hbs ppt.pdfgjzgkxhkhkluyktdkgkhdulfttdlhx
0 likes59 views
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by cognitive and behavioral impairments, resulting in significant social and occupational dysfunction. It affects approximately 5.3 million people in the U.S. and is associated with various risk factors including age, genetics, and vascular diseases. The disease is characterized by the presence of neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the brain, leading to symptoms like memory loss, behavioral changes, and functional decline.
1 of 16
Download to read offline













Ad
Recommended
Pathophysiology and management of alzheimer's disease
Pathophysiology and management of alzheimer's diseaseSoujanya Pharm.D
?
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder leading to cognitive and behavioral impairments, primarily characterized by memory loss, confusion, and difficulties in daily functioning. With increasing age as a significant risk factor, AD has multiple stages from pre-clinical to end-stage, eventually resulting in complete dependence on caregivers. Management includes pharmacological treatments like cholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA receptor antagonists aimed at improving symptoms and quality of life.Presentation for Alzheimers Disease.pptx
Presentation for Alzheimers Disease.pptxravisutar1
?
Alzheimer's disease is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by cognitive and behavioral impairment. It results from an increase in beta-amyloid protein in the brain that leads to nerve cell death. There are two signature lesions in Alzheimer's - neuritic plaques consisting of beta-amyloid deposits outside nerve cells and neurofibrillary tangles of tau protein inside nerve cells. Symptoms include memory loss, confusion, mood changes and difficulty performing daily tasks. Diagnosis involves tests such as brain imaging, lumbar puncture and blood tests. Treatment focuses on maintaining brain function and includes cholinesterase inhibitors, memantine, supportive care and managing behavioral issues.Alzheimers Disease
Alzheimers DiseaseSri Ramachandra University
?
1. Alzheimer's disease is a progressive brain disorder that causes memory loss and cognitive decline, and is the most common form of dementia.
2. It results from an increase in beta-amyloid proteins in the brain that leads to nerve cell death. The disease is incurable and causes impairment in memory, reasoning, language, and perception.
3. Risk factors include age over 65, genetics, hypertension, high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, alcohol use, and mild cognitive impairment. The disease is characterized by two lesions - neuritic plaques containing beta-amyloid protein and neurofibrillary tangles containing tau protein.Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's diseaseDr. Koppala R.V.S. Chaitanya
?
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive brain disorder that destroys memory and thinking skills. It is the most common form of dementia. There is no cure for Alzheimer's, but medications and lifestyle interventions can temporarily slow the worsening of symptoms. The disease is caused by plaques and tangles that build up in the brain, resulting in the loss of connections between neurons. Early symptoms include memory loss and problems with thinking and language, while later stages involve the loss of motor skills and ability to communicate. Current treatments approved by the FDA include cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine, which can temporarily slow cognitive decline.Alzheimers disease by Ritika soni
Alzheimers disease by Ritika soniShimla
?
Ms. Ritika Soni presented on Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's is a progressive brain disorder that causes memory loss and cognitive decline. It was first described by Dr. Alois Alzheimer in 1906 from examining a patient with unusual brain abnormalities. The causes are not fully known but risk factors include age, family history, and head injuries. Diagnosis involves cognitive assessments and brain imaging. Currently, there is no cure, but medications and caregiving can temporarily improve symptoms.ALZHEIMER'S DEMENTIA anu_11034nhjjjjjjjjkk5.pptx
ALZHEIMER'S DEMENTIA anu_11034nhjjjjjjjjkk5.pptxShanuSoni7
?
The document provides an overview of Alzheimer's disease, defining it as a type of dementia characterized by progressive cognitive decline and outlining its symptoms, epidemiology, etiology, and risk factors. Key points include the role of genetics, neuropathology, neurotransmitter changes, and the importance of age and education as risk factors. It also discusses clinical features, including memory impairment and neuropsychiatric symptoms, and emphasizes the need for neuroimaging and assessments to differentiate it from other cognitive disorders.Alzheimers presentation.docx (1)
Alzheimers presentation.docx (1)Ashwani Kumar
?
This document discusses Alzheimer's disease (AD), including its causes, symptoms, stages of progression, diagnosis, and treatment options. Some key points:
- AD is characterized by amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the brain that are associated with loss of neurons and cognitive decline. It is generally diagnosed in those over 65 and causes memory loss and impaired thinking.
- Symptoms progress from mild memory loss to severe cognitive impairment. Stages include mild, moderate and severe.
- Risk factors include age, family history and genetic factors like the APOE gene. Diagnosis involves cognitive tests and brain imaging.
- Current treatments aim to slow progression but do not stop or cure the diseaseAlzheimers presentation.docx
Alzheimers presentation.docxteredeloscobos
?
This document discusses Alzheimer's disease, including its causes, symptoms, stages of progression, diagnosis, current treatments, and potential new treatments in development. Specifically, it describes how Alzheimer's is characterized by beta-amyloid plaque and tau protein tangle buildup in the brain, outlines the four stages of the disease and their symptoms, and discusses several FDA-approved medications commonly used to treat symptoms, including Aricept, Exelon, Razadyne, and Namenda. It also mentions two new compounds in clinical trials, a beta-secretase inhibitor and NIC5-15, that may help slow the disease's progression.Alzheimers presentation.docx
Alzheimers presentation.docxHena Jawaid
?
1) Alzheimer's disease is a progressive brain disorder that destroys memory and thinking skills. It was first described by Alois Alzheimer in 1906 and is the most common form of dementia.
2) The disease is characterized by beta-amyloid plaques and tau protein tangles that build up in the brain, resulting in the loss of connections between neurons and death of brain cells. This leads to the symptoms of impaired memory, thinking, and behavior.
3) While the causes of Alzheimer's are not fully known, genetic and environmental factors are believed to play a role. Risk increases significantly with age, though early-onset Alzheimer's can occur much earlier. There is currently no cure for the disease.alzheimersdisease final.pptx
alzheimersdisease final.pptxKomal Upreti
?
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive brain disorder that causes memory loss and cognitive decline. It was first described by Alois Alzheimer in 1906 from examining brain tissue of a deceased patient. The causes are unknown but risk factors include age, family history, and head injuries. Pathologically, it involves the buildup of beta-amyloid plaques and tau protein tangles in the brain which destroy connections between neurons. There is no cure and the prognosis is a gradual worsening of symptoms ultimately leading to death, on average within 7-10 years of diagnosis.Yoga for Alzheimer's Disease
Yoga for Alzheimer's DiseaseHealth Education Library for People
?
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive, degenerative brain disorder leading to memory impairment and cognitive decline, often associated with factors such as age, hypertension, and genetics. Symptoms include cognitive deficits like memory loss and disorientation, as well as non-cognitive symptoms such as depression and behavioral disturbances. Diagnosis typically involves detailed patient history, family input, laboratory tests to rule out other conditions, and imaging assessments like CT or MRI scans.Alzheimer
AlzheimerAmira Badr
?
This document provides an overview of Alzheimer's disease including its causes, symptoms, stages, diagnosis, and treatment approaches. It discusses how Alzheimer's is characterized by plaques and tangles in the brain made up of beta-amyloid and tau proteins. Current treatment aims to improve cognitive function and behaviors through cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine, though none can stop or reverse the disease. Non-pharmacological interventions like education, communication, and stimulation therapies may provide additional support.ALZHEIMERS DISEASE.pptx
ALZHEIMERS DISEASE.pptxpunith p
?
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia, characterized by progressive memory loss, impaired thinking, and personality changes, with degeneration of neurons and presence of neurofibrillary tangles and plaques. The etiology remains unknown, and it predominantly affects older adults, with an estimated 4.5 million Americans currently affected and projections of 13.2 million by 2050. Diagnosis is primarily based on clinical evaluation and brain imaging, as there is no definitive cure, making caregiving essential in managing the disease's progression.Alzheimer's disease.pptx
Alzheimer's disease.pptxAman Kumar
?
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive and irreversible neurodegenerative condition characterized by the destruction of neurons in brain areas responsible for memory, language, and behavior due to the formation of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. Early symptoms include short-term memory loss and difficulty performing routine tasks, which worsen over time, leading to severe impairment and personality changes. Diagnosis involves physical exams and imaging tests, while treatment options include cholinesterase inhibitors and drugs aimed at reducing beta-amyloid plaques.Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's diseaseSanil Varghese
?
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive brain disorder that causes memory loss and cognitive decline. It was first described by Alois Alzheimer in 1906 after examining brain tissue from a deceased patient. The disease results from the buildup of beta-amyloid plaques and tau protein tangles in the brain, which damage and kill neurons. Risk factors include age, family history, and genetic factors. There is no cure for Alzheimer's, but medications and caregiving can temporarily ease symptoms.Tomser Ali Group No 22 AD.pptxAnxiety-Understanding-and-Managing-It.pptx
Tomser Ali Group No 22 AD.pptxAnxiety-Understanding-and-Managing-It.pptxneestom1998
?
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder causing significant cognitive and behavioral impairments, primarily affecting individuals over 65. Symptoms range from memory loss and confusion in early stages to severe dependence and inability to communicate in later stages, with no known cure and various risk factors including age, genetics, and lifestyle. Management focuses on maintaining brain function and quality of life through pharmacological treatments like cholinesterase inhibitors to alleviate symptoms.Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease SwalihaK
?
Alzheimer's disease is a degenerative brain disorder characterized by progressive memory loss, cognitive decline, and personality changes, primarily affecting older adults. First described by Dr. Alois Alzheimer in 1906, it is associated with the accumulation of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the brain, along with various risk factors including age, hypertension, and genetics. Diagnosis involves a combination of psychiatric assessments and imaging techniques, and while there is no cure, treatments focus on enhancing cognition and maintaining quality of life.Alzheimers disease and its treatments
Alzheimers disease and its treatmentsRavish Yadav
?
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia, characterized by progressive memory loss and cognitive decline due to the accumulation of beta-amyloid protein and tau tangles in the brain. The disease progresses through stages from mild memory impairment to severe incapacitation, requiring total care, and is diagnosed via clinical assessments and imaging techniques. While there is currently no cure, treatments such as cholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA antagonists may help manage symptoms and slow progression.Overview of Alzheimer's disease
Overview of Alzheimer's diseaseVIJAYRAJA DHANRAJ
?
Alzheimer's disease is an irreversible and progressive brain disorder that leads to memory loss and cognitive decline, primarily affecting those aged 65 and older. It is characterized by the presence of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, which disrupt neuronal function and communication. The prevalence of Alzheimer's is projected to significantly increase, with an estimated 115.4 million cases expected by 2050.Alzheimer's disease.pptx
Alzheimer's disease.pptxChirayuRegmi2
?
Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of dementia. It was first described in 1907 when a woman exhibited a progressive dementia over 5 years. It mostly affects those over age 60, with rates of affected individuals rising significantly with age. Risk factors include family history, depression, and lower education. Clinically it presents with amnesia, language problems, and cognitive decline. Diagnosis involves clinical evaluation and tests of cognition along with ruling out other conditions. Pathology shows brain atrophy and plaques and tangles in brain tissue. Current treatments can provide mild cognitive benefits but do not stop progression of the disease.Alzheimer's Disease and its pathophysiology
Alzheimer's Disease and its pathophysiologyAchyut Adhikari
?
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia in older adults, characterized by a progressive decline in cognitive functions, including memory, thinking, and language. The disease's pathophysiology involves the abnormal accumulation of amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain, leading to neuronal damage and eventual brain shrinkage. While there is no cure for AD, treatments focus on symptom management, and lifestyle changes may reduce the risk of developing the disease.Alzheimer disease
Alzheimer diseaseDr. Ramesh Bhandari
?
The document discusses Alzheimer's disease, a progressive form of dementia characterized by memory loss and cognitive decline, primarily affecting older adults. It outlines the causes, symptoms, neurodegenerative processes, and treatment options for Alzheimer's, emphasizing the importance of managing both cognitive and behavioral symptoms. Diagnosis involves a combination of patient history, neurological exams, and imaging tools, while management focuses on symptom treatment and quality of life improvements.Clin Neuro Dementia Alz Lec.
Clin Neuro Dementia Alz Lec.Shaikhani.
?
The document discusses dementia and Alzheimer's disease. It defines dementia as acquired intellectual impairment affecting social and vocational function. Alzheimer's disease and vascular disease are the most common causes. A clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's requires cognitive impairment in at least two areas along with progressive worsening of memory and cognition. Pathologically, Alzheimer's is characterized by neuronal loss, neurofibrillary tangles, and senile plaques composed of amyloid beta protein. Treatment focuses on symptom management with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors or NMDA receptor antagonists.Alzheimer'S Diseases
Alzheimer'S DiseasesAlmasMajeeth
?
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive brain disorder that destroys memory and thinking skills. It is the most common cause of dementia among older adults. The main risk factor is increasing age, and it results from changes in the brain that affect memory, thinking, and behavior. Symptoms include memory loss and difficulties with problem-solving, planning, and language. It is caused by beta-amyloid plaques and tau tangles that interfere with communication between brain cells. There is no cure for Alzheimer's, but treatments can temporarily slow the worsening of dementia symptoms.Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's diseaseMuhammad Ahsan
?
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder leading to dementia, primarily affecting individuals over 65, with an anticipated increase in prevalence globally. Key risk factors include age, gender, race, and family history, while pathophysiology involves amyloid plaques, neurofibrillary tangles, and neuronal degeneration. Current treatment options are varied, focusing on pharmacological and non-pharmacological management, as well as future research into vaccines and gene therapy.LECTURE 8- Dementia DR SHAHB- DR AMAL.pptx
LECTURE 8- Dementia DR SHAHB- DR AMAL.pptxRnoun
?
The document provides an extensive overview of dementia, emphasizing the various forms, causes, and their effects on cognitive function, particularly highlighting Alzheimer's disease and frontotemporal dementia. Key statistics include that dementia affects over 4 million Americans, with significant healthcare costs, and discusses diagnostic criteria, genetic factors, and the progression of symptoms. It outlines the neuropathological changes associated with these conditions, such as the presence of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, and explores different types of dementia including vascular dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies.Neurodegenerative diseases
Neurodegenerative diseases Fabio Grubba
?
This document discusses neurodegenerative diseases, focusing on Alzheimer's disease. It defines neurodegeneration as the progressive loss of neurons, and notes several common neurodegenerative disorders like Parkinson's, Alzheimer's and Huntington's. For Alzheimer's specifically, it describes the disease stages from pre-dementia to advanced, symptoms like memory loss and cognitive decline, pathological features like amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, potential causes like the amyloid and tau hypotheses, and methods of diagnosis including cognitive testing and brain imaging.527751381-Parkinson-Disease-狠狠撸s (1).pdf
527751381-Parkinson-Disease-狠狠撸s (1).pdfSKGAMING32
?
Parkinson's disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by motor symptoms such as tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia, primarily caused by degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons. Risk factors include age, heredity, and environmental exposures, while complications can involve cognitive decline and psychiatric issues. Treatment options range from medication, notably levodopa, to surgical interventions like deep brain stimulation and supportive therapies such as physiotherapy.merged.pdfcvvbbbbbbbbbbbbbhhhbbbbbbbbbiydydd
merged.pdfcvvbbbbbbbbbbbbbhhhbbbbbbbbbiydyddSKGAMING32
?
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by cognitive decline, behavioral impairment, and social dysfunction, ultimately leading to nerve cell death due to β-amyloid protein accumulation. It affects over 5 million people in the U.S. and is linked to various risk factors including age, genetics, and vascular diseases. Treatment options include cholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA receptor antagonists to manage symptoms, but no cure currently exists.More Related Content
Similar to hbs ppt.pdfgjzgkxhkhkluyktdkgkhdulfttdlhx (20)
Alzheimers presentation.docx
Alzheimers presentation.docxHena Jawaid
?
1) Alzheimer's disease is a progressive brain disorder that destroys memory and thinking skills. It was first described by Alois Alzheimer in 1906 and is the most common form of dementia.
2) The disease is characterized by beta-amyloid plaques and tau protein tangles that build up in the brain, resulting in the loss of connections between neurons and death of brain cells. This leads to the symptoms of impaired memory, thinking, and behavior.
3) While the causes of Alzheimer's are not fully known, genetic and environmental factors are believed to play a role. Risk increases significantly with age, though early-onset Alzheimer's can occur much earlier. There is currently no cure for the disease.alzheimersdisease final.pptx
alzheimersdisease final.pptxKomal Upreti
?
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive brain disorder that causes memory loss and cognitive decline. It was first described by Alois Alzheimer in 1906 from examining brain tissue of a deceased patient. The causes are unknown but risk factors include age, family history, and head injuries. Pathologically, it involves the buildup of beta-amyloid plaques and tau protein tangles in the brain which destroy connections between neurons. There is no cure and the prognosis is a gradual worsening of symptoms ultimately leading to death, on average within 7-10 years of diagnosis.Yoga for Alzheimer's Disease
Yoga for Alzheimer's DiseaseHealth Education Library for People
?
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive, degenerative brain disorder leading to memory impairment and cognitive decline, often associated with factors such as age, hypertension, and genetics. Symptoms include cognitive deficits like memory loss and disorientation, as well as non-cognitive symptoms such as depression and behavioral disturbances. Diagnosis typically involves detailed patient history, family input, laboratory tests to rule out other conditions, and imaging assessments like CT or MRI scans.Alzheimer
AlzheimerAmira Badr
?
This document provides an overview of Alzheimer's disease including its causes, symptoms, stages, diagnosis, and treatment approaches. It discusses how Alzheimer's is characterized by plaques and tangles in the brain made up of beta-amyloid and tau proteins. Current treatment aims to improve cognitive function and behaviors through cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine, though none can stop or reverse the disease. Non-pharmacological interventions like education, communication, and stimulation therapies may provide additional support.ALZHEIMERS DISEASE.pptx
ALZHEIMERS DISEASE.pptxpunith p
?
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia, characterized by progressive memory loss, impaired thinking, and personality changes, with degeneration of neurons and presence of neurofibrillary tangles and plaques. The etiology remains unknown, and it predominantly affects older adults, with an estimated 4.5 million Americans currently affected and projections of 13.2 million by 2050. Diagnosis is primarily based on clinical evaluation and brain imaging, as there is no definitive cure, making caregiving essential in managing the disease's progression.Alzheimer's disease.pptx
Alzheimer's disease.pptxAman Kumar
?
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive and irreversible neurodegenerative condition characterized by the destruction of neurons in brain areas responsible for memory, language, and behavior due to the formation of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. Early symptoms include short-term memory loss and difficulty performing routine tasks, which worsen over time, leading to severe impairment and personality changes. Diagnosis involves physical exams and imaging tests, while treatment options include cholinesterase inhibitors and drugs aimed at reducing beta-amyloid plaques.Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's diseaseSanil Varghese
?
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive brain disorder that causes memory loss and cognitive decline. It was first described by Alois Alzheimer in 1906 after examining brain tissue from a deceased patient. The disease results from the buildup of beta-amyloid plaques and tau protein tangles in the brain, which damage and kill neurons. Risk factors include age, family history, and genetic factors. There is no cure for Alzheimer's, but medications and caregiving can temporarily ease symptoms.Tomser Ali Group No 22 AD.pptxAnxiety-Understanding-and-Managing-It.pptx
Tomser Ali Group No 22 AD.pptxAnxiety-Understanding-and-Managing-It.pptxneestom1998
?
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder causing significant cognitive and behavioral impairments, primarily affecting individuals over 65. Symptoms range from memory loss and confusion in early stages to severe dependence and inability to communicate in later stages, with no known cure and various risk factors including age, genetics, and lifestyle. Management focuses on maintaining brain function and quality of life through pharmacological treatments like cholinesterase inhibitors to alleviate symptoms.Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease SwalihaK
?
Alzheimer's disease is a degenerative brain disorder characterized by progressive memory loss, cognitive decline, and personality changes, primarily affecting older adults. First described by Dr. Alois Alzheimer in 1906, it is associated with the accumulation of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the brain, along with various risk factors including age, hypertension, and genetics. Diagnosis involves a combination of psychiatric assessments and imaging techniques, and while there is no cure, treatments focus on enhancing cognition and maintaining quality of life.Alzheimers disease and its treatments
Alzheimers disease and its treatmentsRavish Yadav
?
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia, characterized by progressive memory loss and cognitive decline due to the accumulation of beta-amyloid protein and tau tangles in the brain. The disease progresses through stages from mild memory impairment to severe incapacitation, requiring total care, and is diagnosed via clinical assessments and imaging techniques. While there is currently no cure, treatments such as cholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA antagonists may help manage symptoms and slow progression.Overview of Alzheimer's disease
Overview of Alzheimer's diseaseVIJAYRAJA DHANRAJ
?
Alzheimer's disease is an irreversible and progressive brain disorder that leads to memory loss and cognitive decline, primarily affecting those aged 65 and older. It is characterized by the presence of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, which disrupt neuronal function and communication. The prevalence of Alzheimer's is projected to significantly increase, with an estimated 115.4 million cases expected by 2050.Alzheimer's disease.pptx
Alzheimer's disease.pptxChirayuRegmi2
?
Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of dementia. It was first described in 1907 when a woman exhibited a progressive dementia over 5 years. It mostly affects those over age 60, with rates of affected individuals rising significantly with age. Risk factors include family history, depression, and lower education. Clinically it presents with amnesia, language problems, and cognitive decline. Diagnosis involves clinical evaluation and tests of cognition along with ruling out other conditions. Pathology shows brain atrophy and plaques and tangles in brain tissue. Current treatments can provide mild cognitive benefits but do not stop progression of the disease.Alzheimer's Disease and its pathophysiology
Alzheimer's Disease and its pathophysiologyAchyut Adhikari
?
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia in older adults, characterized by a progressive decline in cognitive functions, including memory, thinking, and language. The disease's pathophysiology involves the abnormal accumulation of amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain, leading to neuronal damage and eventual brain shrinkage. While there is no cure for AD, treatments focus on symptom management, and lifestyle changes may reduce the risk of developing the disease.Alzheimer disease
Alzheimer diseaseDr. Ramesh Bhandari
?
The document discusses Alzheimer's disease, a progressive form of dementia characterized by memory loss and cognitive decline, primarily affecting older adults. It outlines the causes, symptoms, neurodegenerative processes, and treatment options for Alzheimer's, emphasizing the importance of managing both cognitive and behavioral symptoms. Diagnosis involves a combination of patient history, neurological exams, and imaging tools, while management focuses on symptom treatment and quality of life improvements.Clin Neuro Dementia Alz Lec.
Clin Neuro Dementia Alz Lec.Shaikhani.
?
The document discusses dementia and Alzheimer's disease. It defines dementia as acquired intellectual impairment affecting social and vocational function. Alzheimer's disease and vascular disease are the most common causes. A clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's requires cognitive impairment in at least two areas along with progressive worsening of memory and cognition. Pathologically, Alzheimer's is characterized by neuronal loss, neurofibrillary tangles, and senile plaques composed of amyloid beta protein. Treatment focuses on symptom management with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors or NMDA receptor antagonists.Alzheimer'S Diseases
Alzheimer'S DiseasesAlmasMajeeth
?
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive brain disorder that destroys memory and thinking skills. It is the most common cause of dementia among older adults. The main risk factor is increasing age, and it results from changes in the brain that affect memory, thinking, and behavior. Symptoms include memory loss and difficulties with problem-solving, planning, and language. It is caused by beta-amyloid plaques and tau tangles that interfere with communication between brain cells. There is no cure for Alzheimer's, but treatments can temporarily slow the worsening of dementia symptoms.Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's diseaseMuhammad Ahsan
?
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder leading to dementia, primarily affecting individuals over 65, with an anticipated increase in prevalence globally. Key risk factors include age, gender, race, and family history, while pathophysiology involves amyloid plaques, neurofibrillary tangles, and neuronal degeneration. Current treatment options are varied, focusing on pharmacological and non-pharmacological management, as well as future research into vaccines and gene therapy.LECTURE 8- Dementia DR SHAHB- DR AMAL.pptx
LECTURE 8- Dementia DR SHAHB- DR AMAL.pptxRnoun
?
The document provides an extensive overview of dementia, emphasizing the various forms, causes, and their effects on cognitive function, particularly highlighting Alzheimer's disease and frontotemporal dementia. Key statistics include that dementia affects over 4 million Americans, with significant healthcare costs, and discusses diagnostic criteria, genetic factors, and the progression of symptoms. It outlines the neuropathological changes associated with these conditions, such as the presence of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, and explores different types of dementia including vascular dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies.Neurodegenerative diseases
Neurodegenerative diseases Fabio Grubba
?
This document discusses neurodegenerative diseases, focusing on Alzheimer's disease. It defines neurodegeneration as the progressive loss of neurons, and notes several common neurodegenerative disorders like Parkinson's, Alzheimer's and Huntington's. For Alzheimer's specifically, it describes the disease stages from pre-dementia to advanced, symptoms like memory loss and cognitive decline, pathological features like amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, potential causes like the amyloid and tau hypotheses, and methods of diagnosis including cognitive testing and brain imaging.More from SKGAMING32 (10)
527751381-Parkinson-Disease-狠狠撸s (1).pdf
527751381-Parkinson-Disease-狠狠撸s (1).pdfSKGAMING32
?
Parkinson's disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by motor symptoms such as tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia, primarily caused by degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons. Risk factors include age, heredity, and environmental exposures, while complications can involve cognitive decline and psychiatric issues. Treatment options range from medication, notably levodopa, to surgical interventions like deep brain stimulation and supportive therapies such as physiotherapy.merged.pdfcvvbbbbbbbbbbbbbhhhbbbbbbbbbiydydd
merged.pdfcvvbbbbbbbbbbbbbhhhbbbbbbbbbiydyddSKGAMING32
?
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by cognitive decline, behavioral impairment, and social dysfunction, ultimately leading to nerve cell death due to β-amyloid protein accumulation. It affects over 5 million people in the U.S. and is linked to various risk factors including age, genetics, and vascular diseases. Treatment options include cholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA receptor antagonists to manage symptoms, but no cure currently exists.Lecture One.pdfmdndnddndndndndndndndjdjfjfj
Lecture One.pdfmdndnddndndndndndndndjdjfjfjSKGAMING32
?
The document outlines the physiology of blood, detailing its components, functions, and the processes involved in red blood cell formation and metabolism. It discusses the composition of blood, including plasma proteins and the significance of red blood cells in oxygen transport, as well as the impact of factors like anemia and polycythemia on circulatory health. Additionally, it covers the synthesis of hemoglobin and iron metabolism, emphasizing the role of various proteins and the importance of maintaining proper red blood cell levels in the body.Total protein in serum_20241110_145525_0000.pdf
Total protein in serum_20241110_145525_0000.pdfSKGAMING32
?
The document discusses the methods for estimating total protein levels in serum, specifically highlighting Kjeldahl's, Lowry's, and Biuret methods. It details the Biuret method as the most common, describing its procedure, reagents, and normal range values for serum proteins, identifying conditions for hypoproteinemia and hyperproteinemia. Additionally, it includes the calculation formula and steps for performing the test.a8 BSC BWM (BIOMEDICAL WASTE MANAGEMENT) .pptx
a8 BSC BWM (BIOMEDICAL WASTE MANAGEMENT) .pptxSKGAMING32
?
The Ministry of Environment & Forests in India published the Bio-Medical Waste Management Rules in 2016, which regulate the handling of biomedical waste across various health-related entities. Biomedical waste constitutes a minor proportion of total hospital waste, with most being general waste, while a smaller percentage includes hazardous categories such as infectious and chemical waste. India generates approximately 484 tons of biomedical waste per day, with only 447 tons treated, highlighting a significant issue with untreated waste.Presentation (2) (1).pptxUpload a presentation to download Abnormal morpholog...
Presentation (2) (1).pptxUpload a presentation to download Abnormal morpholog...SKGAMING32
?
Calibration is the process of adjusting laboratory instruments so their readings are accurate within a specified tolerance by comparing them to a known standard of higher accuracy. Calibration ensures measurements made with an instrument are accurate and consistent, and is usually performed annually or semi-annually on devices like pH meters, balances, scales, centrifuges and pipettes to check their accuracy and adjust them accordingly, thereby providing reliable experimental results.NABL.pdf NABL.pdfNABL.pdfNABL.NABL.pdfwwww
NABL.pdf NABL.pdfNABL.pdfNABL.NABL.pdfwwwwSKGAMING32
?
NABL is India's sole accreditation body authorized by the government to assess and accredit clinical laboratories. It conducts rigorous evaluations of laboratories' quality management systems, adherence to standards, and technical competence to ensure accurate testing and calibration. Receiving NABL accreditation establishes a laboratory's trustworthiness, benefits healthcare providers through superior results and international recognition, and benefits the public through assurance of accurate medical reports and tests.ftw.pdfThik h mai aa rha hu par presentation nhi dunga
ftw.pdfThik h mai aa rha hu par presentation nhi dungaSKGAMING32
?
This document provides instructions for various features in Microsoft Word, PowerPoint, and Excel. It explains how to create and format documents in Word, such as adding headers and footers. It also describes how to build presentations in PowerPoint, including adding slides and slide transitions. Finally, it outlines the basics of spreadsheets in Excel, such as entering and formatting data, copying and pasting cells, and printing worksheets.marcqi_blood_transfusion.pdfUNDERSTAND WORD FEATURE
marcqi_blood_transfusion.pdfUNDERSTAND WORD FEATURESKGAMING32
?
This document discusses strategies to reduce blood transfusions for patients undergoing hip and knee arthroplasty. It provides evidence that restrictive transfusion protocols with a threshold of 8 g/dL are safe based on multiple studies. Transfusions are associated with increased risks of infection, mortality and costs. The document reviews transfusion rates among MARCQI sites and recommends adoption of restrictive guidelines and use of tranexamic acid to reduce transfusions when possible.ftw SURAJ KUMAR.pdf: Better titles and descriptions lead to more readers
ftw SURAJ KUMAR.pdf: Better titles and descriptions lead to more readersSKGAMING32
?
Suraj Kumar is submitting a report for his BMLS 1st year course on the topics of word processing, building presentations, and the basics of spreadsheets. The document provides instructions on how to perform common tasks in Microsoft Word, PowerPoint, and Excel like creating and formatting documents, adding tables and images, building slideshows with transitions, and entering/editing cell data.Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
MULTI SENSORY EXPERIENCE DESIGN RESEARCH
MULTI SENSORY EXPERIENCE DESIGN RESEARCHSamuel Thuo
?
Excited to share insights from my Dissertation Thesis on Multisensory Experience Design in Art Museums, focusing on Nairobi, Kenya! I have to say that this is the work that set me on my current trajectory and led me to my current design philosophy of design for all senses.
Have you been to a #museum, wanted to touch an exhibit and there you saw an injunction, "Please don't touch"....or "Please speak softly",,,,or "Please no eating in the museum".....or "Please don't use strong perfume".... these injunctions have made museums to be mono-sensory experience oriented, alienating the visitors. These injunctions speak volumes of our innate and inherent desire to want to engage holistically with all our #senses with objects. This is a major problem especially in Kenya's museums, which is a paradox with its rich cultural, and anthropological exhibits that require engagement with all the senses.
Inspired by David Howes' insights from Concordia University, my thesis challenges this status quo by exploring historical precedents. Did you know that in the 18th century, museums encouraged multisensory interaction? Today, there's a global shift towards enhancing museum experiences through multisensory #design, yet Kenya's museums often lag behind international standards.
This research isn't just about aesthetics....it's about fostering meaningful, educational, and socially enriching experiences. By embracing multisensory design, museums can bridge cultural divides and create environments where every visitor feels welcomed and engaged. And want to go back.
Let's spark a conversation about the future of museum experiences. How can we leverage design to make cultural institutions more accessible and inspiring for all? Aimee White Visual Thinking, Graphic Design, Livermore
Aimee White Visual Thinking, Graphic Design, Livermoreaimeewhite13
?
Why Hire a professional Graphic Designer? Learn what makes great design and what it can do for your business.
Unified: Consistency brings trust, recognition, and recall.
If all your work can be recognized by the viewer as coming from you, they will more easily recognize you, gain a sense of trust in your business, and remember you and your message better.
Organized: Well designed content is clean and easy to take in. You want the audience to be able to quickly get your message
and have their eye drawn to elements in the order you choose by placement and scale.
White space is a good thing. It gives the eye room to rest
between elements and see your message as a whole.
Meaningful: Define your goals, your audience, and what critical information they need to know in order to act.
Genuine: Tell your story and engage your audience to
make them care about that information. The emotional
connection or human component is a powerful
compliment to analytical content.
Concept: With clear insight into your intent and your target audience’s needs and issues, design to solve the problems and bring clarity with a solution that’s valuable to the viewer.
Aimee White, Visual Thinking
for Design that Connects.Marketplaces to Buy and Sell Social Media Accounts.pdf
Marketplaces to Buy and Sell Social Media Accounts.pdfjamedthomsn
?
In the bustling world of social media marketing, having a solid Facebook presence can make all the difference. But who has time to build accounts from scratch? Enter SellsUSA, a popular platform known for offering verified, ready-to-use Facebook accounts. Whether you're a marketer, small business owner, or social media manager, buying Facebook accounts from a trusted site like SellsUSA can turbocharge your growth journey. But is it really the best option out there? Let’s dig deep into everything you need to know before making that purchase. Presentation3_architectural presentation case studypptx
Presentation3_architectural presentation case studypptxmaheshwarigarvit2006
?
a case study on house in india最新版美国威斯康星大学普拉特维尔分校毕业证(鲍奥笔毕业证书)原版定制
最新版美国威斯康星大学普拉特维尔分校毕业证(鲍奥笔毕业证书)原版定制taqyea
?
2025原版威斯康星大学普拉特维尔分校毕业证书pdf电子版【q薇1954292140】美国毕业证办理UWP威斯康星大学普拉特维尔分校毕业证书多少钱?【q薇1954292140】海外各大学Diploma版本,因为疫情学校推迟发放证书、证书原件丢失补办、没有正常毕业未能认证学历面临就业提供解决办法。当遭遇挂科、旷课导致无法修满学分,或者直接被学校退学,最后无法毕业拿不到毕业证。此时的你一定手足无措,因为留学一场,没有获得毕业证以及学历证明肯定是无法给自己和父母一个交代的。
【复刻威斯康星大学普拉特维尔分校成绩单信封,Buy University of Wisconsin-Platteville Transcripts】
购买日韩成绩单、英国大学成绩单、美国大学成绩单、澳洲大学成绩单、加拿大大学成绩单(q微1954292140)新加坡大学成绩单、新西兰大学成绩单、爱尔兰成绩单、西班牙成绩单、德国成绩单。成绩单的意义主要体现在证明学习能力、评估学术背景、展示综合素质、提高录取率,以及是作为留信认证申请材料的一部分。
威斯康星大学普拉特维尔分校成绩单能够体现您的的学习能力,包括威斯康星大学普拉特维尔分校课程成绩、专业能力、研究能力。(q微1954292140)具体来说,成绩报告单通常包含学生的学习技能与习惯、各科成绩以及老师评语等部分,因此,成绩单不仅是学生学术能力的证明,也是评估学生是否适合某个教育项目的重要依据!
我们承诺采用的是学校原版纸张(原版纸质、底色、纹路)我们工厂拥有全套进口原装设备,特殊工艺都是采用不同机器制作,仿真度基本可以达到100%,所有成品以及工艺效果都可提前给客户展示,不满意可以根据客户要求进行调整,直到满意为止!
【主营项目】
一、工作未确定,回国需先给父母、亲戚朋友看下文凭的情况,办理毕业证|办理文凭: 买大学毕业证|买大学文凭【q薇1954292140】威斯康星大学普拉特维尔分校学位证明书如何办理申请?
二、回国进私企、外企、自己做生意的情况,这些单位是不查询毕业证真伪的,而且国内没有渠道去查询国外文凭的真假,也不需要提供真实教育部认证。鉴于此,办理美国成绩单威斯康星大学普拉特维尔分校毕业证【q薇1954292140】国外大学毕业证, 文凭办理, 国外文凭办理, 留信网认证Exploring the Diverse Types of Textual Aids
Exploring the Diverse Types of Textual Aidsjenicahmendoza1
?
Exploring the Diverse Types of Textual AidsTransformative Storytelling_ Insights from the Sankofa Writing Intensive.pdf
Transformative Storytelling_ Insights from the Sankofa Writing Intensive.pdfDr. Rema
?
The intensive is structured around workshops and individual writing sessions to facilitate deep reflection and discovery. Participants engage with various genres, from memoirs to reflective essays, each chosen to amplify the introspective process.Simone Laubscher ABC: Redefining Sustainable Luxury in the UAE Fashion Scene
Simone Laubscher ABC: Redefining Sustainable Luxury in the UAE Fashion SceneSimone Laubscher ABC
?
Visionary designer Simone Laubscher ABC is making waves in the United Arab Emirates with her groundbreaking approach to fashion that combines haute couture with conscious living. Known for her eco-luxury ethos and innovative textile work, Simone is fast becoming a household name in the UAE’s rapidly evolving fashion industry.
Rooted in her global upbringing and commitment to sustainability, Simone Laubscher ABC brings a fresh perspective to the Middle Eastern fashion landscape. Her label seamlessly fuses the refinement of European tailoring with the rich cultural vibrancy of the Gulf, creating collections that are not only elegant but environmentally responsible.
Speaking at the launch of her latest collection in Dubai, Simone said:
“Fashion should empower both the wearer and the world around us. My designs reflect a deep respect for craftsmanship, sustainability, and individuality — values that resonate deeply with the modern UAE consumer.”
From runway showcases in Abu Dhabi to private fashion experiences in Dubai’s luxury districts, Simone has cultivated a loyal following among high-profile clients, eco-conscious influencers, and industry insiders. Her brand has become synonymous with timeless design, ethical sourcing, and inclusive silhouettes tailored for confident, forward-thinking women.
Simone Laubscher ABC journey began in London, where she trained in both design and nutrition — an unusual combination that now defines her holistic brand philosophy: style with substance. In the UAE, she has found a perfect platform to expand her influence and elevate conversations around conscious luxury in a region known for opulence and innovation.
As the UAE emerges as a hub for sustainable innovation, Simone is proud to be at the forefront of this movement, collaborating with local artisans and utilizing biodegradable fabrics, plant-based dyes, and zero-waste production methods.
Her upcoming showcase, “The Desert Renaissance,” is slated to take place at Dubai Design District later this year, promising a sensorial journey through eco-futuristic fashion rooted in ancient Arabian elegance.
About Simone Laubscher ABC
Simone Laubscher ABC is a fashion designer and thought leader based in the UAE, known for her sustainable luxury label that champions ethical design and holistic living. Her collections are available through exclusive showrooms and private appointments across the GCC.Quectel M10 AT commands Arduino Microcontroller
Quectel M10 AT commands Arduino MicrocontrollerAdamSunusiHaruna1
?
Quectel M10 AT commands Arduino Microcontroller 最新版西班牙拉蒙鲁尔大学毕业证(鲍搁尝毕业证书)原版定制
最新版西班牙拉蒙鲁尔大学毕业证(鲍搁尝毕业证书)原版定制Taqyea
?
无法毕业?鉴于此购买文凭【q薇1954292140】修改拉蒙鲁尔大学成绩单电子版gpa让学历更出色,URL文凭制作流程确保学历真实性,文凭购买,毕业证办理,文凭办理只是基础业务。【q薇1954292140】一比一还原国外大学毕业证,定制国外大学学历,制作国外大学文凭,复刻国外大学毕业证书。想要真实感受拉蒙鲁尔大学最新版毕业证图片的品质点击查看详解,学位证1:1完美还原海外各大学毕业材料上的工艺:水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠。文字图案浮雕、激光镭射、紫外荧光、温感、复印防伪等防伪工艺。
主营项目:
1、真实教育部国外学历学位认证《西班牙毕业文凭证书快速办理拉蒙鲁尔大学成绩单定制》【q微1954292140】《论文没过拉蒙鲁尔大学正式成绩单》,教育部存档,教育部留服网站100%可查.
2、办理URL毕业证,改成绩单《URL毕业证明办理拉蒙鲁尔大学留信网认证》【Q/WeChat:1954292140】Buy Universitat Ramon Llull Certificates《正式成绩单论文没过》,拉蒙鲁尔大学Offer、在读证明、学生卡、信封、证明信等全套材料,从防伪到印刷,从水印到钢印烫金,高精仿度跟学校原版100%相同.
3、真实使馆认证(即留学人员回国证明),使馆存档可通过大使馆查询确认.
4、留信网认证,国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书,留信网存档可查.
办理URL学历与学位证书投资未来的最佳途径【q微1954292140】办理西班牙URL本科学历,办理拉蒙鲁尔大学成绩单高质量保密的个性化服务高仿真还原西班牙文凭证书和外壳,定制西班牙拉蒙鲁尔大学成绩单和信封。毕业证丢失补办URL毕业证【q微1954292140】假文凭回国找工作拉蒙鲁尔大学offer/学位证学位认证知乎、留信官方学历认证(永久存档真实可查)采用学校原版纸张、特殊工艺完全按照原版一比一制作。帮你解决拉蒙鲁尔大学学历学位认证难题。
【如何快速办理《拉蒙鲁尔大学毕业证URL成绩单》Buy Universitat Ramon Llull Transcripts】
购买日韩成绩单、英国大学成绩单、美国大学成绩单、澳洲大学成绩单、加拿大大学成绩单(q微1954292140)新加坡大学成绩单、新西兰大学成绩单、爱尔兰成绩单、西班牙成绩单、德国成绩单。成绩单的意义主要体现在证明学习能力、评估学术背景、展示综合素质、提高录取率,以及是作为留信认证申请材料的一部分。
拉蒙鲁尔大学成绩单能够体现您的的学习能力,包括拉蒙鲁尔大学课程成绩、专业能力、研究能力。(q微1954292140)具体来说,成绩报告单通常包含学生的学习技能与习惯、各科成绩以及老师评语等部分,因此,成绩单不仅是学生学术能力的证明,也是评估学生是否适合某个教育项目的重要依据!
Buy Universitat Ramon Llull Diploma《正式成绩单论文没过》有文凭却得不到认证。又该怎么办?鉴于此,购买西班牙毕业证【q微1954292140】西班牙文凭购买,西班牙文凭购买,西班牙文凭定制,西班牙文凭补办。专业在线定制西班牙大学文凭,定做西班牙本科文凭,【q微1954292140】复制西班牙Universitat Ramon Llull completion letter。在线快速补办西班牙本科毕业证、硕士文凭证书,购买西班牙学位证、拉蒙鲁尔大学Offer,URL拉蒙鲁尔大学毕业证书多少钱。AI-Driven-Personalization-in-UX-Designing-for-One-in-a-Million.pdf
AI-Driven-Personalization-in-UX-Designing-for-One-in-a-Million.pdfSultan Shalakhti
?
Why you should attend this event
Talk Title: AI-Driven Personalization in UX: Designing for One in a Million
In this session, Sultan Shalakhti explores how artificial intelligence is reshaping user experience through smart, adaptive personalization. From e-commerce to banking, personalized design has become a key differentiator—when done right. Learn how to apply AI tools to enhance user journeys, balance personalization with privacy, and build experiences that feel uniquely human. This talk blends strategy, ethics, and real-world use cases for UX professionals ready to embrace the future.
?
????? ??????: ??????? ??????? ??????? ????????? ?? ????? ????????: ????? ???? ??? ??? ??? ???
??? ??????:
?????? ????? ????? ?? ??? ?????? ?? ???? ??? ??? ???? ?????? ????????? ????? ????? ???????? ?? ???? ??????? ????? ??????????. ?? ??????? ??????????? ??? ?????? ??????? ???? ??????? ?????? ?????? ?? ???? ???????—???? ??? ??? ?????? ?????? ??????. ?????? ??? ????? ????? ????? ?????? ????????? ?????? ??????? ???????? ?????? ??????? ??? ??????? ?????????? ????? ????? ????? ???? ????? ????????. ???? ???? ???? ??? ????????????? ???????????? ??????? ?????? ???????? ????????? ?? ???? UX.
What you will learn in this session
Understand the Core Concepts of AI-Driven Personalization
Explore UX Design Strategies for Hyper-Personalization
Identify Key Tools and Technologies Behind Personalization
Evaluate the Ethical and Privacy Considerations
Apply Personalization Tactics to Real UX ChallengesAd
hbs ppt.pdfgjzgkxhkhkluyktdkgkhdulfttdlhx
- 1. ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE Yash Tripathi BMLS Sec B 230612032159
- 2. DEFINITION: Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder, characterized by cognitive & behavioural impairment that significantly interferes with social & occupational functioning. Alzheimer’s disease is also known as senile dementia of the Alzheimer type (SDAT) or simply Alzheimer’s, the most common form of dementia. It is an incurable, degenerative, terminal disease. AD results from an increase in the production or accumulation of specific protein (β-amyloid protein) in the brain that leads to nerve cell death.
- 3. EPIDEMIOLOGY: ?According to 2015 report, AD affects 5.3 million people in US. ?AD was the 6th leading cause of death in 2015. ?AD and other dementias are more likely common in African Americans, than in whites. ?According to the WHO’s review in 2000, on the “global burden of dementia”: approximate rates of dementia are under 1% in persons aged 60-69 years and 39% in persons aged 90-95 years, prevalence doubles with every 5 years of age (within the above ranges).
- 4. ETIOLOGY: The exact etiology of Alzheimer’s disease is not known and associated with risk factors. But stated that there are several genetical and environmental factors have been explored as potential causes of the Alzheimer’s disease. Other factors include: 1. Advancing age 2. Family history 3. Trauma 4. Education 5. Vascular disease like stroke etc.
- 5. RISK FACTORS: The common risk factors for developing Alzheimer’s disease are: ?Increased age (over 65 years of age) ?Hypertension (high blood pressure) ?Increased cholesterol levels ?Coronary artery disease ?Diabetes Other risk factors are: ?Genetics ?Smoking and alcohol use ?Plasma homocysteine ?Down syndrome ?Mild cognitive impairment
- 6. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: The brain has billions of neurons, each with an axon and many dendrites. To stay healthy, neurons must communicate with each other, carry out metabolism and repair themselves. AD disrupts all three of these essential jobs. There are two signature lesions in Alzheimer’s disease. They are: 1. Neuritic plaques/ β-amyloid plaques, which are dense deposits of protein and cellular material that accumulate outside and around nerve cells. 2. Neurofibrillary tangles (NFT’s), which are twisted fibers that build up inside the nerve cell.
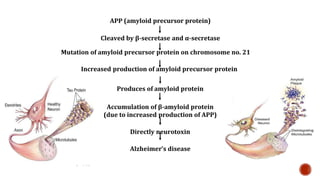
- 7. 1. NEURITIC PLAQUES: Deposits of a protein fragment called β-amyloid, that accumulates in the spaces between the nerve cells (neurons). APP (amyloid precursor protein) is the precursor of amyloid plaque. a) APP sticks through the neuron membrane. b) Enzymes like β-secretase and α-secretase cut the APP into fragments of protein (neurotoxic Aβ42 fragment), including β-amyloid. c) β-amyloid fragments come together in clumps to form plaques. In AD, many of these clumps form, disrupting the work of neurons. This affects the hippocampus and other areas of the cerebral cortex.
- 8. APP (amyloid precursor protein) Cleaved by β-secretase and α-secretase Mutation of amyloid precursor protein on chromosome no. 21 Increased production of amyloid precursor protein Produces of amyloid protein Accumulation of β-amyloid protein (due to increased production of APP) Directly neurotoxin Alzheimer’s disease
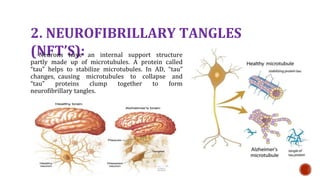
- 9. 2. NEUROFIBRILLARY TANGLES (NFT’S): Neurons have an internal support structure partly made up of microtubules. A protein called “tau” helps to stabilize microtubules. In AD, “tau” changes, causing microtubules to collapse and “tau” proteins clump together to form neurofibrillary tangles.
- 10. CONTD … Although autopsy studies show that most people develop some plaques & tangles as they age Those with AD tend to develop them far more & in a predictable pattern They develop in the areas important for memory before spreading to other regions Plaques & tangles disable/block communication among neurons Gradually spread to other areas of brain Causes symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease
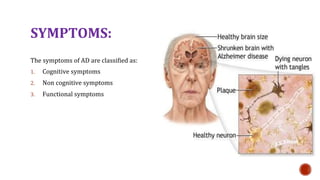
- 11. SYMPTOMS: The symptoms of AD are classified as: 1. Cognitive symptoms 2. Non cognitive symptoms 3. Functional symptoms
- 12. CONTD… 1. Cognitive symptoms: ? Memory loss (poor recall and losing items) ? Aphasia (circumlocution and anomia) ? Apraxia, agnosia, ? Disorientation (impaired perception of time and unable to recognize familiar people) ? Impaired executive function. 2. Non cognitive symptoms: ? Depression, psychotic (hallucination and delusions). symptoms ? Behavioural disturbances (physical and verbal aggression, motor hyperactivity, uncooperativeness, wandering, repetitive mannerisms and activities and combativeness). 3. Functional symptoms: ? Inability to care for self (dressing, bathing, eating etc.)
- 13. PHARMACOLOGICAL TREATMENT: 1. Cholinesterase inhibitors: MOA: These drugs selectively inhibit acetyl cholinesterase, the enzyme responsible for the destruction of acetyl choline. Thus, acetyl choline gets accumulated (improves Ach availability) and produces cholinergic effects. Acetyl CoA + Choline Choline acetyl transferase Acetyl choline (Ach) Acetyl cholinesterase Choline + Acetate Cholinesterase inhibitors (e.g. donepezil, rivastigmine, galantamine)
- 14. CONTD… 2. NMDA receptor antagonists (Memantine): MOA: The N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (also known as NMDA receptor) is a glutamate receptor and ion channel protein found in nerve cells. The NMDA receptor is very important in controlling synaptic plasticity and memory function. NMDA type glutamate receptors may be over activated in AD (glutamatergic excitotoxicity). Memantine binds preferentially to NMDA receptor and blocks it. Blocking usually occurs only under conditions of excessive stimulation and not under neurotransmission.
- 15. CONTD … Memantine Blocks NMDA receptor (blocks glutamate) Prevents too much calcium from moving into the brain cells Reduces excessive stimulation Reduces the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease ? ADRs: Hypertension, cataract, CVA, thromboembolism etc. ? Uses: It is commonly used for moderate-severe dementia in patients with AD. ? Dose: Memantine: 5mg OD (initial dose); 20mg/day (Max. dose)