Food Microbiology, food poisoning and food born diseases notes
Download as PPT, PDF0 likes64 views
This document discusses food microbiology, including a brief history and why it is studied. It outlines common foodborne illnesses and their symptoms. Various pathogens that can cause foodborne disease are described, including bacteria, viruses, protozoa and helminths. It discusses the public health impacts of foodborne illness and that Campylobacter causes the most cases annually while Salmonella causes the most deaths. Intrinsic factors that influence microbial growth such as pH, moisture and temperature are explained. Extrinsic factors such as relative humidity, gases and other microorganisms are also outlined.
1 of 21
Download to read offline




















Recommended
5._Food_Microbiology.ppt



5._Food_Microbiology.pptjayhind9
?
This document provides an overview of food microbiology presented by Mindy Brashears. It discusses the history of food microbiology becoming a science in the 1850s. It also summarizes why food microbiology is studied, including providing safe food and preventing foodborne illness. Key statistics on foodborne illness in the US are presented, noting that Campylobacter causes the most cases annually while Salmonella causes the most deaths. Intrinsic and extrinsic factors that influence microbial growth are reviewed, such as pH, moisture, temperature, and other microorganisms. The hurdle concept of combining preservation methods is also introduced.food microbiology - food and nutrition and health



food microbiology - food and nutrition and healthJanagi Raman S
?
This document provides an overview of food microbiology presented by Mindy Brashears. It discusses the history of food microbiology becoming a science in the 1850s. It explains why studying food microbiology is important for providing safe food and preventing foodborne illness. Key points are that Campylobacter causes the most cases of foodborne illness annually while Salmonella causes the most deaths. The document also reviews microbial growth phases and factors that influence growth such as pH, moisture, temperature, and other microorganisms. It promotes using a hurdle concept to combine preservation methods.5._Food_Microbiology.ppt, Review of Microbiology



5._Food_Microbiology.ppt, Review of MicrobiologyAhmedAbouelwafa7
?
Provide Clean, Safe, Healthful Food to Consumer
Food Permits Growth
Control of Microbial Growth
Prevent Food Spoilage
Prevent Food-borne Illnesses
Food Preservation and ProductionFood as a substrate for microbial growth



Food as a substrate for microbial growthvijayalakshmimvvvcollege
?
This document discusses factors that influence the growth of microorganisms in food. It outlines the history of food microbiology and preservation methods. Intrinsic factors like pH, moisture content and nutrients and extrinsic factors like temperature, atmosphere and water activity determine which microbes can grow. Common preservation methods mentioned include canning, pasteurization, cooking, refrigeration, freezing and drying which make the environment unsuitable for microbial growth.Fermentation in food processing and preservation



Fermentation in food processing and preservationEphraimKachimanga
?
Fermentation is an anaerobic process by which microorganisms like yeast and bacteria convert sugars into acids, gases or alcohols. It has been used for centuries in producing various fermented foods and beverages by utilizing the metabolic activities of microorganisms. Louis Pasteur made significant contributions to fermentation theory by demonstrating that it is caused by living microorganisms rather than decomposition. Factors like temperature, pH, oxygen levels, time and nutrients must be controlled during fermentation to achieve the desired outcomes. Fermentation improves food quality by enhancing flavor, texture, shelf life and nutrition while potentially causing negative effects like histamine intolerance in some individuals.Food Spoilage with processing methods.pptx



Food Spoilage with processing methods.pptxSasiK25
?
Food spoilage is caused by the growth of microorganisms like bacteria, yeasts, and molds. Several factors influence microbial growth in food, including pH, moisture content, temperature, gas concentration, and relative humidity. Food preservation techniques aim to inhibit microbial growth through methods like reducing water activity by drying and salting foods or lowering the pH through fermentation. This prevents food from being damaged or contaminated, rendering it unsuitable for human consumption.FTECH6_UNIT1.pptx



FTECH6_UNIT1.pptxAnnaBelleAnonuevo
?
The document discusses the principles of food processing and preservation. It covers four key points:
1) Food preservation aims to extend shelf life by inhibiting microbial growth and chemical deterioration through methods like controlling temperature, moisture, pH and atmosphere.
2) Common preservation methods include freezing, drying, pickling, canning and salting which inactivate microbes using techniques like heat, cold or high salt levels.
3) Spoilage is caused by enzymes, microbes and chemical/physical factors like oxygen and light. Proper handling and storage conditions are important to prevent damage.
4) Preservatives like sulfites, nitrites and benzoic acid are used as antimicrobials to inhibit bacteria, yeastFood Deterioration and its Control1.pptx



Food Deterioration and its Control1.pptxShamsUlFatah
?
This document discusses food deterioration and its control. It defines food deterioration as the process by which food becomes unacceptable for consumption due to biochemical changes caused by microbes. The main causes of deterioration are listed as biological, chemical, and physical factors. Common microbes like bacteria, yeast, and molds are identified as the main microbial agents that can cause spoilage. Various environmental conditions like temperature, oxygen levels, and moisture that affect microbial growth are outlined. Finally, several common methods for preserving food and extending its shelf life, such as heating, drying, acidification, addition of salt or sugar, modifying atmosphere, and use of chemicals/radiation are described at a high level.Food spoilage, microbiology



Food spoilage, microbiologyMAMATHESH
?
Food spoilage is caused by the growth of microorganisms like bacteria, yeasts, and molds. Several factors influence microbial growth in food, including temperature, pH, moisture content, and nutrient levels. Food preservation techniques aim to inhibit microbial growth through methods like reducing water activity by drying and salting foods or lowering the pH. Proper control of factors like temperature, gases, and humidity during food storage is important for limiting spoilage.Food spoilage & food borne infection



Food spoilage & food borne infectionRachana Choudhary
?
Food spoilage is the process where a food product becomes unsuitable to ingest by the consumer. The cause of such a process is due to many outside factors as a side-effect of the type of product it is, as well as how the product is packaged and stored.1.Review processing and preservation.pptx



1.Review processing and preservation.pptxMUHAMMADNADEEM146570
?
The document summarizes food preservation techniques and food spoilage mechanisms. It classifies foods based on shelf life, functions, processing, and categorizes spoilage as physical, microbial, chemical or enzymatic. Physical spoilage includes moisture changes and crystallization. Microbial spoilage is caused by molds, yeasts and bacteria. Chemical spoilage involves oxidation, proteolysis and Maillard reaction. Enzymatic reactions like pectin hydrolysis and lipolysis also cause food degradation. Various intrinsic and extrinsic factors influence the spoilage process.Food processing Principles and methods.pptx



Food processing Principles and methods.pptxAnjaliPn2
?
The document discusses food processing and preservation. It covers the physiological, psychological, and social functions of food. Food is classified based on nutritive value into basic food groups like basic four, basic five, and basic seven. Methods of food preservation include thermal processing like cooking, blanching, and pasteurization which destroy microorganisms and inactivate enzymes. Other methods are use of chemicals, drying, filtration, fermentation, and irradiation to prevent spoilage from microbes, insects, and chemical/physical factors.FOOD SPOILAGE



FOOD SPOILAGEHARISH J
?
Food spoilage occurs when microorganisms like bacteria, yeasts, and molds degrade the nutritional value, texture, and flavor of food, making it unsuitable for consumption. The main causes of food spoilage are physical changes in conditions like temperature and biological factors such as microbial growth. Spoilage can lead to changes in a food's nutritional content, appearance, and production of toxins. Various signs like odor, sliminess, and discoloration indicate microbial spoilage. Proper food preservation techniques aim to inhibit microbial growth or kill microorganisms to prevent spoilage and potential food poisoning.Food microbiology.ppt



Food microbiology.pptBabuskin srinivasan
?
This document discusses food microbiology and food spoilage. It begins by introducing food storage and factors that contribute to food deterioration like microorganism growth. The major causes of food spoilage are microbial growth, enzymatic reactions, chemical reactions, vermin, and physical changes. Specific microorganisms like bacteria, yeasts and molds are responsible for food spoilage. Factors like temperature, pH, moisture content and nutrients influence microbial growth in food. Food preservation techniques aim to prolong food storage life by preventing microbial spoilage.12780307 (2).ppt



12780307 (2).pptssuser4556c5
?
This document discusses food microbiology. It covers the microorganisms studied in food microbiology including bacteria, fungi, algae, protozoa, viruses, and prions. It describes the intrinsic and extrinsic factors that influence microbial growth in foods such as pH, moisture, temperature, and antimicrobial substances. It also discusses food spoilage, foodborne illness, and how microbes can be used to produce foods like cheese, yogurt, bread, and wine.Focus on... basic food microbiology pt1



Focus on... basic food microbiology pt1Nick Cork
?
This document provides an overview of a webinar series on food microbiology. It begins with introducing basic microbiology concepts like bacterial structure and classification. It then discusses various factors that influence microbial growth in food like pH, water activity, nutrients, and temperature. Several pathogenic bacteria of concern in food production are described in more detail, including E. coli, Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus, Clostridium perfringens, and Clostridium botulinum. The document concludes with briefly outlining the growth characteristics of some significant microorganisms.Biochemical Aspects of Food Spoilage



Biochemical Aspects of Food Spoilagemeetpadhiyar88
?
Biochemical Aspects of food spoilage by enzymes like Lipase and Lipooxygenase, Rancidity and Antioxidants.Food_spoilage_and_poisoning.pptx



Food_spoilage_and_poisoning.pptxArti Mahajan
?
Food spoilage can occur through various means, including microbial growth, chemical changes, and temperature fluctuations. The main types of microorganisms that cause food spoilage are bacteria, molds, and yeasts. Spoilage leads to deterioration and waste of food as well as potential food poisoning. Various prevention methods can be used to delay or reduce spoilage, including refrigeration, freezing, drying, salting, sugaring, canning, and controlling factors like heat, moisture and pH.Food preservation methods



Food preservation methodsRinaldo John
?
Food spoilage results from microbial growth that alters foods visually and makes them unsuitable for consumption. Various preservation methods are used to inhibit microbial growth and activity, including preventing access of microbes, removing microbes, hindering microbe growth through drying, refrigeration, canning or chemical additions, and killing microbes through heating or radiation. Common preservation methods include drying, salting, smoking, refrigeration, freezing, canning, irradiation, and addition of chemical preservatives.Factor affecting growth of microorganisms in food



Factor affecting growth of microorganisms in foodMDHumayunKobir2
?
Md. Humayun Kobir
Dept: Agro Product processing Technology
Jashore University Of Science and Technology,Chapter 4



Chapter 4Hajar Azhari
?
1) Many factors influence the growth and heat resistance of microorganisms in food, including temperature, pH, water activity, redox potential, nutrient levels, and number of microorganisms present.
2) The optimal temperature, pH, and water activity levels vary between bacterial species, with psychrotrophs growing at refrigeration temperatures and thermophiles growing at higher temperatures.
3) Higher numbers of microorganisms, pH levels closer to optimal, and more water or fat content can increase heat resistance by providing a protective environment.Food microbiology-lecture.ppt



Food microbiology-lecture.pptAmrMohammed60
?
1. The document provides an introduction to food microbiology, discussing factors that influence food spoilage such as microorganism growth, pH, moisture content, and temperature.
2. It describes various food preservation methods including inhibiting microorganism growth through reducing water activity via drying or salting, or lowering pH with fermentation or acids.
3. The document also discusses killing microorganisms using heat treatments like pasteurization or sterilization, irradiation, or gases. Combining inhibition and killing principles is often used in food preservation depending on the food.Food Spoilage



Food SpoilageMDHumayunKobir2
?
Md. Humayun Kobir
Dept: Agro Product processing Technology
Jashore University Of Science and Technology,Microbiology Bio 127 Food Microbiology



Microbiology Bio 127 Food MicrobiologyShaina Mavreen Villaroza
?
This document discusses factors that influence microbial growth in foods and food spoilage. It covers intrinsic factors like composition, pH and water activity, and extrinsic factors like temperature and atmosphere. Various methods for controlling microbial growth and food spoilage are described, including removal of microorganisms, low temperature, high temperature processes like canning and pasteurization, controlling water availability, use of chemical preservatives, radiation, and surveillance programs. Fermented foods produced via lactic, propionic, and ethanolic fermentations are also summarized.More Related Content
Similar to Food Microbiology, food poisoning and food born diseases notes (20)
FTECH6_UNIT1.pptx



FTECH6_UNIT1.pptxAnnaBelleAnonuevo
?
The document discusses the principles of food processing and preservation. It covers four key points:
1) Food preservation aims to extend shelf life by inhibiting microbial growth and chemical deterioration through methods like controlling temperature, moisture, pH and atmosphere.
2) Common preservation methods include freezing, drying, pickling, canning and salting which inactivate microbes using techniques like heat, cold or high salt levels.
3) Spoilage is caused by enzymes, microbes and chemical/physical factors like oxygen and light. Proper handling and storage conditions are important to prevent damage.
4) Preservatives like sulfites, nitrites and benzoic acid are used as antimicrobials to inhibit bacteria, yeastFood Deterioration and its Control1.pptx



Food Deterioration and its Control1.pptxShamsUlFatah
?
This document discusses food deterioration and its control. It defines food deterioration as the process by which food becomes unacceptable for consumption due to biochemical changes caused by microbes. The main causes of deterioration are listed as biological, chemical, and physical factors. Common microbes like bacteria, yeast, and molds are identified as the main microbial agents that can cause spoilage. Various environmental conditions like temperature, oxygen levels, and moisture that affect microbial growth are outlined. Finally, several common methods for preserving food and extending its shelf life, such as heating, drying, acidification, addition of salt or sugar, modifying atmosphere, and use of chemicals/radiation are described at a high level.Food spoilage, microbiology



Food spoilage, microbiologyMAMATHESH
?
Food spoilage is caused by the growth of microorganisms like bacteria, yeasts, and molds. Several factors influence microbial growth in food, including temperature, pH, moisture content, and nutrient levels. Food preservation techniques aim to inhibit microbial growth through methods like reducing water activity by drying and salting foods or lowering the pH. Proper control of factors like temperature, gases, and humidity during food storage is important for limiting spoilage.Food spoilage & food borne infection



Food spoilage & food borne infectionRachana Choudhary
?
Food spoilage is the process where a food product becomes unsuitable to ingest by the consumer. The cause of such a process is due to many outside factors as a side-effect of the type of product it is, as well as how the product is packaged and stored.1.Review processing and preservation.pptx



1.Review processing and preservation.pptxMUHAMMADNADEEM146570
?
The document summarizes food preservation techniques and food spoilage mechanisms. It classifies foods based on shelf life, functions, processing, and categorizes spoilage as physical, microbial, chemical or enzymatic. Physical spoilage includes moisture changes and crystallization. Microbial spoilage is caused by molds, yeasts and bacteria. Chemical spoilage involves oxidation, proteolysis and Maillard reaction. Enzymatic reactions like pectin hydrolysis and lipolysis also cause food degradation. Various intrinsic and extrinsic factors influence the spoilage process.Food processing Principles and methods.pptx



Food processing Principles and methods.pptxAnjaliPn2
?
The document discusses food processing and preservation. It covers the physiological, psychological, and social functions of food. Food is classified based on nutritive value into basic food groups like basic four, basic five, and basic seven. Methods of food preservation include thermal processing like cooking, blanching, and pasteurization which destroy microorganisms and inactivate enzymes. Other methods are use of chemicals, drying, filtration, fermentation, and irradiation to prevent spoilage from microbes, insects, and chemical/physical factors.FOOD SPOILAGE



FOOD SPOILAGEHARISH J
?
Food spoilage occurs when microorganisms like bacteria, yeasts, and molds degrade the nutritional value, texture, and flavor of food, making it unsuitable for consumption. The main causes of food spoilage are physical changes in conditions like temperature and biological factors such as microbial growth. Spoilage can lead to changes in a food's nutritional content, appearance, and production of toxins. Various signs like odor, sliminess, and discoloration indicate microbial spoilage. Proper food preservation techniques aim to inhibit microbial growth or kill microorganisms to prevent spoilage and potential food poisoning.Food microbiology.ppt



Food microbiology.pptBabuskin srinivasan
?
This document discusses food microbiology and food spoilage. It begins by introducing food storage and factors that contribute to food deterioration like microorganism growth. The major causes of food spoilage are microbial growth, enzymatic reactions, chemical reactions, vermin, and physical changes. Specific microorganisms like bacteria, yeasts and molds are responsible for food spoilage. Factors like temperature, pH, moisture content and nutrients influence microbial growth in food. Food preservation techniques aim to prolong food storage life by preventing microbial spoilage.12780307 (2).ppt



12780307 (2).pptssuser4556c5
?
This document discusses food microbiology. It covers the microorganisms studied in food microbiology including bacteria, fungi, algae, protozoa, viruses, and prions. It describes the intrinsic and extrinsic factors that influence microbial growth in foods such as pH, moisture, temperature, and antimicrobial substances. It also discusses food spoilage, foodborne illness, and how microbes can be used to produce foods like cheese, yogurt, bread, and wine.Focus on... basic food microbiology pt1



Focus on... basic food microbiology pt1Nick Cork
?
This document provides an overview of a webinar series on food microbiology. It begins with introducing basic microbiology concepts like bacterial structure and classification. It then discusses various factors that influence microbial growth in food like pH, water activity, nutrients, and temperature. Several pathogenic bacteria of concern in food production are described in more detail, including E. coli, Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus, Clostridium perfringens, and Clostridium botulinum. The document concludes with briefly outlining the growth characteristics of some significant microorganisms.Biochemical Aspects of Food Spoilage



Biochemical Aspects of Food Spoilagemeetpadhiyar88
?
Biochemical Aspects of food spoilage by enzymes like Lipase and Lipooxygenase, Rancidity and Antioxidants.Food_spoilage_and_poisoning.pptx



Food_spoilage_and_poisoning.pptxArti Mahajan
?
Food spoilage can occur through various means, including microbial growth, chemical changes, and temperature fluctuations. The main types of microorganisms that cause food spoilage are bacteria, molds, and yeasts. Spoilage leads to deterioration and waste of food as well as potential food poisoning. Various prevention methods can be used to delay or reduce spoilage, including refrigeration, freezing, drying, salting, sugaring, canning, and controlling factors like heat, moisture and pH.Food preservation methods



Food preservation methodsRinaldo John
?
Food spoilage results from microbial growth that alters foods visually and makes them unsuitable for consumption. Various preservation methods are used to inhibit microbial growth and activity, including preventing access of microbes, removing microbes, hindering microbe growth through drying, refrigeration, canning or chemical additions, and killing microbes through heating or radiation. Common preservation methods include drying, salting, smoking, refrigeration, freezing, canning, irradiation, and addition of chemical preservatives.Factor affecting growth of microorganisms in food



Factor affecting growth of microorganisms in foodMDHumayunKobir2
?
Md. Humayun Kobir
Dept: Agro Product processing Technology
Jashore University Of Science and Technology,Chapter 4



Chapter 4Hajar Azhari
?
1) Many factors influence the growth and heat resistance of microorganisms in food, including temperature, pH, water activity, redox potential, nutrient levels, and number of microorganisms present.
2) The optimal temperature, pH, and water activity levels vary between bacterial species, with psychrotrophs growing at refrigeration temperatures and thermophiles growing at higher temperatures.
3) Higher numbers of microorganisms, pH levels closer to optimal, and more water or fat content can increase heat resistance by providing a protective environment.Food microbiology-lecture.ppt



Food microbiology-lecture.pptAmrMohammed60
?
1. The document provides an introduction to food microbiology, discussing factors that influence food spoilage such as microorganism growth, pH, moisture content, and temperature.
2. It describes various food preservation methods including inhibiting microorganism growth through reducing water activity via drying or salting, or lowering pH with fermentation or acids.
3. The document also discusses killing microorganisms using heat treatments like pasteurization or sterilization, irradiation, or gases. Combining inhibition and killing principles is often used in food preservation depending on the food.Food Spoilage



Food SpoilageMDHumayunKobir2
?
Md. Humayun Kobir
Dept: Agro Product processing Technology
Jashore University Of Science and Technology,Microbiology Bio 127 Food Microbiology



Microbiology Bio 127 Food MicrobiologyShaina Mavreen Villaroza
?
This document discusses factors that influence microbial growth in foods and food spoilage. It covers intrinsic factors like composition, pH and water activity, and extrinsic factors like temperature and atmosphere. Various methods for controlling microbial growth and food spoilage are described, including removal of microorganisms, low temperature, high temperature processes like canning and pasteurization, controlling water availability, use of chemical preservatives, radiation, and surveillance programs. Fermented foods produced via lactic, propionic, and ethanolic fermentations are also summarized.More from hellenm7 (6)
Streptococci In medical microbiology and health



Streptococci In medical microbiology and healthhellenm7
?
This document provides information on Streptococci (Gram positive cocci) including classification, pathogenic species, diseases caused, and laboratory diagnosis and treatment. It discusses key points such as:
- Classification based on Lancefield serology and hemolysis patterns on blood agar (α, β, γ hemolysis)
- Major pathogenic species like Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A Strep), S. agalactiae (Group B Strep), and S. pneumoniae (pneumococcus) which cause diseases like pharyngitis, pneumonia, neonatal sepsis through various virulence factors.
- Laboratory diagnosis involves culture techniques, identification tests and sensitivity testing to confirm species and guide appropriate antibioticActinomycetes for health and medical microbiology



Actinomycetes for health and medical microbiologyhellenm7
?
Actinomycetes are a diverse group of gram-positive filamentous bacteria that can cause actinomycosis infections in humans. Important species that cause actinomycosis include Actinomyces israelii, A. odontolyticus, A. gerencseriae, and A. meyeri. Actinomycosis is acquired endogenously, often through dental procedures or trauma, and results in abscesses, tissue destruction, and fibrosis. Clinical presentations vary by site of infection and can include cervicofacial, thoracic, pelvic, cerebral, or appendiceal/colonic infections. Diagnosis involves tissue biopsy and culture, while treatment requires a combination ofRecently uploaded (20)
Top Medical Experts for Women Care Center



Top Medical Experts for Women Care Centerkekancr
?
Our expert team in Fetal Imaging Institute and gynecological care , beyond medical excellence, we offer compassionate counseling and support for prospective parents. We focus on high-quality care for high-risk pregnancies, including early detection of Down syndrome and other conditions.TS Tr?n Qu?c B?o - Ng??i ??a Y T? Vi?t Nam Ra Th? Gi?i Th?ng Qua Gi?i One Cha...



TS Tr?n Qu?c B?o - Ng??i ??a Y T? Vi?t Nam Ra Th? Gi?i Th?ng Qua Gi?i One Cha...Ignite Capital
?
Trong th? gi?i th? thao toàn c?u, n?i các s? ki?n MMA (Mixed Martial Arts) thu hút hàng tri?u ng??i h?m m?, gi?i ??u One Championship n?i lên nh? m?t hi?n t??ng, thu hút h?n 3 t? khán gi? m?i n?m. Và khi gi?i ??u này l?n ??u tiên ??n Vi?t Nam vào tháng 9 n?m 2019, m?t trong nh?ng tên tu?i l?n ??ng sau s? thành c?ng c?a s? ki?n t?i TP.HCM chính là ?ng Tr?n Qu?c B?o, m?t nhà l?nh ??o tiên phong trong l?nh v?c y t?, ??ng th?i là Giám ??c Marketing và K? ho?ch chi?n l??c c?a B?nh vi?n Qu?c t? City.
S? ki?n One Championship t?i Vi?t Nam kh?ng ch? thu hút s? chú ? c?a gi?i th? thao mà còn là m?t minh ch?ng cho t?m ?nh h??ng c?a ?ng Tr?n Qu?c B?o trong vi?c k?t n?i các t? ch?c th? thao qu?c t? v?i h? th?ng y t? và d?ch v? c?p c?u c?a Vi?t Nam. D??i s? l?nh ??o c?a ?ng, B?nh vi?n Qu?c t? City ?? tr? thành nhà cung c?p d?ch v? y t? và c?p c?u chính th?c cho gi?i ??u MMA l?n nh?t th? gi?i này. Kh?ng ch? là m?t c? s? y t?, B?nh vi?n Qu?c t? City ?? ch?ng t? ???c kh? n?ng cung c?p d?ch v? ch?m sóc s?c kh?e toàn di?n, ?áp ?ng yêu c?u cao c?a m?t s? ki?n th? thao qu?c t? quy m? l?n.
Khi gi?i ??u One Championship t? ch?c t?i TP.HCM, ?ng Tr?n Qu?c B?o ?? d?n d?t ??i ng? bác s?, y tá và nh?n viên y t? t? B?nh vi?n Qu?c t? City th?c hi?n các b??c chu?n b? cu?i cùng ?? ??m b?o an toàn cho các v?n ??ng viên. Trong quá trình này, ?ng B?o và ??i ng? y t? ?? th?c hi?n các bu?i di?n t?p chi ti?t trong sàn ??u, ??m b?o m?i tình hu?ng y t? kh?n c?p ??u ???c x? l? m?t cách nhanh chóng và chính xác. S? chu?n b? chu ?áo này kh?ng ch? t?o ra ni?m tin v?ng ch?c cho các v?n ??ng viên mà còn c?ng c? v? th? c?a B?nh vi?n Qu?c t? City nh? m?t trung t?m y t? hàng ??u t?i Vi?t Nam.
D??i s? d?n d?t c?a ?ng Tr?n Qu?c B?o, kh?ng ch? có c?ng tác y t? mà s? k?t n?i gi?a th? thao, du l?ch và y t? ?? ???c phát tri?n m?nh m?, giúp qu?ng bá hình ?nh Vi?t Nam trên b?n ?? th? thao qu?c t?. V?i t?m nhìn chi?n l??c s?c bén, ?ng B?o ?? giúp Vi?t Nam kh?ng ch? tr? thành ?i?m ??n l? t??ng cho các s? ki?n th? thao mà còn n?ng cao uy tín c?a ngành y t? trong m?t b?n bè qu?c t?.
Gi?i One Championship là minh ch?ng cho s? thành c?ng c?a ?ng Tr?n Qu?c B?o trong vi?c k?t n?i các ngành c?ng nghi?p th? thao và y t?, ?óng góp kh?ng nh? vào s? phát tri?n c?a du l?ch th? thao qu?c t? t?i Vi?t Nam. Thành c?ng này kh?ng ch? giúp B?nh vi?n Qu?c t? City kh?ng ??nh ???c vai trò c?a mình trong h? th?ng y t? qu?c gia mà còn n?ng cao v? th? y t? Vi?t Nam trên tr??ng qu?c t?, ch?ng minh r?ng d??i s? l?nh ??o sáng su?t c?a ?ng Tr?n Qu?c B?o, Vi?t Nam ?? s?n sàng chào ?ón nh?ng s? ki?n th? thao t?m c? th? gi?i.Diseases of Cardiovascular system .docx



Diseases of Cardiovascular system .docxAyesha Fatima
?
DISORDERS OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
HYPERTENSION
1. Hypertension is defined as persistently elevated arterial blood pressure (BP).
2. Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a chronic medical condition in which the force of blood against the artery walls is consistently too high, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other health complications.
3. WHO Definition of Hypertension
a. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), hypertension is defined as:
Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP) ≥ 140 mmHg
Diastolic Blood Pressure (DBP) ≥ 90 mmHg
b. Based on repeated measurements under standardized conditions.
Risk factors
Obesity A sedentary lifestyle
Diabetes mellitus High intakes of salt or alcohol
Family history Stress
Cigarette smoking Low birth weight
Hypertension is described as essential (primary, idiopathic) or secondary to other diseases.
Irrespective of the cause, hypertension commonly affects the kidneys.
Essential hypertension
1. A condition of persistently elevated blood pressure without a known secondary cause, often associated with genetic predisposition and lifestyle factors.
Benign (chronic) hypertension
1. The rise in blood pressure is usually slight to moderate and continues to rise slowly over many years.
2. Sometimes complications, such as heart failure, cerebrovascular accident or myocardial infarction are the first indication of hypertension, but often the condition is symptomless and is only discovered during a routine examination.
Malignant (accelerated) hypertension
1. This is a rapid and aggressive acceleration of hypertensive disease.
2. Diastolic pressure in excess of 120 mmHg is common.
3. The effects are serious and quickly become apparent, e.g. haemorrhages into the retina, papilloedema (oedema around the optic disc), encephalopathy (cerebral oedema) and progressive renal disease, leading to cardiac failure.
Secondary hypertension
Hypertension resulting from other diseases accounts for 5% of all cases.
I. Kidney disease
Raised blood pressure is a complication of many kidney diseases. In kidney disease, there is salt and water retention, sometimes with excessive renin activity.
II. Endocrine disorders
a) Adrenal cortex
Secretion of excess aldosterone and cortisol stimulates the retention of excess sodium and water by the kidneys, raising the blood volume and pressure.
b) Adrenal medulla
Secretion of excess adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine) raises blood pressure, e.g. phaeochromocytoma .
III. Stricture of the aorta
Hypertension develops in branching arteries proximal to the site of a stricture, e.g congenital
coarctation.
IV. Drug treatment
Hypertension may be a side-effect of some drugs, e.g. corticosteroids and oral contraceptives.
Effects and complications of hypertension
The effects of long-standing and progressively rising blood pressure are serious.
Hypertension predisposes to atherosclerosis and has specific effects on particular organs.
Heart
Prima Saigon Medical Center: Redefining Healthcare Excellence in Vietnam



Prima Saigon Medical Center: Redefining Healthcare Excellence in VietnamIgnite Capital
?
In the heart of Ho Chi Minh City, a new paradigm in healthcare is taking shape at Prima Saigon Medical Center. Since its establishment, this cutting-edge hospital has emerged as one of Vietnam’s premier medical institutions, setting a new standard for patient care, advanced treatments, and medical innovation.
Opened in 2020, Prima Saigon blends state-of-the-art technology with a commitment to delivering personalized, compassionate care. Designed to cater to both local and international patients, the facility stands as a beacon of medical excellence in Southeast Asia. As medical tourism grows in Vietnam, Prima Saigon has positioned itself as a leading destination for specialized care, attracting patients from across the region and beyond.
The center’s expertise spans a wide range of specialties, from oncology and cardiology to orthopedics and plastic surgery, with a team of world-class medical professionals. Every aspect of the hospital, from its advanced equipment to its patient-centric approach, is geared toward providing the highest quality of care. The hospital's commitment to excellence extends beyond medical treatment, with luxurious accommodations and a serene environment designed to make patients feel at ease throughout their journey to recovery.
What truly sets Prima Saigon apart, however, is its emphasis on holistic care. The hospital goes beyond treating the illness, focusing on the well-being of the patient as a whole. Each patient’s care plan is personalized, ensuring they not only receive the best medical attention but also the emotional and psychological support they need during their treatment.
As Vietnam’s healthcare sector continues to evolve, Prima Saigon stands at the forefront, driving innovation while remaining deeply committed to patient welfare. In just a few short years, it has become a symbol of what’s possible when modern medicine and compassionate care come together—setting the stage for the future of healthcare in Vietnam and beyond.Top Garbhsanskar Centre in Nashik for Moms



Top Garbhsanskar Centre in Nashik for MomsDr Avhad Hospital
?
Prepare for a healthy and blissful pregnancy with Garbhsanskar at our trusted center in Nashik. Embrace ancient wisdom for a joyful motherhood journey.
Contact Details:
Name: Dr. Avhad Hospital
Address: Dr. Avhad Hospital, Dr. Avhad Maternity Home, RD Circle, Rajmata Jijau marg Karmayogi Nagar Govind Nagar- city center mall, Link Road, Nashik, Maharashtra 422008
Phone: 08928251451
Email: dravhadhospital@gmail.com
Website: https://dravhadhospital.com/garbhsanskar-centre-nashik/一比一原版加拿大西叁一大学毕业证(罢奥鲍毕业证书)如何办理



一比一原版加拿大西叁一大学毕业证(罢奥鲍毕业证书)如何办理taqyed
?
Diploma加拿大文凭购买,加拿大文凭定制,加拿大西三一大学文凭补办【q薇1954292140】专业在线定制加拿大大学文凭2025年新版学位证书,定做加拿大本科文凭,【q薇1954292140】复制加拿大Trinity Western University completion letter。在线快速补办加拿大本科毕业证、硕士文凭证书,购买加拿大学位证、西三一大学Offer,加拿大大学文凭在线购买。高仿真还原加拿大文凭证书和外壳,定制加拿大西三一大学成绩单和信封。办留服认证TWU毕业证【q薇1954292140】办理加拿大西三一大学毕业证(TWU毕业证书)【q薇1954292140】极速办西三一大学offer/学位证加拿大毕业证购买、留信官方学历认证(永久存档真实可查)采用学校原版纸张、特殊工艺完全按照原版一比一制作。帮你解决西三一大学学历学位认证难题。
特殊原因导致无法毕业,也可以联系我们帮您办理相关材料:
1:在西三一大学挂科了,不想读了,成绩不理想怎么办???
2:打算回国了,找工作的时候,需要提供认证《TWU成绩单购买办理西三一大学毕业证书范本》【Q/WeChat:1954292140】Buy Trinity Western University Diploma《正式成绩单论文没过》有文凭却得不到认证。又该怎么办???加拿大毕业证购买,加拿大文凭购买,
3:回国了找工作没有西三一大学文凭怎么办?有本科却要求硕士又怎么办?
帮您解决在加拿大西三一大学未毕业难题(Trinity Western University)文凭购买、毕业证购买、大学文凭购买、大学毕业证购买、买文凭、日韩文凭、英国大学文凭、美国大学文凭、澳洲大学文凭、加拿大大学文凭(q薇1954292140)新加坡大学文凭、新西兰大学文凭、爱尔兰文凭、西班牙文凭、德国文凭、教育部认证,买毕业证,毕业证购买,买大学文凭,购买日韩毕业证、英国大学毕业证、美国大学毕业证、澳洲大学毕业证、加拿大大学毕业证(q薇1954292140)新加坡大学毕业证、新西兰大学毕业证、爱尔兰毕业证、西班牙毕业证、德国毕业证,回国证明,留信网认证,留信认证办理,学历认证。从而完成就业。
如果您在英、加、美、澳、欧洲等留学过程中或回国后:
1、在校期间因各种原因未能顺利毕业《TWU成绩单工艺详解》【Q/WeChat:1954292140】《Buy Trinity Western University Transcript快速办理西三一大学教育部学历认证书毕业文凭证书》,拿不到官方毕业证;
2、面对父母的压力,希望尽快拿到;
3、不清楚认证流程以及材料该如何准备;
4、回国时间很长,忘记办理;
5、回国马上就要找工作《正式成绩单西三一大学复刻一套文凭多少米》【q薇1954292140】《学历认证生成授权声明TWU成绩单安全高效的个性服务流程本科学历》办给用人单位看;
6、企事业单位必须要求办理的;
7、需要报考公务员、购买免税车、落转户口、申请留学生创业基金。
加拿大文凭西三一大学成绩单,TWU毕业证【q薇1954292140】办理加拿大西三一大学毕业证(TWU毕业证书)【q薇1954292140】专业定制国外毕业证书西三一大学offer/学位证成绩单温感光标、留信官方学历认证(永久存档真实可查)采用学校原版纸张、特殊工艺完全按照原版一比一制作。帮你解决西三一大学学历学位认证难题。
【q薇1954292140】办理西三一大学毕业证(TWU毕业证书)2025年新版成绩单【q薇1954292140】西三一大学offer/学位证、留信官方学历认证(永久存档真实可查)采用学校原版纸张、特殊工艺完全按照原版一比一制作加拿大西三一大学毕业证(TWU毕业证书)文凭样本
主营项目:
1、真实教育部国外学历学位认证《加拿大毕业文凭证书快速办理西三一大学留学生学历学位认证书》【q薇1954292140】《论文没过西三一大学正式成绩单》,教育部存档,教育部留服网站100%可查.
2、办理TWU毕业证,改成绩单《TWU毕业证明办理西三一大学毕业证丢失补办》【Q/WeChat:1954292140】Buy Trinity Western University Certificates《正式成绩单论文没过》,西三一大学Offer、在读证明、学生卡、信封、证明信等全套材料,从防伪到印刷,从水印到钢印烫金,高精仿度跟学校原版100%相同.
3、真实使馆认证(即留学人员回国证明),使馆存档可通过大使馆查询确认.
4、留信网认证,国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书,留信网存档可查.
《西三一大学办理文凭加拿大毕业证书办理TWU买大学毕业证|买大学文凭》【q薇1954292140】学位证1:1完美还原海外各大学毕业材料上的工艺:水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠。文字图案浮雕、激光镭射、紫外荧光、温感、复印防伪等防伪工艺。
办密封成绩单申请学校加拿大文凭西三一大学成绩单【q薇1954292140】复刻成绩单加拿大西三一大学毕业证(TWU毕业证书)展示成绩单模板 西三一大学毕业证办理,成绩单定制加拿大西三一大学文凭办理,加拿大西三一大学成绩单办理和真实留信认证、留服认证、西三一大学学历认证。学院文凭定制,西三一大学原版文凭补办,扫描件文凭定做,100%文凭复刻。【q薇1954292140】Buy Trinity Western University Diploma购买美国毕业证,购买英国毕业证,购买澳洲毕业证,购买加拿大毕业证,以及德国毕业证,购买法国毕业证(q薇1954292140)购买荷兰毕业证、购买瑞士毕业证、购买日本毕业证、购买韩国毕业证、购买新西兰毕业证、购买新加坡毕业证、购买西班牙毕业证、购买马来西亚毕业证等。包括了本科毕业证,硕士毕业证。
留信认证的作用:
1. 身份认证:留信认证可以证明你的留学经历是真实的,且你获得的学历或学位是正规且经过认证的。这对于一些用人单位来说,尤其是对留学经历有高度要求的公司(如跨国公司或国内高端公司),这是非常重要的一个凭证。
专业评定:留信认证不仅认证你的学位证书,还会对你的所学专业进行评定。这有助于展示你的学术背景,特别是对于国内公司而言,能够清楚了解你所学专业的水平和价值。
国家人才库入库:认证后,你的信息将被纳入国家人才库,并且可以在国家人才网等平台上展示,供包括500强公司等大型公司挑选和聘用人才。这对于回国找工作特别是进入大公司,具有非常积极的作用。
2. 留信认证对就业的好处
提高竞争力:通过留信认证,尤其是对你所学专业的认证,可以大大提高你在国内求职时的竞争力。许多公司对留学生背景和所学专业有很高的要求,认证后的信息能够帮助公司快速识别符合条件的候选人。
增强信任度:公司往往会对没有认证的学历背景产生疑虑,而留信认证为你的学历背景提供了第三方权威机构的背书,增强了雇主的信任。Local Rural Practices of the future. MWC



Local Rural Practices of the future. MWCJosep Vidal-Alaball
?
At #MWC2025, we presented "Local Rural Practices of the Future", a visionary project designed to enhance healthcare access in rural areas through telemedicine, AI, telemonitoring, and point-of-care (PoC) analysis. By integrating these digital health solutions, we aim to improve patient care, reduce unnecessary travel, and support healthcare professionals in remote settings.IgA Vasculitis (Henoch-Schonlein Purpura.pptx



IgA Vasculitis (Henoch-Schonlein Purpura.pptxAndulius Aswoyo
?
IgA Vasculitis (Henoch-Schonlein Purpura)Top 5 Sexologists in Delhi 2025 | Best Experts in Sexual Health



Top 5 Sexologists in Delhi 2025 | Best Experts in Sexual HealthPawan Kumar
?
Looking for the best sexologists in Delhi? Discover the top 5 experts in sexual health for 2025, specializing in erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation, low libido, and holistic treatments. Get expert guidance and personalized care today!
Choosing the Right NDIS Support Coordinator: Key Factors & Expert Tips.



Choosing the Right NDIS Support Coordinator: Key Factors & Expert Tips.Fitnall1
?
Finding the right NDIS support coordinator is essential for maximizing your plan and accessing the best services. This presentation outlines the key factors to consider, including experience, communication, independence, and local knowledge. Learn where to search, the critical questions to ask, and how to make the best choice for your needs.Tran Quoc Bao - Redefining Vietnam’s Healthcare Landscape with Visionary Lead...



Tran Quoc Bao - Redefining Vietnam’s Healthcare Landscape with Visionary Lead...Ignite Capital
?
In 2025, Tran Quoc Bao was honored as Best and Most Influential Hospital CEO in Vietnam by Hospital Insight Magazine, solidifying his place as one of the most transformative figures in the country’s healthcare sector. As CEO of Prima Saigon, Vietnam’s leading international daycare and ambulatory hospital, Bao has taken the institution to unprecedented heights, setting new standards for medical care and patient experience. Under his leadership, Prima Saigon has become a beacon of innovation and excellence in the Vietnamese healthcare space.
But Bao’s influence extends far beyond his role at Prima Saigon. He is also a key member of the Advisory Board for Asian Hospital & Healthcare Management, a prestigious platform shaping healthcare policy across Asia and globally. Through this role, Bao is influencing global healthcare trends and setting new benchmarks for medical care worldwide.
With nearly two decades of experience in healthcare and finance, Bao has held critical positions at leading institutions like City International Hospital, FV Hospital, TMMC Healthcare (Tam Tri Hospital Group), and Cao Tang Hospital. At Cao Tang, Bao led the hospital’s transformation into Vietnam’s first Joint Commission International (JCI)-accredited institution, a milestone that placed Vietnam firmly on the global healthcare map.
Bao’s remarkable career is further bolstered by his financial expertise. Holding multiple prestigious credentials, including CFA?, CMT?, CPWA?, FMVA?, and others, Bao has driven over $2 billion in healthcare mergers and acquisitions, reshaping Vietnam’s healthcare investment landscape. His ability to seamlessly integrate healthcare strategy with financial insight has made him a sought-after thought leader in the sector.
In addition to his professional accomplishments, Bao is a prolific writer, contributing over 20 articles to major publications like Forbes, Bloomberg, and Voice of America, where he shares his expertise on healthcare innovation and investment. His accolades include being named Healthcare Executive of the Year – Vietnam 2019, Medical Tourism Leader of the Year 2021, and receiving recognition as a “Doing Business 2022” Leader by the World Bank Group.
Bao's strategic insights are highly valued by top global consulting firms, including BCG, Bain, and McKinsey, where he advises on major healthcare investments and partnerships in Asia. Through his visionary leadership, Tran Quoc Bao is not just reshaping healthcare in Vietnam—he is setting the stage for the future of global healthcare.Hypertension outline Hypertension Definition, classification Prevalence Compl...



Hypertension outline Hypertension Definition, classification Prevalence Compl...ping618217
?
hypertensinsive agentsLIVER FUNCTION TEST CBME UG PRACTICLAS AND CHARTS.pptx



LIVER FUNCTION TEST CBME UG PRACTICLAS AND CHARTS.pptxManjula N
?
LIVER FUNCTION TEST CBME UG PRACTICLAS AND CHARTSDr. Sobia Ali PPT Feb-2025 (Sarcoidosis uveitis)



Dr. Sobia Ali PPT Feb-2025 (Sarcoidosis uveitis)Sobia Ali
?
This ppt is about a rare case of Granulomatous uveitis presented to us Tran Quoc Bao Makes History as the First Vietnamese Keynote Speaker at Insigh...



Tran Quoc Bao Makes History as the First Vietnamese Keynote Speaker at Insigh...Ignite Capital
?
Insight 2019: Tran Quoc Bao’s Groundbreaking Role in Vietnam’s Healthcare Revolution
At the 2019 Insight Symposium, hosted by the Malaysia Healthcare Tourism Council (MHTC), Tran Quoc Bao made history as the first Vietnamese keynote speaker. His presentation on “Untapped Opportunities of High-Quality Healthcare Demand in Vietnam” showcased the country’s emerging role as a leader in global healthcare, further solidifying his place as a visionary in the field.
As the Chief Planning and Marketing Officer of City International Hospital (CIH) in Ho Chi Minh City, Bao has been instrumental in transforming Vietnam into a global hub for medical tourism. Under his leadership, CIH has grown into a beacon of excellence in Asia’s healthcare landscape, frequently cited by top global media like Bloomberg, Travel & Leisure, and US News.
With a capacity of 320 beds and 21 medical specialties, CIH treats over 400,000 outpatients annually, 25% of whom come from abroad. This impressive reach is a testament to the hospital’s international reputation, which was further solidified when it became a preferred provider for the U.S. Embassy and Consulate in Vietnam.
Bao’s leadership is defined by a series of innovative initiatives. In 2018, he led a partnership with Philips to open a state-of-the-art diagnostic center, enhancing CIH’s diagnostic capabilities. He also oversaw the creation of the Satellite 115 Emergency Center, expanding the hospital’s ability to provide comprehensive interventional care.
Among Bao’s standout achievements is the CIH Stroke Center, one of only 15 such facilities in Ho Chi Minh City. This specialized center has positioned CIH as a leader in stroke care, attracting patients from across Vietnam and beyond.
Bao’s impact extends beyond the hospital. In 2019, he launched the Pharmacity-CIH Convenience Clinic, Southeast Asia’s first healthcare model of its kind. In collaboration with Pharmacity, Vietnam’s leading pharmacy chain, the clinic offers accessible and affordable healthcare, revolutionizing how medical services are delivered to the local population.
Furthermore, Bao’s global vision extended to sports when CIH became the official medical partner for the Immortal Triumph tournament by One Championship. This partnership highlighted CIH’s commitment to world-class emergency and specialized care, further elevating Vietnam’s healthcare profile on the international stage.
Tran Quoc Bao’s innovative leadership continues to shape the future of healthcare, positioning City International Hospital and Vietnam as rising stars in the global medical tourism market. Through his dedication and vision, Bao has not only elevated CIH but has placed Vietnam at the forefront of the healthcare revolution.Tran Quoc Bao Named Best and Most Influential Hospital CEO in Vietnam by Hosp...



Tran Quoc Bao Named Best and Most Influential Hospital CEO in Vietnam by Hosp...Ignite Capital
?
Tran Quoc Bao, named Best and Most Influential Hospital CEO in Vietnam 2025 by Hospital Insight Magazine, is transforming Vietnam’s healthcare landscape with his unique blend of medical expertise and financial acumen. As CEO of Prima Saigon, the country's leading international daycare and ambulatory hospital, Bao has turned the institution into a benchmark of excellence, setting new standards for innovation and patient care.
His leadership at Prima Saigon has propelled the hospital to the forefront of the Vietnamese healthcare sector, but Bao's impact goes beyond national borders. As a member of the Advisory Board for Asian Hospital & Healthcare Management, a prominent publication influencing global healthcare policy, he is helping to shape trends and set standards that extend across Asia and the world.
With nearly two decades of experience, Bao has held key positions at renowned institutions like City International Hospital, FV Hospital, TMMC Healthcare (Tam Tri Hospital Group), and Cao Tang Hospital, where he led the transformation into Vietnam’s first Joint Commission International (JCI)-accredited hospital. This milestone put Vietnam firmly on the global healthcare map, thanks to Bao’s visionary leadership.
His extensive expertise is matched by a distinguished financial background, holding elite credentials such as CFA?, CMT?, CPWA?, FMVA?, and others. Bao’s strategic approach has allowed him to lead $2 billion in healthcare M&A transactions, reshaping Vietnam’s healthcare investment landscape. His ability to blend healthcare with finance has earned him recognition as a thought leader in the field.
Bao has also contributed more than 20 articles to major outlets like Forbes, Bloomberg, and Voice of America, sharing his insights on healthcare innovation and investment. His accolades include being named Healthcare Executive of the Year – Vietnam 2019, Medical Tourism Leader of the Year 2021, and being honored as a “Doing Business 2022” Leader by the World Bank Group.
In addition, Bao's strategic expertise is sought by top global consulting firms like BCG, Bain, and McKinsey, advising on major healthcare investments and partnerships in Asia. With his visionary leadership, Tran Quoc Bao continues to drive the future of healthcare, both in Vietnam and globally.Food Microbiology, food poisoning and food born diseases notes
- 2. A Brief History ? Early Food Preservation ? 900 AD – “Food Poisoning” Recognized ? 1795-Appert Developed Canning ? 1854-1864-FOOD MICROBIOLOGY BECOMES A SCIENCE
- 3. Why Study Food Microbiology? ? Provide Clean, Safe, Healthful Food to Consumer ? Food Permits Growth ? Control of Microbial Growth ? Prevent Food Spoilage ? Prevent Food-borne Illnesses ? Food Preservation and Production
- 4. Food-Borne Illness ? Estimated burden of food – borne illnesses – $6.9 Billion/Year Cost of FBI ? CDC Estimates – 76 Million Cases of FBI Annually – 325,000 Hospitalizations – 5,000 Deaths
- 5. Common symptoms of food born illnesses ? Nausea ? Vomiting: ? Diarrhea: ? Abdominal cramps: ? Fever ? Headache ? Muscle aches ? Fatigue ? Dehydration ? Other symptoms: chills, weakness, dizziness, and in severe cases, organ damage or neurological symptoms
- 6. Agents of Disease (Foodbourne Pathogens) BACTERIA – E coli – Salmonella spp., – Vibrio cholera, – Bacillus cereus, – Clostridium botulinum, – Listeria monocytogenes, – Staphylococcus aureus VIRUSES – Enteroviruses, – Norwalk virus, – Hepatitis virus PROTOZOA – Giardia lamblia, – Cryptosporidium parvum, – Entamoeba histolyticum, – Cyclospora cayetanesis HELMINTHS – Tapeworms (Beef, Fish and Pork), – Flukes (Fish and Shellfish), – Roundworms and Hookworms
- 7. Public health impact of food born illnesses ? Healthcare Burden: ? Economic Costs: ? Morbidity and Mortality: ? Public Awareness and Concern: This can lead to avoiding certain foods or brands, and increased demand for food safety regulations and oversight. ? Social Disruption: closures of food establishments, ? Long-Term Health Impacts: foodborne bacteria can lead to reactive arthritis, kidney failure, or neurological disorders in susceptible individuals. ? Global Health Security: outbreaks (COVID 19) often crossing international borders through the global food supply chain.
- 8. What Organism Causes the Most Cases of Food-Borne Illness Annually? Campylobacter
- 9. What Organism Causes the Most Deaths Due to Food- Borne Illness? Salmonella
- 10. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Factors ? Intrinsic – pH – Moisture Content – Oxidation-reduction Potential – Nutrient Content – Antimicrobial Constituents – Biological Structures
- 11. pH ? Effects of pH – Enzymes – Nutrients ? Other Environmental Factors – Temperature – Salt – Age ? No known pathogen grows below pH of 4.6 – Clostridium botulinum
- 12. Moisture ? Remove and/or Bind Moisture – Humectants – Dehydration ? Water Activity – Aw ? Most Fresh Foods - Aw > 0.99 0 1 Pure water No water
- 13. Microbial Growth and Aw ? Halophilic 0.75 ? Xerophilic molds 0.61 ? Osmophilic yeasts0.61 ? Lowest Aw for Pathogen Growth – 0.86 – Stapholococcus aureus
- 14. Oxidation- Reduction Potential ? O/R Potential - Eh – “…ease with which the substrate loses or gains electrons.” ? Loss of electrons – oxidized ? Gain of electrons – reduced ? Aerobic ? Anaerobic ? Microaerobic ? Facultative anaerobes
- 15. Others ? Nutrients – Fastidius vs non-fastidious ? Biological Structure ? Antimicrobial Factors – Naturally occurring factors
- 16. Extrinsic Factors ? Temperature ? Relative Humidity ? Gases in the Environment ? Presence of Other Microorganisms
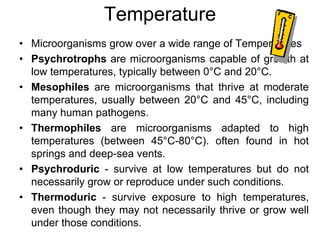
- 17. Temperature ? Microorganisms grow over a wide range of Temperatures ? Psychrotrophs are microorganisms capable of growth at low temperatures, typically between 0°C and 20°C. ? Mesophiles are microorganisms that thrive at moderate temperatures, usually between 20°C and 45°C, including many human pathogens. ? Thermophiles are microorganisms adapted to high temperatures (between 45°C-80°C). often found in hot springs and deep-sea vents. ? Psychroduric - survive at low temperatures but do not necessarily grow or reproduce under such conditions. ? Thermoduric - survive exposure to high temperatures, even though they may not necessarily thrive or grow well under those conditions.
- 18. Other Factors 1. Relative Humidity of Environment – Can change the Aw – Water activity (Aw) is a measure of the amount of water available for microbial growth and chemical reactions within a food product.
- 19. Environmental Gasses ? Oxygen: promotes aerobic microorganisms and spoilage by oxidation. ? Carbon Dioxide. elevated levels can inhibit the growth of aerobic spoilage organisms and slow down enzymatic reactions, However, excessive carbon dioxide levels can also lead to undesirable changes in texture, flavor, and appearance of food products. ? Nitrogen (N2): often used in modified atmosphere packaging to displace oxygen and create an anaerobic environment, which inhibits the growth of aerobic spoilage microorganisms and slows down oxidative reactions. ? Ethylene (C2H4): a natural plant hormone produced by some fruits and vegetables as they ripen. does not cause food spoilage, it can accelerate the ripening and senescence of certain fruits and vegetables, leading to faster deterioration and shorter shelf life if not controlled properly during storage and transportation. ? Sulfur Dioxide used as a preservative in dried fruits and wine to inhibit microbial growth and prevent oxidation. It can also have antimicrobial and antioxidant effects, helping to extend the shelf life of certain food products.
- 20. Presence of Other Microorganisms ? Competitive Exclusion: one species outcompetes another species for nutrients or space, leading to the suppression or elimination of the less competitive species. ? General Microbial Antagonism: inhibition or suppression of microbial growth by one microorganism against another; through production of antimicrobial compounds (bacteriocins), competition for nutrients or space, and alteration of environmental conditions. ? Lactic Acid Antagonism: inhibitory effect exerted by lactic acid bacteria (LAB) against other microorganisms. In fermented products such as yoghurt,
- 21. Other apllications of bacteria in food microbiology ? Microbes that we can exploit ? Bacteria—cheese, yogurt, vinegar, ? Yeasts—bread, beer, liqueurs, wine ? Molds—cheeses ? Bacteria in agriculture Rhizobium spp: ? Nitrogen fixation in root nodules of legumes ? Bacteria used in engineering produce that is resistant to adverse environmental conditions, pests pathogens and spoilage











