Fileorganization AbnMagdy
Download as ppt, pdf2 likes414 views
The document discusses four types of file organization: serial, sequential, indexed sequential, and direct access/random access. Serial files store records in the order they are received with no particular sequence. Sequential files store records in key sequence and require creating a new file when adding or deleting records. Indexed sequential files add an index to a sequential file to allow both sequential and random access by key. Direct access files store records at known addresses to allow directly accessing any record.
1 of 17
Downloaded 23 times















Ad
Recommended
File organization
File organizationGanesh Pawar
╠²
This document discusses different types of file organization, including serial, sequential, direct access/random access, and indexed sequential. Serial files store records in the order received with no particular sequence. Sequential files store records in key sequence and are used as master files. Direct access files allow any record to be accessed directly by calculating its address from a key field. Indexed sequential files combine the sequential ordering of records with a full index to allow both sequential and random access by key.File organization
File organizationComputer Hardware & Trouble shooting
╠²
There are four main types of file organization: serial, sequential, indexed sequential, and direct access/random access. Sequential files store records in a specific key-based order and require rewriting the entire file to add or delete records. Direct access files allow directly reading or writing records based on their address, allowing quick random access but being more complex. Indexed sequential files combine the sequential ordering of records with an index to allow both sequential and random access via the index. Batch processing periodically updates master files in batches while online and real-time processing allow immediate updating as transactions occur.Ie Storage, Multimedia And File Organization
Ie Storage, Multimedia And File OrganizationMISY
╠²
Secondary storage benefits include space, reliability, convenience and economy. Common storage media include hard disks, floppy disks, CDs, DVDs and portable drives. Data is organized on disks through formatting into tracks and sectors. Files can be organized sequentially, directly, or through indexes for access. Multimedia combines various media types for presentations.File organisation
File organisationSamuel Igbanogu
╠²
This document discusses different methods of file organization, including heap, sequential, indexed, inverted, and direct access files. It defines key terms like file, record, database, and describes the characteristics and advantages/disadvantages of each file structure type. Some key points made are that file organization is how computer files are structured logically, sequential files allow only sequential access but are efficient for processing related records, and indexed-sequential files provide flexibility for sequential and random access using an index.File organization
File organizationGokul017
╠²
This document discusses how databases physically organize and access data through different file organizations and indexing methods. It describes three main file organizations (heap, ordered, and hash files), how each supports insert, search, and delete operations, and when each performs best. It also explains what indexing is, different index types like primary and secondary indexes, and how to create indexes using SQL. The document aims to explain how databases optimize data storage and access.File organization
File organizationKanchanPatil34
╠²
This document discusses different file organization structures including sequential, random access, indexed sequential, and partially and fully indexed files. It provides definitions of key concepts and compares the structures in terms of data entry order, duplicate records, access speed, availability of keys, storage location, and frequency of use. Logical and physical data organization and updating sequential files are also covered.Concept of computer files
Concept of computer filesSamuel Igbanogu
╠²
This document defines key concepts related to computer files. It discusses:
1. File organization types including serial, sequential, direct access, and indexed sequential. Sequential files store records in key sequence while direct access allows direct retrieval by calculating a record's address.
2. Methods of accessing files which can be serial, sequential, or direct/random.
3. Criteria for classifying files as master, transactional, or reference files based on their content, organization, and storage medium.
4. An assignment to research operating procedures for computer data processing.File Organization
File OrganizationManyi Man
╠²
This document discusses different file organization methods including sequential files, indexed sequential files, indexed files, and direct/hashed files. Sequential files store records in the order they are entered with each record having a fixed format. Indexed sequential files add an index to allow random access by key fields while maintaining sequential ordering. Indexed files use multiple indexes on different keys to allow searching by different fields. Direct/hashed files directly access records by key values using hashing techniques for fast random access.File organisation
File organisationMukund Trivedi
╠²
The document discusses different methods of organizing computer files, including heap files, sequential files, indexed-sequential files, inverted list files, and direct files. It provides details on each method, such as how records are stored and accessed, their advantages and disadvantages, and examples. Key aspects covered include unordered storage in heap files, ordered storage and efficient sequential access in sequential files, indexed access for both sequential and random access in indexed-sequential files, and direct calculation of record locations in direct files.itft-File design
itft-File designShifali Sharma
╠²
The document discusses file design and organization in information systems. It describes the key components of files, including data items, records, record keys, and entities. It explains different file organizations like sequential, direct access, indexed, and inverted files. It also discusses designing printed outputs, including determining output objectives, contents, layout, and appropriate output media.File organisation in system analysis and design
File organisation in system analysis and designMohitgauri
╠²
This document provides an overview of different file organization strategies, including heap files, sequential files, indexed sequential files, inverted list files, and direct files. It discusses the key characteristics of each method, such as how records are stored and accessed. The main advantages and disadvantages of each approach are also summarized. Some key points covered include that sequential files are best for sequential processing but slow for random access, while direct files allow very fast random access but require more complex hardware and software. The document aims to help readers understand different options for structuring computer files.Lecture #1 Introduction
Lecture #1 IntroductionRico
╠²
The document discusses different types of file organization including sequential, random, indexed sequential, and multikey organization. It describes the key aspects of each type including how records are stored and accessed. The document also outlines different types of files such as master files, transaction files, and control files along with examples and characteristics of each.Concept of computer files for Grade 12 learners
Concept of computer files for Grade 12 learnerswellingtonoboh
╠²
The document outlines key definitions and concepts related to computer files, records, fields, and data items. It explains that computer files are the basic units of stored data, with records consisting of related fields, while fields allocate space for individual items of information. Additionally, it categorizes data items into numeric, alphabetic, and alphanumeric types and describes the structured hierarchy from data to files.File structures
File structuresShyam Kumar
╠²
This document discusses primary and secondary storage. Secondary storage is used for permanent storage of data in files and has greater storage capacity than primary storage. A file contains records with fields, and each record is uniquely identified by a key field like student ID. Logical files connect programs to physical files on secondary storage. Files can be accessed sequentially, randomly using indexing, or directly using the key value.File Management
File ManagementRamasubbu .P
╠²
The document discusses file management concepts including file structures, directories, file allocation methods, and access rights. It describes common file structures like sequential, indexed sequential, and direct files. It also covers directory structures, file sharing concepts like simultaneous access and access rights, and secondary storage management techniques like preallocation and allocation methods.File Types in Data Structure
File Types in Data StructureProf Ansari
╠²
The document explains various file structures and types used for information storage on secondary devices, classifying files based on content, data flow, and update frequency. It describes major file operations such as reading, writing, and deleting files, and details different file structures like sequential files, inverted lists, and index-sequential files, along with their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it introduces concepts of fields, records, and pointers that help in organizing and accessing data within files.File organization 1
File organization 1Rupali Rana
╠²
This document discusses different methods for organizing and indexing data stored on disk in a database management system (DBMS). It covers unordered or heap files, ordered or sequential files, and hash files as methods for physically arranging records on disk. It also discusses various indexing techniques like primary indexes, secondary indexes, dense vs sparse indexes, and multi-level indexes like B-trees and B+-trees that provide efficient access to records. The goal of file organization and indexing in a DBMS is to optimize performance for operations like inserting, searching, updating and deleting records from disk files.File organization in database
File organization in databaseAfrasiyab Haider
╠²
1. File organization in databases involves grouping related data records into tables and storing the tables as files in memory for efficient data access and querying.
2. There are several methods of file organization including sequential, indexed, and hashed. Sequential organization stores records one after the other, indexed uses a record key to order records, and hashed uses a hash function to directly map records to storage blocks.
3. The objectives of file organization are to optimally select and access records quickly, allow efficient data modification, avoid duplicate records, and minimize storage costs.File organization and introduction of DBMS
File organization and introduction of DBMSVrushaliSolanke
╠²
The document provides an introduction to database management systems and databases. It discusses:
1) Why we need DBMS and examples of common databases like bank, movie, and railway databases.
2) The definitions of data, information, databases, and DBMS. A DBMS allows for the creation, storage, and retrieval of data from a database.
3) Different types of file organization methods like heap, sorted, indexed, and hash files and their pros and cons. File organization determines how records are stored and accessed in a database.Fundamental File Processing Operations
Fundamental File Processing OperationsRico
╠²
1) Physical files exist on storage while logical files are how programs view files without knowing the actual physical file.
2) Opening files creates a new file or accesses an existing one, while closing files frees up the file descriptor for another file and ensures all output is written.
3) Core file processing operations include reading, writing, and seeking within a file.358 33 powerpoint-slides_16-files-their-organization_chapter-16
358 33 powerpoint-slides_16-files-their-organization_chapter-16sumitbardhan
╠²
This document discusses file organization and attributes. It defines key terms like fields, records, and files. It describes different file attributes like read-only, hidden, system, and archive. It distinguishes between text files and binary files. Text files store data as ASCII codes while binary files store data in a format similar to memory. Basic file operations are also outlined, including creation, updating, retrieval, and maintenance.Ch 8 data base
Ch 8 data baseKhan Yousafzai
╠²
1. A database is an organized collection of related data stored electronically. It allows for efficient storage and retrieval of information.
2. Data is stored in a database in records that contain fields and items. Records contain related data items grouped together, while fields are areas within records reserved for specific data types.
3. There are different types of files like master files, transaction files, and backup files that are used for different purposes in a database system. Master files contain the most complete data while transaction files contain temporary data used to update master files.Chap01 (ics12)
Chap01 (ics12)usmanahmadawan
╠²
This document provides an overview of key concepts related to databases including:
- The components of a database system including data, hardware, software, personnel, and data models.
- Common data models like hierarchical, network, and relational models.
- The objectives of databases which include data integration, integrity, and independence.
- What a database management system (DBMS) is and some common DBMS vendors.Computers14 Ch6
Computers14 Ch6miuitprofessor
╠²
There are three main methods for organizing data files: sequential, direct, and indexed. Sequential organization stores records in order by a key field, requiring reading all prior records to access a specific one. Direct organization allows random access via a record key and a formula to derive the disk address. Indexed organization stores records sequentially but also has an index containing the record key and associated address for direct access. Data can be processed via batch or transaction processing. Batch processing collects transactions into batches to update the master file periodically, while transaction processing handles each transaction immediately as it occurs.File organization and indexing
File organization and indexingraveena sharma
╠²
File organization determines how data is arranged and addressed on storage devices to facilitate access. There are two main types - fixed and variable length records. Fixed length records store all records of the same size, making insertion and deletion simple. Variable length records have different sizes, and can be implemented via byte strings or fixed length representations using anchor and overflow blocks. Indexing uses an index table to determine record locations, improving access speed over sequential scanning. Common index types are ordered and hashed indexes.Fundamental file structure concepts & managing files of records
Fundamental file structure concepts & managing files of recordsDevyani Vaidya
╠²
This document discusses fundamental concepts for structuring and managing files containing records of data. It covers topics such as stream files, field structures, record structures using length indicators, record access, file access and organization, and considerations for portability and standardization. The key ideas are that files can be organized into logical records and fields to group related data elements together and allow random access within files.Wk 1 - File organization.pptx
Wk 1 - File organization.pptxDORCASGABRIEL1
╠²
This document discusses file organization and different types of file organization structures. It defines file organization as the physical arrangement of records on a storage device. The main types discussed are sequential, indexed sequential, and direct access/random access files. Sequential files store records one after the other in order. Indexed sequential files allow both sequential and random access through the use of an index. Direct access files allow direct reading or writing of records based on their address. The document also discusses factors to consider when choosing a file organization method, such as the frequency of updates and nature of access needed.normalization process in relational data base management
normalization process in relational data base managementssuserf80a8c
╠²
The document discusses the different types of database storage, including primary, secondary, and tertiary storage, as well as file organization methods like heap, sequential, indexed sequential, and hash file organization. It also explains file operations, types of indexes, and their advantages and disadvantages, emphasizing the importance of data access speed, efficiency, and organization in database management. Lastly, it covers various indexing techniques, such as primary, secondary, clustering, and multi-level indexes to optimize query performance.Introduction to File System
Introduction to File SystemSanthiNivas
╠²
This document provides an introduction to files and file systems. It defines what files are, including that they are containers for storing information and come in different types like text, data, binary and graphic files. It outlines key file attributes like name, size, permissions. It also describes different file access methods like sequential, direct/random, and indexed sequential access. File operations like create, write, read, delete and truncate are also covered. The document concludes with definitions of flat file databases and their advantages and disadvantages compared to relational databases.File Management ŌĆō File Concept, access methods, File types and File Operation
File Management ŌĆō File Concept, access methods, File types and File OperationDhrumil Panchal
╠²
El documento presenta conceptos sobre la gesti├│n de archivos, incluyendo m├®todos de acceso, tipos de archivos y operaciones de archivos. Se diferencian entre el acceso secuencial y aleatorio, destacando que los archivos de acceso aleatorio son esenciales para aplicaciones como sistemas de bases de datos. Tambi├®n se explican los tipos de archivos, como archivos ASCII y binarios, y las operaciones comunes en la gesti├│n de archivos, como crear, abrir, leer y eliminar archivos.More Related Content
What's hot (18)
File organisation
File organisationMukund Trivedi
╠²
The document discusses different methods of organizing computer files, including heap files, sequential files, indexed-sequential files, inverted list files, and direct files. It provides details on each method, such as how records are stored and accessed, their advantages and disadvantages, and examples. Key aspects covered include unordered storage in heap files, ordered storage and efficient sequential access in sequential files, indexed access for both sequential and random access in indexed-sequential files, and direct calculation of record locations in direct files.itft-File design
itft-File designShifali Sharma
╠²
The document discusses file design and organization in information systems. It describes the key components of files, including data items, records, record keys, and entities. It explains different file organizations like sequential, direct access, indexed, and inverted files. It also discusses designing printed outputs, including determining output objectives, contents, layout, and appropriate output media.File organisation in system analysis and design
File organisation in system analysis and designMohitgauri
╠²
This document provides an overview of different file organization strategies, including heap files, sequential files, indexed sequential files, inverted list files, and direct files. It discusses the key characteristics of each method, such as how records are stored and accessed. The main advantages and disadvantages of each approach are also summarized. Some key points covered include that sequential files are best for sequential processing but slow for random access, while direct files allow very fast random access but require more complex hardware and software. The document aims to help readers understand different options for structuring computer files.Lecture #1 Introduction
Lecture #1 IntroductionRico
╠²
The document discusses different types of file organization including sequential, random, indexed sequential, and multikey organization. It describes the key aspects of each type including how records are stored and accessed. The document also outlines different types of files such as master files, transaction files, and control files along with examples and characteristics of each.Concept of computer files for Grade 12 learners
Concept of computer files for Grade 12 learnerswellingtonoboh
╠²
The document outlines key definitions and concepts related to computer files, records, fields, and data items. It explains that computer files are the basic units of stored data, with records consisting of related fields, while fields allocate space for individual items of information. Additionally, it categorizes data items into numeric, alphabetic, and alphanumeric types and describes the structured hierarchy from data to files.File structures
File structuresShyam Kumar
╠²
This document discusses primary and secondary storage. Secondary storage is used for permanent storage of data in files and has greater storage capacity than primary storage. A file contains records with fields, and each record is uniquely identified by a key field like student ID. Logical files connect programs to physical files on secondary storage. Files can be accessed sequentially, randomly using indexing, or directly using the key value.File Management
File ManagementRamasubbu .P
╠²
The document discusses file management concepts including file structures, directories, file allocation methods, and access rights. It describes common file structures like sequential, indexed sequential, and direct files. It also covers directory structures, file sharing concepts like simultaneous access and access rights, and secondary storage management techniques like preallocation and allocation methods.File Types in Data Structure
File Types in Data StructureProf Ansari
╠²
The document explains various file structures and types used for information storage on secondary devices, classifying files based on content, data flow, and update frequency. It describes major file operations such as reading, writing, and deleting files, and details different file structures like sequential files, inverted lists, and index-sequential files, along with their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it introduces concepts of fields, records, and pointers that help in organizing and accessing data within files.File organization 1
File organization 1Rupali Rana
╠²
This document discusses different methods for organizing and indexing data stored on disk in a database management system (DBMS). It covers unordered or heap files, ordered or sequential files, and hash files as methods for physically arranging records on disk. It also discusses various indexing techniques like primary indexes, secondary indexes, dense vs sparse indexes, and multi-level indexes like B-trees and B+-trees that provide efficient access to records. The goal of file organization and indexing in a DBMS is to optimize performance for operations like inserting, searching, updating and deleting records from disk files.File organization in database
File organization in databaseAfrasiyab Haider
╠²
1. File organization in databases involves grouping related data records into tables and storing the tables as files in memory for efficient data access and querying.
2. There are several methods of file organization including sequential, indexed, and hashed. Sequential organization stores records one after the other, indexed uses a record key to order records, and hashed uses a hash function to directly map records to storage blocks.
3. The objectives of file organization are to optimally select and access records quickly, allow efficient data modification, avoid duplicate records, and minimize storage costs.File organization and introduction of DBMS
File organization and introduction of DBMSVrushaliSolanke
╠²
The document provides an introduction to database management systems and databases. It discusses:
1) Why we need DBMS and examples of common databases like bank, movie, and railway databases.
2) The definitions of data, information, databases, and DBMS. A DBMS allows for the creation, storage, and retrieval of data from a database.
3) Different types of file organization methods like heap, sorted, indexed, and hash files and their pros and cons. File organization determines how records are stored and accessed in a database.Fundamental File Processing Operations
Fundamental File Processing OperationsRico
╠²
1) Physical files exist on storage while logical files are how programs view files without knowing the actual physical file.
2) Opening files creates a new file or accesses an existing one, while closing files frees up the file descriptor for another file and ensures all output is written.
3) Core file processing operations include reading, writing, and seeking within a file.358 33 powerpoint-slides_16-files-their-organization_chapter-16
358 33 powerpoint-slides_16-files-their-organization_chapter-16sumitbardhan
╠²
This document discusses file organization and attributes. It defines key terms like fields, records, and files. It describes different file attributes like read-only, hidden, system, and archive. It distinguishes between text files and binary files. Text files store data as ASCII codes while binary files store data in a format similar to memory. Basic file operations are also outlined, including creation, updating, retrieval, and maintenance.Ch 8 data base
Ch 8 data baseKhan Yousafzai
╠²
1. A database is an organized collection of related data stored electronically. It allows for efficient storage and retrieval of information.
2. Data is stored in a database in records that contain fields and items. Records contain related data items grouped together, while fields are areas within records reserved for specific data types.
3. There are different types of files like master files, transaction files, and backup files that are used for different purposes in a database system. Master files contain the most complete data while transaction files contain temporary data used to update master files.Chap01 (ics12)
Chap01 (ics12)usmanahmadawan
╠²
This document provides an overview of key concepts related to databases including:
- The components of a database system including data, hardware, software, personnel, and data models.
- Common data models like hierarchical, network, and relational models.
- The objectives of databases which include data integration, integrity, and independence.
- What a database management system (DBMS) is and some common DBMS vendors.Computers14 Ch6
Computers14 Ch6miuitprofessor
╠²
There are three main methods for organizing data files: sequential, direct, and indexed. Sequential organization stores records in order by a key field, requiring reading all prior records to access a specific one. Direct organization allows random access via a record key and a formula to derive the disk address. Indexed organization stores records sequentially but also has an index containing the record key and associated address for direct access. Data can be processed via batch or transaction processing. Batch processing collects transactions into batches to update the master file periodically, while transaction processing handles each transaction immediately as it occurs.File organization and indexing
File organization and indexingraveena sharma
╠²
File organization determines how data is arranged and addressed on storage devices to facilitate access. There are two main types - fixed and variable length records. Fixed length records store all records of the same size, making insertion and deletion simple. Variable length records have different sizes, and can be implemented via byte strings or fixed length representations using anchor and overflow blocks. Indexing uses an index table to determine record locations, improving access speed over sequential scanning. Common index types are ordered and hashed indexes.Fundamental file structure concepts & managing files of records
Fundamental file structure concepts & managing files of recordsDevyani Vaidya
╠²
This document discusses fundamental concepts for structuring and managing files containing records of data. It covers topics such as stream files, field structures, record structures using length indicators, record access, file access and organization, and considerations for portability and standardization. The key ideas are that files can be organized into logical records and fields to group related data elements together and allow random access within files.Similar to Fileorganization AbnMagdy (20)
Wk 1 - File organization.pptx
Wk 1 - File organization.pptxDORCASGABRIEL1
╠²
This document discusses file organization and different types of file organization structures. It defines file organization as the physical arrangement of records on a storage device. The main types discussed are sequential, indexed sequential, and direct access/random access files. Sequential files store records one after the other in order. Indexed sequential files allow both sequential and random access through the use of an index. Direct access files allow direct reading or writing of records based on their address. The document also discusses factors to consider when choosing a file organization method, such as the frequency of updates and nature of access needed.normalization process in relational data base management
normalization process in relational data base managementssuserf80a8c
╠²
The document discusses the different types of database storage, including primary, secondary, and tertiary storage, as well as file organization methods like heap, sequential, indexed sequential, and hash file organization. It also explains file operations, types of indexes, and their advantages and disadvantages, emphasizing the importance of data access speed, efficiency, and organization in database management. Lastly, it covers various indexing techniques, such as primary, secondary, clustering, and multi-level indexes to optimize query performance.Introduction to File System
Introduction to File SystemSanthiNivas
╠²
This document provides an introduction to files and file systems. It defines what files are, including that they are containers for storing information and come in different types like text, data, binary and graphic files. It outlines key file attributes like name, size, permissions. It also describes different file access methods like sequential, direct/random, and indexed sequential access. File operations like create, write, read, delete and truncate are also covered. The document concludes with definitions of flat file databases and their advantages and disadvantages compared to relational databases.File Management ŌĆō File Concept, access methods, File types and File Operation
File Management ŌĆō File Concept, access methods, File types and File OperationDhrumil Panchal
╠²
El documento presenta conceptos sobre la gesti├│n de archivos, incluyendo m├®todos de acceso, tipos de archivos y operaciones de archivos. Se diferencian entre el acceso secuencial y aleatorio, destacando que los archivos de acceso aleatorio son esenciales para aplicaciones como sistemas de bases de datos. Tambi├®n se explican los tipos de archivos, como archivos ASCII y binarios, y las operaciones comunes en la gesti├│n de archivos, como crear, abrir, leer y eliminar archivos.File Structure.pptx
File Structure.pptxzedd15
╠²
This document discusses file structure and organization. It defines what a file is and different types of file organization including sequential, hashed/direct access, and indexed sequential access.
It also covers logical vs physical files, basic file operations, record types, indexing, and different index types like primary, secondary, dense, sparse, and clustered indexes. Indexing improves query performance but decreases performance for insert/update/delete operations due to additional space required.Chapter 3
Chapter 3Cahaya Penyayang
╠²
The document discusses file management in operating systems. It covers topics such as the basic functions of a file system, different file organization techniques like sequential, direct and indexed sequential, file structures, file allocation methods like contiguous, linked and indexed, free space management using free lists or bitmaps, file access control, and backup techniques. File systems are responsible for organizing files and managing access to data on storage devices in a way that facilitates navigation and protects data from corruption or loss.FIle Organization.pptx
FIle Organization.pptxSreenivas R
╠²
The document summarizes different file organization techniques used in database management systems. It discusses sequential, direct access, indexed sequential access, and hash file organizations. Sequential access file organization stores records sequentially and allows sequential retrieval but not random access. Direct access organization allows random retrieval by storing records randomly, while indexed sequential access combines both sequential and direct access organizations. Hash file organization uses a hash function to map records to storage locations, allowing direct access via the hash key.Physical Database Design for database student-1.pdf
Physical Database Design for database student-1.pdfBolando
╠²
The document discusses physical database design and storage architectures. It covers topics like secondary storage devices, buffering blocks, placing file records on disk, different types of files (heap files and sorted files), hashing techniques, and modern storage systems like RAID. The key aspects covered are how databases are typically stored on magnetic disks using physical file structures, different storage devices and hierarchies, placing records on disks, indexing and organizing records in files, and techniques for efficient data access and storage.fileorganizationandintroductionofdbms-210313163900.pdf
fileorganizationandintroductionofdbms-210313163900.pdfFraolUmeta
╠²
Database Management System is a software program that allows for the creation, maintenance and use of databases. It provides convenient methods for defining, storing and retrieving data. There are different types of file organizations used in DBMS, including heap, sorted, indexed and hash. Each type has advantages and disadvantages for storage, retrieval, updating and deleting of records from the database. The document discusses these file organization methods in detail.FILE MANAGEMENT.pptx
FILE MANAGEMENT.pptxjayashri kolekar
╠²
This document discusses computer file systems. It explains that files are used to store information on disks and external storage in a persistent way that allows multiple processes to access the data concurrently. The document then covers file naming conventions, structures, types, attributes, access methods and basic file operations supported by operating systems.Chapter 12.pptx
Chapter 12.pptxAsmaaFaried1
╠²
This document provides an overview of file management and file systems. It discusses the basic components of a file including fields, records, files, and databases. It describes common file organization types like sequential, indexed sequential, indexed, and direct files. It also explains the basic components and objectives of a file management system. Finally, it covers B-trees, which are a balanced tree structure commonly used to organize indexes in databases and file systems to provide efficient searching, insertion, and deletion of items.Operating Systems - File Space Allocation
Operating Systems - File Space Allocationcscprabh
╠²
The document provides an overview of file management in operating systems, detailing file concepts, attributes, operations, access methods, and allocation strategies. It outlines file structures (unstructured, fixed-length records, and tree-based), methods for accessing files (sequential, direct, and indexed sequential), and various allocation techniques (contiguous, linked, indexed). Each section describes the advantages and disadvantages of these systems, emphasizing the complexities of file handling within an operating system.Operating System - File Management concepts
Operating System - File Management conceptscscprabh
╠²
The document discusses file management in operating systems, highlighting key concepts like file attributes, operations (creation, writing, reading, deletion), and file structures. It explains various file access methodsŌĆösequential, direct, and indexed sequentialŌĆöand outlines disk space allocation methods: contiguous, linked, and indexed allocation. Additionally, it touches on the process of swapping and memory compaction as part of managing file systems.File Management in Operating System
File Management in Operating SystemJanki Shah
╠²
The document outlines file management in operating systems, detailing file concepts, types (ordinary, directory, device, and fifo files), and operations (create, delete, open, etc.). It explains the directory structures for organizing files and describes the file system structure, which includes layers for efficient data access and storage. Additionally, it discusses various access methods such as sequential, indexed, and direct access for reading files into memory.Disk Image!...and then what? Strategies for sustainable long-term storage an...
Disk Image!...and then what? Strategies for sustainable long-term storage an...Helen Bailey
╠²
The document presents strategies for sustainable long-term storage and access of digital content, emphasizing the importance of metadata and documentation in preservation efforts. It outlines best practices for storage media, management, and security, advocating for multiple backups in different locations and regular verification of file integrity. Additionally, it highlights the significance of planning against obsolescence and ensuring that files remain usable over time.Unit 6 OSY.pptx aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
Unit 6 OSY.pptx aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaharshlad847
╠²
Unit 6 covers file management, detailing the definition, structure, types, and operations of files within operating systems. It discusses file attributes, access methods, allocation strategies, and directory structures, emphasizing the importance of organization and efficiency in file handling. Various file types and their characteristics, as well as disk organization principles, are also explored, highlighting how these concepts relate to effective file systems.Unit 3 file management
Unit 3 file managementKalai Selvi
╠²
This document discusses file systems and file management. It begins by defining key file concepts like file attributes and operations. It then covers topics like access methods, directory structures, file sharing, protection, and file system implementation details. The objectives are to explain file system functions, describe interfaces, discuss design tradeoffs for components like access methods and directories, and explore file system protection.Application portfolio development.advadisadvan.pptx
Application portfolio development.advadisadvan.pptxAmanJain384694
╠²
This document discusses different types of application portfolio development. It describes the need for an application portfolio to organize information about an organization's IT investments and how they support business goals. It explains that a portfolio approach ensures investments are integrated and aligned with business needs. The document also defines different types of files used in application development like data files, program files, object code files, and text files. It covers various file organization methods like serial, sequential, direct, and indexed sequential and their advantages and applications.Unit 3
Unit 3knoxbusiness
╠²
The document discusses features of good filing systems and procedures. It notes that filing systems should allow information to be easily found and accessed when needed. A good system is tidy, safe, and able to adapt to future needs. Documents should be filed daily according to procedures like checking for release marks and using cross-reference cards. Electronic filing also allows quick access and editing of information but has disadvantages like potential data loss issues. Security measures like backups, access restrictions, and data protection laws help safeguard important information.Ad
Fileorganization AbnMagdy
- 2. TYPES OF FILE ORGANIZATION ’ü« Serial ’ü« Sequential ’ü« Indexed Sequential ’ü« Direct Access /Random Access
- 3. Serial File Organization ’ü« A collection of records ’ü« No particular sequence ’ü« Cannot be used as master ’ü« Used as temporary transaction file ’ü« Records stored in the order received
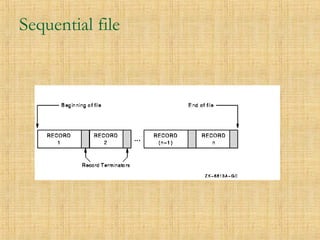
- 4. Sequential File Organization ’ü« A collection of records ’ü« Stored in key sequence ’ü« Adding/deleting record requires making new file ’ü« Used as master files
- 6. Advantages ’ü« Simple file design ’ü« Very efficient when most of the records must be processed e.g. Payroll ’ü« Very efficient if the data has a natural order ’ü« Can be stored on inexpensive devices like magnetic tape.
- 7. Disadvantages ’ü« Entire file must be processed even if a single record is to be searched. ’ü« Transactions have to be sorted before processing ’ü« Overall processing is slow
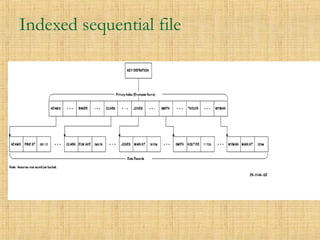
- 8. Indexed sequential file ’ü« Each record of a file has a key field which uniquely identifies that record. ’ü« An index consists of keys and addresses. ’ü« An indexed sequential file is a sequential file (i.e. sorted into order of a key field) which has an index. ’ü« A full index to a file is one in which there is an entry for every record.
- 10. Indexed sequential file ’ü« Indexed sequential files are important for applications where data needs to be accessed..... ’ü▒ sequentially ’ü▒ randomly using the index.
- 11. Indexed sequential file ’ü« An indexed sequential file can only be stored on a random access device e.g. magnetic disc, CD.
- 12. Advantages ’ü« Provides flexibility for users who need both type of accesses with the same file ’ü« Faster than sequential
- 13. Disadvantages ’ü« Extra storage space for the index is required
- 14. Direct (Random) File Organization ’ü« Records are read directly from or written on to the file. ’ü« The records are stored at known address. ’ü« Address is calculated by applying a mathematical function to the key field.
- 15. Direct (Random) File Organization ’ü« A random file would have to be stored on a direct access backing storage medium e.g. magnetic disc, CD, DVD ’ü« Example : Any information retrieval system. Eg Train timetable system.
- 16. Advantages ’ü« Any record can be directly accessed. ’ü« Speed of record processing is very fast. ’ü« Up-to-date file because of online updating. ’ü« Concurrent processing is possible.
- 17. Disadvantages ’ü« More complex than sequential ’ü« Does not fully use memory locations ’ü« More security and backup problems