Fetal nûÑrosonografi
- 1. FETAL NûROSONOGRAFᯠUzm.Dr.BAHRᯠYILDIZ Uzm.Dr.M.EROL YAYLA
- 2. ÇÀÝññÀÝñ°ÏñÀ¿µÇÀ°Âá¯: Serebral ve serebellar hemisferlerin ve craniumun geliéimsel yokluáu ile karakterize nûÑral tû¥p defektidir. Bu anomali yaéam ile baádaémaz.
- 3. ÇÀÝññÀÝñ°ÏñÀ¿µÇÀ°Âá¯: Sonografik ûÑzellikleri : beyin ve callvaryum yokluáu 37-1 Serebrovaskû¥loza ile karakterize rudimente beyin dokusu 37-2,37-3 Fetusa kurbaáa benzeri gûÑrû¥nû¥m veren dáÝéaráÝ doáru ûÏáÝkáÝntáÝláÝ orbitalar.
- 4. ÇÀÝññÀÝñ°ÏñÀ¿µÇÀ°Âá¯: Vaka -1 20 y primigravid ilk olarak 16 w láÝk baévurdu ve usg yapáÝldáÝ
- 5. ÇÀÝññÀÝñ°ÏñÀ¿µÇÀ°Âá¯: Sagital taramada calvaryumun residuel oksipital káÝsmáÝ ve serebrovaskuloza ýçûѯªû¥ýå°ìû¥ý¾û¥ gûÑrû¥nû¥yor.
- 6. ÇÀÝññÀÝñ°ÏñÀ¿µÇÀ°Âá¯: Fetal baéa parasagital taramada beyin-calvaryal doku yokluáu
- 7. ÇÀÝññÀÝñ°ÏñÀ¿µÇÀ°Âá¯: Anencephaly-vaka2 , 26y , G2P1,ä»19w gebe .ä» 7 w sonografik taramasáÝ normal ,ä»2 tarama 16 w da yapáÝldáÝ. Theä»risk for Downä»was 1/550. maternal safp yû¥ksek bulunmué , Kendi û¥nitelerinde 19w láÝk tarama yapáÝlmáÝé.ä»Iliékili baéka anomaly saptanmadáÝ .ä»anne baba terminasyonu onaylamáÝélar . amniosentez 20 w láÝk yapáÝlmáÝé .ä»karyotipleme normal saptanmáÝé .ä», ä»
- 8. ÇÀÝññÀÝñ°ÏñÀ¿µÇÀ°Âá¯: 19 w da yapáÝlan sonografik taramalar anensefaliyi doárulamáÝé.
- 9. ÇÀÝññÀÝñ°ÏñÀ¿µÇÀ°Âá¯: 19 w da yapáÝlan sonografik taramalar anensefaliyi doárulamáÝé
- 12. ÇÀÝññÀÝñ°ÏñÀ¿µÇÀ°Âᯠ, Anencephaly ãvaka3 , Anensefali ile ilgili prenatal ve postnatal bazáÝ sonogramlar ilgilerinize arz
- 16. ÇÀÝññÀÝñ°ÏñÀ¿µÇÀ°Âá¯-vaka4 20 y gebe 20 w da . usg gûÑrû¥ntû¥leri anensefaliyi doáruluyor.
- 18. Akrania Anensefaliye kranial kemiklerin tam veya parsiyel yokluáunun eélik ettiái durum.
- 19. Akrania nin sonografik bulgularáÝ Kalvaryum yokluáunda beyin dokusunun varláÝááÝ Beyin dokusunda dezorganizasyon Belirgin sulkus yapáÝlaráÝ Akrania spinal defektler ,yaráÝk dudak,damak,talipes ,kardiak defektler ve omfalosel eélik edebilir.
- 20. Acraniaä»ä» vaka1 , 25 y g1 , gebeliáin 14w ilk usg yapáÝláÝyor . TáÝbbi ûÑykû¥ doáal . Sonogram solda katarakt ve akrani yi gûÑsteriyor. Hasta terminasyona onay verdi.
- 24. Acraniaä»ä» vaka2 , 29 y g1. daha ûÑnce icsi ile ikiz gebelik ûÑykû¥sû¥ var . Gebeliáin 27 haftasáÝnda yapáÝlmáÝé usg ler gûÑreceksiniz , normal erkek ve acrania láÝ bir káÝz fetus . Gebelik ûÑncesi folat desteái almáÝé
- 26. Acrania vaka3 Acrania Acrania 14 w . Anensefaliye gûÑre beyin daha bû¥yû¥k .
- 27. Acrania vaka3
- 28. Acrania vaka3
- 29. Acrania vaka3 DoáumsonrasáÝ fetus ä» ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»
- 30. Acrania ve cardiac malformationä» vaka4 , 25 y 13 w gebe . TáÝbbi ûÑykû¥ doáal . Usg akrania ve kardiak malformasyon gûÑsteriyordu (belirgin perikardial eff., atrioventricular defect, buyuk damarlar tam belli deáil ). Ebeveyn gebeliáin sonlanmasáÝna onay verdi. Anatomopathological ûÏaláÝémalar sefalik malformasyon kardiak analizler avd ve bû¥yû¥k damar malformasyonlaráÝnáÝ doáruladáÝ.
- 31. Acrania ve cardiac malformationä» vaka4 13w gebe anormal kafatasáÝ ve kranium
- 32. Acrania ve cardiac malformationä» vaka4 13 w gebe . 2D sagittal scan anormal kafatasáÝ ve cranáÝum 3d kurbaga gûÑrû¥nû¥mû¥ ) , ä» ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»
- 33. Acrania ve cardiac malformationä» vaka4 Sagital gûÑrû¥ntû¥de perikardial eff.13 w gebe de avd
- 34. Acraniaä» ,vaka5 34y primipar 16w láÝk akrania láÝ fetus
- 35. Acraniaä» vaka5 Postnatal images
- 36. Acrania ve servikal nûÑral tube defekti 15 w láÝk gebelik longituáÝdinal taramada oklar ile akrania
- 37. Acrania ve servikal nûÑral tube defekti-vaka6 15 w láÝk gebede servikal bûÑlgede genié nûÑûÏral tube defekti
- 38. Sefalosel Sefalosel yalnáÝz meninkslerin yada meninksler ve beynin kalvaryumdaki bir defektten herniasyonun olduáu bir nûÑral tube defektidir.
- 39. Sefaloselde usg bulgularáÝ SáÝváÝ ile dolu olabilen (kranial meningosel ) veya solid komponentler iûÏeren (ensefalosel) bir ekstrakranial kitle KafatasáÝnda ekmijk defekti Ensefalosel ile birlikte daha sáÝk gûÑzlenen ventrikû¥lomegali
- 40. Sefalosel vaka1 - Cephalocele,ä»anterior Usg de sagital ve aksial etmoid kemik ûÑnû¥nde kistik bir kitle ok
- 41. Sefalosel vaka1 - Cephalocele,ä»anterior 29w 3d T2 de kistik kitle ile beyin parenkimi
- 42. Sefalosel vaka1 - Cephalocele,ä»anterior Cerrahi ûÑncesi neonatal dûÑnem Cerrahi sonrasáÝ
- 44. Oksipital sefalosel vaka 2 18 w oksipital ensefaloselli fetus
- 45. Occipital meningoencephalocele-vaka3 Primigravid 18 w láÝk gebe
- 46. Spina bifida Meninkslerin ve /veya spinal kordun bir defekten protruzyonuna izin veren dorsal vertebralaráÝn birleéme defekti ile karakterize bir patolojidir. á¯ki tipi var 1-spina bifida okulta : 2-spina bifida kistika
- 47. Spina bifida 1-spina bifida okulta meninksler veya spinal kordun protruzyonu olmaksáÝzáÝn gûÑrû¥len kapaláÝ spinal defekt 2- spina bifida kistika :protrude meninks ve /veya kordun bir kese iûÏinde olduáu aûÏáÝk spinal defekttir.
- 48. Spina bifida sonografik ûÑzellkiler Posterior osifikasyon merkezlerinde v veya u éeklinde ayráÝlma Anekoik olabilen (meningosel )kese benzeri protrude olmué yapáÝ Ciltte yaráÝklanma Bir spinal defekt tanáÝmlandáÝktan sonra defektin seviyesi ve yaygáÝnláÝááÝ protrude olan kese iûÏinde nûÑral yapáÝlaráÝn var olup olmadáÝááÝ ve eélik eden intrakranial bulgular rapor edilmelidir.
- 49. Spina bifida sonografik ûÑzellikler Kafaya limon éeklini veren frontal kemiklerin yassáÝlaémasáÝ (lemon sign) Sisterna magnanáÝn silinmesi Serebelluma yuvarlak muz éeklini veren serebellar vermisin inferiora yer deáiétirmesi (banana sign) Ventrrikû¥lomegali
- 50. Spina bifida vaka1 Vaka lomber bûÑlgede genié spina bifidayáÝ gûÑsteriyor.
- 51. Spina bifida vaka2 , . yuksek afp seviyelerine sahip bir antenatal tarama SáÝnáÝrda ventrikulomegali
- 52. Spina bifida vaka2 Banana sign in the brain:
- 53. Spina bifida vaka2 Myelo-meningocele :
- 54. Spina bifida vaka2 Posterior duvarda genié defekt
- 55. Spina bifida vaka2 Postnatal gûÑrû¥nû¥m
- 56. Spina bifida vaka 3 43 y G3P2, táÝbbáÝ oyku doáal . 36 w láÝk iken merkeze sevki yapáÝlmáÝé , ilk basamakta usg hidrosefaliyi gûÑsterdi . Bizde bu bulguyu doáruladáÝk Hydrocephalus. Serebellum u gûÑremediáimizden spina bifida ya baáláÝ arnold chiari malformasyonu dû¥éû¥ndû¥k , bu yû¥zden tip 2 arnold chari dû¥éû¥ndû¥k , ve vertebralara baktáÝk iéte bulgularáÝmáÝz
- 57. Spina bifida vaka 3 Hidrosefali
- 58. Spina bifida vaka 3 , vertebra sagital gûÑrû¥nû¥mde orta hatta kocaman kistik lezyon torakolomber bûÑlgede gûÑrû¥lû¥yor
- 59. Spina bifida vaka 3 Defktin transvers gûÑrû¥nû¥mû¥ . ä»
- 60. Spina bifida vaka 3 Postnatal gûÑrû¥nû¥m
- 61. Spina bifida, lumbar vaka4 26y primigravid , G2P1, 36w gebelik te hidrosefali éû¥phesiyle merkezimize gûÑnderildi.. Muayenede lomber seviyede genié kistik kitle fetusta lomber spina bifida ve hidrosefali saptandáÝ . 38 w láÝk doáan fetusun birkaûÏ gûÑrû¥ntû¥
- 62. Spina bifida, lumbar vaka4 Fetusta aéikar hidrosefali
- 63. Spina bifida, lumbar vaka4 Sagital ve transvers planda lomber spina bifida
- 64. Spina bifida, lumbar vaka4 Sagital transvers planda lomber defekt
- 65. Spina bifida, lumbar vaka4
- 66. Spina bifida, lumbar vaka4 Bebeáin postnatal gûÑrû¥nû¥mû¥
- 67. Spina bifida, lumbosacral ,vaka 5 , 35y , G3P2, lumbosakral spina bifida nedeniyle deáerlendirildi. .
- 68. Spina bifida, lumbosacral ,vaka 5 ,
- 69. Spina bifida, lumbosacral ,vaka 5 ,
- 70. Spina bifida, thoraco-lumbar vaka6 42y primigravida, G4P3, 38w gebe koroid plexus kisti ve hidrosefali ûÑn tanáÝsáÝ ile tarafáÝmáÝza refere edildi.ä» Muayenemiz torakolomber spinal bûÑlgede genié kistik bir lezyon ile fetus ta serebral ventrikû¥l dilatasyonunu gûÑsterdi.. Bebek 38w láÝk doádu
- 71. Spina bifida, thoraco-lumbar vaka6 38w gebe ; transvers gûÑrû¥ntû¥de dilate serebral ventrikû¥lleri gûÑsteriyor.
- 72. Spina bifida, thoraco-lumbar vaka6 Transvers v éekli spina bifida Torakolomber sagital
- 73. Spina bifida, thoraco-lumbar vaka6 postanatal
- 74. Dandy walker malformasyonu DûÑrdû¥ncû¥ ventrikû¥lde dilatasyona yol aûÏan serebellar vermisin agenezisi veya hipoplazisi ile karakterize ûÏok deáiéik éidette olabilen bir defekttir.
- 75. Dandy walker malformasyonu(DWM) DWM da sonografi bulgularáÝ Bû¥yû¥klû¥áû¥ ûÏok deáiéik olabilen posterior fossa kisti Serebellar vermisin tam veya parsiyel agenezisi sonucu serebellar hemisferlerin ayráÝlmasáÝ Sisterna magnanáÝn serebellar vermis anomalisi ve posterior fossa kistinden dolayáÝ geniélemesi Ventrikû¥lomegali
- 76. Dandy Walker cyst ãvaka1 Posterior fossada genié kistik lezyon
- 77. Dandy Walkerä»malformation-vaka2 DWM ye baáláÝ hidrosefali
- 79. Dandy-Walker malformation and polycystic kidneyä» 24y G1P0 26w gebe fetal bûÑbrekte patolojik bulgular nedeniyle bize gûÑnderildi.ä»BulgularáÝmáÝz dwm ve bû¥yû¥mû¥é polikistik bûÑbrek ve anhidramniyozu gûÑsteriyordu. 33w láÝk doádu ve 6 saat yaéayabildi. Otopside dwm ye ilave polikistik bûÑbrek asd hipoplastik saá ventrikû¥l pulmoner stenoz saptandáÝ , ,.
- 80. Dandy-Walker malformation and polycystic kidney Transvers te posterior fossa da kist ve serebellar vermis agenezisi
- 81. Dandy-Walker malformation and polycystic kidney Coronalde bû¥yû¥mû¥é fetal bûÑbrekler
- 82. Dandy-Walker malformation and polycystic kidney Coronalde bû¥yû¥mû¥é fetal bûÑbrekler
- 83. Holoprozensefali ûn beynin anormal bûÑlû¥mlenmesinden kaynaklanan bir takáÝm anomaliler grubudur. Holoprosensefali(ûÑn beynin )anormal ayráÝlmasáÝndan kaynaklanan genié spektrumlu anomalileri kapsar
- 84. Holoprozensefali 3 tipi mevcut Alobar : en ciddi form Semilobar orta form Lobar form en hafif
- 85. Holoprozensefali Sonografik bulgular : Geniélemié veya geniélememié olan c éekilli ortak bir ventrikû¥l Mono ventrikû¥lû¥ sardáÝááÝ iûÏin atnaláÝ éekli almáÝé beyin dokusu 3. ventrikû¥l yokluáu ile fû¥zyona uáramáÝé talamus á¯nterhemisferik fissû¥rû¥n yokluáu Monoventrikû¥lû¥n posteriora doáru geniélemesi sonucu oluémué dorsal kese Korpus kallozum yokluáu Cavum septum pellusidum yokluáu Ciddi formlaráÝnda fasyal anomalilerle birliktelik
- 86. Holoprozensefali Ciddi formlaráÝnda fasyal anomalilerle birliktelik Sebosefali Hipotelorizm Siklopi Proboskis Etk delikli burun gibi
- 87. Holoprosencephaly, overview The following are part of the holoprosencephaly complex: arhinencephaly, cebocephaly, ethmocephaly, and cyclopia.
- 89. Holoprosencephaly-case1 The appearance of cyclopia at 16 weeks. Note the proboscis above the fused eye and the midfacial hypoplasia
- 90. Holoprosencephaly-case1 The appearance of cyclopia at 16 weeks. Note the proboscis above the fused eye and the midfacial hypoplasia
- 91. Holoprosencephaly-case1 Sagittal view of alobar holoprosencephaly at 10 weeks.
- 94. ä»
- 95. Fetal nûÑrosonografi corpus , drbahriyildiz
- 96. callosum agenezisi Korpus kallosum serebral hemisferleri birbirine baálayan ûÑárenme hafáÝzada yardáÝmcáÝ olan fibroz bir yoldur Corpus callosum disgenezisi iki hemisfer arasáÝnda baálantáÝ kuran ve orta hattáÝ geûÏen kallosal liflerdeki tam veya káÝsmi bir eksikliái tanáÝmlar 1000 doáumda 1-3 tû¥r.
- 97. callosum agenezisi Sonografik ûÑzellikleri Korpus kallosum yokluáu 3. ventrikû¥l yû¥kselmesi ve dilatasyonu Genié araláÝklarla ayráÝlmáÝé lateral ventrikû¥ller frontal boynuzlar ve medial duvarlaráÝn indentasyonu Lateral ventrikû¥llere gûÑzyaéáÝ damlasáÝ éekli veren geniélemié oksipital boynuzlar (kolposefali) Cavum septum pellucidum yokluáu
- 98. callosum agenezisi ile iliékili patolojiler Acrocallosal syndrome (AR) ôñä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» Aicardi syndrome (X-linked dominant) ôñä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» Andermann syndrome (AR) ôñä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» Cerebro-oculo-facio-skeletal (COFS) syndrome (AR) ôñä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» Fryns syndrome (AR) ôñä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» Marden-Walker syndrome(AR) ôñä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» Meckel Gruber syndrome (AR) ôñä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» Microphtalmia-linear skin defects syndrome (X-linked dominant) ôñä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» Miller Diexer syndrome (lissencephaly syndrome) ôñä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» Neu-Laxova syndrome(AR) ôñä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» Septo-Optic dysplasia sequence ôñä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» Walker-Warburg syndrome (X-linked dominant) ôñä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» Zellweger syndrome (AR) Nadiren ôñä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» Apert syndrome (AR) ôñä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» Baller-Gerold syndrome (AR) ôñä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» Calloso-genital dysplasia syndrome (AR) ôñä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» Coffin-Siris syndrome (?AR) ôñä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» Congenital microgastria-limb reduction complex (unknown) ôñä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» Crouzon syndrome (AD) ôñä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» Duplication 4p syndrome ôñä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» Fetal alcohol syndrome ôñä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» Fetal warfarin syndrome ôñä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» FG syndrome (X-linked recessive) ôñä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» Fronto-nasal dysplasia sequence (sporadic/AD) ôñä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» Gorlin syndrome (AD)
- 100. callosum agenezisi Normal yenidoáan Agenezisli
- 101. callosum agenezisi Corpus kallusum yokluáu ve genié oksipital horn lar
- 102. Oksipital horn seviyelerinde geniélemié ventrikû¥ler lateral ventrikû¥lerde gûÑzyaéáÝ konfigû¥rasyonu-kolposefali dediáimiz olay
- 103. Callosal agenezide teardrop ýçûѯªû¥ýå°ìû¥ý¾û¥
- 104. Callosal agenesis
- 105. Callosal agenesis Normal Cc agenezisi
- 106. Callosal agenezisi Normal Cc agenezisi
- 107. Callosal agenezis Axial ve midcoronal de interhemisferik fissû¥r distansiyonuna sekonder triple line
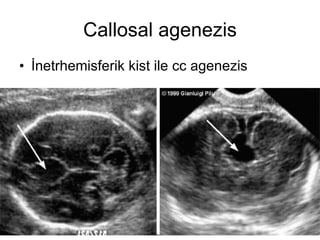
- 108. Callosal agenezis á¯netrhemisferik kist ile cc agenezis
- 109. Sagitalde normal cc
- 110. Coronalde normal cc
- 112. ä»
- 113. Agenesis of the corpus callosum ãvaka2 18 y 29 w láÝk gebe Dilate lateral serebral ventrikû¥ller ve tear drop gûÑrû¥ntû¥
- 114. ä»
- 115. AKUADUKTAL STENOZ AKUADUKTAL STENOZ ,VENTRá¯KûLOMEGALá¯YE YOL AûACAK éEKá¯LDE SYLVá¯AN KANALININ OBSTRûKSá¯YONU ,ATREZá¯SᯠVEYA STENOZU SONUCU OLUéUR.SYLVá¯AN AKUADUKTUS 3.VENTRá¯KûL VE 4. VENTRá¯KûLLERᯠBAáLAR BUDA NORMAL Bá¯R 4.VENTRá¯KûL VARLIáINDA GENá¯éLEMá¯é LATERAL VE 3.VENTRá¯KûLLERᯠAûIKLAR.
- 116. AKUADUKTAL STENOZ Akuaduktal stenozun sonografik ûÑzellikleri Lateral ventrikû¥llerin ciddi olabilecek geniélemesi 3. ventrikû¥l dilatasyonu BaéparmaááÝn fleksiyon ve adduksiyonu (x baáláÝ formda olur)
- 117. AKUADUKTAL STENOZ Aqueductal stenosis vaka1 . Akuaduktal stenoz lu bir fetus un antenatal sonogramlaráÝ , bebek doáduktan sonra MR yapáÝlmáÝé ve akuduktal stenoz tanáÝsáÝ ile hafif hidrosefali saptanmáÝé.vp éant ile hasta takip te durumu iyi
- 118. AKUADUKTAL STENOZ Geniélemié lateral ventrikû¥ller ve geniélemié 3.ventrikû¥l (ikinci gûÑrû¥ntû¥)
- 119. AKUADUKTAL STENOZ
- 120. AKUADUKTAL STENOZ
- 121. AKUADUKTAL STENOZ
- 122. ä»
- 123. GALEN VENᯠANEVRá¯ZMASI Galen veni anevrizmasáÝ sporadik bir olay olarak dû¥éû¥nû¥lû¥r ve erkekelerde daha fazla gûÑrû¥lû¥r. Kongenital kardiak defekt kistik higroma ve hidrops ile iliékili Ventrikû¥lomegali ve sonucunda makrosefali geliéebilir.
- 124. GALEN VENᯠANEVRá¯ZMASI Sonografik ûÑzellikleri Orta hat 3. ventrikû¥l posterirunda lokalize ,ireguler éekilli olabilen kistik boéluk Doplerde tû¥rbû¥lan akáÝm Fetal kardiyomega Li veya non immun hidropsu iûÏerebilir
- 125. GALEN VENᯠANEVRá¯ZMASI Figure 1: Schematic illustration of the venous drainage of the brain. Left: normal; right: pathologic. 1: right internal cerebral vein, 2: left internal cerebral vein, 3-4: right & left basilar veins; 5-6: right & left medial occipital veins; 7: tentorium; 8: left transverse sinus; 9: torcular Herophilus; 10: inferior sagittal sinus; 11: superior sagittal sinus; 12: falx; 13: vein of Galen aneurysm. ä» ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä» ä» ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»
- 127. GALEN VENᯠANEVRá¯ZMASI 32y ilk gebeliái 33 w láÝk grosessese 16 ve 25 w da 2 defa usg yapáÝlmáÝé, ve o zaman herhangi bir yapáÝsal anomali saptanmamáÝé. Muayene 5 mhz dopler ile yapáÝlmáÝé . Cranial axial gûÑrû¥nû¥mde posterior talamusta dû¥zgû¥n sáÝnáÝrláÝ iûÏi sáÝváÝ dolu 24x19 mm oval kir lezyon ,,.oval kitlenin arkasáÝna prob aûÏáÝlandáÝááÝnda tubuler bir anekoik yapáÝ inionda 3 mm uzanáÝm gûÑsteriordu , ,
- 128. GALEN VENᯠANEVRá¯ZMASI Muayene 5 mhz dopler ile yapáÝlmáÝé . Cranial axial gûÑrû¥nû¥mde posterior talamusta dû¥zgû¥n sáÝnáÝrláÝ iûÏi sáÝváÝ dolu 24x19 mm oval kir lezyon ,,.oval kitlenin arkasáÝna prob aûÏáÝlandáÝááÝnda tubuler bir anekoik yapáÝ inionda 3 mm uzanáÝm gûÑsteriordu , ,
- 129. GALEN VENᯠANEVRá¯ZMASI 3 ve 4. ventrikû¥l normal gûÑrû¥nû¥mde baéka ca intracranial patoloji saptanmadáÝ . Kistik lezyonun pulse doplerinde yapáÝnáÝn iûÏi ve bû¥tû¥n uzanáÝmlaráÝnda yû¥ksek háÝzláÝ venoz akáÝm izlendi ä» ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»ä»
- 130. Vein of Galen aneurysm-vaka 2 30w láÝk gebe kardiak tyetmezlik nedeniyle bebek doáumdan 11 saat sonra ex oldu 30w láÝk fetal baéáÝn transvers kesiti 15mm ûÏapáÝnda merkezi hipoekoik yapáÝ ga len veni anevrizmasáÝnáÝ gûÑsteriyor. ,
- 131. Vein of Galen aneurysm-vaka 2 30w láÝk gebe kardiak tyetmezlik nedeniyle bebek doáumdan 11 saat sonra ex oldu 30w láÝk fetal baéáÝn transvers kesiti 15mm ûÏapáÝnda merkezi hipoekoik yapáÝ ga len veni anevrizmasáÝnáÝ gûÑsteriyor
- 132. Vein of Galen aneurysm-vaka 2 Kistik yapáÝda AkáÝm
- 133. Vein of Galen aneurysm-vaka 2 Anevrizma seviyesinde pulzasyon Saá dominant four chamber ve eff
- 134. Vein of Galen aneurysmä» vaka4 340w láÝk gebe Power dopler transverste anevrizma Anevrizmada tû¥rbû¥lan akáÝm
- 135. Vein of Galen aneurysmä» vaka4
- 136. Vein of Galen aneurysmä» vaka4 Gva náÝn yapáÝsáÝ WáÝláÝs pol
- 137. Wp ve gva arasáÝnda baálantáÝlar
- 138. ä»
- 139. Normal anatomy
- 140. Normal anatomy
- 141. ä»
- 142. Coroid plexus kisti Koroid plexusus kistleri coroid plexus ta bulunan yuvarlak veya oval anekoik yapáÝlardáÝr. Bu kistler yaygáÝn ve antenatal sonografik taramalarda %1 oranáÝnda bulunur. Koroid plexus kistleri nûÑroepitelyal káÝvráÝmlarda birikmié hû¥cresel artáÝklar ve bos iûÏerirler.
- 143. Coroid plexus kisti Sonografik ûÑzellikler Koroid plexus ta boyutlaráÝ 0.3-2 cm arasáÝnda deáiéen kistler UnáÝletaral veya bileteral kistler Soliter veya multipl UnáÝlokuler ve ya multáÝlokuler Genié bir kist veya genié bir ventrikû¥l
- 144. Coroid plexus kisti
- 145. Coroid plexus kisti
- 146. ä»
- 147. Porensefalik kistler AynáÝ zamanda porensefali olarak bilinen porensefalik kistler ,ventrikû¥ler sistem veya subaraknoid boéluk ile baélantáÝláÝ ,serebrospinal sáÝváÝ ile dolu kistlerdir.sinir sisteminde kanama infarkt doáum travmasáÝ veya inflamatuar deáiéiklikler sonucu oluéabilirler.etkilenmié beyin parenkimi nekroza uárar geride kistik lezyon kaláÝr.
- 148. Porensefalik kistler Sonografik ûÑzellikleri Beyin parenkimi iûÏerisinde kitle etkisi oluéturmayan bir kist Ventrikû¥l veya subaraknoid boéluk ile iliékili kist Etkilenmié hemisfer boyutunda orta hat kaymasáÝna ve kontrlateral ventrikû¥ler geniélemeye yolaûÏan azalma Aracnoid kistler ile karáÝéabilir.
- 149. Porensefalik kist
- 150. ä»
- 151. éƒÝ°ºÝÞýåý¾ÝÞÇÖý¿Ý¶ƒÝ Serebral kortekste yaráÝklar ile karakterize nadir bir bozukluktur. YaráÝklar unáÝlateral ,bileteral,aûÏáÝk dudakláÝ veya kapaláÝ dudakláÝ defektler éeklinde olabilir. NûÑral gûÑûÏte anormallik sonucu olduáu dû¥éû¥nû¥lmektedir.
- 152. éizensefali Type I: The clefts can be unilateral or bilateral and may be closed (fused lips). In closed-lip (type I), the cleft walls are in apposition, causing obliteration of the CSF space within the cleft. Type II: The clefts can be unilateral or bilateral and may be separated (open lips). In open-lips (type II), the clefts walls are separated. The CSF fills the cleft from the lateral ventricles to the subarachnoid space that surrounds the hemispheres.
- 153. éƒÝ°ºÝÞýåý¾ÝÞÇÖý¿Ý¶ƒÝ Sonografik ûÑzellikleri Ventrikû¥lden kalvaryuma uzanáÝm gûÑsteren serebral kortekste sáÝváÝ dolu bir yaráÝk Ventrikû¥lomegali gûÑzlenebilir.
- 154. §ÂƒÝ°ºÝÞýåý¾ÝÞÇÖý¿Ý¶ƒÝ-Ý¿ý¿¯šý¿1 35w unáÝlateral schisensefali
- 156. Schizencephalyä» vaka2 21 y 27w g2p1 Lat vent subaracnoid boéluk ile baálantáÝláÝ
- 157. ä»
- 159. ä»
- 160. hidranensefali Hidranensefali internal carotid arterlerin táÝkanáÝkláÝááÝ sonucu serebral hemisferlerin tahrip olmasáÝdáÝr. Beyin parenkimi yáÝkáÝláÝr bos ile yerdeáiétirir. Posterior komunáÝcan arterler korunduáu iûÏin orta beyin ve serebellumvardáÝr. Bazal ggl coroid plx ve talamus korunabilir.
- 161. hidranensefali Sonografik ûÑzellikler Neredeyse tamamen bos ile yerdeáiétirmié normal beyin dokularáÝnáÝn yokluáu Tam veya káÝsmi falks yokluáu Orta beyin bazal ggl ve serebellum varláÝááÝ Koroid plx belirlenebilir. Makrosefali oluéabilir.
- 162. hidranensefali
- 163. hidranensefali
- 165. Hidranensefali-vaka2
- 166. Hidranensefali-vaka2
- 167. ä»
- 168. Ventrikû¥lomegali(hidrosefali) Ventrikû¥llerin dilatasyonunu tanáÝmlar Bos akáÝmáÝndaki obstruksiyon sonucu oluéur.
- 169. Ventrikû¥lomegali(hidrosefali) Synonyms: ventriculomegaly, hydrocephalus, acqueductal stenosis, communicating hydrocephalus
- 170. Ventrikû¥lomegali(hidrosefali) Definition: overt enlargement of the lateral ventricles (atrial width > 15 mm) in the absence of other sonographically demonstrable central nervous system anomalies.
- 171. ventrikû¥lomegali Fetal hydrocephalus: lat vent ûÏok geniélemié., korteks incelmié plx coroideuslar asimetrik .
- 172. ä»
- 173. mikrosefali OrtalamanáÝn 2 standart deviasyonu altáÝnda olan anormal derecede kû¥ûÏû¥k kafayáÝ tanáÝmlar
- 174. mikrosefali Table 1. Classification of microcephaly Microcephaly with associated malformationsMicrocephaly without associated malformations Genetic 1. Chromosomal aberrationsDown syndromeTrisomy 13 syndromeTrisomy 18 syndromeTrisomy 22 syndrome4p- syndromeCat cry (5p-) syndrome18p- syndrome18q- syndrome2. Single gene defectsBloom syndrome (AR)Borjeson-Forssman-Lehmann syndrome (XLR)Cockayne syndrome (AR)DeSanctis-Cacchione syndrome (AR)Dubowitz syndrome (AR)Fanconi pancytopenia (AR)Focal dermal hypoplasia (XLD)Incontinentia pigmenti (XLD)Lissencephaly syndrome (AR)Meckel-Gruber syndrome (AR)Menkes syndrome (XLR)Roberts syndrome (AR)Seckel bird-headed dwarfism (AR)Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome (AR)ä»Genetic1. Primary microcephaly (AR)2. Paine syndrome (XLR)3. Alpers disease (AR)4. Inborn errors of metabolismDisorders of folic acid metabolism (AR)Hyperlysinemia (AR)Methylmalonic acidemia (AR)Phenylketonuria (AR)Environmental1. Prenatal infectionsRubella syndromeCytomegalovirus diseaseHerpesvirus hominisToxoplasmosis2. Prenatal exposure to drugs or chemicalsFetal alcohol syndromeFetal hydantoin syndromeAminopterin syndrome 3. Maternal phenylketonuriaEnvironmental1. Prenatal exposure to radiation2. Fetal malnutrition3. Perinatal trauma or hypoxia4. Postnatal infectionsä»Unknown etiology1. Recognized syndromesCoffin-Sins syndromeDeLange syndromeJohanson-Blizzard syndromeLanger-Giedion syndromeRubenstein-Taybi syndromeWilliams syndrome 2. Undefined combinationsUnknown etiology Happy puppet syndr
- 175. Mikrosefali Sonografik ûÑzellikleri Kû¥ûÏû¥k bpd Kû¥ûÏû¥k baé ûÏevresi Anormal baé ûÏevresi/abdominal ûÏevre ve kafa ûÏevresi /femur uzunluáu
- 176. mikrosefali 24 weeks of gestation; 2D ultrasonography; parasagittal planes through the fetal skull showing microcephaly with large subarachnoid space
- 177. mikrosefali
- 178. mikrosefali
- 179. ä»
- 180. Normal fetal brain ,drbahriyildiz
- 181. Normal fetal brain
- 182. Normal fetal brain
- 183. Normal fetal brain
- 184. Normal fetal brain
- 185. Normal fetal brain
- 186. Normal fetal brain