FUNCTIONS AND RELATION DOMAIN AND RANGE OF FUNCTIONS.pptx
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes7 views
N/A
1 of 18
Download to read offline


















Recommended
Domain and range (linear, quadratic, rational functions)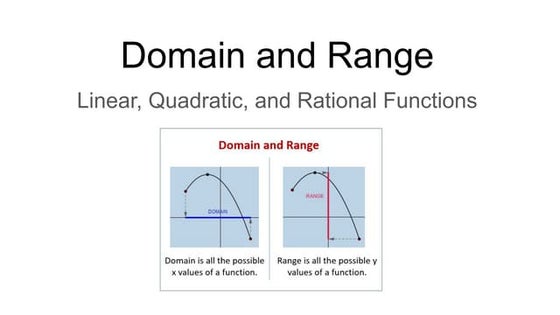



Domain and range (linear, quadratic, rational functions)Rose Mary Tania Arini
Ěý
This document discusses domain and range for different types of functions including linear, quadratic, rational, and irrational functions. It provides examples of finding the domain and range for various functions. The key points are:
- The domain of a function is the set of valid x-values, while the range is the set of y-values.
- For linear, quadratic, and irrational functions, the domain is typically all real numbers, while the range depends on the specific function.
- For rational functions, the domain excludes values that make the denominator equal to zero, while the range typically includes all real numbers.General_Mathematics_Chapter_1_(Part1)_Lesson_1.1_Representation_of_Functions....



General_Mathematics_Chapter_1_(Part1)_Lesson_1.1_Representation_of_Functions....ErickoAlegria2
Ěý
Representation of functionsModule 2 topic 1 notes



Module 2 topic 1 noteschrystal_brinson
Ěý
The document reviews key concepts about functions including domain, range, and evaluating functions. It provides examples of determining if a relation is a function using mapping diagrams and the vertical line test. It also gives examples of finding the domain and range of functions from graphs and equations. Practice problems are included for students to determine domains, ranges, and evaluate functions.2.3 Functions



2.3 Functionssmiller5
Ěý
This document defines and discusses functions. It begins by defining a relation and function, noting that a function is a special type of relation where each input is mapped to exactly one output. It introduces function notation and discusses the domain, codomain, and range of a function. Examples are provided to illustrate determining if a relation defines a function. The document also covers identifying functions from equations or graphs, and the vertical line test. It concludes with a discussion of function notation and classwork assignments.Lesson 2 - Functions and their Graphs - NOTES.ppt



Lesson 2 - Functions and their Graphs - NOTES.pptJaysonMagalong
Ěý
The document provides lesson material on functions and their graphs. It includes sections on defining functions, determining if a relation is a function, functional notation, domain and range, graphing functions, and identifying intervals of increase/decrease. Additional topics covered are relative min/max values, step functions, even and odd functions, and piecewise-defined functions. Examples and exercises are provided to illustrate key concepts.5_domainandRange.ppt



5_domainandRange.pptElmabethDelaCruz1
Ěý
The document discusses key concepts related to functions such as domain, range, input and output values. It provides examples of determining the domain and range of functions based on algebraic rules. The domain of a function is the set of all possible input values, while the range is the set of all possible output values. The domain and range may be all real numbers or limited depending on the specific function.MODULE 2 (Evaluating Functions and Word Problems).pptx



MODULE 2 (Evaluating Functions and Word Problems).pptxjunjunaguatani
Ěý
This presentation contains the idea on how to evaluate functions and it provides different word problems that apply the idea about evaluation of functions.Real meaning of functions



Real meaning of functionsTarun Gehlot
Ěý
The document provides examples and definitions of various types of functions to illustrate to beginning students that functions can take many forms beyond polynomial equations. It defines linear, quadratic, and polynomial functions precisely and provides examples of each. It also introduces other types of functions like absolute value, sequences, Tau, Sigma, the Fibonacci sequence, and arithmetic sequences. The overall purpose is to demonstrate the diversity of functions and convince students that the domain and rule of a function need not be numbers or equations.Precalc 8.19.13



Precalc 8.19.13Ron Eick
Ěý
The document contains information about functions including definitions, examples of graphs, the vertical line test to determine if a relation is a function, examples of finding the domain of functions from equations, and practice problems determining the domain of various functions. Vocabulary terms defined include function, domain, and range. Functions are described as rules that assign each input to exactly one output, usually through an equation.Functions-.pdf



Functions-.pdfarvdexamsection
Ěý
This document discusses functions in Python. It defines functions as collections of statements that perform specific tasks. There are three types of functions: built-in functions, module functions, and user-defined functions. Built-in functions are predefined in Python, module functions are contained in .py files, and user-defined functions are created by the user. The document provides examples of various types of functions and how they can be called and used.General Mathematics - Representation and Types of Functions



General Mathematics - Representation and Types of FunctionsJuan Miguel Palero
Ěý
It is a powerpoint presentation that will help the students to enrich their knowledge about Senior High School subject of General Mathematics. It is comprised about the representation, definition, and types of functions. Inverse trig functions



Inverse trig functionsJessica Garcia
Ěý
The document discusses inverse trigonometric functions and how to define their inverses by restricting the domains of the trig functions. It explains that the sine function's inverse is defined on [-1,1] and the cosine function's inverse is defined on [0,π]. Similarly, the tangent function's inverse is defined on (-π/2, π/2). Graphs and examples of the inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions are provided.Relations and Functions, Dependent and Independent Variables.pptx



Relations and Functions, Dependent and Independent Variables.pptxJayPaulEscarpe
Ěý
1) A relation is represented by a set of ordered pairs and can also be represented in other ways like a table, mapping diagram, graph, or rule.
2) A function is a special type of relation where each element in the domain is mapped to exactly one element in the range.
3) Key aspects of relations and functions include their domain, range, and whether the correspondence is one-to-one, many-to-one, or one-to-many.What is analytic functions



What is analytic functionsTarun Gehlot
Ěý
Any analytic function is locally represented by a convergent power series and is infinitely differentiable. Real analytic functions are defined on an open set of the real line, while complex analytic functions are defined on an open set of the complex plane. Both are infinitely differentiable, but complex analytic functions have additional properties like Liouville's theorem stating bounded complex analytic functions defined on the whole complex plane are constant. Real analytic functions do not have this property and their power series need only converge locally rather than on the entire domain.function



functionsom allul
Ěý
1) Functions relate inputs to outputs through ordered pairs where each input maps to exactly one output. The domain is the set of inputs and the range is the set of outputs.
2) There are different types of functions including linear, quadratic, and composition functions. A linear function's graph is a straight line while a quadratic function's graph is a parabola.
3) Composition functions combine other functions where the output of one becomes the input of another. Together functions provide a powerful modeling tool used across many fields including medicine.Lecture 01-2 (Functions).pptx



Lecture 01-2 (Functions).pptxÅįjâž Ali
Ěý
This document provides information about an Applied Calculus course taught by Imran Qasim at Mehran University of Engineering and Technology. The key points are:
1) The course covers topics in differential and integral calculus, including functions, limits, derivatives, integrals, and their applications.
2) Students are expected to have prior knowledge of functions, limits, and differentiation before taking the course.
3) The course contents will help students develop expertise in techniques for differentiation and integration, as well as apply calculus to solve real-world problems.Presentation1



Presentation1Eko Adi
Ěý
The document defines key concepts relating to functions and relations:
- A relation is a set of ordered pairs where the domain is the set of all x-values and the range is the set of all y-values.
- A function is a special type of relation where each x-value is assigned to exactly one y-value.
- Function notation uses f(x) to represent the output of a function f when the input is x.
- The domain of a function is the set of all valid input values that do not result in undefined outputs like division by zero or square roots of negative numbers.Different-Types-ofgfgfgfgfgfgg-Functions.pptx



Different-Types-ofgfgfgfgfgfgg-Functions.pptxdominicdaltoncaling2
Ěý
gfffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffdfsfwegergS1 0 derivadas



S1 0 derivadasjesquerrev1
Ěý
The document discusses the definition of the derivative and the four-step rule for calculating derivatives. It defines the derivative as the slope of the tangent line to a function's graph at a given point and as the limit of the difference quotient. The four-step rule involves adding an increment to x and y in a function, isolating the change in y, dividing by the change in x, and taking the limit as the change in x approaches zero. The objective is to understand the concept of the derivative from its geometric interpretation and apply formulas to calculate derivatives of algebraic and transcendental functions.Advanced functions part i



Advanced functions part iwendyvazzy
Ěý
This document provides an overview of advanced functions including power functions and characteristics of polynomial functions. Power functions are functions of the form f(x)=xa where a is a fixed number. Polynomial functions have characteristics like reflection, number of x-intercepts, end behavior, and number of maximum/minimum points that depend on whether the degree is odd or even. Finite differences can be used to determine the degree of a polynomial function from its table of values.Function and graphs



Function and graphsRione Drevale
Ěý
This document discusses functions and graphs. It begins by introducing the concept of a function and how functions are used to model real-world phenomena by relating one quantity to another. Examples are given such as relating distance fallen to time for a falling object. The document then discusses different types of functions like quadratic, polynomial, and rational functions. It provides guidelines for graphing these different function types by identifying intercepts, end behavior, maxima/minima, and asymptotes. The document also covers combining functions through composition and finding inverse functions. It concludes by discussing using functions to model real-world scenarios like relating crop yield to rainfall or fish length to age.Function.pptx



Function.pptxahsanalmani2
Ěý
This document discusses sets, functions, and their properties. It defines a function as a relation where each element of the domain is mapped to exactly one element of the codomain. It describes the domain as the set of inputs, codomain as the set of possible outputs, and range as the set of actual outputs. The document provides examples of one-to-one, onto, and bijective functions and discusses their properties. It also gives examples of applications of functions in areas like ATM cards, money over time, and temperature.How to attach file using upload button Odoo 18



How to attach file using upload button Odoo 18Celine George
Ěý
In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to attach file using upload button Odoo 18. Odoo features a dedicated model, 'ir.attachments,' designed for storing attachments submitted by end users. We can see the process of utilizing the 'ir.attachments' model to enable file uploads through web forms in this slide.More Related Content
Similar to FUNCTIONS AND RELATION DOMAIN AND RANGE OF FUNCTIONS.pptx (20)
2.3 Functions



2.3 Functionssmiller5
Ěý
This document defines and discusses functions. It begins by defining a relation and function, noting that a function is a special type of relation where each input is mapped to exactly one output. It introduces function notation and discusses the domain, codomain, and range of a function. Examples are provided to illustrate determining if a relation defines a function. The document also covers identifying functions from equations or graphs, and the vertical line test. It concludes with a discussion of function notation and classwork assignments.Lesson 2 - Functions and their Graphs - NOTES.ppt



Lesson 2 - Functions and their Graphs - NOTES.pptJaysonMagalong
Ěý
The document provides lesson material on functions and their graphs. It includes sections on defining functions, determining if a relation is a function, functional notation, domain and range, graphing functions, and identifying intervals of increase/decrease. Additional topics covered are relative min/max values, step functions, even and odd functions, and piecewise-defined functions. Examples and exercises are provided to illustrate key concepts.5_domainandRange.ppt



5_domainandRange.pptElmabethDelaCruz1
Ěý
The document discusses key concepts related to functions such as domain, range, input and output values. It provides examples of determining the domain and range of functions based on algebraic rules. The domain of a function is the set of all possible input values, while the range is the set of all possible output values. The domain and range may be all real numbers or limited depending on the specific function.MODULE 2 (Evaluating Functions and Word Problems).pptx



MODULE 2 (Evaluating Functions and Word Problems).pptxjunjunaguatani
Ěý
This presentation contains the idea on how to evaluate functions and it provides different word problems that apply the idea about evaluation of functions.Real meaning of functions



Real meaning of functionsTarun Gehlot
Ěý
The document provides examples and definitions of various types of functions to illustrate to beginning students that functions can take many forms beyond polynomial equations. It defines linear, quadratic, and polynomial functions precisely and provides examples of each. It also introduces other types of functions like absolute value, sequences, Tau, Sigma, the Fibonacci sequence, and arithmetic sequences. The overall purpose is to demonstrate the diversity of functions and convince students that the domain and rule of a function need not be numbers or equations.Precalc 8.19.13



Precalc 8.19.13Ron Eick
Ěý
The document contains information about functions including definitions, examples of graphs, the vertical line test to determine if a relation is a function, examples of finding the domain of functions from equations, and practice problems determining the domain of various functions. Vocabulary terms defined include function, domain, and range. Functions are described as rules that assign each input to exactly one output, usually through an equation.Functions-.pdf



Functions-.pdfarvdexamsection
Ěý
This document discusses functions in Python. It defines functions as collections of statements that perform specific tasks. There are three types of functions: built-in functions, module functions, and user-defined functions. Built-in functions are predefined in Python, module functions are contained in .py files, and user-defined functions are created by the user. The document provides examples of various types of functions and how they can be called and used.General Mathematics - Representation and Types of Functions



General Mathematics - Representation and Types of FunctionsJuan Miguel Palero
Ěý
It is a powerpoint presentation that will help the students to enrich their knowledge about Senior High School subject of General Mathematics. It is comprised about the representation, definition, and types of functions. Inverse trig functions



Inverse trig functionsJessica Garcia
Ěý
The document discusses inverse trigonometric functions and how to define their inverses by restricting the domains of the trig functions. It explains that the sine function's inverse is defined on [-1,1] and the cosine function's inverse is defined on [0,π]. Similarly, the tangent function's inverse is defined on (-π/2, π/2). Graphs and examples of the inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions are provided.Relations and Functions, Dependent and Independent Variables.pptx



Relations and Functions, Dependent and Independent Variables.pptxJayPaulEscarpe
Ěý
1) A relation is represented by a set of ordered pairs and can also be represented in other ways like a table, mapping diagram, graph, or rule.
2) A function is a special type of relation where each element in the domain is mapped to exactly one element in the range.
3) Key aspects of relations and functions include their domain, range, and whether the correspondence is one-to-one, many-to-one, or one-to-many.What is analytic functions



What is analytic functionsTarun Gehlot
Ěý
Any analytic function is locally represented by a convergent power series and is infinitely differentiable. Real analytic functions are defined on an open set of the real line, while complex analytic functions are defined on an open set of the complex plane. Both are infinitely differentiable, but complex analytic functions have additional properties like Liouville's theorem stating bounded complex analytic functions defined on the whole complex plane are constant. Real analytic functions do not have this property and their power series need only converge locally rather than on the entire domain.function



functionsom allul
Ěý
1) Functions relate inputs to outputs through ordered pairs where each input maps to exactly one output. The domain is the set of inputs and the range is the set of outputs.
2) There are different types of functions including linear, quadratic, and composition functions. A linear function's graph is a straight line while a quadratic function's graph is a parabola.
3) Composition functions combine other functions where the output of one becomes the input of another. Together functions provide a powerful modeling tool used across many fields including medicine.Lecture 01-2 (Functions).pptx



Lecture 01-2 (Functions).pptxÅįjâž Ali
Ěý
This document provides information about an Applied Calculus course taught by Imran Qasim at Mehran University of Engineering and Technology. The key points are:
1) The course covers topics in differential and integral calculus, including functions, limits, derivatives, integrals, and their applications.
2) Students are expected to have prior knowledge of functions, limits, and differentiation before taking the course.
3) The course contents will help students develop expertise in techniques for differentiation and integration, as well as apply calculus to solve real-world problems.Presentation1



Presentation1Eko Adi
Ěý
The document defines key concepts relating to functions and relations:
- A relation is a set of ordered pairs where the domain is the set of all x-values and the range is the set of all y-values.
- A function is a special type of relation where each x-value is assigned to exactly one y-value.
- Function notation uses f(x) to represent the output of a function f when the input is x.
- The domain of a function is the set of all valid input values that do not result in undefined outputs like division by zero or square roots of negative numbers.Different-Types-ofgfgfgfgfgfgg-Functions.pptx



Different-Types-ofgfgfgfgfgfgg-Functions.pptxdominicdaltoncaling2
Ěý
gfffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffdfsfwegergS1 0 derivadas



S1 0 derivadasjesquerrev1
Ěý
The document discusses the definition of the derivative and the four-step rule for calculating derivatives. It defines the derivative as the slope of the tangent line to a function's graph at a given point and as the limit of the difference quotient. The four-step rule involves adding an increment to x and y in a function, isolating the change in y, dividing by the change in x, and taking the limit as the change in x approaches zero. The objective is to understand the concept of the derivative from its geometric interpretation and apply formulas to calculate derivatives of algebraic and transcendental functions.Advanced functions part i



Advanced functions part iwendyvazzy
Ěý
This document provides an overview of advanced functions including power functions and characteristics of polynomial functions. Power functions are functions of the form f(x)=xa where a is a fixed number. Polynomial functions have characteristics like reflection, number of x-intercepts, end behavior, and number of maximum/minimum points that depend on whether the degree is odd or even. Finite differences can be used to determine the degree of a polynomial function from its table of values.Function and graphs



Function and graphsRione Drevale
Ěý
This document discusses functions and graphs. It begins by introducing the concept of a function and how functions are used to model real-world phenomena by relating one quantity to another. Examples are given such as relating distance fallen to time for a falling object. The document then discusses different types of functions like quadratic, polynomial, and rational functions. It provides guidelines for graphing these different function types by identifying intercepts, end behavior, maxima/minima, and asymptotes. The document also covers combining functions through composition and finding inverse functions. It concludes by discussing using functions to model real-world scenarios like relating crop yield to rainfall or fish length to age.Function.pptx



Function.pptxahsanalmani2
Ěý
This document discusses sets, functions, and their properties. It defines a function as a relation where each element of the domain is mapped to exactly one element of the codomain. It describes the domain as the set of inputs, codomain as the set of possible outputs, and range as the set of actual outputs. The document provides examples of one-to-one, onto, and bijective functions and discusses their properties. It also gives examples of applications of functions in areas like ATM cards, money over time, and temperature.Recently uploaded (20)
How to attach file using upload button Odoo 18



How to attach file using upload button Odoo 18Celine George
Ěý
In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to attach file using upload button Odoo 18. Odoo features a dedicated model, 'ir.attachments,' designed for storing attachments submitted by end users. We can see the process of utilizing the 'ir.attachments' model to enable file uploads through web forms in this slide.FESTIVAL: SINULOG & THINGYAN-LESSON 4.pptx



FESTIVAL: SINULOG & THINGYAN-LESSON 4.pptxDanmarieMuli1
Ěý
Sinulog Festival of Cebu City, and Thingyan Festival of Myanmar.TLE 7 - 3rd Topic - Hand Tools, Power Tools, Instruments, and Equipment Used ...



TLE 7 - 3rd Topic - Hand Tools, Power Tools, Instruments, and Equipment Used ...RizaBedayo
Ěý
Hand Tools, Power Tools, and Equipment in Industrial ArtsHow to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo şÝşÝߣs



How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo şÝşÝߣsCeline George
Ěý
Integrate WhatsApp into Odoo using the WhatsApp Business API or third-party modules to enhance communication. This integration enables automated messaging and customer interaction management within Odoo 17.Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding || Boby Basnet



Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding || Boby BasnetBoby Basnet
Ěý
Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding Full Note
|| Assistant Professor Boby Basnet ||IAAS || AFU || PU || FUA PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...



A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...Beena E S
Ěý
A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by Aaron ShepardThe Story Behind the Abney Park Restoration Project by Tom Walker



The Story Behind the Abney Park Restoration Project by Tom WalkerHistory of Stoke Newington
Ěý
Presented at the 24th Stoke Newington History Talks event on 27th Feb 2025
https://stokenewingtonhistory.com/stoke-newington-history-talks/How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 Employee



How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 EmployeeCeline George
Ěý
In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to configure flexible working schedule in Odoo 18 Employee module. In Odoo 18, the Employee module offers powerful tools to configure and manage flexible working schedules tailored to your organization's needs.Research & Research Methods: Basic Concepts and Types.pptx



Research & Research Methods: Basic Concepts and Types.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
Ěý
This ppt has been made for the students pursuing PG in social science and humanities like M.Ed., M.A. (Education), Ph.D. Scholars. It will be also beneficial for the teachers and other faculty members interested in research and teaching research concepts.Digital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptx



Digital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
Ěý
This ppt is useful for not only for B.Ed., M.Ed., M.A. (Education) or any other PG level students or Ph.D. scholars but also for the school, college and university teachers who are interested to prepare an e-content with AI for their students and others.Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
Finals of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
Prelims of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. Essentials of a Good PMO, presented by Aalok Sonawala



Essentials of a Good PMO, presented by Aalok SonawalaAssociation for Project Management
Ěý
APM event hosted by the South Wales and West of England Network (SWWE Network)
Speaker: Aalok Sonawala
The SWWE Regional Network were very pleased to welcome Aalok Sonawala, Head of PMO, National Programmes, Rider Levett Bucknall on 26 February, to BAWA for our first face to face event of 2025. Aalok is a member of APM’s Thames Valley Regional Network and also speaks to members of APM’s PMO Interest Network, which aims to facilitate collaboration and learning, offer unbiased advice and guidance.
Tonight, Aalok planned to discuss the importance of a PMO within project-based organisations, the different types of PMO and their key elements, PMO governance and centres of excellence.
PMO’s within an organisation can be centralised, hub and spoke with a central PMO with satellite PMOs globally, or embedded within projects. The appropriate structure will be determined by the specific business needs of the organisation. The PMO sits above PM delivery and the supply chain delivery teams.
For further information about the event please click here.Eng7-Q4-Lesson 1 Part 1 Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and T...



Eng7-Q4-Lesson 1 Part 1 Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and T...sandynavergas1
Ěý
Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and Technical TermsSouth Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...



South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...History of Stoke Newington
Ěý
Presented at the 24th Stoke Newington History Talks event on 27th Feb 2025
https://stokenewingtonhistory.com/stoke-newington-history-talks/How to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo şÝşÝߣs



How to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo şÝşÝߣsCeline George
Ěý
In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18. In Odoo, Init Hooks are essential functions specified as strings in the __init__ file of a module.Computer Application in Business (commerce)



Computer Application in Business (commerce)Sudar Sudar
Ěý
The main objectives
1. To introduce the concept of computer and its various parts. 2. To explain the concept of data base management system and Management information system.
3. To provide insight about networking and basics of internet
Recall various terms of computer and its part
Understand the meaning of software, operating system, programming language and its features
Comparing Data Vs Information and its management system Understanding about various concepts of management information system
Explain about networking and elements based on internet
1. Recall the various concepts relating to computer and its various parts
2 Understand the meaning of software’s, operating system etc
3 Understanding the meaning and utility of database management system
4 Evaluate the various aspects of management information system
5 Generating more ideas regarding the use of internet for business purpose Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...



South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...History of Stoke Newington
Ěý
FUNCTIONS AND RELATION DOMAIN AND RANGE OF FUNCTIONS.pptx
- 1. Domain and Range of Functions
- 2. ď‚· When do we say that a function is linear, quadratic, polynomial, rational, or radical? ď‚· How can you find the domain and range of a function?
- 3. Domain of a function the set of all values of the independent variable that have corresponding values of the dependent variable 1 Example: Consider the function . The domain of is the set containing all the first coordinates.
- 4. Range of a function the set of all values of that can be obtained from the possible values of 2 Example: Consider the function . The range of is the set containing all the second coordinates.
- 5. Linear function a function that has a degree of 1 and whose graph is a straight line; the domain and range of a linear function are both the set of real numbers 3 Example: The functions and are linear functions.
- 6. Quadratic function a function that has a degree of 2 and whose graph is a parabola; the domain of a quadratic function is the set of real numbers 4 Example: The functions and are quadratic functions.
- 7. Polynomial function a function involving nonnegative integer powers of the independent variable; the domain of a polynomial function is the set of real numbers; the range of a polynomial function whose degree is odd is the set of real numbers 5 Example: The functions and are polynomial functions. Constant, linear, and quadratic functions are also polynomial functions.
- 8. Rational function a function that can be expressed as a ratio of two polynomials; the domain of a rational function is the set of real numbers except the zeros of its denominator 6 Example: The functions and are rational functions. The domain of is the set of real numbers except . The domain of is the set of real numbers except .
- 9. Radical function a function that contains radical expressions; the domain of a radical function is the set of real numbers except those that make the radicand of radicals with even index negative 7 Example: The functions and are radical functions. What do you think are the domain of and the domain of ?
- 10. Example 1: Find the domain and range of the function .
- 11. Answer: The function is a linear function. The domain and range of a linear function are both the set of the real numbers. Therefore, the domain of the function is and its range is also . Example 1: Find the domain and range of the function .
- 12. Example 2: Find the domain and range of .
- 13. Solution: For a square root function to be defined, the radicand must be nonnegative (i.e. greater than or equal to zero). Example 2: Find the domain and range of . Therefore, the domain of is and its range is since the principal square root a number is always nonnegative.
- 14. Individual Practice: 1. What is the domain and range of . 2. Find the domain and range of using its graph.
- 15. Group Practice: To be done by 2-5 groups A ball is thrown upward with an initial velocity of 32 ft/s from a height of 10 ft. The height at any given time is given by What is the domain and range of this function?
- 16. Domain of a function the set of all values of the independent variable that have corresponding values of the dependent variable 1 Range of a function the set of all values of that can be obtained from the possible values of 2 Linear function a function that has a degree of 1 and whose graph is a straight line; the domain and range of a linear function are both the set of real numbers 3
- 17. Quadratic function a function that has a degree of 2 and whose graph is a parabola; the domain of a quadratic function is the set of real numbers 4 Polynomial function a function involving nonnegative integer powers of the independent variable; the domain of a polynomial function is the set of real numbers; the range of a polynomial function whose degree is odd is the set of real numbers 5 Rational function a function that can be expressed as a ratio of two polynomials; the domain of a rational function is the set of real numbers except the zeros of its denominator 6
- 18. Radical function a function that contains radical expressions; the domain of a radical function is the set of real numbers except those that make the radicand of radicals with even index negative 7








