Gas Gangrene........................pptx
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes90 views
important
1 of 16
Download to read offline















Recommended
gasgangrene-200701120813............pptx



gasgangrene-200701120813............pptxDebdattaMandal5
╠²
Gas gangrene is a rapidly spreading, potentially fatal infection caused by clostridial bacteria. It results in the death of muscle tissue (myonecrosis) and produces gas within tissues. It is commonly caused by Clostridium perfringens entering through wounds, especially injuries from soil, surgery, or gunshot wounds. Symptoms include severe pain, swelling, and crepitus in the wound along with systemic effects like shock. Aggressive debridement surgery and antibiotics including penicillin are used for treatment. Homoeopathic remedies like Arsenicum album, Crotalus, Secale cornutum, and Carbo vegetabilis may provide support.Gas gangrene



Gas gangrenePraful SonnePatil
╠²
This document discusses gas gangrene, a rapidly spreading, potentially fatal infection caused by Clostridium bacteria. It enters the body through wounds or injuries contaminated with soil or feces and releases toxins that cause tissue death. Symptoms include severe pain, swelling, brownish fluid draining from wounds with a foul odor, skin discoloration, and palpable gas in muscles. Diagnosis involves examining wound fluid under a microscope. Treatment requires urgent debridement of dead tissue, antibiotics like penicillin, oxygen therapy, and possibly amputation of infected limbs to save the patient's life. Homeopathic remedies like Arsenicum, Crotalus, and Secale may provide additional support.GANGRENE presentation.pptx



GANGRENE presentation.pptxmusayansa
╠²
Gangrene refers to the death of body tissues due to lack of blood flow or infection. It commonly affects extremities like fingers, toes and limbs. There are several types of gangrene including dry, wet, gas and internal gangrene. Gangrene is caused by lack of blood supply, infection, or trauma. Risk factors include diabetes, vascular disease, injury, smoking, obesity and immunosuppression. Symptoms include skin discoloration, swelling, blisters and pain. Treatment involves controlling risk factors, antibiotics, surgery to remove dead tissue, and in severe cases amputation. Prevention focuses on proper diabetes care, weight control, smoking cessation and infection prevention.Epidemiology ,control and management of gas gangrene



Epidemiology ,control and management of gas gangreneRakhiYadav53
╠²
This document discusses gas gangrene, including its definition, types, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment. It defines gas gangrene as a bacterial infection causing tissue gas in gangrene, usually caused by Clostridium perfringens bacteria. There are two main types - dry gangrene occurs due to blocked arteries while wet gangrene occurs in moist tissues. Treatment involves antibiotics, debridement of dead tissue, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, and sometimes amputation. Prevention emphasizes wound care, foot care for diabetics, and avoiding injuries that could lead to infection.SOFT TISSUE INFECTION 21.10.2021 (1).pptx



SOFT TISSUE INFECTION 21.10.2021 (1).pptxTharshaniDeviSriniva
╠²
Necrotizing fasciitis and gas gangrene are aggressive soft tissue infections that can cause rapid tissue destruction. Necrotizing fasciitis begins as a bacterial infection of the fascia and subcutaneous tissue, often following minor trauma or surgery. It spreads quickly along the fascial plane and can cause sepsis and organ failure if not treated promptly with extensive wound debridement and IV antibiotics. Gas gangrene is caused by Clostridium bacteria invading wounded muscle tissue. It leads to muscle necrosis, toxin production, and gas formation, with high mortality if not surgically treated. Cellulitis is a superficial skin infection that presents with erythema, pain, swelling and warmth over the affected area. It is usuallyGas gangrene



Gas gangreneOM VERMA
╠²
Gas gangrene is a life-threatening bacterial infection that causes tissues to die and release gas. It is caused by Clostridium bacteria entering the body through wounds or injuries. Symptoms include pain, fever, swelling, and blisters with foul-smelling discharge near infected areas. The bacteria produce toxins that destroy muscles and tissues, and the infection spreads rapidly. Treatment involves high doses of antibiotics, removal of dead tissue, and potential amputation to stop the spread. Without prompt treatment, gas gangrene can lead to complications like organ damage and death.GAS GANGRENE.pptx



GAS GANGRENE.pptxSrishtiGupta304
╠²
This document discusses gas gangrene, also known as clostridial myonecrosis, which is a potentially life-threatening bacterial infection caused by Clostridium bacteria. The bacteria release toxins that cause tissue death and gas formation. Risk factors include injuries, surgery, diabetes, and immunosuppression. Symptoms include high fever, pain, swelling, blisters, and blackened skin. Treatment involves antibiotics, surgery to remove dead tissue, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, and managing pain and fever. Preventing the spread of infection is important and involves proper hand hygiene, use of gloves and gowns, disinfecting surfaces, and isolating infected patients.maxamuud.pptx



maxamuud.pptxsamson479977
╠²
This document discusses several bacterial infections including Madura foot, necrotizing fasciitis, clostridial infections (tetanus and gas gangrene). Madura foot is a chronic fungal infection of the foot that causes bone destruction. Necrotizing fasciitis is an acute soft tissue infection characterized by tissue necrosis. Clostridial infections include tetanus, caused by C. tetani toxin, and gas gangrene, caused by C. perfringens, which causes muscle necrosis and systemic toxicity.MPG 507.pptx



MPG 507.pptxMazedurRahman17
╠²
This document provides information about gas gangrene through a presentation on the topic. It defines gas gangrene as a highly lethal soft tissue infection caused by toxin-producing Clostridium bacteria. The presentation describes the causative agents, symptoms, pathogenesis, epidemiology, investigations, treatment and prevention of gas gangrene. The main points are that gas gangrene is caused by Clostridium bacteria entering wounds or injuries, producing toxins and gases that destroy tissue; symptoms include pain, swelling and tissue destruction; and treatment involves surgery, antibiotics and sometimes amputation to prevent spread of the infection.MPG 507.ppt



MPG 507.pptMazedurRahman17
╠²
This document presents information on a course project submitted by six students to their lecturer in the Department of Microbiology at PrimeAsia University. The project focuses on gas gangrene, providing details on the causative agents, symptoms, pathogenesis, epidemiology, investigations, treatment, and prevention of this condition. Gas gangrene is defined as a highly lethal soft tissue infection caused by toxin- and gas-producing Clostridium bacteria, usually Clostridium perfringens, which enters through broken skin and produces toxins and enzymes that destroy tissues and cause gangrene.Gangrene and amputation



Gangrene and amputationmahamed adam
╠²
Gangrene is the death of soft tissue due to loss of blood supply. There are three main types: dry, wet, and gas gangrene. Dry gangrene develops slowly over years from conditions like atherosclerosis or diabetes that impair circulation. Wet gangrene occurs when an infected wound or bedsores cause blocked blood flow. Gas gangrene is a deadly form caused by Clostridium bacteria that produce toxins and gases. Risk factors include old age, diabetes, vascular diseases, injuries, and smoking. Signs may include pain, discoloration, foul discharge, and fever. Treatment involves wound cleaning, antibiotics, surgery like amputation or debridement, and hyperbaric oxygen for gas gangrene. Prevention focusesInflammatory diseases



Inflammatory diseaseslaraib jameel
╠²
Gangrene is the death of body tissue due to lack of blood supply and oxygen. It is usually caused by infection, vascular disease, or physical trauma that blocks blood flow. There are two main types: dry gangrene involves tissue death without infection, while wet gangrene involves tissue death with infection. Gangrene symptoms include pain, swelling, discoloration and foul odor of the affected area. Risk factors include diabetes, vascular diseases, smoking, obesity, and conditions that weaken the immune system. Diagnosis involves examination of the affected area along with blood tests and imaging studies to determine the cause and extent.Gas gangrene 



Gas gangrene BipulBorthakur
╠²
Gas gangrene is a life-threatening infection caused by Clostridium bacteria. It results in tissue death and gas formation in muscles. Common causes are traumatic wounds, surgery, or underlying conditions impairing the immune system. Symptoms include severe pain that spreads from the infection site. Signs include swelling, discoloration of the skin, gas-filled blisters, and a sweet smell. Treatment requires prompt antibiotic therapy with penicillin, sometimes plus clindamycin, as well as extensive surgical debridement of dead tissue. Adjuvant hyperbaric oxygen therapy may improve outcomes by enhancing antibiotic effects and tissue delineation for surgery. Without adequate treatment, gas gangrene can cause complications like organ failure and lead toBest Gangrene Treatment Hospital in Hyderabad.pdf



Best Gangrene Treatment Hospital in Hyderabad.pdfKBK Multi Speciality Hospital
╠²
Check out the Best Gangrene Treatment in Hyderabad for comprehensive treatment without amputation services that are customized.Best Gangrene Treatment Hospital gangrene treatment



Best Gangrene Treatment Hospital gangrene treatmentKBK Multi Speciality Hospital
╠²
Check out the Best Gangrene Treatment in Hyderabad for comprehensive treatment without amputation services that are customized.
gangrene treatment in india without amputation



gangrene treatment in india without amputationKBK Multi Speciality Hospital
╠²
Check out the Best Gangrene Treatment in Hyderabad for comprehensive treatment without amputation services that are customized.
For more info visit
https://kbkhospitals.com/gangrene-treatment-in-hyderabad.php
gangrene treatment without amputation KBK Hospitals



gangrene treatment without amputation KBK HospitalsKBK Multi Speciality Hospital
╠²
Check out the Best Gangrene Treatment in Hyderabad for comprehensive treatment without amputation services that are customized.
For more info visit
https://kbkhospitals.com/gangrene-treatment-in-hyderabad.php
Gas Gangrene.pptx



Gas Gangrene.pptxRamya569989
╠²
Gas gangrene is a life-threatening infection caused by bacteria such as Clostridium perfringens. It occurs most often after injuries or surgery where dead tissue provides an environment for the bacteria to grow and release toxins and gas. Common symptoms include pain, swelling, and skin changes ranging from discoloration to blisters. Gas gangrene spreads rapidly without prompt treatment and can cause death within 48 hours. Treatment requires antibiotics, surgery to remove dead tissue, and sometimes hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Prevention focuses on proper wound care and antibiotic use after injuries.gangrene treatment in india KBK Hospital



gangrene treatment in india KBK HospitalKBK Multi Speciality Hospital
╠²
Check out the Best Gangrene Treatment in Hyderabad for comprehensive treatment without amputation services that are customized.
For more info visit
https://kbkhospitals.com/gangrene-treatment-in-hyderabad.php
Best Gangrene Treatment Hospital in Hyderabad.pptx



Best Gangrene Treatment Hospital in Hyderabad.pptxKBK Multi Speciality Hospital
╠²
Check out the Best Gangrene Treatment in Hyderabad for comprehensive treatment without amputation services that are customized.
Best gangrene treatment without amputuation in hyderabad



Best gangrene treatment without amputuation in hyderabadKBK Multi Speciality Hospital
╠²
Check out the Best Gangrene Treatment in Hyderabad for comprehensive treatment without amputation services that are customized.
For more info visit
https://kbkhospitals.com/gangrene-treatment-in-hyderabad.php
Best Gangrene Treatment Hospital in Hyderabad.pptx



Best Gangrene Treatment Hospital in Hyderabad.pptxKBK Multi Speciality Hospital
╠²
Check out the Best Gangrene Treatment in Hyderabad for comprehensive treatment without amputation services that are customized.
For more info visit
https://kbkhospitals.com/gangrene-treatment-in-hyderabad.php
Limb Salvage in Severe Necrotizing Fascitis.pptx



Limb Salvage in Severe Necrotizing Fascitis.pptxDr Majd ž».┘ģž¼ž» Alhaddadin ž¦┘䞣ž»ž¦ž»┘Ŗ┘å
╠²
A patient with severe limb infection in whom the amputation was the first option.
Dr Majd Alhaddadin, Consultant General and Laparoscopic Surgeon, performed a transmetatrsal amputation with extensive tissue debridement and falp creation, followed by vacuum therapy and 2 stages wound closure. Fortunately xth limb was saved and the patient returned to his normal job. Pathology Gangrene



Pathology Gangrenekdnyanu682003
╠²
Gangrene is the death of body tissue due to reduced blood flow or infection. There are three main types: dry gangrene caused by blocked arteries, wet gangrene which affects moist tissues from blocked veins, and gas gangrene caused by Clostridium bacteria. Signs include black, shrunken tissue in dry gangrene; soft, swollen tissue in wet gangrene; and blisters with foul smell in gas gangrene. Treatment involves antibiotics, supportive care like IV fluids, and potentially amputation or angioplasty depending on the severity and type of gangrene.4. BCM 229 wounds and ulcers.ppt



4. BCM 229 wounds and ulcers.pptAmos15720
╠²
This document discusses different types of wounds and ulcers, including their causes and treatments. It provides details on:
- Incised wounds which are caused by sharp objects and can often be closed within 6 hours. Deep penetrating wounds may involve deeper tissues.
- Lacerated wounds have ragged edges and are commonly infected within 6 hours due to debris. Dead tissue must be removed within 6 hours.
- Crush injuries are difficult to manage due to necrosis and tissue tension. Excision and fasciotomy are often needed to relieve tension.
- Pressure ulcers are caused by excess pressure and typically occur over bony areas. Prevention is key through frequent repositioning and special mattresses.
-More Related Content
Similar to Gas Gangrene........................pptx (20)
Gas gangrene



Gas gangreneOM VERMA
╠²
Gas gangrene is a life-threatening bacterial infection that causes tissues to die and release gas. It is caused by Clostridium bacteria entering the body through wounds or injuries. Symptoms include pain, fever, swelling, and blisters with foul-smelling discharge near infected areas. The bacteria produce toxins that destroy muscles and tissues, and the infection spreads rapidly. Treatment involves high doses of antibiotics, removal of dead tissue, and potential amputation to stop the spread. Without prompt treatment, gas gangrene can lead to complications like organ damage and death.GAS GANGRENE.pptx



GAS GANGRENE.pptxSrishtiGupta304
╠²
This document discusses gas gangrene, also known as clostridial myonecrosis, which is a potentially life-threatening bacterial infection caused by Clostridium bacteria. The bacteria release toxins that cause tissue death and gas formation. Risk factors include injuries, surgery, diabetes, and immunosuppression. Symptoms include high fever, pain, swelling, blisters, and blackened skin. Treatment involves antibiotics, surgery to remove dead tissue, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, and managing pain and fever. Preventing the spread of infection is important and involves proper hand hygiene, use of gloves and gowns, disinfecting surfaces, and isolating infected patients.maxamuud.pptx



maxamuud.pptxsamson479977
╠²
This document discusses several bacterial infections including Madura foot, necrotizing fasciitis, clostridial infections (tetanus and gas gangrene). Madura foot is a chronic fungal infection of the foot that causes bone destruction. Necrotizing fasciitis is an acute soft tissue infection characterized by tissue necrosis. Clostridial infections include tetanus, caused by C. tetani toxin, and gas gangrene, caused by C. perfringens, which causes muscle necrosis and systemic toxicity.MPG 507.pptx



MPG 507.pptxMazedurRahman17
╠²
This document provides information about gas gangrene through a presentation on the topic. It defines gas gangrene as a highly lethal soft tissue infection caused by toxin-producing Clostridium bacteria. The presentation describes the causative agents, symptoms, pathogenesis, epidemiology, investigations, treatment and prevention of gas gangrene. The main points are that gas gangrene is caused by Clostridium bacteria entering wounds or injuries, producing toxins and gases that destroy tissue; symptoms include pain, swelling and tissue destruction; and treatment involves surgery, antibiotics and sometimes amputation to prevent spread of the infection.MPG 507.ppt



MPG 507.pptMazedurRahman17
╠²
This document presents information on a course project submitted by six students to their lecturer in the Department of Microbiology at PrimeAsia University. The project focuses on gas gangrene, providing details on the causative agents, symptoms, pathogenesis, epidemiology, investigations, treatment, and prevention of this condition. Gas gangrene is defined as a highly lethal soft tissue infection caused by toxin- and gas-producing Clostridium bacteria, usually Clostridium perfringens, which enters through broken skin and produces toxins and enzymes that destroy tissues and cause gangrene.Gangrene and amputation



Gangrene and amputationmahamed adam
╠²
Gangrene is the death of soft tissue due to loss of blood supply. There are three main types: dry, wet, and gas gangrene. Dry gangrene develops slowly over years from conditions like atherosclerosis or diabetes that impair circulation. Wet gangrene occurs when an infected wound or bedsores cause blocked blood flow. Gas gangrene is a deadly form caused by Clostridium bacteria that produce toxins and gases. Risk factors include old age, diabetes, vascular diseases, injuries, and smoking. Signs may include pain, discoloration, foul discharge, and fever. Treatment involves wound cleaning, antibiotics, surgery like amputation or debridement, and hyperbaric oxygen for gas gangrene. Prevention focusesInflammatory diseases



Inflammatory diseaseslaraib jameel
╠²
Gangrene is the death of body tissue due to lack of blood supply and oxygen. It is usually caused by infection, vascular disease, or physical trauma that blocks blood flow. There are two main types: dry gangrene involves tissue death without infection, while wet gangrene involves tissue death with infection. Gangrene symptoms include pain, swelling, discoloration and foul odor of the affected area. Risk factors include diabetes, vascular diseases, smoking, obesity, and conditions that weaken the immune system. Diagnosis involves examination of the affected area along with blood tests and imaging studies to determine the cause and extent.Gas gangrene 



Gas gangrene BipulBorthakur
╠²
Gas gangrene is a life-threatening infection caused by Clostridium bacteria. It results in tissue death and gas formation in muscles. Common causes are traumatic wounds, surgery, or underlying conditions impairing the immune system. Symptoms include severe pain that spreads from the infection site. Signs include swelling, discoloration of the skin, gas-filled blisters, and a sweet smell. Treatment requires prompt antibiotic therapy with penicillin, sometimes plus clindamycin, as well as extensive surgical debridement of dead tissue. Adjuvant hyperbaric oxygen therapy may improve outcomes by enhancing antibiotic effects and tissue delineation for surgery. Without adequate treatment, gas gangrene can cause complications like organ failure and lead toBest Gangrene Treatment Hospital in Hyderabad.pdf



Best Gangrene Treatment Hospital in Hyderabad.pdfKBK Multi Speciality Hospital
╠²
Check out the Best Gangrene Treatment in Hyderabad for comprehensive treatment without amputation services that are customized.Best Gangrene Treatment Hospital gangrene treatment



Best Gangrene Treatment Hospital gangrene treatmentKBK Multi Speciality Hospital
╠²
Check out the Best Gangrene Treatment in Hyderabad for comprehensive treatment without amputation services that are customized.
gangrene treatment in india without amputation



gangrene treatment in india without amputationKBK Multi Speciality Hospital
╠²
Check out the Best Gangrene Treatment in Hyderabad for comprehensive treatment without amputation services that are customized.
For more info visit
https://kbkhospitals.com/gangrene-treatment-in-hyderabad.php
gangrene treatment without amputation KBK Hospitals



gangrene treatment without amputation KBK HospitalsKBK Multi Speciality Hospital
╠²
Check out the Best Gangrene Treatment in Hyderabad for comprehensive treatment without amputation services that are customized.
For more info visit
https://kbkhospitals.com/gangrene-treatment-in-hyderabad.php
Gas Gangrene.pptx



Gas Gangrene.pptxRamya569989
╠²
Gas gangrene is a life-threatening infection caused by bacteria such as Clostridium perfringens. It occurs most often after injuries or surgery where dead tissue provides an environment for the bacteria to grow and release toxins and gas. Common symptoms include pain, swelling, and skin changes ranging from discoloration to blisters. Gas gangrene spreads rapidly without prompt treatment and can cause death within 48 hours. Treatment requires antibiotics, surgery to remove dead tissue, and sometimes hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Prevention focuses on proper wound care and antibiotic use after injuries.gangrene treatment in india KBK Hospital



gangrene treatment in india KBK HospitalKBK Multi Speciality Hospital
╠²
Check out the Best Gangrene Treatment in Hyderabad for comprehensive treatment without amputation services that are customized.
For more info visit
https://kbkhospitals.com/gangrene-treatment-in-hyderabad.php
Best Gangrene Treatment Hospital in Hyderabad.pptx



Best Gangrene Treatment Hospital in Hyderabad.pptxKBK Multi Speciality Hospital
╠²
Check out the Best Gangrene Treatment in Hyderabad for comprehensive treatment without amputation services that are customized.
Best gangrene treatment without amputuation in hyderabad



Best gangrene treatment without amputuation in hyderabadKBK Multi Speciality Hospital
╠²
Check out the Best Gangrene Treatment in Hyderabad for comprehensive treatment without amputation services that are customized.
For more info visit
https://kbkhospitals.com/gangrene-treatment-in-hyderabad.php
Best Gangrene Treatment Hospital in Hyderabad.pptx



Best Gangrene Treatment Hospital in Hyderabad.pptxKBK Multi Speciality Hospital
╠²
Check out the Best Gangrene Treatment in Hyderabad for comprehensive treatment without amputation services that are customized.
For more info visit
https://kbkhospitals.com/gangrene-treatment-in-hyderabad.php
Limb Salvage in Severe Necrotizing Fascitis.pptx



Limb Salvage in Severe Necrotizing Fascitis.pptxDr Majd ž».┘ģž¼ž» Alhaddadin ž¦┘䞣ž»ž¦ž»┘Ŗ┘å
╠²
A patient with severe limb infection in whom the amputation was the first option.
Dr Majd Alhaddadin, Consultant General and Laparoscopic Surgeon, performed a transmetatrsal amputation with extensive tissue debridement and falp creation, followed by vacuum therapy and 2 stages wound closure. Fortunately xth limb was saved and the patient returned to his normal job. Pathology Gangrene



Pathology Gangrenekdnyanu682003
╠²
Gangrene is the death of body tissue due to reduced blood flow or infection. There are three main types: dry gangrene caused by blocked arteries, wet gangrene which affects moist tissues from blocked veins, and gas gangrene caused by Clostridium bacteria. Signs include black, shrunken tissue in dry gangrene; soft, swollen tissue in wet gangrene; and blisters with foul smell in gas gangrene. Treatment involves antibiotics, supportive care like IV fluids, and potentially amputation or angioplasty depending on the severity and type of gangrene.4. BCM 229 wounds and ulcers.ppt



4. BCM 229 wounds and ulcers.pptAmos15720
╠²
This document discusses different types of wounds and ulcers, including their causes and treatments. It provides details on:
- Incised wounds which are caused by sharp objects and can often be closed within 6 hours. Deep penetrating wounds may involve deeper tissues.
- Lacerated wounds have ragged edges and are commonly infected within 6 hours due to debris. Dead tissue must be removed within 6 hours.
- Crush injuries are difficult to manage due to necrosis and tissue tension. Excision and fasciotomy are often needed to relieve tension.
- Pressure ulcers are caused by excess pressure and typically occur over bony areas. Prevention is key through frequent repositioning and special mattresses.
-More from DebdattaMandal5 (20)
Recently uploaded (20)
Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In this slide weŌĆÖll discuss on the useful environment methods in Odoo 18. In Odoo 18, environment methods play a crucial role in simplifying model interactions and enhancing data processing within the ORM framework.FESTIVAL: SINULOG & THINGYAN-LESSON 4.pptx



FESTIVAL: SINULOG & THINGYAN-LESSON 4.pptxDanmarieMuli1
╠²
Sinulog Festival of Cebu City, and Thingyan Festival of Myanmar.QuickBooks Desktop to QuickBooks Online How to Make the Move



QuickBooks Desktop to QuickBooks Online How to Make the MoveTechSoup
╠²
If you use QuickBooks Desktop and are stressing about moving to QuickBooks Online, in this webinar, get your questions answered and learn tips and tricks to make the process easier for you.
Key Questions:
* When is the best time to make the shift to QuickBooks Online?
* Will my current version of QuickBooks Desktop stop working?
* I have a really old version of QuickBooks. What should I do?
* I run my payroll in QuickBooks Desktop now. How is that affected?
*Does it bring over all my historical data? Are there things that don't come over?
* What are the main differences between QuickBooks Desktop and QuickBooks Online?
* And moreHow to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



How to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18. In Odoo, Init Hooks are essential functions specified as strings in the __init__ file of a module.EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdf



EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdfLiz Walsh-Trevino
╠²
EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdfHow to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 Employee



How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 EmployeeCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to configure flexible working schedule in Odoo 18 Employee module. In Odoo 18, the Employee module offers powerful tools to configure and manage flexible working schedules tailored to your organization's needs.How to attach file using upload button Odoo 18



How to attach file using upload button Odoo 18Celine George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to attach file using upload button Odoo 18. Odoo features a dedicated model, 'ir.attachments,' designed for storing attachments submitted by end users. We can see the process of utilizing the 'ir.attachments' model to enable file uploads through web forms in this slide.Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Prelims of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Finals of Rass MELAI : a Music, Entertainment, Literature, Arts and Internet Culture Quiz organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptx



Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxmansk2
╠²
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxAPM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...Association for Project Management
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
- Autonomy, Teams and Tension
- Oliver Randall & David Bovis
- Own Your Autonomy
Oliver Randall
Consultant, Tribe365
Oliver is a career project professional since 2011 and started volunteering with APM in 2016 and has since chaired the People Interest Network and the North East Regional Network. Oliver has been consulting in culture, leadership and behaviours since 2019 and co-developed HPTM┬«ŌĆ»an off the shelf high performance framework for teams and organisations and is currently working with SAS (Stellenbosch Academy for Sport) developing the culture, leadership and behaviours framework for future elite sportspeople whilst also holding down work as a project manager in the NHS at North Tees and Hartlepool Foundation Trust.
David Bovis
Consultant, Duxinaroe
A Leadership and Culture Change expert, David is the originator of BTFAŌäó and The Dux Model.
With a Masters in Applied Neuroscience from the Institute of Organisational Neuroscience, he is widely regarded as the ŌĆśGo-ToŌĆÖ expert in the field, recognised as an inspiring keynote speaker and change strategist.
He has an industrial engineering background, majoring in TPS / Lean. David worked his way up from his apprenticeship to earn his seat at the C-suite table. His career spans several industries, including Automotive, Aerospace, Defence, Space, Heavy Industries and Elec-Mech / polymer contract manufacture.
Published in LondonŌĆÖs Evening Standard quarterly business supplement, James CaanŌĆÖs ŌĆśYour businessŌĆÖ Magazine, ŌĆśQuality WorldŌĆÖ, the Lean Management Journal and Cambridge Universities ŌĆśPMAŌĆÖ, he works as comfortably with leaders from FTSE and Fortune 100 companies as he does owner-managers in SMEŌĆÖs. He is passionate about helping leaders understand the neurological root cause of a high-performance culture and sustainable change, in business.
Session | Own Your Autonomy ŌĆō The Importance of Autonomy in Project Management
#OwnYourAutonomy is aiming to be a global APM initiative to position everyone to take a more conscious role in their decision making process leading to increased outcomes for everyone and contribute to ŌĆ£a world in which all projects succeedŌĆØ.
We want everyone to join the journey.
#OwnYourAutonomy is the culmination of 3 years of collaborative exploration within the Leadership Focus Group which is part of the APM People Interest Network. The work has been pulled together using the 5 HPTM® Systems and the BTFA neuroscience leadership programme.
https://www.linkedin.com/showcase/apm-people-network/about/A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...



A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...Beena E S
╠²
A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by Aaron ShepardSOCIAL CHANGE(a change in the institutional and normative structure of societ...



SOCIAL CHANGE(a change in the institutional and normative structure of societ...DrNidhiAgarwal
╠²
This PPT is showing the effect of social changes in human life and it is very understandable to the students with easy language.in this contents are Itroduction, definition,Factors affecting social changes ,Main technological factors, Social change and stress , what is eustress and how social changes give impact of the human's life.The Dravidian Languages: Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Malayalam, Brahui, Kuvi, Tulu



The Dravidian Languages: Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Malayalam, Brahui, Kuvi, TuluDrIArulAram
╠²
The Dravidian Languages by Arul AramBlind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...



Blind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...Ajaz Hussain
╠²
This presentation delves into the systemic blind spots within pharmaceutical science and regulatory systems, emphasizing the significance of "inactive ingredients" and their influence on therapeutic equivalence. These blind spots, indicative of normalized systemic failures, go beyond mere chance occurrences and are ingrained deeply enough to compromise decision-making processes and erode trust.
Historical instances like the 1938 FD&C Act and the Generic Drug Scandals underscore how crisis-triggered reforms often fail to address the fundamental issues, perpetuating inefficiencies and hazards.
The narrative advocates a shift from reactive crisis management to proactive, adaptable systems prioritizing continuous enhancement. Key hurdles involve challenging outdated assumptions regarding bioavailability, inadequately funded research ventures, and the impact of vague language in regulatory frameworks.
The rise of large language models (LLMs) presents promising solutions, albeit with accompanying risks necessitating thorough validation and seamless integration.
Tackling these blind spots demands a holistic approach, embracing adaptive learning and a steadfast commitment to self-improvement. By nurturing curiosity, refining regulatory terminology, and judiciously harnessing new technologies, the pharmaceutical sector can progress towards better public health service delivery and ensure the safety, efficacy, and real-world impact of drug products.Eng7-Q4-Lesson 1 Part 1 Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and T...



Eng7-Q4-Lesson 1 Part 1 Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and T...sandynavergas1
╠²
Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and Technical TermsKaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...Association for Project Management
╠²
Gas Gangrene........................pptx
- 1. Gas Gangrene
- 2. ŌܽGangrene refers to the death of body tissue due to either a lack of blood flow or a serious bacterial infection. Gangrene commonly affects the extremities, including your toes, fingers and limbs, but it can also occur in your muscles and internal organs.
- 3. ŌܽTypes of gangrene:- Ōܽ1.Dry gangrene. Ōܽ2.Wet gangrene. Ōܽ3.Gas gangrene. Ōܽ4.Internal gangrene. Ōܽ5.FournierŌĆÖs gangrene.
- 4. DEFINITION: ŌܽIt is a highly fatal, rapidly spreading infection caused By clostridial organisms which results in myonecrosis. ŌܽGas gangrene also known as Clostridial myositis, clostridial myonecrosis, infective gangrene of the muscles.
- 6. AETIOLOGY: ŌܽThe disease is caused by 1. Clostridium perfringens ( Clostridium.welchii)- the commonest organism (60%). Other organisms are 2. Clostridium septicum 3.Clostridium oedematiens 4.Clostridium histolyticum. These are gram-positive, anaerobic spore-bearing bacilli.
- 7. SOURCE OF INFECTION: ŌܽManured soil or cultivated soil, normal intestines.
- 8. RISK GROUP: ŌܽIn patients who have had lower limb amputations performed for ischaemic gangrene, infection can occur from patient's own bowel organisms. ŌܽHigh velocity gun shot wounds with perforation of hollow viscus are also associated with risk of developing gas gangrene (military wound). ŌܽImmunocompromised patients are at risk.
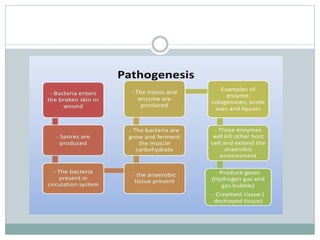
- 11. ŌܽToxins and their effect: Lecithinase Dermonecrosis ,Hemolysis Beta toxins Necrosis of tissue proteinase Breakdown of collagen fibre Hyaluronidase Break the cement substance of muscle cell
- 12. CLINICAL FEATURES: Ōܽ Severe pain and gross oedema of the wound. Ōܽ Sutured wound is under tension. Ōܽ Thin brownish fluid escapes which has sickly sweet odour. Ōܽ Palpable crepitus . Ōܽ Colour changes in the muscles. Ōܽ Skin becomes khaki-coloured due to haemolysis. Ōܽ Anxious and alert Ōܽ Toxic and ill Ōܽ Rapid increase in the pulse rate Ōܽ Hypotension due to suppression of adrenals Ōܽ Vomiting Ōܽ Low grade fever
- 13. DIAGNOSIS: ŌܽTo examine the pus under microscope after staining with Giemsa stain. ŌܽPresence of gas indicates anaerobic metabolism. ŌܽAnaerobic streptococci also produce gas.
- 14. PROPHYLAXIS: 1. Debridement: 2. Prophylactic antibiotics: 3. Judicious and minimal use of tourniquet: If possible, 4. Gentle but effective application of plaster cast
- 15. TREATMENT: ŌĆó Emergency surgery which includes excision of all dead muscles and necrotic tissues by using generous, long incisions-debridement. ŌĆó Penicillin to be continued. ŌĆó Blood transfusions before, during and after surgery. ŌĆó Polyvalent anti-gas gangrene serum. ŌĆó Hyperbaric oxygen will reduce the amount of toxin produced by the organisms (controversial). ŌĆó Do not hesitate to amputate if it saves the life, because this is the only measure in late cases.
- 16. HOMOEOPATHIC TREATMENT: Ōܽ-Arsenicum -Crotalus -Secale -Carbo vegetabilis -Lachesis mutus -Polygonum punctatum -Sulphuricum acidum

























