treatment, and no patients who received 131I lipiodol experienced HCC recurrence.Hingula.ppt- Rasadravya parichaya- NCISM



Hingula.ppt- Rasadravya parichaya- NCISMShri Shivayogeeshwar Rural Ayurvedic Medical college, INCHAL,
Ìę
Hingula(Cinnabar)
Synonyms - Churna Parada, Darada, Mleccha, Rasagarbha,Rasodbhava,
Shukatunda, Hamsapada, Lohagna
Mineralogical Identification
Chemical Formula- HgS
Chemical name- mercury sulfide
Nature â Crystalline
Colour- Bright Red
Crystal- Trigonal.
Clevage- -
Diaphaneity- Transparent to Translucent
Fracture- Uneven
Tenacity- Brittle
Lustre- Vitreous
Streak- Red
Sp. Gravity- 8 to 8.1
Hardness- 2 to 2.5
Sources
- It is found near volcanic region and near mercury mines(extracted).
- It is associated with other minerals like Stibnite, pyrite, realgar, calcite etc.
- Almaden (Spain), California, Texas.
Types
1) Charmara
2) Shukhatunda
3) Hamsapada ( Ap 2/69)
1) Khanija
2) Kritrima (RT 9/4)
Grahya ad Agrahyata
à€à€Șà€Ÿ à€à„à€žà„à€ź à€”à€°à„à€Łà€Ÿà€: à€Șà„à€·à€Ł à€žà„à€źà€šà„à€čà€°: |
à€źà€čà„à€à„à€”à€Ÿà€Čà„ à€à€Ÿà€°à€Șà„à€°à„à€Łà„ à€čà€żà€à€à„à€Č: à€¶à„à€°à„à€·à„à€ à€à€à„à€Żà€€à„ || RT 9/3
Doshas
Andya( Blindness)
Kshinata
Klama
Bhrama
Moha
Prameha ( AP 2/73)
Shodhana
1) Grahya Hingula ChurnaâArdraka rasa bhavana(7)--Shuddhahingula (RT 9/12)
Marana
Other Processing Techniques
Satwa Patana
-Shuddha HingulaâAdhaha patana/Urdhwa patana -Satva (Parada) (RRS â 3/144)
Yogas
Hinguleshwar rasa
Anandabhairava Rasa,
Mrutunjaya Rasa,
Tribhuvana keerti Rasa, etc.
Research Updates
A CONCEPTUAL REVIEW ON HINGULA (CINNABAR- HgS)
https://ijapr.in/index.php/ijapr/article/view/1237
EXTRACTION OF PARAD FROM HINGULA, A TRADITIONAL AYURVEDIC METHOD
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/323601866_EXTRACTION_OF_PARAD_FROM_HINGULA_A_TRADITIONAL_AYURVEDIC_METHOD
DrMahantesh.B.Rudrapuri,
M.D.(Ayu) FAGE , PGDYT
HOD Department of Rasa Shastra&BhaishajyaKalpana
Shri Shivayogeeshwar Rural Ayurvedic Medical College,
INCHAL â 591 102, Dist: Belgaum
Mob: 9972710790
More Related Content
More from fundeni (20)
33



33fundeni
Ìę
The document discusses various treatment options for portal hypertension and its complications. It covers surgical procedures like devascularization operations, portosystemic shunts and splenorenal shunts that are aimed at preventing bleeding, stopping active bleeding, and preventing recurrent variceal bleeding. The choice of surgical treatment depends on factors like the severity of bleeding, liver dysfunction, and type of portal hypertension.32



32fundeni
Ìę
The document discusses different surgical treatments for portal hypertension between 1877-2003. It lists various types of shunt procedures that were developed over time to reduce portal pressure, including Eck-Pavlov-Vidal shunt in 1967, Warren shunt in 1967, and Starzl auxiliary liver transplantation in 1973. The document also discusses surgical treatments for Budd-Chiari syndrome and ascites, such as portocaval shunts, mesenterico-caval shunts, and LeVeen shunts. It concludes by providing data on the types of shunt procedures performed between 1997-2003 for portal hypertension treatment and their results.30



30fundeni
Ìę
TIPSS is a procedure that creates a permanent connection between the portal and hepatic veins to reduce portal hypertension. It has several indications including uncontrolled variceal bleeding and refractory ascites. The procedure involves catheterization of the jugular vein and placement of a stent. Complications can include thrombosis, hemorrhage, and encephalopathy. Success rates are over 80% for variceal bleeding and 50% for ascites, but secondary dysfunction occurs in 40% after 1 year often requiring revision. TIPSS provides immediate reduction in portal pressure and is less invasive than surgical shunting.28



28fundeni
Ìę
The document discusses pathogenesis and management of portal hypertension. It covers hemodynamic assessment of portal hypertension, causes of non-cirrhotic portal hypertension including nodular regenerative hyperplasia. Animal models of portal hypertension are described. The role of nitric oxide and endothelin in regulating vascular tone is discussed. Clinical consequences of cirrhotic portal hypertension include variceal bleeding. Management of acute variceal bleeding involves vasoactive drugs and endoscopic therapy. Secondary prophylaxis to prevent rebleeding involves non-selective beta-blockers or band ligation.24



24fundeni
Ìę
The document discusses guidelines for evaluating and treating hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer. It recommends investigations like CT, MRI, and ultrasound to evaluate metastases. Metastases are considered immediately resectable if the surgery is technically possible and leaves at least 40% of liver volume. Resection may be possible but risky if it requires complex procedures. Factors like number, size and location of metastases impact prognosis but are not absolute contraindications to resection. Repeat resection of recurrent metastases can provide long-term survival.23



23fundeni
Ìę
This document summarizes various radiation therapy modalities for treating hepatic malignant tumors. It discusses external beam radiotherapy techniques like conventional radiotherapy, 3D conformal radiotherapy, stereotactic radiotherapy, and proton radiotherapy. It also covers internal radiotherapy techniques like selective internal radiotherapy using yttrium microspheres, metabolic radiotherapy with iodine-131 lipiodol, and brachytherapy. The document provides details on each technique's dosimetry, efficacy, and safety considerations.21



21fundeni
Ìę
1. The document discusses the history and mechanisms of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for treating hepatic tumors. RFA uses alternating current within 200-1200 MHz to generate heat and coagulate tissue.
2. RFA can be performed percutaneously, laparoscopically, or during open surgery. Different ablation schemes and needle types are used depending on tumor size and location.
3. Complications of RFA include wound infection, bleeding, and abscesses. Studies show high rates of initial tumor necrosis but frequent recurrence within a year.19



19fundeni
Ìę
This document discusses the management of cholangiocarcinoma based on the author's experience at the Mansoura University Gastroenterology Surgical Center in Egypt. Some key points include:
- Cholangiocarcinoma is the second most common malignant liver tumor after hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Surgical resection remains the main treatment when possible but many cases are unresectable due to advanced stage at presentation.
- Of 385 patients treated between 1995-2002, 216 had central cholangiocarcinoma and most (79%) of these were unresectable.
- For unresectable cases, various palliative treatments were used with a mean survival of 5.818



18fundeni
Ìę
The document discusses classification and surgical treatment options for extrahepatic bile duct cancer. It examines preoperative biliary drainage and portal embolization. Surgical techniques discussed include laparoscopy, posterior approach, tumor resection, hepatectomy, and caudate lobe resection. Operative procedures and mortality are analyzed according to tumor location, TNM classification, and staging. Long-term survival outcomes are presented for different patient groups and surgical approaches.11



11fundeni
Ìę
1) This document discusses liver surgery for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), with a focus on techniques and outcomes in Japan.
2) The use of intraoperative ultrasound during liver surgery has enabled more limited and precise resections, such as subsegmentectomies, while preserving important vascular structures.
3) Hepatic resection for HCC has become much safer over time, with mortality rates decreasing to less than 1% at specialized centers due to techniques like intermittent inflow occlusion and precise limited resections guided by intraoperative ultrasound.8



8fundeni
Ìę
This document discusses antiviral therapy peri-liver transplantation. It provides data on primary liver disease in adult transplant recipients, with chronic hepatitis C being the most common at 20.7-40%. It also shows survival rates after transplantation by diagnosis. Therapeutic strategies for patients with HBV, HDV, and HCV undergoing liver transplantation aim to prevent recurrent infection of the graft. Recurrence of HBV infection is related to liver disease and HBV replicative status pre-transplant. Combination therapy with hepatitis B immune globulin and antiviral drugs like lamivudine is most effective for preventing HBV recurrence post-transplant according to various studies cited. Guidelines are provided for HBV prophylaxis and treatment of recurrence after6



6fundeni
Ìę
This document discusses liver transplantation for hepatitis C virus (HCV) disease. It outlines that HCV reinfection is common after transplantation, occurring in 87-97% of cases. There are different patterns of HCV recurrence post-transplant, including minimal liver injury, chronic HCV, and cholestatic HCV. Factors associated with increased rates of fibrosis post-transplant include older recipient age, bolus steroid use for rejection, induction with mycophenolic acid, and short duration of prednisone use. High pre-transplant HCV RNA levels are also associated with worse patient and graft survival outcomes.5



5fundeni
Ìę
- Liver resection (LR) and liver transplantation (LTx) are two treatment options for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This study compares outcomes of 282 patients receiving LR and 187 receiving LTx.
- Patients who received LTx had a higher perioperative mortality rate compared to LR patients (18.1% vs 4.5%), mainly due to sepsis, multiple organ failure, and vascular complications. Late mortality was higher in LR patients and mainly due to tumor recurrence.
- Recurrence rates were significantly higher after LR (47.4% vs 9%), and survival after recurrence was also lower with LR. Factors associated with recurrence and survival included tumor characteristics such as α-fetoprotein levels,8



8fundeni
Ìę
1. Antiviral therapy both before and after liver transplantation is important to prevent recurrent infection of the graft by hepatitis B and C viruses.
2. Combination therapy with hepatitis B immune globulin and antiviral drugs like lamivudine is effective at preventing HBV recurrence in most patients.
3. Recurrence of HCV infection after transplantation is very common, but antiviral treatment with interferon or pegylated interferon plus ribavirin can achieve sustained virologic response in some patients and prevent progression of liver disease.7



7fundeni
Ìę
This summarizes a case study of "domino liver transplantation" where the liver from a patient with familial hypercholesterolemia (FHC) was transplanted into a recipient with hepatocellular carcinoma. Specifically:
1) The donor liver from a woman with FHC was transplanted into a recipient with liver cirrhosis and cancer, normalizing the donor's cholesterol levels.
2) Initial results showed the recipient's liver function normalized while maintaining nearly normal cholesterol levels with treatment.
3) Further long-term follow-up is needed to monitor the recipient's cholesterol and tumor recurrence risk. The transplantation was considered a justified option given the recipient's condition and risk of future hypercholesterolemia4



4fundeni
Ìę
The document summarizes studies on using radioactive iodine-labeled lipiodol (131I lipiodol) as a neoadjuvant treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) prior to liver resection or transplantation. It found that 131I lipiodol allowed resection of larger HCC tumors (>3cm) with 3-year survival of 42%. For liver transplantation, 131I lipiodol prior to the procedure led to 5-year survival of 77% for HCC of all sizes, compared to 18% without neoadjuvant treatment, and no patients who received 131I lipiodol experienced HCC recurrence.Recently uploaded (20)
Hingula.ppt- Rasadravya parichaya- NCISM



Hingula.ppt- Rasadravya parichaya- NCISMShri Shivayogeeshwar Rural Ayurvedic Medical college, INCHAL,
Ìę
Hingula(Cinnabar)
Synonyms - Churna Parada, Darada, Mleccha, Rasagarbha,Rasodbhava,
Shukatunda, Hamsapada, Lohagna
Mineralogical Identification
Chemical Formula- HgS
Chemical name- mercury sulfide
Nature â Crystalline
Colour- Bright Red
Crystal- Trigonal.
Clevage- -
Diaphaneity- Transparent to Translucent
Fracture- Uneven
Tenacity- Brittle
Lustre- Vitreous
Streak- Red
Sp. Gravity- 8 to 8.1
Hardness- 2 to 2.5
Sources
- It is found near volcanic region and near mercury mines(extracted).
- It is associated with other minerals like Stibnite, pyrite, realgar, calcite etc.
- Almaden (Spain), California, Texas.
Types
1) Charmara
2) Shukhatunda
3) Hamsapada ( Ap 2/69)
1) Khanija
2) Kritrima (RT 9/4)
Grahya ad Agrahyata
à€à€Șà€Ÿ à€à„à€žà„à€ź à€”à€°à„à€Łà€Ÿà€: à€Șà„à€·à€Ł à€žà„à€źà€šà„à€čà€°: |
à€źà€čà„à€à„à€”à€Ÿà€Čà„ à€à€Ÿà€°à€Șà„à€°à„à€Łà„ à€čà€żà€à€à„à€Č: à€¶à„à€°à„à€·à„à€ à€à€à„à€Żà€€à„ || RT 9/3
Doshas
Andya( Blindness)
Kshinata
Klama
Bhrama
Moha
Prameha ( AP 2/73)
Shodhana
1) Grahya Hingula ChurnaâArdraka rasa bhavana(7)--Shuddhahingula (RT 9/12)
Marana
Other Processing Techniques
Satwa Patana
-Shuddha HingulaâAdhaha patana/Urdhwa patana -Satva (Parada) (RRS â 3/144)
Yogas
Hinguleshwar rasa
Anandabhairava Rasa,
Mrutunjaya Rasa,
Tribhuvana keerti Rasa, etc.
Research Updates
A CONCEPTUAL REVIEW ON HINGULA (CINNABAR- HgS)
https://ijapr.in/index.php/ijapr/article/view/1237
EXTRACTION OF PARAD FROM HINGULA, A TRADITIONAL AYURVEDIC METHOD
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/323601866_EXTRACTION_OF_PARAD_FROM_HINGULA_A_TRADITIONAL_AYURVEDIC_METHOD
DrMahantesh.B.Rudrapuri,
M.D.(Ayu) FAGE , PGDYT
HOD Department of Rasa Shastra&BhaishajyaKalpana
Shri Shivayogeeshwar Rural Ayurvedic Medical College,
INCHAL â 591 102, Dist: Belgaum
Mob: 9972710790
Non-Invasive ICP Monitoring for Neurosurgeons



Non-Invasive ICP Monitoring for NeurosurgeonsDhaval Shukla
Ìę
This presentation delves into the latest advancements in non-invasive intracranial pressure (ICP) monitoring techniques, specifically tailored for neurosurgeons. It covers the importance of ICP monitoring in clinical practice, explores various non-invasive methods, and discusses their accuracy, reliability, and clinical applications. Attendees will gain insights into the benefits of non-invasive approaches over traditional invasive methods, including reduced risk of complications and improved patient outcomes. This comprehensive overview is designed to enhance the knowledge and skills of neurosurgeons in managing patients with neurological conditions.
Invasive systems are commonly used for monitoring intracranial pressure (ICP) in traumatic brain injury (TBI) and are considered the gold standard. The availability of invasive ICP monitoring is heterogeneous, and in low- and middle-income settings, these systems are not routinely employed due to high cost or limited accessibility. The aim of this presentation is to develop recommendations to guide monitoring and ICP-driven therapies in TBI using non-invasive ICP (nICP) systems.
Solubilization in Pharmaceutical Sciences: Concepts, Mechanisms & Enhancement...



Solubilization in Pharmaceutical Sciences: Concepts, Mechanisms & Enhancement...KHUSHAL CHAVAN
Ìę
This presentation provides an in-depth understanding of solubilization and its critical role in pharmaceutical formulations. It covers:
Definition & Mechanisms of Solubilization
Role of surfactants, micelles, and bile salts in drug solubility
Factors affecting solubilization (pH, polarity, particle size, temperature, etc.)
Methods to enhance drug solubility (Buffers, Co-solvents, Surfactants, Complexation, Solid Dispersions)
Advanced approaches (Polymorphism, Salt Formation, Co-crystallization, Prodrugs)
This resource is valuable for pharmaceutical scientists, formulation experts, regulatory professionals, and students interested in improving drug solubility and bioavailability.Acute & Chronic Inflammation, Chemical mediators in Inflammation and Wound he...



Acute & Chronic Inflammation, Chemical mediators in Inflammation and Wound he...Ganapathi Vankudoth
Ìę
A complete information of Inflammation, it includes types of Inflammation, purpose of Inflammation, pathogenesis of acute inflammation, chemical mediators in inflammation, types of chronic inflammation, wound healing and Inflammation in skin repair, phases of wound healing, factors influencing wound healing and types of wound healing.MORPHOLOGICAL FEATURES OF PNEUMONIA.....



MORPHOLOGICAL FEATURES OF PNEUMONIA.....maheenmazhar021
Ìę
This presentation provides a detailed exploration of the morphological and microscopic features of pneumonia, covering its histopathology, classification, and clinical significance. Designed for medical students, pathologists, and healthcare professionals, this lecture differentiates bacterial vs. viral pneumonia, explains lobar, bronchopneumonia, and interstitial pneumonia, and discusses diagnostic imaging patterns.
đĄ Key Topics Covered:
â
Normal lung histology vs. pneumonia-affected lung
â
Morphological changes in lobar, bronchopneumonia, and interstitial pneumonia
â
Microscopic features: Fibroblastic plugs, alveolar septal thickening, inflammatory cell infiltration
â
Stages of lobar pneumonia: Congestion, Red hepatization, Gray hepatization, Resolution
â
Common causative pathogens (Streptococcus pneumoniae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Mycoplasma, etc.)
â
Clinical case study with diagnostic approach and differentials
đŹ Who Should Watch?
This is an essential resource for medical students, pathology trainees, and respiratory health professionals looking to enhance their understanding of pneumoniaâs morphological aspects.Macafem Reviews 2024 - Macafem for Menopause Symptoms



Macafem Reviews 2024 - Macafem for Menopause SymptomsMacafem Supplement
Ìę
At Macafem, we provide 100% natural support for women navigating menopause. For over 20 years, we've helped women manage symptoms, and in 2024, we're proud to share their heartfelt experiences.SAPIENT Medi-trivia Quiz (FINALS) | TRI-ORTA 2025



SAPIENT Medi-trivia Quiz (FINALS) | TRI-ORTA 2025Dr. Anindya
Ìę
Final Round of SAPIENT Medi-trivia quiz
Part of TRI-ORTA 2025
Venue: GLT, Medical College Kolkata
Date: 25-02-2025Correlation of vitamin D level with prediabetes status_Dr Ahmed Al Montasir_f...



Correlation of vitamin D level with prediabetes status_Dr Ahmed Al Montasir_f...zilkerapurbo
Ìę
Correlation of vitamin D level with prediabetes statusPharm test bank- 12th lehne pharmacology nursing class



Pharm test bank- 12th lehne pharmacology nursing classkoxoyav221
Ìę
A pediatric nursing course is designed to prepare nursing students to provide specialized care for infants, children, and adolescents. The course integrates developmental, physiological, and psychological aspects of pediatric health and illness, emphasizing family-centered care. Below is a detailed breakdown of what you can expect in a pediatric nursing course:
1. Course Overview
Focuses on growth and development, health promotion, and disease prevention.
Covers common pediatric illnesses and conditions.
Emphasizes family dynamics, cultural competence, and ethical considerations in pediatric care.
Integrates clinical skills, including medication administration, assessment, and communication with children and families.
2. Key Topics Covered
A. Growth and Development
Neonates (0-28 days): Reflexes, feeding patterns, thermoregulation.
Infants (1 month - 1 year): Milestones, immunization schedule, nutrition.
Toddlers (1-3 years): Language development, toilet training, injury prevention.
Preschoolers (3-5 years): Cognitive and social development, school readiness.
School-age children (6-12 years): Psychosocial development, peer relationships.
Adolescents (13-18 years): Puberty, identity formation, risk-taking behaviors.
B. Pediatric Assessment
Head-to-toe assessment in children (differences from adults).
Vital signs (normal ranges vary by age).
Pain assessment using age-appropriate scales (FLACC, Wong-Baker, Numeric).
C. Pediatric Disease Conditions
Respiratory disorders: Asthma, bronchiolitis, pneumonia, cystic fibrosis.
Cardiac conditions: Congenital heart defects, Kawasaki disease.
Neurological disorders: Seizures, meningitis, cerebral palsy.
Gastrointestinal disorders: GERD, pyloric stenosis, intussusception.
Endocrine conditions: Diabetes mellitus type 1, congenital hypothyroidism.
Hematologic disorders: Sickle cell anemia, hemophilia, leukemia.
Infectious diseases: Measles, mumps, rubella, chickenpox.
Mental health concerns: Autism spectrum disorder, ADHD, eating disorders.
D. Pediatric Pharmacology
Medication administration (oral, IV, IM, subcutaneous).
Weight-based dosing calculations (mg/kg).
Common pediatric medications (antibiotics, analgesics, vaccines).
Parenteral nutrition and fluid management.
E. Pediatric Emergency & Critical Care
Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) basics.
Recognizing signs of deterioration (early vs. late signs).
Shock, dehydration, respiratory distress management.
F. Family-Centered Care & Communication
Parental involvement in care decisions.
Therapeutic communication with children at different developmental stages.
Cultural considerations in pediatric care.
G. Ethical and Legal Issues in Pediatric Nursing
Informed consent for minors.
Mandatory reporting of abuse and neglect.
Palliative care and end-of-life considerations in pediatrics.
3. Clinical Component
Hands-on experience in pediatric hospital units, clinics, or community settings.
Performing assessments and interventions under supervision.
Case study discMultimodal Approaches to Clitoral Augmentation for FGM (PRP _ filler)"



Multimodal Approaches to Clitoral Augmentation for FGM (PRP _ filler)"Rehab Aboshama
Ìę
Multimodal Approaches to Clitoral Augmentation for FGM (PRP _ filler)"
PresentaciĂł "Projecte Benestar". MWC 2025



PresentaciĂł "Projecte Benestar". MWC 2025Badalona Serveis Assistencials
Ìę
PresentaciĂł que va acompanyar la demostraciĂł prĂ ctica de metge d'InnovaciĂł JosĂ© Ferrer sobre el projecte Benestar de BSA, nom d'IDIAP Pere Gol, el 5 de març de 2025 a l'estand de XarSMART al Mobible Word Congress. Best Sampling Practices Webinar â USP <797> Compliance & Environmental Monito...



Best Sampling Practices Webinar â USP <797> Compliance & Environmental Monito...NuAire
Ìę
Best Sampling Practices Webinar â USP <797> Compliance & Environmental Monitoring
Are your cleanroom sampling practices USP <797> compliant? This webinar, hosted by Pharmacy Purchasing & Products (PP&P Magazine) and sponsored by NuAire, features microbiology expert Abby Roth discussing best practices for surface & air sampling, data analysis, and compliance.
đĄ Key Topics Covered:
âïž Viable air & surface sampling best practices
âïž USP <797> requirements & compliance strategies
âïž How to analyze & trend viable sample data
âïž Improving environmental monitoring in cleanrooms
đ„ Watch Now: https://www.nuaire.com/resources/best-sampling-practices-cleanroom-usp-797
đą Stay informedâfollow Abby Roth on LinkedIn for more cleanroom insights!BIOMECHANICS OF THE MOVEMENT OF THE SHOULDER COMPLEX.pptx



BIOMECHANICS OF THE MOVEMENT OF THE SHOULDER COMPLEX.pptxdrnidhimnd
Ìę
The shoulder complex acts as in coordinated fashion to provide the smoothest and greatest range of motion possible of the upper limb.
Combined motion of GH and ST joint of shoulder complex helps in:
Distribution of motion between other two joints.
Maintenance of glenoid fossa in optimal position.
Maintenance of good length tension
Although some amount of glenohumeral motion may occur while the other shoulder articulations remain stabilized, movement of the humerus more commonly involves some movement at all three shoulder joints.
PARIS SYSTEM FOR URINE CYTOLOGY paris system of reporting urine slidespptx



PARIS SYSTEM FOR URINE CYTOLOGY paris system of reporting urine slidespptxDrDivitasaxena1
Ìę
Paris system for reporting urine cytologyHingula.ppt- Rasadravya parichaya- NCISM



Hingula.ppt- Rasadravya parichaya- NCISMShri Shivayogeeshwar Rural Ayurvedic Medical college, INCHAL,
Ìę
Acute & Chronic Inflammation, Chemical mediators in Inflammation and Wound he...



Acute & Chronic Inflammation, Chemical mediators in Inflammation and Wound he...Ganapathi Vankudoth
Ìę
13
- 1. PRIMARY HILAR TECHNIQUES FOR ISOLATION OF THE GLISSONIAN PEDICLES IN MAJOR AND MINOR LIVER RESECTIONS Authors: I. CĂźmpeanu, M. Bogdan, T. Artenie, R. Petrescu, I. Lucescu Clinical 1-st Department of Surgeryâ Clinical and Emergency Central Military Hospital âDr. Carol Davilaâ - Bucharest April 2003
- 2. MOTTO: âExtra-fascial control of the pedicles has been a definite progress and has simplified considerably sectorectomies and segmentectomiesâ Couinaud C., 1989
- 3. MOTTO: Glissonean pedicle transection method prevented intraoperative metastasis and significantly improved the postoperative survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Tsuruta K. &col., Hepato-Gastroenterology 2002
- 4. Classic hilar dissection: complicated and dangerous A. cisticÄ AH seg IV VPS AHS VPD AHD VP Artera hepaticÄ proprie
- 5. Placa hilarÄ (centralÄ) V-VIII Placa glissonianÄ stangÄ Teci glissoniene II VI-VII IV III Placa vezicularÄ Placa ombilicalÄ GLISSONIAN PLATES AND SHEATHS
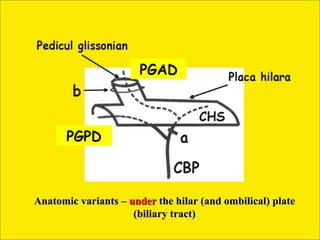
- 6. PGAD PGPD Anatomic variants â under the hilar (and ombilical) plate (biliary tract)
- 8. Right hilar extension (detail)
- 9. Ischaemic limits of segment VI (modal distribution)
- 10. D Isolation of the RPGP (PGPD) Risk of damaging right inferior in the Raynaud-Coucoravas retro-hepatic vein (VRHID) when point (RC) attempting to isolate RPGP (PGPD) - VI (A)=PG angular segment VI - (cadaverous dissection)
- 13. V(S)HM V(S)HD PlacÄ hilarÄ V(S)HS Takasaki-Couinaud Couinaud Lazorthes Launois Launois COMPLEX EXTRAGLISSONIAN APPROACH HILAR PLATE DESCENDING
- 14. 1 3 Placa Lob pÄtrat VB (IVb) CUSA VB Hilar plate descending - Couinaud 2 4 Coborarea PH Posterior approach (segment IX)
- 15. Placa cisticÄ Lig rotund IVb IV Linia SPP PPPS PPS (PGPS) PPD PPPD Couinaud (PGPD) Takasaki-Couinaud
- 16. ISOLATION OF THE GLISSONIAN PEDICLES FOR THE LEFT HEMI-LIVER
- 17. Couinaud technique for the isolation of the LPPP (PPPS)
- 18. Launois technique (posterior approach) for the isolation of the LPPP (PPPS). a)=schematic draw
- 19. III IVb Isolation of glissonian pedicles for II and III
- 20. Lig. rotund Pedicul seg. III Pedicul seg. IV PlacÄ ombilicalÄ PPPS clampat RESECTION OF SEGMENT III
- 21. 2. 1. Resection of segment III 3. 4.
- 22. Ombilical plate â epiportal view
- 23. ISOLATION OF THE GLISSONIAN PEDICLES FOR THE RIGHT HEMI-LIVER
- 24. (IX) TYPE OF PERIHILAR INCISIONS USED FOR EXTRAGLISSONIAN APPROACH
- 25. Placa cisticÄ Lig rotund IVb IV Linia SPP PPPS PPS (PGPS) PPD Couinaud PPPD (PGPD) Takasaki-Couinaud
- 27. LAUNOIS technique for the isolation of the RPPP (PPPD, PGPD)
- 29. Ligature level of the glissonian pedicles (right lobe)
- 30. Posterior approach Launois â anatomic portal variant of the right lobe
- 31. Anterior variants of the RPS (SPD)
- 32. SPD Sector paramedian drept SPP Fosa V.B. Ischaemic limits of the anterior (paramedian) sector of the right lobe, with the visualisation of the MPS and RPS (anterior right glissonian pedicle clamped) â amodal variant of RPS (SPD)
- 33. Scizura portÄ principalÄ Scizura portÄ dreaptÄ
- 34. Linie SPD V.B. Pedicul lateral drept ( clampat ) Modal variant of RPS (SPD)
- 35. SPD V.B. VI Glissonian pedicle for VI â clamped (amodal distribution)









