1 of 2
Download to read offline

Recommended
Slope as rate_of_change



Slope as rate_of_changejennywang1124
Ã˝
This document discusses slope as the rate of change and uses two graphs, y=-2x+4 and y=3x-3, to represent the distance over time of two objects, A and B. It calculates that object A is traveling faster at 3 m/s compared to object B's speed of 2 m/s. The objects pass each other at 1.2 seconds and were initially 7 meters apart, traveling in opposite directions.Algebra 2 Day 3-4



Algebra 2 Day 3-4Kate Nowak
Ã˝
This document provides instructions for finding the x-intercepts of the quadratic equation y = -2x^2 - 5x + 25 using the quadratic formula. It asks how to solve the equation algebraically for the x-intercepts and to express the solution in simplest radical form using the quadratic formula taught on Day 6 for solving quadratics.Differential Equation Tutorial 1



Differential Equation Tutorial 1Yong Sheng
Ã˝
This tutorial document provides 4 partial differential equations and asks the reader to determine the order and linearity of each equation. It also asks the reader to find the values of m that satisfy two ordinary differential equations, where y is defined as a function of m. Specifically, it asks the reader to find the values of m such that y=xm and y=emx cos(nx) are solutions to two given ODEs.Solution3



Solution3H K
Ã˝
Solution to Assignment 3 of Discrete Mathematics. It includes induction, proof by contrapositive, proof by contradiction. AM11 Trigonometry



AM11 TrigonometrySofian Muhd
Ã˝
This document provides information on trigonometric functions including definitions of sine, cosine, and tangent at common angles. It also outlines trigonometric identities, addition and double angle formulas, transformations of trig graphs, and the R-formula for expressing combinations of trig functions as a single trig function. Key concepts covered include the unit circle, quadrantal angles, amplitude, frequency, and period as they relate to trigonometric graphs.Pythagorean theorem and distance formula



Pythagorean theorem and distance formula41625929
Ã˝
The Pythagorean theorem states that for any right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the two legs. It is represented by the equation A2 + B2 = C2, where A and B are the legs and C is the hypotenuse. The distance formula calculates the distance between two points in a plane by taking the square root of the sum of the squares of the differences of their x- and y-coordinates. An example demonstrates using the distance formula to calculate the distance between the points (8, 0) and (4, 2).Dm assignment3



Dm assignment3H K
Ã˝
This document contains an assignment with 5 questions on sets, proofs using induction, contradiction, and contrapositive. The deadline for the assignment is April 26th for Thursday classes and April 27th for Friday classes. The assignment was written by Harshit Kumar on April 13, 2012.New day 7 examples



New day 7 examplesjchartiersjsd
Ã˝
The binomial theorem describes the pattern for expanding binomial expressions in the form (x + y)^n into a sum of terms. It states that the sum of the exponents of each term equals the power of the binomial, the number of terms is always one more than the power, and that the exponents of x and y alternate between decreasing and increasing by 1 for each term. The binomial theorem provides a method for easily writing out the expansion of any binomial and finding individual terms within the expansion.Ratio word problem creation tiny tigershark



Ratio word problem creation tiny tigersharkDonovanLum
Ã˝
Sarin and Toby baked cakes in a 5:3 ratio. Sarin baked 24 more cakes than Toby. To find how many cakes Toby baked, the problem sets up a model with the ratio and that Sarin baked 24 more than Toby. It determines that if the difference between their cakes is 24, and that difference is 2 units in their ratio, then each unit must be 12 cakes. Using the 3:5 ratio and solving for Toby's amount gives the answer that Toby baked 36/96 or 3/8 of the total cakes.Ratio word problem creation tiny tigershark



Ratio word problem creation tiny tigersharkJohann619
Ã˝
Sarin and Toby baked cakes in a 5:3 ratio. Sarin baked 24 more cakes than Toby. To find how many cakes Toby baked, the problem sets up a model with the ratio and that Sarin baked 24 more than Toby. It determines that if the difference between their cakes is 24, and that difference is 2 units in their ratio, then each unit must be 12 cakes. Therefore, if Toby bakes 3 units in their ratio, he must have baked 3 * 12 = 36 cakes. The total cakes they baked was 8 units * 12 cakes per unit = 96 cakes. So Toby baked 36/96 or 3/8 of theCh02 31



Ch02 31schibu20
Ã˝
This document contains solutions to mathematical exercises involving algebraic expressions and equations. The key steps are:
1) Combining like terms and simplifying expressions using algebraic properties such as distribution, difference of squares, and factoring polynomials.
2) Setting expressions equal to each other and solving for variables.
3) The exercises involve simplifying expressions, factoring, solving equations, and rationalizing denominators.Day 11 examples u4w14



Day 11 examples u4w14jchartiersjsd
Ã˝
This document discusses verifying trigonometric identities and determining non-permissible values for identities. It first verifies two identities by showing that = and = 30° are solutions. It then identifies the non-permissible values of θ for the identity tan θ = 1/cot θ on the interval from 0 to 2π as being θ = nπ where n is any integer.On the Stick and Rope Problem - Draft 1



On the Stick and Rope Problem - Draft 1Iwan Pranoto
Ã˝
This document discusses the stick and rope problem of finding a smooth function that maximizes the area under the graph subject to the constraint that the length of the graph is a given fixed value.
The problem is analyzed for the case where both ends of the rope are fixed at zero. It is shown that when the fixed length is between 1 and π/2, the optimal solution is a segment of a circle with its center on the vertical line at t=1/2.
The proof uses Lagrange multipliers to derive an equation that the optimal function must satisfy, showing it is the equation of a circle. Boundary conditions then determine the circle's parameters. Special cases for longer rope lengths are also discussedπιασαμε τα ορια 



πιασαμε τα ορια Μαυρουδης Μακης
Ã˝
This document contains 7 limit problems worked out step-by-step with explanations of the reasoning. The problems involve various algebraic expressions containing polynomials, rational expressions, and variables approaching different limits. The solutions find the limits by simplifying the expressions, factorizing where possible, and evaluating the behavior of terms as the variable approaches the limit.Funções trigonométricas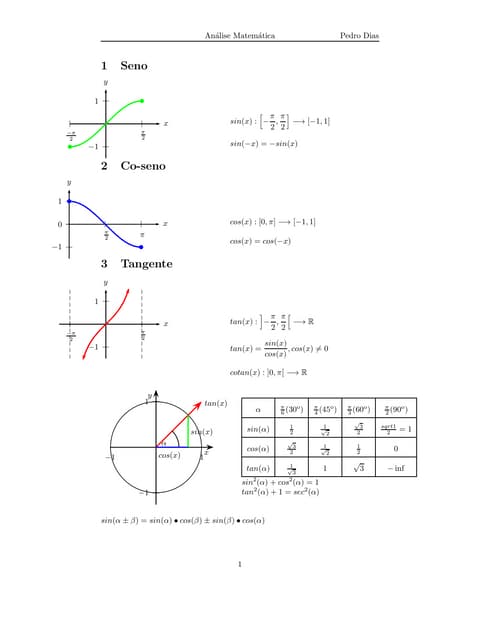



Funções trigonométricasPedro Dias
Ã˝
This document provides definitions and properties for trigonometric functions including sine, cosine, and tangent. It defines the domains and ranges of sine, cosine, and tangent. Examples of trigonometric ratios are given for common angles like 30, 45, 60, and 90 degrees. Trigonometric identities are also listed, such as the sine and cosine of sums and differences of angles.Factoring pst



Factoring pstMyra Ramos
Ã˝
The document provides instructions on factoring polynomials using perfect square trinomials. It begins with examples of multiplying perfect square binomials and identifies the pattern. Students are shown how to determine if a trinomial is a perfect square and factor it using the formula. The document concludes with examples of factoring various polynomials using perfect square trinomials.Day 7 examples u7w14



Day 7 examples u7w14jchartiersjsd
Ã˝
The document discusses binomial expansion, which is the process of multiplying out terms with two variables according to their power using the binomial theorem. It provides examples of expanding binomial expressions like (x + y)2, (x + y)3, and (x + y)4. It also notes that the sum of the exponents in each term equals the overall power, and the number of terms is always one more than the power. Finally, it provides the binomial theorem for expanding any binomial expression and finding a particular term.Stevie Wallace



Stevie Wallace41106247
Ã˝
The document discusses the Pythagorean theorem and distance formula. The Pythagorean theorem states that for a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. It is used to find the length of one side of a right triangle given the other two sides. The distance formula calculates the distance between two points in a coordinate plane by taking the square root of the sum of the squared differences between the x- and y-coordinates.Algebra q



Algebra qDidik Sadianto
Ã˝
This document contains 10 math problems for an algebra test, ranging from finding integer pairs that satisfy an equation to evaluating infinite sums involving binary expansions of numbers. The problems cover a variety of algebra topics including functions, inequalities, number bases, and series.March 7



March 7khyps13
Ã˝
1. The document discusses factoring perfect square trinomials, which are polynomials where the first term is a perfect square, the third term is a perfect square, and the coefficient of the second term is twice the square root of the product of the first and third term coefficients.
2. To factor a perfect square trinomial, take the square root of the first term, add it to the square root of the third term, and place it in parentheses twice to get the two factors.
3. Examples are provided of determining if a trinomial is a perfect square and factoring perfect square trinomials like x2 + 10x + 25 as (x + 5)2.Alg2 lesson 7-5



Alg2 lesson 7-5Carol Defreese
Ã˝
This document provides instructions and examples for solving polynomial equations and determining the number and type of roots. It contains examples of writing polynomial functions with specified real and complex roots. It also gives examples of determining the possible number of positive real zeros, negative real zeros, and imaginary zeros based on the sign changes in a polynomial function.Math integration-homework help



Math integration-homework helpExpertsmind IT Education Pvt Ltd.
Ã˝
The document contains solutions to three math homework problems:
1) An integral problem involving trigonometric substitutions and integration by parts. The solution finds the integral I=1/2[x cos(ln(x))+xsin(ln(x))]+C.
2) A differential equation problem solved using an integrating factor. The solution finds the particular solution as Y=(2x+1)e^2x + ex + (x+1).
3) An eigenproblem with solutions for the eigenvectors and eigenvalues. The roots are found to be real and equal to 2.An engineer 1+1=2



An engineer 1+1=2Byron Willems
Ã˝
The document discusses rewriting a simple mathematical equation, 1+1=2, in a more "elegant" and "comprehensive" manner using advanced mathematical notation and terms. It proceeds to transform the simple equation through multiple steps incorporating logarithmic, exponential, trigonometric and other advanced functions. The resulting equation is much longer and more complex, though purportedly more "professional". The presentation is intended in jest to show that engineers can also overcomplicate simple concepts.Potw Solution



Potw SolutionKim94
Ã˝
This document provides steps to solve a polynomial equation of the form x^4 + x^2 + 1 = 0. First, find a common denominator to simplify the expression. Next, solve the quartic equation for x^4 + 1 and substitute that expression into the original equation. Finally, simplify the resulting expression.Algebra s



Algebra sDidik Sadianto
Ã˝
This document contains 10 math problems with solutions. Problem 1 asks the reader to calculate the product of the smallest and largest prime factors of the number of words in the problem statement. The answer is 1681. Problem 2 asks what percentage of gold King Midas would need to earn today to end up with as much gold as he started with after spending a certain percentage yesterday. The answer is 100x-1%. Problem 3 asks the reader to find all integer pairs (a,b) such that ab + a - 3b = 5. The answer lists the four pairs.Unit 5.6



Unit 5.6nglaze10
Ã˝
The document discusses identifying the slope and y-intercept of a line from its equation. It provides examples of finding the slope and y-intercept for different line equations by rewriting the equations in slope-intercept form as needed. Specifically, it shows identifying the slope as 3 and the y-intercept as 4 for the equation y = 3x + 4, and identifying the slope as -3 and y-intercept as 2 for the equation 3x + y = 2 after rewriting it as y = -3x + 2.

Apresentação 1.0anabritesilva
Ã˝
Este documento trata de conceitos básicos de apresentações de slides. Ele aborda tópicos como estrutura de slides, formatação de texto e imagens, e dicas para uma apresentação eficiente.More Related Content
What's hot (18)
Ratio word problem creation tiny tigershark



Ratio word problem creation tiny tigersharkDonovanLum
Ã˝
Sarin and Toby baked cakes in a 5:3 ratio. Sarin baked 24 more cakes than Toby. To find how many cakes Toby baked, the problem sets up a model with the ratio and that Sarin baked 24 more than Toby. It determines that if the difference between their cakes is 24, and that difference is 2 units in their ratio, then each unit must be 12 cakes. Using the 3:5 ratio and solving for Toby's amount gives the answer that Toby baked 36/96 or 3/8 of the total cakes.Ratio word problem creation tiny tigershark



Ratio word problem creation tiny tigersharkJohann619
Ã˝
Sarin and Toby baked cakes in a 5:3 ratio. Sarin baked 24 more cakes than Toby. To find how many cakes Toby baked, the problem sets up a model with the ratio and that Sarin baked 24 more than Toby. It determines that if the difference between their cakes is 24, and that difference is 2 units in their ratio, then each unit must be 12 cakes. Therefore, if Toby bakes 3 units in their ratio, he must have baked 3 * 12 = 36 cakes. The total cakes they baked was 8 units * 12 cakes per unit = 96 cakes. So Toby baked 36/96 or 3/8 of theCh02 31



Ch02 31schibu20
Ã˝
This document contains solutions to mathematical exercises involving algebraic expressions and equations. The key steps are:
1) Combining like terms and simplifying expressions using algebraic properties such as distribution, difference of squares, and factoring polynomials.
2) Setting expressions equal to each other and solving for variables.
3) The exercises involve simplifying expressions, factoring, solving equations, and rationalizing denominators.Day 11 examples u4w14



Day 11 examples u4w14jchartiersjsd
Ã˝
This document discusses verifying trigonometric identities and determining non-permissible values for identities. It first verifies two identities by showing that = and = 30° are solutions. It then identifies the non-permissible values of θ for the identity tan θ = 1/cot θ on the interval from 0 to 2π as being θ = nπ where n is any integer.On the Stick and Rope Problem - Draft 1



On the Stick and Rope Problem - Draft 1Iwan Pranoto
Ã˝
This document discusses the stick and rope problem of finding a smooth function that maximizes the area under the graph subject to the constraint that the length of the graph is a given fixed value.
The problem is analyzed for the case where both ends of the rope are fixed at zero. It is shown that when the fixed length is between 1 and π/2, the optimal solution is a segment of a circle with its center on the vertical line at t=1/2.
The proof uses Lagrange multipliers to derive an equation that the optimal function must satisfy, showing it is the equation of a circle. Boundary conditions then determine the circle's parameters. Special cases for longer rope lengths are also discussedπιασαμε τα ορια 



πιασαμε τα ορια Μαυρουδης Μακης
Ã˝
This document contains 7 limit problems worked out step-by-step with explanations of the reasoning. The problems involve various algebraic expressions containing polynomials, rational expressions, and variables approaching different limits. The solutions find the limits by simplifying the expressions, factorizing where possible, and evaluating the behavior of terms as the variable approaches the limit.Funções trigonométricas



Funções trigonométricasPedro Dias
Ã˝
This document provides definitions and properties for trigonometric functions including sine, cosine, and tangent. It defines the domains and ranges of sine, cosine, and tangent. Examples of trigonometric ratios are given for common angles like 30, 45, 60, and 90 degrees. Trigonometric identities are also listed, such as the sine and cosine of sums and differences of angles.Factoring pst



Factoring pstMyra Ramos
Ã˝
The document provides instructions on factoring polynomials using perfect square trinomials. It begins with examples of multiplying perfect square binomials and identifies the pattern. Students are shown how to determine if a trinomial is a perfect square and factor it using the formula. The document concludes with examples of factoring various polynomials using perfect square trinomials.Day 7 examples u7w14



Day 7 examples u7w14jchartiersjsd
Ã˝
The document discusses binomial expansion, which is the process of multiplying out terms with two variables according to their power using the binomial theorem. It provides examples of expanding binomial expressions like (x + y)2, (x + y)3, and (x + y)4. It also notes that the sum of the exponents in each term equals the overall power, and the number of terms is always one more than the power. Finally, it provides the binomial theorem for expanding any binomial expression and finding a particular term.Stevie Wallace



Stevie Wallace41106247
Ã˝
The document discusses the Pythagorean theorem and distance formula. The Pythagorean theorem states that for a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. It is used to find the length of one side of a right triangle given the other two sides. The distance formula calculates the distance between two points in a coordinate plane by taking the square root of the sum of the squared differences between the x- and y-coordinates.Algebra q



Algebra qDidik Sadianto
Ã˝
This document contains 10 math problems for an algebra test, ranging from finding integer pairs that satisfy an equation to evaluating infinite sums involving binary expansions of numbers. The problems cover a variety of algebra topics including functions, inequalities, number bases, and series.March 7



March 7khyps13
Ã˝
1. The document discusses factoring perfect square trinomials, which are polynomials where the first term is a perfect square, the third term is a perfect square, and the coefficient of the second term is twice the square root of the product of the first and third term coefficients.
2. To factor a perfect square trinomial, take the square root of the first term, add it to the square root of the third term, and place it in parentheses twice to get the two factors.
3. Examples are provided of determining if a trinomial is a perfect square and factoring perfect square trinomials like x2 + 10x + 25 as (x + 5)2.Alg2 lesson 7-5



Alg2 lesson 7-5Carol Defreese
Ã˝
This document provides instructions and examples for solving polynomial equations and determining the number and type of roots. It contains examples of writing polynomial functions with specified real and complex roots. It also gives examples of determining the possible number of positive real zeros, negative real zeros, and imaginary zeros based on the sign changes in a polynomial function.Math integration-homework help



Math integration-homework helpExpertsmind IT Education Pvt Ltd.
Ã˝
The document contains solutions to three math homework problems:
1) An integral problem involving trigonometric substitutions and integration by parts. The solution finds the integral I=1/2[x cos(ln(x))+xsin(ln(x))]+C.
2) A differential equation problem solved using an integrating factor. The solution finds the particular solution as Y=(2x+1)e^2x + ex + (x+1).
3) An eigenproblem with solutions for the eigenvectors and eigenvalues. The roots are found to be real and equal to 2.An engineer 1+1=2



An engineer 1+1=2Byron Willems
Ã˝
The document discusses rewriting a simple mathematical equation, 1+1=2, in a more "elegant" and "comprehensive" manner using advanced mathematical notation and terms. It proceeds to transform the simple equation through multiple steps incorporating logarithmic, exponential, trigonometric and other advanced functions. The resulting equation is much longer and more complex, though purportedly more "professional". The presentation is intended in jest to show that engineers can also overcomplicate simple concepts.Potw Solution



Potw SolutionKim94
Ã˝
This document provides steps to solve a polynomial equation of the form x^4 + x^2 + 1 = 0. First, find a common denominator to simplify the expression. Next, solve the quartic equation for x^4 + 1 and substitute that expression into the original equation. Finally, simplify the resulting expression.Algebra s



Algebra sDidik Sadianto
Ã˝
This document contains 10 math problems with solutions. Problem 1 asks the reader to calculate the product of the smallest and largest prime factors of the number of words in the problem statement. The answer is 1681. Problem 2 asks what percentage of gold King Midas would need to earn today to end up with as much gold as he started with after spending a certain percentage yesterday. The answer is 100x-1%. Problem 3 asks the reader to find all integer pairs (a,b) such that ab + a - 3b = 5. The answer lists the four pairs.Unit 5.6



Unit 5.6nglaze10
Ã˝
The document discusses identifying the slope and y-intercept of a line from its equation. It provides examples of finding the slope and y-intercept for different line equations by rewriting the equations in slope-intercept form as needed. Specifically, it shows identifying the slope as 3 and the y-intercept as 4 for the equation y = 3x + 4, and identifying the slope as -3 and y-intercept as 2 for the equation 3x + y = 2 after rewriting it as y = -3x + 2.Viewers also liked (20)


Apresentação 1.0anabritesilva
Ã˝
Este documento trata de conceitos básicos de apresentações de slides. Ele aborda tópicos como estrutura de slides, formatação de texto e imagens, e dicas para uma apresentação eficiente.



GeometriaIsabel21Pinto
Ã˝
O documento apresenta os trabalhos realizados por alunos do 6o ano da Escola E.B. Alexandre Herculano sobre a geometria do prisma triangular e as simetrias e isometrias, incluindo os nomes dos autores de cada trabalho.





LinkLivia França
Ã˝
1) O documento explica como criar links hipertexto em HTML usando a tag <A> para ligar partes de um documento ou diferentes documentos;
2) Os atributos href, TARGET e NAME da tag <A> determinam respectivamente o arquivo de destino, o frame de destino e uma √¢ncora dentro do documento;
3) Caminhos relativos e absolutos podem ser usados para especificar o arquivo de destino, sendo o caminho relativo usado quando os arquivos est√£o no mesmo servidor.J.bat



J.batBiel2013a
Ã˝
This document does not contain any meaningful information to summarize in 3 sentences or less. It only contains repeated keyboard characters with no spaces or punctuation.

Atividade Vagas Global versao1Sabrina Oliveira
Ã˝
O documento instrui o leitor a repetir um procedimento ensinado em 10 sites diferentes e clicar em um banner de publicidade antes de fechar o navegador para registrar sua atividade completa.



Gest√£o da zona costeira e os terrenos de marinhaLuana Neves
Ã˝
1. O documento discute a gestão da zona costeira brasileira e os terrenos de marinha, patrimônio público da União localizado ao longo da costa.
2. A pesquisa propõe a atualização do conceito de terrenos de marinha para melhor alinhar com o Plano Nacional de Gerenciamento Costeiro e contemplar aspectos como preservação ambiental, inclusão social, direitos coletivos e uso sustentável da orla.
3. Os terrenos de marinha representam um desafio para o ordenamento territorial da zona

















More from jchartiersjsd (20)
Day 8 examples u7w14



Day 8 examples u7w14jchartiersjsd
Ã˝
This document contains 5 problems involving finding terms in expansions of polynomials. The problems involve finding specific terms that contain a given power of x in expansions of polynomials such as (3x^4 - 1)^9, (-x^3 + 2)^6, (x + 1)^3x, (x + 1)^x, and determining the value of m if one term in the expansion of (2x - m)^7 is -262500x^2y^5.Day 4 examples u7w14



Day 4 examples u7w14jchartiersjsd
Ã˝
This document discusses how to calculate arrangements when some items must be together or apart. It explains that when items need to be together, they should be counted as a single item to reduce the total items being arranged. Then the total number of arrangements is calculated by finding the total possible arrangements and subtracting the arrangements that do not satisfy the constraints of certain items being together or apart. Examples provided include arranging people in a row when some must or cannot sit together and arranging books on a shelf keeping books of each subject together.Day 3 examples u7w14



Day 3 examples u7w14jchartiersjsd
Ã˝
Permutations refer to arrangements of objects in a definite order. Some key points:
- Permutations are represented by "nPn" where n is the total number of objects and r is the number being arranged.
- Permutations are used to calculate possibilities like license plates, phone numbers, and locker combinations.
- Restrictions like starting/ending conditions or requiring alternating arrangements reduce the number of possible permutations.
- Objects that are identical only count once toward the total number of permutations rather than being distinguishable.Day 2 examples u7w14



Day 2 examples u7w14jchartiersjsd
Ã˝
Factorial notation represents the product of all positive integers less than or equal to the given number. For example, 5! = 5 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 1 and 8! = 8 x 7 x 6 x 5 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 1. The document also provides examples of simplifying factorials without a calculator by using properties such as 5! + 4! = 6 x 4! and (k + 1)! + k! = (k + 2)k!.Day 1 examples u7w14



Day 1 examples u7w14jchartiersjsd
Ã˝
This document provides examples and explanations of the fundamental counting principle and addition counting principle to solve combinatorics problems. It gives 8 examples of using the fundamental counting principle to count the number of possible outcomes of independent events. These include counting the number of volleyball shoe combinations, outfits that can be created from different clothing items, ways to select committees from groups of people, and 3-digit numbers with no repeating digits. It also provides 5 examples of using the addition counting principle to count outcomes when events are dependent, such as selecting a president and vice president of opposite sexes from a group.Day 7 examples u6w14



Day 7 examples u6w14jchartiersjsd
Ã˝
This document discusses graphing composite functions. It provides examples of determining the composite functions f(g(x)) and g(f(x)) for various functions f(x) and g(x), sketching the graphs of the composite functions, and stating their domains. It also gives examples of determining possible functions f(x) and g(x) that satisfy given composite functions.Day 5 examples u6w14



Day 5 examples u6w14jchartiersjsd
Ã˝
1. The document discusses composite functions, which involve combining two functions f(x) and g(x) where the output of one is used as the input of the other. It provides examples of evaluating composite functions using tables and graphs.
2. Key steps for evaluating composite functions are: 1) Substitute the inner function into the outer function and 2) Simplify the expression. Order matters as f(g(x)) and g(f(x)) may have different values.
3. Examples are worked through to find composite functions given basic functions like f(x) = x + 1 and g(x) = 2x as well as more complex rational functions.Day 4 examples u6w14



Day 4 examples u6w14jchartiersjsd
Ã˝
The graph is a linear function with a domain of all real numbers and a range of real numbers greater than or equal to 3. The graph is a line with a y-intercept of 3 that increases at a rate of 1 as x increases.Day 3 examples u6w14



Day 3 examples u6w14jchartiersjsd
Ã˝
Rational functions are functions of the form f(x) = p(x)/q(x) where p(x) and q(x) are polynomials. For example, comparing rational functions like 2x/(x^2 - 4) and (x-1)/(x+1). Horizontal asymptotes of rational functions occur when the degree of the polynomial in the numerator is less than the degree of the polynomial in the denominator.Day 1 examples u6w14



Day 1 examples u6w14jchartiersjsd
Ã˝
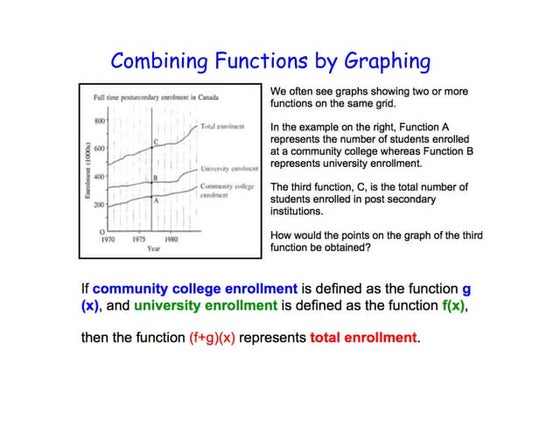
This document discusses how to find the sum, difference, product, and quotient of functions. The sum of functions is found by adding the y-coordinates of each function. The difference is found by subtracting the y-coordinates. The product is represented as h(x) = f(x)g(x) and the quotient is represented as h(x) = f(x)/g(x). Examples are provided for adding and subtracting functions.Mental math test outline



Mental math test outlinejchartiersjsd
Ã˝
The document outlines a mental math test covering polynomials. It includes short answer questions testing long division, synthetic division, the remainder theorem, and finding the degree, leading coefficient, and y-intercept of polynomials. The test also covers matching graphs to polynomial equations and word problems involving fully factoring polynomials and two graphs. Multiple choice questions will require explaining solutions, while long answer questions involve fully factoring polynomials and word problems.Day 8 examples u5w14



Day 8 examples u5w14jchartiersjsd
Ã˝
The document contains two polynomial word problems. The first asks to write a function V(x) to express the volume of a box with dimensions x, x+2, x+10 in terms of x, and find possible x values if the volume is 96 cm^3. The second problem describes a block of ice that is initially 3 ft by 4 ft by 5 ft, and asks to write a function to model reducing each dimension by the same amount to reach a volume of 24 ft^3, and determine how much to remove from each dimension.Day 7 examples u5w14



Day 7 examples u5w14jchartiersjsd
Ã˝
The document provides 3 polynomial word problems: 1) finding the equation for a polynomial given its graph f(x) = -(x - 2)2(x + 1), 2) determining the polynomial P(x) when divided by (x - 3) with a quotient of 2x^2 + x - 6 and remainder of 4, and 3) finding the value of a if (x - 2) is a factor of ax^3 + 4x^2 + x - 2. It also gives a 4th problem of determining the value of k when 2x^3 + kx^2 - 3x + 2 is divided by x - 2 with a remainder of 4.Day 5 examples u5w14



Day 5 examples u5w14jchartiersjsd
Ã˝
Polynomial functions are described by their degree and have certain characteristics. The graph of a polynomial is smooth and continuous without sharp corners. Odd degree polynomials rise on the left and fall on the right, while even degree polynomials rise on both sides. The number of x-intercepts and local maxima/minima are limited by the degree. Polynomials can be matched based on their degree, leading coefficient, even/odd nature, and number of x-intercepts and local extrema. The x-intercepts of a polynomial correspond to the roots of the equation, and a repeated root indicates a zero of higher multiplicity which affects the graph.Day 3 examples u5w14



Day 3 examples u5w14jchartiersjsd
Ã˝
This document asks which of the following binomials are factors of the expression 9x - 12. The options given are x + 3 and x - 2. Of these two options, x - 2 is a factor of 9x - 12, since (3x - 4)(3x - 4) = 9x^2 - 12x + 12 = 9x - 12.Day 10 examples u4f13
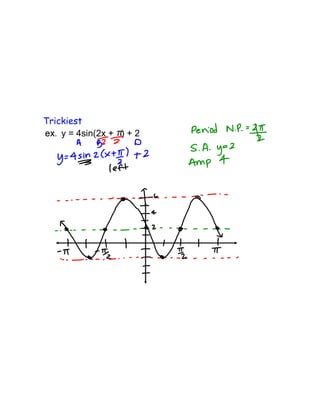
- 1. Trickiest y = 4sin(2x + ) + 2