Hydrology presentation
- 2. Water is constantly moving through the components of the water cycle. Precipitation: water that falls to the earth in the form of ice, rain, snow, sleet, hail, etc. Runoff: the process whereby water that falls to earth moves across the surface of the earth and eventually into bodies of water https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/c/c1/Precipitation_by_type.png https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/2b/View_of_urban_runoff_discharging_to_coastal_waters.jpg/200px-
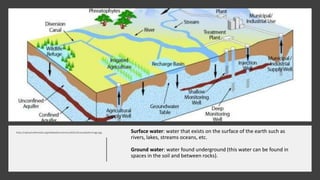
- 3. https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/b/b1/Groundwaterimage.jpg Surface water: water that exists on the surface of the earth such as rivers, lakes, streams oceans, etc. Ground water: water found underground (this water can be found in spaces in the soil and between rocks).
- 4. Evapotranspiration Transpiration: the process in the leaves of plants that releases water in the form of vapor (gas) into the atmosphere. Evaporation: the process whereby a substance changes from a liquid to a gas https://lemondeetnous.cafe-sciences.org/wp- content/uploads/sites/4/2016/04/evapotranspiration-300x248.gif https://dr282zn36sxxg.cloudfront.net/datastreams/f- d:ad4457d07b5d13b54eaea736942bafef1166b9930ebcdb39498f0e 3c%2BIMAGE_THUMB_POSTCARD_TINY%2BIMAGE_THUMB_POSTC ARD_TINY.1 https://images.pexels.com/photos/38435/leaf-rain-coffee-water- 38435.jpeg?auto=compress&cs=tinysrgb&fit=crop&h=627&w=1200
- 5. Condensation: the process whereby a substance changes from a gas to a liquid Percolation/Infiltration: the movement of water through the soil as water falls onto the earth. This leads to the recharge of groundwater https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d8/Condensation_on_water_bottle.jpg/1200px- Condensation_on_water_bottle.jpg https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/e2/Stormwater_Management_with_trees.webm/1280px--Stormwater_Management_with_trees.webm.jpg
- 7. Where is freshwater found? In the atmosphere as rain, clouds, snow etc. On Earthâs surface in rivers, lakes and oceans Below the surface as groundwater in aquifers and underground rivers http://www.thegeographeronline.net/uploads/2/6/6/2/26629356/8167998_orig.jpg?412
- 8. Wetlands âĒ Land that is covered with water much of the year is called wetland. âĒ Estuaries are wetlands. https://www.goodfreephotos.com/albums/other-landscapes/wetlands- landscape-under-the-clouds.jpg
- 9. Most of the water on Earth is salty Oceans hold 97.5% of the earths supply of water. https://c1.staticflickr.com/1/607/31520427614_ddb8a4c9f7_n.jpg
- 10. Ocean currents âĒ The movement of the ocean currents is affected by tides, winds, and temperature as well as the level of salt concentration in a given area (salinity). https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/cd/Circulation_of_Ocean_Currents_Ar ound_the_Western_Antarctic_Ice_Shelves.ogv/300px-- Circulation_of_Ocean_Currents_Around_the_Western_Antarctic_Ice_Shelves.ogv.jpg http://astronomyonline.org/SolarSystem/Images/Earth_Moon/OceanCurrent.jpg http://www.thegeographeronline.net/uploads/2/6/6/2/26629356/4648314_orig.jpg
- 11. What is brackish water? Brackish water is a mixture of freshwater from rivers and streams with saltwater from the ocean. Brackish water is found in estuaries and any wetland that has a mixture of salty sea water and fresh water. https://wikiislam.net/wiki/images/a/a1/Estuary.jpg https://santosasandyputra.files.wordpress.com/2015/12/estuary.jpg?w=1000
- 12. What is groundwater? Groundwater is water that enters the ground as rain or other precipitation infiltrates or percolates down from the surface and collects between rocks and in soil. We access groundwater by drilling wells into the water table and pumping out the water. https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/candimgs/Mi8WsV/f- d62fa713af72548f922d754148b3c962d1d070e90a9f2069c4bcae0a3IMAGE_THUMB_POSTCARDIMAGE_THUMB_POSTCARD.1 https://c1.staticflickr.com/1/461/31551458883_75b534e3f4_z.jpg
- 13. Humans use water âĒ cooking âĒ irrigation for agriculture âĒ bathing http://www.groundreport.com/wp- content/uploads/2016/05/Pot_irrigation_by_On-line_drippers.jpg https://3.bp.blogspot.com/- gj5Lb2Q1Pic/WtTAVVsfODI/AAAAAAABy1Y/YjGWI1jwdh48wG- zfXOnxkyV6XsX60YxACLcBGAs/s1600/10.jpg https://farm3.staticflickr.com/2131/2347718246_9066990814_z.jpg
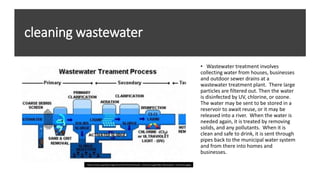
- 14. cleaning wastewater âĒ Wastewater treatment involves collecting water from houses, businesses and outdoor sewer drains at a wastewater treatment plant. There large particles are filtered out. Then the water is disinfected by UV, chlorine, or ozone. The water may be sent to be stored in a reservoir to await reuse, or it may be released into a river. When the water is needed again, it is treated by removing solids, and any pollutants. When it is clean and safe to drink, it is sent through pipes back to the municipal water system and from there into homes and businesses. https://scioly.org/wiki/images/thumb/3/35/Wastewater_treatment.jpg/550px-Wastewater_treatment.jpgeg
- 15. The impact of agriculture on our water supply Agriculture is the largest user of our water supply. Farmers use groundwater to irrigate crops, which can lead to aquifer depletion. https://dr282zn36sxxg.cloudfront.net/datastreams/f- d:1ff6a33744edb29849414eaedaff8a61e691af61c1e027d0d620f2e2%2BIMAGE_THUMB_POSTCAR D_TINY%2BIMAGE_THUMB_POSTCARD_TINY.1
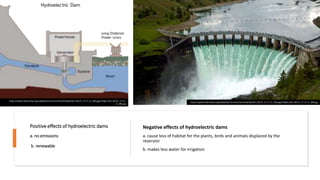
- 16. Positive effects of hydroelectric dams a. no emissions b. renewable Negative effects of hydroelectric dams a. cause loss of habitat for the plants, birds and animals displaced by the reservoir b. makes less water for irrigation https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/2011-06-07_17-17-11_996.jpg/1200px-2011-06-07_17-17- 11_996.jpg https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/2011-06-07_17-17-11_996.jpg/1200px-2011-06-07_17-17-11_996.jpg
- 17. We can reduce our water use a. install low-flow toilets and shower heads b. wash full loads of laundry and dishes c. use drip irrigation for agriculture and rain barrels for home irrigation https://images-wixmp-ed30a86b8c4ca887773594c2.wixmp.com/f/c90f197d-070e-4123-a441-1b38e11cf402/d2hdku6-d1ec9dc6-0837-4b12-94f2- 9087ce4802dd.png?token=eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJpc3MiOiJ1cm46YXBwOjdlMGQxODg5ODIyNjQzNzNhNWYwZDQxNWVhMGQyNmU wIiwic3ViIjoidXJuOmFwcDo3ZTBkMTg4OTgyMjY0MzczYTVmMGQ0MTVlYTBkMjZlMCIsImF1ZCI6WyJ1cm46c2VydmljZTpmaWxlLmRvd25sb2FkIl0sIm9iaiI6 W1t7InBhdGgiOiIvZi9jOTBmMTk3ZC0wNzBlLTQxMjMtYTQ0MS0xYjM4ZTExY2Y0MDIvZDJoZGt1Ni1kMWVjOWRjNi0wODM3LTRiMTItOTRmMi05MDg3Y2U 0ODAyZGQucG5nIn1dXX0.V7wtZqPbkoS6GSLSPGOjAF6f1QwNqtSGGHft0w9CMck



































![Koppen classification and land area characteristics [autosaved]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/koppenclassificationandlandareacharacteristicsautosaved-210129205232-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)


























