1 of 16
Download to read offline















Recommended
switch mode Power supply



switch mode Power supplyBits
╠²
The document discusses switch mode power supplies (SMPS) which are used in computers. An SMPS takes a single AC input and converts it to multiple DC outputs required by different computer components. It provides efficient power regulation by converting AC to DC and regulating voltages like 3.3V, 5V and 12V used by the microprocessor, chipset and disk drives respectively. The document also describes the different types of power supplies and connectors used in older and modern computers.Study of power supply used in computers



Study of power supply used in computerssyed mehdi raza
╠²
The document discusses power supplies used in computers. It begins by introducing switching mode power supplies (SMPS) which convert high voltage AC to low voltage DC required by electronic devices. It then identifies various specifications to consider when selecting an SMPS, including size, wattage, connectors, and form factor. Different SMPS connectors are discussed, including ATX, 24-pin, Molex, SATA, and PCI-E connectors which provide power to various computer components from the SMPS.Smps



SmpsAMZAD KHAN
╠²
SMPS (switch mode power supply) converts AC voltage to DC voltage to power computer components. It uses a fan to dissipate heat. SMPS has input and output sockets for AC voltage and provides DC voltage through connectors on the motherboard and devices. It includes various power connectors like ATX, peripheral, and floppy drive connectors to supply power to different components.Smps



SmpsAmzad Khan
╠²
SMPS (switch mode power supply) converts AC voltage to DC voltage to power computer components. It uses a fan to dissipate heat. SMPS has input sockets for AC power and sometimes provides output AC power to monitors. It supplies DC power to devices through connectors on the motherboard and peripherals like ATX, peripheral, floppy drive, and Molex connectors. Splitters are sometimes used to provide additional power connections when there are not enough built-in connectors.Deep dive into_pc_power supplies_2019



Deep dive into_pc_power supplies_2019youmansb
╠²
The document provides information about PC power supplies:
- Power supplies are the most failure-prone and replaced component in PCs. A malfunctioning power supply can cause other components to malfunction or be damaged.
- Power supplies convert electrical power to energy for components using constant voltage switching regulation to output steady voltages regardless of input.
- Power supplies have independent voltage rails (+3.3V, +5V, +12V) to power different components, though cheaper models have less independent circuitry.
- Form factors like ATX, SFX, EPS define standard sizes for compatibility and replacement of power supplies. Larger power supplies use EPS formats.Power Supply



Power SupplyAshish KC
╠²
This lecture slide describes in detail about the power supply unit in the computer system and its various types.Computer hardware



Computer hardwaresuraj pandey
╠²
The document discusses computer hardware and power supplies. It defines computer hardware as the physical parts of a computer system like the case, monitor, keyboard, and internal components. It then discusses different types of power supplies including AT, ATX, and ATX12V power supplies. These convert AC power to DC voltages needed by computer components like the motherboard and convert higher voltages to lower ones needed by CPUs. Switched mode power supplies are also covered, describing how they more efficiently regulate and deliver power than linear supplies.Presentation (1) (1).pptx



Presentation (1) (1).pptxKranthikumargurajala
╠²
This document discusses various power supply connectors used in PC systems. It describes the main power connectors for AT and ATX power supplies, including the 24-pin ATX connector. Additional connectors covered include the 4-pin and 8-pin ATX 12V connectors for powering the CPU, Molex connectors for peripherals, SATA connectors for hard drives, and 6-pin and 8-pin PCIe connectors for graphics cards. Floppy drive connectors are also briefly mentioned. Diagrams and pinouts are provided for each connector type.Power supply



Power supplymelary24
╠²
A power supply converts high voltage alternating current (AC) from a wall outlet to lower voltage direct current (DC) needed to power a computer. It regulates voltages like +3.3V, +5V and +12V and protects the system from overloads. Standards like ATX define form factors and connectors to ensure compatibility between power supplies and computer components. Power supplies are rated based on their ability to continuously supply power on the +12V rail, which powers today's processors and graphics cards.Power Supply



Power SupplyMOHIT DADU
╠²
This will give the information related to power supply into the computer system and provide the basic information about common power supply in AT and ATX Standards and Efficiency of Power supply Unit.Power supply



Power supplyshaylor_swift
╠²
The document discusses different power supply standards for PCs, including AT, ATX, and BTX. It provides details on the connectors, pinouts, and voltages associated with each standard. It also addresses questions about compatibility between different form factors and how to identify a defective power supply.Power sources complete



Power sources completeAnand Kumar
╠²
The document discusses power supplies and voltage regulation for embedded systems. It describes how AC voltage from wall outlets must be converted to lower DC voltage and how this can be done using AC adapters, plug packs or by incorporating a bridge rectifier. It also discusses using linear regulators and switching regulators to provide a constant voltage from a varying power source like a battery. Linear regulators are simple to use but less efficient while switching regulators require more components but are more versatile. Low dropout regulators consume less power and are well-suited for low power embedded applications.Unit 3- power supplies



Unit 3- power suppliesBalaji Bhanu
╠²
The document discusses various components of computer power supplies. It describes how power supplies convert AC power to DC power required by computer components. Power supplies have cables that supply different voltages to parts like the motherboard. Power supply wattage requirements depend on the system configuration, with 500W sufficient for most average systems. Graphics cards may use additional 6-pin or 8-pin power connectors. The document also discusses switch mode power supplies, universal power cables, and uninterruptted power supplies (UPS).Power supply



Power supplyjaihra17
╠²
The power supply unit (PSU) supplies power to computer components by converting AC power from wall outlets to lower DC voltages. It connects to the motherboard and other components using various cables that provide different voltages like +3.3V, +5V, and +12V. Common power cables include the ATX 24-pin main power cable for the motherboard, 4-pin and 8-pin cables for additional +12V power to components like CPUs, and SATA and PCIe cables to provide power to hard drives and graphics cards.video.ppt



video.pptssuser66b5c5
╠²
The document discusses different types of power supplies used in computers. It describes linear power supplies which use transformers to convert voltage and have good line and load regulation. It then focuses on switched mode power supplies (SMPS) which have higher efficiency. An SMPS uses a switching regulator to convert high voltage DC to lower DC levels needed by components. It discusses AT and ATX power supply formats used in older and newer computers respectively. The document also covers characteristics like wattage, efficiency and regulation as well as potential power problems and protective devices like surge suppressors and UPS systems.Chapter-5.ppt



Chapter-5.pptManuE45
╠²
The document discusses different types of power supplies used in computers. It describes linear power supplies which use transformers to convert voltage and have good line and load regulation. It then focuses on switched mode power supplies (SMPS) which have higher efficiency. An SMPS uses a switching regulator to convert high voltage DC to lower DC levels needed by components. It discusses AT and ATX power supply formats used in older and newer computers respectively. The document also covers characteristics like wattage, efficiency and regulation as well as potential power problems and protective devices like surge suppressors and UPS systems.4_INFRARED REMOTE USED FOR 8



4_INFRARED REMOTE USED FOR 8SURAJ MAHAPATRA
╠²
An infrared remote control is used to control the speed of an induction motor in 8 steps. A microcontroller reads coded data from the remote control and activates output pins to change the firing time of thyristors, which drives the fan motor. The microcontroller receives signals from IR sensors connected to the remote and controls the system. A regulated power supply provides power and a transformer steps down the voltage.PCS - FIT ITE Chapter 1



PCS - FIT ITE Chapter 1Pacific Coast School
╠²
This document provides an overview of the key components and concepts related to personal computer hardware and software. It discusses IT certifications like CompTIA A+ and describes the basic components of a computer system, including the case, motherboard, CPU, memory, storage, ports, cables, power supply, cooling systems, and expansion cards. The roles and characteristics of these various internal and external components are explained.Chapter 4 Form Factors & Power Supplies



Chapter 4 Form Factors & Power SuppliesPatty Ramsey
╠²
The document discusses computer form factors, power supplies, and electrical troubleshooting. It covers different form factors like ATX, microATX and BTX that specify motherboard and case dimensions. Power supplies convert alternating current to direct current needed by components. Electrical issues can be caused by static electricity, electromagnetic interference, power surges or inadequate power supplies. Troubleshooting involves checking for loose connections, overheating, defective fans or capacitors, and replacing the power supply if needed.Chapter 4 Form Factors Power Supplies



Chapter 4 Form Factors Power SuppliesPatty Ramsey
╠²
The document discusses different computer components related to power and electricity, including form factors, power supplies, cases, and how electricity is measured. It covers topics like ATX, MicroATX, and BTX form factors; desktop and tower cases; voltages, amps, ohms, and watts; AC and DC power; surge protection; UPS systems; and how computers meet Energy Star standards through power management features. The document provides information to help understand and troubleshoot electrical issues in personal computers.IMD 203 - Ch04



IMD 203 - Ch04ALBAKRI MOHAMMAD
╠²
The document discusses computer form factors, power supplies, electrical concepts, and troubleshooting power issues. It covers different motherboard and case form factors like ATX, common components in circuits like capacitors and resistors, how to measure electricity, and how to protect computers from electrical threats. It also explains how computers meet Energy Star standards through features like sleep modes that reduce power consumption.8 power supplies



8 power supplieshafizhanif86
╠²
The power supply takes electricity from the wall and transforms it into lower voltages to power computer components. It provides power to the motherboard via a 20- or 24-pin connector and to peripherals like hard drives via Molex, SATA, and other connectors. Power supplies come in different form factors and wattages must match the needs of the system. Proper grounding and surge protection helps prevent damage from power issues.Cockpit White Box



Cockpit White Boxncct
╠²
final Year Projects, Final Year Projects in Chennai, Software Projects, Embedded Projects, Microcontrollers Projects, DSP Projects, VLSI Projects, Matlab Projects, Java Projects, .NET Projects, IEEE Projects, IEEE 2009 Projects, IEEE 2009 Projects, Software, IEEE 2009 Projects, Embedded, Software IEEE 2009 Projects, Embedded IEEE 2009 Projects, Final Year Project Titles, Final Year Project Reports, Final Year Project Review, Robotics Projects, Mechanical Projects, Electrical Projects, Power Electronics Projects, Power System Projects, Model Projects, Java Projects, J2EE Projects, Engineering Projects, Student Projects, Engineering College Projects, MCA Projects, BE Projects, BTech Projects, ME Projects, MTech Projects, Wireless Networks Projects, Network Security Projects, Networking Projects, final year projects, ieee projects, student projects, college projects, ieee projects in chennai, java projects, software ieee projects, embedded ieee projects, "ieee2009projects", "final year projects", "ieee projects", "Engineering Projects", "Final Year Projects in Chennai", "Final year Projects at Chennai", Java Projects, ASP.NET Projects, VB.NET Projects, C# Projects, Visual C++ Projects, Matlab Projects, NS2 Projects, C Projects, Microcontroller Projects, ATMEL Projects, PIC Projects, ARM Projects, DSP Projects, VLSI Projects, FPGA Projects, CPLD Projects, Power Electronics Projects, Electrical Projects, Robotics Projects, Solor Projects, MEMS Projects, J2EE Projects, J2ME Projects, AJAX Projects, Structs Projects, EJB Projects, Real Time Projects, Live Projects, Student Projects, Engineering Projects, MCA Projects, MBA Projects, College Projects, BE Projects, BTech Projects, ME Projects, MTech Projects, M.Sc Projects, Final Year Java Projects, Final Year ASP.NET Projects, Final Year VB.NET Projects, Final Year C# Projects, Final Year Visual C++ Projects, Final Year Matlab Projects, Final Year NS2 Projects, Final Year C Projects, Final Year Microcontroller Projects, Final Year ATMEL Projects, Final Year PIC Projects, Final Year ARM Projects, Final Year DSP Projects, Final Year VLSI Projects, Final Year FPGA Projects, Final Year CPLD Projects, Final Year Power Electronics Projects, Final Year Electrical Projects, Final Year Robotics Projects, Final Year Solor Projects, Final Year MEMS Projects, Final Year J2EE Projects, Final Year J2ME Projects, Final Year AJAX Projects, Final Year Structs Projects, Final Year EJB Projects, Final Year Real Time Projects, Final Year Live Projects, Final Year Student Projects, Final Year Engineering Projects, Final Year MCA Projects, Final Year MBA Projects, Final Year College Projects, Final Year BE Projects, Final Year BTech Projects, Final Year ME Projects, Final Year MTech Projects, Final Year M.Sc Projects, IEEE Java Projects, ASP.NET Projects, VB.NET Projects, C# Projects, Visual C++ Projects, Matlab Projects, NS2 Projects, C Projects, Microcontroller Projects, ATMEL Projects, PIC Projects, ARM Projects, DSP Projects, VLSI Projects, FPGA Projects, CPLD Projects, Power Electronics Projects, Electrical Projects, Robotics Projects, Solor Projects, MEMS Projects, J2EE Projects, J2ME Projects, AJAX Projects, Structs Projects, EJB Projects, Real Time Projects, Live Projects, Student Projects, Engineering Projects, MCA Projects, MBA Projects, College Projects, BE Projects, BTech Projects, ME Projects, MTech Projects, M.Sc Projects, IEEE 2009 Java Projects, IEEE 2009 ASP.NET Projects, IEEE 2009 VB.NET Projects, IEEE 2009 C# Projects, IEEE 2009 Visual C++ Projects, IEEE 2009 Matlab Projects, IEEE 2009 NS2 Projects, IEEE 2009 C Projects, IEEE 2009 Microcontroller Projects, IEEE 2009 ATMEL Projects, IEEE 2009 PIC Projects, IEEE 2009 ARM Projects, IEEE 2009 DSP Projects, IEEE 2009 VLSI Projects, IEEE 2009 FPGA Projects, IEEE 2009 CPLD Projects, IEEE 2009 Power Electronics Projects, IEEE 2009 Electrical Projects, IEEE 2009 Robotics Projects, IEEE 2009 Solor Projects, IEEE 2009 MEMS Projects, IEEE 2009 J2EE P46 Watts Up Power Supplies



46 Watts Up Power SuppliesImmanuelA
╠²
The power supply converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) and provides stable DC current to components. It contains cooling fans, heat sinks, electromagnetic interference filters, input and output capacitors, and other circuitry. When choosing a power supply, consider its ratings and the power needs of the computer components.Power supply and (sata and pata)



Power supply and (sata and pata)abdulsamad alhamawande
╠²
The document discusses power supplies and the differences between IDE and SATA interfaces. It provides details on how power supplies work, converting alternating current to direct current and regulating voltage. While SATA allows higher bandwidths than IDE, a SATA hard drive is not necessarily faster as most drives cannot sustain speeds above IDE's maximum throughput. The key difference is that SATA uses fewer pins and a simpler serial interface compared to the older parallel IDE interface.More Related Content
Similar to 15 SMPS.ppt simple mail protocol systeyk (20)
Power supply



Power supplymelary24
╠²
A power supply converts high voltage alternating current (AC) from a wall outlet to lower voltage direct current (DC) needed to power a computer. It regulates voltages like +3.3V, +5V and +12V and protects the system from overloads. Standards like ATX define form factors and connectors to ensure compatibility between power supplies and computer components. Power supplies are rated based on their ability to continuously supply power on the +12V rail, which powers today's processors and graphics cards.Power Supply



Power SupplyMOHIT DADU
╠²
This will give the information related to power supply into the computer system and provide the basic information about common power supply in AT and ATX Standards and Efficiency of Power supply Unit.Power supply



Power supplyshaylor_swift
╠²
The document discusses different power supply standards for PCs, including AT, ATX, and BTX. It provides details on the connectors, pinouts, and voltages associated with each standard. It also addresses questions about compatibility between different form factors and how to identify a defective power supply.Power sources complete



Power sources completeAnand Kumar
╠²
The document discusses power supplies and voltage regulation for embedded systems. It describes how AC voltage from wall outlets must be converted to lower DC voltage and how this can be done using AC adapters, plug packs or by incorporating a bridge rectifier. It also discusses using linear regulators and switching regulators to provide a constant voltage from a varying power source like a battery. Linear regulators are simple to use but less efficient while switching regulators require more components but are more versatile. Low dropout regulators consume less power and are well-suited for low power embedded applications.Unit 3- power supplies



Unit 3- power suppliesBalaji Bhanu
╠²
The document discusses various components of computer power supplies. It describes how power supplies convert AC power to DC power required by computer components. Power supplies have cables that supply different voltages to parts like the motherboard. Power supply wattage requirements depend on the system configuration, with 500W sufficient for most average systems. Graphics cards may use additional 6-pin or 8-pin power connectors. The document also discusses switch mode power supplies, universal power cables, and uninterruptted power supplies (UPS).Power supply



Power supplyjaihra17
╠²
The power supply unit (PSU) supplies power to computer components by converting AC power from wall outlets to lower DC voltages. It connects to the motherboard and other components using various cables that provide different voltages like +3.3V, +5V, and +12V. Common power cables include the ATX 24-pin main power cable for the motherboard, 4-pin and 8-pin cables for additional +12V power to components like CPUs, and SATA and PCIe cables to provide power to hard drives and graphics cards.video.ppt



video.pptssuser66b5c5
╠²
The document discusses different types of power supplies used in computers. It describes linear power supplies which use transformers to convert voltage and have good line and load regulation. It then focuses on switched mode power supplies (SMPS) which have higher efficiency. An SMPS uses a switching regulator to convert high voltage DC to lower DC levels needed by components. It discusses AT and ATX power supply formats used in older and newer computers respectively. The document also covers characteristics like wattage, efficiency and regulation as well as potential power problems and protective devices like surge suppressors and UPS systems.Chapter-5.ppt



Chapter-5.pptManuE45
╠²
The document discusses different types of power supplies used in computers. It describes linear power supplies which use transformers to convert voltage and have good line and load regulation. It then focuses on switched mode power supplies (SMPS) which have higher efficiency. An SMPS uses a switching regulator to convert high voltage DC to lower DC levels needed by components. It discusses AT and ATX power supply formats used in older and newer computers respectively. The document also covers characteristics like wattage, efficiency and regulation as well as potential power problems and protective devices like surge suppressors and UPS systems.4_INFRARED REMOTE USED FOR 8



4_INFRARED REMOTE USED FOR 8SURAJ MAHAPATRA
╠²
An infrared remote control is used to control the speed of an induction motor in 8 steps. A microcontroller reads coded data from the remote control and activates output pins to change the firing time of thyristors, which drives the fan motor. The microcontroller receives signals from IR sensors connected to the remote and controls the system. A regulated power supply provides power and a transformer steps down the voltage.PCS - FIT ITE Chapter 1



PCS - FIT ITE Chapter 1Pacific Coast School
╠²
This document provides an overview of the key components and concepts related to personal computer hardware and software. It discusses IT certifications like CompTIA A+ and describes the basic components of a computer system, including the case, motherboard, CPU, memory, storage, ports, cables, power supply, cooling systems, and expansion cards. The roles and characteristics of these various internal and external components are explained.Chapter 4 Form Factors & Power Supplies



Chapter 4 Form Factors & Power SuppliesPatty Ramsey
╠²
The document discusses computer form factors, power supplies, and electrical troubleshooting. It covers different form factors like ATX, microATX and BTX that specify motherboard and case dimensions. Power supplies convert alternating current to direct current needed by components. Electrical issues can be caused by static electricity, electromagnetic interference, power surges or inadequate power supplies. Troubleshooting involves checking for loose connections, overheating, defective fans or capacitors, and replacing the power supply if needed.Chapter 4 Form Factors Power Supplies



Chapter 4 Form Factors Power SuppliesPatty Ramsey
╠²
The document discusses different computer components related to power and electricity, including form factors, power supplies, cases, and how electricity is measured. It covers topics like ATX, MicroATX, and BTX form factors; desktop and tower cases; voltages, amps, ohms, and watts; AC and DC power; surge protection; UPS systems; and how computers meet Energy Star standards through power management features. The document provides information to help understand and troubleshoot electrical issues in personal computers.IMD 203 - Ch04



IMD 203 - Ch04ALBAKRI MOHAMMAD
╠²
The document discusses computer form factors, power supplies, electrical concepts, and troubleshooting power issues. It covers different motherboard and case form factors like ATX, common components in circuits like capacitors and resistors, how to measure electricity, and how to protect computers from electrical threats. It also explains how computers meet Energy Star standards through features like sleep modes that reduce power consumption.8 power supplies



8 power supplieshafizhanif86
╠²
The power supply takes electricity from the wall and transforms it into lower voltages to power computer components. It provides power to the motherboard via a 20- or 24-pin connector and to peripherals like hard drives via Molex, SATA, and other connectors. Power supplies come in different form factors and wattages must match the needs of the system. Proper grounding and surge protection helps prevent damage from power issues.Cockpit White Box



Cockpit White Boxncct
╠²
final Year Projects, Final Year Projects in Chennai, Software Projects, Embedded Projects, Microcontrollers Projects, DSP Projects, VLSI Projects, Matlab Projects, Java Projects, .NET Projects, IEEE Projects, IEEE 2009 Projects, IEEE 2009 Projects, Software, IEEE 2009 Projects, Embedded, Software IEEE 2009 Projects, Embedded IEEE 2009 Projects, Final Year Project Titles, Final Year Project Reports, Final Year Project Review, Robotics Projects, Mechanical Projects, Electrical Projects, Power Electronics Projects, Power System Projects, Model Projects, Java Projects, J2EE Projects, Engineering Projects, Student Projects, Engineering College Projects, MCA Projects, BE Projects, BTech Projects, ME Projects, MTech Projects, Wireless Networks Projects, Network Security Projects, Networking Projects, final year projects, ieee projects, student projects, college projects, ieee projects in chennai, java projects, software ieee projects, embedded ieee projects, "ieee2009projects", "final year projects", "ieee projects", "Engineering Projects", "Final Year Projects in Chennai", "Final year Projects at Chennai", Java Projects, ASP.NET Projects, VB.NET Projects, C# Projects, Visual C++ Projects, Matlab Projects, NS2 Projects, C Projects, Microcontroller Projects, ATMEL Projects, PIC Projects, ARM Projects, DSP Projects, VLSI Projects, FPGA Projects, CPLD Projects, Power Electronics Projects, Electrical Projects, Robotics Projects, Solor Projects, MEMS Projects, J2EE Projects, J2ME Projects, AJAX Projects, Structs Projects, EJB Projects, Real Time Projects, Live Projects, Student Projects, Engineering Projects, MCA Projects, MBA Projects, College Projects, BE Projects, BTech Projects, ME Projects, MTech Projects, M.Sc Projects, Final Year Java Projects, Final Year ASP.NET Projects, Final Year VB.NET Projects, Final Year C# Projects, Final Year Visual C++ Projects, Final Year Matlab Projects, Final Year NS2 Projects, Final Year C Projects, Final Year Microcontroller Projects, Final Year ATMEL Projects, Final Year PIC Projects, Final Year ARM Projects, Final Year DSP Projects, Final Year VLSI Projects, Final Year FPGA Projects, Final Year CPLD Projects, Final Year Power Electronics Projects, Final Year Electrical Projects, Final Year Robotics Projects, Final Year Solor Projects, Final Year MEMS Projects, Final Year J2EE Projects, Final Year J2ME Projects, Final Year AJAX Projects, Final Year Structs Projects, Final Year EJB Projects, Final Year Real Time Projects, Final Year Live Projects, Final Year Student Projects, Final Year Engineering Projects, Final Year MCA Projects, Final Year MBA Projects, Final Year College Projects, Final Year BE Projects, Final Year BTech Projects, Final Year ME Projects, Final Year MTech Projects, Final Year M.Sc Projects, IEEE Java Projects, ASP.NET Projects, VB.NET Projects, C# Projects, Visual C++ Projects, Matlab Projects, NS2 Projects, C Projects, Microcontroller Projects, ATMEL Projects, PIC Projects, ARM Projects, DSP Projects, VLSI Projects, FPGA Projects, CPLD Projects, Power Electronics Projects, Electrical Projects, Robotics Projects, Solor Projects, MEMS Projects, J2EE Projects, J2ME Projects, AJAX Projects, Structs Projects, EJB Projects, Real Time Projects, Live Projects, Student Projects, Engineering Projects, MCA Projects, MBA Projects, College Projects, BE Projects, BTech Projects, ME Projects, MTech Projects, M.Sc Projects, IEEE 2009 Java Projects, IEEE 2009 ASP.NET Projects, IEEE 2009 VB.NET Projects, IEEE 2009 C# Projects, IEEE 2009 Visual C++ Projects, IEEE 2009 Matlab Projects, IEEE 2009 NS2 Projects, IEEE 2009 C Projects, IEEE 2009 Microcontroller Projects, IEEE 2009 ATMEL Projects, IEEE 2009 PIC Projects, IEEE 2009 ARM Projects, IEEE 2009 DSP Projects, IEEE 2009 VLSI Projects, IEEE 2009 FPGA Projects, IEEE 2009 CPLD Projects, IEEE 2009 Power Electronics Projects, IEEE 2009 Electrical Projects, IEEE 2009 Robotics Projects, IEEE 2009 Solor Projects, IEEE 2009 MEMS Projects, IEEE 2009 J2EE P46 Watts Up Power Supplies



46 Watts Up Power SuppliesImmanuelA
╠²
The power supply converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) and provides stable DC current to components. It contains cooling fans, heat sinks, electromagnetic interference filters, input and output capacitors, and other circuitry. When choosing a power supply, consider its ratings and the power needs of the computer components.Power supply and (sata and pata)



Power supply and (sata and pata)abdulsamad alhamawande
╠²
The document discusses power supplies and the differences between IDE and SATA interfaces. It provides details on how power supplies work, converting alternating current to direct current and regulating voltage. While SATA allows higher bandwidths than IDE, a SATA hard drive is not necessarily faster as most drives cannot sustain speeds above IDE's maximum throughput. The key difference is that SATA uses fewer pins and a simpler serial interface compared to the older parallel IDE interface.More from perweeng31 (6)
Recently uploaded (20)
A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...



A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...Beena E S
╠²
A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by Aaron ShepardComputer Network Unit IV - Lecture Notes - Network Layer



Computer Network Unit IV - Lecture Notes - Network LayerMurugan146644
╠²
Title:
Lecture Notes - Unit IV - The Network Layer
Description:
Welcome to the comprehensive guide on Computer Network concepts, tailored for final year B.Sc. Computer Science students affiliated with Alagappa University. This document covers fundamental principles and advanced topics in Computer Network. PDF content is prepared from the text book Computer Network by Andrew S. Tenanbaum
Key Topics Covered:
Main Topic : The Network Layer
Sub-Topic : Network Layer Design Issues (Store and forward packet switching , service provided to the transport layer, implementation of connection less service, implementation of connection oriented service, Comparision of virtual circuit and datagram subnet), Routing algorithms (Shortest path routing, Flooding , Distance Vector routing algorithm, Link state routing algorithm , hierarchical routing algorithm, broadcast routing, multicast routing algorithm)
Other Link :
1.Introduction to computer network - /slideshow/lecture-notes-introduction-to-computer-network/274183454
2. Physical Layer - /slideshow/lecture-notes-unit-ii-the-physical-layer/274747125
3. Data Link Layer Part 1 : /slideshow/lecture-notes-unit-iii-the-datalink-layer/275288798
Target Audience:
Final year B.Sc. Computer Science students at Alagappa University seeking a solid foundation in Computer Network principles for academic.
About the Author:
Dr. S. Murugan is Associate Professor at Alagappa Government Arts College, Karaikudi. With 23 years of teaching experience in the field of Computer Science, Dr. S. Murugan has a passion for simplifying complex concepts in Computer Network
Disclaimer:
This document is intended for educational purposes only. The content presented here reflects the authorŌĆÖs understanding in the field of Computer NetworkSouth Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...



South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...History of Stoke Newington
╠²
Presented at the 24th Stoke Newington History Talks event on 27th Feb 2025
https://stokenewingtonhistory.com/stoke-newington-history-talks/Blind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...



Blind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...Ajaz Hussain
╠²
This presentation delves into the systemic blind spots within pharmaceutical science and regulatory systems, emphasizing the significance of "inactive ingredients" and their influence on therapeutic equivalence. These blind spots, indicative of normalized systemic failures, go beyond mere chance occurrences and are ingrained deeply enough to compromise decision-making processes and erode trust.
Historical instances like the 1938 FD&C Act and the Generic Drug Scandals underscore how crisis-triggered reforms often fail to address the fundamental issues, perpetuating inefficiencies and hazards.
The narrative advocates a shift from reactive crisis management to proactive, adaptable systems prioritizing continuous enhancement. Key hurdles involve challenging outdated assumptions regarding bioavailability, inadequately funded research ventures, and the impact of vague language in regulatory frameworks.
The rise of large language models (LLMs) presents promising solutions, albeit with accompanying risks necessitating thorough validation and seamless integration.
Tackling these blind spots demands a holistic approach, embracing adaptive learning and a steadfast commitment to self-improvement. By nurturing curiosity, refining regulatory terminology, and judiciously harnessing new technologies, the pharmaceutical sector can progress towards better public health service delivery and ensure the safety, efficacy, and real-world impact of drug products.Mate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptx



Mate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptxLiny Jenifer
╠²
A powerpoint presentation on the short story Mate by Kate Greenville. This presentation provides information on Kate Greenville, a character list, plot summary and critical analysis of the short story.Reordering Rules in Odoo 17 Inventory - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



Reordering Rules in Odoo 17 Inventory - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In Odoo 17, the Inventory module allows us to set up reordering rules to ensure that our stock levels are maintained, preventing stockouts. Let's explore how this feature works.TLE 7 - 3rd Topic - Hand Tools, Power Tools, Instruments, and Equipment Used ...



TLE 7 - 3rd Topic - Hand Tools, Power Tools, Instruments, and Equipment Used ...RizaBedayo
╠²
Hand Tools, Power Tools, and Equipment in Industrial ArtsHow to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
Integrate WhatsApp into Odoo using the WhatsApp Business API or third-party modules to enhance communication. This integration enables automated messaging and customer interaction management within Odoo 17.How to Configure Restaurants in Odoo 17 Point of Sale



How to Configure Restaurants in Odoo 17 Point of SaleCeline George
╠²
Odoo, a versatile and integrated business management software, excels with its robust Point of Sale (POS) module. This guide delves into the intricacies of configuring restaurants in Odoo 17 POS, unlocking numerous possibilities for streamlined operations and enhanced customer experiences.Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil Sir



Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil SirGUJARATCOMMERCECOLLE
╠²
Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil SirHow to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



How to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18. In Odoo, Init Hooks are essential functions specified as strings in the __init__ file of a module.Computer Application in Business (commerce)



Computer Application in Business (commerce)Sudar Sudar
╠²
The main objectives
1. To introduce the concept of computer and its various parts. 2. To explain the concept of data base management system and Management information system.
3. To provide insight about networking and basics of internet
Recall various terms of computer and its part
Understand the meaning of software, operating system, programming language and its features
Comparing Data Vs Information and its management system Understanding about various concepts of management information system
Explain about networking and elements based on internet
1. Recall the various concepts relating to computer and its various parts
2 Understand the meaning of softwareŌĆÖs, operating system etc
3 Understanding the meaning and utility of database management system
4 Evaluate the various aspects of management information system
5 Generating more ideas regarding the use of internet for business purpose Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In this slide weŌĆÖll discuss on the useful environment methods in Odoo 18. In Odoo 18, environment methods play a crucial role in simplifying model interactions and enhancing data processing within the ORM framework.APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...Association for Project Management
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
- Autonomy, Teams and Tension
- Oliver Randall & David Bovis
- Own Your Autonomy
Oliver Randall
Consultant, Tribe365
Oliver is a career project professional since 2011 and started volunteering with APM in 2016 and has since chaired the People Interest Network and the North East Regional Network. Oliver has been consulting in culture, leadership and behaviours since 2019 and co-developed HPTM┬«ŌĆ»an off the shelf high performance framework for teams and organisations and is currently working with SAS (Stellenbosch Academy for Sport) developing the culture, leadership and behaviours framework for future elite sportspeople whilst also holding down work as a project manager in the NHS at North Tees and Hartlepool Foundation Trust.
David Bovis
Consultant, Duxinaroe
A Leadership and Culture Change expert, David is the originator of BTFAŌäó and The Dux Model.
With a Masters in Applied Neuroscience from the Institute of Organisational Neuroscience, he is widely regarded as the ŌĆśGo-ToŌĆÖ expert in the field, recognised as an inspiring keynote speaker and change strategist.
He has an industrial engineering background, majoring in TPS / Lean. David worked his way up from his apprenticeship to earn his seat at the C-suite table. His career spans several industries, including Automotive, Aerospace, Defence, Space, Heavy Industries and Elec-Mech / polymer contract manufacture.
Published in LondonŌĆÖs Evening Standard quarterly business supplement, James CaanŌĆÖs ŌĆśYour businessŌĆÖ Magazine, ŌĆśQuality WorldŌĆÖ, the Lean Management Journal and Cambridge Universities ŌĆśPMAŌĆÖ, he works as comfortably with leaders from FTSE and Fortune 100 companies as he does owner-managers in SMEŌĆÖs. He is passionate about helping leaders understand the neurological root cause of a high-performance culture and sustainable change, in business.
Session | Own Your Autonomy ŌĆō The Importance of Autonomy in Project Management
#OwnYourAutonomy is aiming to be a global APM initiative to position everyone to take a more conscious role in their decision making process leading to increased outcomes for everyone and contribute to ŌĆ£a world in which all projects succeedŌĆØ.
We want everyone to join the journey.
#OwnYourAutonomy is the culmination of 3 years of collaborative exploration within the Leadership Focus Group which is part of the APM People Interest Network. The work has been pulled together using the 5 HPTM® Systems and the BTFA neuroscience leadership programme.
https://www.linkedin.com/showcase/apm-people-network/about/How to Modify Existing Web Pages in Odoo 18



How to Modify Existing Web Pages in Odoo 18Celine George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to modify existing web pages in Odoo 18. Web pages in Odoo 18 can also gather user data through user-friendly forms, encourage interaction through engaging features. South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...



South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...History of Stoke Newington
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...Association for Project Management
╠²
15 SMPS.ppt simple mail protocol systeyk
- 1. SMPS ’üĄ SMPS is the Switched Mode Power Supply circuit which is designed for obtaining the regulated DC output voltage from an unregulated DC or AC voltage. ’üĄ Switch mode power supply is a linear power supply. ’üĄ There are four main types of SMPS such as. ’üĄ DC to DC Converter. ’üĄ AC to DC Converter ’üĄ Fly back Converter (The Fly back converter is used for Low power applications. ) ’üĄ Forward Converter
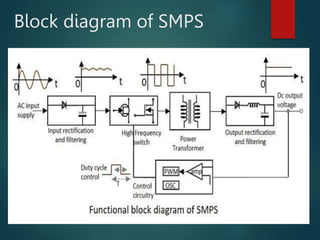
- 2. Block diagram of SMPS
- 3. 1.Input Rectifier stage: It is used to convert AC to DC.
- 4. SMPS
- 5. SMPS parts and Connectors ’üĄ Power-IN. The power-IN connector as shown in the figure is the input for MAINS supply. A power cable is inserted here, the other end of which is connected to mains supply. The input supply gets converted to DC supply. ’üĄ Power-OUT. The power-OUT connector is connected directly to the Power-IN connector from inside the supply unit. It supplies the same AC supply that is fed to power-IN socket. The power-OUT connector is used to give supply to monitors or any display unit. ’üĄ FAN. If you look at the back side of Computer-SMPS, you will find a FAN at the right side. The FAN as you can see, blows the air out and is only used to dissipate the internal heat from the SMPS since the switching is done at high frequencies which create a lot of heat inside.
- 6. ATX connector ’üĄ As you can see in the image, it is a 24-pin female connector which is used to supply DC supply to the motherboards. Various color-coded wires connect to this connector and each colored wire supplies distinct DC voltage which is explained in the chart below
- 7. . Wire Colour DC Voltage Red +5V Yellow +12V Black Ground Blue -12V Grey Power Good Green Power On Purple +5V Standby Orange +3.3V Brown/Orange White +3.3V Sense -5V(Optional)
- 8. ’üĄ ATX-12V connector. Latest SMPS power supplies are accompanied by an extra 4-pin connector which supplies 12 volts to energize the central processing unit and other components of the motherboard.
- 9. ’üĄ AT Connectors. Earlier motherboards used to support AT connectors( 6- pin each) also called P8 and P9 connectors to supply power to these motherboards(upto 486 boards)
- 10. . Wire Colour DC Voltage Red +5V White -5V Black Ground Blue -12V Yellow +12V Orange +5V(PG)
- 11. ’üĄ 4-PIN connectors. There are multiple 4-pin connectors that draw out from the SPMS unit. These connectors are used to supply DC power to various peripherals of computer like a floppy disk drive, hard disk drive or DVD- writers.
- 12. Connecting to Drives Pin Number Wire Color Signal 1 Yellow +12 V(Used in motor) 2 Black +12 V Ground 3 Black +5 V Ground 4 Red +5 V(Used in logic circuit)
- 13. ’üĄ SATA-output connector. To feed the power to latest SATA hard drives, these connectors are used.
- 14. How to test computer SMPS ’üĄ To check the supply, whether it is working properly or not, you can test it before fitting it in the cabinet. There is a simple way to test the SMPS, you just have to short the green wired connector to any black colored(ground) connector. If the SMPS is working perfectly, the fan of the supply will start working
- 15. Power Supply Problems ’üĄ Line Noise ’üĄ Surges ’üĄ Lightning Strikes ’üĄ Brownouts ’üĄ Blackouts













