DLL_SCIENCE 6_Q2_W8.docx
- 1. GRADES 1 to 12 DAILY LESSON LOG School: Grade Level: VI Teacher: Credit to the author of this file Learning Area: SCIENCE Teaching Dates and Time: JANUARY 9-13, 2023 (WEEK 8) Quarter: 2ND QUARTER MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY I. OBJECTIVES A.(Content Standards) The learners demonstrate understanding of how non flowering plants reproduce B. (Performance Standards) The learners should be able to make a multimedia presentation on how parts of the reproductive system of spore bearing and cone-bearing plants ensure their survival Make a multimedia/flyer on how plants can be propagated vegetative C. ( Learning Competencies) Explain the life cycle of cone- bearing plants. S6LT-IIg-h-4 Discuss the mechanism of reproduction among cone-bearing plants. S6LT-IIg-h-4 Design a multimedia presentation or flyers on how parts of the reproductive system of spore-bearing and cone-bearing plants. S6LT-IIg-h- II. ( Content) Reproduction of Non Flowering plants III. ( Learning Resources) A. (References) 1. (Teacher’s Guide Pages) 2. (Learner’s Materials pages) 3. (Textbook Pages) 4. ( Additional Materials from LR Portal) B. (Other Learning Resources) Power point presentation, LCD Projector, Show me board, marking pen, laptop/netbook, Knowledge Channel Package/ Science Modules IV. (Procedures) A. ( Review previous Lesson) What are conifers? Other term used with conifers. What do they produce? Identify samples of cone-bearing plants. What are the different characteristics of a cone-bearing plant? What are cone-bearing plants? Who can explain the life cycle of cone-bearing plants? How do cone-bearing plants reproduce? Why cone-bearing plants reproductive structures are wing-like structure? What is the difference between a spore-bearing plant and a cone- bearing plant? Give samples of a spore bearing plants, spore-bearing plants. What are the characteristics of ferns? Mosses? Cone-bearing plants? Follow up if the task of each group is already done. B. (Establishing purpose for the lesson/ Motivation) Are gymnosperm or cone- bearing plants important? Present the picture of the life cycle of a cone-bearing plant. Allow the learners to say something about it. Present a picture of a plant Cross Word Puzzle Across: 1. Vascular Tissue System 2. the primary pollinator of conifers 3. plants that do not produce flowers and Would you like to have an activity regarding your lessons on spore and cone-bearing plants, children? Unlocking of Difficulties 1. multimedia Teacher supervises the groups while making their hands on activity on the task they choose.
- 2. How do these plants reproduce? spores instead ____. Down: 1. produce by cone- bearing plants ”naked___” 2. plants that do not produce flowers 3. sample of a cone- bearing tree. 1 1 2 3 3 2. flyers 3. experiment 4. model 5. brochure 6. design C. ( Presenting examples or presentation/ instances of the new lesson) Video viewing Let the learners view a video about the life cycle of a cone- bearing plant. Problems: 1. What are the mechanisms of reproduction among cone- bearing plants? Describe. Giving of hypothesis Maybe the mechanism of reproduction among cone- bearing plants are ___________________________ ___________________________ ____________ Setting of Standards/Rubrics group activity -Note down important details -Keep quite -Share your ideas Let them read about plant propagation. What are the different types of propagating plants? Which method can we use to propagate cone-bearing plants? Is it applicable to cone-bearing plants? Why? Present some samples of a multimedia presentation, flyers or brochure, seed model and story about seed ask different questions regarding the topic or samples presented Use the rest of the time for brainstorming and making of the Multimedia presentation *Power point Presentation * Movie Maker
- 3. Video watching D. ( Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills) Why seeds of conifers or gymnosperm are called “Naked Seeds”? How does the reproductive structure of conifers develop? How many kinds of cones are there in conifers? What are they called? What is the video all about? What are the different mechanisms in reproducing cone- bearing plants? Why the seeds of conifers are having wing-like parts? Allow the pupils to look for a cone-bearing seed outside the classroom. Let them study and describe the cone sample they found. Collaborative work 1. group the pupils into 5 2. let them choose the topic or task Task Design an experiment to test the effect on the rate of germination for various amounts of soil additive (Eggshell and Nitrogen- Ammonium nitrate) Make a multimedia presentation on how parts of spore-bearing plants and cone-bearing plants ensure their survival Make a flyer or brochure on how plants can be propagated vegetatively Create a seed model that can be move by wind, water or by other forces. Present to the class and let the class decide which is most original and effective Write a story about the life of a pollen grain. Select a pollen grain from a seeded plant or seedless plant. Group presentation E. ( Discussing new concepts & practicing new skills #2) Teacher explains to the learners that the conifers have wing-like structure because this is used for Hands On! Teacher reminds the pupils the steps in using the MS Publisher Discussing the outputs of the group.
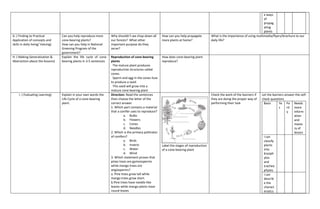
- 4. their reproduction. and MS Power point in creating their flyers/brochures. Allow them to work in group and decide or plan what to do with the task given to them. F. Developing Mastery (Leads to Formative Assessment 3) Call on a learner to explain the life cycle of a conifer/cone- bearing plant. Using the picture. Allow the learners to explain further how cone-bearing plants reproduce. Let the learners answer the self- check questions Basis Ye s Pa rtl y Needs more inform ation and maste ry of lesson I can classify plants into bryoph ytes and tracheo phytes I can describ e the charact erisitcs of the bryoph ytes and tracheo phytes I can show how spore and cone bearing plants reprodu ce I can illustrat
- 5. e ways of propag ating plants G. ( Finding to Practical Application of concepts and skills in daily living/ Valuing) Can you help reproduce more cone-bearing plants? How can you help in National Greening Program of the government? Why shouldn’t we chop down all our forests? What other important purpose do they serve? How can you help propagate more plants at home? What is the importance of using multimedia/flyers/brochure to our daily life? H. ( Making Generalization & Abstraction about the lessons) Explain the life cycle of cone- bearing plants in 3-5 sentences Reproduction of cone-bearing plants The mature plant produces reproductive structures called cones. Sperm and egg in the cones fuse to produce a seed. This seed will grow into a mature cone bearing plant How does cone-bearing plant reproduce? I. ( Evaluating Learning) Explain in your own words the Life Cycle of a cone-bearing plant. Direction: Read the sentences then choose the letter of the correct answer 1. Which part contains a material that a conifer uses to reproduce? a. Bulbs b. Flowers c. Cones d. Needles 2. Which is the primary pollinator of conifers? a. Birds b. Insects c. Water d. Wind 3. Which statement proves that pines trees are gymnosperms while mango trees are angiosperms? a. Pine trees grow tall while mango trees grow short b.Pine trees have needle-like leaves while mango plants have round leaves Label the stages of reproduction of a cone-bearing plant Check the work of the learners if they are doing the proper way of performing their task Let the learners answer the self- check questions Basis Ye s Pa rtl y Needs more inform ation and maste ry of lesson I can classify plants into bryoph ytes and tracheo phytes I can describ e the charact erisitcs
- 6. c.Pine trees grow in cold climate while mango trees grow in tropical climate d.Pine trees are cone-bearing plants while mango trees are flowering plants of the bryoph ytes and tracheo phytes I can show how spore and cone bearing plants reprodu ce I can illustrat e ways of propag ating plants J. ( Additional activities for application or remediation) Illustrate/ draw the life Cycle of a Cone-bearing plant. Bring laptop/netbook V. ( Remarks) VI. ( Reflection) A.( No. of learners who earned 80% in the evaluation) B.( No. of learners who requires additional acts for remediation who scored below 80%) C.( Did the remedial instruction really work? No of learners who caught up with the lesson) D.( No. of learners who continue to require remediation) E. (Which of the strategies work well? Why did this work? F. (What difficulties did I encounter which my principal/
- 7. supervisor can help me solve?) G. ( What innovations or localized materials did I used/ discover which I wish to share with other teacher?)