Introductiontoagile Scrum 120808133533 Phpapp01
- 1. Scrum: WhatŌĆÖs In It for Me? Prepared by Lisa Monta├▒o
- 2. Agenda ’ü«ŌĆł Overview of Agile and Scrum ’ü«ŌĆł Scrum: Product Vision & Product Owner Role ’ü«ŌĆł Scrum: Practices and ScrumMaster Role ’ü«ŌĆł WhatŌĆÖs in it for me? 2
- 3. Overview of Agile and Scrum
- 4. Overview of Agile and Scrum Agile Manifesto ’ü«ŌĆł Agile is a set of values: ’ü«ŌĆł Individuals and interactions over processes and tools ’ü«ŌĆł Workingsoftware (Products) over comprehensive documentation ’ü«ŌĆł Customer collaboration over contract negotiation ’ü«ŌĆł Responding to change over following a plan 4
- 5. Overview of Agile and Scrum 12 Agile Principles 1 Highest priority is to satisfy the customer through early and continuous delivery of valuable software/products 2 Welcome changing requirements 3 Deliver working software (product) frequently 4 Business people and developers must work together daily throughout the project 5
- 6. Overview of Agile and Scrum 12 Agile Principles 5 Build projects around motivated individuals 6 Most efficient and effective method of conveying information is face-to-face conversation 7 Working software (product) is the primary measure of progress 8 Agile processes promote sustainable development (maintain a constant pace indefinitely) 6
- 7. Overview of Agile and Scrum 12 Agile Principles 9 Continuous attention to technical excellence and good design enhances agility 10 Simplicity (art of maximizing amount of work not done) is essential 11 Best architectures, requirements, and designs emerge from self-organizing teams 12 At regular intervals, team reflects on how to become more effective, then fine-tunes and adjusts http://agilemanifesto.org/principles.html 7
- 8. Overview of Agile and Scrum What is Scrum? ’ü«ŌĆł Scrum is an Agile framework that supports lightweight processes that emphasize: ’ü«ŌĆł Incremental deliveries ’ü«ŌĆł Quality of Product ’ü«ŌĆł Continuous improvement ’ü«ŌĆł Discovery of people s potential ’ü«ŌĆł Scrum is simple to understand, requires discipline in order to be successful ’ü«ŌĆł Scrum is not a methodology 8
- 9. Overview of Agile and Scrum Foundations of Scrum ’ü«ŌĆł Empiricism ’ü«ŌĆł Detailed up-front planning and defined processes are replaced by just-in-time Inspect and Adapt cycles ’ü«ŌĆł Self-Organization ’ü«ŌĆł Small teams manage their own workload and organize themselves around clear goals and constraints ’ü«ŌĆł Prioritization ’ü«ŌĆł Do the next right thing ’ü«ŌĆł Rhythm ’ü«ŌĆł Allows teams to avoid daily noise and focus on delivery ’ü«ŌĆł Collaboration ’ü«ŌĆł Leaders and customers work with the Team, rather than directing them 9
- 10. Overview of Agile and Scrum CoreValues ’ü«ŌĆł Transparency ’ü«ŌĆł Everything about a project is visible to everyone ’ü«ŌĆł Commitment ’ü«ŌĆł Making realistic commitments ’ü«ŌĆł Courage ’ü«ŌĆł Have the courage to commit, to act, to be open and to expect respect ’ü«ŌĆł Focus ’ü«ŌĆł Focus all of your efforts and skills on doing the work that you have committed to doing ’ü«ŌĆł Respect ’ü«ŌĆł Respect and trust the different people who comprise a team10
- 11. Scrum: Product Vision and Product Owner Role
- 12. Scrum: Vision and Product ProductVision ’ü«ŌĆł A goal to aspire to ’ü«ŌĆł Can be summarized in a short statement of intent ’ü«ŌĆł Communicate it to the team 12
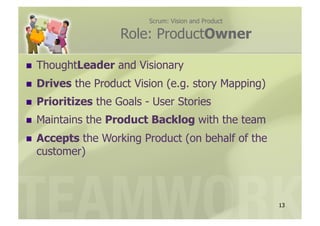
- 13. Scrum: Vision and Product Role: ProductOwner ’ü«ŌĆł ThoughtLeader and Visionary ’ü«ŌĆł Drives the Product Vision (e.g. story Mapping) ’ü«ŌĆł Prioritizes the Goals - User Stories ’ü«ŌĆł Maintains the Product Backlog with the team ’ü«ŌĆł Acceptsthe Working Product (on behalf of the customer) 13
- 14. Scrum: Practices and ScrumMaster Role
- 15. Scrum: Sprint Role: ScrumMaster ’ü«ŌĆł Servant Leader ’ü«ŌĆł Facilitates the Process ’ü«ŌĆł Supports the Team ’ü«ŌĆł Removes Organizational Impediments ’ü«ŌĆł Socializes Scrum to Management ’ü«ŌĆł Enables close collaboration across all roles and functions 15
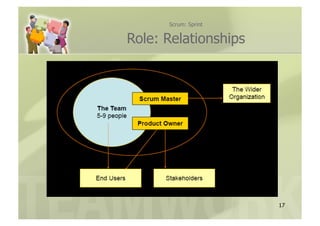
- 16. Scrum: Sprint Role: Team ’ü«ŌĆł CrossFunctional ’ü«ŌĆł 5-9 Members ’ü«ŌĆł SelfOrganizing ’ü«ŌĆł Focused on meeting Commitments 16
- 18. Scrum Diagram 18
- 19. Scrum: Sprint Flow & Artifacts: Planning ’ü«ŌĆł SprintPlanning meeting held prior to beginning of each Sprint ’ü«ŌĆł Duration and time-effort are fixed in any given Sprint is to have prioritized Sprint Backlog, broken ’ü«ŌĆł Goal down into tasks, that the Team can commit to ’ü«ŌĆł During planning, Team commits to scope that can be completed in the Sprint, taking into account the Definition of Done 19
- 20. Scrum: Sprint Flow & Artifacts: DailyStandup ’ü«ŌĆł Meetings held in same location, same time, every day ’ü«ŌĆł Timeboxed at 15minutes ’ü«ŌĆł Encourages self-organization, rhythm, and collaboration ’ü«ŌĆł Not a status meeting ’ü«ŌĆł Each team member speaks to: ’ü«ŌĆł What did I accomplish in the last 24 hours? ’ü«ŌĆł What do I plan to accomplish in the next 24 hours? ’ü«ŌĆł Any impediments getting in the way of my work? 20
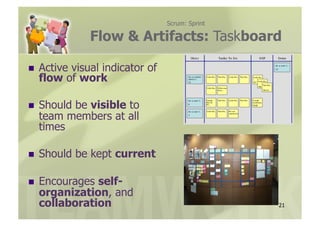
- 21. Scrum: Sprint Flow & Artifacts: Taskboard ’ü«ŌĆł Active visual indicator of flow of work ’ü«ŌĆł Should be visible to team members at all times ’ü«ŌĆł Should be kept current ’ü«ŌĆł Encouragesself- organization, and collaboration 21
- 22. Scrum: Sprint Flow & Artifacts: SprintReview ’ü«ŌĆł Occurs at the end of each Sprint ’ü«ŌĆł Inspect and Adapt the product (Empiricism) ’ü«ŌĆł Theteam meets with the Product Owner (and Stakeholders) to demonstrate the working software from the Sprint ’ü«ŌĆł Thisis a hands-on software demo (not a PowerPoint) that usually requires some prep beforehand 22
- 23. Scrum: Sprint Flow & Artifacts: Retrospective ’ü«ŌĆł Occurs at the end of each Sprint ’ü«ŌĆł Inspect and Adapt the process (Empiricism) ’ü«ŌĆł Teamand ScrumMaster meet to reflect on what went well and what can be improved ’ü«ŌĆł Toneof the meeting is that everyone did their best and now look to how can we improve ’ü«ŌĆł Retrospectives must conclude with team commitments to action 23
- 24. What is in it for me? {Customer} ’ü«ŌĆł As a Customer, I want to be able to ’ü«ŌĆł Have opportunity to provide feedback early ’ü«ŌĆł Go to market faster with quality ’ü«ŌĆł Faster return on investment 24
- 25. What is in it for me? {Leadership} ’ü«ŌĆł As a Leader, I want ’ü«ŌĆł To understand progress in terms of real progress made on the product ’ü«ŌĆł Better engaged & accountable team 25
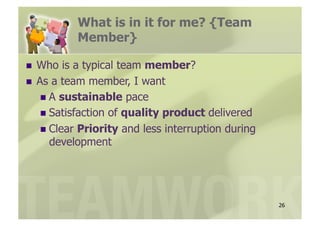
- 26. What is in it for me? {Team Member} ’ü«ŌĆł Who is a typical team member? ’ü«ŌĆł As a team member, I want ’ü«ŌĆł A sustainable pace ’ü«ŌĆł Satisfaction of quality product delivered ’ü«ŌĆł Clear Priority and less interruption during development 26
- 27. How do you learn Scrum? By Doing! ’ü«ŌĆł Apply a few practices at a time ’ü«ŌĆł Understand the values and foundations ’ü«ŌĆł Inspect and Adapt ’ü«ŌĆł Experience the Joy of Doing Scrum 27
- 28. How do you learn Scrum? Experiential Training. 28
- 29. User groups /Communities ’ü«ŌĆł ALN ŌĆō Agile Leadership Network ’ü«ŌĆł Scrum Alliance ŌĆō Scrum User Groups ’ü«ŌĆł Online User Groups Scrum Alliance 29
- 30. Scrum Certifications 30
- 31. Q&A 31
- 32. ’ü«ŌĆł Scrum is a lightweight framework with a simple set of rules, built on foundations and values ’ü«ŌĆł Scrumenables teams to discover their true potential and deliver quality software that adds business value 32
- 33. Pay It Forward/Donation Only Trainings ŌĆóŌĆł Phoenix, AZ- Aug 17 ŌĆō Agile & Scrum Training ŌĆóŌĆł http://agile.conscires.com/agile-training-scrum-training-phoenix-03/ ŌĆóŌĆł Seattle, WA- Aug 17 ŌĆō Agile & Scrum Training ŌĆóŌĆł http://agile.conscires.com/1-day-agile-scrum-training-in-seattle-09/ ŌĆóŌĆł Denver, CO- Aug 24 ŌĆō Agile & Scrum Training ŌĆóŌĆł http://agile.conscires.com/1-day-agile-scrum-training-denver-09/ ŌĆóŌĆł San Diego, CA - Aug 31ŌĆō Agile & Scrum Training ŌĆóŌĆł http://agile.conscires.com/1-day-agile-scrum-training-sandiego-07/ ŌĆóŌĆł Los Angeles, CA- Sept 7 ŌĆō Agile & Scrum Training ŌĆóŌĆł http://agile.conscires.com/1-day-agile-scrum-training-losangeles-03/ ŌĆóŌĆł Austin, TX- Sept 14 ŌĆō Agile & Scrum Training ŌĆóŌĆł http://agile.conscires.com/agile-training-scrum-training-austin-02/ 33
- 34. Certified ScrumMaster & Product Owner Trainings in US ŌĆóŌĆł August 27-28ŌĆō CSM Training in St. Louis, MO ŌĆóŌĆł http://agile.conscires.com/csm-training-st-louis-01/ ŌĆóŌĆł August 27-28ŌĆō CSM Training in Irvine, CA ŌĆóŌĆł http://agile.conscires.com/csm-training-irvine-15/ ŌĆóŌĆł August 30-31ŌĆō CSPO Training in Irvine, CA ŌĆóŌĆł http://agile.conscires.com/cspo-training-irvine-05/ ŌĆóŌĆł August 30-31ŌĆō CSM Training in Raleigh, NC ŌĆóŌĆł http://agile.conscires.com/certified-scrummaster-training-raleigh-01/ ŌĆóŌĆł Sept 13-14 ŌĆō CSM Training in Charlotte, NC ŌĆóŌĆł http://agile.conscires.com/certified-scrummaster-training-charlotte-02/ ŌĆóŌĆł Sept 13-14 ŌĆō CSM Training in Philadelphia, PA ŌĆóŌĆł http://agile.conscires.com/certified-scrummaster-training-philadelphia-01/ ŌĆóŌĆł Sept 13-14 ŌĆō CSM Training in Orlando, FL ŌĆóŌĆł http://agile.conscires.com/certified-scrummaster-training-orlando-03/ 34
- 35. 1 day Trainings in India ŌĆóŌĆł Trivandrum- September 15th ŌĆō Agile & Scrum Training ŌĆóŌĆł http://agile.conscires.com/1-day-agile-scrum-training-trivandrum-05/ ŌĆóŌĆł Bangalore, September 22nd ŌĆō Agile & Scrum Training ŌĆóŌĆł http://agile.conscires.com/1-day-agile-scrum-training-bangalore-06/ ŌĆóŌĆł Delhi, September 29th ŌĆō Agile & Scrum Training ŌĆóŌĆł http://agile.conscires.com/1-day-agile-scrum-training-delhi-03/ ŌĆóŌĆł Pune, September 30th ŌĆō Agile & Scrum Training ŌĆóŌĆł http://agile.conscires.com/1-day-agile-scrum-training-pune-01/ 35
- 36. Thank you ! ’ü«ŌĆł More Resources at ’ü«ŌĆł http://agile.conscires.com/suggested-reading-list- and-resources/ Contact Info Lisa Monta├▒o lisa.montano@conscires.com +1-949-444-8946 36