Binary search in data structure
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes2,608 views
Binary search is a fast search algorithm that works on sorted data by comparing the middle element of the collection to the target value. It divides the search space in half at each step to quickly locate an element. The algorithm gets the middle element, compares it to the target, and either searches the left or right half recursively depending on if the target is less than or greater than the middle element. An example demonstrates finding the value 23 in a sorted array using this divide and conquer approach.
1 of 5
Download to read offline


![Algorithm of Binary search
It can be done by the following step:
1. get the middle element
MID= INT((BEG+END)/2)
2. if the middle element equals to the searched value, the algorithm stops.
3.Otherwise
a)If Item<DATA[MID],then appear left half
DATA[BEG]ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.DATA[MID-1]
b)If item>DATA[MID],then appear right half
DATA[BEG]ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.DATA[MID+1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/binarysearch-200312062402/85/Binary-search-in-data-structure-3-320.jpg)


Recommended
Binary search



Binary searchAparnaKumari31
╠²
Binary search is an algorithm that finds the position of a target value within a sorted array. It works by recursively dividing the array range in half and searching only within the appropriate half. The time complexity is O(log n) in the average and worst cases and O(1) in the best case, making it very efficient for searching sorted data. However, it requires the list to be sorted for it to work.linked list in data structure 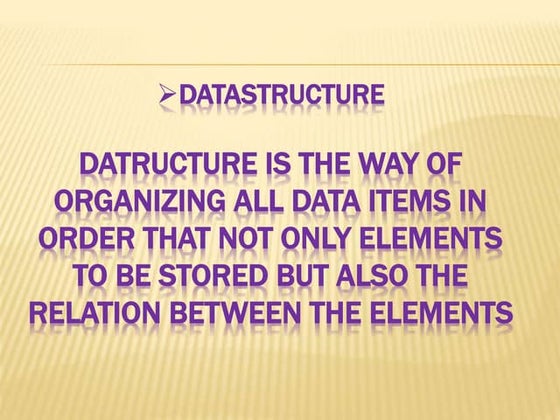



linked list in data structure shameen khan
╠²
This document discusses data structures and linked lists. It provides definitions and examples of different types of linked lists, including:
- Single linked lists, which contain nodes with a data field and a link to the next node.
- Circular linked lists, where the last node links back to the first node, forming a loop.
- Doubly linked lists, where each node contains links to both the previous and next nodes.
- Operations on linked lists such as insertion, deletion, traversal, and searching are also described.heap Sort Algorithm



heap Sort AlgorithmLemia Algmri
╠²
define the heap algorithm and the Max Heap
and Min Heap with example for each type and the insertion for new item .
Data Structure and Algorithms Linked List



Data Structure and Algorithms Linked ListManishPrajapati78
╠²
The document discusses different types of linked lists including:
- Singly linked lists that can only be traversed in one direction.
- Doubly linked lists that allow traversal in both directions using forward and backward pointers.
- Circular linked lists where the last node points back to the first node allowing continuous traversal.
- Header linked lists that include a header node at the beginning for simplified insertion and deletion. Header lists can be grounded where the last node contains a null pointer or circular where the last node points to the header.
- Two-way or doubly linked lists where each node contains a forward and backward pointer allowing bidirectional traversal through the list.Binary Search



Binary Searchkunj desai
╠²
This document describes binary search and provides an example of how it works. It begins with an introduction to binary search, noting that it can only be used on sorted lists and involves comparing the search key to the middle element. It then provides pseudocode for the binary search algorithm. The document analyzes the time complexity of binary search as O(log n) in the average and worst cases. It notes the advantages of binary search are its efficiency, while the disadvantage is that the list must be sorted. Applications mentioned include database searching and solving equations.B and B+ tree



B and B+ treeAshish Arun
╠²
This PPT is all about the Tree basic on fundamentals of B and B+ Tree with it's Various (Search,Insert and Delete) Operations performed on it and their Examples... Queue in Data Structure 



Queue in Data Structure Janki Shah
╠²
Contents:
1. What is Queue?
2. Operations perform on Queue with Algorithm & Example
3. Types of Queue with required exampleBinary Search Tree in Data Structure



Binary Search Tree in Data StructureDharita Chokshi
╠²
Content of slide
Tree
Binary tree Implementation
Binary Search Tree
BST Operations
Traversal
Insertion
Deletion
Types of BST
Complexity in BST
Applications of BSTBinary Search - Design & Analysis of Algorithms



Binary Search - Design & Analysis of AlgorithmsDrishti Bhalla
╠²
Binary search is an efficient algorithm for finding a target value within a sorted array. It works by repeatedly dividing the search range in half and checking the value at the midpoint. This eliminates about half of the remaining candidates in each step. The maximum number of comparisons needed is log n, where n is the number of elements. This makes binary search faster than linear search, which requires checking every element. The algorithm works by first finding the middle element, then checking if it matches the target. If not, it recursively searches either the lower or upper half depending on if the target is less than or greater than the middle element.Searching techniques in Data Structure And Algorithm



Searching techniques in Data Structure And Algorithm03446940736
╠²
Searching techniques in Data Structure And Algorithm
with animations with algorithms and details
try it to believe it
best way to explain every word
single linked list



single linked listSathasivam Rangasamy
╠²
This document discusses the implementation of a single linked list data structure. It describes the nodes that make up a linked list, which have an info field to store data and a next field pointing to the next node. The document outlines different ways to represent linked lists, including static arrays and dynamic pointers. It also provides algorithms for common linked list operations like traversing, inserting, and deleting nodes from the beginning, end, or a specified position within the list.Stacks IN DATA STRUCTURES



Stacks IN DATA STRUCTURESSowmya Jyothi
╠²
1) Stacks are linear data structures that follow the LIFO (last-in, first-out) principle. Elements can only be inserted or removed from one end called the top of the stack.
2) The basic stack operations are push, which adds an element to the top of the stack, and pop, which removes an element from the top.
3) Stacks have many applications including evaluating arithmetic expressions by converting them to postfix notation and implementing the backtracking technique in recursive backtracking problems like tower of Hanoi.Data Structures : hashing (1)



Data Structures : hashing (1)Home
╠²
Hashing is the process of converting a given key into another value. A╠²hash function╠²is used to generate the new value according to a mathematical algorithm. The result of a hash function is known as a╠²hash value╠²or simply, a╠²hash.
Linked list



Linked listakshat360
╠²
Linked lists are linear data structures where each node contains a data field and a pointer to the next node. There are two types: singly linked lists where each node has a single next pointer, and doubly linked lists where each node has next and previous pointers. Common operations on linked lists include insertion and deletion which have O(1) time complexity for singly linked lists but require changing multiple pointers for doubly linked lists. Linked lists are useful when the number of elements is dynamic as they allow efficient insertions and deletions without shifting elements unlike arrays.Hashing Technique In Data Structures



Hashing Technique In Data StructuresSHAKOOR AB
╠²
This document discusses different searching methods like sequential, binary, and hashing. It defines searching as finding an element within a list. Sequential search searches lists sequentially until the element is found or the end is reached, with efficiency of O(n) in worst case. Binary search works on sorted arrays by eliminating half of remaining elements at each step, with efficiency of O(log n). Hashing maps keys to table positions using a hash function, allowing searches, inserts and deletes in O(1) time on average. Good hash functions uniformly distribute keys and generate different hashes for similar keys.Data Structure (Queue)



Data Structure (Queue)Adam Mukharil Bachtiar
╠²
Queue is a first-in first-out (FIFO) data structure where elements can only be added to the rear of the queue and removed from the front of the queue. It has two pointers - a front pointer pointing to the front element and a rear pointer pointing to the rear element. Queues can be implemented using arrays or linked lists. Common queue operations include initialization, checking if empty/full, enqueue to add an element, and dequeue to remove an element. The document then describes how these operations work for queues implemented using arrays, linked lists, and circular arrays. It concludes by providing exercises to implement specific queue tasks.Linear search-and-binary-search



Linear search-and-binary-searchInternational Islamic University
╠²
This document provides an overview of linear search and binary search algorithms.
It explains that linear search sequentially searches through an array one element at a time to find a target value. It is simple to implement but has poor efficiency as the time scales linearly with the size of the input.
Binary search is more efficient by cutting the search space in half at each step. It works on a sorted array by comparing the target to the middle element and determining which half to search next. The time complexity of binary search is logarithmic rather than linear.Binary Tree Traversal



Binary Tree TraversalDhrumil Panchal
╠²
This presentation is useful to study about data structure and topic is Binary Tree Traversal. This is also useful to make a presentation about Binary Tree Traversal.Linked list



Linked listKalaivaniKS1
╠²
Linked lists are linear data structures where elements are linked using pointers. The three main types are singly, doubly, and circular linked lists. Linked lists allow dynamic memory allocation and fast insertion/deletion compared to arrays but slower access. A linked list contains nodes, each with a data field and pointer to the next node. Basic operations on linked lists include insertion, deletion, traversal, and search. Doubly linked lists include pointers to both the next and previous nodes.Hashing



HashingAmar Jukuntla
╠²
Hashing is a technique used to uniquely identify objects by assigning each object a key, such as a student ID or book ID number. A hash function converts large keys into smaller keys that are used as indices in a hash table, allowing for fast lookup of objects in O(1) time. Collisions, where two different keys hash to the same index, are resolved using techniques like separate chaining or linear probing. Common applications of hashing include databases, caches, and object representation in programming languages.Arrays



ArraysSARITHA REDDY
╠²
The document discusses arrays in data structures using C programming language. It defines what an array is and describes different types of arrays like one-dimensional, two-dimensional, and multi-dimensional arrays. It also explains array operations such as insertion, deletion, traversal, reversing, sorting, and searching. Additionally, it covers merging of arrays, arrays of pointers, and using arrays to represent polynomials.Linked list



Linked listTrupti Agrawal
╠²
This document discusses linked lists and polynomials represented as linked lists. It provides details on singly linked lists, including how to implement insertion and deletion of nodes. It also describes how to represent stacks and queues as dynamically linked lists. Finally, it discusses representing polynomials using arrays or linked lists, and how to perform addition and multiplication of polynomials in each representation.Bubble sort | Data structure |



Bubble sort | Data structure |MdSaiful14
╠²
Bubble sort is a simple sorting algorithm that compares adjacent elements and swaps them if they are not in order. It has a worst-case and average time complexity of O(n2) where n is the number of items, making it inefficient for large data sets. The algorithm makes multiple passes through the array, swapping adjacent elements that are out of order until the array is fully sorted. It is one of the simplest sorting algorithms to implement but does not perform well for large data sets due to its quadratic time complexity.Priority queues



Priority queuesPriyanka Rana
╠²
Describes basic understanding of priority queues, their applications, methods, implementation with sorted/unsorted list, sorting applications with insertion sort and selection sort with their running times.Applications of stack



Applications of stackeShikshak
╠²
The document discusses applications of stacks, including reversing strings and lists, Polish notation for mathematical expressions, converting between infix, prefix and postfix notations, evaluating postfix and prefix expressions, recursion, and the Tower of Hanoi problem. Recursion involves defining a function in terms of itself, with a stopping condition. Stacks can be used to remove recursion by saving local variables at each step.Data Types - Premetive and Non Premetive 



Data Types - Premetive and Non Premetive Raj Naik
╠²
This document discusses data types in C programming. It describes primitive data types like integers, floats, characters and their syntax. It also covers non-primitive data types like arrays, structures, unions, and linked lists. Arrays store a collection of similar data types, structures group different data types, and unions store different types in the same memory location. Linked lists are dynamic data structures using pointers. The document also provides overviews of stacks and queues, describing their LIFO and FIFO properties respectively.Introduction to data structure ppt



Introduction to data structure pptNalinNishant3
╠²
In computer science, a data structure is a data organization, management, and storage format that enables efficient access and modification. More precisely, a data structure is a collection of data values, the relationships among them, and the functions or operations that can be applied to the data. https://apkleet.com
<a href="https://apkleet.com" >games apk </a>Breadth First Search & Depth First Search



Breadth First Search & Depth First SearchKevin Jadiya
╠²
The slides attached here describes how Breadth first search and Depth First Search technique is used in Traversing a graph/tree with Algorithm and simple code snippet.
Optimal Binary Search tree ppt seminar.pptx



Optimal Binary Search tree ppt seminar.pptxssusered44c8
╠²
The document discusses optimal binary search trees. It begins by defining binary trees and binary search trees, noting that binary search trees require that left child nodes be less than the parent and right child nodes be greater. It then explains that an optimal binary search tree arranges elements in a binary structure to minimize search costs. The document provides an example comparing search costs between different binary tree structures. It outlines the optimal binary search tree algorithm, which calculates costs c[i,j] of reaching nodes i through j recursively to find the lowest cost tree structure.IRJET- A Survey on Different Searching Algorithms



IRJET- A Survey on Different Searching AlgorithmsIRJET Journal
╠²
The document summarizes and compares several common search algorithms:
- Binary search has the best average time complexity of O(log n) but only works on sorted data. Linear search has average time complexity of O(n) and works on any data but is less efficient.
- Hybrid search combines linear and binary search to search unsorted arrays more efficiently than linear search. Interpolation search is an improvement on binary search that may search in different locations based on the search key value.
- Jump search works on sorted data by jumping in blocks of size sqrt(n) and doing a linear search within blocks. It has better average performance than linear search but only works on sorted data.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Binary Search - Design & Analysis of Algorithms



Binary Search - Design & Analysis of AlgorithmsDrishti Bhalla
╠²
Binary search is an efficient algorithm for finding a target value within a sorted array. It works by repeatedly dividing the search range in half and checking the value at the midpoint. This eliminates about half of the remaining candidates in each step. The maximum number of comparisons needed is log n, where n is the number of elements. This makes binary search faster than linear search, which requires checking every element. The algorithm works by first finding the middle element, then checking if it matches the target. If not, it recursively searches either the lower or upper half depending on if the target is less than or greater than the middle element.Searching techniques in Data Structure And Algorithm



Searching techniques in Data Structure And Algorithm03446940736
╠²
Searching techniques in Data Structure And Algorithm
with animations with algorithms and details
try it to believe it
best way to explain every word
single linked list



single linked listSathasivam Rangasamy
╠²
This document discusses the implementation of a single linked list data structure. It describes the nodes that make up a linked list, which have an info field to store data and a next field pointing to the next node. The document outlines different ways to represent linked lists, including static arrays and dynamic pointers. It also provides algorithms for common linked list operations like traversing, inserting, and deleting nodes from the beginning, end, or a specified position within the list.Stacks IN DATA STRUCTURES



Stacks IN DATA STRUCTURESSowmya Jyothi
╠²
1) Stacks are linear data structures that follow the LIFO (last-in, first-out) principle. Elements can only be inserted or removed from one end called the top of the stack.
2) The basic stack operations are push, which adds an element to the top of the stack, and pop, which removes an element from the top.
3) Stacks have many applications including evaluating arithmetic expressions by converting them to postfix notation and implementing the backtracking technique in recursive backtracking problems like tower of Hanoi.Data Structures : hashing (1)



Data Structures : hashing (1)Home
╠²
Hashing is the process of converting a given key into another value. A╠²hash function╠²is used to generate the new value according to a mathematical algorithm. The result of a hash function is known as a╠²hash value╠²or simply, a╠²hash.
Linked list



Linked listakshat360
╠²
Linked lists are linear data structures where each node contains a data field and a pointer to the next node. There are two types: singly linked lists where each node has a single next pointer, and doubly linked lists where each node has next and previous pointers. Common operations on linked lists include insertion and deletion which have O(1) time complexity for singly linked lists but require changing multiple pointers for doubly linked lists. Linked lists are useful when the number of elements is dynamic as they allow efficient insertions and deletions without shifting elements unlike arrays.Hashing Technique In Data Structures



Hashing Technique In Data StructuresSHAKOOR AB
╠²
This document discusses different searching methods like sequential, binary, and hashing. It defines searching as finding an element within a list. Sequential search searches lists sequentially until the element is found or the end is reached, with efficiency of O(n) in worst case. Binary search works on sorted arrays by eliminating half of remaining elements at each step, with efficiency of O(log n). Hashing maps keys to table positions using a hash function, allowing searches, inserts and deletes in O(1) time on average. Good hash functions uniformly distribute keys and generate different hashes for similar keys.Data Structure (Queue)



Data Structure (Queue)Adam Mukharil Bachtiar
╠²
Queue is a first-in first-out (FIFO) data structure where elements can only be added to the rear of the queue and removed from the front of the queue. It has two pointers - a front pointer pointing to the front element and a rear pointer pointing to the rear element. Queues can be implemented using arrays or linked lists. Common queue operations include initialization, checking if empty/full, enqueue to add an element, and dequeue to remove an element. The document then describes how these operations work for queues implemented using arrays, linked lists, and circular arrays. It concludes by providing exercises to implement specific queue tasks.Linear search-and-binary-search



Linear search-and-binary-searchInternational Islamic University
╠²
This document provides an overview of linear search and binary search algorithms.
It explains that linear search sequentially searches through an array one element at a time to find a target value. It is simple to implement but has poor efficiency as the time scales linearly with the size of the input.
Binary search is more efficient by cutting the search space in half at each step. It works on a sorted array by comparing the target to the middle element and determining which half to search next. The time complexity of binary search is logarithmic rather than linear.Binary Tree Traversal



Binary Tree TraversalDhrumil Panchal
╠²
This presentation is useful to study about data structure and topic is Binary Tree Traversal. This is also useful to make a presentation about Binary Tree Traversal.Linked list



Linked listKalaivaniKS1
╠²
Linked lists are linear data structures where elements are linked using pointers. The three main types are singly, doubly, and circular linked lists. Linked lists allow dynamic memory allocation and fast insertion/deletion compared to arrays but slower access. A linked list contains nodes, each with a data field and pointer to the next node. Basic operations on linked lists include insertion, deletion, traversal, and search. Doubly linked lists include pointers to both the next and previous nodes.Hashing



HashingAmar Jukuntla
╠²
Hashing is a technique used to uniquely identify objects by assigning each object a key, such as a student ID or book ID number. A hash function converts large keys into smaller keys that are used as indices in a hash table, allowing for fast lookup of objects in O(1) time. Collisions, where two different keys hash to the same index, are resolved using techniques like separate chaining or linear probing. Common applications of hashing include databases, caches, and object representation in programming languages.Arrays



ArraysSARITHA REDDY
╠²
The document discusses arrays in data structures using C programming language. It defines what an array is and describes different types of arrays like one-dimensional, two-dimensional, and multi-dimensional arrays. It also explains array operations such as insertion, deletion, traversal, reversing, sorting, and searching. Additionally, it covers merging of arrays, arrays of pointers, and using arrays to represent polynomials.Linked list



Linked listTrupti Agrawal
╠²
This document discusses linked lists and polynomials represented as linked lists. It provides details on singly linked lists, including how to implement insertion and deletion of nodes. It also describes how to represent stacks and queues as dynamically linked lists. Finally, it discusses representing polynomials using arrays or linked lists, and how to perform addition and multiplication of polynomials in each representation.Bubble sort | Data structure |



Bubble sort | Data structure |MdSaiful14
╠²
Bubble sort is a simple sorting algorithm that compares adjacent elements and swaps them if they are not in order. It has a worst-case and average time complexity of O(n2) where n is the number of items, making it inefficient for large data sets. The algorithm makes multiple passes through the array, swapping adjacent elements that are out of order until the array is fully sorted. It is one of the simplest sorting algorithms to implement but does not perform well for large data sets due to its quadratic time complexity.Priority queues



Priority queuesPriyanka Rana
╠²
Describes basic understanding of priority queues, their applications, methods, implementation with sorted/unsorted list, sorting applications with insertion sort and selection sort with their running times.Applications of stack



Applications of stackeShikshak
╠²
The document discusses applications of stacks, including reversing strings and lists, Polish notation for mathematical expressions, converting between infix, prefix and postfix notations, evaluating postfix and prefix expressions, recursion, and the Tower of Hanoi problem. Recursion involves defining a function in terms of itself, with a stopping condition. Stacks can be used to remove recursion by saving local variables at each step.Data Types - Premetive and Non Premetive 



Data Types - Premetive and Non Premetive Raj Naik
╠²
This document discusses data types in C programming. It describes primitive data types like integers, floats, characters and their syntax. It also covers non-primitive data types like arrays, structures, unions, and linked lists. Arrays store a collection of similar data types, structures group different data types, and unions store different types in the same memory location. Linked lists are dynamic data structures using pointers. The document also provides overviews of stacks and queues, describing their LIFO and FIFO properties respectively.Introduction to data structure ppt



Introduction to data structure pptNalinNishant3
╠²
In computer science, a data structure is a data organization, management, and storage format that enables efficient access and modification. More precisely, a data structure is a collection of data values, the relationships among them, and the functions or operations that can be applied to the data. https://apkleet.com
<a href="https://apkleet.com" >games apk </a>Breadth First Search & Depth First Search



Breadth First Search & Depth First SearchKevin Jadiya
╠²
The slides attached here describes how Breadth first search and Depth First Search technique is used in Traversing a graph/tree with Algorithm and simple code snippet.
Similar to Binary search in data structure (20)
Optimal Binary Search tree ppt seminar.pptx



Optimal Binary Search tree ppt seminar.pptxssusered44c8
╠²
The document discusses optimal binary search trees. It begins by defining binary trees and binary search trees, noting that binary search trees require that left child nodes be less than the parent and right child nodes be greater. It then explains that an optimal binary search tree arranges elements in a binary structure to minimize search costs. The document provides an example comparing search costs between different binary tree structures. It outlines the optimal binary search tree algorithm, which calculates costs c[i,j] of reaching nodes i through j recursively to find the lowest cost tree structure.IRJET- A Survey on Different Searching Algorithms



IRJET- A Survey on Different Searching AlgorithmsIRJET Journal
╠²
The document summarizes and compares several common search algorithms:
- Binary search has the best average time complexity of O(log n) but only works on sorted data. Linear search has average time complexity of O(n) and works on any data but is less efficient.
- Hybrid search combines linear and binary search to search unsorted arrays more efficiently than linear search. Interpolation search is an improvement on binary search that may search in different locations based on the search key value.
- Jump search works on sorted data by jumping in blocks of size sqrt(n) and doing a linear search within blocks. It has better average performance than linear search but only works on sorted data.Data analysis and algorithms - UNIT 2.pptx



Data analysis and algorithms - UNIT 2.pptxsgrishma559
╠²
The document summarizes algorithms related to divide and conquer and greedy algorithms. It discusses binary search, finding maximum and minimum, merge sort, quick sort, and Huffman codes. The key steps of divide and conquer algorithms are to divide the problem into subproblems, conquer the subproblems by solving them recursively, and combine the solutions to solve the overall problem. Greedy algorithms make locally optimal choices at each step to find a global optimal solution. Huffman coding assigns variable-length codes to characters based on frequency to compress data.Rahat & juhith



Rahat & juhithRj Juhith
╠²
This document discusses linear search and binary search algorithms. Linear search sequentially checks each element of an unsorted array to find a target value, resulting in O(n) time complexity. Binary search works on a sorted array, comparing the target to the middle element and recursively searching half the array, requiring O(log n) time. The document provides pseudocode for both algorithms and compares their performance on different sized inputs. It also discusses properties of greedy algorithms and provides an example of when a greedy solution fails to find the optimal result.Array 2



Array 2Abbott
╠²
The document discusses arrays and their representation in memory. It contains 3 main points:
1) It introduces linear arrays and how they are represented in memory with sequential and contiguous locations. It also discusses multidimensional arrays.
2) It provides algorithms for common linear array operations like traversing, inserting, deleting and searching using binary search. It explains how each algorithm works through examples.
3) It discusses how 2D arrays are represented in memory and visualized, using an example of storing student exam marks in a 2D array.data_structure_Chapter two_computer.pptx



data_structure_Chapter two_computer.pptxMohammed472103
╠²
The document discusses various searching and sorting algorithms that use the divide and conquer approach. It describes linear search, binary search, and merge sort algorithms. Linear search has a time complexity of O(n) as it must examine each element to find the target. Binary search has a time complexity of O(log n) as it divides the search space in half each iteration. Merge sort also has a time complexity of O(n log n) as it divides the list into single elements and then merges them back together in sorted order.Data Structures & Algorithms - Lecture 2



Data Structures & Algorithms - Lecture 2Faculty of Computers and Informatics, Suez Canal University, Ismailia, Egypt
╠²
Data Structures and Algorithms using C++ programming language.Unit 6 dsa SEARCHING AND SORTING



Unit 6 dsa SEARCHING AND SORTINGPUNE VIDYARTHI GRIHA'S COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NASHIK
╠²
This document discusses various searching and sorting algorithms. It begins by defining searching as finding an element in a given list. Linear search and binary search are described as two common searching algorithms. Linear search has O(n) time complexity while binary search has O(log n) time complexity but requires a sorted list. The document also discusses different sorting algorithms like bubble sort, insertion sort, and merge sort, and defines key concepts related to sorting like stability, efficiency, and passes.Ocw chp6 2searchbinary



Ocw chp6 2searchbinaryPrashant Rai
╠²
The document discusses binary search and its advantages over sequential search. It explains that binary search improves search efficiency by dividing the search space in half at each step, allowing it to find an item in a sorted list in O(log n) time compared to O(n) for sequential search. The key steps of binary search are outlined, including comparing the search key to the middle element, and recursively searching either the left or right half depending on whether the key is smaller or larger than the middle element. Examples are provided to illustrate how binary search works on a sorted array to find a target value.Binary Search.pptx



Binary Search.pptxSheherBano57
╠²
The document describes the binary search algorithm. It works by repeatedly dividing in half the range of indices in a sorted array where the target value could be, until finding the exact index. It has a worst-case time complexity of O(log n), making it more efficient than linear search. Binary search requires the list to be sorted beforehand and is useful for searching databases, files, and other sorted data structures.FALLSEM2022-23_BCSE202L_TH_VL2022230103292_Reference_Material_II_08-08-2022_D...



FALLSEM2022-23_BCSE202L_TH_VL2022230103292_Reference_Material_II_08-08-2022_D...AntareepMajumder
╠²
This document provides an introduction to data structures and algorithms. It defines key terms like data structure, abstract data type, and algorithm. It also covers different types of data structures like arrays, linked lists, stacks, and queues. Specifically, it discusses the List abstract data type and implementations of lists using arrays and linked lists. It provides examples of common list operations like insertion, deletion, searching, and printing when using arrays and linked lists to represent a list. The running time of these operations is discussed as well.Lecture#1(Algorithmic Notations).ppt



Lecture#1(Algorithmic Notations).pptMuhammadTalhaAwan1
╠²
This document discusses data structures and algorithms. It provides grading schemes for theory and lab components. It acknowledges reference sources used to prepare the lecture. Key points covered include: what data structures are and why they are important for organizing data efficiently; characteristics of good data structures like time and space complexity; definitions of algorithms and examples like searching and sorting; and algorithmic notations used to describe processes like linear and binary search of arrays.Data Structure and Algorithms Arrays



Data Structure and Algorithms ArraysManishPrajapati78
╠²
This slide explains some basics concepts of array and operation performed on arrays like searching and sorting.Mastering on Divide and Conquer Algorithm



Mastering on Divide and Conquer AlgorithmMahmud Hasan Tanvir
╠²
This presentation dives into the divide and conquer algorithm approach, detailing its three-step process to solve complex problems efficiently. It includes a focus on binary search as a prime example, showing how this technique breaks down problems to achieve faster solutions. Perfect for computer science students and enthusiasts looking to strengthen their understanding of algorithmic problem-solving.ARRAY in python and c with examples .pptx



ARRAY in python and c with examples .pptxabhishekmaurya102515
╠²
A one-dimensional array stores elements linearly such that they can be accessed using an index, the document provides an example of finding the address of an element in a 1D array and taking user input to store in an array and display all elements, and abstract data types provide only the interface of a data structure without implementation details.Associative Learning



Associative LearningIndrajit Sreemany
╠²
This document proposes modifications to the Apriori algorithm for association rule mining. It begins with an introduction to association rule learning and the Apriori algorithm. It then describes the proposed modifications which include:
1. Adding a "tag" field to transactions to reduce the search space when finding frequent itemsets.
2. A modified approach to generating association rules that aims to produce fewer rules while maximizing correct classification of data.
An example is provided to illustrate how the tag-based search works. The proposed modifications are intended to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the association rule mining process. The document concludes by discussing experimental results comparing the proposed approach to other rule learning algorithms on an iris dataset.COMPUTER PROGRAMMING UNIT 1 Lecture 6



COMPUTER PROGRAMMING UNIT 1 Lecture 6Vishal Patil
╠²
This document provides information about linear and binary search algorithms. It discusses the basic concepts of linear search, including traversing an unsorted list sequentially until the target element is found or the list is exhausted. It also outlines the steps of a linear search algorithm. Next, it introduces binary search, which can only be used on sorted lists, and outlines the iterative process of comparing the target to the midpoint and narrowing the search range accordingly. Examples of both linear and binary search are given. Finally, it provides a few review questions related to searching concepts.Introduction to Datamining Concept and Techniques



Introduction to Datamining Concept and TechniquesSŲĪn C├▓m Nhom
╠²
This document provides an introduction to data mining techniques. It discusses data mining concepts like data preprocessing, analysis, and visualization. For data preprocessing, it describes techniques like similarity measures, down sampling, and dimension reduction. For data analysis, it explains clustering, classification, and regression methods. Specifically, it gives examples of k-means clustering and support vector machine classification. The goal of data mining is to retrieve hidden knowledge and rules from data.Updated Lab3.docx



Updated Lab3.docxAleezaAnjum
╠²
This document outlines a lab manual for a Data Structures and Algorithms course. The lab covers basic operations on arrays in C++, including insertion, deletion, traversal, and searching algorithms. It provides pseudocode and C++ code examples for inserting and deleting elements from an array, traversing a linear array, and using linear and binary search algorithms. The objectives are to understand array operations, write algorithms, and implement them in code using the Dev C++ tool.Data Structures & Algorithms - Lecture 2



Data Structures & Algorithms - Lecture 2Faculty of Computers and Informatics, Suez Canal University, Ismailia, Egypt
╠²
More from Meherul1234 (8)
Breadth-first search in alogorithm



Breadth-first search in alogorithmMeherul1234
╠²
Breadth-first search (BFS) is a technique for traversing graphs where the algorithm starts at a root node and explores all neighboring nodes at the present depth prior to moving on to the nodes at the next depth level. BFS guarantees to find a solution if one exists and to find the shortest solution path. An example shows using BFS to find the shortest path between two nodes by exploring all adjacent nodes at each level before moving deeper in the graph. Applications of BFS include finding shortest paths and checking for bipartiteness in graphs.Recursion in data structure



Recursion in data structureMeherul1234
╠²
@Recursion is a process in which a function calls itself as a subroutine. This allows the function to be repeated several times.
@Recursion property
@Tower of Hanoi
Transistor in electronics



Transistor in electronicsMeherul1234
╠²
@A╠²transistor╠²is a device that regulates current or voltage flow and acts as a switch or gate for electronic signals.
@Working of npn transistor
@Working of pnp transistorThe bus interface unit (biu)



The bus interface unit (biu)Meherul1234
╠²
$This unit handles all transfer of data and addresses on the buses for the EU(execution unit).
$Segment register
$Instruction queue
$Instruction pointerDecision tree in System Design



Decision tree in System DesignMeherul1234
╠²
@It is the process of choosing a course of action from among alternatives to achieve a desired goal.
@Uses of decision tree
@Advantages of decision treeAnalog to analog conversion



Analog to analog conversionMeherul1234
╠²
#Analog signals are modified to represent analog data.
#Analog to Analog conversion can be done in three ways
Programmable Peripheral Interface



Programmable Peripheral InterfaceMeherul1234
╠²
Programmable Interface Device used to interface a I/O device to the microprocessor
Intel has designed several PPI chips (e.g. 8155, 8156, 8255) to interface I/O devices.
*Analog to digital conversion
*Digital to Analog conversionError handling



Error handlingMeherul1234
╠²
How to write an error handler.
Normally, it displays a message indicating the cause of the error and may also terminate script execution when a PHP script encounters an error.
Now, while this behavior is acceptable during the development phase, it cannot continue once a PHP application has been released to actual users.
In "live" situations, it is unprofessional to display cryptic error messages (which are usually incomprehensible to non-technical users).
It is more professional to intercept these errors and either resolve them (if resolution is possible), or notify the user with an easily-understood error message (if not).
Recently uploaded (20)
Blind spots in AI and Formulation Science, IFPAC 2025.pdf



Blind spots in AI and Formulation Science, IFPAC 2025.pdfAjaz Hussain
╠²
The intersection of AI and pharmaceutical formulation science highlights significant blind spotsŌĆösystemic gaps in pharmaceutical development, regulatory oversight, quality assurance, and the ethical use of AIŌĆöthat could jeopardize patient safety and undermine public trust. To move forward effectively, we must address these normalized blind spots, which may arise from outdated assumptions, errors, gaps in previous knowledge, and biases in language or regulatory inertia. This is essential to ensure that AI and formulation science are developed as tools for patient-centered and ethical healthcare.Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding || Boby Basnet



Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding || Boby BasnetBoby Basnet
╠²
Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding Full Note
|| Assistant Professor Boby Basnet ||IAAS || AFU || PU || FUHow to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
Integrate WhatsApp into Odoo using the WhatsApp Business API or third-party modules to enhance communication. This integration enables automated messaging and customer interaction management within Odoo 17.Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In this slide weŌĆÖll discuss on the useful environment methods in Odoo 18. In Odoo 18, environment methods play a crucial role in simplifying model interactions and enhancing data processing within the ORM framework.APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
-Autonomy, Teams and Tension: Projects under stress
-Tim Lyons
-The neurological levels of
team-working: Harmony and tensions
With a background in projects spanning more than 40 years, Tim Lyons specialised in the delivery of large, complex, multi-disciplinary programmes for clients including Crossrail, Network Rail, ExxonMobil, Siemens and in patent development. His first career was in broadcasting, where he designed and built commercial radio station studios in Manchester, Cardiff and Bristol, also working as a presenter and programme producer. Tim now writes and presents extensively on matters relating to the human and neurological aspects of projects, including communication, ethics and coaching. He holds a MasterŌĆÖs degree in NLP, is an NLP Master Practitioner and International Coach. He is the Deputy Lead for APMŌĆÖs People Interest Network.
Session | The Neurological Levels of Team-working: Harmony and Tensions
Understanding how teams really work at conscious and unconscious levels is critical to a harmonious workplace. This session uncovers what those levels are, how to use them to detect and avoid tensions and how to smooth the management of change by checking you have considered all of them.APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...Association for Project Management
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
- Autonomy, Teams and Tension
- Oliver Randall & David Bovis
- Own Your Autonomy
Oliver Randall
Consultant, Tribe365
Oliver is a career project professional since 2011 and started volunteering with APM in 2016 and has since chaired the People Interest Network and the North East Regional Network. Oliver has been consulting in culture, leadership and behaviours since 2019 and co-developed HPTM┬«ŌĆ»an off the shelf high performance framework for teams and organisations and is currently working with SAS (Stellenbosch Academy for Sport) developing the culture, leadership and behaviours framework for future elite sportspeople whilst also holding down work as a project manager in the NHS at North Tees and Hartlepool Foundation Trust.
David Bovis
Consultant, Duxinaroe
A Leadership and Culture Change expert, David is the originator of BTFAŌäó and The Dux Model.
With a Masters in Applied Neuroscience from the Institute of Organisational Neuroscience, he is widely regarded as the ŌĆśGo-ToŌĆÖ expert in the field, recognised as an inspiring keynote speaker and change strategist.
He has an industrial engineering background, majoring in TPS / Lean. David worked his way up from his apprenticeship to earn his seat at the C-suite table. His career spans several industries, including Automotive, Aerospace, Defence, Space, Heavy Industries and Elec-Mech / polymer contract manufacture.
Published in LondonŌĆÖs Evening Standard quarterly business supplement, James CaanŌĆÖs ŌĆśYour businessŌĆÖ Magazine, ŌĆśQuality WorldŌĆÖ, the Lean Management Journal and Cambridge Universities ŌĆśPMAŌĆÖ, he works as comfortably with leaders from FTSE and Fortune 100 companies as he does owner-managers in SMEŌĆÖs. He is passionate about helping leaders understand the neurological root cause of a high-performance culture and sustainable change, in business.
Session | Own Your Autonomy ŌĆō The Importance of Autonomy in Project Management
#OwnYourAutonomy is aiming to be a global APM initiative to position everyone to take a more conscious role in their decision making process leading to increased outcomes for everyone and contribute to ŌĆ£a world in which all projects succeedŌĆØ.
We want everyone to join the journey.
#OwnYourAutonomy is the culmination of 3 years of collaborative exploration within the Leadership Focus Group which is part of the APM People Interest Network. The work has been pulled together using the 5 HPTM® Systems and the BTFA neuroscience leadership programme.
https://www.linkedin.com/showcase/apm-people-network/about/QuickBooks Desktop to QuickBooks Online How to Make the Move



QuickBooks Desktop to QuickBooks Online How to Make the MoveTechSoup
╠²
If you use QuickBooks Desktop and are stressing about moving to QuickBooks Online, in this webinar, get your questions answered and learn tips and tricks to make the process easier for you.
Key Questions:
* When is the best time to make the shift to QuickBooks Online?
* Will my current version of QuickBooks Desktop stop working?
* I have a really old version of QuickBooks. What should I do?
* I run my payroll in QuickBooks Desktop now. How is that affected?
*Does it bring over all my historical data? Are there things that don't come over?
* What are the main differences between QuickBooks Desktop and QuickBooks Online?
* And moreHow to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 Employee



How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 EmployeeCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to configure flexible working schedule in Odoo 18 Employee module. In Odoo 18, the Employee module offers powerful tools to configure and manage flexible working schedules tailored to your organization's needs.Eng7-Q4-Lesson 1 Part 1 Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and T...



Eng7-Q4-Lesson 1 Part 1 Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and T...sandynavergas1
╠²
Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and Technical TermsA PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...



A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...Beena E S
╠²
A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by Aaron ShepardDigital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptx



Digital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
╠²
This ppt is useful for not only for B.Ed., M.Ed., M.A. (Education) or any other PG level students or Ph.D. scholars but also for the school, college and university teachers who are interested to prepare an e-content with AI for their students and others.Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptx



Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxmansk2
╠²
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxKaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Finals of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. N.C. DPI's 2023 Language Diversity Briefing



N.C. DPI's 2023 Language Diversity BriefingMebane Rash
╠²
The number of languages spoken in NC public schools.EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdf



EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdfLiz Walsh-Trevino
╠²
EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdfAPM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...Association for Project Management
╠²
Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Binary search in data structure
- 1. OBJECTIVE OF PRESENTATION ŌĆó Define Binary search. ŌĆó Example and solve with Binary search.
- 2. Binary search ŌĆó Binary search is a fast search algorithm with run-time complexity. ŌĆó This search algorithm works on the principle of divide and conquer. ŌĆó For this algorithm to work properly, the data collection should be in the sorted form. ŌĆó Binary search looks for a particular item by comparing the middle most item of the collection.
- 3. Algorithm of Binary search It can be done by the following step: 1. get the middle element MID= INT((BEG+END)/2) 2. if the middle element equals to the searched value, the algorithm stops. 3.Otherwise a)If Item<DATA[MID],then appear left half DATA[BEG]ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.DATA[MID-1] b)If item>DATA[MID],then appear right half DATA[BEG]ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.DATA[MID+1]
- 4. EXAMPLE Let DATA be the following sorted 10 element array: DATA: 2,5,8,12,16,23,38,56,72,91 Find ITEM=23.
- 5. End of the presentation Thank You






