G4 PROBABLITY.pptx
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes31 views
The document discusses probability distributions and their applications in engineering. It defines probability distributions as mathematical functions that describe the likelihood of different outcomes in random events. There are two main types: discrete distributions which model events with a finite number of outcomes, and continuous distributions which model events with an infinite number of possible outcomes. The normal distribution, which follows a bell curve, is commonly used as it models many real-world phenomena. The document provides examples of using Python to plot a normal distribution and calculate probabilities based on the normal curve.
1 of 21
Download to read offline





![CALCULATING PROBABILITY:
A] X<4.5 B] 4.5Ī▄ X Ī▄6.5 C] X>6.5
*CODE:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/g4probablity-230404194313-2dea9938/85/G4-PROBABLITY-pptx-8-320.jpg)











Recommended
template.pptx



template.pptxuzmasulthana3
?
- Univariate normal distribution describes the distribution of a single random variable and is characterized by its bell-shaped curve. The mean, median, and mode are equal and located at the center. Approximately 68% of the data falls within one standard deviation of the mean.
- Multivariate normal distribution describes the joint distribution of multiple random variables. It generalizes the univariate normal distribution to multiple dimensions. The variables have a consistent relationship that can be modeled as a covariance matrix.
- Examples of data that may follow a normal distribution include heights, test scores, measurement errors, and stock price changes over time. Normal distributions are widely used in statisticsSTSTISTICS AND PROBABILITY THEORY .pptx



STSTISTICS AND PROBABILITY THEORY .pptxVenuKumar65
?
The document discusses key concepts in probability theory including probability, random experiments, sample spaces, events, random variables, probability distributions, and Bayes' theorem. It covers the binomial, Poisson, and normal distributions and their characteristics and applications. Decision theory is introduced as analyzing choices under uncertainty involving defining problems, identifying outcomes, assessing criteria, and evaluating alternatives to make optimal decisions.Lecture 4 - probability distributions (2).pptx



Lecture 4 - probability distributions (2).pptxSinimol Aniyankunju
?
The document discusses probability distributions and statistical analysis. It introduces key concepts like the binomial distribution, normal distribution, and standard normal distribution. It explains how probability distributions can model expected outcomes from random processes and how they are used to determine if observed data aligns with or differs from expectations through statistical analysis. Examples are provided for calculating probabilities and areas under curves for the binomial and normal distributions.Sampling distribution by Dr. Ruchi Jain



Sampling distribution by Dr. Ruchi JainRuchiJainRuchiJain
?
This document discusses different types of frequency distributions including theoretical, empirical, binomial, Poisson, and normal distributions. It provides details on the key characteristics of each distribution such as their assumptions, formulas, and appropriate uses. The normal distribution is described as the most useful theoretical distribution for continuous variables and an approximation of the binomial distribution for large sample sizes. Properties of the normal distribution include being bell-shaped and symmetrical with the mean, median, and mode all equal.Quantitative Methods for Management_MBA_Bharathiar University probability dis...



Quantitative Methods for Management_MBA_Bharathiar University probability dis...Victor Seelan
?
unit 3 probability distribution
Probability ©C definitions ©C addition and multiplication Rules (only statements) ©C simple business application problems ©C probability distribution ©C expected value concept ©C theoretical probability distributions ©C Binomial, Poison and Normal ©C Simple problems applied to business.Probability introduction for non-math people



Probability introduction for non-math peopleGuangYang92
?
Probability distributions describe the likelihood of different outcomes and how that likelihood may change based on various factors. Understanding basic probability concepts such as events, outcomes, and how to calculate probabilities is important for interpreting machine learning results, even without advanced math knowledge. Common probability distributions include the binomial, normal, and exponential distributions. The appropriate distribution depends on factors like whether outcomes are continuous or discrete, and whether trials are independent or related.COM 201_Inferential Statistics_18032022.pptx



COM 201_Inferential Statistics_18032022.pptxAkinsolaAyomidotun
?
This document provides an introduction to inferential statistics. It defines key terms like probability, random variables, and probability distributions such as the normal distribution. It discusses how inferential statistics can be used to make generalizations about populations based on samples. Hypothesis testing is introduced as a core technique in inferential statistics for testing proposed relationships. Concepts discussed in more depth include the normal distribution, parameters like the mean and standard deviation, sampling error, confidence intervals, and significance levels.Discrete and continuous probability models



Discrete and continuous probability modelsAkshay Kumar Mishra
?
This document discusses different types of probability distributions used in statistics. There are two main types: continuous and discrete distributions. Continuous distributions are used when variables are measured on a continuous scale, while discrete distributions are used when variables can only take certain values. Some important continuous distributions mentioned are the normal, lognormal, and exponential distributions. Important discrete distributions include the binomial, hypergeometric, and Poisson distributions. Key terms like mean, variance, and standard deviation are also defined. Examples are provided to illustrate how these probability distributions are applied in fields like quality control and reliability engineering.Discrete distributions: Binomial, Poisson & Hypergeometric distributions



Discrete distributions: Binomial, Poisson & Hypergeometric distributionsScholarsPoint1
?
The PPT covered the distinguish between discrete and continuous distribution. Detailed explanation of the types of discrete distributions such as binomial distribution, Poisson distribution & Hyper-geometric distribution.Probability distribution 10



Probability distribution 10Sundar B N
?
Most important distribution like Poisson Distribution, Normal Distribution and Binomial Distribution is addressedPA_EPGDM_2_2023.pptx



PA_EPGDM_2_2023.pptxsomenathtiwary
?
This document outlines the syllabus for a course titled "Predictive Analytics" taught by K. Mohanasundaram. The syllabus covers topics such as introduction to business analytics, mathematical modelling, data prediction techniques, regression analysis methods like simple linear regression, logistic regression, and forecasting techniques. It recommends textbooks and references for the course and provides an introduction to concepts like uncertainty modelling using probability distributions and random variables.Different types of distributions



Different types of distributionsRajaKrishnan M
?
This document provides an introduction to probability theory and different probability distributions. It begins with defining probability as a quantitative measure of the likelihood of events occurring. It then covers fundamental probability concepts like mutually exclusive events, additive and multiplicative laws of probability, and independent events. The document also introduces random variables and common probability distributions like the binomial, Poisson, and normal distributions. It provides examples of how each distribution is used and concludes with characteristics of the normal distribution.Probability, Discrete Probability, Normal Probabilty



Probability, Discrete Probability, Normal ProbabiltyFaisal Hussain
?
This document provides an overview of probability and probability distributions. It defines probability as the chances of an event occurring among possible outcomes. It discusses discrete and continuous random variables, and how discrete probability distributions list each possible value and its probability, with the probabilities summing to 1. Normal distributions are introduced as the most important continuous probability distribution, with a bell-shaped, symmetric curve defined by a mean and approaching but not touching the x-axis. Examples are given of constructing discrete probability distributions from frequency data.Inorganic CHEMISTRY



Inorganic CHEMISTRYSaikumar raja
?
This document provides an outline and summaries of topics related to error analysis:
- It outlines topics including binomial distribution, Poisson distribution, normal distribution, confidence interval, and least squares analysis.
- The binomial distribution section provides an example of calculating the probability of getting 2 and 3 heads out of 6 coin tosses.
- The normal distribution section explains how to calculate the probability of scoring between 90-110 on an IQ test with a mean of 100 and standard deviation of 10.
- The confidence interval section provides an example of calculating the 95% confidence interval for the population mean boiling temperature based on 6 sample measurements.Module-2_Notes-with-Example for data science



Module-2_Notes-with-Example for data sciencepujashri1975
?
The document discusses several key concepts in probability and statistics:
- Conditional probability is the probability of one event occurring given that another event has already occurred.
- The binomial distribution models the probability of success in a fixed number of binary experiments. It applies when there are a fixed number of trials, two possible outcomes, and the same probability of success on each trial.
- The normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution that is symmetric and bell-shaped. It is characterized by its mean and standard deviation. Many real-world variables approximate a normal distribution.
- Other concepts discussed include range, interquartile range, variance, and standard deviation. The interquartile range describes the spread of a dataset's middle 50%RM



RMEvanNathan3
?
This document discusses different types of theoretical frequency distributions including binomial, Poisson, and normal distributions. It provides definitions and characteristics for each distribution. The binomial distribution requires a fixed number of trials with the same probability of success for each trial. The Poisson distribution is used when the probability of an event is very small but the number of trials is large. The normal distribution results from an infinite binomial expansion and is a continuous, bell-shaped distribution.Discreet and continuous probability



Discreet and continuous probabilitynj1992
?
The document discusses discrete and continuous probability distributions, explaining that a discrete distribution applies to variables that can take on countable values while a continuous distribution is used for variables that can take any value within a range. It provides examples of discrete variables like coin flips and continuous variables like weights. The document also outlines the differences between discrete and continuous probability distributions in how they are represented and calculated. Approaches to Probability Bayes' Theorem Binominal Distribution Poisson Dist...



Approaches to Probability Bayes' Theorem Binominal Distribution Poisson Dist...Sundar B N
?
Basic Concepts of Probability
Approaches to Probability
Bayes' Theorem
Binominal Distribution
Poisson Distribution
Normal DistributionTheory of probability and probability distribution



Theory of probability and probability distributionpolscjp
?
Probability refers to the likelihood of an event occurring. It can be expressed as a fraction between 0 and 1, with the total number of possible outcomes as the denominator and number of favorable outcomes as the numerator. A random variable is a value that can vary in an experiment but whose outcome is uncertain before the experiment. Probability distributions specify the probabilities of random variables taking on particular values. There are discrete and continuous probability distributions. Important discrete distributions include binomial and Poisson, while the normal distribution is the most important continuous distribution.Probability Distributions 



Probability Distributions Anthony J. Evans
?
?This presentation forms part of a free, online course on analytics
http://econ.anthonyjevans.com/courses/analytics/Presentation_advance_1n.pptx



Presentation_advance_1n.pptxsharonmarishkawilfre
?
This document provides an introduction to uncertainty in measurements. It discusses types of uncertainties including type A and type B uncertainties, standard uncertainty, confidence intervals, and expanded uncertainty. It explains key concepts such as degrees of freedom, standard deviation, standard error, t-distributions, and how to calculate confidence intervals and combined uncertainties. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to evaluate uncertainties and calculate best estimates, standard uncertainties, coverage factors, and confidence intervals for measurements.ststs nw.pptx



ststs nw.pptxMrymNb
?
Statistical concepts and their applications in various fields:
- Statistics involves collecting and analyzing numerical data to draw valid conclusions. It requires careful research planning and design.
- Descriptive statistics summarize data through measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode) and variability (range, standard deviation).
- Inferential statistics test hypotheses and make estimates about populations based on samples.
- Biostatistics is applied in community medicine, public health, cancer research, pharmacology, and demography to study disease trends, treatment effectiveness, and population attributes. It is also used in advanced biomedical technologies and ecology.Statistical Analysis with R- III



Statistical Analysis with R- IIIAkhila Prabhakaran
?
The document discusses various probability distributions including the normal, binomial, Poisson, uniform, and chi-square distributions. It provides examples of when each distribution would be used and explains key properties such as mean, variance, and standard deviation. It also covers topics like the central limit theorem, sampling distributions, and how inferential statistics is used to generalize from samples to populations.Module Five Normal Distributions & Hypothesis TestingTop of F.docx



Module Five Normal Distributions & Hypothesis TestingTop of F.docxroushhsiu
?
Module Five: Normal Distributions & Hypothesis Testing
Top of Form
Bottom of Form
Īż
Introduction & Goals
This week's investigations introduce and explore one of the most common distributions (one you may be familiar with): the Normal Distribution. In our explorations of the distribution and its associated curve, we will revisit the question of "What is typical?" and look at the likelihood (probability) that certain observations would occur in a given population with a variable that is normally distributed. We will apply our work with Normal Distributions to briefly explore some big concepts of inferential statistics, including the Central Limit Theorem and Hypothesis Testing. There are a lot of new ideas in this weekĪ»s work. This week is more exploratory in nature.
Goals:
Īż Explore the Empirical Rule
Īż Become familiar with the normal curve as a mathematical model, its applications and limitations
Īż Calculate z-scores & explain what they mean
Īż Use technology to calculate normal probabilities
Īż Determine the statistical significance of an observed difference in two means
Īż Use technology to perform a hypothesis test comparing means (z-test) and interpret its meaning
Īż Use technology to perform a hypothesis test comparing means (t-test) (optional)
Īż Gather data for Comparative Study Final Project.
Īż
DoW #5: The SAT & The ACT
Two Common Tests for college admission are the SAT (Scholastic Aptitude Test) and the ACT (American College Test). The scores for these tests are scaled so that they follow a normal distribution.
Īż The SAT reported that its scores were normally distributed with a mean ”╠=896 ?and a standard deviation ”ę=174
Īż The ACT reported that its scores were normally distributed with a mean ?”╠=20.6 and a standard deviation ”ę=5.2.
We have two questions to consider for this weekĪ»s DoW:
2. A high school student Bobby takes both of these tests. On the SAT, he achieves a score of 1080. On the ACT, he achieves a score of 30.? He cannot decide which score is the better one to send with his college applications.
. Question: Which test score is the stronger score to send to his colleges?
Īż A hypothetical group called SAT Prep claims that students who take their SAT Preparatory course score higher on the SAT than the general population. To support their claim, they site a study in which a?random sample of 50 SAT Prep students?had a mean SAT score of 1000. They claim that since this mean is higher than the known mean of 896 for all SAT scores, their program must improve SAT scores.
. Question: Is this difference in the mean scores statistically significant? Does SAT Prep truly improve SAT Scores?
.
Investigation 1: What is Normal?
One reason for gathering data is to see which observations are most likely. For instance, when we looked at the raisin data in DoW #3, we were looking to see what the most likely number of raisins was for each brand of raisins. ?We cannot ever be certain of the exact number of raisins in a box (because it varies) ...22PCOAM16 Unit 2 Session 13 Radial Basis Functions and Splines.pptx



22PCOAM16 Unit 2 Session 13 Radial Basis Functions and Splines.pptxGuru Nanak Technical Institutions
?
22PCOAM16 Unit 2 Session 13 Radial Basis Functions and Splines.pptxMore Related Content
Similar to G4 PROBABLITY.pptx (20)
Discrete distributions: Binomial, Poisson & Hypergeometric distributions



Discrete distributions: Binomial, Poisson & Hypergeometric distributionsScholarsPoint1
?
The PPT covered the distinguish between discrete and continuous distribution. Detailed explanation of the types of discrete distributions such as binomial distribution, Poisson distribution & Hyper-geometric distribution.Probability distribution 10



Probability distribution 10Sundar B N
?
Most important distribution like Poisson Distribution, Normal Distribution and Binomial Distribution is addressedPA_EPGDM_2_2023.pptx



PA_EPGDM_2_2023.pptxsomenathtiwary
?
This document outlines the syllabus for a course titled "Predictive Analytics" taught by K. Mohanasundaram. The syllabus covers topics such as introduction to business analytics, mathematical modelling, data prediction techniques, regression analysis methods like simple linear regression, logistic regression, and forecasting techniques. It recommends textbooks and references for the course and provides an introduction to concepts like uncertainty modelling using probability distributions and random variables.Different types of distributions



Different types of distributionsRajaKrishnan M
?
This document provides an introduction to probability theory and different probability distributions. It begins with defining probability as a quantitative measure of the likelihood of events occurring. It then covers fundamental probability concepts like mutually exclusive events, additive and multiplicative laws of probability, and independent events. The document also introduces random variables and common probability distributions like the binomial, Poisson, and normal distributions. It provides examples of how each distribution is used and concludes with characteristics of the normal distribution.Probability, Discrete Probability, Normal Probabilty



Probability, Discrete Probability, Normal ProbabiltyFaisal Hussain
?
This document provides an overview of probability and probability distributions. It defines probability as the chances of an event occurring among possible outcomes. It discusses discrete and continuous random variables, and how discrete probability distributions list each possible value and its probability, with the probabilities summing to 1. Normal distributions are introduced as the most important continuous probability distribution, with a bell-shaped, symmetric curve defined by a mean and approaching but not touching the x-axis. Examples are given of constructing discrete probability distributions from frequency data.Inorganic CHEMISTRY



Inorganic CHEMISTRYSaikumar raja
?
This document provides an outline and summaries of topics related to error analysis:
- It outlines topics including binomial distribution, Poisson distribution, normal distribution, confidence interval, and least squares analysis.
- The binomial distribution section provides an example of calculating the probability of getting 2 and 3 heads out of 6 coin tosses.
- The normal distribution section explains how to calculate the probability of scoring between 90-110 on an IQ test with a mean of 100 and standard deviation of 10.
- The confidence interval section provides an example of calculating the 95% confidence interval for the population mean boiling temperature based on 6 sample measurements.Module-2_Notes-with-Example for data science



Module-2_Notes-with-Example for data sciencepujashri1975
?
The document discusses several key concepts in probability and statistics:
- Conditional probability is the probability of one event occurring given that another event has already occurred.
- The binomial distribution models the probability of success in a fixed number of binary experiments. It applies when there are a fixed number of trials, two possible outcomes, and the same probability of success on each trial.
- The normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution that is symmetric and bell-shaped. It is characterized by its mean and standard deviation. Many real-world variables approximate a normal distribution.
- Other concepts discussed include range, interquartile range, variance, and standard deviation. The interquartile range describes the spread of a dataset's middle 50%RM



RMEvanNathan3
?
This document discusses different types of theoretical frequency distributions including binomial, Poisson, and normal distributions. It provides definitions and characteristics for each distribution. The binomial distribution requires a fixed number of trials with the same probability of success for each trial. The Poisson distribution is used when the probability of an event is very small but the number of trials is large. The normal distribution results from an infinite binomial expansion and is a continuous, bell-shaped distribution.Discreet and continuous probability



Discreet and continuous probabilitynj1992
?
The document discusses discrete and continuous probability distributions, explaining that a discrete distribution applies to variables that can take on countable values while a continuous distribution is used for variables that can take any value within a range. It provides examples of discrete variables like coin flips and continuous variables like weights. The document also outlines the differences between discrete and continuous probability distributions in how they are represented and calculated. Approaches to Probability Bayes' Theorem Binominal Distribution Poisson Dist...



Approaches to Probability Bayes' Theorem Binominal Distribution Poisson Dist...Sundar B N
?
Basic Concepts of Probability
Approaches to Probability
Bayes' Theorem
Binominal Distribution
Poisson Distribution
Normal DistributionTheory of probability and probability distribution



Theory of probability and probability distributionpolscjp
?
Probability refers to the likelihood of an event occurring. It can be expressed as a fraction between 0 and 1, with the total number of possible outcomes as the denominator and number of favorable outcomes as the numerator. A random variable is a value that can vary in an experiment but whose outcome is uncertain before the experiment. Probability distributions specify the probabilities of random variables taking on particular values. There are discrete and continuous probability distributions. Important discrete distributions include binomial and Poisson, while the normal distribution is the most important continuous distribution.Probability Distributions 



Probability Distributions Anthony J. Evans
?
?This presentation forms part of a free, online course on analytics
http://econ.anthonyjevans.com/courses/analytics/Presentation_advance_1n.pptx



Presentation_advance_1n.pptxsharonmarishkawilfre
?
This document provides an introduction to uncertainty in measurements. It discusses types of uncertainties including type A and type B uncertainties, standard uncertainty, confidence intervals, and expanded uncertainty. It explains key concepts such as degrees of freedom, standard deviation, standard error, t-distributions, and how to calculate confidence intervals and combined uncertainties. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to evaluate uncertainties and calculate best estimates, standard uncertainties, coverage factors, and confidence intervals for measurements.ststs nw.pptx



ststs nw.pptxMrymNb
?
Statistical concepts and their applications in various fields:
- Statistics involves collecting and analyzing numerical data to draw valid conclusions. It requires careful research planning and design.
- Descriptive statistics summarize data through measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode) and variability (range, standard deviation).
- Inferential statistics test hypotheses and make estimates about populations based on samples.
- Biostatistics is applied in community medicine, public health, cancer research, pharmacology, and demography to study disease trends, treatment effectiveness, and population attributes. It is also used in advanced biomedical technologies and ecology.Statistical Analysis with R- III



Statistical Analysis with R- IIIAkhila Prabhakaran
?
The document discusses various probability distributions including the normal, binomial, Poisson, uniform, and chi-square distributions. It provides examples of when each distribution would be used and explains key properties such as mean, variance, and standard deviation. It also covers topics like the central limit theorem, sampling distributions, and how inferential statistics is used to generalize from samples to populations.Module Five Normal Distributions & Hypothesis TestingTop of F.docx



Module Five Normal Distributions & Hypothesis TestingTop of F.docxroushhsiu
?
Module Five: Normal Distributions & Hypothesis Testing
Top of Form
Bottom of Form
Īż
Introduction & Goals
This week's investigations introduce and explore one of the most common distributions (one you may be familiar with): the Normal Distribution. In our explorations of the distribution and its associated curve, we will revisit the question of "What is typical?" and look at the likelihood (probability) that certain observations would occur in a given population with a variable that is normally distributed. We will apply our work with Normal Distributions to briefly explore some big concepts of inferential statistics, including the Central Limit Theorem and Hypothesis Testing. There are a lot of new ideas in this weekĪ»s work. This week is more exploratory in nature.
Goals:
Īż Explore the Empirical Rule
Īż Become familiar with the normal curve as a mathematical model, its applications and limitations
Īż Calculate z-scores & explain what they mean
Īż Use technology to calculate normal probabilities
Īż Determine the statistical significance of an observed difference in two means
Īż Use technology to perform a hypothesis test comparing means (z-test) and interpret its meaning
Īż Use technology to perform a hypothesis test comparing means (t-test) (optional)
Īż Gather data for Comparative Study Final Project.
Īż
DoW #5: The SAT & The ACT
Two Common Tests for college admission are the SAT (Scholastic Aptitude Test) and the ACT (American College Test). The scores for these tests are scaled so that they follow a normal distribution.
Īż The SAT reported that its scores were normally distributed with a mean ”╠=896 ?and a standard deviation ”ę=174
Īż The ACT reported that its scores were normally distributed with a mean ?”╠=20.6 and a standard deviation ”ę=5.2.
We have two questions to consider for this weekĪ»s DoW:
2. A high school student Bobby takes both of these tests. On the SAT, he achieves a score of 1080. On the ACT, he achieves a score of 30.? He cannot decide which score is the better one to send with his college applications.
. Question: Which test score is the stronger score to send to his colleges?
Īż A hypothetical group called SAT Prep claims that students who take their SAT Preparatory course score higher on the SAT than the general population. To support their claim, they site a study in which a?random sample of 50 SAT Prep students?had a mean SAT score of 1000. They claim that since this mean is higher than the known mean of 896 for all SAT scores, their program must improve SAT scores.
. Question: Is this difference in the mean scores statistically significant? Does SAT Prep truly improve SAT Scores?
.
Investigation 1: What is Normal?
One reason for gathering data is to see which observations are most likely. For instance, when we looked at the raisin data in DoW #3, we were looking to see what the most likely number of raisins was for each brand of raisins. ?We cannot ever be certain of the exact number of raisins in a box (because it varies) ...Recently uploaded (20)
22PCOAM16 Unit 2 Session 13 Radial Basis Functions and Splines.pptx



22PCOAM16 Unit 2 Session 13 Radial Basis Functions and Splines.pptxGuru Nanak Technical Institutions
?
22PCOAM16 Unit 2 Session 13 Radial Basis Functions and Splines.pptxInsertion Sort, Merge Sort. Time complexity of all sorting algorithms and t...



Insertion Sort, Merge Sort. Time complexity of all sorting algorithms and t...Dr. Madhuri Jawale
?
Insertion Sort,
Merge Sort.
Time complexity of all sorting algorithms and their comparison.
Standard-Representation-for-Logic-Functions (1).pptx



Standard-Representation-for-Logic-Functions (1).pptxsashiP
?
presentation on logic functions of digital logic designIntroduction to Edge and Fog Computing.pdf



Introduction to Edge and Fog Computing.pdfHitesh Mohapatra
?
Edge computing and fog computing can both be defined as technological platforms that bring computing processes closer to where data is generated and collected from. This article explains the two concepts in detail and lists the similarities and differences between them.Material Handling : Scope , Importance, Objectives, Principles, Classificatio...



Material Handling : Scope , Importance, Objectives, Principles, Classificatio...VirajPasare
?
Material handling
Scope of Material handling
Importance of Material Handling
Objectives of Material handling
Principles of Material Handling
Classification of Material Handling
Selection of Material Handling Equipment's
Battery charging technology for electric vehicle.pptx



Battery charging technology for electric vehicle.pptxVirajPasare
?
Battery Charging : Level 1, Level 2, Level 3, Fast or DC Charging, Voltage and Current Specifications, Opportunity Charging, Multi Stage Charging, Bulk, Absorption, Float, Trickle Charging, Pulse Charging, Constant Current Charging, Constant Voltage Charging, Constant Current Constant Voltage Charging, Wire Less Charging, Battery Swapping.22PCOAM16_UNIT 2_Session 10 Multi Layer Perceptrons.pptx



22PCOAM16_UNIT 2_Session 10 Multi Layer Perceptrons.pptxGuru Nanak Technical Institutions
?
22PCOAM16_UNIT 2_Session 10 Multi Layer Perceptrons.pptx╔ń─┌├ŃÅŖ╗ß┘Y┴Ž_Data-Centric AI in The Age of Large Language Models



╔ń─┌├ŃÅŖ╗ß┘Y┴Ž_Data-Centric AI in The Age of Large Language Models▒Ę┤ĪĄ■│ó┤Ī│¦ųĻ╩Į╗ß╔ń
?
ż│ż╬┘Y┴ŽżŪżŽĪóLLMż╬│╔╣”ż╦żŽźŪ®`ź┐ż╬┘|ż╚ČÓśöąįż¼▓╗┐╔ŪĘżŪżóżļż│ż╚ż“šh├„żĘżŲżżż▐ż╣ĪŻÅŠ└┤ż╬źŌźŪźļĖ─╔Ųųąą─ż╬źóźūźĒ®`ź┴ż╦īØżĘĪóźŪ®`ź┐ųąą─ż╬AIķ_░kż“╠ß░ĖżĘĪóżĶżĻä┐┬╩Ą─żŪ═Ė├„ąįż╬Ė▀żżLLMż╬śŗ║Bż╦Ž“ż▒ż┐Š▀╠ÕĄ─ż╩╩ųĘ©ż“ĮBĮķżĘżŲżżż▐ż╣ĪŻźŪ®`ź┐ż╬ūŅ▀m╗»żõ╗Ņė├ĘĮĘ©Īóž¤╚╬żóżļAIķ_░kż╬ųžę¬ąįż╦ż─żżżŲżŌ┤źżņżķżņżŲż¬żĻĪóLLMż╬źčźšź®®`ź▐ź¾ź╣Ž“╔Žż╦Ž“ż▒ż┐ą┬ż┐ż╩ęĢĄŃż“╠ß╣®ż╣żļ─┌╚▌żŪż╣ĪŻ
This paper explains that the success of LLMs depends heavily on the quality and diversity of data. Instead of focusing solely on model improvements, it proposes a data-centric approach to AI development, introducing concrete methods for building more efficient and transparent LLMs. It also discusses data optimization, utilization strategies, and the importance of responsible AI development, offering a fresh perspective on enhancing LLM performance.22PCOAM16_UNIT 2_ Session 12 Deriving Back-Propagation .pptx



22PCOAM16_UNIT 2_ Session 12 Deriving Back-Propagation .pptxGuru Nanak Technical Institutions
?
22PCOAM16_UNIT 2_ Session 12 Deriving Back-Propagation .pptxUnit 1- Python- Features, Variables, Data Types, Operators and Expressions



Unit 1- Python- Features, Variables, Data Types, Operators and ExpressionsGawaliSwapnali13
?
Course ESIT135 Problem Solving using Python-Unit 1 Aerodynamic Stability Tests for Cable-Stayed Bridges.pdf



Aerodynamic Stability Tests for Cable-Stayed Bridges.pdfKamel Farid
?
what are types of tests required of cable stayed bridges Introduction to Stack, ? Stack ADT, ? Implementation of Stack using array, ...



Introduction to Stack, ? Stack ADT, ? Implementation of Stack using array, ...Dr. Madhuri Jawale
?
Introduction to Stack,
? Stack ADT,
? Implementation of Stack using array,
? Concept of implicit and explicit stack.22PCOAM16 Unit 2 Session 13 Radial Basis Functions and Splines.pptx



22PCOAM16 Unit 2 Session 13 Radial Basis Functions and Splines.pptxGuru Nanak Technical Institutions
?
G4 PROBABLITY.pptx
- 1. APPLICATION OF PROBABLITY IN ENGINEERING - BY GROUP 4
- 2. What is probability distribution? ? Probability distribution is a mathematical function that describes the likelihood of occurrence of different outcomes in a random event. In other words, it is a way of representing the uncertainty associated with a random variable. A random variable is a variable that can take on different values based on the outcome of a random event. ? A probability distribution assigns a probability to each possible outcome of a random event. The probabilities are usually represented as values between 0 and 1, where 0 represents an impossible outcome and 1 represents a certain outcome. The sum of all probabilities in a probability distribution must equal 1, since one of the possible outcomes must occur. ? There are different types of probability distributions, including discrete distributions and continuous distributions. Discrete distributions, such as the Bernoulli and binomial distributions, are used to model events with a finite number of outcomes. Continuous distributions, such as the normal and exponential distributions, are used to model events with an infinite number of possible outcomes. ? The shape of a probability distribution is determined by its parameters, which can be estimated from data or derived from physical laws. Once a probability distribution has been determined, it can be used to make predictions about the outcome of future events, estimate the likelihood of specific outcomes, and perform various statistical analyses. ?
- 3. Types of probability distribution 1. Discrete Distributions: These distributions are used to model events with a finite or countably infinite number of outcomes. Examples include the Bernoulli, Binomial, Poisson, and Geometric distributions. 2. Continuous Distributions: These distributions are used to model events with an uncountably infinite number of outcomes, such as real numbers. Examples include the Normal, Exponential, Uniform, and Log-Normal distributions. 3. Univariate Distributions: These distributions describe the behavior of a single random variable. Examples include the Normal and Exponential distributions. 4. Multivariate Distributions: These distributions describe the behavior of multiple random variables. Examples include the Multivariate Normal and Dirichlet distributions. 5. Symmetric Distributions: These distributions have a mean that is equal to the median, and the distribution is symmetrical around the mean. Examples include the Normal and Uniform distributions. 6. Skewed Distributions: These distributions have a mean that is not equal to the median, and the distribution is not symmetrical around the mean. Examples include the Log-Normal and Pareto distributions.
- 4. NORMAL DISTRIBUTION - BONUS EXAMPLE USING A PYTHON PROGRAM
- 5. BASICS OF NORMAL DISTRIBUTION: ? A Normal Distribution is also known as a Gaussian distribution. ? The normal distribution is magical because most of the naturally occurring phenomenon follows a normal distribution. For example, blood pressure, IQ scores, heights follow the normal distribution
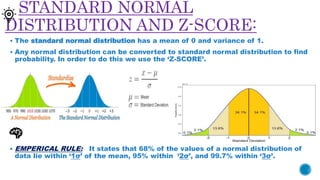
- 6. STANDARD NORMAL DISTRIBUTION AND Z-SCORE: ? The standard normal distribution has a mean of 0 and variance of 1. ? Any normal distribution can be converted to standard normal distribution to find probability. In order to do this we use the Ī«Z-SCOREĪ». ? EMPERICAL RULE: It states that 68% of the values of a normal distribution of data lie within Ī«1”ęĪ» of the mean, 95% within Ī«2”ęĪ», and 99.7% within Ī«3”ęĪ».
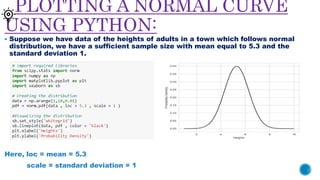
- 7. PLOTTING A NORMAL CURVE USING PYTHON: ? Suppose we have data of the heights of adults in a town which follows normal distribution, we have a sufficient sample size with mean equal to 5.3 and the standard deviation 1. Here, loc = mean = 5.3 scale = standard deviation = 1
- 8. CALCULATING PROBABILITY: A] X<4.5 B] 4.5Ī▄ X Ī▄6.5 C] X>6.5 *CODE:
- 9. REAL WORLD APPLICATIONS: ? In the investment world, the periodic (daily, monthly, even annual) returns of assets like stocks and bonds are assumed to follow a normal distribution. ? In the corporate world, the distribution of the severity of manufacturing defects was found to be normally distributed (this makes sense: usually you make it right, a few times you make it slightly wrong, and once in a blue moon you completely mess it up) ? The process improvement framework Six Sigma was basically built around this observation. ? In data science and statistics, statistical inference (and hypothesis testing) relies heavily on the normal distribution.
- 12. Binomial Distribution Q.What ia binomial distribution? The binomial distribution is one of the most commonly used distributions in statistics. It describes the probability of obtaining k successes in n binomial experiments. If a random variable X follows a binomial distribution, then the probability that X = k successes can be found by the following formula: P(X=k) = nCk * pk * (1-p)n-k where: ?n: number of trials ?k: number of successes ?p: probability of success on a given trial ?nCk: the number of ways to obtain k successes in n trials
- 13. Generating an array that follows binomial distribution using python Each number in the resulting array represents the number of Ī░successesĪ▒ experienced during 10 trials where the probability of success in a given trial was 0.25.
- 14. Eg.Q1:Tanish makes 60% of his free-throw attempts. If he shoots 12 free throws, what is the probability that he makes exactly 10? The probability that Tanish makes exactly 10 free throws is 0.0639.
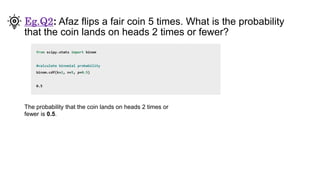
- 15. Eg.Q2: Afaz flips a fair coin 5 times. What is the probability that the coin lands on heads 2 times or fewer? The probability that the coin lands on heads 2 times or fewer is 0.5.
- 16. Visualizing a Binomial Distribution Code: The x-axis describes the number of successes during 10 trials and the y-axis displays the number of times each number of successes occurred during 1,000 experiments.











