Algebra Rules - Addition and Subtraction - Corollary
- 1. Algebra ŌĆō Class 3a Basic Rules of Algebra ŌĆō Corollary 1 Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
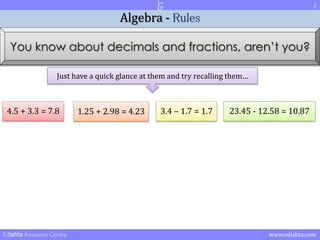
- 2. 2 Algebra - Rules You know about decimals and fractions, arenŌĆÖt you? Just have a quick glance at them and try recalling themŌĆ” 4.5 + 3.3 = 7.8 1.25 + 2.98 = 4.23 3.4 ŌĆō 1.7 = 1.7 23.45 - 12.58 = 10.87 Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
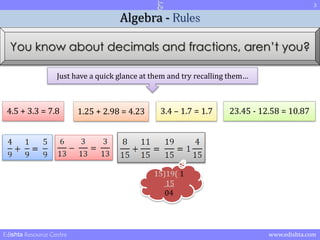
- 3. 3 Algebra - Rules You know about decimals and fractions, arenŌĆÖt you? Just have a quick glance at them and try recalling themŌĆ” 4.5 + 3.3 = 7.8 1.25 + 2.98 = 4.23 3.4 ŌĆō 1.7 = 1.7 23.45 - 12.58 = 10.87 15)19( 1 15 04 Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
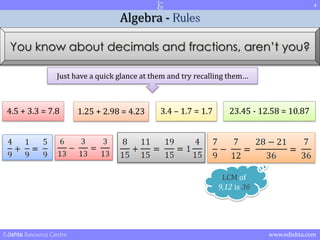
- 4. 4 Algebra - Rules You know about decimals and fractions, arenŌĆÖt you? Just have a quick glance at them and try recalling themŌĆ” 4.5 + 3.3 = 7.8 1.25 + 2.98 = 4.23 3.4 ŌĆō 1.7 = 1.7 23.45 - 12.58 = 10.87 LCM of 9,12 is 36 Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
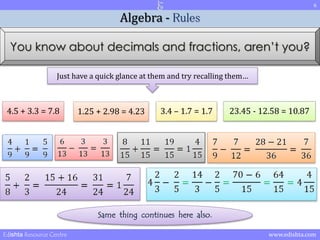
- 5. 5 Algebra - Rules You know about decimals and fractions, arenŌĆÖt you? Just have a quick glance at them and try recalling themŌĆ” 4.5 + 3.3 = 7.8 1.25 + 2.98 = 4.23 3.4 ŌĆō 1.7 = 1.7 23.45 - 12.58 = 10.87 4 X 3 = 12 12 + 2 = 14 Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
- 6. 6 Algebra - Rules You know about decimals and fractions, arenŌĆÖt you? Just have a quick glance at them and try recalling themŌĆ” 4.5 + 3.3 = 7.8 1.25 + 2.98 = 4.23 3.4 ŌĆō 1.7 = 1.7 23.45 - 12.58 = 10.87 Same thing continues here also. Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
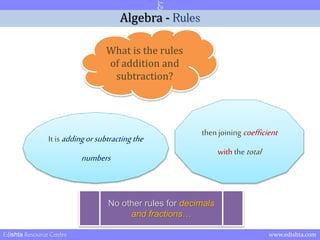
- 7. Algebra - Rules What is the rules of addition and subtraction? It is adding or subtracting the numbers then joining coefficient with the total No other rules for decimals and fractionsŌĆ” Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
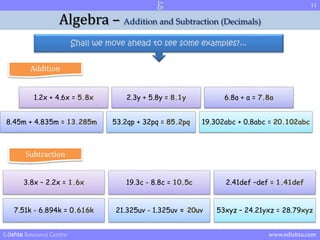
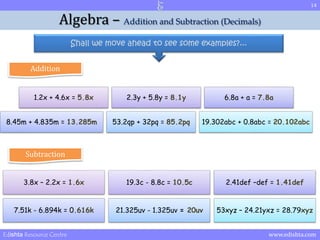
- 8. 8 Algebra ŌĆō Addition and Subtraction (Decimals) Shall we move ahead to see some examples?... Addition 1.2x + 4.6x = 5.8x 2.3y + 5.8y = 8.1y 6.8a + a = 7.8a 8.45m + 4.835m = 13.285m 53.2qp + 32pq = 85.2pq 19.302abc + 0.8abc = 20.102abc Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
- 9. 9 Algebra ŌĆō Addition and Subtraction (Decimals) (a= 1a) Shall we move ahead to see some examples?... Addition 1.2x + 4.6x = 5.8x 2.3y + 5.8y = 8.1y 6.8a + a = 7.8a 8.45m + 4.835m = 13.285m 53.2qp + 32pq = 85.2pq 19.302abc + 0.8abc = 20.102abc 1.2 4.6 5.8 Coeff. is x so Ans. is 5.8x 2.3 5.8 8.1 Coeff. is y so Ans. is 8.1y Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
- 10. 10 Algebra ŌĆō Addition and Subtraction (Decimals) Shall we move ahead to see some examples?... Addition 1.2x + 4.6x = 5.8x 2.3y + 5.8y = 8.1y 6.8a + a = 7.8a 8.45m + 4.835m = 13.285m 53.2qp + 32pq = 85.2pq 19.302abc + 0.8abc = 20.102abc 8.45 + 4.835 13.285 and m so 13.285m 19.302 + 0.8 ` 20.102 So 20.102abc Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
- 11. 11 Algebra ŌĆō Addition and Subtraction (Decimals) Shall we move ahead to see some examples?... Addition 1.2x + 4.6x = 5.8x 2.3y + 5.8y = 8.1y 6.8a + a = 7.8a 8.45m + 4.835m = 13.285m 53.2qp + 32pq = 85.2pq 19.302abc + 0.8abc = 20.102abc Subtraction 3.8x ŌĆō 2.2x = 1.6x 19.3c - 8.8c = 10.5c 2.41def ŌĆōdef = 1.41def 7.51k - 6.894k = 0.616k 21.325uv - 1.325uv = 20uv 53xyz ŌĆō 24.21yxz = 28.79xyz Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
- 12. 12 Algebra ŌĆō Addition and Subtraction (Decimals) Shall we move ahead to see some examples?... Addition 1.2x + 4.6x = 5.8x 2.3y + 5.8y = 8.1y 6.8a + a = 7.8a 3.8 -2.2 1.6 19.3 - 8.8 10.5 8.45m + 4.835m = 13.285m 53.2qp + 32pq = 85.2pq 19.302abc + 0.8abc = 20.102abc Coeff. is x so Ans. is 1.6x Coeff. is c so Ans. is 10.5c Subtraction (def= 1def) 3.8x ŌĆō 2.2x = 1.6x 19.3c - 8.8c = 10.5c 2.41def ŌĆōdef = 1.41def 7.51k - 6.894k = 0.616k 21.325uv - 1.325uv = 20uv 53xyz ŌĆō 24.21yxz = 28.79xyz Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
- 13. 13 Algebra ŌĆō Addition and Subtraction (Decimals) Shall we move ahead to see some examples?... Addition 1.2x + 4.6x = 5.8x 2.3y + 5.8y = 8.1y 6.8a + a = 7.8a 7.51 8.45m + 4.835m = 13.285m 53.2qp + 32pq = 85.2pq 19.302abc + 0.8abc = 20.102abc Subtraction - 6.894 0.616 and k so Ans. is 0.616k 3.8x ŌĆō 2.2x = 1.6x 19.3c - 8.8c = 10.5c 2.41def ŌĆōdef = 1.41def 7.51k - 6.894k = 0.616k 21.325uv - 1.325uv = 20uv 53xyz ŌĆō 24.21yxz = 28.79xyz xyz= yxz Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
- 14. 14 Algebra ŌĆō Addition and Subtraction (Decimals) Shall we move ahead to see some examples?... Addition 1.2x + 4.6x = 5.8x 2.3y + 5.8y = 8.1y 6.8a + a = 7.8a 8.45m + 4.835m = 13.285m 53.2qp + 32pq = 85.2pq 19.302abc + 0.8abc = 20.102abc Subtraction 3.8x ŌĆō 2.2x = 1.6x 19.3c - 8.8c = 10.5c 2.41def ŌĆōdef = 1.41def 7.51k - 6.894k = 0.616k 21.325uv - 1.325uv = 20uv 53xyz ŌĆō 24.21yxz = 28.79xyz Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
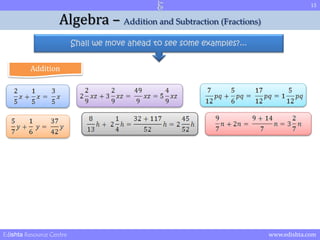
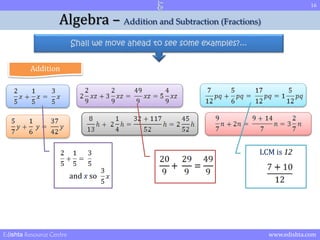
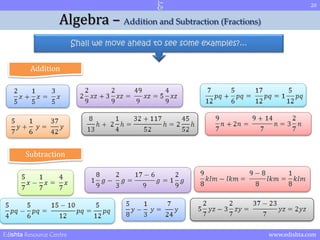
- 15. 15 Algebra ŌĆō Addition and Subtraction (Fractions) Shall we move ahead to see some examples?... Addition Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
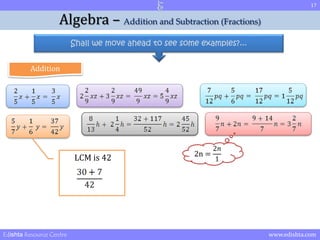
- 16. 16 Algebra ŌĆō Addition and Subtraction (Fractions) Shall we move ahead to see some examples?... Addition LCM is 12 and x so Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
- 17. 17 Algebra ŌĆō Addition and Subtraction (Fractions) Shall we move ahead to see some examples?... Addition LCM is 42 2n = Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
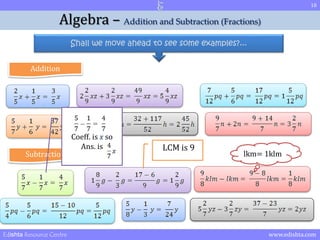
- 18. 18 Algebra ŌĆō Addition and Subtraction (Fractions) Shall we move ahead to see some examples?... Addition Coeff. is x so Ans. is LCM is 9 Subtraction lkm= 1klm Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
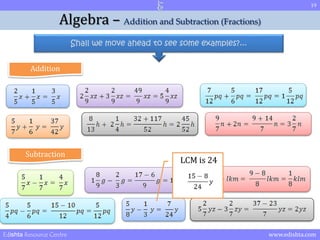
- 19. 19 Algebra ŌĆō Addition and Subtraction (Fractions) Shall we move ahead to see some examples?... Addition Subtraction LCM is 24 Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
- 20. 20 Algebra ŌĆō Addition and Subtraction (Fractions) Shall we move ahead to see some examples?... Addition Subtraction Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
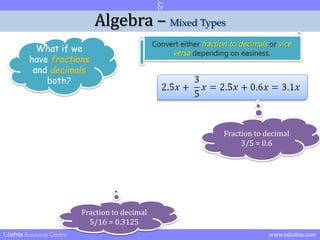
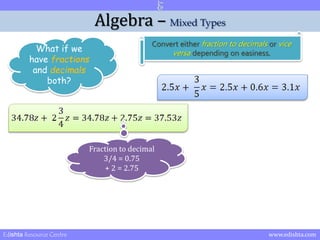
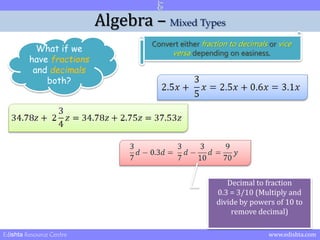
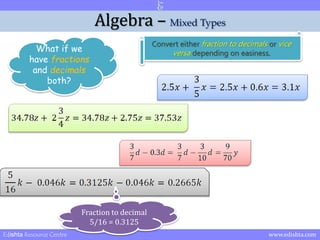
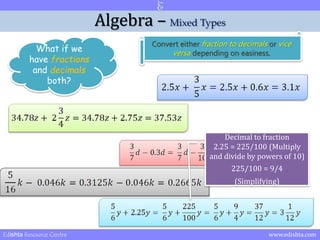
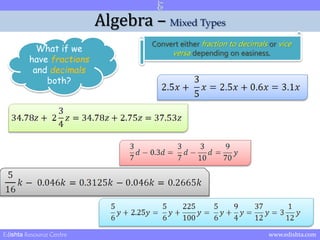
- 21. Algebra ŌĆō Mixed Types What if we have fractions and decimals both? Convert either fraction to decimals or vice versa depending on easiness. Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
- 22. Algebra ŌĆō Mixed Types What if we have fractions and decimals both? Convert either fraction to decimals or vice versa depending on easiness. Fraction to decimal 3/5 = 0.6 Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
- 23. Algebra ŌĆō Mixed Types What if we have fractions and decimals both? Convert either fraction to decimals or vice versa depending on easiness. Fraction to decimal 3/4 = 0.75 + 2 = 2.75 Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
- 24. Algebra ŌĆō Mixed Types What if we have fractions and decimals both? Convert either fraction to decimals or vice versa depending on easiness. Decimal to fraction 0.3 = 3/10 (Multiply and divide by powers of 10 to remove decimal) Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
- 25. Algebra ŌĆō Mixed Types What if we have fractions and decimals both? Convert either fraction to decimals or vice versa depending on easiness. Fraction to decimal 5/16 = 0.3125 Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
- 26. Algebra ŌĆō Mixed Types What if we have fractions and decimals both? Convert either fraction to decimals or vice versa depending on easiness. Decimal to fraction 2.25 = 225/100 (Multiply and divide by powers of 10) 225/100 = 9/4 (Simplifying) Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
- 27. Algebra ŌĆō Mixed Types What if we have fractions and decimals both? Convert either fraction to decimals or vice versa depending on easiness. Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
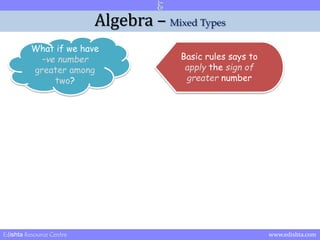
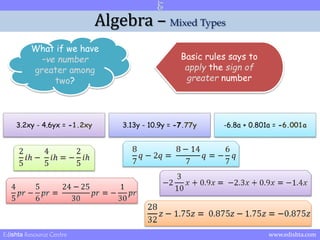
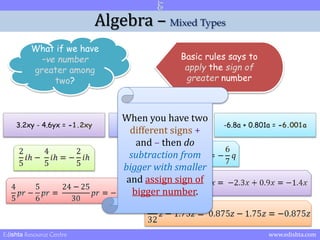
- 28. Algebra ŌĆō Mixed Types What if we have ŌĆōve number greater among two? Basic rules says to apply the sign of greater number Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
- 29. Algebra ŌĆō Mixed Types What if we have ŌĆōve number greater among two? Basic rules says to apply the sign of greater number 3.2xy - 4.6yx = -1.2xy 3.13y - 10.9y = -7.77y -6.8a + 0.801a = -6.001a Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
- 30. Algebra ŌĆō Mixed Types What if we have ŌĆōve number greater among two? Basic rules says to apply the sign of greater number When you have two different signs + 3.2xy - 4.6yx = -1.2xy 3.13y - 10.9y = -7.77y -6.8a + 0.801a = -6.001a and ŌĆō then do subtraction from bigger with smaller and assign sign of bigger number. Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
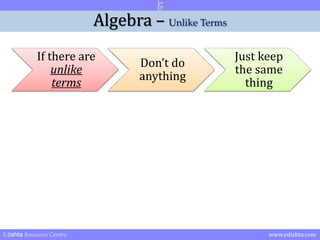
- 31. Algebra ŌĆō Unlike Terms If there are unlike terms DonŌĆÖt do anything Just keep the same thing Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
- 32. Algebra ŌĆō Unlike Terms If there are unlike terms DonŌĆÖt do anything Just keep the same thing 5.2x + 2.548xy = 5.2x + 2.548xy 8.75t + 4.37y = 8.75t + 4.37y Edishta Resource Centre www.edishta.com
















![Grade 8 Simplifying Expressions and Solving Equations Cambridge [PPT]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/g8unit09simplifyingexpressionsandsolvingequations-201206022011-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)






















































