PsychofArt - Day 28 classical conditioning
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes160 views
This document summarizes classical conditioning, which is a form of learning in which a neutral stimulus becomes associated with an unconditioned stimulus to produce a conditioned response. It provides examples of classical conditioning, such as Pavlov's experiment where a dog learned to associate the ringing of a bell with food. The key terms of classical conditioning are defined, including unconditioned stimulus, neutral stimulus, conditioned stimulus, unconditioned response, and conditioned response. Extinction of conditioned responses and spontaneous recovery are also described.
1 of 26
Download to read offline




![How Does Learning Work?
US + Neutral Stimulus = UR
US + Neutral Stimulus = UR
US + Neutral Stimulus = UR
US + Neutral Stimulus = UR
[ . . . ]
US + Neutral Stimulus = UR
US + Neutral Stimulus = UR
US + Neutral Stimulus = UR
CS = CR (Phew, Finally)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day28-classicalconditioning-181126124723/85/PsychofArt-Day-28-classical-conditioning-5-320.jpg)




















Recommended
Scoring IBDP visual arts CS F&P - Function and Purpose.pdf



Scoring IBDP visual arts CS F&P - Function and Purpose.pdfJoshua Eckert
╠²
Criterion B (to be retired fall 2025)Formal Analy scoring_ 7 vs 6, 5, 4 (2023).pdf



Formal Analy scoring_ 7 vs 6, 5, 4 (2023).pdfJoshua Eckert
╠²
Formal Analy scoring_ 7 vs 6, 5, 4 (2023)Designing interiors - how to make an interesting room with an interesting cam...



Designing interiors - how to make an interesting room with an interesting cam...Joshua Eckert
╠²
See titleColor Mixing Challenge - activity for high school art



Color Mixing Challenge - activity for high school artJoshua Eckert
╠²
9th and 10th-grade activity - color mixingMarketing and Entrepreneurship 101



Marketing and Entrepreneurship 101Joshua Eckert
╠²
1. The document discusses entrepreneurship and the importance of creating "remarkable" products that stand out and capture people's attention. It notes that average products no longer work for gaining customers.
2. A key idea is the "Purple Cow Theory" which says that a new product or idea must be so surprising and original that it spreads through word of mouth. It must stop people in their tracks and make them take notice.
3. The document uses examples like a man obsessed with his dog and a woman obsessed with mochi to show that everyone has the potential to be innovative in some niche area, and that is where opportunities lie for new products.Intro to Augmented Reality



Intro to Augmented RealityJoshua Eckert
╠²
The document discusses the differences between virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR). AR has limitations in that it cannot detect physical spaces and objects in the real world. To achieve true mixed reality, a device would need complex hardware and software to digitally map physical spaces and understand how virtual objects interact with real world walls, furniture etc. The key distinction between AR, VR and MR is that MR experiences allow users to do things not possible on traditional screens by merging real and virtual worlds.Claudia Carr



Claudia CarrJoshua Eckert
╠²
Claudia Carr's artwork combines elements of landscape, still life, and abstraction by making still life objects appear as landscapes. Her work challenges viewers to determine if they are viewing landscapes, still lifes, or abstractions. She achieves this blend of genres by arranging still life objects in her studio in ways that mimic landscapes.How to Draw Better Shadows



How to Draw Better ShadowsJoshua Eckert
╠²
1) The document discusses techniques for rendering realistic light and shadow in 2D artwork, focusing on diffused light and direct light.
2) With diffused light, values should be slightly different on front-facing, side-facing, and top-facing planes, and shadows are soft with strong local color. With direct light, shadow shapes are most important and contrast is highest in the foreground.
3) The document emphasizes the importance of understanding how light affects relative values - a black surface in light can have a higher value than a white surface in shadow. Rendering light and shadow realistically requires seeing past local color and value.2D to 3D



2D to 3DJoshua Eckert
╠²
Wreck-It Ralph is a movie about video game characters that can move between 2D and 3D games. The document discusses how characters like Ralph can transition between different dimensions by walking through walls and rotating the camera around them as they explore new areas. It also references moving to the 4th dimension.Advanced techniques for painting realistic color, light, and shadow



Advanced techniques for painting realistic color, light, and shadowJoshua Eckert
╠²
This document provides an overview of techniques for rendering realistic light and shadow in 2D artwork. It discusses two main types of lighting - diffused light and direct light - and how they affect values, colors, and shadow shapes in a scene. For diffused light, it emphasizes how top-facing planes have slightly different values than side-facing planes. For direct light, it stresses paying most attention to dramatic shadow shapes while local color and value matter less. The document concludes by showing examples from artists who demonstrate masterful use of light and shadow to create a sense of depth and realism in their compositions.Psych of art - Day 13b - Nature Nurture Lab



Psych of art - Day 13b - Nature Nurture LabJoshua Eckert
╠²
The document discusses the debate between nature vs. nurture perspectives on human behavior and cognition. An environmentalist believes that one's environment and upbringing primarily shape who they are, while a nativist believes innate instincts are mostly determinative. The document presents several examples of debates around the origins of behaviors and abilities, such as why some find rotten meat disgusting or whether gender differences in math ability are due to nature or nurture. It suggests that both genetic and environmental factors likely contribute to human traits in complex ways.Psych of Art - Day 13 - Oxytocin and cute aggression



Psych of Art - Day 13 - Oxytocin and cute aggressionJoshua Eckert
╠²
1. The document discusses differences between brains and computers, noting that brains are more resilient when damaged and can perform tasks like guessing intent that computers cannot.
2. It also discusses fixed action patterns in animals that are triggered by releasing stimuli to produce specific behaviors, and how more advanced animal brains like mice integrate multiple stimuli, hormones, and learning to modify behaviors.
3. The document examines various hormones and neurotransmitters like oxytocin, dopamine, testosterone, and their context-dependent effects on behaviors. It provides examples of how closely related animals sometimes adopt babies of other species due to similar brain wiring for "baby-mania".Psych of Art - Day 10



Psych of Art - Day 10Joshua Eckert
╠²
This document discusses physicalism and dualism views of the human mind and brain. It provides an overview of the triune brain model of brain evolution, with the lizard brain forming the core and newer mammalian and primate brains developing additional layers. The document notes that humans have a large cortex making up 80% of our brain mass, which enables advanced functions like imagination, tool use, social learning, and complex language that are unique to humans. It questions how we learn what different brain areas do.Psych of Art - Libertarianism



Psych of Art - LibertarianismJoshua Eckert
╠²
This document discusses and clarifies the differences between liberals, libertarians, and conservatives on various political issues. It also discusses scenarios involving freedom of speech and whether speech was violated in each case. The document then discusses issues around public art funding, including who should decide what art the public sees and at what point funding should be cut. It also discusses tests for determining good versus bad art.PsychofArt - Day 2



PsychofArt - Day 2Joshua Eckert
╠²
The document discusses different perspectives on modern art and whether it can be objectively judged as "good" or "bad". It notes that rules of modern art emphasize surprising the viewer while traditional art aims to move the viewer emotionally. It also argues that people claiming their favorite art is objectively good is a common perspective, regardless of the type of art. The document explores several modern and traditional artworks and asks how viewers determine if they are good or bad. It poses questions about what fans of different art styles may think of each other's preferences and why modern art is often associated with liberal politics. Finally, it previews discussing art censorship in the next class.PsychofArt - Day 31 - abstraction, women artists



PsychofArt - Day 31 - abstraction, women artistsJoshua Eckert
╠²
The document discusses several topics related to art including why some artists choose abstraction over realism, why genius is often associated with youth, why most innovative historical artists were male, and what can be done about underrepresentation of women in art. It explores Cezanne's transition to abstraction, challenges assumptions that creativity peaks young through examples, and hypothesizes that women lacked opportunities for training, patrons, and intellectual exchange that may have limited female artistic achievement historically.PsychofArt - Day 25 impressionism, color



PsychofArt - Day 25 impressionism, colorJoshua Eckert
╠²
This document discusses perception and whether different people see the same color differently. It then mentions Impressionism and repeatedly references "The Bellelli Family - unveiled 1867". It also includes the names of several famous Impressionist artists and asks whether all artists are highly emotional.Illustrated numbers Art Lesson



Illustrated numbers Art LessonJoshua Eckert
╠²
This document highlights two artists, Eric Guillon and Lorelay Bove, who both create illustrated numbers and science-inspired works of art. Eric Guillon's style is described as mad scientist, and he is featured in the Artist Spotlight section. Similarly, Lorelay Bove is also highlighted in the Artist Spotlight with her art described as having a mad scientist style.PsychofArt - Day 18 - Color



PsychofArt - Day 18 - ColorJoshua Eckert
╠²
The document discusses how natural selection led humans to favor certain traits. It suggests natural selection favored those who feared spiders, loved baby faces, and hated rotten meat. These groups all survived and passed on their traits, while indifferent individuals died off. The document also claims natural selection favored those attracted to flowers. The following sections discuss why neutral colors are popular, perceptions of Ancient Rome and Greece, and origins of pigments like Naples yellow and the world's blackest black.PsychofArt - Day 17



PsychofArt - Day 17Joshua Eckert
╠²
This document discusses the debate between nature and nurture perspectives on human development and behavior. It presents views from both environmentalism and nativism. Environmentalism posits that people are blank slates shaped entirely by their environment of parents and peers. Nativism argues that genes predominantly determine behavior and thinking, with little influence from environment. The document explores this debate through examples related to food preferences, violence, gender differences in math ability, and handwriting preferences. It suggests that both nature and nurture likely play roles.PsychofArt - Day 16



PsychofArt - Day 16Joshua Eckert
╠²
This document discusses human instincts and how they interact with culture. It provides examples of fixed action patterns in animals triggered by releasing stimuli. There is a debate around whether human behaviors like finding incest disgusting are due to culture or innate instincts. The document considers possible human instincts like finding siblings attractive as disgusting, finding babies cute, and having positive or negative reactions to praise and criticism. It acknowledges that discovering human instincts could be unsettling if it meant natural behaviors were acceptable or unchangeable, but argues that human nature also allows rising above instincts through logic and society can influence behavior through laws and norms. Both nature and nurture likely interact to shape human thoughts and actions.PsychofArt - Day 8-9 (Should the arts receive public funding?)



PsychofArt - Day 8-9 (Should the arts receive public funding?)Joshua Eckert
╠²
This document discusses differences between liberals and libertarians, as well as conservatives and libertarians. Libertarians support minimal government intervention and no restrictions on issues like abortion, drugs, guns, and same-sex marriage. The document also presents several scenarios involving freedom of speech and asks whether speech was violated. It discusses public funding for art and which art the public should see. It outlines different tests art critics use to evaluate art, such as originality, historical context, craftsmanship, and subjective impact.PsychofArt - Day 3 - Dualism - The relationship between minds, brains, and souls



PsychofArt - Day 3 - Dualism - The relationship between minds, brains, and soulsJoshua Eckert
╠²
This document contains a summary of key concepts in philosophy of mind including dualism and physicalism. It discusses whether aspects of personal identity like memories and thoughts are physical or non-physical. Examples are provided of movies that take either a dualist or physicalist view. Evidence for and against dualism is explored through examples like splitting the corpus callosum and the effects of brain changes. The document questions whether describing humans as "just" or "merely" animals understates our uniqueness. It argues we are both part of the natural world and something unprecedented.Costume Design vs Fashion Design



Costume Design vs Fashion DesignJoshua Eckert
╠²
Costume design focuses on creating costumes according to a theme or for a specific character, such as for performances in theater, film, television, and Broadway, whereas fashion design is about street-wear and trends for everyday people. Costume designers draw inspiration from research and a character's personality, background, and time period while fashion designers aim to set trends for popular styles.Jean Nouvel



Jean NouvelJoshua Eckert
╠²
The document discusses how an architectural design was influenced by Islamic architecture and the way it casts light patterns. It also notes that each "Little World" within the design is unique. Finally, it mentions breaking the square as part of the design concept.Advanced perspective tips & tricks



Advanced perspective tips & tricksJoshua Eckert
╠²
This document discusses perspective drawing techniques including vanishing points, 3D letters, stairs, shapes, reflections, shadows, and drawing animals in perspective. It notes that perspective drawings often include at least one vanishing point off the page and that two vanishing points should be far apart for accurate perspective drawings.Intellectual Honesty & Research Integrity.pptx



Intellectual Honesty & Research Integrity.pptxNidhiSharma495177
╠²
Research Publication & Ethics contains a chapter on Intellectual Honesty and Research Integrity.
Different case studies of intellectual dishonesty and integrity were discussed.Blind spots in AI and Formulation Science, IFPAC 2025.pdf



Blind spots in AI and Formulation Science, IFPAC 2025.pdfAjaz Hussain
╠²
The intersection of AI and pharmaceutical formulation science highlights significant blind spotsŌĆösystemic gaps in pharmaceutical development, regulatory oversight, quality assurance, and the ethical use of AIŌĆöthat could jeopardize patient safety and undermine public trust. To move forward effectively, we must address these normalized blind spots, which may arise from outdated assumptions, errors, gaps in previous knowledge, and biases in language or regulatory inertia. This is essential to ensure that AI and formulation science are developed as tools for patient-centered and ethical healthcare.More Related Content
More from Joshua Eckert (20)
Claudia Carr



Claudia CarrJoshua Eckert
╠²
Claudia Carr's artwork combines elements of landscape, still life, and abstraction by making still life objects appear as landscapes. Her work challenges viewers to determine if they are viewing landscapes, still lifes, or abstractions. She achieves this blend of genres by arranging still life objects in her studio in ways that mimic landscapes.How to Draw Better Shadows



How to Draw Better ShadowsJoshua Eckert
╠²
1) The document discusses techniques for rendering realistic light and shadow in 2D artwork, focusing on diffused light and direct light.
2) With diffused light, values should be slightly different on front-facing, side-facing, and top-facing planes, and shadows are soft with strong local color. With direct light, shadow shapes are most important and contrast is highest in the foreground.
3) The document emphasizes the importance of understanding how light affects relative values - a black surface in light can have a higher value than a white surface in shadow. Rendering light and shadow realistically requires seeing past local color and value.2D to 3D



2D to 3DJoshua Eckert
╠²
Wreck-It Ralph is a movie about video game characters that can move between 2D and 3D games. The document discusses how characters like Ralph can transition between different dimensions by walking through walls and rotating the camera around them as they explore new areas. It also references moving to the 4th dimension.Advanced techniques for painting realistic color, light, and shadow



Advanced techniques for painting realistic color, light, and shadowJoshua Eckert
╠²
This document provides an overview of techniques for rendering realistic light and shadow in 2D artwork. It discusses two main types of lighting - diffused light and direct light - and how they affect values, colors, and shadow shapes in a scene. For diffused light, it emphasizes how top-facing planes have slightly different values than side-facing planes. For direct light, it stresses paying most attention to dramatic shadow shapes while local color and value matter less. The document concludes by showing examples from artists who demonstrate masterful use of light and shadow to create a sense of depth and realism in their compositions.Psych of art - Day 13b - Nature Nurture Lab



Psych of art - Day 13b - Nature Nurture LabJoshua Eckert
╠²
The document discusses the debate between nature vs. nurture perspectives on human behavior and cognition. An environmentalist believes that one's environment and upbringing primarily shape who they are, while a nativist believes innate instincts are mostly determinative. The document presents several examples of debates around the origins of behaviors and abilities, such as why some find rotten meat disgusting or whether gender differences in math ability are due to nature or nurture. It suggests that both genetic and environmental factors likely contribute to human traits in complex ways.Psych of Art - Day 13 - Oxytocin and cute aggression



Psych of Art - Day 13 - Oxytocin and cute aggressionJoshua Eckert
╠²
1. The document discusses differences between brains and computers, noting that brains are more resilient when damaged and can perform tasks like guessing intent that computers cannot.
2. It also discusses fixed action patterns in animals that are triggered by releasing stimuli to produce specific behaviors, and how more advanced animal brains like mice integrate multiple stimuli, hormones, and learning to modify behaviors.
3. The document examines various hormones and neurotransmitters like oxytocin, dopamine, testosterone, and their context-dependent effects on behaviors. It provides examples of how closely related animals sometimes adopt babies of other species due to similar brain wiring for "baby-mania".Psych of Art - Day 10



Psych of Art - Day 10Joshua Eckert
╠²
This document discusses physicalism and dualism views of the human mind and brain. It provides an overview of the triune brain model of brain evolution, with the lizard brain forming the core and newer mammalian and primate brains developing additional layers. The document notes that humans have a large cortex making up 80% of our brain mass, which enables advanced functions like imagination, tool use, social learning, and complex language that are unique to humans. It questions how we learn what different brain areas do.Psych of Art - Libertarianism



Psych of Art - LibertarianismJoshua Eckert
╠²
This document discusses and clarifies the differences between liberals, libertarians, and conservatives on various political issues. It also discusses scenarios involving freedom of speech and whether speech was violated in each case. The document then discusses issues around public art funding, including who should decide what art the public sees and at what point funding should be cut. It also discusses tests for determining good versus bad art.PsychofArt - Day 2



PsychofArt - Day 2Joshua Eckert
╠²
The document discusses different perspectives on modern art and whether it can be objectively judged as "good" or "bad". It notes that rules of modern art emphasize surprising the viewer while traditional art aims to move the viewer emotionally. It also argues that people claiming their favorite art is objectively good is a common perspective, regardless of the type of art. The document explores several modern and traditional artworks and asks how viewers determine if they are good or bad. It poses questions about what fans of different art styles may think of each other's preferences and why modern art is often associated with liberal politics. Finally, it previews discussing art censorship in the next class.PsychofArt - Day 31 - abstraction, women artists



PsychofArt - Day 31 - abstraction, women artistsJoshua Eckert
╠²
The document discusses several topics related to art including why some artists choose abstraction over realism, why genius is often associated with youth, why most innovative historical artists were male, and what can be done about underrepresentation of women in art. It explores Cezanne's transition to abstraction, challenges assumptions that creativity peaks young through examples, and hypothesizes that women lacked opportunities for training, patrons, and intellectual exchange that may have limited female artistic achievement historically.PsychofArt - Day 25 impressionism, color



PsychofArt - Day 25 impressionism, colorJoshua Eckert
╠²
This document discusses perception and whether different people see the same color differently. It then mentions Impressionism and repeatedly references "The Bellelli Family - unveiled 1867". It also includes the names of several famous Impressionist artists and asks whether all artists are highly emotional.Illustrated numbers Art Lesson



Illustrated numbers Art LessonJoshua Eckert
╠²
This document highlights two artists, Eric Guillon and Lorelay Bove, who both create illustrated numbers and science-inspired works of art. Eric Guillon's style is described as mad scientist, and he is featured in the Artist Spotlight section. Similarly, Lorelay Bove is also highlighted in the Artist Spotlight with her art described as having a mad scientist style.PsychofArt - Day 18 - Color



PsychofArt - Day 18 - ColorJoshua Eckert
╠²
The document discusses how natural selection led humans to favor certain traits. It suggests natural selection favored those who feared spiders, loved baby faces, and hated rotten meat. These groups all survived and passed on their traits, while indifferent individuals died off. The document also claims natural selection favored those attracted to flowers. The following sections discuss why neutral colors are popular, perceptions of Ancient Rome and Greece, and origins of pigments like Naples yellow and the world's blackest black.PsychofArt - Day 17



PsychofArt - Day 17Joshua Eckert
╠²
This document discusses the debate between nature and nurture perspectives on human development and behavior. It presents views from both environmentalism and nativism. Environmentalism posits that people are blank slates shaped entirely by their environment of parents and peers. Nativism argues that genes predominantly determine behavior and thinking, with little influence from environment. The document explores this debate through examples related to food preferences, violence, gender differences in math ability, and handwriting preferences. It suggests that both nature and nurture likely play roles.PsychofArt - Day 16



PsychofArt - Day 16Joshua Eckert
╠²
This document discusses human instincts and how they interact with culture. It provides examples of fixed action patterns in animals triggered by releasing stimuli. There is a debate around whether human behaviors like finding incest disgusting are due to culture or innate instincts. The document considers possible human instincts like finding siblings attractive as disgusting, finding babies cute, and having positive or negative reactions to praise and criticism. It acknowledges that discovering human instincts could be unsettling if it meant natural behaviors were acceptable or unchangeable, but argues that human nature also allows rising above instincts through logic and society can influence behavior through laws and norms. Both nature and nurture likely interact to shape human thoughts and actions.PsychofArt - Day 8-9 (Should the arts receive public funding?)



PsychofArt - Day 8-9 (Should the arts receive public funding?)Joshua Eckert
╠²
This document discusses differences between liberals and libertarians, as well as conservatives and libertarians. Libertarians support minimal government intervention and no restrictions on issues like abortion, drugs, guns, and same-sex marriage. The document also presents several scenarios involving freedom of speech and asks whether speech was violated. It discusses public funding for art and which art the public should see. It outlines different tests art critics use to evaluate art, such as originality, historical context, craftsmanship, and subjective impact.PsychofArt - Day 3 - Dualism - The relationship between minds, brains, and souls



PsychofArt - Day 3 - Dualism - The relationship between minds, brains, and soulsJoshua Eckert
╠²
This document contains a summary of key concepts in philosophy of mind including dualism and physicalism. It discusses whether aspects of personal identity like memories and thoughts are physical or non-physical. Examples are provided of movies that take either a dualist or physicalist view. Evidence for and against dualism is explored through examples like splitting the corpus callosum and the effects of brain changes. The document questions whether describing humans as "just" or "merely" animals understates our uniqueness. It argues we are both part of the natural world and something unprecedented.Costume Design vs Fashion Design



Costume Design vs Fashion DesignJoshua Eckert
╠²
Costume design focuses on creating costumes according to a theme or for a specific character, such as for performances in theater, film, television, and Broadway, whereas fashion design is about street-wear and trends for everyday people. Costume designers draw inspiration from research and a character's personality, background, and time period while fashion designers aim to set trends for popular styles.Jean Nouvel



Jean NouvelJoshua Eckert
╠²
The document discusses how an architectural design was influenced by Islamic architecture and the way it casts light patterns. It also notes that each "Little World" within the design is unique. Finally, it mentions breaking the square as part of the design concept.Advanced perspective tips & tricks



Advanced perspective tips & tricksJoshua Eckert
╠²
This document discusses perspective drawing techniques including vanishing points, 3D letters, stairs, shapes, reflections, shadows, and drawing animals in perspective. It notes that perspective drawings often include at least one vanishing point off the page and that two vanishing points should be far apart for accurate perspective drawings.Recently uploaded (20)
Intellectual Honesty & Research Integrity.pptx



Intellectual Honesty & Research Integrity.pptxNidhiSharma495177
╠²
Research Publication & Ethics contains a chapter on Intellectual Honesty and Research Integrity.
Different case studies of intellectual dishonesty and integrity were discussed.Blind spots in AI and Formulation Science, IFPAC 2025.pdf



Blind spots in AI and Formulation Science, IFPAC 2025.pdfAjaz Hussain
╠²
The intersection of AI and pharmaceutical formulation science highlights significant blind spotsŌĆösystemic gaps in pharmaceutical development, regulatory oversight, quality assurance, and the ethical use of AIŌĆöthat could jeopardize patient safety and undermine public trust. To move forward effectively, we must address these normalized blind spots, which may arise from outdated assumptions, errors, gaps in previous knowledge, and biases in language or regulatory inertia. This is essential to ensure that AI and formulation science are developed as tools for patient-centered and ethical healthcare.BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAH



BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHcoacharyasetiyaki
╠²
BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHOne Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



One Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss the one click RFQ Cancellation in odoo 18. One-Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 is a feature that allows users to quickly and easily cancel Request for Quotations (RFQs) with a single click.Meeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoy



Meeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoyEconomic and Social Research Institute
╠²
NAPD Annual Symposium
ŌĆ£Equity in our Schools: Does the system deliver for all young people?ŌĆØAzure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHat



Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠²
Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHatFull-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Full-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠²
Full-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatHannah Borhan and Pietro Gagliardi OECD present 'From classroom to community ...



Hannah Borhan and Pietro Gagliardi OECD present 'From classroom to community ...EduSkills OECD
╠²
Hannah Borhan, Research Assistant, OECD Education and Skills Directorate and Pietro Gagliardi, Policy Analyst, OECD Public Governance Directorate present at the OECD webinar 'From classroom to community engagement: Promoting active citizenship among young people" on 25 February 2025. You can find the recording of the webinar on the website https://oecdedutoday.com/webinars/
How to create security group category in Odoo 17



How to create security group category in Odoo 17Celine George
╠²
This slide will represent the creation of security group category in odoo 17. Security groups are essential for managing user access and permissions across different modules. Creating a security group category helps to organize related user groups and streamline permission settings within a specific module or functionality.Effective Product Variant Management in Odoo 18



Effective Product Variant Management in Odoo 18Celine George
╠²
In this slide weŌĆÖll discuss on the effective product variant management in Odoo 18. Odoo concentrates on managing product variations and offers a distinct area for doing so. Product variants provide unique characteristics like size and color to single products, which can be managed at the product template level for all attributes and variants or at the variant level for individual variants.How to Configure Deliver Content by Email in Odoo 18 Sales



How to Configure Deliver Content by Email in Odoo 18 SalesCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to configure proforma invoice in Odoo 18 Sales module. A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice that serves as a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer.RRB ALP CBT 2 RAC Question Paper MCQ (Railway Assistant Loco Pilot)



RRB ALP CBT 2 RAC Question Paper MCQ (Railway Assistant Loco Pilot)SONU HEETSON
╠²
RRB ALP CBT 2 RAC Question Paper MCQ PDF Free Download. Railway Assistant Loco Pilot Mechanic Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Important Questions.Chapter 2. Strategic Management: Corporate Governance.pdf



Chapter 2. Strategic Management: Corporate Governance.pdfRommel Regala
╠²
This course provides students with a comprehensive understanding of strategic management principles, frameworks, and applications in business. It explores strategic planning, environmental analysis, corporate governance, business ethics, and sustainability. The course integrates Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to enhance global and ethical perspectives in decision-making.Unit 1 Computer Hardware for Educational Computing.pptx



Unit 1 Computer Hardware for Educational Computing.pptxRomaSmart1
╠²
Computers have revolutionized various sectors, including education, by enhancing learning experiences and making information more accessible. This presentation, "Computer Hardware for Educational Computing," introduces the fundamental aspects of computers, including their definition, characteristics, classification, and significance in the educational domain. Understanding these concepts helps educators and students leverage technology for more effective learning.Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠²
Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatPsychofArt - Day 28 classical conditioning
- 2. Unlearned or Learned? Sugar cookies in the oven smell good Seeing lightning means thunder comes next Praise feels good Lacoste is for old people ŌĆ£JawsŌĆØ music means something bad is coming Baby animals are cute Spiders are scary
- 3. How Does Learning Work? Classical Conditioning ŌĆō Pavlov
- 4. How Does Learning Work? US (Unconditioned Stimulus) NS (Neutral Stimulus) CS (Conditioned Stimulus) NS = CS always UR (Unconditioned Response) CR (Conditioned Response) UR = CR always
- 5. How Does Learning Work? US + Neutral Stimulus = UR US + Neutral Stimulus = UR US + Neutral Stimulus = UR US + Neutral Stimulus = UR [ . . . ] US + Neutral Stimulus = UR US + Neutral Stimulus = UR US + Neutral Stimulus = UR CS = CR (Phew, Finally)
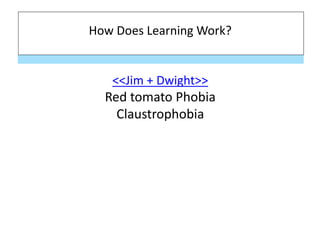
- 6. How Does Learning Work? <<Jim + Dwight>> Red tomato Phobia Claustrophobia
- 7. Partner exercise: 1) Identify in the Jim/Dwight video: US (Unconditioned Stimulus) NS (Neutral Stimulus) ’ā¤same as’āĀ CS (Cond Stimulus) UR (Uncond Response) ’ā¤same as’āĀ CR (Cond Response) 2) Using Classical Conditioning lingo (US, NS, CS, UR, CR), explain how a na├»ve dog owner accidentally trains her dog to jump up on everyone who steps into the house. Then, how would she stop the dogŌĆÖs behavior?
- 9. Challenge 1: If you were a cigarette company, how would you make smoking cool? Challenge 2: If you were a public health non-profit, how would you make smoking uncool?
- 10. Why it works: Attractive, happy people + cigs Attractive, happy people + cigs Attractive, happy people + cigs Attractive, happy people + cigs
- 11. ANTI-Smoking ad: Why it works: Tobacco pushers + Rich, lonely old white men Tobacco pushers + Rich, lonely old white men Tobacco pushers + Rich, lonely old white men Tobacco pushers + Rich, lonely old white men Anti-smoking activists + Cool, young rebels Anti-smoking activists + Cool, young rebels Anti-smoking activists + Cool, young rebels Anti-smoking activists + Cool, young rebels BIG INSIGHT: Nobody cares how many smokers die from tobacco. We just want a circle of fun, awesome friends & lovers surrounding us.
- 12. Marketing Politics (Trying to control the Classical Conditioning) Left wants me to think: Republicans + Selfish, science-hating rednecks Republicans + Selfish, science-hating rednecks Republicans + Selfish, science-hating rednecks Republicans + Selfish, science-hating rednecks ____ Right wants me to think: Democrats + Weak, entitled crybabies Democrats + Weak, entitled crybabies Democrats + Weak, entitled crybabies Democrats + Weak, entitled crybabies
- 13. Creating a conditioned response = Classical conditioning US + NS = UR CS = CR Killing a conditioned response = Extinction Key Vocab:
- 14. How Does Extinction Work? Bell + (no food) = salivate Bell + (no food) = salivate Bell + (no food) = salivate Bell + (no food) = (nothing) Bell + (no food) = (nothing) US + CS = CR US + CS = CR US + CS = (nothing) US + CS = (nothing)
- 15. Spontaneous Recovery Bell + (no food) = salivate Bell + (no food) = salivate Bell + (no food) = salivate Bell + (no food) = (nothing) Bell + (no food) = (nothing) Bell + (no food) = (nothing) Bell + (no food) = (nothing) Bell + (no food) = (nothing) Bell + (no food) = salivate Bell + (no food) = (nothing) US + CS = CR US + CS = CR US + CS = (nothing) US + CS = (nothing) US + CS = (nothing) US + CS = (nothing) US + CS = (nothing) US + CS = CR
- 17. Unlearned or Learned? Sugar cookies in the oven smell good Seeing lightning means thunder comes next Praise feels good Lacoste is for old people ŌĆ£JawsŌĆØ music means something bad is imminent Baby animals are cute Spiders are scary
- 18. Prepared Learning in Humans Spider + Frightening experience = Fear Spider = Fear Puppy + Frightening experience = Fear Puppy + Frightening experience = Fear Puppy + Frightening experience = Fear Puppy + Frightening experience = Fear Puppy + Frightening experience = Fear Puppy = Fear (WeŌĆÖre predisposed) (not predisposed)
- 19. What adjectives do you associate with each packaging?







