Eu.s vitbok konsekvenser för jÃĊrnvÃĊgen trpforum-2012-01-11
- 1. Railway Group EU:s vitbok â vika krav stÃĊlls pÃċ jÃĊrnvÃĊgen? KTH Railway Group Bo-Lennart Nelldal Professor 2012-01-11 KTH Railway Group âḃ Center for research and education in Railway technology - Railway development in Sweden 1
- 2. EUs white paper 2011 MÃċlsÃĊttningar för transporter Railway Group âḃ 30 % av vÃĊgtransporterna över 300 km bör fram till 2030 flyttas över till jÃĊrnvÃĊg eller sjötransporter âḃ Mer ÃĊn 50 % fram till 2050 med hjÃĊlp av effektiva och miljövÃĊnliga godskorridorer. âḃ Fram till 2030 tredubbla nÃĊtet för höghastighetstÃċg och upprÃĊtthÃċlla ett tÃĊtt jÃĊrnvÃĊgsnÃĊt i alla medlemsstater. âḃ Fram till 2050 fÃĊrdigstÃĊlla det europeiska nÃĊtet för höghastighetstÃċg âḃ 2050 bör huvuddelen av persontransporterna pÃċ medellÃċnga strÃĊckor ske med tÃċg KTH Railway Group âḃ Center for research and education in Railway technology - Railway development in Sweden 2
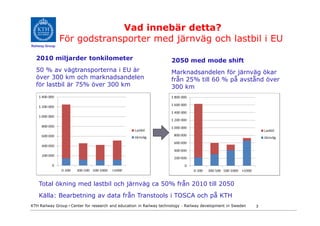
- 3. Vad innebÃĊr detta? För godstransporter med jÃĊrnvÃĊg och lastbil i EU Railway Group 2010 miljarder tonkilometer 2050 med mode shift 50 % av vÃĊgtransporterna i EU ÃĊr Marknadsandelen för jÃĊrnvÃĊg ökar över 300 km och marknadsandelen frÃċn 25% till 60 % pÃċ avstÃċnd över för lastbil ÃĊr 75% över 300 km 300 km Total ökning med lastbil och jÃĊrnvÃĊg ca 50% frÃċn 2010 till 2050 KÃĊlla: Bearbetning av data frÃċn Transtools i TOSCA och pÃċ KTH KTH Railway Group âḃ Center for research and education in Railway technology - Railway development in Sweden 3
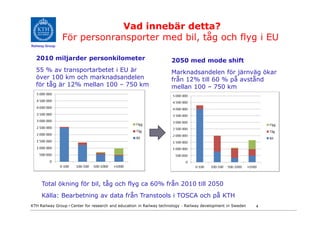
- 4. Vad innebÃĊr detta? För personransporter med bil, tÃċg och flyg i EU Railway Group 2010 miljarder personkilometer 2050 med mode shift 55 % av transportarbetet i EU ÃĊr Marknadsandelen för jÃĊrnvÃĊg ökar över 100 km och marknadsandelen frÃċn 12% till 60 % pÃċ avstÃċnd för tÃċg ÃĊr 12% mellan 100 â 750 km mellan 100 â 750 km Total ökning för bil, tÃċg och flyg ca 60% frÃċn 2010 till 2050 KÃĊlla: Bearbetning av data frÃċn Transtools i TOSCA och pÃċ KTH KTH Railway Group âḃ Center for research and education in Railway technology - Railway development in Sweden 4
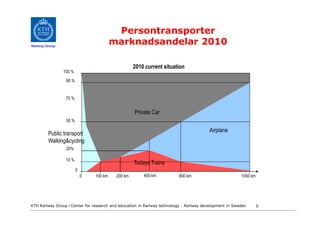
- 5. Persontransporter Railway Group marknadsandelar 2010 2010 current situation 100 % 90 % 70 % Private Car 50 % Airplane Public transport Walking&cycling 20% 10 % Todays Trains 0 0 100 km 200 km 400 km 600 km 1050 km KTH Railway Group âḃ Center for research and education in Railway technology - Railway development in Sweden 5
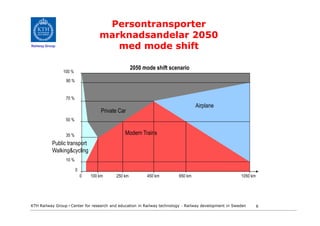
- 6. Persontransporter marknadsandelar 2050 Railway Group med mode shift 2050 mode shift scenario 100 % 90 % 70 % Airplane Private Car 50 % 35 % Modern Trains Public transport Walking&cycling 10 % 0 0 100 km 250 km 450 km 650 km 1050 km KTH Railway Group âḃ Center for research and education in Railway technology - Railway development in Sweden 6
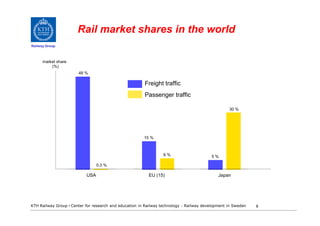
- 7. Ãr en sÃċ hög marknadsandel realistisk Railway Group för jÃĊrnvÃĊg i ett lÃċngsiktigt perspektiv? JÃĊmför best practice i dag i ett internationellt perspektiv âḃ Godstransporter i USA med tunga och lÃċnga godstÃċg pÃċ en kontinent utan grÃĊnser âḃ Persontransporter i Japan med ett vÃĊl utbyggt höghastighethetsnÃĊt âḃ Ãven i Europa varierar marknadsandelen mycket beroende pÃċ jÃĊrnvÃĊgsnÃĊtets standard KTH Railway Group âḃ Center for research and education in Railway technology - Railway development in Sweden 7
- 8. Rail market shares in the world Railway Group market share (%) 49 % Freight traffic Passenger traffic 30 % 15 % 6% 5% 0,3 % USA EU (15) Japan KTH Railway Group âḃ Center for research and education in Railway technology - Railway development in Sweden 8
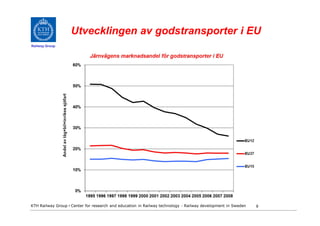
- 9. Utvecklingen av godstransporter i EU Railway Group KTH Railway Group âḃ Center for research and education in Railway technology - Railway development in Sweden 9
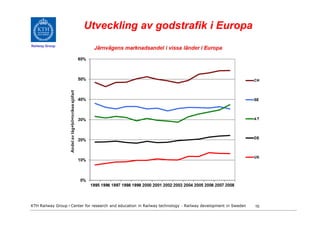
- 10. Utveckling av godstrafik i Europa Railway Group KTH Railway Group âḃ Center for research and education in Railway technology - Railway development in Sweden 10
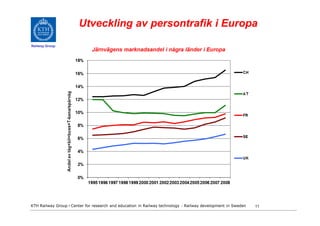
- 11. Utveckling av persontrafik i Europa Railway Group KTH Railway Group âḃ Center for research and education in Railway technology - Railway development in Sweden 11
- 12. Resultat av förslagen i EU:s vitbok Railway Group Resultat koldioxidutslÃĊpp: âḃ KoldioxidutslÃĊppen blir ca 20% lÃĊgre med mode shift ÃĊn baseline 2050 âḃ Möjlighet finns att minska koldioxidsutslÃĊppen med ca 35% om lÃċgemitterande elproduktion kan utnyttjas EfterfrÃċgan pÃċ jÃĊrnvÃĊgstransporter âḃ Persontrafik pÃċ jÃĊrnvÃĊg 6-7 ggr sÃċ stor som i dag och 4-5 ggr sÃċ stor som 2050 baseline âḃ Godstrafik pÃċ jÃĊrnvÃĊg 3-4 ggr sÃċ stor som i dag och 2-3 ggr sÃċ stor som 2050 baseline KTH Railway Group âḃ Center for research and education in Railway technology - Railway development in Sweden 12
- 13. Vad behövs för att utveckla den Railway Group europeiska infrastrukturen? âḃ En gemensam vision och plan för bÃċde ett höghastighetsnÃĊt och för godskorridorer â inte bara en sammanlÃĊggning av nationella planer âḃ à tgÃĊrder för att vidmakthÃċlla och förbÃĊttra infrastrukturen i de nya EU-lÃĊnderna EU12 âḃ En gemensam standard för godstrafik med lÃĊngre godstÃċg, högre axellast och större lastprofil âḃ En snabbare utveckling av ERTMS level 3 med flytande block som verkligen ger högre kapacitet âḃ Medel för att stimulera utbyggnad av infrastrukturen som kombineras med krav KTH Railway Group âḃ Center for research and education in Railway technology - Railway development in Sweden 13
- 14. Europa â Railway Group gröna godskorridorer Prioriterat jÃĊrnvÃĊgsnÃĊt för godstransporter âḃ Kapacitetsstarkt âḃ Avreglerat âḃ Konkurrenskraftiga banavgifter âḃ LÃċnga tÃċg âḃ Interoperabelt âḃ Intermodalt KTH Railway Group âḃ Center for research and education in Railway technology - Railway development in Sweden 14
- 15. Vad krÃĊvs för att nÃċ sÃċ hög Railway Group marknadsandel? För persontransporter: âḃ Utbyggt höghastighetsnÃĊt frÃċn 6000 till 36 000 km, 30% av huvudnÃĊtet âḃ Uppgraderat konventionellt nÃĊt âḃ Effektivare tÃċg för att minska kostnaden âḃ Avreglering för att sÃĊnka priserna För godstransporter: âḃ Effektiva godskorridorer utan grÃĊnser âḃ BÃĊttre service genom avreglering âḃ Effektivare tÃċg (lÃĊngre, tyngre, bredare, högre) för att minska kostnaden âḃ Utvecklad kombitrafik med automatisk terminalhantering KTH Railway Group âḃ Center for research and education in Railway technology - Railway development in Sweden 15
- 16. ḟáöĠṁġóĠṗĠõġÙẅḟĠṁġóḟŵġÙĠõġÙÃċĠṁ hastighetsrekord Railway Group 574,8 km/h pÃċ ny bana Operativt planeras för 360 km/h Gröna tÃċget hastighetsrekord 303 km/h pÃċ gammal bana i Sverige KTH Railway Group âḃ Center for research and education in Railway technology - Railway development in Sweden 16
- 17. Godstransporter Railway Group Vagnslast- och systemtÃċg: LÃċnga och tunga godstÃċg 1500 m och 30 tons axellast Kombitransporter: LinjetÃċg med automatisk lastning och lossning KTH Railway Group âḃ Center for research and education in Railway technology - Railway development in Sweden 17
- 18. Hur öka kapaciteten? Railway Group âḃ Persontrafik: DubbeldÃĊckare och wide body tÃċg, lÃĊngre tÃċg: + 25-50% âḃ GodstÃċg: LÃĊngre tÃċg, tyngre tÃċg, högre axellast och metervikt, större lastprofil: +25-50% âḃ Nytt signalsystem ERTMS level 3: +40% âḃ Bygga höghastighetsbanor: 2-3 gÃċnger högre kapacitet för gods- och regionaltÃċg pÃċ det konventionella nÃĊtet nör snabbtÃċgen lyfts bort 6-10 högre kapacitet för snabbtÃċgen pÃċ höghastighetsbanan Kortare restider och bÃĊttre punktlighet âḃ En ökning av kapaciteten 4-5 gÃċnger ÃĊr fullt möjlig men krÃĊver investeringar I nya banor KTH Railway Group âḃ Center for research and education in Railway technology - Railway development in Sweden 18
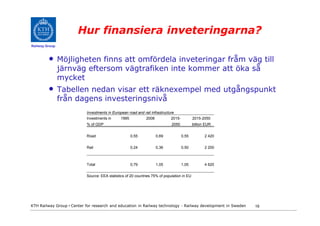
- 19. Hur finansiera inveteringarna? Railway Group âḃ Möjligheten finns att omfördela inveteringar frÃċm vÃĊg till jÃĊrnvÃĊg eftersom vÃĊgtrafiken inte kommer att öka sÃċ mycket âḃ Tabellen nedan visar ett rÃĊknexempel med utgÃċngspunkt frÃċn dagens investeringsnivÃċ Investments in European road and rail infrastructure Investments in 1995 2008 2015- 2015-2050 % of GDP 2050 billion EUR Road 0,55 0,69 0,55 2 420 Rail 0,24 0,36 0,50 2 200 Total 0,79 1,05 1,05 4 620 Source: EEA statistics of 20 countries 75% of population in EU KTH Railway Group âḃ Center for research and education in Railway technology - Railway development in Sweden 19
- 20. Behov av forskning och utveckling Railway Group Persontransporter Godstransporter âḃ Teknik för högre hastigheter âḃ LÃĊtta vagnar med lÃĊgre buller âḃLöpverk för bÃĊttre komfort och lÃĊgre âḃ Löpverk med bÃĊttre gÃċng och lÃĊgre spÃċrkrafter spÃċrkrafter âḃ Utrymmeseffektiva tÃċg âḃ Elektropneumatisk broms radiostyrda lok âḃ ModulÃĊra tÃċg âḃ Automatkoppel som gÃċr att fjÃĊrrstryra âḃ Kostnadseffektiva tÃċg âḃ Terminalteknik för automatisk hantering Infrastruktur Trafikstyrning âḃ Kostnadseffektiva slab track âḃ Systemperspektiv pÃċ jÃĊrnvÃĊgen âḃ UnerhÃċllsfria slipers âḃ Intilligent planering och trafikstyrning âḃ LÃċgkostnadspÃċr âḃ ERTMS level 3 âḃ Effektivare banmatning âḃ Automatisk tÃċgdrift KTH Railway Group âḃ Center for research and education in Railway technology - Railway development in Sweden 20
- 21. Slutsatser Railway Group âḃ EU:s vitbok innebÃĊr en radikal förÃĊndring av Europas transportsystem â sÃĊrskilt för lÃċngvÃĊga transporter âḃ Marknadsandelarna med mode shift ungefÃĊr samma som i best practice för jÃĊrnvÃĊg i dag âḃ EfterfrÃċgan pÃċ jÃĊrnvÃĊg blir 4-5 gÃċnger större ÃĊn i dag âḃ Ett utbyggt höghastighetsnÃĊt som frigör kapacitet och grÃĊnslösa godskorridorer ÃĊr förutsÃĊttning âḃ Ger ökad rörlighet och effektivare godstransporter âḃ Stora investeringar men viss omfördelning frÃċn vÃĊg till jÃĊrnvÃĊg kan vara en lösning âḃ Det behövs mer forskning och utveckling av jÃĊrnvÃĊgssystemet KTH Railway Group âḃ Center for research and education in Railway technology - Railway development in Sweden 21
- 22. Railway Group Tack! bo-lennart.nelldal@abe.kth.se Hemsida: www.infra.kth.se/tol/jvg KTH Railway Group âḃ Center for research and education in Railway technology - Railway development in Sweden 22