3 Types of Government -- Compare & Contrast -- simple grade 6 & 7 ss.ppt
Download as PPTX, PDF4 likes1,552 views
Describe the ways government systems distribute power: unitary, confederation, and federal. SS6 - CG1a, CG4a, CG6a SS7 ŌĆō CG1a, CG4a, CG6a
1 of 11
Downloaded 15 times









Recommended
Email Your Local Representatives



Email Your Local RepresentativesMike Snyder
╠²
Instructions assignment for English 2010. How to use local government websites to find and email Utah state representatives.Sequence in literature



Sequence in literatureCarrie SInone
╠²
The document discusses the concept of sequence in literature. It explains that sequence refers to the order of events in a story, which may be explicit if the author uses words like first or next, or may jump around more. Readers can look for keywords like first or after to determine sequence. The document also provides an example story about two frogs who want to visit the city, but end up returning to their village after one frog mistakes their village for the city by looking in the wrong direction.Forms of government



Forms of governmentEssential Person
╠²
My name is Kenzhekulov Maisalbek from International Ataturk Alatoo University Department International Relations and In this presentation I`m telling about the Forms of government .Subject: Foreign Policy Analysis
Lecturer: Dr. Ibrahim KoncakDifferent forms of government



Different forms of governmentloneal2
╠²
The document provides an overview of different forms of government including republic, parliamentary, monarchy, theocracy, totalitarian, dictatorship, and oligarchy. It gives brief descriptions of each type and examples of countries that use each form. The summary focuses on the key information without opinions or evaluations.Types of government



Types of governmentsarzahop
╠²
There are several types of governments discussed in the document. Representative democracies are systems where citizens vote for representatives to make laws and govern on their behalf, as seen in countries like the United States, France, and Russia. Constitutional monarchies have a monarch whose powers are limited by an elected lawmaking body, as in the United Kingdom, Sweden, and Spain. Dictatorships concentrate power in a single leader, like Cuba under Fidel Castro, Germany under Hitler, and Iraq under Saddam Hussein.Unit 3 Forms Of Government Types Powerpoint.Cm



Unit 3 Forms Of Government Types Powerpoint.CmHeatherP
╠²
There are three main types of governments: autocracy, oligarchy, and democracy. Autocracy is rule by one person, such as a dictator or absolute monarch. Oligarchy involves rule by a small, powerful group. Democracy is rule by the people, which can take the form of direct democracy, where citizens vote on issues, or representative democracy, where citizens elect representatives. The two major forms of representative democracy are parliamentary democracy, where the prime minister is chosen from the party with the most seats in parliament, and presidential democracy, where citizens directly elect both legislators and the president.Sequence of events



Sequence of eventsaledocente
╠²
The document discusses sequence and order of events using time-order words and expressions like first, next, then, finally, in the morning, after that, later that day. It provides examples of a story using sequence clue words to describe meeting a new friend at recess, playing ball games together that day, trading baseball cards after one game, and making plans to have dinner at the friend's apartment on his birthday.Sequence of events



Sequence of eventsBrenda Obando
╠²
I do not have enough context to summarize a news article or draw pictures. Could you please provide the full text of the news article? That would allow me to understand the events and represent them accurately.Magna carta ppt



Magna carta pptChrisLeSage
╠²
The Magna Carta was created in 1215 and forced King John to obey the same laws as his subjects, establishing equality under the law. Dissatisfied barons rebelled in response to the king raising taxes without permission. They compelled the king to agree to the Magna Carta's limitations on royal power through clauses protecting individual liberties and access to fair trials. While only three clauses remain valid law today, the Magna Carta established principles of shared rule of law and legal equality that continue influencing modern democratic legal systems.Magna Carta Powerpoint 



Magna Carta Powerpoint Josiemahon
╠²
The Magna Carta is a document signed in 1215 between King John of England and rebel barons. It established limitations on the power of the monarchy by guaranteeing basic rights and protecting the interests of feudal barons from arbitrary authority. The Magna Carta promised that taxes would only be imposed with baronial consent, established free procedures for justice, and limited other feudal payments to the king. It helped form the basis of constitutional law in England.Forms of Government



Forms of GovernmentJoe Welch
╠²
The document outlines several forms of government: monarchy, where power is held by a hereditary monarch like Saudi Arabia; dictatorship, where one individual seizes power by force with no limits like Hitler in Nazi Germany; democracy, where power is shared by citizens through elected representatives like the US; communist states where all property is publicly owned for the good of the country; anarchy, where there is no government and a state of disorder occurs; and theocracy, where religious authorities govern.Government ppt



Government pptSusan124
╠²
Forms of government can be categorized based on who rules (types) and how power is distributed (systems). The main types are autocracy, where one ruler holds power; oligarchy, where a small group rules; and democracy, where citizens participate. Systems include unitary states with centralized power, confederations with weak central authority, and federations with shared power between national and regional levels.Grade 5 economic policies under spanish rule



Grade 5 economic policies under spanish ruleHularjervis
╠²
The document discusses the colonial economic policies implemented by Spain in the Philippines. These policies included tributes, encomienda land grants, and forced labor systems like polo y servicio. The Bandala system required Filipinos to sell their harvests to the government. The Galleon Trade monopoly benefited Spanish traders more than Filipinos. Overall, these colonial policies exploited Filipino labor and resources to benefit Spain financially rather than developing the Philippine economy for all its people.CHECKS AND BALANCES



CHECKS AND BALANCEScrow0317
╠²
The document discusses the concepts of checks and balances, separation of powers, and federalism in the US government. It explains that checks and balances prevents any one branch from becoming too powerful by giving each branch some control over the others. For example, if the president vetoes a bill, Congress can override the veto with a two-thirds vote. Separation of powers divides power among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. Federalism shares power between national and state governments across three levels: federal, state, and local.power sharing



power sharingmayank raghuvanshi
╠²
The document discusses different forms of power sharing in a democracy. It describes power sharing horizontally among different organs of government to maintain checks and balances. It also describes vertical power sharing between central, state, and local governments. Additionally, it discusses power sharing socially by reserving positions for women, scheduled castes, and scheduled tribes, and among political parties through coalition governments. The goal of power sharing is to accommodate diverse social groups, avoid conflicts, and ensure no single group can impose its will without consideration of others.Power Sharing



Power SharingNitin Chhaperwal
╠²
This document discusses different forms of power sharing in government. It explains that power sharing occurs horizontally among the different organs of government (legislature, executive, judiciary) to create a system of checks and balances. It also occurs vertically between central/federal governments and state/provincial governments. Additionally, power is shared among social groups through reservations and with political parties through coalition governments. The document provides examples of power sharing in India and Belgium across different levels and groups.Lesson Plan One Us Govt. U22



Lesson Plan One Us Govt. U22Jenny Hulbert
╠²
Federalism is a system of government where power is distributed between a central federal authority and constituent political units like states or provinces. It involves a combination of national and regional interests through a complex system of checks and balances between the central government and regional governments. In the United States, power has shifted over time away from state governments towards the central federal government. The US Constitution outlines certain expressed and implied powers for the national government while reserving other powers to the states, though the boundaries of these powers are sometimes unclear. One controversial issue debated during presidential elections is education, even though the Constitution assigns no explicit role for the federal government in state education systems.unitary and federal form of government-nityamukta.pptx



unitary and federal form of government-nityamukta.pptxAryamansingh71
╠²
The document discusses unitary and federal forms of government. A unitary government has all power centralized in one central authority, while a federal government divides power between a central government and regional/local governments. Some key advantages of unitary governments are rapid decision making and less potential for disagreements, but they may struggle to effectively govern large or diverse countries. Federal systems help prevent tyranny and allow for more localized governance, but can be more expensive and complex. Most modern systems exhibit elements of both.Systems of government powerpoint (unitary, confederation, federal)updated 2010



Systems of government powerpoint (unitary, confederation, federal)updated 2010North Gwinnett Middle School
╠²
This document discusses different systems of government and how power is distributed in each. It explains that there are three main ways power can be shared: unitary governments have one central authority that controls everything; confederations involve a voluntary association of independent states under a weak central power; and federal governments share power between a central national government and states or provinces that have considerable self-rule. The document provides examples of countries that use each system and diagrams to illustrate how power is divided in unitary, confederation, and federal systems.How do governments distribute power pink



How do governments distribute power pinkklgriffin
╠²
The document summarizes different types of governments:
Federal governments share power between a central government and state/local governments, like the US and Germany. Unitary governments concentrate all power in the central authority, examples given are Saudi Arabia and the UK. Confederations give most power to independent member states who voluntarily cooperate, with limits, like the European Union and OPEC.Systems of government powerpoint (unitary, confederation, federal)updated 2010



Systems of government powerpoint (unitary, confederation, federal)updated 2010North Gwinnett Middle School
╠²
This document discusses different systems of government and how power is distributed in each. It begins by asking the reader to identify the different levels of government where they live. It then explains that governments are organized to protect citizens and manage conflict. There are different types of governments like democracies, republics, and monarchies. Geographers study the types of governments and how power is distributed through systems. The main systems are unitary, confederation, and federal. Unitary governments have one central power. Confederation governments give some power to members. Federal governments share power between a central and state/provincial governments. Diagrams and country examples are provided to illustrate each system.Forms of power sharing.



Forms of power sharing.SujRit
╠²
This document discusses different forms of power sharing in government. It describes power sharing as a system that provides all major community segments a share of government. There are several forms of power sharing, including horizontal power sharing among the different organs of government like the legislature, executive, and judiciary based on checks and balances. Vertical power sharing occurs among different levels of government, like federal systems. Power is also shared among different social communities and religious or minority groups to maintain peace and give all citizens a voice. Finally, power sharing occurs among political parties, pressure groups, and social movements to foster more effective governance.Gov't distribute power citizen participation parliamentary and presidential



Gov't distribute power citizen participation parliamentary and presidentialmarypardee
╠²
This document provides information about different forms of government and how they distribute power. It discusses federal, unitary, and confederation systems. A federal system divides power between a central authority and regional authorities. In a unitary system, power is held by one central authority. A confederation involves independent states banding together but retaining considerable independence, with regional authorities holding most power. Examples of each type are provided.10 soc sc_powersharing



10 soc sc_powersharingLokik Sharma
╠²
Power sharing is a key principle of democracy where political power is distributed among citizens, social groups, different levels and branches of government, and pressure groups. In India, power is shared through a federal system between the central and state governments, with reserved political representation for minorities, OBCs, SC, ST and women. Power is also shared among competing political parties through elections and coalition governments, as well as interest groups who influence decision making.Government civics Elluminate class 6



Government civics Elluminate class 6sajjansokhal
╠²
This document provides information about different forms of government, including federal, unitary, and confederation systems. It defines each system and how power is distributed. For federal governments, power is divided between a central authority and several regional authorities. In unitary systems, power is held by one central authority. Confederations are voluntary associations of independent states that delegate some powers to a central authority but retain considerable independence. The document also discusses authoritarian, oligarchic, and democratic forms of government in terms of citizen participation. It provides examples of different countries that use each system of government.3 Proscons Of Federalism



3 Proscons Of Federalismldelzeitmcintyre
╠²
The document discusses different systems of government structure - unitary, confederate, and federal - and analyzes which works best for governing diverse populations. It defines each system and provides examples. A federal system is said to work best for diversity as it features a decentralized division of power between national and regional authorities, each with their own jurisdictions and procedures. The document outlines the division of power in federalism between enumerated, reserved, and concurrent powers and discusses strengths like addressing regional needs, but also weaknesses like potential overlap, contradiction, or negation between policy levels.Power sharing in india



Power sharing in indiaHimanshu Gusain
╠²
The document discusses power sharing in Indian democracy. It explains that power sharing is essential to democracy as it allows communities and social groups to have a say in governance. In India, power is shared through various mechanisms - horizontally among different branches of government, vertically between federal, state and local governments, through representation of communities in government, and by forming coalition governments among political parties. Power sharing helps reduce conflicts, avoids majority tyranny, and respects the spirit of democracy.More Related Content
Viewers also liked (8)
Sequence of events



Sequence of eventsBrenda Obando
╠²
I do not have enough context to summarize a news article or draw pictures. Could you please provide the full text of the news article? That would allow me to understand the events and represent them accurately.Magna carta ppt



Magna carta pptChrisLeSage
╠²
The Magna Carta was created in 1215 and forced King John to obey the same laws as his subjects, establishing equality under the law. Dissatisfied barons rebelled in response to the king raising taxes without permission. They compelled the king to agree to the Magna Carta's limitations on royal power through clauses protecting individual liberties and access to fair trials. While only three clauses remain valid law today, the Magna Carta established principles of shared rule of law and legal equality that continue influencing modern democratic legal systems.Magna Carta Powerpoint 



Magna Carta Powerpoint Josiemahon
╠²
The Magna Carta is a document signed in 1215 between King John of England and rebel barons. It established limitations on the power of the monarchy by guaranteeing basic rights and protecting the interests of feudal barons from arbitrary authority. The Magna Carta promised that taxes would only be imposed with baronial consent, established free procedures for justice, and limited other feudal payments to the king. It helped form the basis of constitutional law in England.Forms of Government



Forms of GovernmentJoe Welch
╠²
The document outlines several forms of government: monarchy, where power is held by a hereditary monarch like Saudi Arabia; dictatorship, where one individual seizes power by force with no limits like Hitler in Nazi Germany; democracy, where power is shared by citizens through elected representatives like the US; communist states where all property is publicly owned for the good of the country; anarchy, where there is no government and a state of disorder occurs; and theocracy, where religious authorities govern.Government ppt



Government pptSusan124
╠²
Forms of government can be categorized based on who rules (types) and how power is distributed (systems). The main types are autocracy, where one ruler holds power; oligarchy, where a small group rules; and democracy, where citizens participate. Systems include unitary states with centralized power, confederations with weak central authority, and federations with shared power between national and regional levels.Grade 5 economic policies under spanish rule



Grade 5 economic policies under spanish ruleHularjervis
╠²
The document discusses the colonial economic policies implemented by Spain in the Philippines. These policies included tributes, encomienda land grants, and forced labor systems like polo y servicio. The Bandala system required Filipinos to sell their harvests to the government. The Galleon Trade monopoly benefited Spanish traders more than Filipinos. Overall, these colonial policies exploited Filipino labor and resources to benefit Spain financially rather than developing the Philippine economy for all its people.Similar to 3 Types of Government -- Compare & Contrast -- simple grade 6 & 7 ss.ppt (20)
CHECKS AND BALANCES



CHECKS AND BALANCEScrow0317
╠²
The document discusses the concepts of checks and balances, separation of powers, and federalism in the US government. It explains that checks and balances prevents any one branch from becoming too powerful by giving each branch some control over the others. For example, if the president vetoes a bill, Congress can override the veto with a two-thirds vote. Separation of powers divides power among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. Federalism shares power between national and state governments across three levels: federal, state, and local.power sharing



power sharingmayank raghuvanshi
╠²
The document discusses different forms of power sharing in a democracy. It describes power sharing horizontally among different organs of government to maintain checks and balances. It also describes vertical power sharing between central, state, and local governments. Additionally, it discusses power sharing socially by reserving positions for women, scheduled castes, and scheduled tribes, and among political parties through coalition governments. The goal of power sharing is to accommodate diverse social groups, avoid conflicts, and ensure no single group can impose its will without consideration of others.Power Sharing



Power SharingNitin Chhaperwal
╠²
This document discusses different forms of power sharing in government. It explains that power sharing occurs horizontally among the different organs of government (legislature, executive, judiciary) to create a system of checks and balances. It also occurs vertically between central/federal governments and state/provincial governments. Additionally, power is shared among social groups through reservations and with political parties through coalition governments. The document provides examples of power sharing in India and Belgium across different levels and groups.Lesson Plan One Us Govt. U22



Lesson Plan One Us Govt. U22Jenny Hulbert
╠²
Federalism is a system of government where power is distributed between a central federal authority and constituent political units like states or provinces. It involves a combination of national and regional interests through a complex system of checks and balances between the central government and regional governments. In the United States, power has shifted over time away from state governments towards the central federal government. The US Constitution outlines certain expressed and implied powers for the national government while reserving other powers to the states, though the boundaries of these powers are sometimes unclear. One controversial issue debated during presidential elections is education, even though the Constitution assigns no explicit role for the federal government in state education systems.unitary and federal form of government-nityamukta.pptx



unitary and federal form of government-nityamukta.pptxAryamansingh71
╠²
The document discusses unitary and federal forms of government. A unitary government has all power centralized in one central authority, while a federal government divides power between a central government and regional/local governments. Some key advantages of unitary governments are rapid decision making and less potential for disagreements, but they may struggle to effectively govern large or diverse countries. Federal systems help prevent tyranny and allow for more localized governance, but can be more expensive and complex. Most modern systems exhibit elements of both.Systems of government powerpoint (unitary, confederation, federal)updated 2010



Systems of government powerpoint (unitary, confederation, federal)updated 2010North Gwinnett Middle School
╠²
This document discusses different systems of government and how power is distributed in each. It explains that there are three main ways power can be shared: unitary governments have one central authority that controls everything; confederations involve a voluntary association of independent states under a weak central power; and federal governments share power between a central national government and states or provinces that have considerable self-rule. The document provides examples of countries that use each system and diagrams to illustrate how power is divided in unitary, confederation, and federal systems.How do governments distribute power pink



How do governments distribute power pinkklgriffin
╠²
The document summarizes different types of governments:
Federal governments share power between a central government and state/local governments, like the US and Germany. Unitary governments concentrate all power in the central authority, examples given are Saudi Arabia and the UK. Confederations give most power to independent member states who voluntarily cooperate, with limits, like the European Union and OPEC.Systems of government powerpoint (unitary, confederation, federal)updated 2010



Systems of government powerpoint (unitary, confederation, federal)updated 2010North Gwinnett Middle School
╠²
This document discusses different systems of government and how power is distributed in each. It begins by asking the reader to identify the different levels of government where they live. It then explains that governments are organized to protect citizens and manage conflict. There are different types of governments like democracies, republics, and monarchies. Geographers study the types of governments and how power is distributed through systems. The main systems are unitary, confederation, and federal. Unitary governments have one central power. Confederation governments give some power to members. Federal governments share power between a central and state/provincial governments. Diagrams and country examples are provided to illustrate each system.Forms of power sharing.



Forms of power sharing.SujRit
╠²
This document discusses different forms of power sharing in government. It describes power sharing as a system that provides all major community segments a share of government. There are several forms of power sharing, including horizontal power sharing among the different organs of government like the legislature, executive, and judiciary based on checks and balances. Vertical power sharing occurs among different levels of government, like federal systems. Power is also shared among different social communities and religious or minority groups to maintain peace and give all citizens a voice. Finally, power sharing occurs among political parties, pressure groups, and social movements to foster more effective governance.Gov't distribute power citizen participation parliamentary and presidential



Gov't distribute power citizen participation parliamentary and presidentialmarypardee
╠²
This document provides information about different forms of government and how they distribute power. It discusses federal, unitary, and confederation systems. A federal system divides power between a central authority and regional authorities. In a unitary system, power is held by one central authority. A confederation involves independent states banding together but retaining considerable independence, with regional authorities holding most power. Examples of each type are provided.10 soc sc_powersharing



10 soc sc_powersharingLokik Sharma
╠²
Power sharing is a key principle of democracy where political power is distributed among citizens, social groups, different levels and branches of government, and pressure groups. In India, power is shared through a federal system between the central and state governments, with reserved political representation for minorities, OBCs, SC, ST and women. Power is also shared among competing political parties through elections and coalition governments, as well as interest groups who influence decision making.Government civics Elluminate class 6



Government civics Elluminate class 6sajjansokhal
╠²
This document provides information about different forms of government, including federal, unitary, and confederation systems. It defines each system and how power is distributed. For federal governments, power is divided between a central authority and several regional authorities. In unitary systems, power is held by one central authority. Confederations are voluntary associations of independent states that delegate some powers to a central authority but retain considerable independence. The document also discusses authoritarian, oligarchic, and democratic forms of government in terms of citizen participation. It provides examples of different countries that use each system of government.3 Proscons Of Federalism



3 Proscons Of Federalismldelzeitmcintyre
╠²
The document discusses different systems of government structure - unitary, confederate, and federal - and analyzes which works best for governing diverse populations. It defines each system and provides examples. A federal system is said to work best for diversity as it features a decentralized division of power between national and regional authorities, each with their own jurisdictions and procedures. The document outlines the division of power in federalism between enumerated, reserved, and concurrent powers and discusses strengths like addressing regional needs, but also weaknesses like potential overlap, contradiction, or negation between policy levels.Power sharing in india



Power sharing in indiaHimanshu Gusain
╠²
The document discusses power sharing in Indian democracy. It explains that power sharing is essential to democracy as it allows communities and social groups to have a say in governance. In India, power is shared through various mechanisms - horizontally among different branches of government, vertically between federal, state and local governments, through representation of communities in government, and by forming coalition governments among political parties. Power sharing helps reduce conflicts, avoids majority tyranny, and respects the spirit of democracy.[POWER SHARING] INDIA![[POWER SHARING] INDIA](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/powersharinginindia-150708151226-lva1-app6892-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[POWER SHARING] INDIA](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/powersharinginindia-150708151226-lva1-app6892-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[POWER SHARING] INDIA](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/powersharinginindia-150708151226-lva1-app6892-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[POWER SHARING] INDIA](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/powersharinginindia-150708151226-lva1-app6892-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
[POWER SHARING] INDIAToppersPedia - Free Quality Education
╠²
All are made by me just the name says different coz I made for people .. So if it's your school project .. DOWNLOAD IT CHANGE NAME AND THEME. SUBMIT LOLdevryu.instructure.com ersity Topic Week 3 The Division of Power ul.pdf



devryu.instructure.com ersity Topic Week 3 The Division of Power ul.pdfherminaherman
╠²
devryu.instructure.com ersity Topic: Week 3: The Division of Power ules Week 3: The Division
of Power . due Jan 21 This is a graded discussion: 20 points possible WEEK 3: THE DIVISION
OF POWER As we have seen through our readings, governments differ on where the power of
the state should be held. Unitary systems concentrate the power within the central government
and little or no authority is granted to the component areas. In contrast, federal systems allow
first-order civil divisions to have some autonomy, while the central government maintains
authority over some areas. Take a moment to compare and contrast the strengths and weaknesses
of each system. Search entries or author Unread | subscribe Reply Joel Terwilliger (instructor)
Yesterday is the centralization of power in a nation\'s capital with little autonomy for & Jones,
2014, p. 55). This system has the control and makes the decisions over citizen\'s lives (taxes,
education, and laws) and the local leaders. With this type of system, The unitary system from our
text, subdivisions (Roskin, Cord, Medeiros,
Solution
Strengths
Unitary System - One of the main strengths in this system is the National Unity promotion and
this can get to help the system to witstand many troublesome incidents.
Federal System- The main strengths of this system is that it pops out to be successful in good,
large as well as culturally diverse countries where justice can be done to each and every area of
the place.
Weakness
Unitary system - The weakness is that the public policies may not get to fil the needs of all the
people all in all.
Federal system - Here, one of the main weakness is that there can be a conflict that can arise
between state and the federal governments which can create hectic problems on the whole..Powersharing



Powersharingsai raju
╠²
This document discusses power sharing in governance. It defines power sharing as a system that provides all major segments of society with a permanent share of power. It describes several types of power sharing, including among different levels of government, social groups, and political parties. Power sharing helps reduce conflict, prevent tyranny of the majority, keep a country united, and uphold democratic principles by giving citizens a chance to share in power. Maintaining social harmony and democracy are key reasons for implementing power sharing systems.The United States Constitution divides power between the federal and.docx



The United States Constitution divides power between the federal and.docxwsusan1
╠²
The United States Constitution divides power between the federal and state governments. In this assignment, you will describe those powers.
Assignment Guidelines:
Address the following questions in 1,000ŌĆō1,250 words:╠²
What powers are extended to the federal government? Explain in detail.
What components of the US Constitution describe and detail the powers extended to the federal government?
What powers are extended to the state governments? Explain in detail.
What components of the US Constitution describe and detail the powers extended to the state governments?
What are the power limitations of the federal government? Explain.
What are the power limitations of the state governments? Explain.
Are there any similarities or overlapping of powers between the two levels of government? Explain and describe those similarities or overlapping powers, if any.
How do the state governments and the federal government deal with those powers that are similar or overlap?╠²Which government has supremacy when there are similarities or overlap?╠²Explain.
Be sure to reference all sources using proper APA style.
.Powersharinginindia 150527161221-lva1-app6892



Powersharinginindia 150527161221-lva1-app6892Deepam Aggarwal
╠²
About power-sharing in the constitution of India
About different Institutions in the constitution
Government and its governance
Politics
Sst group ppt



Sst group pptPranav Krishnan
╠²
Power sharing is a technique in democracy where power is distributed across different levels and groups rather than being concentrated in one place. In India, power is shared horizontally between the legislature, executive, and judiciary branches, and vertically between national, state, and local governments. Power is also shared among political parties, pressure groups, and social/religious communities to give diverse groups representation and prevent any one group from dominating. Similarly in the US, power is shared between the national and state governments through a federal system to balance unity and diversity.Systems of government powerpoint (unitary, confederation, federal)updated 2010



Systems of government powerpoint (unitary, confederation, federal)updated 2010North Gwinnett Middle School
╠²
Systems of government powerpoint (unitary, confederation, federal)updated 2010



Systems of government powerpoint (unitary, confederation, federal)updated 2010North Gwinnett Middle School
╠²
Recently uploaded (20)
Research & Research Methods: Basic Concepts and Types.pptx



Research & Research Methods: Basic Concepts and Types.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
╠²
This ppt has been made for the students pursuing PG in social science and humanities like M.Ed., M.A. (Education), Ph.D. Scholars. It will be also beneficial for the teachers and other faculty members interested in research and teaching research concepts.Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Finals of Rass MELAI : a Music, Entertainment, Literature, Arts and Internet Culture Quiz organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. How to Configure Restaurants in Odoo 17 Point of Sale



How to Configure Restaurants in Odoo 17 Point of SaleCeline George
╠²
Odoo, a versatile and integrated business management software, excels with its robust Point of Sale (POS) module. This guide delves into the intricacies of configuring restaurants in Odoo 17 POS, unlocking numerous possibilities for streamlined operations and enhanced customer experiences.How to attach file using upload button Odoo 18



How to attach file using upload button Odoo 18Celine George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to attach file using upload button Odoo 18. Odoo features a dedicated model, 'ir.attachments,' designed for storing attachments submitted by end users. We can see the process of utilizing the 'ir.attachments' model to enable file uploads through web forms in this slide.How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
Integrate WhatsApp into Odoo using the WhatsApp Business API or third-party modules to enhance communication. This integration enables automated messaging and customer interaction management within Odoo 17.APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
-Autonomy, Teams and Tension: Projects under stress
-Tim Lyons
-The neurological levels of
team-working: Harmony and tensions
With a background in projects spanning more than 40 years, Tim Lyons specialised in the delivery of large, complex, multi-disciplinary programmes for clients including Crossrail, Network Rail, ExxonMobil, Siemens and in patent development. His first career was in broadcasting, where he designed and built commercial radio station studios in Manchester, Cardiff and Bristol, also working as a presenter and programme producer. Tim now writes and presents extensively on matters relating to the human and neurological aspects of projects, including communication, ethics and coaching. He holds a MasterŌĆÖs degree in NLP, is an NLP Master Practitioner and International Coach. He is the Deputy Lead for APMŌĆÖs People Interest Network.
Session | The Neurological Levels of Team-working: Harmony and Tensions
Understanding how teams really work at conscious and unconscious levels is critical to a harmonious workplace. This session uncovers what those levels are, how to use them to detect and avoid tensions and how to smooth the management of change by checking you have considered all of them.Blind spots in AI and Formulation Science, IFPAC 2025.pdf



Blind spots in AI and Formulation Science, IFPAC 2025.pdfAjaz Hussain
╠²
The intersection of AI and pharmaceutical formulation science highlights significant blind spotsŌĆösystemic gaps in pharmaceutical development, regulatory oversight, quality assurance, and the ethical use of AIŌĆöthat could jeopardize patient safety and undermine public trust. To move forward effectively, we must address these normalized blind spots, which may arise from outdated assumptions, errors, gaps in previous knowledge, and biases in language or regulatory inertia. This is essential to ensure that AI and formulation science are developed as tools for patient-centered and ethical healthcare.Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In this slide weŌĆÖll discuss on the useful environment methods in Odoo 18. In Odoo 18, environment methods play a crucial role in simplifying model interactions and enhancing data processing within the ORM framework.SOCIAL CHANGE(a change in the institutional and normative structure of societ...



SOCIAL CHANGE(a change in the institutional and normative structure of societ...DrNidhiAgarwal
╠²
This PPT is showing the effect of social changes in human life and it is very understandable to the students with easy language.in this contents are Itroduction, definition,Factors affecting social changes ,Main technological factors, Social change and stress , what is eustress and how social changes give impact of the human's life.How to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



How to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18. In Odoo, Init Hooks are essential functions specified as strings in the __init__ file of a module.A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...



A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...Beena E S
╠²
A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by Aaron ShepardAPM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...Association for Project Management
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
- Autonomy, Teams and Tension
- Oliver Randall & David Bovis
- Own Your Autonomy
Oliver Randall
Consultant, Tribe365
Oliver is a career project professional since 2011 and started volunteering with APM in 2016 and has since chaired the People Interest Network and the North East Regional Network. Oliver has been consulting in culture, leadership and behaviours since 2019 and co-developed HPTM┬«ŌĆ»an off the shelf high performance framework for teams and organisations and is currently working with SAS (Stellenbosch Academy for Sport) developing the culture, leadership and behaviours framework for future elite sportspeople whilst also holding down work as a project manager in the NHS at North Tees and Hartlepool Foundation Trust.
David Bovis
Consultant, Duxinaroe
A Leadership and Culture Change expert, David is the originator of BTFAŌäó and The Dux Model.
With a Masters in Applied Neuroscience from the Institute of Organisational Neuroscience, he is widely regarded as the ŌĆśGo-ToŌĆÖ expert in the field, recognised as an inspiring keynote speaker and change strategist.
He has an industrial engineering background, majoring in TPS / Lean. David worked his way up from his apprenticeship to earn his seat at the C-suite table. His career spans several industries, including Automotive, Aerospace, Defence, Space, Heavy Industries and Elec-Mech / polymer contract manufacture.
Published in LondonŌĆÖs Evening Standard quarterly business supplement, James CaanŌĆÖs ŌĆśYour businessŌĆÖ Magazine, ŌĆśQuality WorldŌĆÖ, the Lean Management Journal and Cambridge Universities ŌĆśPMAŌĆÖ, he works as comfortably with leaders from FTSE and Fortune 100 companies as he does owner-managers in SMEŌĆÖs. He is passionate about helping leaders understand the neurological root cause of a high-performance culture and sustainable change, in business.
Session | Own Your Autonomy ŌĆō The Importance of Autonomy in Project Management
#OwnYourAutonomy is aiming to be a global APM initiative to position everyone to take a more conscious role in their decision making process leading to increased outcomes for everyone and contribute to ŌĆ£a world in which all projects succeedŌĆØ.
We want everyone to join the journey.
#OwnYourAutonomy is the culmination of 3 years of collaborative exploration within the Leadership Focus Group which is part of the APM People Interest Network. The work has been pulled together using the 5 HPTM® Systems and the BTFA neuroscience leadership programme.
https://www.linkedin.com/showcase/apm-people-network/about/Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...Association for Project Management
╠²
3 Types of Government -- Compare & Contrast -- simple grade 6 & 7 ss.ppt
- 1. The 3 Types of Government Sixth and Seventh Grade Social Studies
- 2. Compare & Contrast Various Forms of Government Describe the ways government systems distribute power: unitary, confederation, and federal SS6 - CG1a, CG4a, CG6a SS7 ŌĆō CG1a, CG4a, CG6a
- 3. Essential Question Compare & Contrast How are the 3 systems (not types!) of government similar and how are they different?
- 4. The 3 Types of Government Different Ways Governments Distribute Power
- 5. Federal (Federation) Different Ways Governments Distribute Power Power is divided between 1 CENTRAL AND MANY REGIONAL authorities.
- 6. The 3 Types of Government Different Ways Governments Distribute Power Power is divided between 1 central and many regional authorities.
- 7. Unitary Power is held by 1 CENTRAL authority. Different Ways Governments Distribute Power
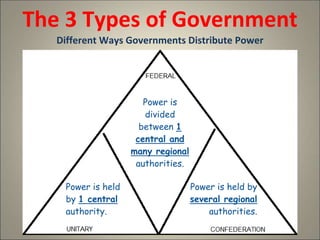
- 8. The 3 Types of Government Different Ways Governments Distribute Power Power is divided between 1 central and many regional authorities. Power is held by 1 central authority.
- 9. Confederation Different Ways Governments Distribute Power Power is held by SEVERAL REGIONAL authorities.
- 10. The 3 Types of Government Different Ways Governments Distribute Power Power is divided between 1 central and many regional authorities. Power is held by 1 central authority. Power is held by several regional authorities.
- 11. Essential Question Compare & Contrast How are the 3 systems (not types!) of government similar and how are they different?











