Computerized System Validation.vinay (1).pptx
- 1. COMPUTERIZED SYSTEM VALIDATION Presented To – Mrs.Surbhi kamboj Presented By – VINAY Roll No. – 2224PH1006 M.Pharm QA (2022-24) KIET SCHOOL OF PHARMACY SEMINA R
- 2. COMPUTER SYSTEM VALIDATION (CSV)  “Confirmation by examination and provision of objective evidence that software specifications conform to user needs and intended uses, and that the particular requirements implemented through software can be consistently fulfilled” – General Principles of Software Validation: Final Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff
- 3. UNDERSTAND THE KEY POINTS, LET’S BREAKDOWN THE DEFINITION.  “Confirmation by examination” – must have defined user needs and intended uses. The user can be a patient, someone in the hospital, a lab tech, a QA engineer, a manufacturing person. Examine the software to confirm that it functions as defined in the requirements and that it will be suitable for its intended use.  “provision of objective evidence” – there must be defined software requirements. Document all validation activities and test results.  “user needs and intended uses” – examine the software to ensure that it meets the user needs and defined requirements. This could include design reviews, code reviews, testing, etc. Define what the user needs to do with the software and how they will use the software.
- 4. UNDERSTAND THE KEY POINTS, LET’S BREAKDOWN THE DEFINITION.  “particular requirements implemented through software” – confirm that the requirements can be consistently fulfilled (not just in a single situation). This could include stress testing multiple data sets, performance testing with many users in many locations, testing with multiple browsers or web apps, testing from multiple devices (and even mobile apps), etc. Define how the software needs to work to enable the intended use.  “consistently fulfilled” – need to have objective evidence of this confirmation (for inspections). Document all validation activities and test results. The examination needs to confirm that the software will work in all anticipated situations.
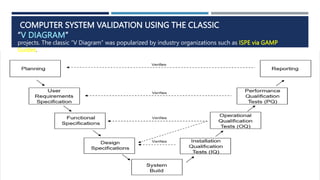
- 5. COMPUTER SYSTEM VALIDATION USING THE CLASSIC “V DIAGRAM” projects. The classic “V Diagram” was popularized by industry organizations such as ISPE via GAMP Guides.
- 6. LET’S BREAK DOWN EACH PART A LITTLE BIT FURTHER, STARTING WITH PLANNING.  Validation Plan The Validation Plan defines what will be validated and the approach you will use. It also defines roles and responsibilities along with the most important part, the Acceptance Criteria.
- 7. USER REQUIREMENTS SPECIFICATION (URS)  The User Requirements Specification describes what the user needs from the software and how they will use it. It also contains any critical constraints such as regulations, safety requirements, operational requirements, etc.  For example, here’s a list of a few User Requirements that might be needed for a lab system.  System must track training of lab analysts on lab methods/techniques  System must track samples coming into the lab  System must automatically assign lab analysts to test samples based on availability and training  System must send sample testing pass/fail outcomes to the ERP  System must comply with 21 CFR 11
- 8. FUNCTIONAL SPECIFICATIONS (FS)  The Functional Specification document describes how the software needs to work and look to meet the user needs. The document might include descriptions of how specific screens and reports should look, or describe data that needs to be captured.  The Functional Requirements can also include logic and calculations along with how it will comply with regulatory requirements. For example, the Part 11 compliance requirements might detail how passwords or the audit trail should work.
- 9. DESIGN SPECIFICATIONS (DS)  Database Design – file structures, field definitions, data flow diagrams, entity relationship diagrams  Logic/Process Design – pseudo code for logic and calculations  Security Design – virus protection, hacker protection  Interface Design – what data will move from one system to another; how and how often, and failure handling  Architecture Design – required hardware, operating systems, application versions, middleware, etc.  Network Requirements  Specific peripheral devices – scanners, printers, etc.
- 10. DESIGN SPECIFICATIONS (DS)  System Build  In the System Build step, you develop or purchase your software and then configure it to the previous specification documents. This step includes unit testing and integration testing.  Installation Qualification Tests (IQ) Tests  The Installation Qualification tests provide confirmation that the software or system is installed and setup according to the Design Specification. Usually the software is first installed in a test or validation environment, but there can be exceptions in situations such as manufacturing.
- 11. OPERATIONAL QUALIFICATION (OQ) TESTS  Operational Qualification testing is often referred to as Functional Testing or System Testing. OQ tests confirm that all functionality defined in the Functional Specification is present and working correctly, and that there are no bugs. OQ tests can also include confirmation of any design elements not tested during IQ, such as configuration, are working as specified.
- 12. PERFORMANCE QUALIFICATION (PQ) TESTS  Performance Qualification testing is often called User Acceptance testing. PQ testing confirms that the software will meet the users’ needs and is suitable for their intended use, as defined in the User Requirements Specification. Testing can follow Use Cases, SOPs, user-defined scenarios, etc. For simple software like reports or spreadsheets, OQ and PQ testing are often combined.
- 13. REPORTING  The last step in this validation method is to write the Validation Report, often called the Validation Summary or System Certification. This report provides confirmation that all activities specified in the validation plan have been completed. The Validation Report summarizes the testing results and provides confirmation that all acceptance criteria have been met and the software is ready for deployment.
- 14. OTHER COMPUTER SYSTEM VALIDATION TERMINOLOGY SOFTWARE VERIFICATION THE FDA STATES THAT:  Software verification looks for consistency, completeness, and correctness of the software and its supporting documentation, as it is being developed, and provides support for a subsequent conclusion that software is validated.
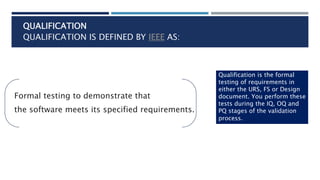
- 15. QUALIFICATION QUALIFICATION IS DEFINED BY IEEE AS: Formal testing to demonstrate that the software meets its specified requirements. Qualification is the formal testing of requirements in either the URS, FS or Design document. You perform these tests during the IQ, OQ and PQ stages of the validation process.
- 17. REFERENCES:  What is Computer System Validation and How Do You Do It? (validationcenter.com)  FDA Computer System & Software Validation - What You’ve Known For 20+ Years Is Changing (greenlight.guru)
- 18. THANK YOU