Is moon
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes65 views
Gathered from many sources of ∫›∫›fl£share users, some of the pictures are not ours, we give credits to the owners. Our purpose of creating this slideshare are to pass our project and to inform others as well.
1 of 33
Download to read offline
































Recommended
The Moon phases



The Moon phasesqiqi septa
Ã˝
The document discusses the phases of the moon. It explains that the moon appears to have phases because it revolves around Earth while also rotating on its axis. As the moon orbits Earth in its elliptical path, the angle of the sunlit side facing Earth changes, leading to different portions being illuminated and visible from Earth over the course of a lunar cycle. The document outlines the eight main phases of the moon - new moon, waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, full moon, waning gibbous, last quarter, and waning crescent - and provides a brief description and illustration of each phase.Our Moon



Our Moonduncanpatti
Ã˝
Power Point notes that I use in class. I did not make this presentation. I got it from the internet, the reference is on the first page. I may have altered it from it\'s origninal state though.Moon Motions and Eclipses



Moon Motions and EclipsesShane Riordan
Ã˝
The document summarizes the motions and phases of the Earth-Moon system. It explains that the moon orbits Earth over the course of about a month in an elliptical orbit, appearing larger when closer (perigee) and smaller when farther (apogee). The changing positions result in the phases of the moon as the illuminated side facing Earth waxes and wanes over the lunar cycle. Eclipses occur when the sun, Earth, and moon align, causing the moon to block the sun during a solar eclipse or Earth to block the sun's light during a lunar eclipse.Astronomy lunar phases eclipses and tides



Astronomy lunar phases eclipses and tidesMaria Donohue
Ã˝
The phases of the moon are caused by the changing positions of the sun, Earth, and moon relative to one another. A new moon occurs when the moon is between the Earth and sun so its night side faces Earth. A full moon happens when the moon is on the opposite side of Earth from the sun, so its full day side faces Earth. Eclipses occur when the sun, Earth, and moon align so that one passes in front of the other, casting a shadow. Lunar eclipses happen during a full moon when Earth blocks the sun's light from reaching the moon. Solar eclipses occur during a new moon when the moon passes between the sun and Earth, casting its shadow on Earth. The moonPhases of the moon (Teach)



Phases of the moon (Teach)Moira Whitehouse
Ã˝
In depth description of the Moon/s phases and why they are as they are. Uses some great internet animations of various situations explaining why we see what we see from Earth. Also discusses the tides and why they are caused by the moon's gravity.Phases of the moon 



Phases of the moon MARICRIS EGONIA
Ã˝
The document discusses the phases of the moon, including terminology like waxing, waning, and gibbous. It notes that the moon revolves around Earth every 28 days and goes through phases as the illuminated portion changes from new to full and back again. Key phases mentioned are new, crescent, quarter, and full moon. The document also briefly discusses lunar and solar eclipses.Moon phases



Moon phasesbcross14
Ã˝
The moon orbits around the Earth rather than the Sun. The different phases of the moon, such as new, crescent, quarter, gibbous, and full, are caused by the changing orientation of the illuminated half of the moon relative to the Earth and Sun over the course of its orbit. The moon progresses through eight phases from new to full and back to new over the course of around 29.5 days as it orbits the Earth.The Moon



The MoonRodeliza Japson
Ã˝
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It has no atmosphere and its surface is marked by craters and dust. The same side always faces Earth. The Moon's diameter is about one quarter that of Earth and it has lower gravity and density than Earth. Temperatures vary greatly from 130°C during the day to -110°C at night. Large flat plains called maria cover parts of the near side, formed by ancient lava flows. Craters and long valleys called rilles are also features of its surface. The Moon orbits Earth about every 27 days in a cycle linked to eclipses.The moon



The moonFerchita Solarte
Ã˝
The document discusses various terms related to the moon including its phases, features, effect on tides, and history of exploration. It defines waxing as when the moon appears to grow in size, waning as when it decreases in size, and gibbous as between a half circle and full circle of illumination. It notes the moon's seas are dark patches formed by ancient lava flows and that phases refer to how much is illuminated each day. A harvest moon is a full moon near the autumn equinox that rises earlier each night. The first men on the moon were Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin in 1969.Earth Moon System



Earth Moon SystemTeach5ch
Ã˝
The document summarizes various topics relating to Earth's seasons, phases of the moon, eclipses, and tides. It explains that Earth's rotation causes day and night, while its revolution around the sun causes years. It describes how the tilt of the Earth on its axis causes seasons. It also discusses the phases of the moon and how they are caused by the relative positions of the Earth, moon, and sun. Lunar and solar eclipses occur when the moon passes between the Earth and sun. Tides are caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and sun on Earth's oceans.Eclipses And Tides



Eclipses And Tidesshas595
Ã˝
The document discusses different types of eclipses including solar and lunar eclipses. A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between the earth and sun, blocking the sun from view. A lunar eclipse occurs when the earth passes between the sun and moon, casting the moon in earth's shadow. The document provides details on the different types of solar and lunar eclipses as well as explanations for why eclipses do not occur every month and why the moon appears red during a lunar eclipse.Phases of moon



Phases of moon5048500
Ã˝
The document discusses the phases of the Moon as seen from Earth. It explains that as the Moon orbits Earth over the course of about 27 days, we see it go through phases from New Moon to Full Moon and back to New Moon again. These phases include the crescent moon, first quarter moon, waxing and waning gibbous moons, and last quarter moon. The illuminated portion of the Moon changes depending on where it is in its orbit relative to the Earth and Sun.Astronomy- Motion, eclipses, tides, moon



Astronomy- Motion, eclipses, tides, moonbarresee
Ã˝
The document discusses planetary motion, eclipses, tides, and phases of the moon. It explains that planets orbit stars in ellipses rather than perfect circles, and that closer planets move faster due to gravity. It describes solar and lunar eclipses, noting that solar eclipses occur when the moon passes between Earth and the sun, while lunar eclipses occur when Earth passes between the sun and moon. It also discusses how the moon's gravity causes ocean tides, with high tide occurring when the moon is overhead or opposite the tide location. Finally, it outlines the phases of the moon as it revolves around Earth.Moon



MoonOyster River HS
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of the Moon including its location, physical characteristics, surface features, phases and movements. Key details include that the Moon is Earth's only natural satellite, has no atmosphere or liquid water, and its surface contains craters, highlands, and low-lying volcanic plains called maria. The Moon revolves around Earth every 27 days while rotating on its axis in the same time, keeping the same hemisphere facing Earth. Its phases are caused by the varying illumination of its surface from Earth's perspective over the course of its revolution.Our moon 



Our moon garlicandwater
Ã˝
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite, located approximately 384,000 km away. It has no atmosphere and extreme surface temperatures, ranging from 130°C during the day to -190°C at night. The Moon's surface is marked by impact craters formed by meteorites, and it revolves around Earth every 27 days while rotating on its axis at the same rate, so the same side always faces Earth. The Moon has different illuminated phases that change as it orbits Earth, from new to waxing crescent to first quarter to waxing gibbous to full and then waning phases back to new. Humans first explored the Moon in the 1960s and 1970s through a series of Apollo missions that walked 12The Sun The Earth The Moon



The Sun The Earth The Moonredcedarmedia
Ã˝
The document provides information about the solar system and related space topics from a 4th grade science perspective. It discusses that the Sun is at the center of the solar system with 8 planets revolving around it, including Earth which is the only planet that supports life. It also mentions that the solar system is part of the Milky Way galaxy, and describes some of the other planets and objects that can be seen in the night sky like stars, constellations, comets, and meteors. Some key facts about the Sun and Earth are also highlighted such as their sizes, distances, and rotations.Earth science, the earth and moon



Earth science, the earth and moonKendall Mayhew
Ã˝
This is a PowerPoint that is about Exploring Earth Science. This is geared towards 3rd grade students. This is very picture heavy so it will easily keep the attention of young children. It is also full of helpful informationEarth Science: Sun-Earth-Moon Love Affair



Earth Science: Sun-Earth-Moon Love AffairPaula Marie Llido
Ã˝
Chapter 15 Earth Science: Sun-Earth-Moon Love Affair
-Sun
-Earth
-Moon
-Movement of Earth
-Tilt and Season
-Solstices and Equinoxes
-Latitude and Climate
-Phase of Moon
-Eclipes
-TidesThe Sun-Earth-Moon System Notes PowerPoint



The Sun-Earth-Moon System Notes PowerPointRuhee M
Ã˝
The Sun, the Earth, and the Sun System
Contains: Earth, The Moon-Earth's Satellites, and Exploring Earth's MoonSun, Moon, and Earth system



Sun, Moon, and Earth systemVictor F. Melitante Jr.
Ã˝
The solar system is made up of the Sun, the planets that orbit the Sun, their satellites, dwarf planets and many, many small objects, like asteroids and comets. All of these objects move and we can see these movements. We notice the Sun rises in the eastern sky in the morning and sets in the western sky in the evening. We observe different stars in the sky at different times of the year.Sp11 -notes--moon and eclipses



Sp11 -notes--moon and eclipsesdolandese
Ã˝
1) The Earth, Sun and Moon exist in a complex system of orbits where the Moon revolves around the Earth and the Earth revolves around the Sun.
2) As the Moon orbits the Earth, the illuminated portion that we see from Earth changes in a cycle called phases, ranging from new moon to full moon and back over about two weeks.
3) Lunar and solar eclipses occur when the Moon passes between the Earth and Sun, casting its shadow on either the Moon or Earth, and can be total or partial depending on the alignment of the three bodies.Earth, Sun, Moon Rotation Flipbook



Earth, Sun, Moon Rotation Flipbookkarenlfrench
Ã˝
The moon orbits the Earth in a nearly perfect circle over the course of approximately 27 days, with the same side always facing the Earth. The Earth rotates on its axis over the course of 24 hours, causing the cycle of day and night, and revolves around the sun over the course of 365 days, causing the seasons. Additionally, the sun rotates on its axis once every 27 days.Moon



MoonDurant Road Middle
Ã˝
The document discusses key facts about the moon, including that it orbits Earth and reflects sunlight from its surface. It also explains the phases of the moon, which are caused by the moon orbiting Earth as the sun lights different parts of its surface over the course of about 29 days. The moon's gravitational pull causes ocean tides on Earth. Diagrams show each moon phase as the portion of the lit surface visible from Earth changes from new to full to new again in a repeating cycle.Season, Phases of the Moon, and Tides



Season, Phases of the Moon, and TidesJimnaira Abanto
Ã˝
The document discusses Earth's movements and their effects. It explains that Earth rotates daily on its axis and revolves yearly around the sun, causing seasons. It also describes the moon's phases as it revolves around Earth, and how eclipses occur when the sun, Earth, and moon are aligned. Further, it outlines how the moon's gravity creates tides on Earth, with high tide during maximum pull and low tide when the pull is weakest.Earth in Space 



Earth in Space Edzon Tatualia
Ã˝
The document summarizes key facts about Earth:
- Earth is the third planet from the sun and formed around 4.5-4.6 billion years ago. It is the only known planet capable of sustaining life.
- With a diameter of around 8,000 miles, Earth is the fifth largest planet in the solar system and has one moon. The presence of water covering over 70% of the surface allows life to thrive.
- Earth rotates on its axis once every 24 hours and revolves around the sun once every 365 days, causing seasons and influencing climate.Phases of the moon



Phases of the moonpbainbridge
Ã˝
The document discusses the phases of the moon, beginning with the New Moon phase where the illuminated side faces away from Earth. It then explains the order and characteristics of the subsequent phases: Waxing Crescent where a small portion is lit, First Quarter where half is lit on the right side, Waxing Gibbous where nearly all of the right side is lit, Full Moon where the entire side facing Earth is illuminated, Waning Gibbous where the left side becomes illuminated, Last Quarter where half is lit on the left, and Waning Crescent where a small portion on the left remains lit before repeating the cycle.Moon



MoonDurant Road Middle
Ã˝
The Moon orbits Earth and is illuminated by sunlight reflected off its surface. It takes approximately 29 days for the Moon to orbit Earth and undergo all its phases from New Moon to Full Moon and back again. The gravitational pull of the Moon causes ocean tides on Earth.Eclipse Grade Four Lesson



Eclipse Grade Four LessonJenifer Cajayon
Ã˝
The document discusses eclipses and Jupiter's moon Ganymede. It begins with an introduction to astronomical objects like planets and asteroids. It then discusses shadows and the terms umbra and penumbra in relation to eclipses. It notes that Jupiter has 64 moons, and that its largest moon Ganymede is around 4.5 billion years old, similar in age to Jupiter. The document includes questions about eclipses and safety tips for viewing a solar eclipse. It concludes with a short assignment to research and report on eclipses in the Philippines.Eclipses by WSTA412



Eclipses by WSTA412ferrazs
Ã˝
An eclipse occurs when a celestial body passes in front of the sun, blocking its light. There are two types of eclipses: lunar eclipses, where the earth casts a shadow on the moon, and solar eclipses, where the moon casts a shadow on earth. During a lunar eclipse, the earth blocks the sun's light from reaching the moon, causing it to glow red. A total lunar eclipse occurs when the moon passes completely into the earth's shadow, while a partial lunar eclipse happens when it only partially enters the shadow.Moon Characteristics and Motion



Moon Characteristics and Motiondwinter1
Ã˝
The moon is tidally locked to Earth, meaning the same side always faces Earth. This is why there is a big difference between the appearance of the near side, which faces Earth, and the far side. The near side has many visible maria (dark plains) while the far side has fewer maria and a thicker crust with more craters. Additionally, the Earth and moon orbit a common center of gravity called the barycenter, located about 900 miles from Earth's surface. Both bodies revolve around this point, which itself revolves around the sun.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
The moon



The moonFerchita Solarte
Ã˝
The document discusses various terms related to the moon including its phases, features, effect on tides, and history of exploration. It defines waxing as when the moon appears to grow in size, waning as when it decreases in size, and gibbous as between a half circle and full circle of illumination. It notes the moon's seas are dark patches formed by ancient lava flows and that phases refer to how much is illuminated each day. A harvest moon is a full moon near the autumn equinox that rises earlier each night. The first men on the moon were Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin in 1969.Earth Moon System



Earth Moon SystemTeach5ch
Ã˝
The document summarizes various topics relating to Earth's seasons, phases of the moon, eclipses, and tides. It explains that Earth's rotation causes day and night, while its revolution around the sun causes years. It describes how the tilt of the Earth on its axis causes seasons. It also discusses the phases of the moon and how they are caused by the relative positions of the Earth, moon, and sun. Lunar and solar eclipses occur when the moon passes between the Earth and sun. Tides are caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and sun on Earth's oceans.Eclipses And Tides



Eclipses And Tidesshas595
Ã˝
The document discusses different types of eclipses including solar and lunar eclipses. A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between the earth and sun, blocking the sun from view. A lunar eclipse occurs when the earth passes between the sun and moon, casting the moon in earth's shadow. The document provides details on the different types of solar and lunar eclipses as well as explanations for why eclipses do not occur every month and why the moon appears red during a lunar eclipse.Phases of moon



Phases of moon5048500
Ã˝
The document discusses the phases of the Moon as seen from Earth. It explains that as the Moon orbits Earth over the course of about 27 days, we see it go through phases from New Moon to Full Moon and back to New Moon again. These phases include the crescent moon, first quarter moon, waxing and waning gibbous moons, and last quarter moon. The illuminated portion of the Moon changes depending on where it is in its orbit relative to the Earth and Sun.Astronomy- Motion, eclipses, tides, moon



Astronomy- Motion, eclipses, tides, moonbarresee
Ã˝
The document discusses planetary motion, eclipses, tides, and phases of the moon. It explains that planets orbit stars in ellipses rather than perfect circles, and that closer planets move faster due to gravity. It describes solar and lunar eclipses, noting that solar eclipses occur when the moon passes between Earth and the sun, while lunar eclipses occur when Earth passes between the sun and moon. It also discusses how the moon's gravity causes ocean tides, with high tide occurring when the moon is overhead or opposite the tide location. Finally, it outlines the phases of the moon as it revolves around Earth.Moon



MoonOyster River HS
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of the Moon including its location, physical characteristics, surface features, phases and movements. Key details include that the Moon is Earth's only natural satellite, has no atmosphere or liquid water, and its surface contains craters, highlands, and low-lying volcanic plains called maria. The Moon revolves around Earth every 27 days while rotating on its axis in the same time, keeping the same hemisphere facing Earth. Its phases are caused by the varying illumination of its surface from Earth's perspective over the course of its revolution.Our moon 



Our moon garlicandwater
Ã˝
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite, located approximately 384,000 km away. It has no atmosphere and extreme surface temperatures, ranging from 130°C during the day to -190°C at night. The Moon's surface is marked by impact craters formed by meteorites, and it revolves around Earth every 27 days while rotating on its axis at the same rate, so the same side always faces Earth. The Moon has different illuminated phases that change as it orbits Earth, from new to waxing crescent to first quarter to waxing gibbous to full and then waning phases back to new. Humans first explored the Moon in the 1960s and 1970s through a series of Apollo missions that walked 12The Sun The Earth The Moon



The Sun The Earth The Moonredcedarmedia
Ã˝
The document provides information about the solar system and related space topics from a 4th grade science perspective. It discusses that the Sun is at the center of the solar system with 8 planets revolving around it, including Earth which is the only planet that supports life. It also mentions that the solar system is part of the Milky Way galaxy, and describes some of the other planets and objects that can be seen in the night sky like stars, constellations, comets, and meteors. Some key facts about the Sun and Earth are also highlighted such as their sizes, distances, and rotations.Earth science, the earth and moon



Earth science, the earth and moonKendall Mayhew
Ã˝
This is a PowerPoint that is about Exploring Earth Science. This is geared towards 3rd grade students. This is very picture heavy so it will easily keep the attention of young children. It is also full of helpful informationEarth Science: Sun-Earth-Moon Love Affair



Earth Science: Sun-Earth-Moon Love AffairPaula Marie Llido
Ã˝
Chapter 15 Earth Science: Sun-Earth-Moon Love Affair
-Sun
-Earth
-Moon
-Movement of Earth
-Tilt and Season
-Solstices and Equinoxes
-Latitude and Climate
-Phase of Moon
-Eclipes
-TidesThe Sun-Earth-Moon System Notes PowerPoint



The Sun-Earth-Moon System Notes PowerPointRuhee M
Ã˝
The Sun, the Earth, and the Sun System
Contains: Earth, The Moon-Earth's Satellites, and Exploring Earth's MoonSun, Moon, and Earth system



Sun, Moon, and Earth systemVictor F. Melitante Jr.
Ã˝
The solar system is made up of the Sun, the planets that orbit the Sun, their satellites, dwarf planets and many, many small objects, like asteroids and comets. All of these objects move and we can see these movements. We notice the Sun rises in the eastern sky in the morning and sets in the western sky in the evening. We observe different stars in the sky at different times of the year.Sp11 -notes--moon and eclipses



Sp11 -notes--moon and eclipsesdolandese
Ã˝
1) The Earth, Sun and Moon exist in a complex system of orbits where the Moon revolves around the Earth and the Earth revolves around the Sun.
2) As the Moon orbits the Earth, the illuminated portion that we see from Earth changes in a cycle called phases, ranging from new moon to full moon and back over about two weeks.
3) Lunar and solar eclipses occur when the Moon passes between the Earth and Sun, casting its shadow on either the Moon or Earth, and can be total or partial depending on the alignment of the three bodies.Earth, Sun, Moon Rotation Flipbook



Earth, Sun, Moon Rotation Flipbookkarenlfrench
Ã˝
The moon orbits the Earth in a nearly perfect circle over the course of approximately 27 days, with the same side always facing the Earth. The Earth rotates on its axis over the course of 24 hours, causing the cycle of day and night, and revolves around the sun over the course of 365 days, causing the seasons. Additionally, the sun rotates on its axis once every 27 days.Moon



MoonDurant Road Middle
Ã˝
The document discusses key facts about the moon, including that it orbits Earth and reflects sunlight from its surface. It also explains the phases of the moon, which are caused by the moon orbiting Earth as the sun lights different parts of its surface over the course of about 29 days. The moon's gravitational pull causes ocean tides on Earth. Diagrams show each moon phase as the portion of the lit surface visible from Earth changes from new to full to new again in a repeating cycle.Season, Phases of the Moon, and Tides



Season, Phases of the Moon, and TidesJimnaira Abanto
Ã˝
The document discusses Earth's movements and their effects. It explains that Earth rotates daily on its axis and revolves yearly around the sun, causing seasons. It also describes the moon's phases as it revolves around Earth, and how eclipses occur when the sun, Earth, and moon are aligned. Further, it outlines how the moon's gravity creates tides on Earth, with high tide during maximum pull and low tide when the pull is weakest.Earth in Space 



Earth in Space Edzon Tatualia
Ã˝
The document summarizes key facts about Earth:
- Earth is the third planet from the sun and formed around 4.5-4.6 billion years ago. It is the only known planet capable of sustaining life.
- With a diameter of around 8,000 miles, Earth is the fifth largest planet in the solar system and has one moon. The presence of water covering over 70% of the surface allows life to thrive.
- Earth rotates on its axis once every 24 hours and revolves around the sun once every 365 days, causing seasons and influencing climate.Phases of the moon



Phases of the moonpbainbridge
Ã˝
The document discusses the phases of the moon, beginning with the New Moon phase where the illuminated side faces away from Earth. It then explains the order and characteristics of the subsequent phases: Waxing Crescent where a small portion is lit, First Quarter where half is lit on the right side, Waxing Gibbous where nearly all of the right side is lit, Full Moon where the entire side facing Earth is illuminated, Waning Gibbous where the left side becomes illuminated, Last Quarter where half is lit on the left, and Waning Crescent where a small portion on the left remains lit before repeating the cycle.Moon



MoonDurant Road Middle
Ã˝
The Moon orbits Earth and is illuminated by sunlight reflected off its surface. It takes approximately 29 days for the Moon to orbit Earth and undergo all its phases from New Moon to Full Moon and back again. The gravitational pull of the Moon causes ocean tides on Earth.Eclipse Grade Four Lesson



Eclipse Grade Four LessonJenifer Cajayon
Ã˝
The document discusses eclipses and Jupiter's moon Ganymede. It begins with an introduction to astronomical objects like planets and asteroids. It then discusses shadows and the terms umbra and penumbra in relation to eclipses. It notes that Jupiter has 64 moons, and that its largest moon Ganymede is around 4.5 billion years old, similar in age to Jupiter. The document includes questions about eclipses and safety tips for viewing a solar eclipse. It concludes with a short assignment to research and report on eclipses in the Philippines.Similar to Is moon (20)
Eclipses by WSTA412



Eclipses by WSTA412ferrazs
Ã˝
An eclipse occurs when a celestial body passes in front of the sun, blocking its light. There are two types of eclipses: lunar eclipses, where the earth casts a shadow on the moon, and solar eclipses, where the moon casts a shadow on earth. During a lunar eclipse, the earth blocks the sun's light from reaching the moon, causing it to glow red. A total lunar eclipse occurs when the moon passes completely into the earth's shadow, while a partial lunar eclipse happens when it only partially enters the shadow.Moon Characteristics and Motion



Moon Characteristics and Motiondwinter1
Ã˝
The moon is tidally locked to Earth, meaning the same side always faces Earth. This is why there is a big difference between the appearance of the near side, which faces Earth, and the far side. The near side has many visible maria (dark plains) while the far side has fewer maria and a thicker crust with more craters. Additionally, the Earth and moon orbit a common center of gravity called the barycenter, located about 900 miles from Earth's surface. Both bodies revolve around this point, which itself revolves around the sun.Earth's moon



Earth's moonMichael Maggiar
Ã˝
This is a presentation about our Earth's moon. It is extremely extensive and is wonderful for academic purposes. It's extremely easy to edit, and this is sure to get you that A+ you've been wanting. earth's moon (1).ppt



earth's moon (1).pptNikhilNag5
Ã˝
The document provides information about the Moon through a series of slides. It discusses the Moon's location in our solar system, its physical features such as craters and maria, phases of the Moon, lunar eclipses and solar eclipses. The document also covers tides caused by the Moon's gravity, past exploration of the Moon including Apollo missions, and possibilities for future lunar bases. Photos and diagrams accompany the text to illustrate different phases of the Moon, lunar terrain, and other concepts. Additional online photo resources are also listed.The earth and the moon



The earth and the moonMichelle Jeffcoat
Ã˝
The document describes key facts about the Earth, moon, eclipses, and lunar landforms. It states that the Earth orbits the sun in an elliptical path and rotates on its axis, causing day and night. The moon revolves around the Earth while the same side always faces it. Solar eclipses occur when the moon blocks the sun, and lunar eclipses happen when the Earth blocks the sun from the moon. Common lunar landforms include craters, maria (areas of hardened lava), and ray craters.our_moon.ppt



our_moon.pptKeenlearner4
Ã˝
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite and orbits our planet about every 27 days. It has no atmosphere and experiences extreme temperature ranges. The lunar surface features highlands, craters, and low-lying maria plains filled with hardened lava. The side facing Earth always appears the same while the far side has more craters and few maria. Phases and eclipses occur due to the relative positions of the Moon, Earth, and Sun. Twelve American astronauts walked on the Moon between 1969-1972, with future lunar bases potentially allowing long-term human habitation.Our moon



Our moonNeilfieOrit2
Ã˝
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite and orbits our planet about every 27 days. It has no atmosphere and experiences extreme temperature ranges. The lunar surface features highlands, craters, and low-lying maria plains filled with hardened lava. The side facing Earth always appears the same while the far side has more craters and few maria. The Moon's phases and eclipses are caused by its orbit around Earth. Humans first explored the Moon in 1969 and collected rocks and data, but future missions may establish lunar bases.Solar and lunar_eclipses1



Solar and lunar_eclipses1Ravin Ravi
Ã˝
There are two types of eclipses: solar and lunar. A lunar eclipse occurs when the moon passes into the Earth's shadow, appearing red or dark. A solar eclipse happens when the moon passes between the Earth and sun, casting its shadow on Earth. There are three types of each: total, partial, and penumbral/annular. Lunar eclipses are more common as anyone experiencing nighttime can see it, while only a small area experiences a solar eclipse due to the moon's small umbral shadow. Eclipses occur during eclipse seasons when the sun, Earth, and moon are directly aligned.Solar and lunar_eclipses1



Solar and lunar_eclipses1Manan Patel
Ã˝
There are two types of eclipses: solar and lunar. A lunar eclipse occurs when the moon passes into the Earth's shadow, appearing red or dark. A solar eclipse happens when the moon passes between the Earth and sun, casting its shadow on Earth. There are three types of each: total, partial, and penumbral/annular. Lunar eclipses are more common as anyone experiencing nighttime can see it, while only a small area experiences a solar eclipse due to the moon's small umbral shadow. Eclipses occur during eclipse seasons when the sun, Earth, and moon are directly aligned.Solar and lunar_eclipses



Solar and lunar_eclipsesMakati Science High School
Ã˝
There are two types of eclipses: lunar eclipses, which occur when the moon passes into Earth's shadow, and solar eclipses, which occur when the moon passes between Earth and the sun. Lunar eclipses can be total, partial, or penumbral depending on how far into Earth's shadow the moon passes. Solar eclipses can be total, partial, or annular depending on the moon's position in its orbit. Eclipses do not occur every month because the moon's orbit is tilted relative to Earth's orbit around the sun, so the three objects do not align perfectly except during eclipse seasons.Astonishing Astronomy 101 - Chapter 1



Astonishing Astronomy 101 - Chapter 1Don R. Mueller, Ph.D.
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of astronomy topics including:
- The basic properties of Earth, Moon, Sun and other planets in our solar system.
- How the tilt of Earth's axis causes the seasons and the celestial sphere model used to understand sky motions.
- Key events like solstices, equinoxes, and lunar phases that occur as Earth orbits the Sun and the Moon orbits Earth.
- The causes and viewing locations of solar and lunar eclipses when the Sun, Earth and Moon are directly aligned.
- Concepts like sidereal time, precession and time zones used to measure and communicate about time and sky positions.Astronomy by jatin



Astronomy by jatindgupta330
Ã˝
Gravity causes planets to orbit stars in ellipses, with those closer to the star moving faster. The moon orbits Earth, causing tides and eclipses. Its phases are due to the changing portion illuminated by the sun from Earth's perspective over the lunar month.Astronomy by jatin



Astronomy by jatinDlgltsbm
Ã˝
Gravity causes planets to orbit stars in ellipses, with those closer to the star moving faster. The moon orbits Earth, causing tides and eclipses. Its phases are due to the changing portion illuminated by the sun from Earth's perspective over the lunar month.Astronomy by jatin



Astronomy by jatindgupta330
Ã˝
Gravity causes planets to orbit stars in ellipses, with those closer to the star moving faster. The moon's gravity also causes ocean tides on Earth. Eclipses occur when the sun, Earth, and moon align, blocking light. The phases of the moon are caused by the changing portion of the moon illuminated by the sun as it orbits Earth monthly.Astronomy by jatin



Astronomy by jatinDlgltsbm
Ã˝
Gravity causes planets to orbit stars in ellipses, with those closer to the star moving faster. The moon's gravity also causes ocean tides on Earth. Eclipses occur when the sun, Earth, and moon align, blocking light. The phases of the moon are caused by the changing portion of the moon illuminated by the sun as it orbits Earth monthly.Astronomy by jatin



Astronomy by jatindgupta330
Ã˝
Gravity causes planets to orbit stars in ellipses, with those closer to the star moving faster. The moon's gravity also causes ocean tides on Earth. Eclipses occur when the sun, Earth, and moon align, blocking light. The phases of the moon are caused by the changing portion of the moon illuminated by the sun as it orbits Earth monthly.The earth and beyond ( latest)



The earth and beyond ( latest)SandraKirolos1992
Ã˝
- Historical models assumed Earth was the center of the solar system, with planets circling it. Copernicus developed the first sun-centered model. Galileo observed moons orbiting Jupiter, showing Earth was not uniquely orbited.
- Earth rotates on a tilted axis once every 24 hours, causing day and night. Its yearly revolution around the sun and axial tilt cause the seasons.
- The solar system includes the sun and objects that orbit it, such as planets, asteroids, comets, and other planetary bodies. It is located within the Milky Way galaxy.COT 2.pptx



COT 2.pptxApril Rose Garcia
Ã˝
The document discusses different types of eclipses. It explains that a solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes in front of the sun, casting its shadow on Earth. There are three types of solar eclipses: total, annular, and partial. A lunar eclipse occurs when the moon passes through Earth's shadow. The moon's shadow consists of the umbra, where the sun is completely covered, the penumbra where it is only partially covered, and the antumbra. Students are assigned group projects to diagram and present the alignments of celestial bodies during eclipses, compare solar and lunar eclipses, and provide safety guidelines for viewing a solar eclipse.Solar_and_Lunar_Eclipses1.ppt



Solar_and_Lunar_Eclipses1.pptkaren2747
Ã˝
There are two types of eclipses: lunar eclipses, which occur when the moon passes into Earth's shadow, and solar eclipses, which occur when the moon passes between Earth and the sun. Lunar eclipses can be total, partial, or penumbral depending on how far into Earth's shadow the moon passes. Solar eclipses can be total, partial, or annular depending on the moon's position in its orbit. Eclipses do not occur daily because the moon's orbit is tilted relative to Earth's orbit around the sun, so the three bodies do not align perfectly most months.Recently uploaded (20)
CBSE Arabic Grammar - Class 10 ppt.pptx



CBSE Arabic Grammar - Class 10 ppt.pptxsuhail849886
Ã˝
cbse arabic grammar
grade 10 cbse arabic grammar
cbse class 10 arabic grammar
arabic marathon cbse arabic 10
nominal sentences
Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ã˝
Finals of Rass MELAI : a Music, Entertainment, Literature, Arts and Internet Culture Quiz organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. Blind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...



Blind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...Ajaz Hussain
Ã˝
This presentation delves into the systemic blind spots within pharmaceutical science and regulatory systems, emphasizing the significance of "inactive ingredients" and their influence on therapeutic equivalence. These blind spots, indicative of normalized systemic failures, go beyond mere chance occurrences and are ingrained deeply enough to compromise decision-making processes and erode trust.
Historical instances like the 1938 FD&C Act and the Generic Drug Scandals underscore how crisis-triggered reforms often fail to address the fundamental issues, perpetuating inefficiencies and hazards.
The narrative advocates a shift from reactive crisis management to proactive, adaptable systems prioritizing continuous enhancement. Key hurdles involve challenging outdated assumptions regarding bioavailability, inadequately funded research ventures, and the impact of vague language in regulatory frameworks.
The rise of large language models (LLMs) presents promising solutions, albeit with accompanying risks necessitating thorough validation and seamless integration.
Tackling these blind spots demands a holistic approach, embracing adaptive learning and a steadfast commitment to self-improvement. By nurturing curiosity, refining regulatory terminology, and judiciously harnessing new technologies, the pharmaceutical sector can progress towards better public health service delivery and ensure the safety, efficacy, and real-world impact of drug products.How to Modify Existing Web Pages in Odoo 18



How to Modify Existing Web Pages in Odoo 18Celine George
Ã˝
In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to modify existing web pages in Odoo 18. Web pages in Odoo 18 can also gather user data through user-friendly forms, encourage interaction through engaging features. EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdf



EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdfLiz Walsh-Trevino
Ã˝
EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdfYear 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptx



Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxmansk2
Ã˝
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxHow to attach file using upload button Odoo 18



How to attach file using upload button Odoo 18Celine George
Ã˝
In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to attach file using upload button Odoo 18. Odoo features a dedicated model, 'ir.attachments,' designed for storing attachments submitted by end users. We can see the process of utilizing the 'ir.attachments' model to enable file uploads through web forms in this slide.Eng7-Q4-Lesson 1 Part 1 Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and T...



Eng7-Q4-Lesson 1 Part 1 Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and T...sandynavergas1
Ã˝
Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and Technical TermsThe Battle of Belgrade Road: A WW1 Street Renaming Saga by Amir Dotan



The Battle of Belgrade Road: A WW1 Street Renaming Saga by Amir DotanHistory of Stoke Newington
Ã˝
Presented at the 24th Stoke Newington History Talks event on 27th Feb 2025
https://stokenewingtonhistory.com/stoke-newington-history-talks/Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil Sir



Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil SirGUJARATCOMMERCECOLLE
Ã˝
Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil SirHow to Manage Putaway Rule in Odoo 17 Inventory



How to Manage Putaway Rule in Odoo 17 InventoryCeline George
Ã˝
Inventory management is a critical aspect of any business involved in manufacturing or selling products.
Odoo 17 offers a robust inventory management system that can handle complex operations and optimize warehouse efficiency. Computer Application in Business (commerce)



Computer Application in Business (commerce)Sudar Sudar
Ã˝
The main objectives
1. To introduce the concept of computer and its various parts. 2. To explain the concept of data base management system and Management information system.
3. To provide insight about networking and basics of internet
Recall various terms of computer and its part
Understand the meaning of software, operating system, programming language and its features
Comparing Data Vs Information and its management system Understanding about various concepts of management information system
Explain about networking and elements based on internet
1. Recall the various concepts relating to computer and its various parts
2 Understand the meaning of software’s, operating system etc
3 Understanding the meaning and utility of database management system
4 Evaluate the various aspects of management information system
5 Generating more ideas regarding the use of internet for business purpose APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
Ã˝
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
-Autonomy, Teams and Tension: Projects under stress
-Tim Lyons
-The neurological levels of
team-working: Harmony and tensions
With a background in projects spanning more than 40 years, Tim Lyons specialised in the delivery of large, complex, multi-disciplinary programmes for clients including Crossrail, Network Rail, ExxonMobil, Siemens and in patent development. His first career was in broadcasting, where he designed and built commercial radio station studios in Manchester, Cardiff and Bristol, also working as a presenter and programme producer. Tim now writes and presents extensively on matters relating to the human and neurological aspects of projects, including communication, ethics and coaching. He holds a Master’s degree in NLP, is an NLP Master Practitioner and International Coach. He is the Deputy Lead for APM’s People Interest Network.
Session | The Neurological Levels of Team-working: Harmony and Tensions
Understanding how teams really work at conscious and unconscious levels is critical to a harmonious workplace. This session uncovers what those levels are, how to use them to detect and avoid tensions and how to smooth the management of change by checking you have considered all of them.How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo ∫›∫›fl£s



How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo ∫›∫›fl£sCeline George
Ã˝
Integrate WhatsApp into Odoo using the WhatsApp Business API or third-party modules to enhance communication. This integration enables automated messaging and customer interaction management within Odoo 17.How to Configure Restaurants in Odoo 17 Point of Sale



How to Configure Restaurants in Odoo 17 Point of SaleCeline George
Ã˝
Odoo, a versatile and integrated business management software, excels with its robust Point of Sale (POS) module. This guide delves into the intricacies of configuring restaurants in Odoo 17 POS, unlocking numerous possibilities for streamlined operations and enhanced customer experiences.Database population in Odoo 18 - Odoo slides



Database population in Odoo 18 - Odoo slidesCeline George
Ã˝
In this slide, we’ll discuss the database population in Odoo 18. In Odoo, performance analysis of the source code is more important. Database population is one of the methods used to analyze the performance of our code. Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ã˝
APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
Ã˝
Is moon
- 2. What is the moon? • A natural satellite • One of more than the 96 moons in our solar system • The only moon of the planet Earth
- 3. LOCATION AND SIZE • About 384,000 kilometers (240,000 miles) from Earth • 3,468 kilometers (2,155 miles) in diameter • About ¼ the size of Earth
- 4. Movements of the Moon • Orbit is an ellipse, not circular • Apogee (farthest from Earth) • Perigee (closest to Earth) • Revolution – Moon orbits the Earth every 27 1/3 days • The moon rises in the East and sets in the West • The moon rises and sets 50 minutes later each day • Rotation – Moon turns on its axis every 27 days • Same side of the Moon always faces Earth
- 5. As the Moon completes its revolution in about a month’s time, we always see the same side facing us. Movements of the Moon
- 6. Because the moon’s period of rotation is equal to its period of revolution (Scientists call this SYNCHRONOUS ROTATION). Movements of the Moon
- 7. Galileo, with the aid of his telescope, was the first to explore the moon’s surface. He found that its surface is covered with crates, mountains, valleys and flat plains. Movements of the Moon
- 8. The Moon’s Surface • No atmosphere • No liquid water • Extreme temperatures – Daytime = 130°C (265° F) – Nighttime = -190°C (-310°F) • 1/6 of Earth’s gravity
- 9. The Moon’s Surface • Lunar rocks and dust cover most of the surface • This layer is called the regolith • 1 – 6 meters deep • The lack of an atmosphere let many more meteorites strike the moon’s surface, creating this layer of crushed rock. • Anorthosites are light-colored, coarse-grained rocks found in the lunar highlands. • Breccia contains fragments of other rocks that have melted together, and are found everywhere on the moon.
- 10. Lunar Features – Craters • Bowl shaped depressions • Up to 2500 kilometers (1,553 miles) across • Most formed by meteorite impact on the Moon • Some formed by volcanic action inside the Moon
- 11. Lunar Features – Craters • When meteorites struck the surface they “displaced material” • Like a “splash” • Marks left are called rays
- 12. DO YOU KNOW? There are about 30,000 craters of varying sizes. TRIVIA
- 13. Lunar Features – Highlands • Mountains up to 7500 meters (25,000 feet) tall • Rilles (trenchlike valleys)
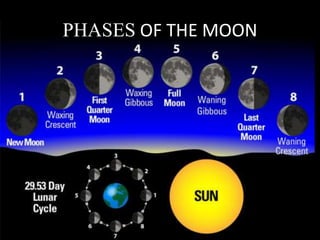
- 14. PHASES OF THE MOON
- 15. 1. New Moon • The Moon's not illuminated side is facing the Earth. • The Moon is not visible (except during a solar eclipse).
- 16. 2. Waxing Crescent • The Moon appears to be partly but less than one- half illuminated by direct sunlight. • The fraction of the Moon's disk that is illuminated is increasing.
- 17. 3. First Quarter • One-half of the Moon appears to be illuminated by direct sunlight. • The fraction of the Moon's disk that is illuminated is increasing.
- 18. 4. Waxing Gibbous • The Moon appears to be more than one-half but not fully illuminated by direct sunlight. • The fraction of the Moon's disk that is illuminated is increasing.
- 19. 5. Full Moon • The Moon's illuminated side is facing the Earth. • The Moon appears to be completely illuminated by direct sunlight.
- 20. 6. Waning Gibbous • The Moon appears to be more than one-half but not fully illuminated by direct sunlight. • The fraction of the Moon's disk that is illuminated is decreasing.
- 21. 7. Last Quarter • One-half of the Moon appears to be illuminated by direct sunlight. • The fraction of the Moon's disk that is illuminated is decreasing.
- 22. 8. Waning Crescent • The Moon appears to be partly but less than one- half illuminated by direct sunlight • The fraction of the Moon's disk that is illuminated is decreasing.
- 23. Waxing or Waning? Waxing means the moon is “growing”. If the moon is getting bright from the right, it is waxing. Waning means the moon is “shrinking”. If the moon is dark on the right, it is waning.
- 24. WHAT ARE THOSE?
- 25. Lunar Eclipse A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes directly behind Earth and into its shadow. This can occur only when the Sun, Earth, and Moon are exactly or very closely aligned (in syzygy), with Earth between the other two.
- 26. Two types of Lunar Eclipse 1. Partial Lunar Eclipse • A portion of the Moon passes through Earth's umbral shadow. • These events are easy to see, even with the unaided eye.
- 27. 2. Total Lunar Eclipse Two types of Lunar Eclipse • The entire Moon passes through Earth's umbral shadow. • These events are quite striking due to the Moon's vibrant red color during the total phase (totality).
- 28. Solar Eclipse A solar eclipse occurs when an observer (on Earth) passes through the shadow cast by the Moon which fully or partially blocks ("occults") the Sun.
- 29. Two types of Solar Eclipse 1. Partial Solar Eclipse A partial solar eclipse happens when the Moon only partially covers the disk of the Sun.
- 30. Two types of Solar Eclipse 2. Total Solar Eclipse • A total solar eclipse happens when the Moon totally covers the disk of the Sun. • An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon appears smaller than the Sun as it passes centrally across the solar disk and a bright ring, or annulus, of sunlight remains visible during the eclipse.
- 31. Saros is the roughly 18-year periodic cycle of the Earth-Moon-Sun system. Every 6,585 days, the Earth, Moon, and Sun are in exactly the same position. When there is a lunar eclipse, there will also be one exactly 6,585 days later. Saros
- 33. Presented by: Sid Marnny Lopena Jymuelle Abejo Drake Lewis Garcia Bernadette Villa
Editor's Notes
- #4: About 384,000 kilometers (240,000 miles) from Earth 3,468 kilometers (2,155 miles) in diameter About ¼ the size of Earth
- #5: Orbit is an ellipse, not circular ***Apogee*** (farthest from Earth) ***Perigee*** (closest to Earth) Revolution – Moon orbits the Earth every 27 1/3 days The moon rises in the East and sets in the West The moon rises and sets 50 minutes later each day Rotation – Moon turns on its axis every 27 days Same side of the Moon always faces Earth
- #14: Mountains up to 7500 meters (25,000 feet) tall Rilles (trenchlike valleys)




